Woodbine Group
| Woodbine Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Cenomanian[1] | |
 Cross section of Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex geologic formations | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Underlies | Eagle Ford Shale, Woodbine Formation |
| Overlies | Buda Limestone, Kiamichi Formation |
| Area | Texas to Oklahoma and Arkansas |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Sandstone |
| Other | Siltstone, mudstone |
| Location | |
| Region | North America |
| Country | United States of America |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Woodbine, Texas[2] |
| Named by | Robert Thomas Hill[2] |
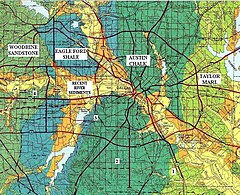 Geologic map of Dallas, with Woodbine at left. | |

The Woodbine Group is a geological formation in east Texas whose strata date back to the Early to Middle Cenomanian age of the Late Cretaceous.[1] It is the producing formation of the giant East Texas Oil Field (also known as the "Black Giant") from which over 5.42 billion barrels of oil have been produced.[3] The Woodbine overlies the Maness Shale, Buda Limestone, or older rocks, and underlies the Eagle Ford Group or Austin Chalk. In outcrop the Woodbine Group has been subdivided into the Lewisville Sandstone, Dexter Sandstone, and/or Pepper Shale formations.[1] Thin-bedded sands of the Woodbine and Eagle Ford are collectively referred to as the "Eaglebine" oil and gas play in the southwestern portion of the East Texas region.[4]
Dinosaur and crocodilian remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.[5] This fossil formation preserves organisms that were endemic to Appalachia.[6]
The Woodbine Group was first mapped and named by Robert T. Hill, known as the "Father of Texas Geology", for outcrops near the small town of Woodbine, Texas in 1901.[2] The Woodbine represents ancient river and delta systems that originated from erosion of the Ouachita Uplift in modern-day Oklahoma and Arkansas and the Sabine Uplift in modern-day Texas and Louisiana. Sediments from these deltas flowed into the East Texas and Brazos Basins of the ancient East Texas shelf.[7]
The Arlington Archosaur Site is a location in Arlington, Texas that currently excavates fossils from the Woodbine Group. It became available to access by the University of Texas at Arlington (UTA) in spring of 2008. UTA and the Dallas Paleontological Society have excavated at the site up to present day, where work continues.[8]
Vertebrate paleofauna
[edit]- Scolomastax sahlsteini: A paralligatorid endemic to Appalachia.[9]
- Ampelognathus coheni: A small-bodied ornithopod[10]
- Protohadros byrdi: "Partial skull, teeth, partial postcranium."[11] A hadrosaur found in Flower Mound, Texas in the early 1990s.
- Dallasaurus turneri: Full skeleton.
- Woodbinesuchus byersmauricei: Lower jaw and a variety of postcranial elements, such as vertebrae, limb bones, shoulder and hip bones, and bony armor.[12]
- Unnamed theropod[13]
- Deltasuchus motherali: Parts of the upper skull, most likely the apex predator in its ecosystem.[14]
- Terminonaris robusta: A pholidosaurid crocodyliform whose remains have been found in North America and Europe.[15]
- Flexomornis howei: A enantiornithe bird.[16]
- Pleurochayah appalachius: A recently described species of bothremydid turtle, which is also known as a side-necked turtle.[17]
- Mawsonia sp., a giant Coelacanth known from Africa and South America, but fossils of the genus were described in 2021.[18]
- Bardackichthys carteri: an ichthyodectiform fish.[19]
- Indeterminate Nodosauridae.[20]
- Indeterminate Carcharodontosauridae.[21]
- Indeterminate Tyrannosauroidea.[21]
- Indeterminate Ornithomimosauria.[21]
- Indeterminate Dromaeosauridae.[21]
- Indeterminate Troodontidae.[21]
- Indeterminate Coelurosauria.[21]
Other fossils
[edit]Other vertebrate fossils that have been identified in the Woodbine include lungfish, fish, turtles, sharks, and coprolites containing bones.[13] Invertebrate fossils found in the Woodbine include ammonites, Inoceramus, oysters, crustaceans,[22] and agglutinated foraminifera.[23]
- Necrocarcinus christinae: a podotreme crab.[24]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Denne, R. A., Breyer, J. A., Callender, A. D., Hinote, R. E., Kariminia, M., Kosanke, T. H., Kita, Z., Lees, J. A., Rowe, H., Spaw, J. M., and Tur, N. (2016). Biostratigraphic and geochemical constraints on the stratigraphy and depositional environments of the Eagle Ford and Woodbine Groups of Texas: in Breyer, J. A. (ed.), The Eagle Ford Shale: A renaissance in U.S. oil production, AAPG Memoir 110, p. 1-84.
- ^ a b c Hill, R. T. (1901). Geography and geology of the black and grand prairies, Texas: Part 7—Texas: 21st Annual Report of the USGS, 666 p.
- ^ Dokur, M., and Hentz, T.F. (2012). Reservoir Characterization of the Upper Cretaceous Woodbine Group in Northeast Texas Field, Texas. AAPG Search and Discovery Article #20152.
- ^ Hentz, T. F., Ambrose, W. A., and Smith, D. C. (2014). Eaglebine play of the southwestern East Texas basin: Stratigraphic and depositional framework of the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) Woodbine and Eagle Ford Groups: AAPG Bulletin, v. 98, p. 2551-2580.
- ^ Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, North America)." in Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. p. 574-588. ISBN 0-520-24209-2.
- ^ Adams, Thomas L.; Noto, Christopher; Drumheller, Stephanie K. (2017). "New Data on Mid- Cretaceous Ecosystems and Faunal Diversity in Appalachia: Insights from the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) of North Texas". Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs. 1. doi:10.1130/abs/2017SC-289203.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Denne, R. A., and Breyer, J. A. (2016). Regional depositional episodes of the Cenomanian-Turonian Eagle Ford and Woodbine groups of Texas: in Breyer, J. A. (ed.), The Eagle Ford Shale: A renaissance in U.S. oil production, AAPG Memoir 110, p. 85-125.
- ^ About Arlington Archosaur Site
- ^ Noto, Christopher R.; Drumheller, Stephanie K.; Adams, Thomas L.; Turner, Alan H. (2020). "An Enigmatic Small Neosuchian Crocodyliform from the Woodbine Formation of Texas". The Anatomical Record. 303 (4): 801–812. doi:10.1002/ar.24174. ISSN 1932-8494. PMID 31173481.
- ^ Tykoski, Ronald S.; Contreras, Dori L.; Noto, Christopher (2023-10-13). "The first small-bodied ornithopod dinosaur from the Lewisville Formation (middle Cenomanian) of TexasCitation for this article: Tykoski, R. S., Contreras, D. L., & Noto, C. (2023) The first small-bodied ornithopod dinosaur from the Lewisville Formation (middle Cenomanian) of Texas. Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology . https://doi.org/10.1080/02724634.2023.2257238". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. doi:10.1080/02724634.2023.2257238. ISSN 0272-4634.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|title= - ^ "Table 19.1," in Weishampel, et al. (2004). Page 417.
- ^ Lee, Yuong–Nam (1997). The Archosauria from the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) in Texas: Journal of Paleontology, v. 71, n.6, p. 1147–1156
- ^ a b Fossils at AAS
- ^ Adams, T.L.; Noto, C.R.; Drumheller, S. (2017). "A large neosuchian crocodyliform from the Upper Cretaceous (Cenomanian) Woodbine Formation of North Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 37 (4): e1349776. Bibcode:2017JVPal..37E9776A. doi:10.1080/02724634.2017.1349776. S2CID 133647239.
- ^ Adams, T. L.; Polcyn, M. J.; Mateus, O.; Winkler, D. A.; Jacobs, L. L. (January 2011). "First occurrence of the long-snouted crocodyliform Terminonaris (Pholidosauridae) from the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) of Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (3): 712–716. Bibcode:2011JVPal..31..712A. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.572938. S2CID 86061260. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ TYKOSKI, RONALD S.; FIORILLO, ANTHONY R. (January 2010). "An enantiornithine bird from the lower middle Cenomanian of Texas". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 30 (1): 288–292. Bibcode:2010JVPal..30..288T. doi:10.1080/02724630903416068. S2CID 84037461. Retrieved 16 November 2020.
- ^ Adrian, Brent; Smith, Heather F.; Noto, Christopher R.; Grossman, Aryeh (2021). "An early bothremydid from the Arlington Archosaur Site of Texas". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 9555. Bibcode:2021NatSR..11.9555A. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-88905-1. PMC 8137945. PMID 34017016.
- ^ Cavin, Lionel; Toriño, Pablo; Van Vranken, Nathan; Carter, Bradley; Polcyn, Michael J.; Winkler, Dale (2021). "The first late cretaceous mawsoniid coelacanth (Sarcopterygii: Actinistia) from North America: Evidence of a lineage of extinct 'living fossils'". PLOS ONE. 16 (11): e0259292. Bibcode:2021PLoSO..1659292C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0259292. PMC 8584698. PMID 34762682.
- ^ Hacker, Riley J.; Shimada, Kenshu (July 2021). "A new ichthyodectiform fish (Actinopterygii: Teleostei) from the Arlington Member (mid-Cenomanian) of the Upper Cretaceous Woodbine Formation in Texas, USA". Cretaceous Research. 123: 104798. Bibcode:2021CrRes.12304798H. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2021.104798. ISSN 0195-6671. S2CID 233806833.
- ^ Lee, Yuong-Nam (November 1997). "The Archosauria from the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) in Texas". Journal of Paleontology. 71 (6): 1147–1156. Bibcode:1997JPal...71.1147L. doi:10.1017/s0022336000036088. ISSN 0022-3360. S2CID 131923994.
- ^ a b c d e f Noto, Christopher R.; D’Amore, Domenic C.; Drumheller, Stephanie K.; Adams, Thomas L. (2022-01-25). "A newly recognized theropod assemblage from the Lewisville Formation (Woodbine Group; Cenomanian) and its implications for understanding Late Cretaceous Appalachian terrestrial ecosystems". PeerJ. 10: e12782. doi:10.7717/peerj.12782. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 8796713. PMID 35127286.
- ^ Stephenson, L. W. (1952). Larger invertebrate fossils of the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) of Texas: USGS Professional Paper 242, 226 p.
- ^ Loeblich, Alfred R. (1946). "Foraminifera from the Type Pepper Shale of Texas". Journal of Paleontology. 20 (2): 130–139. JSTOR 1299379.
- ^ van Bakel, Barry W. M.; Ossó, Àlex; Jackson, John (2022-11-01). "A new podotreme crab, Necrocarcinus christinae sp. nov., from the Woodbine Formation (Cenomanian) of Texas (USA); the first example of spermathecal apertures in a necrocarcinid brachyuran". Cretaceous Research. 139: 105301. Bibcode:2022CrRes.13905301V. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2022.105301. ISSN 0195-6671. S2CID 250570872.
