Prerequisites for this course
- Experience working with data (Excel)
- A drive to learn.
- No programming required, but may be helpful.
Database
- Databases store and organize data.
- Contain multiple tables which makes data easily accessible.
- Each Table is a spreadsheet-like in nature. They contain rows and columns.
Query
- A single request or action on the database.
- They can be SELECT, UPDATE, INSERT or DELETE
SELECT Example
SELECT * FROM TABLE;DBMS: database management system
- A program which interacts with the database, user and other applications to capture and analyze data.
- MySQL, SQL Server Management Studio and PostgreSQL are examples.
SQL: Structured Query Language
- A programming language made to capture and analyze data in a database.
- SQL is considered a declaritive language meaning the user simply needs to state what they want returned and not have to worry about how it is done.
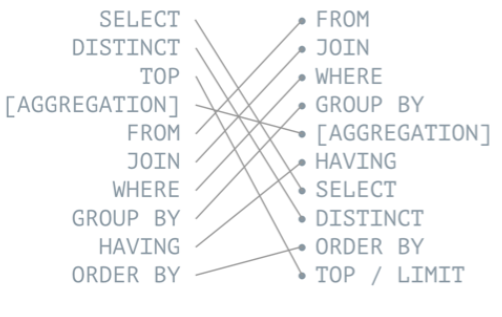
SQL Order of Operations
- The order that SQL runs.
- SQL runs differently than the order you type in.
- For this reason, the order of operations must be obeyed for the Query to perform as expected.
- MySQL Installer
- Recommend to use the 'web' installer.
- Download MySQL Server and MySQL Workbench.
- Find a CSV that has some data.
- Define Data Types.
- Import via the Import Data Wizard.
SELECT TOP(100) * FROM table_name;WHERE- A WHERE function filters your dataset with a single or multiple conditions.
- You can use
AND,ORorBETWEENkeywords to build a specific query.
SELECT
TOP(100) *
FROM
table_name
WHERE
col_name > some_value; -
CASE- A CASE function 'labels' a row based on a certain condition.
- This 'label' can be in its own column, or overwrite an original column.
- Very useful for creating buckets for numeric data and feature engineering.
SELECT CASE WHEN col_name > some_value THEN 'label1', WHEN col_name < some_value THEN 'label2', ELSE 'label3' END AS 'new_col' FROM table_name;
-
GROUP BY- A GROUP BY groups rows with the same value into summary rows.
- An aggregate function can be used to group the result-set by one or more columns
- Aggregate functions include:
COUNT(),SUM(),MEAN()
SELECT country, COUNT(id) as "# per Country" FROM country_table GROUP BY country;
Two very popular python libraries named pandas and numpy will be used heavily in this course as they provide simple to use functions for common tasks.
Some common tasks include:
- Reading data from
- a CSV
- a Database
- JSON file
- API
- Analyzing Data
- Selecting Data - df.loc[] or np.where()
- Numerical computation
- Categorical computation
- Loading data to:
- A CSV -- pd.to_csv()
- A Table -- pd.to_sql()
- JSON file -- pd.to_json()
- Many other file formats.
SELECT DISTINCT <TOP_specification> <select_list>
FROM <left_table>
<join_type> JOIN <right_table> ON <join_condition>
WHERE <where_condition>
GROUP BY <group_by_list>
HAVING <having_condition>
ORDER BY <order_by_list>