xylem
(redirected from Woody tissue)Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Encyclopedia.
Related to Woody tissue: Secondary xylem
xy·lem
(zī′ləm)n.
The tissue of vascular plants that conducts water and minerals, provides support, and consists of tracheary elements and parenchyma cells. Woody tissue is made of secondary xylem produced by the vascular cambium.
[German, from Greek xulon, wood.]
American Heritage® Dictionary of the English Language, Fifth Edition. Copyright © 2016 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
xylem
(ˈzaɪləm; -lɛm)n
(Botany) a plant tissue that conducts water and mineral salts from the roots to all other parts, provides mechanical support, and forms the wood of trees and shrubs. It is of two types (protoxylem and metaxylem), both of which are made up mainly of vessels and tracheids. See also protoxylem, metaxylem
[C19: from Greek xulon wood]
Collins English Dictionary – Complete and Unabridged, 12th Edition 2014 © HarperCollins Publishers 1991, 1994, 1998, 2000, 2003, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2011, 2014
xy•lem
(ˈzaɪ ləm, -lɛm)n.
a compound tissue in vascular plants that helps provide support and that conducts water and nutrients upward from the roots, consisting of tracheids, vessels, parenchyma cells, and woody fibers.
[1870–75; < German < Greek xýl(on) wood (see phloem)]
Random House Kernerman Webster's College Dictionary, © 2010 K Dictionaries Ltd. Copyright 2005, 1997, 1991 by Random House, Inc. All rights reserved.
xylem
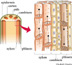
Xylem cells in the stem carry water from a plant's roots to its leaves. The phloem distributes food that is made in the plant's leaves to other parts of the plant. The cambium cells divide into either xylem or phloem cells. The cortex and pith, seen in the stem cross section, provide structural support.
xy·lem
(zī′ləm) A tissue in vascular plants that carries water and dissolved minerals up from the roots through the stem to the leaves and provides support for the softer tissues. Xylem consists of various elongated cells that function as tubes. In a tree trunk, the innermost part of the wood is dead but structurally strong xylem, while the outer part consists of living xylem, and beyond it, layers of cambium and phloem. See more at cambium, photosynthesis. Compare phloem.
The American Heritage® Student Science Dictionary, Second Edition. Copyright © 2014 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
xylem
Tissue in plants that carries water and mineral salts from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Dictionary of Unfamiliar Words by Diagram Group Copyright © 2008 by Diagram Visual Information Limited
ThesaurusAntonymsRelated WordsSynonymsLegend:
Switch to new thesaurus
| Noun | 1. | xylem - the woody part of plants: the supporting and water-conducting tissue, consisting primarily of tracheids and vessels vascular tissue - tissue that conducts water and nutrients through the plant body in higher plants tracheid - long tubular cell peculiar to xylem ligneous plant, woody plant - a plant having hard lignified tissues or woody parts especially stems |
Based on WordNet 3.0, Farlex clipart collection. © 2003-2012 Princeton University, Farlex Inc.