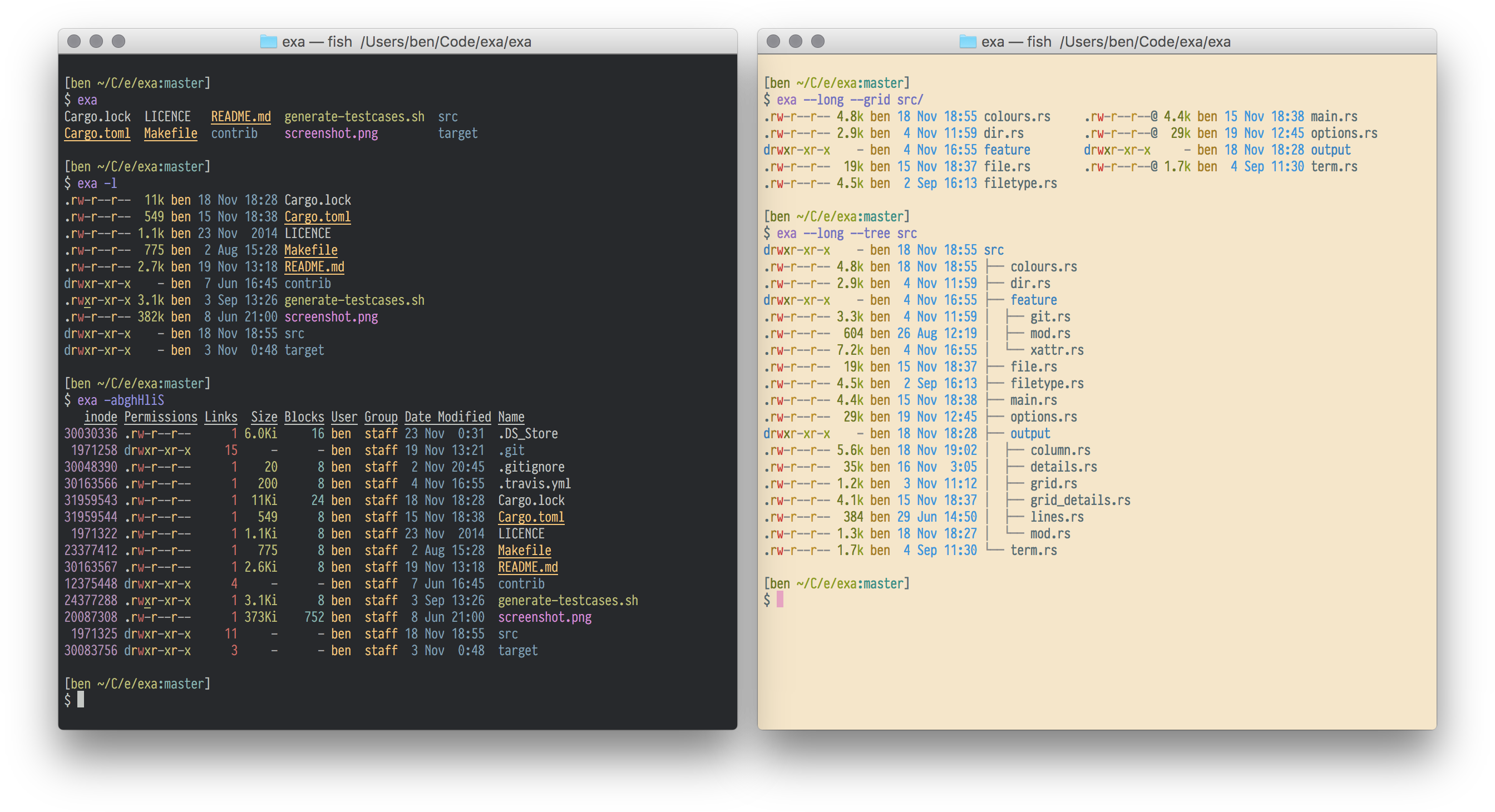
exa is a modern replacement for the venerable file-listing command-line program ls that ships with Unix and Linux operating systems, giving it more features and better defaults.
It uses colours to distinguish file types and metadata.
It knows about symlinks, extended attributes, and Git.
And it’s small, fast, and just one single binary.
By deliberately making some decisions differently, exa attempts to be a more featureful, more user-friendly version of ls.
For more information, see exa’s website.
exa’s options are almost, but not quite, entirely unlike ls’s.
- -1, --oneline: display one entry per line
- -G, --grid: display entries as a grid (default)
- -l, --long: display extended details and attributes
- -R, --recurse: recurse into directories
- -T, --tree: recurse into directories as a tree
- -x, --across: sort the grid across, rather than downwards
- -F, --classify: display type indicator by file names
- --colo[u]r: when to use terminal colours
- --colo[u]r-scale: highlight levels of file sizes distinctly
- --icons: display icons
- --no-icons: don't display icons (always overrides --icons)
- -a, --all: show hidden and 'dot' files
- -d, --list-dirs: list directories like regular files
- -L, --level=(depth): limit the depth of recursion
- -r, --reverse: reverse the sort order
- -s, --sort=(field): which field to sort by
- --group-directories-first: list directories before other files
- -D, --only-dirs: list only directories
- --git-ignore: ignore files mentioned in
.gitignore - -I, --ignore-glob=(globs): glob patterns (pipe-separated) of files to ignore
Pass the --all option twice to also show the . and .. directories.
These options are available when running with --long (-l):
- -b, --binary: list file sizes with binary prefixes
- -B, --bytes: list file sizes in bytes, without any prefixes
- -g, --group: list each file’s group
- -h, --header: add a header row to each column
- -H, --links: list each file’s number of hard links
- -i, --inode: list each file’s inode number
- -m, --modified: use the modified timestamp field
- -S, --blocks: list each file’s number of file system blocks
- -t, --time=(field): which timestamp field to use
- -u, --accessed: use the accessed timestamp field
- -U, --created: use the created timestamp field
- -@, --extended: list each file’s extended attributes and sizes
- --changed: use the changed timestamp field
- --git: list each file’s Git status, if tracked or ignored
- --time-style: how to format timestamps
- --no-permissions: suppress the permissions field
- --octal-permissions: list each file's permission in octal format
- --no-filesize: suppress the filesize field
- --no-user: suppress the user field
- --no-time: suppress the time field
Some of the options accept parameters:
- Valid --color options are always, automatic, and never.
- Valid sort fields are accessed, changed, created, extension, Extension, inode, modified, name, Name, size, type, and none. Fields starting with a capital letter sort uppercase before lowercase. The modified field has the aliases date, time, and newest, while its reverse has the aliases age and oldest.
- Valid time fields are modified, changed, accessed, and created.
- Valid time styles are default, iso, long-iso, and full-iso.
exa is available for macOS and Linux. More information on how to install exa is available on the Installation page.
On Alpine Linux, enable community repository and install the exa package.
apk add exa
On Arch, install the exa package.
pacman -S exa
On Android / Termux, install the exa package.
pkg install exa
On Debian, install the exa package.
apt install exa
On Fedora, install the exa package.
dnf install exa
On Gentoo, install the sys-apps/exa package.
emerge sys-apps/exa
If you’re using Homebrew on macOS, install the exa formula.
brew install exa
If you're using MacPorts on macOS, install the exa port.
port install exa
On nixOS, install the exa package.
nix-env -i exa
On openSUSE, install the exa package.
zypper install exa
On Ubuntu 20.10 (Groovy Gorilla) and later, install the exa package.
sudo apt install exa
On Void Linux, install the exa package.
xbps-install -S exa
Compiled binary versions of exa are uploaded to GitHub when a release is made.
You can install exa manually by downloading a release, extracting it, and copying the binary to a directory in your $PATH, such as /usr/local/bin.
For more information, see the Manual Installation page.
If you already have a Rust environment set up, you can use the cargo install command:
cargo install exa
Cargo will build the exa binary and place it in $HOME/.cargo.
To build without Git support, run cargo install --no-default-features exa is also available, if the requisite dependencies are not installed.
exa is written in Rust. You will need rustc version 1.56.1 or higher. The recommended way to install Rust for development is from the official download page, using rustup.
Once Rust is installed, you can compile exa with Cargo:
cargo build
cargo test
-
The just command runner can be used to run some helpful development commands, in a manner similar to
make. Runjust --tasksto get an overview of what’s available. -
If you are compiling a copy for yourself, be sure to run
cargo build --releaseorjust build-releaseto benefit from release-mode optimisations. Copy the resulting binary, which will be in thetarget/releasedirectory, into a folder in your$PATH./usr/local/binis usually a good choice. -
To compile and install the manual pages, you will need pandoc. The
just mancommand will compile the Markdown into manual pages, which it will place in thetarget/mandirectory. To use them, copy them into a directory thatmanwill read./usr/local/share/manis usually a good choice. -
exa depends on libgit2 for certain features. If you’re unable to compile libgit2, you can opt out of Git support by running
cargo build --no-default-features. -
If you intend to compile for musl, you will need to use the flag
vendored-opensslif you want to get the Git feature working. The full command iscargo build --release --target=x86_64-unknown-linux-musl --features vendored-openssl,git.
For more information, see the Building from Source page.
exa uses Vagrant to configure virtual machines for testing.
Programs such as exa that are basically interfaces to the system are notoriously difficult to test. Although the internal components have unit tests, it’s impossible to do a complete end-to-end test without mandating the current user’s name, the time zone, the locale, and directory structure to test. (And yes, these tests are worth doing. I have missed an edge case on many an occasion.)
The initial attempt to solve the problem was just to create a directory of “awkward” test cases, run exa on it, and make sure it produced the correct output. But even this output would change if, say, the user’s locale formats dates in a different way. These can be mocked inside the code, but at the cost of making that code more complicated to read and understand.
An alternative solution is to fake everything: create a virtual machine with a known state and run the tests on that. This is what Vagrant does. Although it takes a while to download and set up, it gives everyone the same development environment to test for any obvious regressions.
First, initialise the VM:
host$ vagrant up
The first command downloads the virtual machine image, and then runs our provisioning script, which installs Rust and exa’s build-time dependencies, configures the environment, and generates some awkward files and folders to use as test cases. Once this is done, you can SSH in, and build and test:
host$ vagrant ssh
vm$ cd /vagrant
vm$ cargo build
vm$ ./xtests/run
All the tests passed!
Of course, the drawback of having a standard development environment is that you stop noticing bugs that occur outside of it.
For this reason, Vagrant isn’t a necessary development step — it’s there if you’d like to use it, but exa still gets used and tested on other platforms.
It can still be built and compiled on any target triple that it supports, VM or no VM, with cargo build and cargo test.