Transport for Athens
This article may need to be rewritten to comply with Wikipedia's quality standards, as this article is close to becoming a clone of public transport in Athens. (November 2022) |
 | |
 | |
Native name | Συγκοινωνίες Αθηνών |
|---|---|
Romanized name | Sygkoinonies Athinon |
| Company type | Anonymi Etaireia (SA) |
| Industry | Public transport |
| Founded | 22 December 1993 in Athens, Greece |
| Headquarters | Metsovou 15 , 106 82 Athens Greece |
Area served | Greater Athens |
| Owner | Government of Greece (100%) |
| Subsidiaries |
|
| Website | oasa |
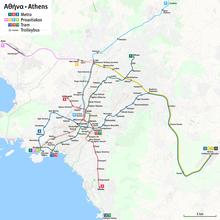
Transport for Athens (Greek: Συγκοινωνίες Αθηνών, romanized: Sygkoinonies Athinon), officially the Athens Urban Transport Organisation (Greek: Οργανισμός Αστικών Συγκοινωνιών Αθηνών, Organismos Astikon Sygkoinonion Athinon, ΟΑΣΑ), is the operator of public transport in Athens, Greece. Transport for Athens, through its subsidiary companies, operates metro, tram, trolleybus and bus services in the Athens metropolitan area.
Companies
[edit]As of July 2011, the Athens Mass Transit System consists of:
- OSY S.A. (Greek: Οδικές Συγκοινωνίες Α.Ε. (abbr. ΟΣΥ), lit. 'Road Transit S.A.')
- Βus network (internal combustion engine buses, trolleybuses and battery electric buses).
- STASY S.A. (Greek: Σταθερές Συγκοινωνίες Α.Ε. (abbr. ΣΤΑΣΥ), lit. 'Fixed Transit S.A.')
- The Athens Tram system
- The Athens Metro with 3 lines.
Transport for Athens also coordinates the Athens Suburban Railway, using Hellenic Railways Organisation (OSE) lines, operated by Hellenic Train S.A. under the Proastiakos brand. The section between Piraeus, Magoula and Koropi is regarded as the urban part.
Recent History
[edit]In March 2011, with the Greek Government Law 3920[1] Attiko Metro Operational Company (AMEL S.A.) absorbed Athens-Piraeus Electric Railways S.A. and TRAM S.A. and was renamed "STASY S.A." (Greek: ΣΤΑΣΥ Α.Ε.). Also ETHEL S.A. absorbed ILPAP S.A. and was renamed as "OSY S.A." (Greek: ΟΣΥ Α.Ε.). The mergers were officially announced on June 10, 2011.[2][3] While mergers at the top management level took place quickly, integration of the former companies at operations and support level proceeds slowly.
ISAP, ETHEL and ILPAP were wholly owned by OASA. AMEL and Tram S.A. until June 2011 were subsidiaries of Attiko Metro S.A. (Greek: Αττικό Μετρό Α.Ε.), a company that also wholly owned by the Greek government.[4][5]
Hellenic Train (formerly Trainose until May 2022) S.A., which absorbed the former Proastiakos S.A. in 2007, became independent of the OSE group in 2008 and until 2017 it is a separate private company.
OASA regularly conducts street photography and videography competitions both in black-and-white and in colour for photos taken while inside its means of transport.[6]
Fare collection system
[edit]Up until the 80s, fare collectors were commonplace in all means of mass transport in Athens. Their replacement was a money box placed at the front end of the vehicles, next to the driver, where passengers would deposit their fare in cash, usually coinage. A decade later, they were replaced with validation machines and paper tickets. The end of the single-use paper ticket came in 2017,[7] when it was succeeded by the ATH.ENA electronic stored-value cards and tickets (stylized as ATH.ENA CARD and ATH.ENA TICKET respectively). Tickets are now rechargeable and can be loaded with up to 5-day unlimited ticket, but not with long term fare products, discount tickets (support discontinued in January 2019)[8] or monetary value. Cards (personalised and anonymised) can hold all fare types and a maximum of €50, with the exception of discount tickets which are tied to personalised cards.
Tickets and cards are validated contaclessly in validation machines inside buses, trolleybuses and trams. Suburban railway trains and the Athens Metro utilize turnstiles.
The ATH.ENA ticket and ATH.ENA card can also be used in suburban railway trains starting from Magoula or Dhekelia and onwards.
In addition to ATH.ENA Ticket and ATH.ENA Card, OASA introduced the contactless payment system in Athens and surrounding areas, which is codenamed tap2ride.[9]It was introduced on a pilot basis in Athens Airport Express buses (Χ93, Χ95, Χ96, Χ97) on 24 April 2024.[10] It will be fully implemented on 15 January 2025 on all means of transport.
All contactless debit and credit cards issued in Greece and also most international cards supporting contactless payment, are accepted for travel on all means of transport (Buses, Trolleybuses, Metro, Tram and Suburban Railway). This works in the same way for the passenger as an ATH.ENA Ticket and ATH.ENA Card, including the use of Fare capping.[11] Mobile payments - such as Apple Pay, Google Pay and Samsung Pay - are also accepted in the same way as contactless payment cards. The fares are the same as those charged on a debit or credit card, including the same daily capping.
Depots
[edit]Metro
[edit]Eirini depot (Line 1)
Sepolia depot (Lines 2 & 3)
Eleonas depot (Lines 2 & 3)
Tram
[edit]Elliniko depot
Trolleybus
[edit]Attiki depot (Closed for trolleybuses. Used by maintenance vehicles only)
Gazi depot (Closed between 2011 and 2014. Converted to an event venue)
Kokkinos Mylos depot
Neo Faliro depot (Closed)
Rouf depot (Opened in 2011 to gradually replace Attiki, Neo Faliro and Gazi)
Bus
[edit]Agios Dimitrios depot
Ano Liosia depot
Anthousa depot
Elliniko depot (Closed in 2018 to make space for the Hellenikon Metropolitan Park)
Petrou Ralli depot
Rentis depot
Thriaseio depot (Used only for laying up retired buses)
Votanikos depot
Gallery
[edit]-
Athens Metro train (3rd generation stock)
-
Athens Tram Citadis 305 vehicle (2nd generation)
-
Athens Suburban Railway train
-
Express bus between the city and the airport
-
Athens trolley bus in downtown Athens
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Law 3920, Government Gazette issue A-33, 2011-03-03.
- ^ Ministerial Decision 28737/2637, Government Gazette issue B-1454, 2011-06-17
- ^ Ministerial Decision 28738/2638, Government Gazette issue B-1454, 2011-06-17
- ^ "Enabling Legislation, Law 1955/91". Archived from the original on 2005-11-04. Retrieved 2006-02-16.
- ^ "Tram Sa". Archived from the original on 2009-03-01. Retrieved 2009-12-31.
- ^ "OASA Photography & video competition".
- ^ IEFIMERIDA.GR, NEWSROOM (2017-11-07). "Εως τις 15 Νοεμβρίου η χρήση των χάρτινων εισιτηρίων -Πότε θα κλείσουν οι μπάρες". iefimerida.gr (in Greek). Retrieved 2022-09-30.
- ^ "ATH.ENA Card". www.athenacard.gr. Retrieved 2022-09-30.
- ^ "Έρχεται το 100% ηλεκτρονικό εισιτήριο στον ΟΑΣΑ το 2024 – Πώς θα αγοράζουμε εισιτήριο μόνο με κάρτα ή το κινητό". ypodomes.com (in gr). 12 January 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2025.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Ξεκίνησε από σήμερα το tap & pay σε επιλεγμένα λεωφορεία – Πότε θα επεκταθεί σε όλα τα Μέσα Μαζικής Μεταφοράς της Αθήνας". ypodomes.com (in gr). 24 April 2024. Retrieved 11 January 2025.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Σε "ψηφιακή" εποχή οι αστικές συγκοινωνίες στην Αθήνα από τον ΟΑΣΑ – Πότε ξεκινούν οι ανέπαφες πληρωμές σε όλα τα μέσα". ypodomes.com (in gr). 11 January 2025. Retrieved 11 January 2025.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)






