BIOS settings have been a source of uncertainty for many people in the PC space. The BIOS plays a key role in the functioning of the overall system, and it can severely limit your hardware and software integration if configured incorrectly.
Basic Input/Output System or BIOS is a computer software program used to start or boot when a computer system is turned on. The very basic function of the BIOS is detecting connected peripheral devices (like a keyboard and mouse) while also ensuring that the operating system gets surfaced in the memory once the PC is switched on. These two functions set the foundation for computer operation.
Once the computer is booted up, the next step for the BIOS is to act as an intermediary between the Operating System and hardware devices. It influences the correct flow of data as and when required. There are numerous settings in the scope of BIOS that may or may not be applicable to your system. It is mostly dependent on what motherboard variant and CPU your system features. We recommend looking at system-specific configurations along with this guide.
Common BIOS settings you need to tweak
This article will cover some of the most common and essential BIOS settings that need to be tweaked. For most people, the following settings will suffice:
1) General overclocking settings
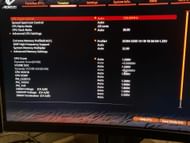
Overclocking is a highly important aspect for those who want to gain maximum performance from their system. If you do want to overclock, the BIOS enables you to do so without having to download any external applications.
Spread Spectrum - The availability of these settings is variably dependent on your motherboard brand. If you do have this setting and want to overclock your system, we recommend turning it off. Keeping it on may cause overclock instability.
Overclock mode - This setting essentially enables overclocking. Auto mode runs everything at the stock frequency and voltage. Most people won’t need to overclock their systems, and keeping this in Auto mode will be a safe option. If you do want to overclock, switch the overclock mode to manual. With the manual mode selected, you can change the CPU frequency and voltage below. Overclocking should be done with pre-handed extensive research and based on the cooling solution installed. It is possible that your hardware may get damaged. We won’t delve further into overclocking specifics, as this article only seeks to give a brief layout of the BIOS settings.
DRAM Frequency - This option can be used to increase or decrease your memory timing. Sometimes, if your memory is underclocked by default, you should change it to the original memory frequency. Or you can also slightly overclock if the need arises.
DRAM Voltage - This can be used to change the voltage allowance of the RAM stick. We recommend keeping this on auto. However, if you have overclocked your memory frequency, you may need to slightly increase the voltage allowance.
2) Boot order

The boot order is an important setting to tweak while installing a new operating system. The boot order refers to the order in which Windows will give boot priority. You can have multiple storage sources of the operating system plugged in, but which one will be given priority can be decided by the boot order.
Suppose you already have windows installed on your Hard Disk Drive and plug in a USB drive with Linux. If you want Linux to be booted, you will have to put the USB stick on first priority in boot order when you are in the BIOS settings. If the storage medium on the first priority does not read, the BIOS will read and boot into the next one according to the boot priority.
3) Secure boot
Secure boot is a security feature that was developed to protect against malware. Secure boot works on several secure boot keys to verify that the system only boots into a trusted operating system. This means that if your PC is infected with malware, the secure boot feature will ensure that the malware does not boot before your operating system and take over your computer.
Secure boot should be kept on for the most part in the BIOS settings, but it can cause issues and limit the installation of certain operating systems, so you may temporarily turn it off for that time period.
Note: For Valorant, you'll need to ensure Secure Boot and TPM are enabled in BIOS settings. This is for Windows 11 only.
4) Fast boot
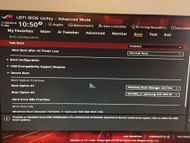
Fast boot is a BIOS settings feature that can be toggled on or off to prioritize faster booting at the cost of losing background checks and security features. We generally recommend keeping fast boot turned off. If you are running your operating system on an SSD, the boot times are already fast enough. However, if you truly value faster boot times, you may keep it on.
People using HDDs shouldn't even bother fiddling with this setting, as it will make no difference to the overall boot time.
5) BIOS password
Operating systems like Windows usually allow you to secure your system with password verification before logging in. However, if someone gets access to your BIOS, they can compromise your system. If your system usually has sensitive data, it is recommended to also enforce the BIOS settings password. This acts as an extra layer of security for your computer system.
Having a BIOS password in place when you know your PC isn't in the most homely space ensures that your precious data stays safe from malicious tinkerers. But make sure that you remember the password to prevent undue hassle.