Patent DefinitionIntroductionA patent is a property right that a sovereign has granted to an inventor. In exchange for a complete disclosure of the idea, this grant gives the inventor exclusive ownership of the patented method, design, or creation. They are a kind of incorporeal right.  Applications for patents are normally handled and approved by government organizations. Applications are processed, and approvals are given in the United States by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), a division of the Department of Commerce. Key Takeaways
Knowing about PatentsIn the United States, patents typically last for 20 years from the date the application was submitted to the USPTO; however, there are several situations when the period could be extended. Only the United States and U.S. Territories are eligible for U.S. patents. It is crucial to learn about the intellectual property laws of other countries and apply for protection with their regulatory authorities if seeking protection outside of the U.S. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office states that anybody can acquire a patent if they: "Invent or discover any unique and useful technique, the machine, manufacturing, or composition of matter, as well as any new and useful improvement thereof, can be eligible for a patent, provided that it satisfies all legal criteria." Different PatentsUtility, design, and plant patents are the three categories of patents accessible in the U.S., and each has different demands and deadlines. 1. Utility Patents Patents for invention, often known as utility patents, provide individuals with legal protection when they invent new and effective techniques, goods, tools, or materials. More than 90% of all patents granted by the U.S. government fall under the utility patent category, making them the most prevalent form of patent. As long as maintenance costs are paid, a utility patent is valid for 20 years from the date of application. Utility patent applications submitted after December 12, 1980, are liable to maintenance costs. 2. Patents on designs Patents for unique, innovative, and elegant designs of manufactured goods are known as design patents. Design patents preserve an object's appearance or design. They demand the originality and utility of the innovation to which the design relates. For applications submitted after May 13, 2015, the duration of a design patent is 15 years. Patents issued prior to May 13, 2015, are valid for 14 years from the filing date. Design patents do not need maintenance costs. 3. Plant Patents Anybody who creates, reveals, or develops an innovative form of plant that is capable of reproduction is eligible for a plant patent. These patents are free of maintenance costs and are valid for 20 years after filing. Patents encourage businesses or people to continue creating new goods or services without worrying about being copied. For instance, large pharmaceutical companies invest billions of dollars in R&D. Without patents, their medications, and pharmaceuticals could be copied and marketed by businesses that didn't do research or put out the required money for R&D. In other words, patents assist businesses in protecting their intellectual property so that they can become more successful. However, patents also provide businesses the opportunity to talk about their innovativeness. A Patent Application's ProcessAn applicant should check the Patent and Trademark Office's database before submitting a formal application to determine whether another individual or organization has already filed for a patent for a similar idea. The innovation must be unique or improved to an earlier design to be eligible for a patent. Applicants must keep detailed records of the invention's design and production processes. The individual or organization that submitted the patent application is responsible for enforcing it. The applicant must submit certain documentation and pay related costs in order to file for a patent in the United States. Drawings, descriptions, and claims of the invention to be patented are all included in written paperwork. The inventor must sign and submit a formal oath or statement declaring that the innovation or modification to an existing invention is real. The application is examined after the fee is paid and either accepted or rejected. "Patents encourage a company's growth while protecting its intellectual property and ensuring their financial success." Patent StatisticsEach year, the USPTO receives approximately 500,000 patent applications, of which only over 300,000 are finally approved. Almost 11,000 people work for the agency, with about 75% of them working as patent examiners and the rest in the legal and technical fields. The USPTO published its ten millionth patent in June 2018. The technology sector finds a lot of patents granted, with Apple receiving 2,000 in 2018. Moreover, patents were given to Microsoft and Google. Nonetheless, IBM regularly gets more than any other firm in the United States. According to CNN Business, IBM received over 9,000 patents in 2017. 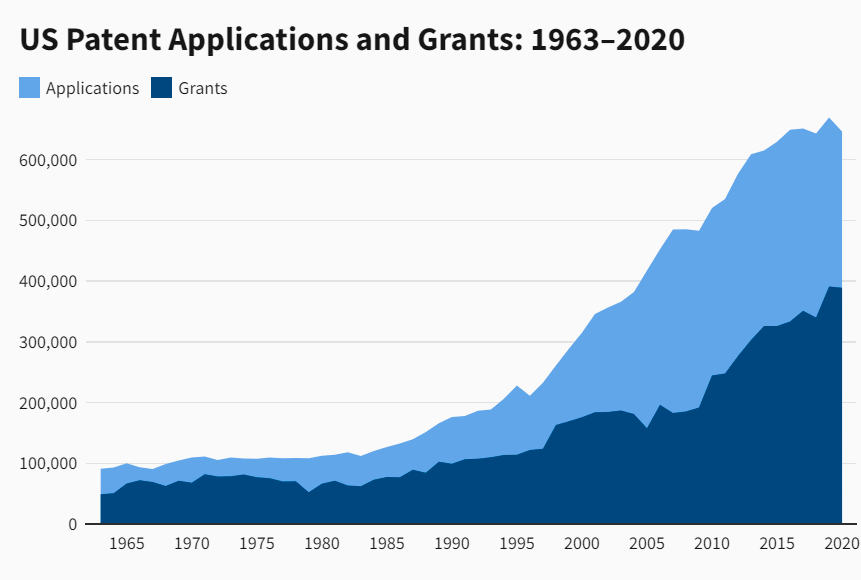 A few Patent Examples
Patents vs. Trademarks vs. Copyrights
FAQs about patents1. What Exactly is a Patent? A patent grants a person or organization the legal right to an invention without the interference of other individuals who may want to copy, use, or sell it. Governmental agencies can grant patents, which have a 20-year lifespan on average. 2. What Are Some Examples of Patents? The telephone, dishwasher, and lightbulb are some well-known items patented in the past. 3. Which of the Three Patent Types Exists? The three main types of patents are utility, design, and plant. Design patents cover a product's look or design, whereas utility patents are issued for innovative, useful ideas. Patents for plants that can reproduce are given to applicants. 4. How Much Does a Patent Cost? The kind of applicant, the provisional or nonprovisional status, and associated costs like search fees, examination fees, and post-allowance fees, among others, all affect the price of a patent. If you need legal advice, you might estimate spending between $5,000 and $45,000 in fees. 5. How Much Time Does a Patent Have? Utility and plant patents are valid for 20 years from the filing date, while design patents are valid for 15 years if submitted after May 13, 2015, or 14 years if filed before May 13, 2015. Next TopicPDF Definition |