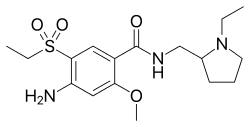
Amisulpride
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Solian, Barhemsys, others |
| Other names | Aminosultopride; AST; APD-421; APD421; APD-403; APD403; DAN-2163; DAN2163 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| Drug class | Dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist; Serotonin 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 receptor antagonist; Antipsychotic; Antidepressant; Antiemetic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 48%[5][6] |
| Protein binding | 16%[6] |
| Metabolism | Liver (minimal; most excreted unchanged)[6] |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours[5] |
| Excretion | Kidney[5] (23–46%),[7][8] Faecal[6] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.068.916 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H27N3O4S |
| Molar mass | 369.48 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Amisulpride, sold under the brand names Solian and Barhemsys, is a medication used in the treatment of schizophrenia, acute psychotic episodes, depression, and nausea and vomiting.[9][6] It is specifically used at lower doses intravenously to prevent and treat postoperative nausea and vomiting;[9] at low doses by mouth to treat depression; and at higher doses by mouth to treat psychosis.[6][10][11]
It is usually classed with the atypical antipsychotics. Chemically it is a benzamide and like other benzamide antipsychotics, such as sulpiride, it is associated with a high risk of elevating blood levels of the lactation hormone, prolactin (thereby potentially causing the absence of the menstrual cycle, breast enlargement, even in males, breast milk secretion not related to breastfeeding, impaired fertility, impotence, breast pain, etc.), and a low risk, relative to the typical antipsychotics, of causing movement disorders.[12][13][14]
Amisulpride is indicated for use in the United States in adults for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class; and to treat PONV in those who have received antiemetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis.[9]
Amisulpride is believed to work by blocking, or antagonizing, the dopamine D2 receptor, reducing its signalling. The effectiveness of amisulpride in treating dysthymia and the negative symptoms of schizophrenia is believed to stem from its blockade of the presynaptic dopamine D2 and D3 autoreceptors. These presynaptic receptors regulate the release of dopamine into the synapse, so by blocking them amisulpride increases dopamine concentrations in the synapse. This increased dopamine concentration is theorized to act on dopamine D1 receptors to relieve depressive symptoms (in dysthymia) and the negative symptoms of schizophrenia.[11]
It was introduced by Sanofi-Aventis in the 1990s. Its patent expired by 2008, and generic formulations became available.[15] It is marketed in all English-speaking countries except for Canada.[14]
Medical uses
[edit]Schizophrenia
[edit]Although according to other studies it appears to have comparable efficacy to olanzapine in the treatment of schizophrenia,[16] amisulpride augmentation, similarly to sulpiride augmentation, has been considered a viable treatment option (although this is based on low-quality evidence) in clozapine-resistant cases of schizophrenia.[17][18] Another recent study concluded that amisulpride is an appropriate first-line treatment for the management of acute psychosis.[19]
Depression
[edit]Amisulpride is approved and used at low doses in the treatment of dysthymia and major depressive disorder.[10][20][11][21][22][23] Whereas typical doses used in schizophrenia block postsynaptic dopamine D2-like receptors and reduce dopaminergic neurotransmission, low doses of amisulpride preferentially block presynaptic dopamine D2 and D3 autoreceptors and thereby disinhibit dopamine release and enhance dopaminergic neurotransmission.[24][25] A 2010 Cochrane review found that low-dose amisulpride was effective in the treatment of dysthymia.[26] Likewise, a 2024 literature review found that low-dose amisulpride was effective for dysthymia.[27] The drug is approved for depression specifically in Italy, Greece, and certain other European countries.[11][10]
Postoperative nausea and vomiting
[edit]Amisulpride is indicated for use in the United States in adults for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class; and to treat PONV in those who have received antiemetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis.[9]
Available forms
[edit]Amisulpride is available in the form of 100, 200, and 400 mg oral tablets.[28] In the United States, it is available in the form of a 5 mg/2 mL (2.5 mg/mL) solution for intravenous administration.[29]
Contraindications
[edit]Amisulpride's use is contraindicated in the following disease states and populations[6][30][12]
- Pheochromocytoma
- Concomitant prolactin-dependent tumours e.g. prolactinoma, breast cancer
- Movement disorders (e.g. Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies)
- Lactation
- Children before the onset of puberty
Neither is it recommended to use amisulpride in patients with hypersensitivities to amisulpride or the excipients found in its dosage form.[6]
Adverse effects
[edit]- Very Common (≥10% incidence)[4]
- Extrapyramidal side effects (EPS; including dystonia, tremor, akathisia, parkinsonism).
- Insomnia
- Somnolence
- Hypersalivation
- Nausea
- Headache
- Hyperactivity
- Vomiting
- Hyperprolactinaemia (which can lead to galactorrhoea, breast enlargement and tenderness, sexual dysfunction, etc.)
- Weight gain (produces less weight gain than chlorpromazine, clozapine, iloperidone, olanzapine, paliperidone, quetiapine, risperidone, sertindole, zotepine and more (although not statistically significantly) weight gain than haloperidol, lurasidone, ziprasidone and approximately as much weight gain as aripiprazole and asenapine)[13]
- Anticholinergic side effects (although it does not bind to the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and hence these side effects are usually quite mild) such as
- - constipation
- - dry mouth
- - disorder of accommodation
- - Blurred vision
- Rare (<1% incidence)[4][6][31][30][12]
- Blood dyscrasias such as leucopenia, neutropenia and agranulocytosis
- QT interval prolongation (in a recent meta-analysis of the safety and efficacy of 15 antipsychotic drugs amisulpride was found to have the 2nd highest effect size for causing QT interval prolongation[13])
Hyperprolactinaemia results from antagonism of the D2 receptors located on the lactotrophic cells found in the anterior pituitary gland. Amisulpride has a high propensity for elevating plasma prolactin levels as a result of its poor blood–brain barrier penetrability and hence the resulting greater ratio of peripheral D2 occupancy to central D2 occupancy. This means that to achieve the sufficient occupancy (~60–80%[32]) of the central D2 receptors in order to elicit its therapeutic effects a dose must be given that is enough to saturate peripheral D2 receptors including those in the anterior pituitary.[33][34]
Discontinuation
[edit]The British National Formulary recommends a gradual withdrawal when discontinuing antipsychotics to avoid acute withdrawal syndrome or rapid relapse.[35] Symptoms of withdrawal commonly include nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.[36] Other symptoms may include restlessness, increased sweating, and trouble sleeping.[36] Less commonly there may be a feeling of the world spinning, numbness, or muscle pains.[36] Symptoms generally resolve after a short period of time.[36]
There is tentative evidence that discontinuation of antipsychotics can result in psychosis.[37] It may also result in reoccurrence of the condition that is being treated.[38] Rarely tardive dyskinesia can occur when the medication is stopped.[36]
Overdose
[edit]Torsades de pointes is common in overdose.[39][40] Amisulpride is moderately dangerous in overdose (with the TCAs being very dangerous and the SSRIs being modestly dangerous).[41][42]
Interactions
[edit]Amisulpride should not be used in conjunction with drugs that prolong the QT interval (such as citalopram, bupropion, clozapine, tricyclic antidepressants, sertindole, ziprasidone, etc.),[41] reduce heart rate and those that can induce hypokalaemia. Likewise it is imprudent to combine antipsychotics due to the additive risk for tardive dyskinesia and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.[41]
Pharmacology
[edit]Pharmacodynamics
[edit]| Site | Ki (nM) | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| SERT | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| NET | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| DAT | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT1A | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT1B | 1744 | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT1D | 1341 | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT1E | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT2A | 8304 | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT2B | 13 | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT2C | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT3 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT5A | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT6 | 4154 | Human | [44] |
| 5-HT7 | 11.5 | Human | [44] |
| α1A | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| α1B | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| α1D | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| α2A | 1114 | Human | [44] |
| α2C | 1540 | Human | [44] |
| β1 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| β2 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| β3 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| D1 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| D2 | 3.0 | Human | [44] |
| D3 | 3.5 | Rat | [44] |
| D4 | 2369 | Human | [44] |
| D5 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| H1 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| H2 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| H4 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| M1 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| M2 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| M3 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| M4 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| M5 | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| σ1 | 10000+ | Rat | [44] |
| σ2 | 10000+ | Rat | [44] |
| MOR | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| DOR | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| KOR | 10000+ | Human | [44] |
| GHBHigh | 50 (IC50) | Rat | [45] |
| NMDA (PCP) |
10000+ | Rat | [46] |
| Values are Ki (nM). The smaller the value, the more strongly the drug binds to the site. | |||
Amisulpride functions primarily as a dopamine D2 and D3 receptor antagonist. It has high affinity for these receptors with dissociation constants of 3.0 and 3.5 nM, respectively.[44] Although standard doses used to treat psychosis inhibit dopaminergic neurotransmission, low doses preferentially block inhibitory presynaptic autoreceptors. This results in a facilitation of dopamine activity, and for this reason, low-dose amisulpride has also been used to treat dysthymia.[6]
Amisulpride and its relatives sulpiride, levosulpiride, and sultopride have been shown to bind to the high-affinity GHB receptor at concentrations that are therapeutically relevant (IC50 = 50 nM for amisulpride).[45]
Amisulpride, sultopride and sulpiride respectively present decreasing in vitro affinities for the D2 receptor (IC50 = 27, 120 and 181 nM) and the D3 receptor (IC50 = 3.6, 4.8 and 17.5 nM).[47]
Though it was long widely assumed that dopaminergic modulation is solely responsible for the respective antidepressant and antipsychotic properties of amisulpride, it was subsequently found that the drug also acts as a potent antagonist of the serotonin 5-HT7 receptor (Ki = 11.5 nM).[44] Several of the other atypical antipsychotics such as risperidone and ziprasidone are potent antagonists at the 5-HT7 receptor as well, and selective antagonists of the receptor show antidepressant properties themselves. To characterize the role of the 5-HT7 receptor in the antidepressant effects of amisulpride, a study prepared 5-HT7 receptor knockout mice.[44] The study found that in two widely used rodent models of depression, the tail suspension test, and the forced swim test, those mice did not exhibit an antidepressant response upon treatment with amisulpride.[44] These results suggest that 5-HT7 receptor antagonism mediates the antidepressant effects of amisulpride.[44]
Amisulpride also appears to bind with high affinity to the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor (Ki = 13 nM), where it acts as an antagonist.[44] The clinical implications of this, if any, are unclear.[44] In any case, there is no evidence that this action mediates any of the therapeutic effects of amisulpride.[44]
Amisulpride shows stereoselectivity in its actions.[48] Aramisulpride ((R)-amisulpride) has higher affinity for the 5-HT7 receptor (Ki = 47 nM vs. 1,900 nM) while esamisulpride ((S)-amisulpride) has higher affinity for the D2 receptor (4.0 nM vs. 140 nM).[48][49]
Through a high direct unmetabolized excretion, it has, despite its high usual dose, also high affinity for dopamine-D2-D3-receptors. Also the available literature gives us hints about also relatively high receptor dissociation kinetics (through a delayed but high occupancy at dopamine receptors after 6 hours from a 100 mg exposure). Moreover, this dopamine exposure could be slightly more "balanced" providing some little advantages over haloperidol in using it for drug exposure. Due to its lack of compensatory serotonin effects and also not having an anticholinergic profile, it may not considered as an effective alternative if akathasia is a problem.[5][34][50]
Pharmacokinetics
[edit]The oral bioavailability of amisulpride is 48%.[5][6] Its plasma protein binding is 16%.[6] The drug is metabolized by the liver but its metabolism is minimal.[6] Its elimination half-life is 12 hours.[5] Amisulpride is eliminated in urine (23–46%) and feces and is excreted mostly unchanged.[5][6][7][8]
Chemistry
[edit]Amisulpride is a benzamide derivative. It is structurally related to other benzamide dopamine receptor antagonists employed as antipsychotics and antiemetics including levosulpiride, metoclopramide, nemonapride, remoxipride, sulpiride, sultopride, tiapride, and veralipride. Chemically, it is also known as aminosultopride, differing from sultopride only in possessing an amino substituent on its benzene ring.
History
[edit]Amisulpride was introduced by Sanofi-Aventis in the 1990s.[citation needed] Its patent expired by 2008, and generic formulations became available.[15]
United States clinical development
[edit]The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a 10 mg/4mL amisulpride IV formulation for use in post-operative nausea based on evidence from four clinical trials of 2323 subjects undergoing surgery or experiencing nausea and vomiting after the surgery.[51] The trials were conducted at 80 sites in the United States, Canada and Europe.[51]
Two trials (Trials 1 and 2) enrolled subjects scheduled to have surgery.[51] Subjects were randomly assigned to receive either amisulpride or a placebo drug at the beginning of general anesthesia.[51] In Trial 1, subjects received amisulpride or placebo alone, and in Trial 2, they received amisulpride or placebo in combination with one medication approved for prevention of nausea and vomiting.[51] Neither the subjects nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was complete.[51]
The trials counted the number of subjects who had no vomiting and did not use additional medications for nausea or vomiting in the first day (24 hours) after the surgery.[51] The results then compared amisulpride to placebo.[51]
The other two trials (Trials 3 and 4) enrolled subjects who were experiencing nausea and vomiting after surgery.[51] In Trial 3, subjects did not receive any medication to prevent nausea and vomiting before surgery and in Trial 4 they received the medication, but the treatment did not work.[51] In both trials, subjects were randomly assigned to receive either amisulpride or placebo.[51] Neither the subjects nor the health care providers knew which treatment was being given until after the trial was complete.[51]
The trials counted the number of subjects who had no vomiting and did not use additional medications for nausea or vomiting in the first day (24 hours) after the treatment.[51] The trial compared amisulpride to placebo.[51]
The FDA has not approved amisulpride for use in any psychiatric indication. LB Pharmaceuticals is developing N-methyl amisulpride for the use in the treatment of schizophrenia; a Phase 2 first-in-patient study is planned for 2023.[52]
Society and culture
[edit]Brand names
[edit]Brand names include: Amazeo, Amipride (AU), Amival, Deniban, Solian (AU, IE, RU, UK, ZA), Soltus, Sulpitac (IN), Sulprix (AU), Midora (RO) and Socian (BR).[53][54]
Availability
[edit]Amisulpride is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in the United States in psychiatric indications, but it is approved and in use throughout Europe,[54] Asia, Mexico, New Zealand and Australia[6] to treat psychosis and schizophrenia.[55][56]
An IV formulation of Amisulpride was approved for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting ("PONV") in the United States in February 2020.[57][9][51]
Research
[edit]Bipolar depression
[edit]SEP-4199 (non-racemic amisulpride), an 85:15 ratio of aramisulpride ((R)-amisulpride) to esamisulpride ((S)-amisulpride), which is theorized to provide more balanced serotonin 5-HT7 and dopamine D2 receptor antagonism than racemic amisulpride (a 50:50 ratio of its (R)- and (S)-enantiomers), is or was under development by Sunovion Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of bipolar depression in the United States and other countries.[58][59][60] However, its development may have been discontinued.[58][59]
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting
[edit]The intravenous formulation of amisulpride approved for treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting is additionally under development for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting.[61]
Chemical derivatives
[edit]A more lipophilic and centrally permeable derivative of amisulpride, N-methylamisulpride (developmental code name LB-102), is under development by LB Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of schizophrenia in the United States and other countries.[62][60]
See also
[edit]- ENX-104 (an analogue under development for use at low doses to treat depression)
References
[edit]- ^ "Australian Product Information – Solian (Amisulpride) Tablets And Solution". TGA eBS. Retrieved 10 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Amisulpride (Barhemsys) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 2 September 2020. Retrieved 24 September 2020.
- ^ Anvisa (31 March 2023). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 4 April 2023). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ a b c d "Amisulpride 100 mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 5 July 2019. Archived from the original on 26 February 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g Rosenzweig P, Canal M, Patat A, Bergougnan L, Zieleniuk I, Bianchetti G (January 2002). "A review of the pharmacokinetics, tolerability and pharmacodynamics of amisulpride in healthy volunteers". Human Psychopharmacology. 17 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1002/hup.320. PMID 12404702. S2CID 23877366.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Solian tablets and solution product information" (PDF). TGA eBusiness Services. Sanofi-Aventis Australia Pty Ltd. 27 September 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b Caccia S (May 2000). "Biotransformation of post-clozapine antipsychotics: pharmacological implications". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 38 (5): 393–414. doi:10.2165/00003088-200038050-00002. PMID 10843459. S2CID 68853079.
- ^ a b Noble S, Benfield P (December 1999). "Amisulpride: A Review of its Clinical Potential in Dysthymia". CNS Drugs. 12 (6): 471–483. doi:10.2165/00023210-199912060-00005. S2CID 71691764.
- ^ a b c d e "Barhemsys (amisulpride) injection, for intravenous use" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). February 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b c "Amisulpride". AdisInsight. 24 October 2021. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ a b c d Pani L, Gessa GL (2002). "The substituted benzamides and their clinical potential on dysthymia and on the negative symptoms of schizophrenia". Mol Psychiatry. 7 (3): 247–253. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001040. PMID 11920152.
- ^ a b c d Rossi S, ed. (2013). Australian Medicines Handbook (2013 ed.). Adelaide: The Australian Medicines Handbook Unit Trust. ISBN 978-0-9805790-9-3.
- ^ a b c Leucht S, Cipriani A, Spineli L, Mavridis D, Orey D, Richter F, et al. (September 2013). "Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis". Lancet. 382 (9896): 951–962. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60733-3. PMID 23810019. S2CID 32085212.
- ^ a b Brayfield A, ed. (June 2017). "Amisulpride: Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference". MedicineComplete. Pharmaceutical Press. Retrieved 5 August 2017.
- ^ a b De Silva V, Hanwella R (April 2008). "Pharmaceutical patents and the quality of mental healthcare in low- and middle-income countries". The Psychiatrist. 32 (4): 121–23. doi:10.1192/pb.bp.107.015651.
- ^ Komossa K, Rummel-Kluge C, Hunger H, Schmid F, Schwarz S, Silveira da Mota Neto JI, et al. (January 2010). "Amisulpride versus other atypical antipsychotics for schizophrenia". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2013 (1): CD006624. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006624.pub2. PMC 4164462. PMID 20091599.
- ^ Solanki RK, Singh P, Munshi D (October–December 2009). "Current perspectives in the treatment of resistant schizophrenia". Indian Journal of Psychiatry. 51 (4): 254–260. doi:10.4103/0019-5545.58289. PMC 2802371. PMID 20048449.
- ^ Mouaffak F, Tranulis C, Gourevitch R, Poirier MF, Douki S, Olié JP, et al. (2006). "Augmentation strategies of clozapine with antipsychotics in the treatment of ultraresistant schizophrenia". Clinical Neuropharmacology. 29 (1): 28–33. doi:10.1097/00002826-200601000-00009. PMID 16518132. S2CID 29682562.
- ^ Nuss P, Hummer M, Tessier C (March 2007). "The use of amisulpride in the treatment of acute psychosis". Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 3 (1): 3–11. doi:10.2147/tcrm.2007.3.1.3. PMC 1936283. PMID 18360610.
- ^ Zangani C, Giordano B, Stein HC, Bonora S, D'Agostino A, Ostinelli EG (November 2021). "Efficacy of amisulpride for depressive symptoms in individuals with mental disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Hum Psychopharmacol. 36 (6): e2801. doi:10.1002/hup.2801. PMC 8596405. PMID 34727399.
- ^ Green B (2002). "Focus on amisulpride". Curr Med Res Opin. 18 (3): 113–117. doi:10.1185/030079902125000363. PMID 12094819.
- ^ Montgomery SA (December 2002). "Dopaminergic deficit and the role of amisulpride in the treatment of mood disorders". Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 17 Suppl 4: S9–15, discussion S16–7. PMID 12685917.
- ^ Rittmannsberger H (June 2019). "Amisulpride as an Augmentation Agent in Treatment Resistant Depression: A Case Series and Review of the Literature". Psychiatr Danub. 31 (2): 148–156. doi:10.24869/psyd.2019.148. PMID 31291218.
- ^ Curran MP, Perry CM (2002). "Spotlight on amisulpride in schizophrenia". CNS Drugs. 16 (3): 207–211. doi:10.2165/00023210-200216030-00007. PMID 11888341.
- ^ McKeage K, Plosker GL (2004). "Amisulpride: a review of its use in the management of schizophrenia". CNS Drugs. 18 (13): 933–956. doi:10.2165/00023210-200418130-00007. PMID 15521794.
- ^ Komossa K, Depping AM, Gaudchau A, Kissling W, Leucht S (December 2010). "Second-generation antipsychotics for major depressive disorder and dysthymia". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (12): CD008121. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD008121.pub2. PMID 21154393.
- ^ Mathias L, Quagliato LA, Carta MG, Nardi AE, Cheniaux E (July 2024). "Challenges in the treatment of dysthymia: a narrative review". Expert Rev Neurother. 24 (7): 633–642. doi:10.1080/14737175.2024.2360671. PMID 38805342.
- ^ Lindsay Murray M, Little M, Ovidiu Pascu M, Hoggett K (2015). Toxicology Handbook - Epub3. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-7295-8496-8. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs". accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ a b c Joint Formulary Committee (2013). British National Formulary (BNF) (65 ed.). London, UK: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 978-0-85711-084-8.
- ^ a b Truven Health Analytics, Inc. DRUGDEX System (Internet) [cited 2013 Sep 19]. Greenwood Village, CO: Thomsen Healthcare; 2013.
- ^ Brunton L, Chabner B, Knollman B (2010). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- ^ McKeage K, Plosker GL (2004). "Amisulpride: a review of its use in the management of schizophrenia". CNS Drugs. 18 (13): 933–956. doi:10.2165/00023210-200418130-00007. PMID 15521794. S2CID 9054960.
- ^ a b Natesan S, Reckless GE, Barlow KB, Nobrega JN, Kapur S (October 2008). "Amisulpride the 'atypical' atypical antipsychotic--comparison to haloperidol, risperidone and clozapine". Schizophrenia Research. 105 (1–3): 224–235. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2008.07.005. PMID 18710798. S2CID 11315672.
- ^ Joint Formulary Committee, ed. (March 2009). "4.2.1". British National Formulary (57 ed.). United Kingdom: Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. p. 192. ISBN 978-0-85369-845-6.
Withdrawal of antipsychotic drugs after long-term therapy should always be gradual and closely monitored to avoid the risk of acute withdrawal syndromes or rapid relapse.
- ^ a b c d e Haddad PM, Dursun S, Deakin B (2004). Adverse Syndromes and Psychiatric Drugs: A Clinical Guide. OUP Oxford. pp. 207–216. ISBN 978-0-19-852748-0.
- ^ Moncrieff J (July 2006). "Does antipsychotic withdrawal provoke psychosis? Review of the literature on rapid onset psychosis (supersensitivity psychosis) and withdrawal-related relapse". Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 114 (1): 3–13. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0447.2006.00787.x. PMID 16774655. S2CID 6267180.
- ^ Sacchetti E, Vita A, Siracusano A, Fleischhacker W (2013). Adherence to Antipsychotics in Schizophrenia. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 85. ISBN 978-8-84-702679-7.
- ^ Isbister GK, Balit CR, Macleod D, Duffull SB (August 2010). "Amisulpride overdose is frequently associated with QT prolongation and torsades de pointes". Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology. 30 (4): 391–395. doi:10.1097/JCP.0b013e3181e5c14c. PMID 20531221. S2CID 205710487.
- ^ Joy JP, Coulter CV, Duffull SB, Isbister GK (August 2011). "Prediction of torsade de pointes from the QT interval: analysis of a case series of amisulpride overdoses". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 90 (2): 243–245. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.107. PMID 21716272. S2CID 26412012.
- ^ a b c Taylor D, Paton C, Shitij K (2012). Maudsley Prescribing Guidelines in Psychiatry (11th ed.). West Sussex: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-0-47-097948-8.
- ^ Levine M, Ruha AM (July 2012). "Overdose of atypical antipsychotics: clinical presentation, mechanisms of toxicity and management". CNS Drugs. 26 (7): 601–611. doi:10.2165/11631640-000000000-00000. PMID 22668123. S2CID 24628641.
- ^ Roth BL, Driscol J. "PDSP Ki Database". Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (PDSP). University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and the United States National Institute of Mental Health. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw Abbas AI, Hedlund PB, Huang XP, Tran TB, Meltzer HY, Roth BL (July 2009). "Amisulpride is a potent 5-HT7 antagonist: relevance for antidepressant actions in vivo". Psychopharmacology. 205 (1): 119–128. doi:10.1007/s00213-009-1521-8. PMC 2821721. PMID 19337725.
- ^ a b Maitre M, Ratomponirina C, Gobaille S, Hodé Y, Hechler V (April 1994). "Displacement of [3H] gamma-hydroxybutyrate binding by benzamide neuroleptics and prochlorperazine but not by other antipsychotics". European Journal of Pharmacology. 256 (2): 211–214. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(94)90248-8. PMID 7914168.
- ^ Schoemaker H, Claustre Y, Fage D, Rouquier L, Chergui K, Curet O, et al. (January 1997). "Neurochemical characteristics of amisulpride, an atypical dopamine D2/D3 receptor antagonist with both presynaptic and limbic selectivity". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 280 (1): 83–97. PMID 8996185.
- ^ Blomme A, Conraux L, Poirier P, Olivier A, Koenig JJ, Sevrin M, et al. (2000). "Amisulpride, Sultopride and Sulpiride: Comparison of Conformational and Physico-Chemical Properties". Molecular Modeling and Prediction of Bioactivity. Springer US. pp. 404–405. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-4141-7_97. ISBN 978-1-4613-6857-1.
- ^ a b Hopkins SC, Wilkinson S, Corriveau TJ, Nishikawa H, Nakamichi K, Loebel A, et al. (September 2021). "Discovery of Nonracemic Amisulpride to Maximize Benefit/Risk of 5-HT7 and D2 Receptor Antagonism for the Treatment of Mood Disorders". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 110 (3): 808–815. doi:10.1002/cpt.2282. PMC 8453756. PMID 33961287.
- ^ Grattan V, Vaino AR, Prensky Z, Hixon MS (August 2019). "Antipsychotic Benzamides Amisulpride and LB-102 Display Polypharmacy as Racemates, S Enantiomers Engage Receptors D2 and D3, while R Enantiomers Engage 5-HT7". ACS Omega. 4 (9): 14151–14154. doi:10.1021/acsomega.9b02144. PMC 6714530. PMID 31497735.
- ^ Jethwa KD (2015). "Pharmacological management of antipsychotic-induced akathisia: An update and treatment algorithm". BJPsych Advances. 21 (5): 342–344. doi:10.1192/apt.bp.114.013797. S2CID 146670706.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o "Drug Trials Snapshots: Barhemsys". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 26 February 2020. Retrieved 27 March 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Investor Presentation" (PDF). LB Pharmaceuticals. December 2022.
- ^ "Amisulpride international". Drugs.com. 3 February 2020. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b "Active substance: amisulpride" (PDF). 28 September 2017. EMA/658194/2017; Procedure no.: PSUSA/00000167/201701. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2018. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ Lecrubier Y, Azorin M, Bottai T, Dalery J, Garreau G, Lempérière T, et al. (2001). "Consensus on the Practical Use of Amisulpride, an Atypical Antipsychotic, in the Treatment of Schizophrenia". Neuropsychobiology. 44 (1): 41–46. doi:10.1159/000054913. PMID 11408792. S2CID 21103201.
- ^ Kaplan A (2004). "Psychotropic Medications Around the World". Psychiatric Times. 21 (5).
- ^ "Barhemsys: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- ^ a b "SEP 4199". AdisInsight. Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
- ^ a b "Delving into the Latest Updates on Aramisulpride/Esamisulpride with Synapse". Synapse. 15 October 2024. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ a b Wu J, Kwan AT, Rhee TG, Ho R, d'Andrea G, Martinotti G, et al. (2023). "A narrative review of non-racemic amisulpride (SEP-4199) for treatment of depressive symptoms in bipolar disorder and LB-102 for treatment of schizophrenia". Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 16 (11): 1085–1092. doi:10.1080/17512433.2023.2274538. PMID 37864424.
- ^ "Amisulpride - Acacia Pharma". AdisInsight. 15 March 2023. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ "N-methyl amisulpride". AdisInsight. 26 December 2023. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
External links
[edit]- "Amisulpride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
