Hemodialysis catheter malposition induced by a
brachiocephalic vein stenosed stent.
The venous was drained from thyroid gland via inferior thyroid vein to left
brachiocephalic vein. The type II of thyroid gland abnormality was not observed in the male cadavers (Table II).
CT study of the thorax revealed a nodule, 32x20 mm in diameter, located posterior to the manubrium sterni and in front of the left
brachiocephalic vein. By Tc-99 m MIBI scan, the nodule was seen as an intense focus in the anterior mediastinum, and ectopic parathyroid adenoma was diagnosed.
More rarely cases of LSIVC, possible routes for the return of blood to RA are via the azygos vein to SVC, via the left
brachiocephalic vein to the right SVC, or via the hemiazygos vein to PLSVC(3).
The vein between the CS and left
brachiocephalic vein is called a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC), which finally drained into the right atrium.
(1) Nevertheless, prompt and accurate diagnosis is critical, as these dislocations involve a high risk for injury to the posterior structures, particularly the
brachiocephalic vein, right common carotid artery, and aortic arch.
A variety of rare complications such as perforation of the left
brachiocephalic vein and massive hemothorax, chylothorax, internal mammary artery malposition of catheter, and inadvertent placement of a CVC in the left pericardiophrenic vein have been reported previously [5-8].
Under ultrasound-guidance, the catheter was directed into the left
brachiocephalic vein. Normal saline solution was injected without any complications.
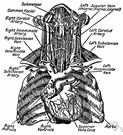
Caption: Figure 1: Dissected body with the clavicles (RC and LC) in situ, right and left internal jugular vein (RIJV and LIJV), right and left external jugular vein (REJV and LEJV), right and left supraclavicular (RSC and LSC) branches of cephalic vein, right and left cephalic vein (RCV and LCV), right and left infraclavicular (RIC and LIC) branch of cephalic vein, right and left axillary veins (RAV and LAV), left
brachiocephalic vein (LBC), superior vena cava (SVC), aorta (A), deltoid muscle (D), and pectoral major muscle (P).
Life-threatening structures that may be affected include the pharynx; esophagus; trachea; thyroid gland; innominate artery;
brachiocephalic vein; subclavian artery and vein; common, internal, and external carotid arteries; jugular vein; and vertebral artery (3).
In the upper extremities, these areas include the subclavian vein at the costoclavicular junction and the left
brachiocephalic vein as it crosses a relatively fixed, pulsatile fulcrum of brachiocephalic artery and aorta.
 brachiocephalic vein - veins formed by the union of the internal jugular and subclavian veins
brachiocephalic vein - veins formed by the union of the internal jugular and subclavian veins