Flukes
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Trematoda is a class within the phylum Platyhelminthes, which contains two groups of parasitic worms, commonly referred to as flukes.
- Aspidogastrea are parasites of freshwater and marine molluscs and vertebrates (cartilaginous and bony fishes and turtles), but do not infect humans.
- Digenea infect all classes of vertebrates, including humans.
Flukes can be classified into two groups, on the basis of the system which they infect. Tissue flukes, are species which infect the bile ducts, lungs, or other biological tissues. This group includes the lung fluke, Paragonimus westermani, and the liver flukes, Clonorchis sinensis and Fasciola hepatica. The other group are known as blood flukes, and inhabit the blood in some stages of their life cycle. Blood flukes include various species of the genus Schistosoma (see Category:Schistosoma).
| Upload media | |||||
| Instance of | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
Liver Flukes
[edit]See also Category:Liver flukes
-
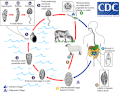
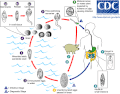
Life cycle of Clonorchis sinensis (Chinese or oriental liver fluke).
-
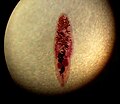
Clonorchis sinensis egg.
-
Life cycle of Fasciola hepatica
-
Egg of Fasciola hepatica (the "sheep liver fluke")
-
Fascioloides magna ("giant liver fluke")
-
Life cycle of Opisthorchis viverrini ("Southeast Asian liver fluke") and O. felineus ("cat liver fluke").
-
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
Intestinal Flukes
[edit]-
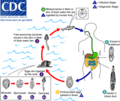
Life cycle of Fasciolopsis buski, the largest intestinal fluke of humans.
-
Egg of Fasciolopsis buski.
-
Botulus microporus, lives in the intestines of Lancetfish.
-
Digenea Helicometria sp. infects the digestive tract of fish