[USPRwire, Fri Apr 05 2019] The high cost of prosthetic surgeries, regulatory guidelines, and the complex prosthetic procedure of
glenoid fossa is hampering the demand for
glenoid fossa prosthesis market.
The
Glenoid Fossa lies in which part of the human body?
One of the morphological parameters of TMJ is measuring thickness of the roof of the
glenoid fossa, which is, in radiologic analysis, indirectly related to ZACD presence (2,3).
Grade 1: The air cells extended between the mastoid process and the deepest point of the
glenoid fossa;
Furthermore, the acromial coverage provided by the variable acromial length has been theorised to increase or decrease the size of the deltoid moment arm, thus causing a decentralization of the deltoid force vector on the rotational centre of
glenoid fossa (Moor et al., 2014a; Viehofer et al.).
Computed tomography (CT) imaging showed vasogenic edema in the left temporal lobe secondary to intracranial displacement of the left mandibular condyle through a 1.3 x 0.7 cm defect of the
glenoid fossa of the temporal bone.
ID refers to an abnormal positional relationship of the articular disc in relation to the mandibular condyle and the articular eminence in the
glenoid fossa, in the temporal bone [5, 10, 11, 14].
White et al., "Trans-subscapularis portal versus low-anterior portal for low anchor placement on the inferior
glenoid fossa: a cadaveric shoulder study with computed tomographic analysis," Arthroscopy: The Journal of Arthroscopic & Related Surgery, vol.
In type II, the temporomandibular joint, ramus, and
glenoid fossa are hypoplastic and malformed.
The presence of advancement devices seems to induce adaptive changes in the condylar cartilage (Liu, Kaneko, & Soma, 2007a; Sato, Muramoto, & Soma, 2006),
glenoid fossa and articular eminence (Liu, Kaneko, & Soma, 2007b; Tuominen, Kantomaa, Pirttiniemi, & Poikela, 1996; Woodside, Metaxas, & Altuna, 1987), but little has been described about the effects of PDT.
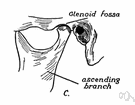 glenoid fossa - a deep concavity in the temporal bone at the root of the zygomatic arch that receives the condyle of the mandible
glenoid fossa - a deep concavity in the temporal bone at the root of the zygomatic arch that receives the condyle of the mandible