Archaic humans

−10 — – −9 — – −8 — – −7 — – −6 — – −5 — – −4 — – −3 — – −2 — – −1 — – 0 — |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Archaic humans[a] is a broad category denoting all species of the genus Homo that are not Homo sapiens (modern humans), which are sometimes also called Homo sapiens sapiens, in which case the singular use of sapiens has been applied to some archaic humans as well. Among the earliest modern human remains are those from Jebel Irhoud in Morocco (about 315 ka), Florisbad in South Africa (259 ka),[1][2][3][4][5][6] Omo-Kibish I (Omo I) in southern Ethiopia (c. 233 or 195 ka),[2][7] and Apidima Cave in Southern Greece (210 ka).[8] Some examples of archaic humans include H. antecessor (1200–770 ka), H. bodoensis (1200–300 ka), H. heidelbergensis (600–200 ka), Neanderthals (H. neanderthalensis; 430–40 ka),[9] H. rhodesiensis (300–125 ka) and Denisovans (H. denisova; 285–52 ka).
Traditionally, the hominins after the middle Pleistocene (middle Homo) belong to Homo sapiens. This entire group is referred to as late Homo, which in turn is broken down into three temporal groups: early archaic Homo (or, transitional types), late archaic (including Neanderthals), and anatomically modern Homo sapiens.[10]
Most archaic humans had a brain size averaging 1,200 to 1,400 cubic centimeters, which overlaps with the range of modern humans. Notable exceptions include Homo naledi and Homo floresiensis, having cranial capacities of 465-610 and 380 cubic centimeters, respectively.
Archaic humans are distinguished from anatomically modern humans by having a thick skull, prominent supraorbital ridges (brow ridges) and the lack of a prominent chin.[11][12]
Anatomically modern humans appeared around 300,000 years ago in Africa,[4][5][6] and 70,000 years ago gradually supplanted the "archaic" human varieties. Non-modern varieties of Homo are certain to have survived until after 30,000 years ago, and perhaps until as recently as 12,000 years ago.[b] According to recent genetic studies, modern humans may have bred with two or more groups of archaic humans, including Neanderthals and Denisovans.[13] Other studies have cast doubt on admixture being the source of the shared genetic markers between archaic and modern humans, pointing to an ancestral origin of the traits which originated 500,000–800,000 years ago.[14][15][16] In August 2023, scientists reported the discovery of an unknown ancient human hominin that may have lived 300,000 years ago in China.[17][18]
Terminology and definition
[edit]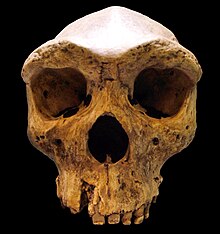
The category archaic human lacks a single, agreed definition.[11] According to one definition, Homo sapiens is a single species comprising several subspecies that include the archaics and modern humans. Under this definition, modern humans are referred to as Homo sapiens sapiens and archaics are also designated with the prefix "Homo sapiens". For example, the Neanderthals are Homo sapiens neanderthalensis, and Homo heidelbergensis is Homo sapiens heidelbergensis. Other taxonomists prefer not to consider archaics and modern humans as a single species but as several different species. In this case the standard taxonomy is used, i.e. Homo rhodesiensis, or Homo neanderthalensis.[11]
The evolutionary dividing lines that separate modern humans from archaic humans and archaic humans from Homo erectus are unclear. The earliest known fossils of anatomically modern humans such as the Omo remains from 233,000 to 195,000 years ago, Homo sapiens idaltu from 160,000 years ago, and Qafzeh remains from 90,000 years ago are recognizably modern humans. These early modern humans possess a number of archaic traits, such as moderate, but not prominent, brow ridges.
Brain size expansion
[edit]
The emergence of archaic humans is sometimes used as an example of punctuated equilibrium.[19] This occurs when a species undergoes significant biological evolution within a relatively short period. Subsequently, the species undergoes very little change for long periods until the next punctuation. The brain size of archaic humans expanded significantly from 900 cm3 (55 cu in) in erectus to 1,300 cm3 (79 cu in). Since the peak of human brain size during the archaics, it has begun to decline.[20]
Life-History Evolution
[edit]The ontogenetic development of archaic humans may be of relevance to the emergence of modern human ontogeny.[21] Comparisons of modern human and fossil hominin brain and tooth development imply that Homo erectus ontogeny was more similar to that of modern chimpanzees than modern humans,[22] while Neanderthals experienced a life-history similar to modern humans, possibly due to convergent evolution.[21] Biological anthropologist Tanya Smith has argued that the use of modern humans and extant apes as references when studying the life-history of archaic humans is unreliable, as it assumes that extinct hominins developed similarly to either reference.[23]
Origin of language
[edit]Robin Dunbar has argued that archaic humans were the first to use language. Based on his analysis of the relationship between brain size and hominin group size, he concluded that because archaic humans had large brains, they must have lived in groups of over 120 individuals. Dunbar argues that it was not possible for hominins to live in such large groups without using language, otherwise there could be no group cohesion and the group would disintegrate. By comparison, chimpanzees live in smaller groups of up to 50 individuals.[24][25]
Fossils
[edit]- Altamura Man
- Atapuerca Mountains, Sima de los Huesos
- Cro-magnon Man
- Dragon Man
- Kabwe skull
- Ndutu cranium
- Saldanha man
- Steinheim skull
See also
[edit]References
[edit]Footnotes
- ^ There is no universal consensus on this terminology, and varieties of "archaic humans" are included under the binomial name of either H. sapiens or H. erectus by some authors.
- ^ Which of these, if any, are included under the term "archaic human" is a matter of definition and varies among authors.
Citations
- ^ Stringer, C. (2016). "The origin and evolution of Homo sapiens". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 371 (1698): 20150237. doi:10.1098/rstb.2015.0237. PMC 4920294. PMID 27298468.
- ^ a b Hammond, Ashley S.; Royer, Danielle F.; Fleagle, John G. (Jul 2017). "The Omo-Kibish I pelvis". Journal of Human Evolution. 108: 199–219. Bibcode:2017JHumE.108..199H. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2017.04.004. ISSN 1095-8606. PMID 28552208.
- ^ White, Tim D.; Asfaw, B.; DeGusta, D.; Gilbert, H.; Richards, G. D.; Suwa, G.; Howell, F. C. (2003). "Pleistocene Homo sapiens from Middle Awash, Ethiopia". Nature. 423 (6491): 742–747. Bibcode:2003Natur.423..742W. doi:10.1038/nature01669. PMID 12802332. S2CID 4432091.
- ^ a b Callaway, Ewan (7 June 2017). "Oldest Homo sapiens fossil claim rewrites our species' history". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2017.22114. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ a b Sample, Ian (7 June 2017). "Oldest Homo sapiens bones ever found shake foundations of the human story". The Guardian. Retrieved 7 June 2017.
- ^ a b Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Ben-Ncer, Abdelouahed; Bailey, Shara E.; Freidline, Sarah E.; Neubauer, Simon; Skinner, Matthew M.; Bergmann, Inga; Le Cabec, Adeline; Benazzi, Stefano; Harvati, Katerina; Gunz, Philipp (2017). "New fossils from Jebel Irhoud, Morocco and the pan-African origin of Homo sapiens" (PDF). Nature. 546 (7657): 289–292. Bibcode:2017Natur.546..289H. doi:10.1038/nature22336. PMID 28593953. S2CID 256771372.
- ^ Vidal, Celine M.; Lane, Christine S.; Asfawrossen, Asrat; et al. (Jan 2022). "Age of the oldest known Homo sapiens from eastern Africa". Nature. 601 (7894): 579–583. Bibcode:2022Natur.601..579V. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04275-8. PMC 8791829. PMID 35022610.
- ^ Katerina Harvati; Carolin Röding; Abel M. Bosman; Fotios A. Karakostis; Rainer Grün; Chris Stringer; Panagiotis Karkanas; Nicholas C. Thompson; Vassilis Koutoulidis; Lia A. Moulopoulos; Vassilis G. Gorgoulis; Mirsini Kouloukoussa (2019). "Apidima Cave fossils provide earliest evidence of Homo sapiens in Eurasia". Nature. 571 (7766): 500–504. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1376-z. PMID 31292546. S2CID 195873640.
- ^ Hublin, J. J. (2009). "The origin of Neandertals". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106 (38): 16022–16027. Bibcode:2009PNAS..10616022H. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904119106. JSTOR 40485013. PMC 2752594. PMID 19805257.
- ^ Early and Late "Archaic" Homo Sapiens and "Anatomically Modern" Homo Sapiens
- ^ a b c Dawkins (2005). "Archaic homo sapiens". The Ancestor's Tale. Boston: Mariner. ISBN 978-0618619160.
- ^ Barker, Graeme (1999). Companion Encyclopedia of Archaeology. Routledge. ISBN 978-0415213295 – via Google Books.
- ^ Mitchell, Alanna (January 30, 2012). "DNA Turning Human Story Into a Tell-All". The New York Times. Retrieved January 31, 2012.
- ^ Telegraph Reporters (14 August 2012). "Neanderthals did not interbreed with humans, scientists find". Telegraph.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2022-01-12.
- ^ "Neanderthals 'unlikely to have interbred with human ancestors'". The Guardian. Press Association. 4 February 2013.
- ^ Lowery, Robert K.; Uribe, Gabriel; Jimenez, Eric B.; Weiss, Mark A.; Herrera, Kristian J.; Regueiro, Maria; Herrera, Rene J. (2013). "Neanderthal and Denisova genetic affinities with contemporary humans: Introgression versus common ancestral polymorphisms". Gene. 530 (1): 83–94. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.06.005. PMID 23872234.
- ^ Israely, Yogev (7 August 2023). "Remains found in China may belong to previously unknown human lineage - Scientists in eastern China examined a jawbone, fragments of a skull and various foot bones from a hominin that lived approximately 300,000 years ago; Findings suggest this particular lineage bears a closer resemblance to Homo sapiens, or modern-day humans". YNet News. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Wu, Xiujie; et al. (1 September 2023). "Morphological and morphometric analyses of a late Middle Pleistocene hominin mandible from Hualongdong, China". Journal of Human Evolution. 182. Bibcode:2023JHumE.18203411W. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2023.103411. PMID 37531709. S2CID 260407114. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Schultz, S.; Nelson, E.; Dunbar, R. (Aug 2012). "Hominin cognitive evolution: identifying patterns and processes in the fossil and archaeological record". Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 367 (1599): 2130–2140. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0115. PMC 3385680. PMID 22734056.
- ^ Zyga, Lisa (15 March 2010). "Cro Magnon skull shows that our brains have shrunk". phys.org. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ^ a b Hublin, Jean-Jacques; Neubauer, Simon; Gunz, Philipp (2015). "Brain ontogeny and life history in Pleistocene hominins". Philosophical Transactions: Biological Sciences. 370 (1663): 1–11. ISSN 0962-8436.
- ^ Schwartz, Gary T. (2012). "Growth, Development, and Life History throughout the Evolution of Homo". Current Anthropology. 53 (S6): S395–S408. doi:10.1086/667591. ISSN 0011-3204.
- ^ Smith, Tanya M. (2013). "Teeth and Human Life-History Evolution". Annual Review of Anthropology. 42: 191–208. ISSN 0084-6570.
- ^ "Behavioral and Brain Sciences". Cambridge Core. Archived from the original on June 26, 2009.
- ^ Dunbar (1993). Grooming, Gossip, and the Evolution of Language. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674363366.
External links
[edit]- Early and Late "Archaic" Homo Sapiens and "Anatomically Modern" Homo Sapiens (archived 16 August 2009)
- Origins of Modern Humans: Multiregional or Out of Africa?
- Homo sapiens, Museum of Natural History (archived 9 July 2009)
- Human Timeline (Interactive) – Smithsonian, National Museum of Natural History (August 2016).
