Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
6297 results about "Wafer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, a wafer (also called a slice or substrate) is a thin slice of semiconductor, such as a crystalline silicon (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. The wafer serves as the substrate for microelectronic devices built in and upon the wafer. It undergoes many microfabrication processes, such as doping, ion implantation, etching, thin-film deposition of various materials, and photolithographic patterning. Finally, the individual microcircuits are separated by wafer dicing and packaged as an integrated circuit.
Wafer processing apparatus with heated, rotating substrate support
ActiveUS9018567B2Easy constructionEasy and economical to constructMuffle furnacesCharge supportsEngineeringSemiconductor
A semiconductor substrate processing apparatus (1), comprising a substrate support assembly (30), including a substrate support (32) defining an outer support surface (34) for supporting a substrate or substrate carrier (24) thereon, and a heater (50) comprising a heat dissipating portion (54) that is disposed within the substrate support (32) and that extends underneath and substantially parallel to the support surface (34), said substrate support (32) being rotatably mounted around a rotation axis (L) that extends through said support surface (34), such that the support surface (34) is rotatable relative to the heat dissipating portion (54) of the heater (50).
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method and apparatus for forming a ferroelectric layer
InactiveUS20050019960A1Improve crystal structureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCarbideChemical vapor deposition
Methods and apparatus for depositing a layer including providing at least one precursor vapor to a process chamber, providing a gas to the process chamber, separate from the at least one precursor vapor, and forming a compound layer from the at least one precursor vapor and the gas on a wafer in the process chamber. The deposition may be a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) deposition method, a metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) deposition method, an atomic layer deposition (ALD) deposition method, or other similar deposition method. The compound layer may be at least one of an oxide, nitride, carbide, or other similar layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for improving optical proximity correction
ActiveUS7350183B2Improve variationDefect minimizationPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentLine widthComputer science
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method of forming ultra thin chips of power devices
InactiveUS20080242052A1Prevent be breakStrengthen it hold powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThinningBackplane
A method for making thin semiconductor devices is disclosed. Starting from wafer with pre-fabricated front-side devices, the method includes:Thinning wafer central portion from its back-side to produce a thin region while preserving original wafer thickness in the wafer periphery for structural strength.Forming ohmic contact at wafer back-side.Separating and collecting pre-fabricated devices. This further includes:Releasably bonding wafer back-side onto single-sided dicing tape, in turn supported by a dicing frame. Providing a backing plate to match the thinned out wafer central portion. Sandwiching the dicing tape between wafer and backing plate then pressing the dicing tape to bond with the wafer.With a step-profiled chuck to support wafer back-side, the pre-fabricated devices are separated from each other and from the wafer periphery in one dicing operation with dicing depth slightly thicker than the wafer central portion. The separated thin semiconductor devices are then picked up and collected.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON LTD
Methods of analyzing and utilizing landscapes to reduce or eliminate inaccuracy in overlay optical metrology
ActiveUS20160313658A1Limit scopeSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusOptical metrologyMeasurement precision
Methods are provided for deriving a partially continuous dependency of metrology metric(s) on recipe parameter(s), analyzing the derived dependency, determining a metrology recipe according to the analysis, and conducting metrology measurement(s) according to the determined recipe. The dependency may be analyzed in form of a landscape such as a sensitivity landscape in which regions of low sensitivity and / or points or contours of low or zero inaccuracy are detected, analytically, numerically or experimentally, and used to configure parameters of measurement, hardware and targets to achieve high measurement accuracy. Process variation is analyzed in terms of its effects on the sensitivity landscape, and these effects are used to characterize the process variation further, to optimize the measurements and make the metrology both more robust to inaccuracy sources and more flexible with respect to different targets on the wafer and available measurement conditions.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Fabrication method for wafer-level mono-axial strain Si on AlN-buried insulation layer based on non-crystallization and scale effect
ActiveCN106098609AImprove cooling effectImprove insulation performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerScale effects
The invention discloses a fabrication method for wafer-level mono-axial strain Si on a AlN-buried insulation layer based on non-crystallization and a scale effect. The fabrication method is implemented according to the following steps of depositing a SiO2 layer at a Si layer at a top layer of a Si wafer on the cleaned AlN-buried insulation layer; performing ion injection on the Si layer at the top layer to form a non-crystallization layer, and removing the SiO2 layer on the non-crystallization layer; depositing a tensile stress SiN thin film or a press stress SiN thin film on the Si layer at the top layer, etching the SiN thin film to a mono-axial tensile stress SiN strip-shaped array or a mono-axial press stress SiN strip-shaped array, annealing the wafer to make the non-crystallization layer re-crystallized, and enabling the AlN-buried insulation layer to generate plastic deformation; and etching the SiN strip-shaped array to obtain the wafer-level mono-axial strain Si on the AlN-buried insulation layer. The wafer-level mono-axial strain Si has the advantages of high heat dissipation and large strain, and the fabrication method can be used for fabricating a wafer-level mono-axial strain Si material on the AlN-buried insulation layer.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Integrated wafer level package
InactiveCN102111116ALow area costReduce manufacturing costImpedence networksFilter bankAcoustic wave
An integrated wafer level package comprises a first wafer provided with a first surface and a corresponding second surface, and a second wafer provided with a first surface and a corresponding second surface; a distance is kept between the two wafers; the second surface of the first wafer and the first surface of the second wafer are opposite to each other to form a first space; a first bulk acoustic wave filter is arranged on the second surface of the first wafer and a second bulk acoustic wave filter is arranged on the first surface of the second wafer, and the two bulk acoustic wave filters are directly opposite to each other to form a second space; a seal ring arranged between the two wafers circles the two bulk acoustic wave filters to form sealing, and the seal ring and the two bulk acoustic wave filters form a cavity; and at least an external electric connector is arranged and is in electric coupling with at least one of the two bulk acoustic wave filters. The integrated wafer level package has the advantages of lower manufacturing cost and high product quality; and by adopting the integrated wafer level package, two or more filter components can be packed into a wafer level package to prevent the filters from the environment pollution of ambient atmosphere.
Owner:张浩
Method for preparing and applying single orientation Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound micro-interconnecting welding point structure
ActiveCN103658899AAvoid premature failureUniform orientation distributionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess conditionsIntermetallic
The invention provides a method for preparing and applying a single orientation Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound micro-interconnecting welding point structure. The method for preparing the single orientation Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound micro-interconnecting welding point structure comprises the first step of arraying a Cu welding disc on a wafer through the electroplating technology, the second step of manufacturing bosses by preparing brazing filler metal prepared on the Cu welding disc, the third step of carrying out hot-wind remelting on the manufactured bosses for 30s-120s, the fourth step of carrying out solid-phase aging processes on chips obtained in the third step, the fifth step of placing the welding point bosses prepared in the fourth step into hydrochloric acid, oscillating the welding point bosses through ultrasound, washing and drying the welding point bosses to obtain a preferred orientation Cu6Sn5 welding disc, the sixth step of reversely buckling the welding point bosses prepared in the fifth step into a corresponding circuit board Cu metal layer, and obtaining the single orientation Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound micro-interconnecting welding point structure through the reflow welding technology. Uniform and stable welding point structure can be obtained when the single orientation Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound micro-interconnecting welding point structure is applied to large two-level packaging at the appropriate conditions.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +3
System and method for integrated data transfer, archiving and purging of semiconductor wafer data
InactiveUS20060009942A1Improved metrologyImproved inspection tool useProgramme controlDigital data information retrievalData transmissionData conversion
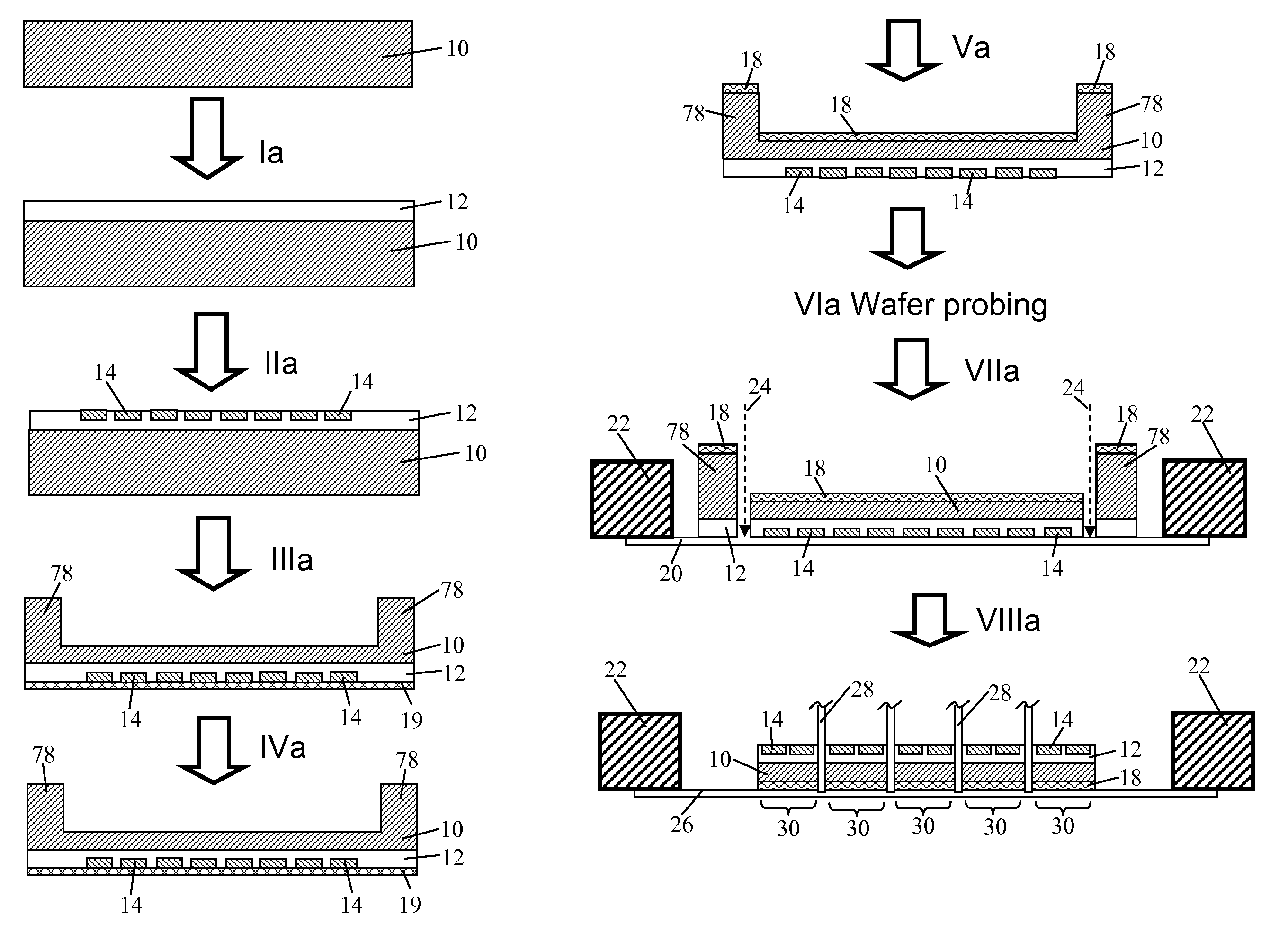
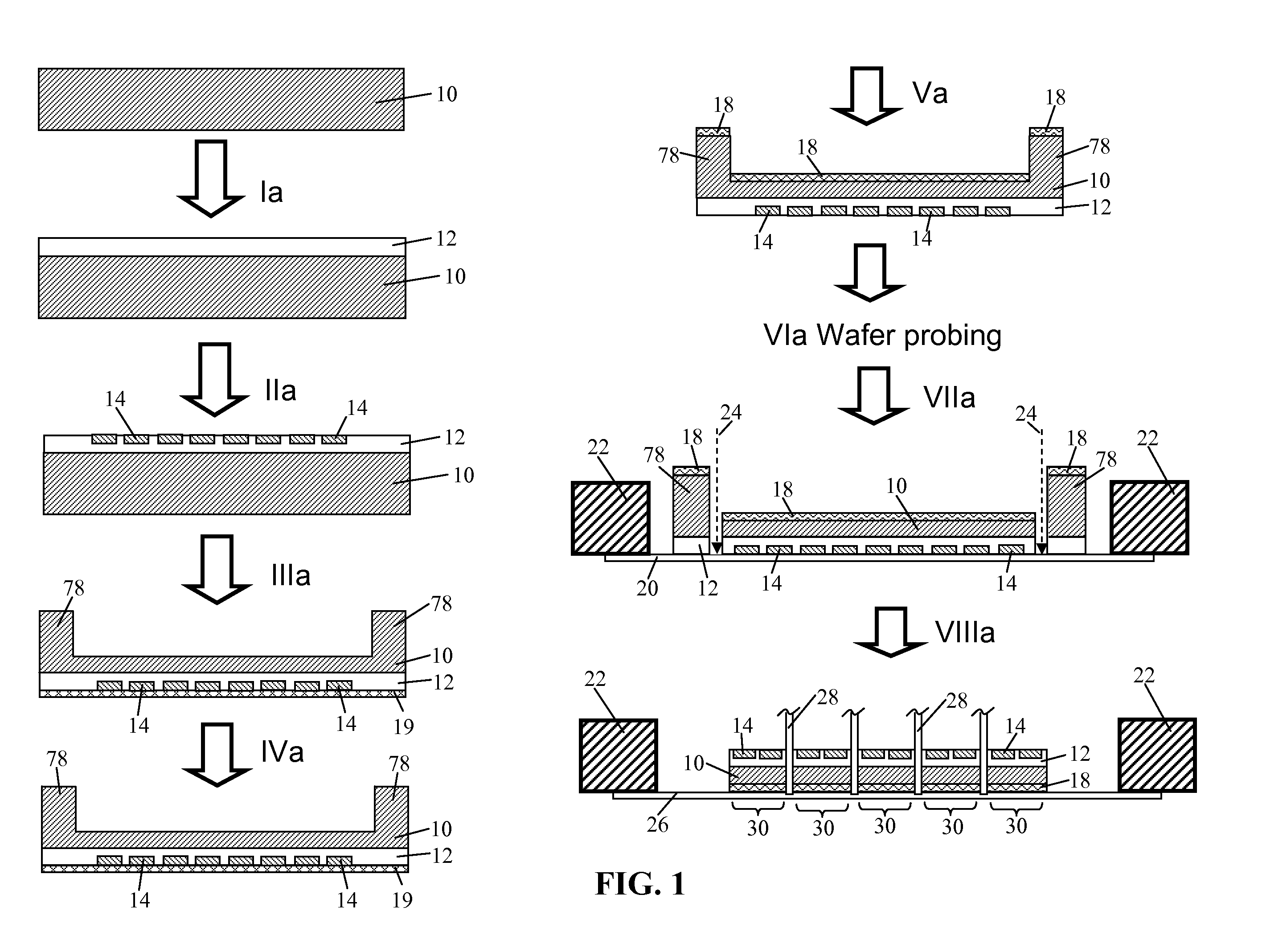
A system for the integrated archiving, restoring, purging, importing and exporting of semiconductor wafer data, the system including: a data acquisition system 00 for acquiring scan data from differing types of semiconductor wafer scanning tools such as wafer dimensional tools 10, wafer inspection tools 12, and wafer nanotopography tools 14; a buffer system 02 for providing temporary storage for scan data transmitted over a network from the data acquisition system and for providing fault tolerance; a server system 04 for providing storage for the scan data transmitted from the buffer system 02 and converting the scan data into a format used by and stored in a database 08 management system; and an analysis system 06 client station including a display and communicating with the server system 04 over the network, the analysis system 06 and the server system 04 managing the purging, archiving, restoring, importing and exporting of scan data.
Owner:ADE CORPORATION
Integrated circuit layout design methodology with process variation bands
ActiveUS8799830B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareConstraint-based CADIntegrated circuit layoutProcess conditions
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Sub-nanometer overlay, critical dimension, and lithography tool projection optic metrology systems based on measurement of exposure induced changes in photoresist on wafers
InactiveUS20060050283A1Large working distanceDetermination is complex and lengthyUsing optical meansPhotosensitive material processingMetrologyLithographic artist
A method of processing a substrate on which a layer of photoresist has been applied, the method involving: exposing the layer of photoresist to radiation that carries spatial information to generate exposure-induced changes in the layer of photoresist that form a pattern having one or more features; and before developing the exposed photoresist, interferometrically obtaining measurements of the pattern in the exposed layer of photoresist for determining at least one of (1) locations of the one or more features of the pattern and (2) magnitudes of the exposure-induced changes.
Owner:ZETETIC INST
Illuminator for dark field inspection
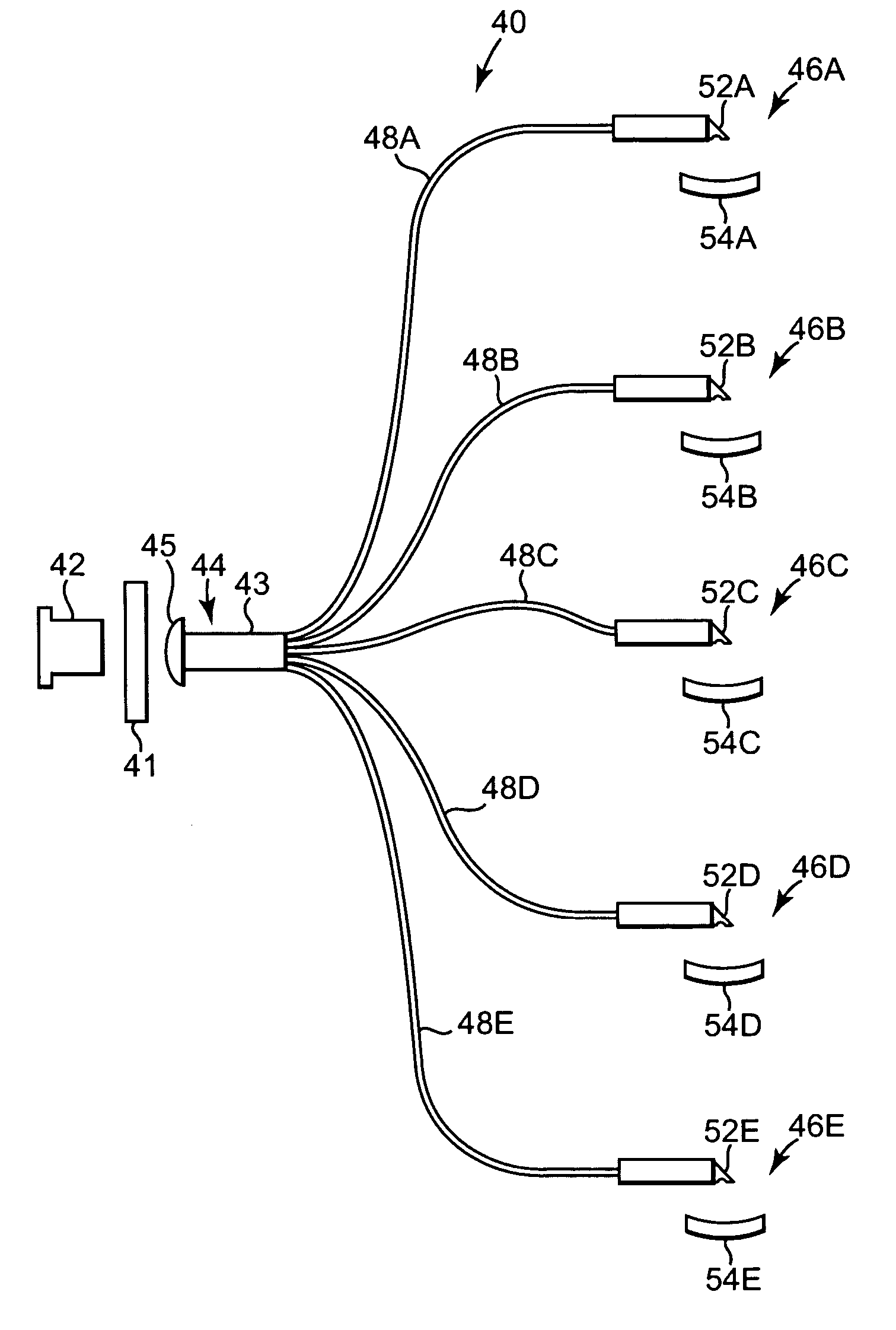
InactiveUS20060012778A1Uniform lightReduce the angle of incidenceOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFiber bundleLight beam
Light from a single source is divided among several illumination arms, each of which directs light via a multimode fiber bundle from the source to the wafer location. The arms are arranged circumferentially around a common illumination region, so that the region is illuminated from several directions. For each arm, light exiting the fiber bundle enters a turning prism, reflects off the hypotenuse of the prism, and is diverged in one dimension by a negative cylindrical surface on the exiting face of the prism. The beam then reflects off an anamorphic mirror and propagates to the illumination region on the wafer. The beam has an asymmetric footprint, so that it illuminates a nearly circular region of the wafer when viewed at normal incidence. The fiber bundle is at the front focal plane in the meridional dimension. The illumination region is at the rear focal plane in both dimensions.
Owner:AUGUST TECH
Exposure apparatus and exposure method using same
InactiveUS6842500B1Reduced strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusX-rayPhotoelectric effect
An exposure apparatus (EA2) that uses X-ray radiation in a photolithographic process and can obtain various measurements regarding the X-ray radiation used, by obtaining and analyzing readings of the photoelectric effect on various reflective surfaces (5, 60a, 60b, 7, 7a, 9a, 9b, 9c and 9d) or optical elements (50a and 51). With the measurements of the X-ray radiation, the exposure apparatus can control the exposure dose during the mask (8) and wafer (10) illumination process. The exposure system also has the ability to detect deformation in the mirrors (9a, 9b, 9c and 9d) of the projection optical system caused by heat generated by absorption of the X-ray radiation. This is accomplished by analyzing the photoelectric effect occurring on the mirror surfaces and correcting the deformation of the mirrors based on this analysis.
Owner:NIKON CORP
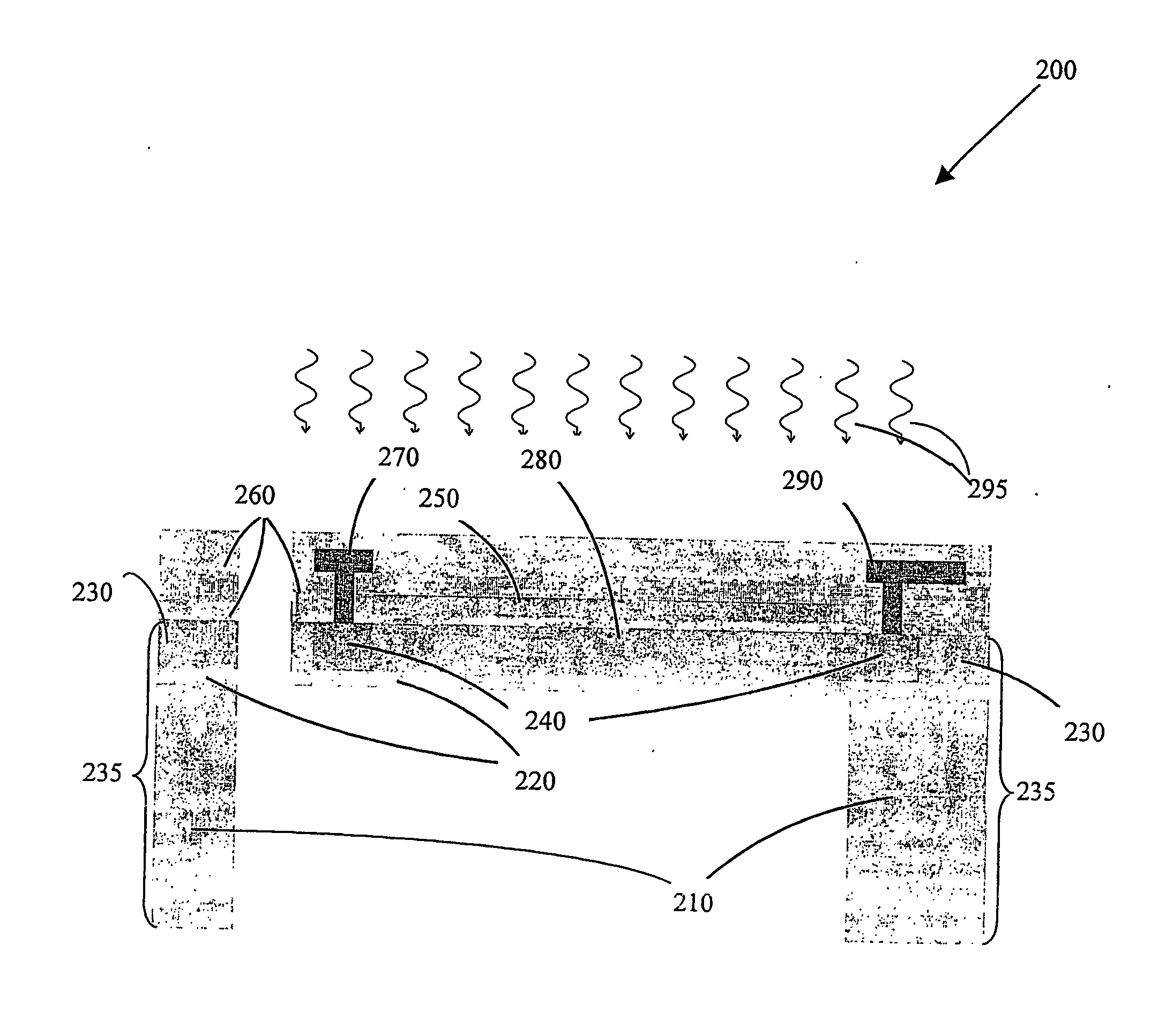
Tmos-infrared uncooled sensor and focal plane array
ActiveUS20060244067A1Increase costImprove performanceMirrorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSensor arrayIntegrator
An array of uncooled infrared sensors based on a micro-machined temperature sensitive MOS transistor. The sensor array is fabricated using a commercial CMOS process on SOI wafers, followed by backside silicon dry etching for each sensor pixel. Active sensor pixels may include either, an integrator and buffer, or simply the sensing transistor, serving also as the selection device. The transistor bias controls the selected device and the sensitivity of the sensor. PMOS transistors and switched operation are used for noise minimization.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Non-resolving mask tiling method for flare reduction
InactiveUS6989229B2Photo-taking processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferEngineering
Photoresist on a wafer is exposed using tiles on a mask that improve flare performance. Features that are not to be exposed on the photoresist correspond to features on the mask. The various features are surrounded by other features that vary and thus affect flare differently. Selected features have tiles added nearby but also far enough away to improve uniformity in the effects of flare on the various features that are intended to be present in the photoresist. The tiles are made either very small in width or partially absorbing so that the tiles are not resolved in the photoresist. Thus the tiles reduce flare but do not alter the desired pattern in the photoresist.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Wafer-level assembly method for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS20060012020A1Minimal laborReduces cost savingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
A wafer-level assembly method for bonding chips to other wafers or to arrays of circuits. The method allows an array of chips, held on a temporary carrier, to be separated by expanding said carrier so that said chips can be aligned and bonded to a substrate with dimensions that would not otherwise permit registration of the chips.
Owner:GILLEO KENNETH B
Wafer drying device and method based on Marangoni effect
InactiveCN108831849AKeep dryImprove securitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGreen environmentWafer
The invention discloses a wafer drying device and method based on a Marangoni effect, wherein the wafer drying device comprises: a water tank for containing deionized water; a wafer lifting device forlifting a wafer from the deionized water; a nitrogen gas source; a nitrogen gas spraying system for spraying a hot nitrogen gas onto the meniscus area of the wafer and deionized water when the waferis lifted in order to induce a temperature gradient in the meniscus area to generate a Marangoni flow downward from the meniscus area, so as to peel off a water absorbing film and achieve ultra-cleandrying of the wafer; and a controller for controlling the wafer lifting device, the nitrogen gas source and the nitrogen gas spraying system. The device and method perform Marangoni drying by using the green environment-friendly hot nitrogen gas instead of a combustible explosive and toxic organic steam, avoids the use of a protection device, simplifies a supply system and improves safety. The wafer lifting device is fixed at two positions and lifts the wafer step by step in order to prevent inability to dry a clamp-wafer contact area and to achieve complete wafer drying.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Three dimensional chip structure implementing machine trained network
ActiveUS20190043832A1Facilitate time borrowingReduce loadExclusive-OR circuitsError detection/correctionNODALNetwork on
Some embodiments provide a three-dimensional (3D) circuit structure that has two or more vertically stacked bonded layers with a machine-trained network on at least one bonded layer. As described above, each bonded layer can be an IC die or an IC wafer in some embodiments with different embodiments encompassing different combinations of wafers and dies for the different bonded layers. The machine-trained network in some embodiments includes several stages of machine-trained processing nodes with routing fabric that supplies the outputs of earlier stage nodes to drive the inputs of later stage nodes. In some embodiments, the machine-trained network is a neural network and the processing nodes are neurons of the neural network. In some embodiments, one or more parameters associated with each processing node (e.g., each neuron) is defined through machine-trained processes that define the values of these parameters in order to allow the machine-trained network (e.g., neural network) to perform particular operations (e.g., face recognition, voice recognition, etc.). For example, in some embodiments, the machine-trained parameters are weight values that are used to aggregate (e.g., to sum) several output values of several earlier stage processing nodes to produce an input value for a later stage processing node.
Owner:XCELSIS CORP
Graphite bearing disc used for production process of LED epitaxial wafer
ActiveCN104409402AReduced swirl areaImprove the problem of low luminous intensitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystallographyLuminous intensity
The invention discloses a graphite bearing disc used for a production process of an LED epitaxial wafer. The graphite bearing disc comprises a plurality of wafer grooves formed in the bearing disc, wherein the wafer grooves are used for containing epitaxial wafer substrates. The graphite bearing disc is characterized in that a convex part structure is arranged on a central region of the bearing disc so that the vortex area of the central region of the bearing disc in an epitaxial production process can be reduced, and the problem that the light intensity of a partial region, which is formed towards the center of a shaft of the bearing disc, of the epitaxial wafer of an inner ring is low can be solved; and therefore, the brightness uniformity of the inner ring is improved and the whole uniformity of the brightness of the epitaxial wafers of the inner and outer rings is improved.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Production method of 50-micron ultrathin chips
ActiveCN103515316AReduce crackingReduce quality problemsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityChip size
The invention provides a production method of 50-micron ultrathin chips. An adhesive film is pasted to the surface of a wafer graph, and a film cutter is inclined to cut the film; the wafer is thinned through coarse grinding, fine grinding, polishing and eroding, four feeding speeds exist only in the coarse grinding, and three speeds exist in the polishing; a film is tightly stretched on the back face of the thinned wafer, the adhesive film on the front face of the wafer is torn off, and feeding and discharging are performed automatically; scribing is performed with a step mode and an anti-cracking scribing process of the double-shaft scribing technology, and production of the 50-microns ultrathin chips is completed. The production method can guarantee the processing capability of a back-end process along with increasing of sizes of the chips, reduce the quality abnormities that in the scribing process, the surfaces of the chips are cracked and the back faces are stretched to be broken, reduce the resistance borne by a scribing cutter in the cutting process, effectively solve the quality problem that the chips are cracked and stretched to be broken, achieve the processing of the ultrathin chips and provide technical preparation for the development direction of high-density, high-performance, light and thin IC packaging products.
Owner:TIANSHUI HUATIAN TECH +1
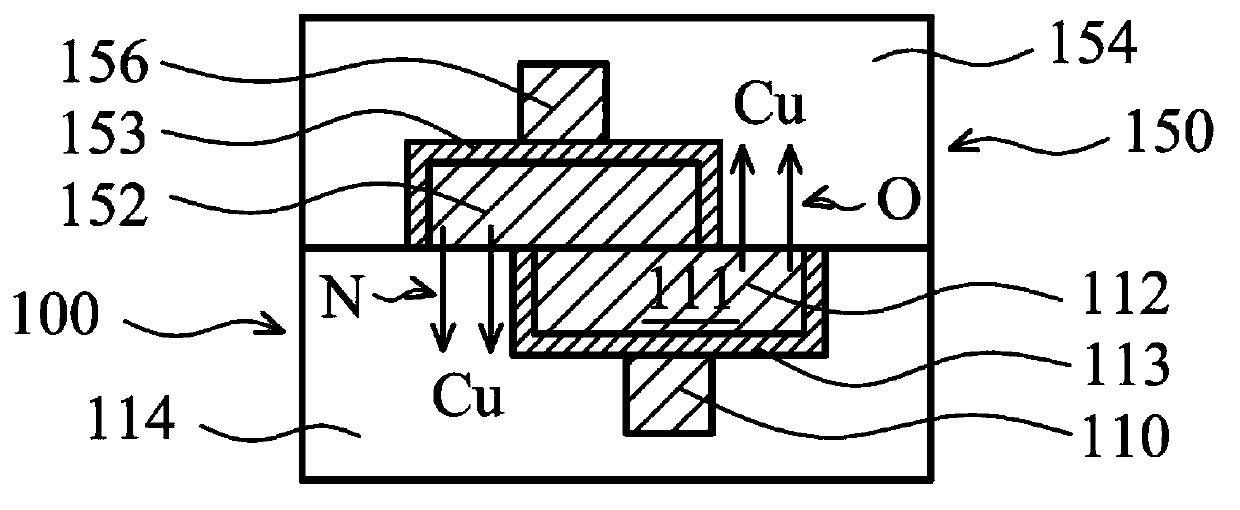
Hybrid bonding mechanisms for semiconductor wafers
The embodiments of diffusion barrier layer described above provide mechanisms for forming a copper diffusion barrier layer to prevent device degradation for hybrid bonding of wafers. The diffusion barrier layer(s) encircles the copper-containing conductive pads used for hybrid bonding. The diffusion barrier layer can be on one of the two bonding wafers or on both bonding wafers.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Image sensor package with grain receiving opening and method of the same
The present invention discloses an image sensor package which is provided with the grain accommodating through holes and a method thereof. The image sensor package comprises the following components: a substrate which is provided with a grain through hole and a contact pad through hole structure formed therein, wherein the terminal contact pad is formed at the lower surface of the contact pad through hole structure, and a conductive projection is coupled to the terminal contact pad which is formed on the upper surface of the substrate; a grain which has a micro lens area is provided at the inner part of the through hole of the grain; a bonding wire which is formed on the grain and the substrate, wherein the bonding wire is coupled to the grain and the contact pad of the bonding wire; a transparent panel which is provided on the grain in the through hole of the grain with an adhering mode for generating a clearance between the transparent panel and the grain; and a protecting layer which covers the bonding wire and is filled to the clearance between the edge of the grain and the side wall of the grain through hole of the wafer. The invention is suitable for the packaging of the image sensor.
Owner:ADVANCED CHIP ENG TECH INC
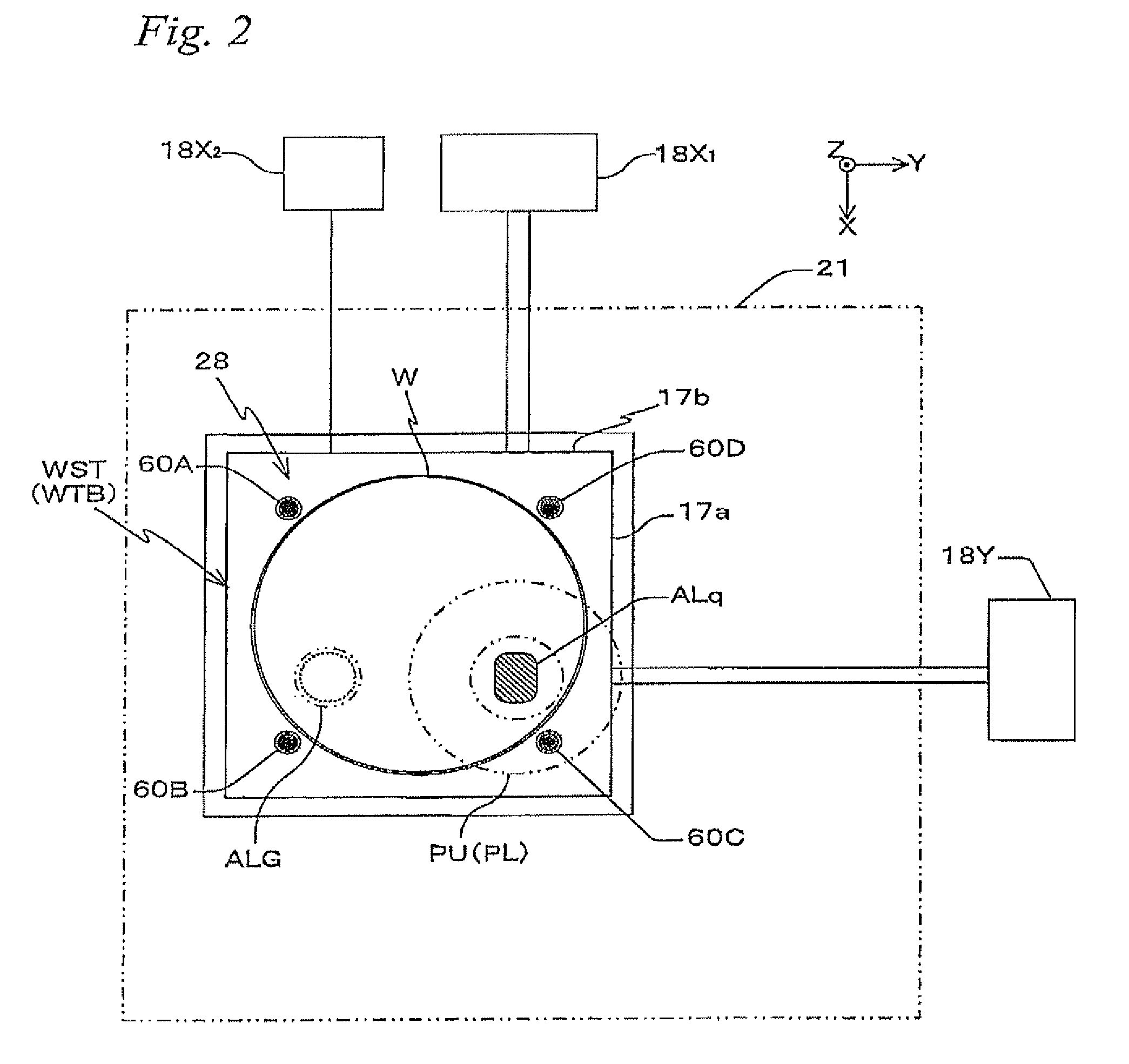
Detection method for optimum position detection formula, alignment method, exposure method, device production method, device, and measurement and/or inspection apparatus
InactiveUS20060040191A1Reduce the impactReduce impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharacter and pattern recognitionLocation detectionData selection
An alignment method enabling reduction of the effects on throughput and nonlinear correction for the optimum shot alignment for each wafer. According to the present invention, the nonlinear error is corrected by EGA calculation having higher order terms. One or more correction conditions (correction coefficients) are selected with reference EGA log data or overlay measurement data in advance for each process condition and registered in an exposure apparatus. At the time of lot processing of the exposure apparatus, the shot alignment of several sample shots is detected to detect the trend in nonlinear error and a single optimum correction coefficient is selected based on this from the registered plurality of correction coefficients. Further, after ordinary EGA, higher order EGA is performed using the selected correction coefficient to correct the nonlinear component and position each shot area.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Silicon-glass-silicon structure surface acoustic wave temperature and pressure integrated sensor and preparation thereof
ActiveCN105784189AAvoid disturbanceImprove reliabilityForce measurementThermometers using physical/chemical changesBond interfaceOptoelectronics
The invention provides a silicon-glass-silicon structure surface acoustic wave temperature and pressure integrated sensor and preparation thereof, and relates to a sensor. The sensor has a silicon-glass-silicon sandwich structure. A pressure sensor is integrated on a silicon-based pressure-sensitive film of the upper layer. A temperature sensor is integrated on a silicon substrate of the bottom part. The silicon substrate and the upper layer are isolated by a glass framework. The manufacturing method comprises the steps that the silicon substrate is prepared; the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film is prepared; a sandwich structure cavity is formed by the silicon substrate, the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film and the glass framework through bonding; the substrate layer of an SOI wafer is etched with the buried silicon oxide layer in the SOI wafer acting as a corrosion auto-stop layer so that the device layer of the SOI wafer is remained to act as the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film of the pressure sensor; four electrode regions are formed on the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film through etching, and the etching regions are arranged above the electrode regions of the temperature sensor and the pressure sensor with the bonding interface of the glass framework and the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film and the inlaid electrodes in the silicon-based pressure-sensitive film acting as the etching stop layer respectively; and array devices are split and then single devices are obtained.
Owner:厦门纵能电子科技有限公司
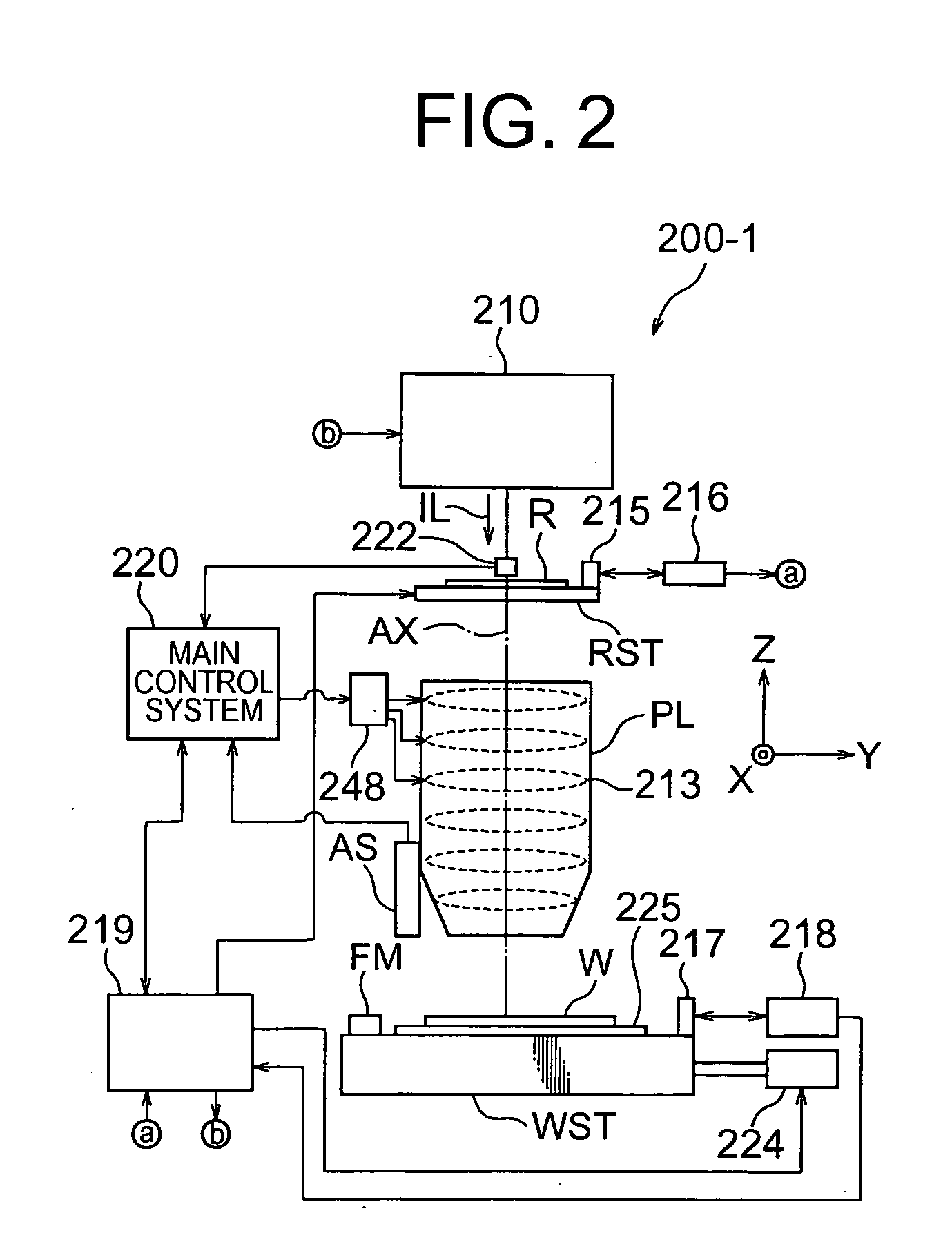
Exposure apparatus, exposure method, and device manufacturing method
ActiveUS8786829B2Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusEngineeringEncoder
Owner:NIKON CORP
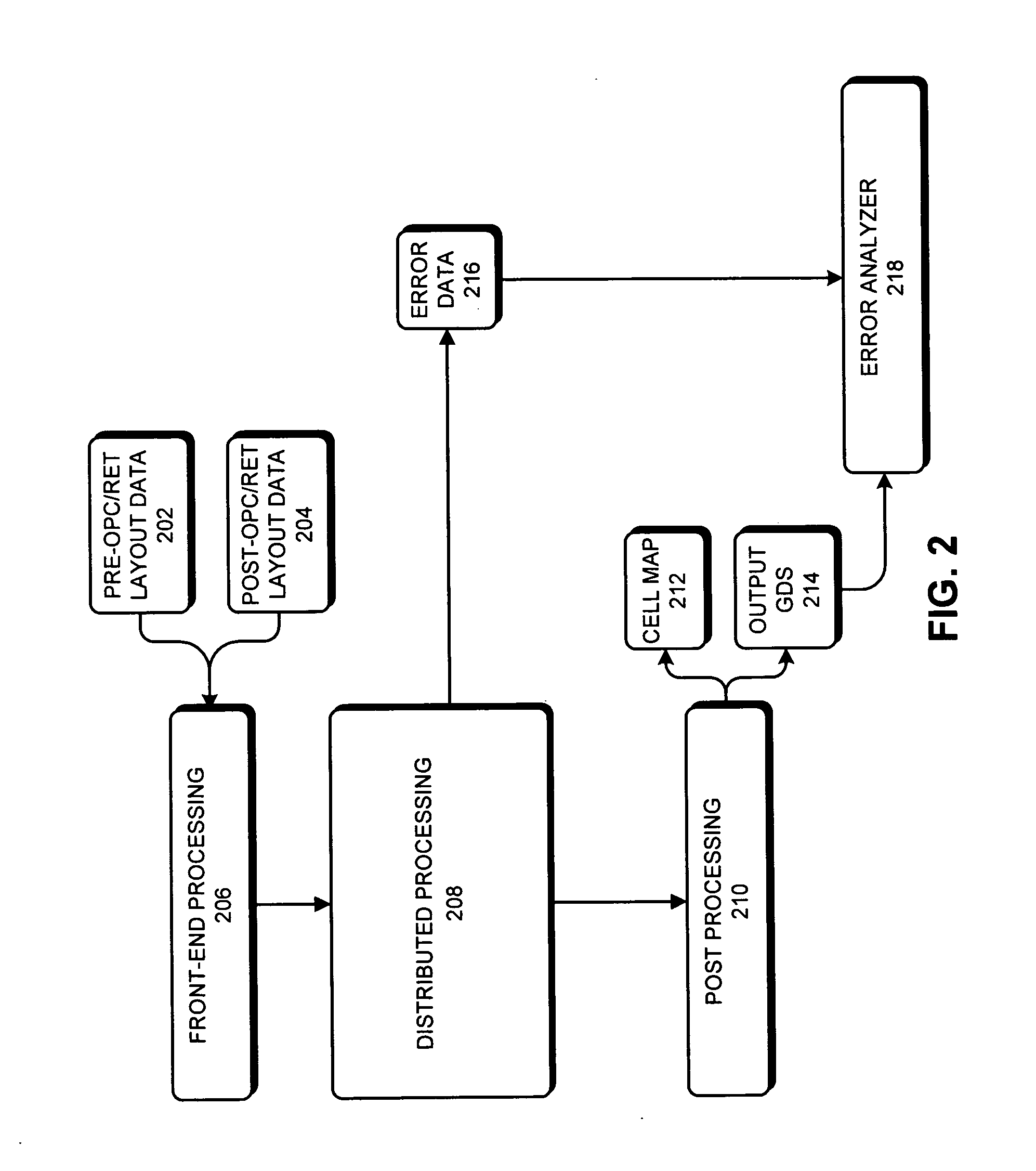
Distributed hierarchical partitioning framework for verifying a simulated wafer image
ActiveUS20070055953A1Character and pattern recognitionOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGraphicsTheoretical computer science
A system that verifies a simulated wafer image against an intended design. During operation, the system receives a design. Next, the system generates a skeleton from the design, wherein the skeleton specifies cell placements and associated bounding boxes for the cell placements, but does not include geometries for the cell placements. The system then computes environments for cell placements based on the skeleton. Next, the system generates templates for cell placements, wherein a template for a cell placement specifies the cell placement and the environment surrounding the cell placement. The system then generates the simulated wafer image by performing model-based simulations for cell placements associated with unique templates.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Optoelectronic systems providing high-power high-brightness laser light based on field coupled arrays, bars and stacks of semicondutor diode lasers
ActiveUS20090116525A1Improve discriminationEfficient couplingLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrayLow leakage
A semiconductor diode laser having a broad vertical waveguide and a broad lateral waveguide is disclosed emitting laser-light in a single vertical mode and a single lateral mode narrow beam. The vertical waveguide comprises a coupled cavity structure, wherein light, generated in the active medium placed in the first cavity leaks into the second cavity and returns back. Phase matching conditions govern the selection of a single vertical mode. A multi-stripe lateral waveguide comprises preferably a lateral photonic band crystal with a lateral optical defect created by selected pumping of multistripes. This approach allows the selection of a single lateral mode having a higher optical confinement factor and / or a lower absorption loss and / or a lower leakage loss compared to the rest lateral optical modes. This enables a single lateral mode lasing from a broad area field coupled laser array. A laser system comprised of multiple field coupled laser arrays on a single wafer and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser bar emitting a coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. A laser system comprised of multiple ultra-broad field coupled laser bars on different wafers and a set of external mirrors enables an ultra-broad field coupled laser stack emitting coherent laser light in a single vertical optical mode and a single lateral optical mode. This allows realization of ultrahigh power ultrahigh brightness laser systems based on semiconductor diode lasers.
Owner:VI SYST GMBH
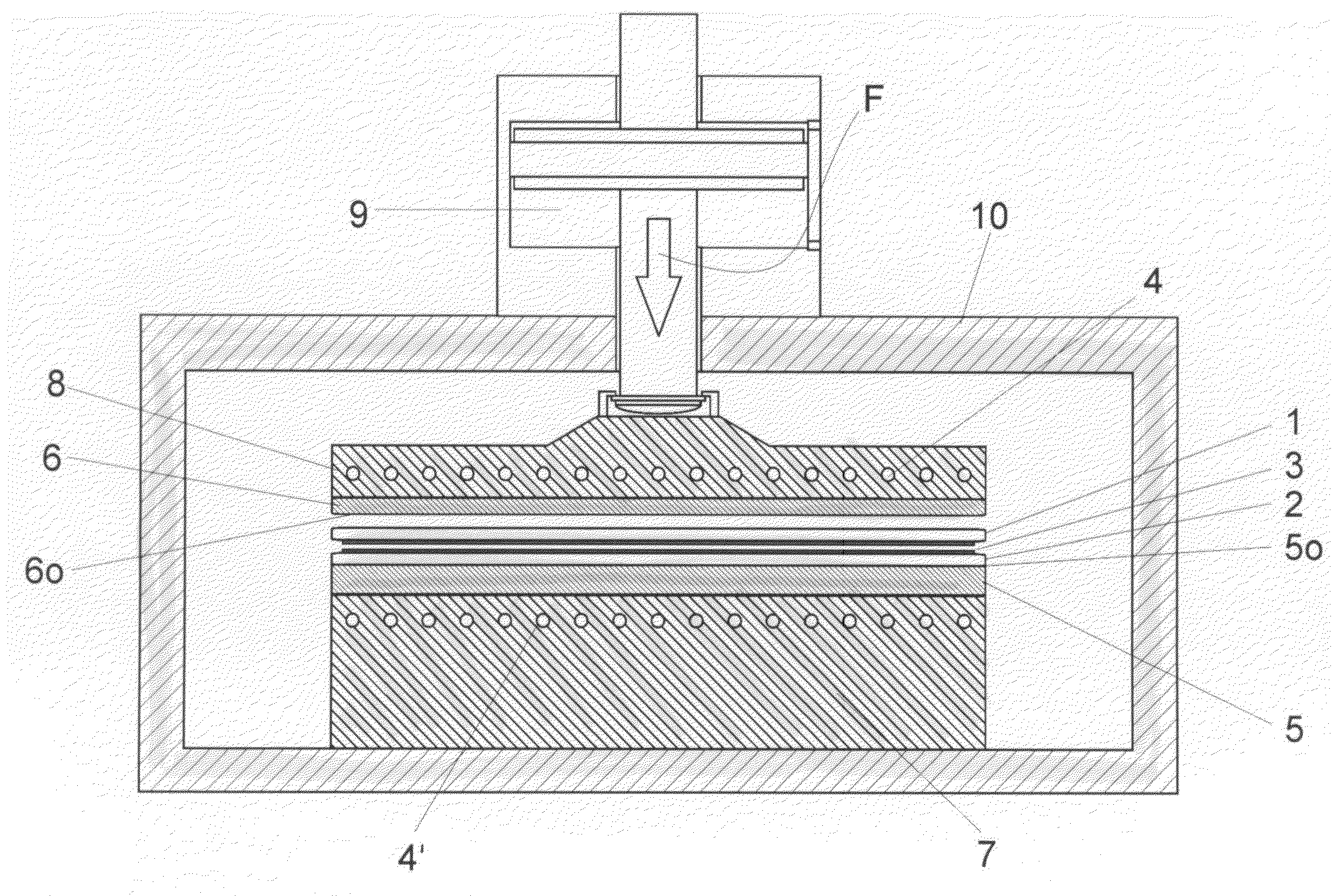
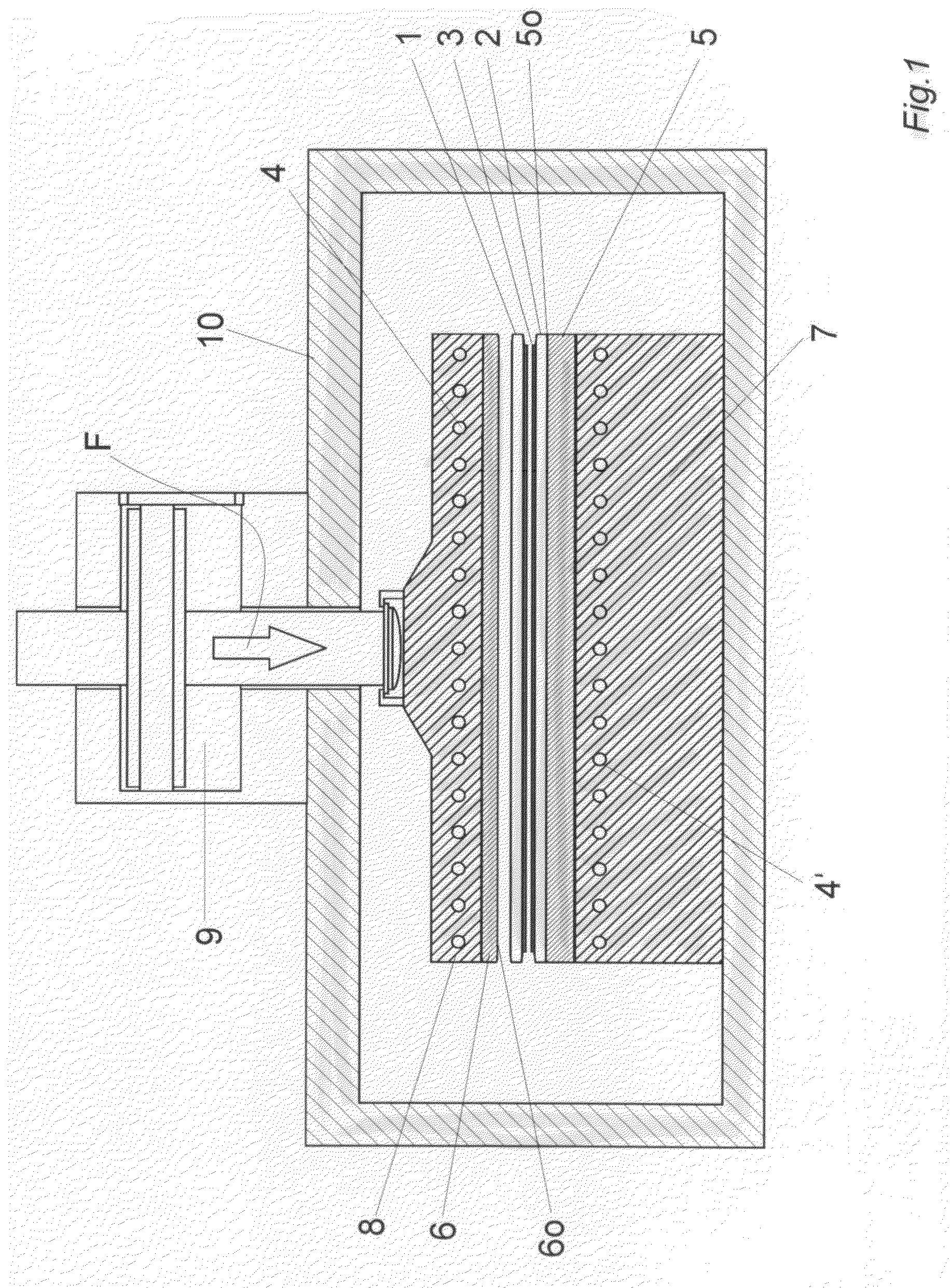
Process and device for bonding wafers
ActiveUS20080153258A1Avoid pollutionScratches and deposits can be avoidedLaminationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical elementEngineering
The invention relates to a process and a device for bonding at least two substrates (1, 2), in particular semiconductor substrates or wafers, having the following features: a) a lower pressure plate (5) for holding the substrates (1, 2) and transferring pressure and, in particular, heat to the substrates (1, 2), b) an upper pressure plate (6) located opposite the lower pressure plate (5) for transferring pressure and, in particular, heat to the substrates (1, 2), c) heating means (7, 8) for heating up the substrates (1, 2), in particular to temperatures above 250° C., and d) pressure charging means, in particular an actuator (9), for charging the lower (5) and / or upper pressure plate (6) with a pressing force F, in particular higher than 500 N, preferably higher than 1,000 N. According to the invention, the upper pressure plate (6) and / or the lower pressure plate (5) are substantially free from the chemical elements Ti and Mo at least on one substrate contact surface (5o, 6o) facing the substrates.
Owner:THALLNER ERICH
Preparation method of film bulk acoustic wave resonator with isolation layer and bulk acoustic wave resonator
ActiveCN109981069AAvoid it happening againAvoid enteringImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorHigh energy
The invention relates to the technical field of acoustic wave resonator preparation, in particular to a preparation method of a film bulk acoustic wave resonator with an isolation layer and the bulk acoustic wave resonator. The method comprises the following steps: injecting high-energy ions from the lower surface of a single crystal wafer, enabling the high-energy ions to enter the single crystalwafer to form a damage layer, and dividing the single crystal wafer into an upper piezoelectric layer and a single crystal film layer to obtain a damaged single crystal wafer; sequentially preparinga graphical lower electrode, a graphical sacrificial layer, an isolation layer and a bonding layer on the lower surface of the single crystal film layer; stacking the substrate and the bonding layer,performing wafer splitting treatment, stripping the upper piezoelectric layer at the upper end of the single crystal film layer, and preparing an upper electrode on the upper surface of the single crystal film layer; and forming a sacrificial layer release hole required by the graphical sacrificial layer on the upper surface of the single crystal film layer, and releasing the sacrificial layer toobtain the high-quality cavity type bulk acoustic wave resonator of the single crystal film body.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Wafer three-dimensional integrated lead wire process for three-dimensional memory and structure thereof
ActiveCN107644837AReduce manufacturing costImprove yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionThree dimensional integration
The invention provides a wafer three-dimensional integrated lead wire process and a structure thereof. The process can be applied to a wafer three-dimensional integration process for the wafers of a three-dimensional memory. A dielectric layer 13 is arranged between a first wafer 11 and a three-dimensional memory device 14 and a contact hole 15 for metal interconnection is configured to be in contact with the dielectric layer 13. The invention provides a new lead wire process, making it possible to pass through a thick device layer for wire leading on a backside.
Owner:YANGTZE MEMORY TECH CO LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: [email protected]