Fossil-Fuels DefinitionFossil Fuels are a type of energy source formed over millions of years from the remains of dead plants and animals. These fuels, including coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite resources used to power human civilization for hundreds of years.  1. CoalCoal is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from the remains of plants that lived in swamps and bogs. As these plants died, their remains were buried under sediment and compressed by the weight of the overlying material. Over time, heat and pressure transformed the plant material into coal. Coal is a non-renewable energy source and is one of the most abundant fossil fuels on earth. Coal has been used for various purposes, including heating homes, generating electricity, and powering industrial processes. It is the most widely used fossil fuel for electricity generation, accounting for over 40% of global electricity production. One of the benefits of coal as a fossil fuel is that it is relatively inexpensive and widely available. This has made it an attractive energy source for many countries, particularly those with large coal reserves. Coal-fired power plants can also be built relatively quickly and provide a reliable electricity source. However, using coal as a fossil fuel also has significant drawbacks. Burning coal releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Coal-fired power plants are also a major source of air pollution, releasing sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter into the air, which can negatively impact human health and the environment. In addition, coal mining can be a dangerous and environmentally damaging process. Coal mining can result in soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat destruction, and it can also be hazardous for miners who work in the mines. Despite these challenges, coal will likely remain an important energy source for many countries in the coming years, particularly as developing countries seek to meet their growing energy needs. However, efforts are underway to reduce the environmental impact of coal, including using cleaner technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, and developing alternative energy sources. 2. Oil and Natural GasOil and natural gas are two of the most important fossil fuels used for energy production worldwide. Fossil fuels are formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient plants and animals, which have been buried and compressed under high pressure and heat. Oil and natural gasare formed from the remains of marine organisms, such as plankton and algae, that lived in ancient seas. When these organisms died, their remains sank to the bottom of the ocean and were covered by sediment. Over time, heat and pressure transformed the organic material into oil and gas. These fuels are non-renewable, meaning they are finite and will eventually be depleted. Oil, or petroleum, is a thick, dark liquid extracted from underground reservoirs through drilling. It produces gasoline, diesel fuel, heating oil, and other products. Oil is a highly valuable resource because it is a dense source of energy that can be easily transported and stored. However, its extraction, transportation, and use can have significant environmental impacts, such as air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change. Natural gas is a fossil fuel composed mainly of colorless and odorless methane. It is usually found in underground reservoirs or associated with oil deposits. Natural gas is used primarily for heating and electricity generation. It is also used as a feedstock for producing chemicals and other products. Natural gas is considered a cleaner-burning fossil fuel than oil or coal, as it produces lower levels of air pollutants and greenhouse gases per unit of energy generated. However, its extraction and transport can also have negative environmental impacts, such as methane leaks, a potent greenhouse gas. Overall, while oil and natural gas are important energy sources that have enabled significant technological advances and economic growth, their continued use also poses significant environmental challenges that must be addressed. The transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency measures, is necessary to mitigate the impacts of fossil fuel on the environment and ensure a stable and secure energy future. Fossil fuels are extracted from the ground through a process known as Drilling or Mining. Once extracted, they can be refined into various products, including gasoline, diesel fuel, heating oil, and propane. These products are used to power vehicles, generate electricity, heat homes, and produce various consumer goods. 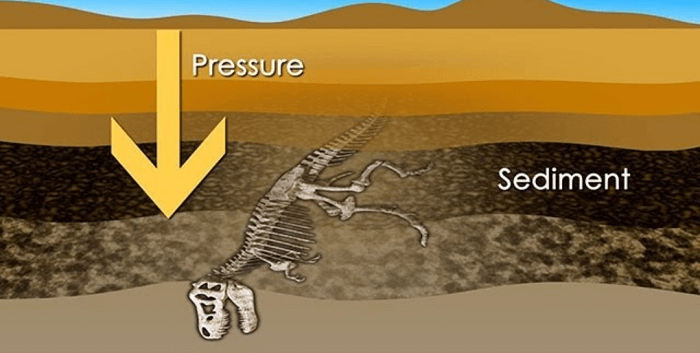 The above picture depicts that pressure plays an important role in forming fossils and fossil fuels. Uses of Fossil FuelsFossil Fuels, including coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas, are used for various purposes in modern society. Here are some of the most common uses of fossil fuels:
Drawbacks of Fossil FuelsDespite their widespread use, fossil fuels have several drawbacks. One major concern is their impact on the environment. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Fossil fuel extraction can also cause environmental damage, including air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and oil spills. Fossil fuels have been essential to modern society, but their use has significant drawbacks and negative impacts on the environment and human health. Here are some of the most important drawbacks of fossil fuels:
Their negative environmental and human health impacts are significant and cannot be ignored. The transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency measures, is necessary to mitigate these impacts and ensure a more sustainable energy future. In recent years, there has been growing interest in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate their environmental impact. Nowadays, automatic solar lights are being used in street lightning. However, renewable energy sources still need help with cost, storage, and reliability, which have limited their widespread adoption. ConclusionFossil Fuels are an important energy source that has powered human civilization for centuries. However, their finite supply and environmental impact make it important to consider alternative energy sources for the future. Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. Fossil fuels have been essential to modern society, but their use has significant drawbacks and negative impacts on the environment and human health. Next TopicFungi Definition |