Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3657results about How to "Extended half-life" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS20050014934A1Reducing FcRn binding affinityReduced half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against virusesHalf-lifeAntibody
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Multispecific antibodies
ActiveUS20080069820A1High binding affinityHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against growth factorsAntibody ingredientsSpecific antibody
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS7217797B2Function increaseExtended half-lifeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesAntiendomysial antibodiesBiochemistry
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
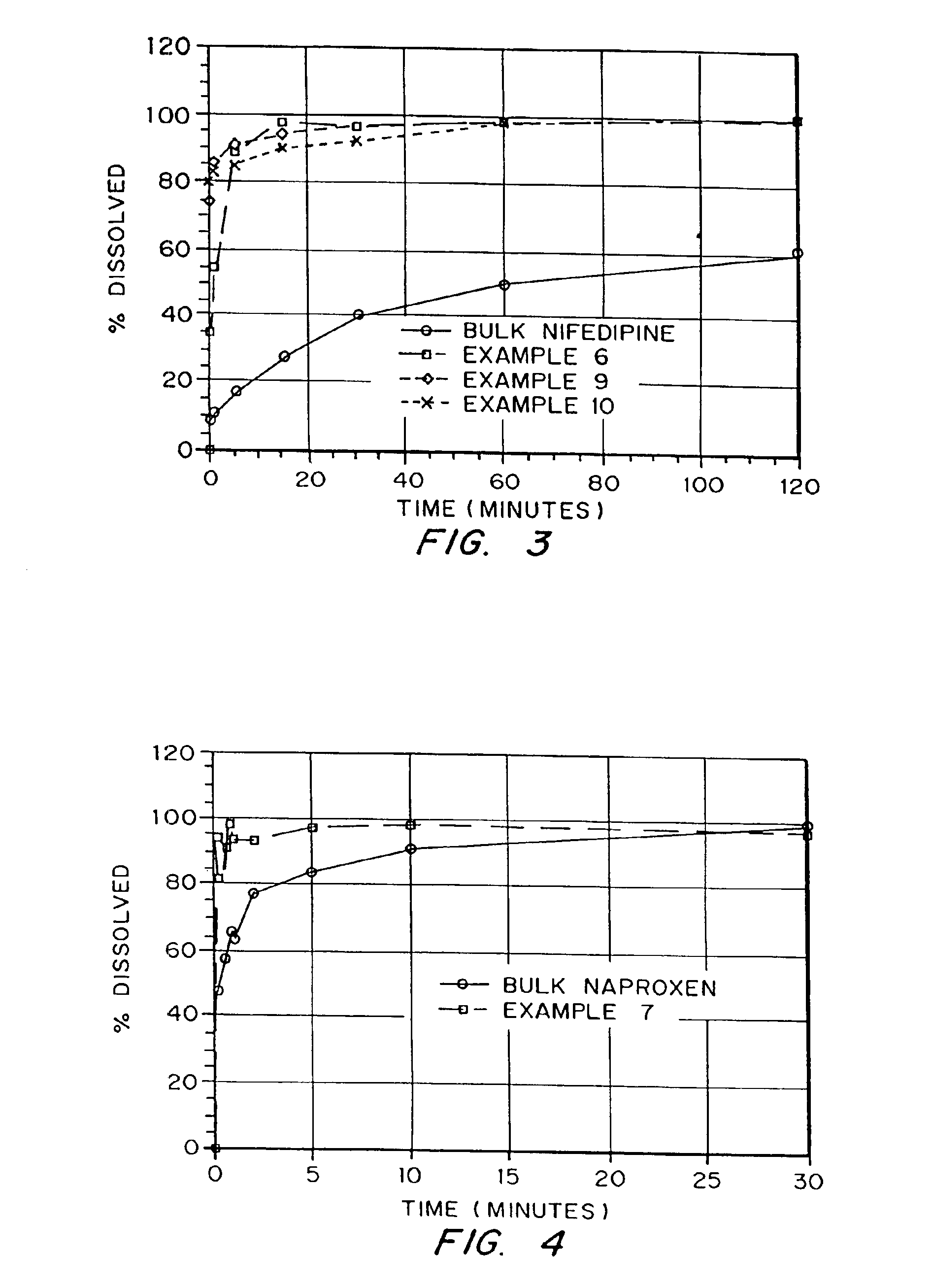
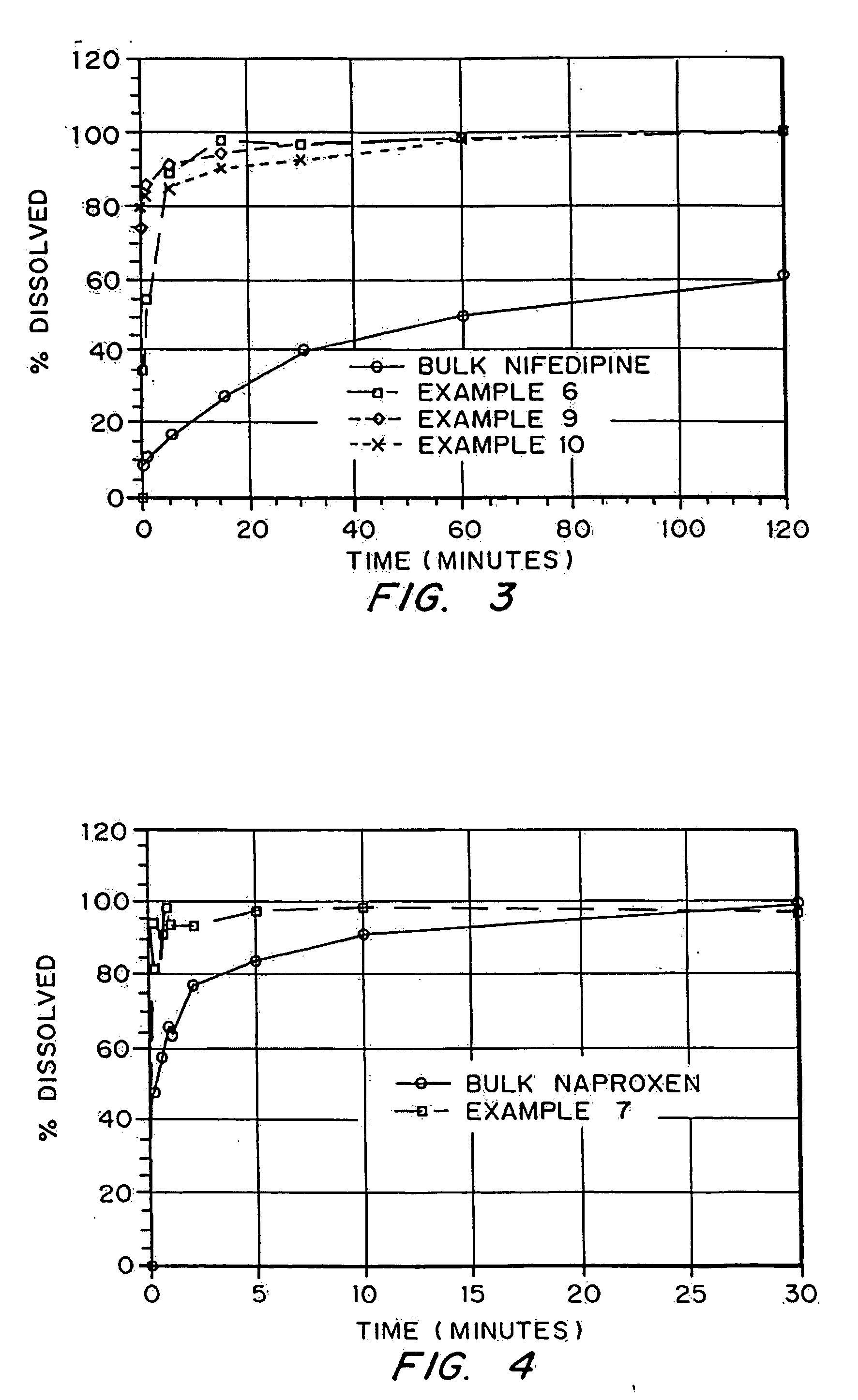
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Fc VARIANTS WITH ALTERED BINDING TO FcRn
ActiveUS20090163699A1Extended half-lifeNervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsWild typeChemistry
The present application relates to a variant Fc region comprising at least one modification relative to a wild-type human Fc region, where the modification selected from the group consisting of 434S, 252Y / 428L, 252Y / 434S, and 428L / 434S, and the numbering is according to the EU index.
Owner:XENCOR
Peptide agonists of GLP-1 activity
InactiveUS6528486B1Lower blood sugar levelsEffective and stablePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderD-GlucoseGlycemic
The present invention relates to novel peptide conjugates which have increased stability and are useful in the treatment of excess levels of blood glucose.
Owner:ZP HLDG SPV
Fc-erythropoietin fusion protein with improved pharmacokinetics
InactiveUS20050192211A1Improve pharmacokineticsSimplify erythropoietin therapyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsErythropoietinNucleic acid
The present invention provides Fc-erythropoietin (“Fc-EPO”) fusion proteins with improved pharmacokinetics. Nucleic acids, cells, and methods relating to the production and practice of the invention are also provided.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Transfection of blood cells with mRNA for immune stimulation and gene therapy
InactiveUS20060188490A1Improve stabilityIncrease transfectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAntigenCancer prevention
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition containing blood cells or haemopoietic cells, e.g. red blood cells (erythrocytes), granulocytes, mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and / or blood platelets, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient and / or vehicle, wherein the cells are transfected with at least one mRNA comprising at least one region coding for at least one antigen. The invention further discloses a method of preparing the aforesaid pharmaceutical composition and the use of blood cells transfected in this way for the preparation of drugs or pharmaceutical compositions for immune stimulation against the antigens encoded by the mRNA. The subjects according to the invention are used especially for the therapy and / or prophylaxis of carcinoses or infectious diseases and can also be employed in gene therapy.
Owner:CUREVAC AG
Compositions and methods for immunomodulation in an organism using IL-15 and soluble IL-15Ra
ActiveUS8124084B2Extended half-lifeImprove bioavailabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological bodyVaccination
The present invention relates to a therapeutic polypeptide and methods for its creation and use for modulating an immune response in a host organism in need thereof. In particular, the invention relates to the administration to an organism in need thereof, of an effective amount of a pre-coupled polypeptide complex comprising a lymphokine polypeptide portion, for example IL-15 (SEQ ID NO: 5, 6), IL-2 (SEQ ID NO: 10, 12) or combinations of both, and an interleukin receptor polypeptide portion, for example IL-15Ra (SEQ ID NO: 7, 8), IL-2Ra (SEQ ID NO: 9, 11) or combinations of both, for augmenting the immune system in, for example, cancer, SCID, AIDS, or vaccination; or inhibiting the immune system in, for example, rheumatoid arthritis, or Lupus. The therapeutic complex of the invention surprisingly demonstrates increased half-life, and efficacy in vivo.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Biosynthetic polypeptides utilizing non-naturally encoded amino acids
InactiveUS20060019347A1Increasing therapeutic half-lifeImprove stabilityVirus peptidesVasoactive intestinal peptideChemistryAmino acid
Owner:AMBRX
Fc fusion
InactiveUS20060083747A1Extended half-lifeHigh affinityAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderEpitopeIn vivo
The present invention relates to a simple method for generating antibody-based structures suitable for in vivo use. In particular, the invention relates to a method for the generation of antibody-based structures suitable for in vivo use comprising the steps of: (a) selecting an antibody single variable domain having an epitope binding specificity; and (b) attaching the single domain of step (a) to an effector group. Uses of molecules generated using the method of the Invention are also described.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Fc variants with altered binding to FcRn
The present application relates to optimized IgG immunoglobulin engineering methods for their generation, and their application, particularly for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:XENCOR
Serum albumin binding proteins with long half-lives
InactiveUS20070269422A1Increased serum half-lifeReduce dosing frequencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igePrimate
The present invention relates to amino acid sequences that are capable of binding to serum albumin; to compounds, proteins and polypeptides comprising or essentially consisting of such amino acid sequences; to nucleic acids that encode such amino acid sequences, proteins or polypeptides; to compositions, and in particular pharmaceutical compositions, that comprise such amino acid sequences, proteins and polypeptides; and to uses of such amino acid sequences, proteins and polypeptides. Particularly, the amino acid sequences and compounds of the present invention bind to or otherwise associate with serum albumin in such a way that, when the amino acid sequence or compound is bound to or otherwise associated with a serum albumin molecule in a primate, it exhibits a serum half-life of at least 50% of the natural half-life of serum albumin in said primate.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Stabilized single domain antibodies
InactiveUS20070178082A1Extended half-lifeAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticSingle-domain antibodySerum protein
The present invention relates to heterospecific polypeptide constructs comprising at least one single domain antibody directed against a therapeutic and / or diagnostic target and at least one single domain antibody directed against a serum protein, said construct having a prolonged lifetime in biological circulatory systems. The invention further relates to methods for stabilising VHHs in biological circulatory systems.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Phenyl guanidine sodium channel blockers
InactiveUS6858615B2Increased mucociliary clearanceAbsorbed less rapidlyBiocideSenses disorderStructural variableGuanidine
The present invention relates to a compound represented by formula (I): in which at least one of R3 and R4 is a group represented by formula (A): where the structural variables are as defined herein. The compounds are useful for blocking sodium channels.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Phenolic guanidine sodium channel blockers
InactiveUS6858614B2Increased mucociliary clearanceAbsorbed less rapidlyBiocideSenses disorderGuanidineSodium channel blocker
The present invention relates to compounds represented by formula (I): in which at least one of R3 and R4 is a group represented by formula (A): where the structural variables are defined herein. The compounds are useful for blocking sodium channels.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
G-CSF conjugates
InactiveUS6555660B2Improved propertyReduced in vitroBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to polypeptide conjugates comprising a polypeptide exhibiting G-CSF activity and having an amino acid sequence that differs from the amino acid sequence of human G-CSF in at least one specified introduced and / or removed amino acid residue comprising an attachment group for a non-polypeptide moiety, and having at least one non-polypeptide moiety attached to an attachment group of the polypeptide. The attachment group may e.g. be a lysine, cysteine, aspartic acid or glutamic acid residue or a glycosylation site, and the non-polypeptide moiety may e.g. be a polymer such as polyethylene glycol or an oligosaccharide. The conjugate, which has a reduced in vitro bioactivity compared to hG-CSF, has one or more improved properties such as increased biological half-life and increased stimulation of neutrophils.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Ligands that have binding specificity for VEGF and/or EGFR and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS20070003549A1Not effectiveExtended half-lifeNervous disorderAntipyreticVascular endothelial growth factorCancer therapy
Disclosed are ligands that have binding specificity for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), or for VEGF and EGFR. Also disclosed are methods of using these ligands. In particular, the use of these ligands for cancer therapy is described.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Methods for production of unstructured recombinant polymers and uses thereof
ActiveUS20080286808A1Extended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsToxinPolymer
Owner:AMUNIX PHARMA INC
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS20050048116A1Fast dissolutionHigh dissolution ratePowder deliveryGranular deliveryDrugs solutionMicroparticle
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution and hydrophilic or hydrophobic excipients that stabilize the drug and inhibit crystallization, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. Hydrophobic or hydrophilic excipients may be selected to stabilize the drug in crystalline form by inhibiting crystal growth or to stabilize the drug in amorphous form by preventing crystallization. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid-compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Yeast-dendritic cell vaccines and uses thereof
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Methods of synthesis and use of chemospheres
InactiveUS20110104052A1Prevents immunoclearanceExtended half-lifePowder deliveryBiocideDiagnostic agentComputed tomography
The present invention provides, in general, compositions comprising a hydrogel and an agent, for example a therapeutic agent or an imaging agent, for locoregional delivery. In certain preferred embodiments of the invention, the hydrogel compositions are detectable by Magnetic Responance and CT Scan and are used for locoregional delivery of therapeutic agents, for example chemotherapeutic agents. The invention also features polymer matrix compositions comprising nanoparticles that can be loaded after polymerization with bioactive agents, for example a diagnostic agent or therapeutic agent.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS20050032114A1Reducing FcRn binding affinityReduced half-lifeAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHalf-lifeAntibody
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Alteration of FcRn binding affinities or serum half-lives of antibodies by mutagenesis
ActiveUS20050276799A1Reducing FcRn binding affinityReduced half-lifeImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsImmunoglobulins against virusesSerum igeHalf-life
The present invention provides for a modified antibody of class IgG, in which at least one amino acid from the heavy chain constant region selected from the group consisting of amino acid residues 250, 314, and 428 is substituted with another amino acid which is different from that present in the unmodified antibody, thereby altering the binding affinity for FcRn and / or the serum half-life in comparison to the unmodified antibody.
Owner:ABBOTT BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (glp-1) pharmaceutical formulations
InactiveUS20080260838A1Improved GLP- pharmacokinetic profileIncreased GLP- half-lifePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseDiabetes mellitus
A composition is disclosed comprising glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) particles in combination with diketopiperazine (DKP) that is stable both in vitro and in vivo. The composition has utility as a pharmaceutical formulation for treating diseases such as diabetes, cancers, and obesity but is not limited to such diseases or conditions. In particularly, the composition has utility as a pharmaceutical formulation for pulmonary delivery.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Modified human growth hormone polypeptides and their uses
InactiveUS20050170404A1Increase stabilityIncrease aqueous solubilitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSomatotropic hormoneHuman growth hormone
Owner:AMBRX
Interfacial biomaterials
InactiveUS20030185870A1Enough timeExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding domainBiological organism
An interfacial biomaterial prepared using a plurality of binding agents, each binding agent including a first ligand that specifically binds a non-biological substrate and a second ligand that specifically binds a biological substrate. Also provided is an interfacial biomaterial prepared using a plurality of binding agents, each binding agent including a ligand that specifically binds a non-biological substrate and a non-binding domain that shows substantially no binding to a biological substrate. Also provided are methods for preparing a binding agent, methods for preparing an interfacial biomaterial, and methods for using interfacial biomaterials.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Skin penetrating device and method for subcutaneous solid drug delivery
ActiveUS8353863B2Easy to keepHigh hardnessMedical devicesIntravenous devicesTherapeutic effectBody tissue
Embodiments described herein provide a skin penetrating device and method for the subcutaneous delivery of therapeutic agents in solid form. One embodiment provides such a device comprising an elongated shaft having proximal and distal ends and a skin penetrating element detachably coupled to the shaft. At least a portion of the penetrating element is fabricated from a solid form therapeutic agent composition that dissolves in body tissue and is absorbed into the blood stream so as to produce a therapeutic effect. The penetrating element has shape for penetrating and lodging beneath the skin when inserted through the skin by force applied from the shaft. The penetrating element is configured to detach from the shaft when the shaft is pulled away from the skin so as to leave the element in place beneath the skin where it is absorbed by body tissue and the therapeutic agent is released.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Sodium channel blockers
InactiveUS7192958B2More potent and/or absorbed less rapidlyLess reversibleBiocideSenses disorderChannel blockerCalcium channel blocker
The present invention relates to compounds represented by formula (I):in which at least one of R3 and R4 is a group represented by formula (A):where the structural variables are defined herein. The compounds are useful for blocking sodium channels.
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Sodium channel blockers
InactiveUS7186833B2More potent and/or absorbed less rapidlyLess reversibleOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderOrganic chemistryMedicinal chemistry
Owner:PARION SCI DURHAM NC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: [email protected]