Portal:Outer space
Introduction

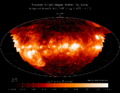
Outer space (or simply space) is the expanse that exists beyond Earth's atmosphere and between celestial bodies. It contains ultra-low levels of particle densities, constituting a near-perfect vacuum of predominantly hydrogen and helium plasma, permeated by electromagnetic radiation, cosmic rays, neutrinos, magnetic fields and dust. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvins (−270 °C; −455 °F).
The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. Most of the remaining mass-energy in the observable universe is made up of an unknown form, dubbed dark matter and dark energy.
Outer space does not begin at a definite altitude above Earth's surface. The Kármán line, an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. Certain portions of the upper stratosphere and the mesosphere are sometimes referred to as "near space". The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which entered into force on 10 October 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.
The concept that the space between the Earth and the Moon must be a vacuum was first proposed in the 17th century after scientists discovered that air pressure decreased with altitude. The immense scale of outer space was grasped in the 20th century when the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy was first measured. Humans began the physical exploration of space later in the same century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights. This was followed by crewed rocket flights and, then, crewed Earth orbit, first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961. The economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is very high, limiting human spaceflight to low Earth orbit and the Moon. On the other hand, uncrewed spacecraft have reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. (Full article...)
Selected article
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. It has no natural satellite. It is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows. Because Venus is an inferior planet from Earth, it never appears to venture far from the Sun: its elongation reaches a maximum of 47.8°. Venus reaches its maximum brightness shortly before sunrise or shortly after sunset, for which reason it has been referred to by ancient cultures as the Morning Star or Evening Star.
Venus is a terrestrial planet and is sometimes called Earth's "sister planet" because of their similar size, gravity, and bulk composition (Venus is both the closest planet to Earth and the planet closest in size to Earth). However, it has also been shown to be very different from Earth in other respects. It has the densest atmosphere of the four terrestrial planets, consisting of more than 96% carbon dioxide. The atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface is 92 times that of Earth's. With a mean surface temperature of 735 K (462 °C; 863 °F), Venus is by far the hottest planet in the Solar System. It has no carbon cycle to lock carbon back into rocks and surface features, nor does it seem to have any organic life to absorb it in biomass. Venus is shrouded by an opaque layer of highly reflective clouds of sulfuric acid, preventing its surface from being seen from space in visible light. Venus may have possessed oceans in the past, but these would have vaporized as the temperature rose due to a runaway greenhouse effect. The water has most probably photodissociated, and, because of the lack of a planetary magnetic field, the free hydrogen has been swept into interplanetary space by the solar wind.
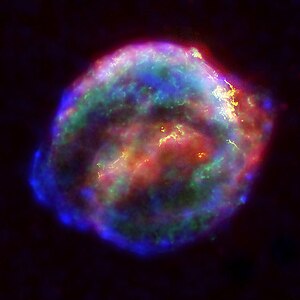
Selected picture
Space-related portals
General images
Did you know (auto-generated)

- ... that, for the Space 220 Restaurant, Disney reached out to NASA engineers to understand what a space elevator might look like?
- ... that some severe environmental impacts of the invasion of Ukraine can be seen from space?
- ... that the space industry of India has supported the launch of more than 100 domestic satellites and more than 300 foreign satellites?
- ... that Nature's Fynd, producer of microbe-based meat substitutes, is working with NASA to develop a bioreactor for use in space travel?
- ... that Louis W. Roberts was among the highest ranking African-American space program staff at NASA while the Apollo program was underway?
Space news
Upcoming spaceflight launches
Astronomical events
Topics
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus