Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
124 results about "A-site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The A-site (A for aminoacyl) of a ribosome is a binding site for charged t-RNA molecules during protein synthesis. One of three such binding sites, the A-site is the first location the t-RNA binds during the protein synthesis process, the other two sites being P-site (peptidyl) and E-site (exit).
Fad2 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
ActiveUS20140090116A1Minimal adverse impactFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesA-siteBioinformatics
Methods and compositions for gene disruption, gene editing or gene stacking within a FAD2 loci by cleaving, in a site directed manner, a location in a FAD2 gene in a soybean cell, to generate a break in the FAD2 gene and then optionally integrating into the break a nucleic acid molecule of interest is disclosed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Fad2 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
Enzymes for the detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030134349A1Simple structureLow detection sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesA-siteA-DNA
The present invention relates to novel enzymes designed for direct detection, characterization and quantitation of nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The present invention provides enzymes that recognize specific nucleic acid cleavage structures formed on a target RNA sequence and that cleave the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner to produce non-target cleavage products. The present invention provides enzymes having an improved ability to specifically cleave a DNA member of a complex comprising DNA and RNA nucleic acid strands.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Method for preparing DNA coding compound library, initial head fragment compound and prepared DNA coding compound
ActiveCN108070009ASpeed up the screening processShorten the development cycleSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesChemical reactionPharmacophore
The invention discloses a method for preparing a DNA coding compound library containing two or more pharmacophores. A novel initial head fragment used by the method has two or more chemically-modifiedlinking groups and comprises a nucleotide chain, 5' and 3' of the nucleotide chain respectively have a group R1 and a group R2 capable of performing chemical reaction, n connecting heads are arrangedon the nucleotide chain, each of the connecting heads is a long chain extended after a nucleotide monomer on the nucleotide chain is modified, and the long chain has a site G capable of performing chemical reaction. The site G of the initial head fragment respectively reacts with a fragment compound to generate a fragment compound residue B connecting the site G with the fragment compound together, a DNA coding compound is formed, and finally, the DNA coding compound library containing the two or more pharmacophores can be obtained. Through the method disclosed by the invention and the initial head fragment, the DNA coding compound library containing the two or more pharmacophores can be efficiently, simply and quickly obtained.
Owner:上海药明康德新药开发有限公司
Method for producing target substance capturing protein and method for selecting component materials thereof
InactiveUS20060275811A1Convenient and practical selectionValid choicePeptide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingBinding domain
A combination of polypeptide chains used as a plurality of target substance-binding domains are selected by: (1) reacting a target substance with a first polypeptide chain with a known target substance-binding domain to obtain a first complex; (2) reacting the first complex with a second polypeptide chain library composed of polypeptide chains each having a site to be associated with the first polypeptide chain to obtain second complexes in which the second polypeptide chain is bonded with the target substance in the first complex; (3) washing the second complexes to obtain a third complex in which the first polypeptide chain and the second polypeptide chain are associated with each other and bonded with the target substance; and (4) obtaining a nucleic acid sequence of the second polypeptide chain from the third complex.
Owner:CANON KK
Enzymatic DNA molecules
InactiveUS7141665B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingEnzyme
The present invention discloses deoxyribonucleic acid enzymes—catalytic or enzymatic DNA molecules—capable of cleaving nucleic acid sequences or molecules, particularly RNA, in a site-specific manner, as well as compositions including same. Methods of making and using the disclosed enzymes and compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
D-amino acid oxidase mutant and application thereof
The invention discloses a D-amino acid oxidase mutant and application thereof. The mutant is obtained by carrying out single mutagenesis or multiple mutagenesis on a 52nd site, a 54th site, a 58th site, a 213rd site and a 335th site of amino acid with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein glycine at the 52nd site is mutated into leucine, asparagine at the 54th site is mutated into valine, phenylalanine at the 58th site is mutated into glutamine, methionine at the 213rd site is mutated into serine, and serine at the 335th site is mutated into glycine. According to the D-amino acid oxidase mutant and the application thereof, a D-amino acid oxidase gene with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 is mutated by utilizing a site-saturation mutagenesis technology, so thatthe enzyme activity and the product conversion rate are far higher than those of a wild type, and therefore the product yield in a 4-(hydroxymethylphosphoryl)-2-carbonyl-butanoic acid production process is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Inducible self-cleaving protease tag and method of purifying recombinant proteins using the same
A method of purifying a protein is disclosed which entails: a) fusing a site-specific affinity-tagged cysteine protease domain to a target protein to form a tagged fusion protein; b) activating the site-specific cysteine protease domain of the tagged fusion protein by subjecting the site-specific affinity-tagged cysteine protease domain to an inducer, which induces autoprocessing at a cleavage site; thereby releasing untagged target protein; and c) isolating the untagged target protein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Site-directed mutation modified algin lyase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111424027AHigh catalytic efficiencyIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesArginineProtein molecules
The invention discloses a site-directed mutation modified algin lyase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The algin lyase mutant provided by the invention is obtained by replacing glutamic acid at position 212 of the an algin lyase with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 by histidine and / or replacing arginine at position 222 by lysine. According to the invention, the active center amino acid of the algin lyase is determined through molecular docking simulation, and site-directed saturated mutation is carried out to change aminoacid residues near active sites of protein molecules, so that catalytic efficiency of the algin lyase is improved, and the yield of the algin lyase is further improved. According to the invention, constructed recombinant escherichia coli with enhanced secretion capacity of algin lyase can improve enzyme activity of the algin lyase by 2.83 times compared with an original strain. The improved genetic engineering bacteria have obviously improved enzyme production capacity, and activity of algin lyase produced by shake flask fermentation reaches 15000U / mL or above, so that the improved genetic engineering bacteria are more suitable for industrial application, production cost can be reduced, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombined alkaline pectinase with high pH stability and specific enzyme activity and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103881996AImproves pH stabilityImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionPectinaseA-site
The invention discloses recombined alkaline pectinase with good pH stability and high specific enzyme activity and a construction method thereof. A Site-directed mutagenesis technique is adopted for mutagenesis of an alkaline pectinase coding gene pel168 of bacillus subtilis 168 and 457-bit guanine G is transformed into thymine T so that the 132-bit valine V of the mature peptide of the coded pectinase is mutated into phenylalanine F, a mutant gene pel168V132F is expressed in colon bacillus Rosset Blue (DE3) and subjected to inducible expression, bacterium breaking and purification, the purified enzyme is subjected to enzyme activity measurement, and the relative activity of the obtained pectinase mutant PEL168V132F is much higher than that of the original pectinase PEL168 when the pH is 3, 5 and 6; and meanwhile, the specific enzyme activity is 2.25 times that of the original pectinase, thus good foundation is laid for wide application of the alkaline pectinase.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Method and kit for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in range of whole transcriptome
ActiveCN111154837AAccurate resolutionHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBase JChemical treatment
The invention provides a method and kit for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in a range of a whole transcriptome. According to the method, on the basis of an N6-allyl label of in-vivo ribonucleic acid (RNA) adenine and chemical treatment, base mutation of the in-vivo ribonucleic acid (RNA) adenine in a process of reverse transcription into DNA is induced, andthen a mutation site is recognized by means of nucleic acid sequencing, so that an a6A site is obtained, and the a6A site is a site originally modified by m6A in cell RNA. By means of the method, thespecific label of N6-allyladenine in a cell is achieved for the first time, and the label not only can be used for replacing an N6-methyladenosine site in the cell, but also can be positioned by means of mutation sequencing. Compared with existing gene sequencing technologies applied to m6A detection, the method for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-base resolution in the range of the whole transcriptome has the advantage that due to the fact that the mutation site can be accurate down to single-base resolution, the precision of m6A site detection based on m6A antibody immunoprecipitation and a massively parallel sequencing method which are currently and generally adopted is improved, so that the method for detecting RNA N6-methyladenosine modification at single-baseresolution in the range of the whole transcriptome is a direct high-throughput single-base identification method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Therapeutic compositions and methods of using same
InactiveUS20060122118A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsA-siteBlood vessel
A targeted composition comprising a modulation molecule, such as an siRNA oligo or a small molecule, and a translocation peptide is disclosed. Methods of making and using the composition are also disclosed. The disclosed composition can be employed in a variety of therapeutic and research applications, in which it is desirable to deliver a modulation molecule, such as an siRNA oligo or a small molecule, to a particular site, such as a site of vascularization. In one aspect of a composition of the invention, a translocation peptide directs the modulation molecule to a selected location, and a modulation molecule modulates the expression or activity of a selected target disposed at or near the selected location.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Method for porcine H11 site-specific insertion by using site specific cleavage system
ActiveCN104531686ASolve the problem of inconvenient design and difficult detectionImprove efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionLibrary creationSystems designGene
The invention provides a method for porcine H11 site-specific insertion by using a site specific cleavage system. The method comprises the following steps: 1) designing5'-terminal homologous arm and 3'-terminal homologous arm of knocked-out gene and corresponding universal primers; 2) introducing the above homologous arms, the universal primers and gene to be inserted into a vector in order to a targeting vector; 3) transferring into cells; and 4) carrying out PCR amplification, and identifying the insertion result. The targeting vector is designed mainly relying on the porcine H11 site cleavage system, and the vector can accurately introduce exogenous gene into the porcine the H11 site in order to solve the problems of low efficiency of traditional targeting techniques, inconvenient designing of PCR detection primers and large detection difficulty. The site-specific insertion method provided by the invention allows the exogenous gene to be stably expressed in H11, and builds a stable platform for pig transgene.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer set for amplification of CYP2C19 gene, reagent for amplification of CYP2C19 gene comprising the same, and use of the same
InactiveCN101501223AReduce effortLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerNucleotide sequencing
Disclosed is a primer set for amplifying a target region in CYP2C19 gene which contains a site to be detected by a gene amplification method, and which enables to amplify the region specifically. Two pairs of primer sets are used, each of which comprises a forward primer comprising a nucleotide sequence depicted in each of SEQ ID NOs:12 and 32 and a reverse primer comprising a nucleotide sequence depicted in each of SEQ ID NOs:22 and 48, respectively. These primer sets enable to amplify two regions each containing a site having each of two types of polymorphisms occurring in CYP2C19 gene (CYP2C19 gene*2, CYP2C19*3) simultaneously in a single reaction solution.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Anti-mcam antibodies and associated methods of use
Described herein are anti-MCAM antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof that are capable of inhibiting the interaction between MCAM and its ligand, a protein comprising a laminin α-4 chain. These anti-MCAM antibodies and antigen binding fragments thereof may be useful for, for example, treating inflammatory conditions characterized by the infiltration of MCAM-expressing cells into a site of inflammation in the body.
Owner:PROTHENA BIOSCI LTD
Method for preparation of recobinant DNA
InactiveUS20110244521A1Reduce laborShorten operation timeFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionDna recognitionA-site
The problem to be solved in the present invention is to provide a simplified and efficiently improved DNA recombination method.The above problem can be solved with the present method for preparing a recombinant DNA by inserting a DNA fragment of interest into a vector DNA, the method comprising the step of carrying out the following reactions at the same reacting location at the substantially simultaneouse time: (a) a reaction for simultaneously cleaving a site of the vector for inserting the fragment and a DNA containing the fragment in the presence of a restriction enzyme whose DNA recognition site and DNA cleavage site are discrete; and (b) a reaction for inserting the fragment into the vector in the presence of a DNA ligase.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
Detection of nuceic acids by multiple sequential invasive cleavages
InactiveUS20050003432A1Reduce interactionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNon targeted
The present invention relates to means for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences, as well as variations in nucleic acid sequences. The present invention also relates to methods for forming a nucleic acid cleavage structure on a target sequence and cleaving the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner. The structure-specific nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave the target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof. The present invention further relates to methods and devices for the separation of nucleic acid molecules based on charge. The present invention also provides methods for the detection of non-target cleavage products via the formation of a complete and activated protein binding region. The invention further provides sensitive and specific methods for the detection of nucleic acid from various viruses in a sample.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Lipase mutant with improved thermal stability
ActiveCN108118043AHigh catalytic efficiencyIncrease the Tm valueHydrolasesFermentationCandida rugosaMutant
The present invention provides a Candida rugosa lipase mutant, wherein Candida rugosa (ATCC NO:14830) lipase LIP1 (CRL1) is subjected to thermal stability modification by using a site-directed mutation technology so as to optimize the practicality in the high temperature industrial environment. According to the present invention, the CRL1 gene is used as the template, the protein rational design technology is used, and the amino acid Asp at 4578 site of the CRL1 lipase gene sequence is substituted with Phe so as to obtain the lipase mutant with the improved thermal stability, wherein the application range and the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme are improved; and the CRL1 is subjected to site-directed mutation by using the molecular biology method to obtain the lipase mutant, wherein theTm value of the lipase mutant is increased by 9.4 DEG C, the optimum temperature is increased by 10 DEG C, and the T1 / 2 (50 DEG C) is 6.5 times the T1 / 2 (50 DEG C) of the parent lipase.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Associated protein for regulating and controlling round-leaf characteristics of cucumbers as well as coding gene thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN108148821ASerrated neatlyCucumber Leaf Shape ImprovementTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyAgc kinase
The invention discloses an associated protein for regulating and controlling round-leaf characteristics of cucumbers as well as a coding gene thereof and application thereof. An amino acid sequence ofthe protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2; protein kinase, which belongs to an AGC kinase family, of serine / threonine is coded by a PID gene; a coding gene of the protein is a base sequence as shown ina sequence table SEQ ID NO:1; guanine (G), at a site 1092bp, of the base sequence is substituted by adenine (A), Val (valine) at a site 346 of a coded amino acid residue sequence is mutated to be Met(methionine); the protein inhibits polar translocation of auxin, causes polar defect of auxin transport, has a blade edge smooth plant phenotype, has unapparent saw-tooth bugles, and has nearly roundleaves; a main root is not developed, and a main lateral root does not have obvious difference; male and female flowers are free of calyxes, and female flowers are not developed and the like. The geneand the protein can provide a basis for improving cucumber leaf type, increasing the yield, cultivating ideal plants and researching an auxin signal channel molecule regulation mechanism.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
FAD3 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC +1
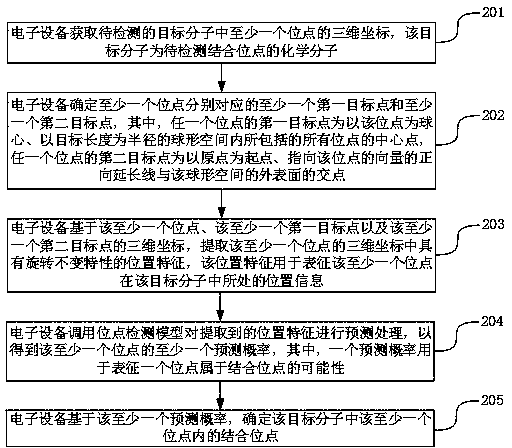
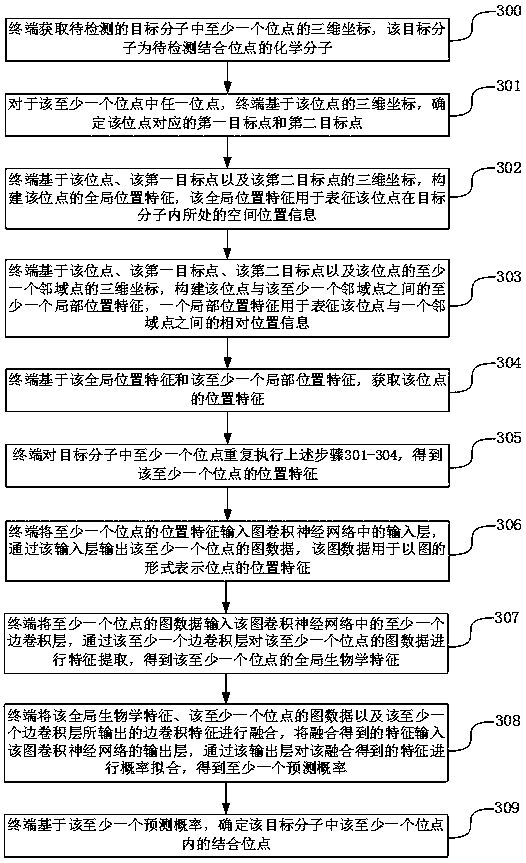
Molecular binding site detection method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN111243668AHas rotation invariant propertiesThe positional characteristics of the rotation invariant property are fully reflectedChemical property predictionMolecular entity identificationVoxelA-site
The invention discloses a molecular binding site detection method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of computers. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring three-dimensional coordinates of each site in a target molecule; determining a first target point and a second target point corresponding to each site, extracting position features with rotation invariant characteristics in the three-dimensional coordinates of each site, calling a site detection model to predict the extracted position features, obtaining a prediction probability that each site belongs to a binding site or not, and determining a binding site based on the prediction probability. The first target point and the second target point are related to each site andhave certain spatial representativeness; the method is beneficial to constructing the position characteristics which can comprehensively reflect the detail structure of the target molecule and have the rotation invariant characteristic, detail loss caused by designing voxel characteristics for the target molecule is avoided, and the accuracy of the molecular binding site detection process is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Site for stably expressing protein in CHO cell gene NW_003613781.1 and application of site
ActiveCN114058625AShorten development timeSolving the problem of ambiguous integration sitesHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsBase JA-site
The invention discloses a site for stably expressing protein in a CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cell gene NW_003613781.1 and application of the site. The obtained stable expression site is positioned on a basic group in a 100bp range of the upstream and downstream of the 1497187 basic group of the CHO cell gene NW_003613781.1, namely the 1497087-1497287 basic group, and an exogenous protein gene can be integrated and stably expressed. According to the invention, the target gene is subjected to site-specific integration to the stable expression region in a site-specific integration manner, so that the problem of unclear integration sites caused by random integration is solved. According to the invention, by site-specific integration of an exogenous gene in the range of 1497087-1497287 bases upstream and downstream at the 1497187 base of a stable expression site NW_003613781.1 in a CHO genome, the expression instability and repeated and tedious cell strain screening process caused by a position effect are overcome.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Plant site-directed recombination method mediated by repeated fragments
The invention provides a plant site-directed recombination method mediated by repeated fragments. Specifically, the present invention provides a donor DNA with a specific repeat sequence, and a reagent combination for gene editing. According to the invention, the donor DNA with a specific structure is adopted, and a specific site of a target gene is cut by means of a site-directed cutting nuclease, so that the donor DNA fragment is efficiently integrated into a cutting site.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through recombinant Escherichia coli
InactiveCN104099350AIncrease productionHigh affinityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention relates to a recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1, and tyrosine is mutated into any one of alanine, valine and leucine in the 52 position of the sequence. The invention further relates to recombinant Escherichia coli containing the recombinant lactate dehydrogenase gene and a method for synthetizing D-phenyllactic acid through the recombinant Escherichia coli. According to the method, the tyrosine on a substrate recognition site of D-LDH is replaced by smaller hydrophobic amino acid residue-valine with a site-directed mutagenesis technology, so that the affinity and the catalytic efficiency of the D-LDH to substrate phenylpyruvic acid are improved, after conversion of an expression host, the yield of phenyllactic acid is significantly increased when being compared with that of un-mutated strains, and after whole-cell conversion for 6 h, the yield of the phenyllactic acid is increased from 18 g / L to 24.6 g / L.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase by calcium ion binding site amino acid residue mutation
InactiveCN103740669AEase of industrial productionStrong specificityGlycosyltransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionArginineBinding site
The invention provides a mutant of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGT enzyme for short) with capability for high-yield of beta-cyclodextrin and mutating method thereof, and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention employs a site-directed mutagenesis method for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of CGT enzyme, and provides a mutating scheme for improving beta-cyclodextrin production capability of Bacillus circulans STB01CGT, that is alanine at the 315th position of the calcium ion binding site in CGT enzyme is changed into arginine (Arg) or aspartic acid (Asp), and the mutants A315R and A315D are obtained. Compared with the wild CGT enzyme, the two mutants have higher beta-cyclodextrin production capability, and are suitable for industrial production of beta-cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and construction method thereof
ActiveCN105087535AHigh activityImprove antioxidant capacityBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliA-DNA
The invention discloses a site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase and a construction method thereof. The photolyase has an amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a DNA photolyase gene from the existing WT escherichia coli, designing a mutation primer to obtain a mutated gene fragment, and connecting the mutated gene fragment with a pET22b plasmid to construct a recombinant expression plasmid pET22b-A377N; and converting the recombinant expression plasmid into an escherichia coli competent cell to construct a genetic engineering bacterium BL21(DE3) / pET22b-A377N for mutant enzyme expression. The site-directed mutagenesis escherichia coli DNA photolyase obtains better expression under a 1mM ITPG condition at 18 DEG C. The expressed photolyase is more stable in activity, and the antioxidation effect of the photolyase is significantly improved.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Site for stably expressing protein in CHO cell gene NW_003614092.1 and application of site
ActiveCN114085841AShorten development timeSolving the problem of ambiguous integration sitesHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsA-siteCell strain
The invention discloses a site for stably expressing protein in the CHO cell gene NW_003614092.1 and application of the site. The obtained stable expression site is positioned on a base in a 200-bp base range with the 1159467 base of the CHO cell gene NW_003614092.1 as a central point, namely, the 1159367 to 1159567 base, and can integrate an exogenous protein gene and perform stable expression. According to the invention, a target gene is subjected to site-specific integration to a stable expression region in a site-specific integration manner, so the problem of unclear integration sites caused by random integration is solved; and through site-specific integration of an exogenous gene in the range of 1159367 to 1159567bases, relative to the stable expression site at the 1159467 base in the CHO cell gene NW_003614092.1, expression instability and a repeated and tedious cell strain screening process caused by a position effect are overcome.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting cancer, and antibody capable of recognizing pancreas-specific ribonuclease 1
ActiveCN104364374ADigestive systemMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPancreas CancersRibonuclease
Pancreatic cancer can be detected by producing a monoclonal antibody which can bind to pancreas-specific RNase 1 when no sugar chain is bound to a site located in the pancreas-specific RNase 1 and capable of being modified with an N-type sugar chain and of which the binding to the pancreas-specific RNase 1 is inhibited when an N-type sugar chain is bound to the site, also producing a monoclonal antibody which can bind to the pancreas-specific RNase 1 simultaneously with the binding of the aforementioned antibody to the pancreas-specific RNase 1, and determining the ratio of A to B using the antibodies, wherein A represents the amount of the site located in the pancreas-specific RNase 1 and capable of being modified with an N-type sugar chain wherein an N-type sugar chain is bound or unbound to the site; and B represents the amount of the site located in the pancreas-specific RNase 1 and capable of being modified with an N-type sugar chain.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
CRICPR-Cas9-based method for in-vitro modifying adenovirus vectors
The invention discloses a CRICPR-Cas9-based method for in-vitro modifying adenovirus vectors and further provides a molecular cloning method suitable for modifying large plasmid vectors. The CRICPR-Cas9-based method includes: designing proper sgRNA according to a to-be-modified site of a starting plasmid; adopting Cas9 protein and the sgRNA to in-vitro cut the starting plasmid; connecting the starting plasmid which is cut with a target gene on the basis of a homologous recombination method to complete modifying. By using the CRICPR-Cas9-based method, the problem that proper restriction enzyme cutting sites are difficult to find for modifying the large plasmid vectors through conventional molecular biologic means is solved effectively. The method is an improvement of a site mutation kit which generally includes site mutation of target protein and building of truncation with deleted structural domain. By the method, the technical problem that secondary mutation (random mutation caused by PCR enzyme fidelity) is easy to be caused when the site mutation kit is used for mutation of large vectors exceeding 10kb is solved effectively.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT
Multiple fluorophore detector system
ActiveUS8940882B2High sensitivityImprove efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideA-site
A detector oligonucleotide comprises multiple pairs of a donor fluorophore and a quencher molecule, which donor fluorophores and quencher molecules are separated by a site that is capable of being cleaved when in double-stranded form. The detector oligonucleotide may be made double-stranded in a manner that depends on the presence of a target nucleic acid, allowing the cleavage sites to be cleaved. Separation of the donor fluorophores and the quencher molecules decreases fluorescence quenching and generates a detectable change in a fluorescence parameter of the fluorophores of the detector oligonucleotide. By using multiple donor / quencher pairs, the present detector oligonucleotide advantageously generates a high signal to noise ratio and high efficiency in detection of a target nucleic acid.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: [email protected]