WO2024191390A1 - A pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib - Google Patents
A pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2024191390A1 WO2024191390A1 PCT/TR2024/050230 TR2024050230W WO2024191390A1 WO 2024191390 A1 WO2024191390 A1 WO 2024191390A1 TR 2024050230 W TR2024050230 W TR 2024050230W WO 2024191390 A1 WO2024191390 A1 WO 2024191390A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- pharmaceutical composition
- regorafenib
- pharmaceutically acceptable
- poloxamer
- acceptable excipient
- Prior art date
Links
- 229960004836 regorafenib Drugs 0.000 title claims abstract description 70
- 239000002138 L01XE21 - Regorafenib Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 68
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 57
- 150000004934 Regorafenib derivatives Chemical group 0.000 title 1
- FNHKPVJBJVTLMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N regorafenib Chemical compound C1=NC(C(=O)NC)=CC(OC=2C=C(F)C(NC(=O)NC=3C=C(C(Cl)=CC=3)C(F)(F)F)=CC=2)=C1 FNHKPVJBJVTLMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 77
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 58
- RVGRUAULSDPKGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Poloxamer Chemical compound C1CO1.CC1CO1 RVGRUAULSDPKGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 43
- 229960000502 poloxamer Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 43
- 229920001983 poloxamer Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 43
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 36
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 59
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 claims description 34
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 24
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical group CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000007962 solid dispersion Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 claims description 20
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000008202 granule composition Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 18
- DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanal;sodium Chemical compound [Na].CC(O)=O.OCC(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C=O DPXJVFZANSGRMM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- 229920002785 Croscarmellose sodium Polymers 0.000 claims description 14
- 229960001681 croscarmellose sodium Drugs 0.000 claims description 14
- 235000010947 crosslinked sodium carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 14
- WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidone Chemical compound C=CN1CCCC1=O WHNWPMSKXPGLAX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 13
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000008199 coating composition Substances 0.000 claims description 11
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 claims description 11
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 11
- 229940069328 povidone Drugs 0.000 claims description 11
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000001953 recrystallisation Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920000858 Cyclodextrin Polymers 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000002202 Polyethylene glycol Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 9
- 229940075614 colloidal silicon dioxide Drugs 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000007884 disintegrant Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000314 lubricant Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 229920000168 Microcrystalline cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000001768 carboxy methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- -1 glycerol ethers Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- 235000019813 microcrystalline cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000008108 microcrystalline cellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 229940016286 microcrystalline cellulose Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- VBICKXHEKHSIBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-monostearoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(O)CO VBICKXHEKHSIBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 4
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920002153 Hydroxypropyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 claims description 4
- OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium sulfate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O OSGAYBCDTDRGGQ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008121 dextrose Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002334 glycols Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000010977 hydroxypropyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000001863 hydroxypropyl cellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000003605 opacifier Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 229940032147 starch Drugs 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 claims description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N lactose group Chemical group OC1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O2)CO)[C@H](O1)CO GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920000609 methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000010981 methylcellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000001923 methylcellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 235000019812 sodium carboxymethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920001027 sodium carboxymethylcellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- OKMWKBLSFKFYGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-behenoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(O)CO OKMWKBLSFKFYGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1,3-diazinane-5-carboximidamide Chemical compound CN1CC(C(N)=N)C(=O)NC1=O IXPNQXFRVYWDDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002134 Carboxymethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N D-Glucitol Natural products OC[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-FSIIMWSLSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N D-glucitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-JGWLITMVSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002307 Dextran Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004375 Dextrin Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001353 Dextrin Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000005913 Maltodextrin Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920002774 Maltodextrin Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000881 Modified starch Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001213 Polysorbate 20 Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N Sucrose Chemical compound O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@@]1(CO)O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O1 CZMRCDWAGMRECN-UGDNZRGBSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229930006000 Sucrose Natural products 0.000 claims description 2
- TVXBFESIOXBWNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Xylitol Natural products OCCC(O)C(O)C(O)CCO TVXBFESIOXBWNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] Chemical compound [O--].[Al+3].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])([O-])[O-] YKTSYUJCYHOUJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium stearate Chemical compound [Ca+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O CJZGTCYPCWQAJB-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000013539 calcium stearate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008116 calcium stearate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010948 carboxy methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008112 carboxymethyl-cellulose Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940105329 carboxymethylcellulose Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229960000913 crospovidone Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940096516 dextrates Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000019425 dextrin Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000019700 dicalcium phosphate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940095079 dicalcium phosphate anhydrous Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- MVPICKVDHDWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethyl 3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropanoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)CCN1CCCC1 MVPICKVDHDWCJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940049654 glyceryl behenate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940075507 glyceryl monostearate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008172 hydrogenated vegetable oil Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001095 magnesium carbonate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium carbonate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=O ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910000021 magnesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000395 magnesium oxide Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium oxide Inorganic materials [Mg]=O CPLXHLVBOLITMK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N magnesium;oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[Mg+2] AXZKOIWUVFPNLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940035034 maltodextrin Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N meso ribitol Natural products OCC(O)C(O)C(O)CO HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001788 mono and diglycerides of fatty acids Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010486 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000256 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010482 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000244 polyoxyethylene sorbitan monooleate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940068977 polysorbate 20 Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940068968 polysorbate 80 Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000053 polysorbate 80 Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000013809 polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920000523 polyvinylpolypyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- HFHDHCJBZVLPGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N schardinger α-dextrin Chemical compound O1C(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(O)C2O)C(CO)OC2OC(C(C2O)O)C(CO)OC2OC2C(O)C(O)C1OC2CO HFHDHCJBZVLPGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010413 sodium alginate Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000661 sodium alginate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940005550 sodium alginate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940080313 sodium starch Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000008109 sodium starch glycolate Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920003109 sodium starch glycolate Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940079832 sodium starch glycolate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940045902 sodium stearyl fumarate Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000600 sorbitol Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010356 sorbitol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- 229960004274 stearic acid Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000005720 sucrose Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000003445 sucroses Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MDYZKJNTKZIUSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyloxapol Chemical compound O=C.C1CO1.CC(C)(C)CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 MDYZKJNTKZIUSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229920001664 tyloxapol Polymers 0.000 claims description 2
- 229960004224 tyloxapol Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000811 xylitol Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 235000010447 xylitol Nutrition 0.000 claims description 2
- HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N xylitol Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)CO HEBKCHPVOIAQTA-SCDXWVJYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229960002675 xylitol Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc stearate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 2
- FUFJGUQYACFECW-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium hydrogenphosphate Chemical compound [Ca+2].OP([O-])([O-])=O FUFJGUQYACFECW-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims 1
- 229920002503 polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene Polymers 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 32
- 238000004090 dissolution Methods 0.000 description 21
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 14
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 13
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 9
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 8
- 229940088679 drug related substance Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 235000010979 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 229920003088 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 229940090374 stivarga Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 241001489705 Aquarius Species 0.000 description 6
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron oxide Chemical compound [Fe]=O UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000008186 active pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000001866 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000004372 Polyvinyl alcohol Substances 0.000 description 4
- 231100001125 band 2 compound Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- 235000010980 cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 4
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 206010073071 hepatocellular carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 231100000844 hepatocellular carcinoma Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- UFVKGYZPFZQRLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Chemical compound OC1C(O)C(OC)OC(CO)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC2C(C(O)C(OC3C(C(O)C(O)C(CO)O3)O)C(CO)O2)O)C(CO)O1 UFVKGYZPFZQRLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229940057948 magnesium stearate Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 229920002451 polyvinyl alcohol Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000004408 titanium dioxide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920001450 Alpha-Cyclodextrin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 229920003119 EUDRAGIT E PO Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229940043377 alpha-cyclodextrin Drugs 0.000 description 3
- WHGYBXFWUBPSRW-FOUAGVGXSA-N beta-cyclodextrin Chemical compound OC[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)O)O[C@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O3)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O[C@@H]1CO WHGYBXFWUBPSRW-FOUAGVGXSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229960004853 betadex Drugs 0.000 description 3
- NEDGUIRITORSKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N butyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate;2-(dimethylamino)ethyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate;methyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)=C.CCCCOC(=O)C(C)=C.CN(C)CCOC(=O)C(C)=C NEDGUIRITORSKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 3
- GDSRMADSINPKSL-HSEONFRVSA-N gamma-cyclodextrin Chemical compound OC[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)O)O[C@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O3)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O[C@@H]1CO GDSRMADSINPKSL-HSEONFRVSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229940080345 gamma-cyclodextrin Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229920000639 hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000012729 immediate-release (IR) formulation Substances 0.000 description 3
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000007916 tablet composition Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000011282 treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 206010009944 Colon cancer Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000001333 Colorectal Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010052358 Colorectal cancer metastatic Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 206010051066 Gastrointestinal stromal tumour Diseases 0.000 description 2
- ZUAAPNNKRHMPKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid;butanedioic acid;methanol;propane-1,2-diol Chemical compound OC.CC(O)=O.CC(O)CO.OC(=O)CCC(O)=O ZUAAPNNKRHMPKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007894 caplet Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920002301 cellulose acetate Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002496 gastric effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 201000011243 gastrointestinal stromal tumor Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 229960003943 hypromellose Drugs 0.000 description 2
- LDHBWEYLDHLIBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M iron(3+);oxygen(2-);hydroxide;hydrate Chemical compound O.[OH-].[O-2].[Fe+3] LDHBWEYLDHLIBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000013081 microcrystal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000006070 nanosuspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000001694 spray drying Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-4,5-dimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)-3-[(2s,3r,4s,5r,6r)-3,4,5-trimethoxy-6-(methoxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[(2r,3r,4s,5r,6r)-4,5,6-trimethoxy-2-(methoxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)[C@@H](COC)O[C@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](OC)[C@@H](OC)[C@H](O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@@H](OC)[C@H](OC)O[C@@H]2COC)OC)O[C@@H]1COC LNAZSHAWQACDHT-XIYTZBAFSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-[4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxyoxane-3,4,5-triol Chemical compound OCC1OC(OC2C(O)C(O)C(O)OC2CO)C(O)C(O)C1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WAVYAFBQOXCGSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-fluoropyrimidine Chemical compound FC1=NC=CC=N1 WAVYAFBQOXCGSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N Alpha-Lactose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MLDQJTXFUGDVEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N BAY-43-9006 Chemical compound C1=NC(C(=O)NC)=CC(OC=2C=CC(NC(=O)NC=3C=C(C(Cl)=CC=3)C(F)(F)F)=CC=2)=C1 MLDQJTXFUGDVEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000005623 Carcinogenesis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical compound CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920003134 Eudragit® polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000663 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004354 Hydroxyethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000005517 L01XE01 - Imatinib Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002147 L01XE04 - Sunitinib Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005511 L01XE05 - Sorafenib Substances 0.000 description 1
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037273 Pathologic Processes Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108091000080 Phosphotransferase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229920003171 Poly (ethylene oxide) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003463 adsorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005054 agglomeration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002776 aggregation Effects 0.000 description 1
- HFHDHCJBZVLPGP-RWMJIURBSA-N alpha-cyclodextrin Chemical compound OC[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1O)O)O[C@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O[C@H]3O[C@H](CO)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]3O)O)O3)[C@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO)O[C@@H]1O[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]3O[C@@H]1CO HFHDHCJBZVLPGP-RWMJIURBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000011123 anti-EGFR therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960000074 biopharmaceutical Drugs 0.000 description 1
- XAAHAAMILDNBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L calcium hydrogenphosphate dihydrate Chemical compound O.O.[Ca+2].OP([O-])([O-])=O XAAHAAMILDNBPS-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 230000036952 cancer formation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 231100000504 carcinogenesis Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 239000012876 carrier material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003915 cell function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002512 chemotherapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001531 copovidone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003618 dip coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000007908 dry granulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002389 essential drug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000013265 extended release Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007941 film coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007888 film coating Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009501 film coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013020 final formulation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009477 fluid bed granulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004108 freeze drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001903 high density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004700 high-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009474 hot melt extrusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012943 hotmelt Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000004677 hydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000019447 hydroxyethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920003132 hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940031704 hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- KTUFNOKKBVMGRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imatinib Chemical compound C1CN(C)CCN1CC1=CC=C(C(=O)NC=2C=C(NC=3N=C(C=CN=3)C=3C=NC=CC=3)C(C)=CC=2)C=C1 KTUFNOKKBVMGRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002411 imatinib Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003834 intracellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001788 irregular Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004898 kneading Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002207 metabolite Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001394 metastastic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 206010061289 metastatic neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229920003145 methacrylic acid copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000008520 organization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007500 overflow downdraw method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010951 particle size reduction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009054 pathological process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940124531 pharmaceutical excipient Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940127557 pharmaceutical product Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 102000020233 phosphotransferase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000651 prodrug Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940002612 prodrug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000000275 quality assurance Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZOPOQLDXFHBOIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N regorafenib hydrate Chemical compound O.C1=NC(C(=O)NC)=CC(OC=2C=C(F)C(NC(=O)NC=3C=C(C(Cl)=CC=3)C(F)(F)F)=CC=2)=C1 ZOPOQLDXFHBOIH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002399 regorafenib monohydrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000012776 robust process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009490 roller compaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009097 single-agent therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009491 slugging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007909 solid dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007614 solvation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000935 solvent evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960003787 sorafenib Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000012430 stability testing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001796 sunitinib Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WINHZLLDWRZWRT-ATVHPVEESA-N sunitinib Chemical compound CCN(CC)CCNC(=O)C1=C(C)NC(\C=C/2C3=CC(F)=CC=C3NC\2=O)=C1C WINHZLLDWRZWRT-ATVHPVEESA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004094 surface-active agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000005591 trimellitate group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000005747 tumor angiogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005550 wet granulation Methods 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K9/00—Medicinal preparations characterised by special physical form
- A61K9/20—Pills, tablets, discs, rods
- A61K9/28—Dragees; Coated pills or tablets, e.g. with film or compression coating
- A61K9/2806—Coating materials
- A61K9/2833—Organic macromolecular compounds
- A61K9/2853—Organic macromolecular compounds obtained otherwise than by reactions only involving carbon-to-carbon unsaturated bonds, e.g. polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, poloxamers, poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/435—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having six-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- A61K31/44—Non condensed pyridines; Hydrogenated derivatives thereof
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) a core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) a coating comprising poloxamer (polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene copolymer) and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the invention further relates to a process for the preparation of the said pharmaceutical composition and its use for treating disorders.
- Regorafenib is chemically known as 4-[4-( ⁇ [4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] carbamoyl ⁇ amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide (I).
- Regorafenib is a low molecule inhibitor of multiple membrane-bound and intracellular kinases involved in normal cellular functions and in pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment.
- Regorafenib is marketed as Stivarga® by Bayer Pharma in Europe since 2013.
- the marketed product is approved in the form of 40 mg film coated tablet.
- Stivarga® is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with, or are not considered candidates for, available therapies.
- CRC metastatic colorectal cancer
- These include fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy and an anti-EGFR therapy, unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) who progressed on or are intolerant to prior treatment with imatinib and sunitinib and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have been previously treated with sorafenib.
- regorafenib is a white to slightly pink or slightly brownish solid substance, practically insoluble in water.
- Regorafenib is BCS Class II compound based on Biopharmaceutical Classification System.
- BCS Class II compounds are drug substances with low solubility and high permeability. The bioavailability of these compounds is limited by their solubility (solvation rate). Hence, the absorption of a poorly water-soluble compound from orally administered solid dosage form is controlled by its dissolution rate in the gastrointestinal fluid present at the absorption site. It is known in the pharmaceutical arts that low-solubility drugs often show poor bioavailability or irregular absorption, the degree of irregularity being affected by factors such as dose level, fed state of the patient, and form of the drug.
- WO 2006026500 discloses a composition comprising a solid dispersion comprising regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable matrix, wherein the matrix comprises at least one polymer from the group consisting of polyvinylpyrrolidone, copovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol or polyethylene oxide.
- CN 111166724 A discloses a regorafenib nano dispersion, a tablet and a preparation method thereof; the dispersion can be prepared by dissolving regorafenib in solvent, separately dissolving a carrier material in water, and performing liquid phase precipitation and crystallization reaction to obtain regorafenib nano-suspension; it is spray dried to spray-dried to obtain a regorafenib nano-dispersion.
- CN 106913527 A discloses immediate-release pellet and immediate-release pellet consisting blank pellet core and a regorafenib-containing layer wrapped outside the pellet core is characterized in that the drug-containing layer contains micronized regorafenib and a binder.
- CN ‘527 discloses polyvinylpyrrolidone and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for preparation of regorafenib containing layer solution.
- WO 2014039677 discloses a pharmaceutical composition comprising regorafenib, a hydrate, solvate, metabolite or pharmaceutically acceptable salt of regorafenib, or a polymorph thereof and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient wherein the pharmaceutical composition is coated by a coating comprising a polyvinyl alcohol based polymer and optionally one or more further pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
- polyvinyl alcohol based polymer coating effectively controls particular impurity AFP-PMA as compared to conventional HPMC coating.
- solid dispersion system comes into contact with gastrointestinal media, dissolution will occur to a supersaturated state, which is more or less stabilized by the polymer. This has been shown to significantly enhance the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble BCS Class II compounds or drugs.
- One major challenge in administration of these compounds or drugs is the high inter-individual variability of drug performance.
- Another inherent issue of amorphous solid dispersions is the instability of the solid state which results in a tendency for recrystallisation of the drug and/or excipients during storage. This may be accompanied by a break-down of dissolution and bioavailability.
- WO 2021156172 A1 discloses a pharmaceutical composition comprising a solid dispersion comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient inside of the solid dispersion, and at least one stabilizing agent, wherein the stabilizing agent is outside of the solid dispersion and the pharmaceutical composition is enteric coated.
- the stabilizing agent is hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS).
- HPMCAS hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a core comprising regorafenib and a coating comprising poloxamer not only provides storage stable composition but also shows similar impurity profile and bioequivalance profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
- a main object of the present invention is to provide a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib, which is devoid of above mentioned problems associated with solid dispersion of regorafenib.
- Yet another object of the invention is to provide a commercially scalable, cost effective, environment friendly and robust process for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition comprising regorafenib.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 5 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and wherein the weight percent is based on the total weight of the composition.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 1 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and wherein the weight percent is based on the total weight of the composition.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and povidone, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and povidone, and ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 1 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. wherein the solid dispersion containing 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib based on the total weight of the composition.
- the present invention provides a tablet comprising: i) 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib, ii) about 0.1 wt.% to about 5 wt.% of poloxamer, iii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of diluents, iv) 5 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of disintegrants, v) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more lubricant, vi) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more glidant, and vii)10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of recrystallization inhibitor based on the total weight of the composition, wherein the poloxamer is present in a coating.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition of any of the above aspects, wherein the said composition remains stable after storage for 3 months at 40°C and 75% relative humidity (RH).
- the present invention discloses a use of such pharmaceutical composition as medicament in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- CRC metastatic colorectal cancer
- HCC hepatocellular carcinoma
- % means the percentage by the total weight of the composition unless otherwise stipulated.
- composition or “formulation” as used in the present invention means a coated solid pharmaceutical composition, wherein the solid pharmaceutical composition includes, without limitation, tablets, caplets, pellets, granules, capsules and beads.
- Regorafenib as used in the present invention includes, but is not limited to, Regorafenib per se or its pharmaceutically acceptable hydrates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutically acceptable solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable enantiomers, pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs thereof or anhydrous regorafenib, and also its various crystalline and amorphous forms.
- the composition of present invention comprises anhydrous form of regorafenib or regorafenib monohydrate, which may be in the crystalline form, amorphous form or mixture thereof. More preferably, the composition of present invention comprises anhydrous regorafenib.
- core means as used in the present invention means uncoated solid pharmaceutical composition includes, without limitation, tablets, caplets, pellets, granules, capsule and beads. Preferably, tablets or granules.
- solid dispersion refers to a system in a solid state comprising at least two components, wherein one component is dispersed throughout the other component or components.
- solid dispersion refers to stable solid dispersions comprising amorphous drug substance and carrier.
- solid dispersion as used herein also refers to stable solid dispersions comprising amorphous drug substance and carrier with or without adsorbent/ absorbent.
- amorphous drug substance it is meant that the amorphous solid contains drug substance in a substantially amorphous solid state form i.e. at least about 80% of the drug substance in the dispersion is in an amorphous form. More preferably at least about 90% and most preferably at least about 95% of the drug substance in the dispersion is in amorphous form.
- stable or “stability” means that the pharmaceutical dosage form is physically and chemically stable, whereas “chemically stable” means that the solid pharmaceutical dosage form when stored at 40 °C and 75 % relative humidity for 3 or 6 months, each of the degradation impurity and total impurities remain within ICH limit.
- similarity factor or f2 factor as used herein refers to one way of comparing dissolution profiles of two different products.
- Test and reference or two strengths, or pre- and post-approved products from the same manufacturer. Tests are recommended to be performed under the same test conditions.
- the dissolution time points for both the profiles should be the same, for example for immediate release products e.g. 10, 15, 30, 45, 60 minutes and for extended release products, e.g., 1 , 2, 3, 5 and 8 hours.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: a. core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and b. coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- a composition of the present invention comprises 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib, preferably 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib based on the total weight of the composition.
- a composition of the present invention comprises coating comprising poloxamer in amount from about 0.1 to 5 wt.%, preferably, about 0.1 to 1 wt.% based on the total weigh of the composition.
- a pharmaceutical composition of the present invention further comprises one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
- the excipients to be used in accordance with the present invention are well known and are those excipients which are conventionally used by the person skilled in the art. Depending on the dosage form chosen for the pharmaceutical composition, the person skilled in the art will be able to select suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients.
- the pharmaceutical excipient can be selected from excipient can be selected from diluent, disintegrant, lubricant, glidant and recrystallization inhibitor.
- Diluent includes, but are not limited to, lactose, mannitol, xylitol, dextrose, sucrose, sorbitol, microcrystalline cellulose, starch, dextrates, dextran, dextrin, dextrose, maltodextrin, calcium carbonate, dibasic calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate, magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide and mixtures thereof.
- the amount of diluent is preferably from about 10 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, more preferably from about 10 wt.% to about 30 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
- Disintegrant includes, but are not limited to, sodium starch glycolate, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, calcium carboxymethyl cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, Crospovidone, polyvinylpyrrolidone, methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, lower alkyl-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, starch, pregelatinized starch, and sodium alginate and mixtures thereof.
- the amount of the disintegrant is preferably from 5 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, more preferably from 20 wt.% to 40 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
- Suitable lubricants and/or glidants are selected from magnesium stearate, hydrogenated vegetable oil, glyceryl behenate, glyceryl monostearate, stearic acid, sodium stearyl fumarate, sodium starch fumarate, calcium stearate, zinc stearate, aluminum silicate, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide, sucrose esters of fatty acid, waxes, silica gel, or mixtures thereof.
- the present invention comprises a lubricant in an amount of from about 0.1 wt.% to about 10 wt.%, preferably, 0.1 wt.% to about 2 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
- the recrystallization inhibitor includes, but are not limited to, polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone), tyloxapol, fatty acid glycerol polyethylene glycol esters, fatty acid polyethylene glycol esters, polyethylene glycols, glycerol ethers, a cyclodextrin (for example alpha-, beta- or gamma-cyclodextrin, e.g.
- a cyclodextrin for example alpha-, beta- or gamma-cyclodextrin, e.g.
- the recrystallization inhibitor is polyvinylpyrrolidone.
- the present invention comprises a recrystallization inhibitor in an amount of from about 10 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, preferably, 10 wt.% to about 40 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition
- the present invention provides a tablet comprising: i) 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib, ii) about 0.1 wt.% to about 5 wt.% of poloxamer, iii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of diluents, iv) 5 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of disintegrants, v) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more lubricant, vi) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more glidant, and vii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of recrystallization inhibitor based on the total weight of the composition, wherein the poloxamer is present in a coating.
- the core of the present invention is further be coated with poloxamer, a film- forming polymer and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, using techniques well known in the art e.g., spray coating in a conventional coating pan, or a fluidized bed processor, or dip coating. Alternatively, coating can also be performed using a hot melt technique.
- the coating comprises poloxamer and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the pharmaceutically acceptable excipient includes film-forming polymers, opacifiers, plasticizer, flow aids/glidant or pigment.
- the suitable film-forming polymer is selected from the group comprising hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose phthalate, cellulose acetate trimellitate, methacrylic acid copolymers e.g., Eudragit®, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, or mixtures thereof.
- a preferred film- forming polymer is hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose.
- Other suitable filmforming polymers which are known in the art may also be used.
- the film coating may also contain opacifiers like titanium dioxide, plasticizer like polyethylene glycol, flow aids like talc and pigment like iron oxide yellow or red iron oxide.
- the process for the preparation of the coating composition comprises mixing poloxamer with suitable coating excipients such as a film- forming polymer, opacifiers, plasticizer and pigment in a suitable solvent.
- suitable coating excipients such as a film- forming polymer, opacifiers, plasticizer and pigment
- the coating can also be prepared by mixing poloxamer and marketed coating material like Aquarius primeTM in suitable solvent.
- the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
- the process to obtain solid dispersion of the present invention includes, but is not limited to, solvent evaporation method, fusion method, kneading method, melting method, spray drying method, co-grinding method, lyophilization technique, hot melt extrusion, melt agglomeration, supercritical fluid (SCF) technology and the like.
- the solid dispersion of the present invention is prepared by dissolving regorafenib in a suitable solvent with or without additional excipient and spray it onto pharmaceutically acceptable excipients using suitable technology like fluid bed technology.
- Suitable solvents in the present invention includes, but are not limited to, ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, acetone, N,N-dimethylformamide, water or mixture thereof.
- the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be obtained by using known conventional methods.
- the process to obtain granulates includes, but is not limited to, wet granulation, fluid bed granulation, spray drying, dry granulation, slugging, and roller compaction.
- composition of the present invention is very suitable for production on commercial scale making use of equipment and techniques commonly used in industry.
- the following examples are intended to illustrate the scope of the present invention but not to limit it thereto.
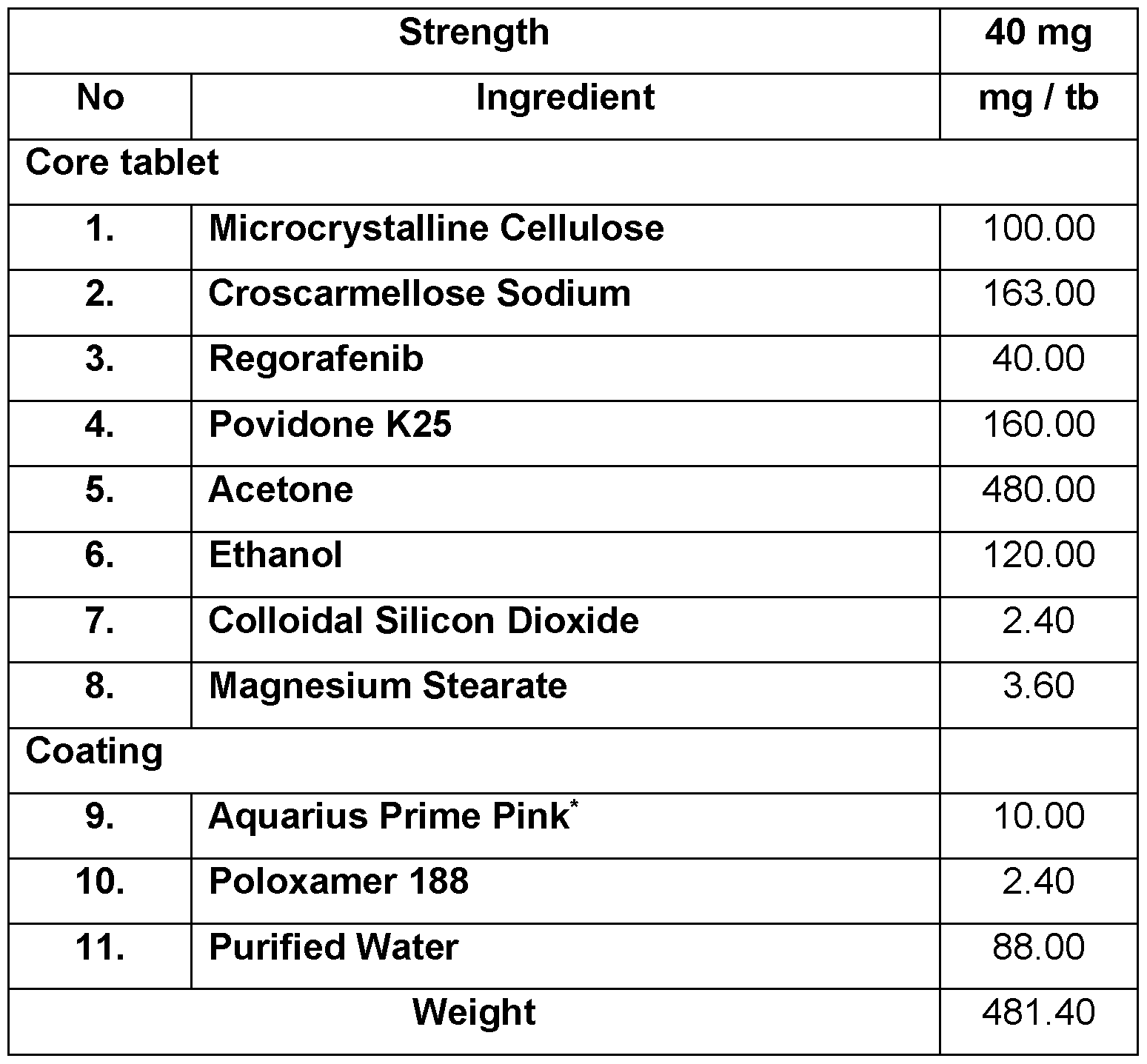
- Example 1 A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising poloxamer
- ‘Aquarius Prime Pink contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide Process for the preparation:
- Regorafenib (40 mg) and povidone (160 mg) were dissolved in a mixture of acetone (480 mg) and ethanol (120 mg) to obtain solution;
- step 2 The granules were obtained by spraying the solution of step 1 onto the mixture of microcrystalline cellulose (100 mg) and croscarmellose sodium (150 mg); 3. The granules of step 2 were dried and mixed with colloidal silicon dioxide (2.4 mg), croscarmellose sodium (13 mg) and magnesium stearate (3,6 mg) to obtain granule mixture;
- step 3 The granule mixture obtained in step 3 was compressed to obtain tablets; and 5. the tablets were coated with mixture of poloxamer (2.4 mg) and Aquarius
- Example 2 A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising Eudragit E PO
- Eudragit E PO contains basic butylated methacrylate copolymer, sodium laurylsulpate, stearic acid, talc, titanium dioxide
- Process for the preparation The tablets were prepared using same process of example 1 by replacing coating of poloxamer and Aquarius Prime Pink with Eudragit E PO.
- Example 3 A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising poloxamer
- ‘Aquarius Prime Pink contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide
- step 2 The granules were obtained by spraying the solution of step 1 onto the mixture of milled mixture of silicified microcrystalline cellulose (157.80 mg) and croscarmellose sodium (150 mg); 3. The granules of step 2 were dried, milled, and mixed with magnesium stearate
- step 4 The granules of step 3 were milled and mixed with colloidal silicon dioxide (2.4 mg), croscarmellose sodium (4.20 mg) and magnesium stearate (5 mg) respectively; 5. The granules obtained in step 4 were compressed to obtain tablets; and
- Example 4 Dissolution Data of Example 1 and Example 2 at pH: 4,5 Acetate + 0,1 %SLS 50 rpm with USP, Method II - Pedal at 37°C
- Example-1 , Example-2 and reference product Stivarga® tablet were performed using standard USP apparatus II, paddles, at 50 rpm in 900 ml at pH: 4.5 Acetate + 0.1% SLS.
- the drug release was determined by using an HPLC method.
- Example 5 Stability Result of Example 1
- Example 1 The tablets prepared in Example 1 were packed in HDPE bottles together with silica gel and stored for 30 days under conditions of 25°C/60% RH and 30 °C, 75% RH.
- Table-6 It can be seen from the stability results given in table-6, pertain to increase rate of specific impurity AFP-PMA, it is evident that coating material of the present invention i.e. containing Poloxamer is equally capable to control the said impurity as controlled by the PVA coating employed in EP 2892507 B1 .
- the pharmaceutical composition comprising intragranular component comprising a core comprising regorafenib and a coating comprising poloxamer not only provides storage stable composition but also shows similar impurity profile and bioequivalence profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Preparation (AREA)
Abstract
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) a core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) a coating comprising poloxamer (polyoxyethylene–polyoxypropylene copolymer) and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The invention further relates to a process for the preparation of the said pharmaceutical composition and its use for treating disorders.
Description
A PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION OF REGORAFENIB
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) a core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) a coating comprising poloxamer (polyoxyethylene-polyoxypropylene copolymer) and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The invention further relates to a process for the preparation of the said pharmaceutical composition and its use for treating disorders.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
Regorafenib is chemically known as 4-[4-({[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl) phenyl] carbamoyl} amino)-3-fluorophenoxy]-N-methylpyridine-2-carboxamide (I).
Regorafenib is a low molecule inhibitor of multiple membrane-bound and intracellular kinases involved in normal cellular functions and in pathologic processes such as oncogenesis, tumor angiogenesis, and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment.
Regorafenib is marketed as Stivarga® by Bayer Pharma in Europe since 2013. The marketed product is approved in the form of 40 mg film coated tablet.
Stivarga® is indicated as monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) who have been previously treated with, or are not considered candidates for, available therapies. These include fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy, an anti-VEGF therapy and an anti-EGFR therapy, unresectable or
metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST) who progressed on or are intolerant to prior treatment with imatinib and sunitinib and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have been previously treated with sorafenib.
According to European Public Assessment Report (EPAR), regorafenib is a white to slightly pink or slightly brownish solid substance, practically insoluble in water. Regorafenib is BCS Class II compound based on Biopharmaceutical Classification System.
BCS Class II compounds are drug substances with low solubility and high permeability. The bioavailability of these compounds is limited by their solubility (solvation rate). Hence, the absorption of a poorly water-soluble compound from orally administered solid dosage form is controlled by its dissolution rate in the gastrointestinal fluid present at the absorption site. It is known in the pharmaceutical arts that low-solubility drugs often show poor bioavailability or irregular absorption, the degree of irregularity being affected by factors such as dose level, fed state of the patient, and form of the drug.
Therefore, it is desirable to design a formulation which improves the rate of dissolution and thus improving the bioavailability of the BCS Class II compounds or drugs.
There are many techniques known in the art to improve the dissolution of the low- solubility drugs including particle size reduction, nanosuspension technology, using surfactant, and solid dispersion.
WO 2006026500 discloses a composition comprising a solid dispersion comprising regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable matrix, wherein the matrix comprises at least one polymer from the group consisting of polyvinylpyrrolidone, copovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol or polyethylene oxide.
CN 111166724 A discloses a regorafenib nano dispersion, a tablet and a preparation method thereof; the dispersion can be prepared by dissolving regorafenib in solvent,
separately dissolving a carrier material in water, and performing liquid phase precipitation and crystallization reaction to obtain regorafenib nano-suspension; it is spray dried to spray-dried to obtain a regorafenib nano-dispersion.
CN 106913527 A discloses immediate-release pellet and immediate-release pellet consisting blank pellet core and a regorafenib-containing layer wrapped outside the pellet core is characterized in that the drug-containing layer contains micronized regorafenib and a binder. CN ‘527 discloses polyvinylpyrrolidone and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose for preparation of regorafenib containing layer solution.
WO 2014039677 discloses a pharmaceutical composition comprising regorafenib, a hydrate, solvate, metabolite or pharmaceutically acceptable salt of regorafenib, or a polymorph thereof and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient wherein the pharmaceutical composition is coated by a coating comprising a polyvinyl alcohol based polymer and optionally one or more further pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. According to WO ‘677, polyvinyl alcohol based polymer coating effectively controls particular impurity AFP-PMA as compared to conventional HPMC coating.
!n general, it is believed that solid dispersion system comes into contact with gastrointestinal media, dissolution will occur to a supersaturated state, which is more or less stabilized by the polymer. This has been shown to significantly enhance the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble BCS Class II compounds or drugs. One major challenge in administration of these compounds or drugs is the high inter-individual variability of drug performance. Another inherent issue of amorphous solid dispersions is the instability of the solid state which results in a tendency for recrystallisation of the drug and/or excipients during storage. This may be accompanied by a break-down of dissolution and bioavailability.
To avoid the variation in dissolution and bioavailability of solid dispersion of regorafenib, inventors of WO 2021156172 A1 have discovered that inclusion of stabilizing agent in the pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib provides a stable dissolution and high bioavailability with decreased variability. WO ‘172 discloses a pharmaceutical composition comprising a solid dispersion comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient inside of the solid dispersion,
and at least one stabilizing agent, wherein the stabilizing agent is outside of the solid dispersion and the pharmaceutical composition is enteric coated. Specifically, WO ‘172 discloses the stabilizing agent is hydroxypropylmethylcellulose acetate succinate (HPMCAS). The pharmaceutical composition containing regorafenib and HPMCAS shows stable dissolution and high bioavailability, wherein the variability of the bioavailability is decreased.
Therefore, there still exists need to provide a stable composition of regorafenib with suitable excipient(s) that provides stable and improved dissolution rate, and thus provide desired bioavailability, which is prepared by an economically viable process and is also suitable for use on a commercial scale. To achieve this goal, it is also very important to select the excipient(s) for the preparation of solid dispersion and the excipient(s) to be used for the preparation of final formulation like coated tablet. These excipient(s) should not hinder the dissolution of compound as well as they should not have any adverse impact on stability of the composition and the excipient(s) should provide stable dissolution.
The inventors of the present invention have surprisingly found that a pharmaceutical composition comprising a core comprising regorafenib and a coating comprising poloxamer not only provides storage stable composition but also shows similar impurity profile and bioequivalance profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
OBJECT OF THE INVENTION
A main object of the present invention is to provide a stable pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib, which has a similar impurity profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib, which has a similar dissolution profile and bioequivalence profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
Yet another object of the present invention is to provide a pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib, which is devoid of above mentioned problems associated with solid dispersion of regorafenib.
Yet another object of the invention is to provide a commercially scalable, cost effective, environment friendly and robust process for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition comprising regorafenib.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
In one aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 5 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and wherein the weight percent is based on the total weight of the composition.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient,
ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 1 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and wherein the weight percent is based on the total weight of the composition.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and povidone, and ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and povidone, and ii) coating comprising 0.1 to 1 wt.% of poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. wherein the solid dispersion containing 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib based on the total weight of the composition.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a tablet comprising: i) 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib, ii) about 0.1 wt.% to about 5 wt.% of poloxamer, iii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of diluents, iv) 5 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of disintegrants, v) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more lubricant, vi) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more glidant, and vii)10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of recrystallization inhibitor based on the total weight of the composition,
wherein the poloxamer is present in a coating.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: i) prepare core comprising regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; ii) coating the core obtained in step (i) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient in suitable solvent to obtain solution or suspension; b. prepare granules by mixing solution or suspension of step a) with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and povidone in suitable solvent to obtain solution; b. prepare granules by mixing solution of step a) with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises:
a. dissolve regorafenib and povidone in a mixture of acetone and ethanol to obtain solution; b. prepare granules by mixing solution of step a) with microcrystal ine cellulose and croscarmellose sodium; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and povidone in a mixture of acetone and ethanol to obtain solution; b. prepare granules by spraying the solution of step a) onto the mixture of microcrystaline cellulose and croscarmellose sodium; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition of any of the above aspects, wherein the said composition remains stable after storage for 3 months at 40°C and 75% relative humidity (RH).
In another aspect, the present invention discloses a use of such pharmaceutical composition as medicament in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
The details of one or more embodiments of the present invention are set forth in the description below. Other features, objects and advantages of the invention will be apparent from the description.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PRESENT INVENTION
The present invention will now be more specifically illustrated as hereunder.
The term “%”, “wt.%” or “%w/w” used in this specification means the percentage by the total weight of the composition unless otherwise stipulated.
The term "about" can indicate a difference of 10 percent of the value specified. Numerical ranges as used herein are meant to include every number and subset of numbers enclosed within that range, whether particularly disclosed or not. Further, these numerical ranges should be construed as providing support for a claim directed to any number or subset of numbers in that range.
The term “composition” or “formulation” as used in the present invention means a coated solid pharmaceutical composition, wherein the solid pharmaceutical composition includes, without limitation, tablets, caplets, pellets, granules, capsules and beads.
The term “Regorafenib” as used in the present invention includes, but is not limited to, Regorafenib per se or its pharmaceutically acceptable hydrates, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, pharmaceutically acceptable solvates, pharmaceutically acceptable enantiomers, pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives, pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs thereof or anhydrous regorafenib, and also its various crystalline and amorphous forms. Preferably, the composition of present invention comprises anhydrous form of regorafenib or regorafenib monohydrate, which may be in the crystalline form, amorphous form or mixture thereof. More preferably, the composition of present invention comprises anhydrous regorafenib.
The term “core” means as used in the present invention means uncoated solid pharmaceutical composition includes, without limitation, tablets, caplets, pellets, granules, capsule and beads. Preferably, tablets or granules.
The term "solid dispersion" refers to a system in a solid state comprising at least two components, wherein one component is dispersed throughout the other component
or components. The term "solid dispersion" as used herein, refers to stable solid dispersions comprising amorphous drug substance and carrier. Further the term "solid dispersion" as used herein also refers to stable solid dispersions comprising amorphous drug substance and carrier with or without adsorbent/ absorbent. By "amorphous drug substance," it is meant that the amorphous solid contains drug substance in a substantially amorphous solid state form i.e. at least about 80% of the drug substance in the dispersion is in an amorphous form. More preferably at least about 90% and most preferably at least about 95% of the drug substance in the dispersion is in amorphous form.
The term "stable" or "stability" means that the pharmaceutical dosage form is physically and chemically stable, whereas "chemically stable" means that the solid pharmaceutical dosage form when stored at 40 °C and 75 % relative humidity for 3 or 6 months, each of the degradation impurity and total impurities remain within ICH limit.
The term "similarity factor" or f2 factor as used herein refers to one way of comparing dissolution profiles of two different products. (Multisource Pharmaceutical Products: Guidelines on Registration Requirements to establish Interchangeability, Quality Assurance and Safety: Medicines, Essential Drugs and Medicines Policy, World Health Organization, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland) This model independent mathematical approach compares the dissolution profile of the two products: test and reference (or two strengths, or pre- and post-approved products from the same manufacturer). Tests are recommended to be performed under the same test conditions. The dissolution time points for both the profiles should be the same, for example for immediate release products e.g. 10, 15, 30, 45, 60 minutes and for extended release products, e.g., 1 , 2, 3, 5 and 8 hours. Only one time point should be considered after 85% dissolution of the reference product. An f2 value of 50 or greater (50-100) ensures sameness or equivalence of the two curves, and thus the performance of the two products. The similarity factor f2 should be computed using the equation: f2 =50 log {[l+(l/n) t=1 n (Rt - Tt ) 2 ]-0-5 100} where Rt and Tt are the cumulative percentage of the drug dissolved at each of the selected n time points of the comparator (reference) and (test) product respectively.
In one aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: a. core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and b. coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
In one embodiment, a composition of the present invention comprises 1 to 20 wt.% of regorafenib, preferably 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib based on the total weight of the composition.
In one embodiment, a composition of the present invention comprises coating comprising poloxamer in amount from about 0.1 to 5 wt.%, preferably, about 0.1 to 1 wt.% based on the total weigh of the composition.
In embodiments, a pharmaceutical composition of the present invention further comprises one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The excipients to be used in accordance with the present invention are well known and are those excipients which are conventionally used by the person skilled in the art. Depending on the dosage form chosen for the pharmaceutical composition, the person skilled in the art will be able to select suitable pharmaceutically acceptable excipients. The pharmaceutical excipient can be selected from excipient can be selected from diluent, disintegrant, lubricant, glidant and recrystallization inhibitor.
Diluent includes, but are not limited to, lactose, mannitol, xylitol, dextrose, sucrose, sorbitol, microcrystalline cellulose, starch, dextrates, dextran, dextrin, dextrose, maltodextrin, calcium carbonate, dibasic calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate, magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide and mixtures thereof.
The amount of diluent is preferably from about 10 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, more preferably from about 10 wt.% to about 30 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
Disintegrant includes, but are not limited to, sodium starch glycolate, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, calcium carboxymethyl cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, Crospovidone, polyvinylpyrrolidone, methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, lower alkyl-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, starch, pregelatinized starch, and sodium alginate and mixtures thereof. The amount of the disintegrant is preferably from 5 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, more preferably from 20 wt.% to 40 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
Suitable lubricants and/or glidants are selected from magnesium stearate, hydrogenated vegetable oil, glyceryl behenate, glyceryl monostearate, stearic acid, sodium stearyl fumarate, sodium starch fumarate, calcium stearate, zinc stearate, aluminum silicate, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide, sucrose esters of fatty acid, waxes, silica gel, or mixtures thereof. The present invention comprises a lubricant in an amount of from about 0.1 wt.% to about 10 wt.%, preferably, 0.1 wt.% to about 2 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition.
The recrystallization inhibitor includes, but are not limited to, polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone), tyloxapol, fatty acid glycerol polyethylene glycol esters, fatty acid polyethylene glycol esters, polyethylene glycols, glycerol ethers, a cyclodextrin (for example alpha-, beta- or gamma-cyclodextrin, e.g. alkylated, hydroxyalkylated, carboxyalkylated or alkyloxycarbonyl-alkylated derivatives, or mono- or diglycosyl- alpha-, beta- or gamma-cyclodextrin, mono- or dimaltosyl-alpha-, beta- or gamma- cyclodextrin or panosyl-cyclodextrin), polysorbate 20, polysorbate 80 or mixtures of thereof. Preferably, the recrystallization inhibitor is polyvinylpyrrolidone. The present invention comprises a recrystallization inhibitor in an amount of from about 10 wt.% to about 50 wt.%, preferably, 10 wt.% to about 40 wt.% based on the total weight of the composition
In another aspect, the present invention provides a tablet comprising: i) 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib, ii) about 0.1 wt.% to about 5 wt.% of poloxamer, iii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of diluents, iv) 5 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of disintegrants, v) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more lubricant,
vi) 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more glidant, and vii) 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of recrystallization inhibitor based on the total weight of the composition, wherein the poloxamer is present in a coating.
The core of the present invention is further be coated with poloxamer, a film- forming polymer and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, using techniques well known in the art e.g., spray coating in a conventional coating pan, or a fluidized bed processor, or dip coating. Alternatively, coating can also be performed using a hot melt technique.
The coating comprises poloxamer and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The pharmaceutically acceptable excipient includes film-forming polymers, opacifiers, plasticizer, flow aids/glidant or pigment. The suitable film-forming polymer is selected from the group comprising hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, ethyl cellulose, methyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose phthalate, cellulose acetate trimellitate, methacrylic acid copolymers e.g., Eudragit®, polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyvinyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol, or mixtures thereof. A preferred film- forming polymer is hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Other suitable filmforming polymers which are known in the art may also be used. The film coating may also contain opacifiers like titanium dioxide, plasticizer like polyethylene glycol, flow aids like talc and pigment like iron oxide yellow or red iron oxide.
The process for the preparation of the coating composition comprises mixing poloxamer with suitable coating excipients such as a film- forming polymer, opacifiers, plasticizer and pigment in a suitable solvent. The coating can also be prepared by mixing poloxamer and marketed coating material like Aquarius prime™ in suitable solvent.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising: i) core comprising solid dispersion of regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and
ii) coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
The process to obtain solid dispersion of the present invention includes, but is not limited to, solvent evaporation method, fusion method, kneading method, melting method, spray drying method, co-grinding method, lyophilization technique, hot melt extrusion, melt agglomeration, supercritical fluid (SCF) technology and the like.
In one embodiment, the solid dispersion of the present invention is prepared by dissolving regorafenib in a suitable solvent with or without additional excipient and spray it onto pharmaceutically acceptable excipients using suitable technology like fluid bed technology.
Suitable solvents in the present invention includes, but are not limited to, ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, acetone, N,N-dimethylformamide, water or mixture thereof.
The pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be obtained by using known conventional methods. The process to obtain granulates includes, but is not limited to, wet granulation, fluid bed granulation, spray drying, dry granulation, slugging, and roller compaction.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: i) prepare core comprising regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; ii) coating the core obtained in step (i) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient in suitable solvent to obtain solution or suspension; b. prepare granules by mixing solution or suspension of step a) with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient;
c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and povidone in a mixture of acetone and ethanol to obtain solution; b. prepare granules by mixing solution of step a) with microcrystal ine cellulose and croscarmellose sodium; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
In another aspect, the present invention provides a process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and povidone in a mixture of acetone and ethanol to obtain solution; b. prepare granules by spraying the solution of step a) onto the mixture of microcrystaline cellulose and croscarmellose sodium; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium and magnesium stearate to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
Moreover, the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention is very suitable for production on commercial scale making use of equipment and techniques commonly used in industry.
The following examples are intended to illustrate the scope of the present invention but not to limit it thereto.
Examples
Example 1 : A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising poloxamer
‘Aquarius Prime Pink contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide Process for the preparation:
1. Regorafenib (40 mg) and povidone (160 mg) were dissolved in a mixture of acetone (480 mg) and ethanol (120 mg) to obtain solution;
2. The granules were obtained by spraying the solution of step 1 onto the mixture of microcrystalline cellulose (100 mg) and croscarmellose sodium (150 mg);
3. The granules of step 2 were dried and mixed with colloidal silicon dioxide (2.4 mg), croscarmellose sodium (13 mg) and magnesium stearate (3,6 mg) to obtain granule mixture;
4. The granule mixture obtained in step 3 was compressed to obtain tablets; and 5. the tablets were coated with mixture of poloxamer (2.4 mg) and Aquarius
Prime Pink (10 mg).
Example 2: A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising Eudragit E PO
*Eudragit E PO contains basic butylated methacrylate copolymer, sodium laurylsulpate, stearic acid, talc, titanium dioxide Process for the preparation: The tablets were prepared using same process of example 1 by replacing coating of poloxamer and Aquarius Prime Pink with Eudragit E PO.
Example 3: A tablet composition comprising Regorafenib & coating comprising poloxamer
‘Aquarius Prime Pink contains hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, talc, red iron oxide, yellow iron oxide
Process for the preparation: 1. Regorafenib (40 mg) and povidone (160 mg) were dissolved in a mixture of acetone (480 mg) and ethanol (120 mg) to obtain solution;
2. The granules were obtained by spraying the solution of step 1 onto the mixture of milled mixture of silicified microcrystalline cellulose (157.80 mg) and croscarmellose sodium (150 mg); 3. The granules of step 2 were dried, milled, and mixed with magnesium stearate
(5 mg) and the mixture was dry granulated by roller compactor;
4. The granules of step 3 were milled and mixed with colloidal silicon dioxide (2.4 mg), croscarmellose sodium (4.20 mg) and magnesium stearate (5 mg) respectively;
5. The granules obtained in step 4 were compressed to obtain tablets; and
6. The tablets were coated with mixture of poloxamer (2.7 mg) and Aquarius Prime Pink (12 mg).
Example 4: Dissolution Data of Example 1 and Example 2 at pH: 4,5 Acetate + 0,1 %SLS 50 rpm with USP, Method II - Pedal at 37°C
Dissolution of Example-1 , Example-2 and reference product Stivarga® tablet were performed using standard USP apparatus II, paddles, at 50 rpm in 900 ml at pH: 4.5 Acetate + 0.1% SLS. The drug release was determined by using an HPLC method.
From the above dissolution data, it is evident that dissolution of example-1 (poloxamer in coating) is better than example-2. When f2 value is more than 50 indicates the sameness or equivalence of Example-1 with reference product in terms of its dissolution and performance.
Example 5: Stability Result of Example 1
The tablets prepared in Example 1 were packed in HDPE bottles together with silica gel and stored for 30 days under conditions of 25°C/60% RH and 30 °C, 75% RH.
It can be seen from the above tables that the produced amount of the AFP-PMA is less than 0.050% in above mentioned stability conditions for Examples 1 .
The monthly increase rate of AFP-PMA impurity of Example 1 of the present invention and examples given in EP 2892507 B1 patent are compared herein below Table 6.
Table-6
It can be seen from the stability results given in table-6, pertain to increase rate of specific impurity AFP-PMA, it is evident that coating material of the present invention i.e. containing Poloxamer is equally capable to control the said impurity as controlled by the PVA coating employed in EP 2892507 B1 .
The pharmaceutical composition comprising intragranular component comprising a core comprising regorafenib and a coating comprising poloxamer not only provides storage stable composition but also shows similar impurity profile and bioequivalence profile when compared to the reference product Stivarga® tablet.
Claims
1. A pharmaceutical composition comprising: a. a core comprising regorafenib and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient, and b. a coating comprising poloxamer and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
2. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 1 , wherein the core comprising a solid dispersion of regorafenib & at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient.
3. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 1 , wherein regorafenib is present in an amount from 1 to 20 wt.%.
4. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 1 , wherein poloxamer is present in an amount from about 0.1 % to about 5 wt.%.
5. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 1 , wherein the pharmaceutically acceptable excipient is selected from diluent, disintegrant, lubricant, glidant, recrystallization inhibitor, film- forming polymers, opacifiers, plasticizer and pigment.
6. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 5, wherein diluent is selected from lactose, mannitol, xylitol, dextrose, sucrose, sorbitol, microcrystalline cellulose, starch, dextrates, dextran, dextrin, dextrose, maltodextrin, calcium carbonate, dibasic calcium phosphate, calcium sulfate, magnesium carbonate, magnesium oxide and mixtures thereof.
7. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 5, wherein disintegrant is selected from sodium starch glycolate, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, calcium carboxymethyl cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, Crospovidone, polyvinylpyrrolidone, methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, lower alkyl-substituted hydroxypropyl cellulose, starch, pregelatinized starch, and sodium alginate and mixtures thereof.
8. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 5, wherein the lubricants and/or glidants are selected from magnesium stearate, hydrogenated vegetable oil, glyceryl behenate, glyceryl monostearate, stearic acid, sodium stearyl fumarate, sodium starch fumarate, calcium stearate, zinc stearate, aluminum silicate, talc, colloidal silicon dioxide, sucrose esters of fatty acid, waxes, silica gel and mixtures thereof.
9. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 5, wherein the recrystallization inhibitor is selected from polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone), tyloxapol, fatty acid glycerol polyethylene glycol esters, fatty acid polyethylene glycol esters, polyethylene glycols, glycerol ethers, cyclodextrin, polysorbate 20, polysorbate 80 and mixtures of thereof.
10. A process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition as claimed in any of the claims above comprises: a. dissolve regorafenib and a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient in suitable solvent to obtain solution or suspension; b. prepare granules by mixing solution or suspension of step a) with a pharmaceutically acceptable excipient; c. dry the granules of step b), and optionally mix with pharmaceutically acceptable excipients to obtain granule mixture; d. optionally, compress the granule mixture obtained in step c) to obtain tablets; e. coat the granules obtained in step c) or tablets obtained in step d) with coating composition comprising poloxamer.
11 . The process for the preparation of the pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 10, wherein the solvent is selected from ethanol, methanol, isopropanol, acetone, N,N-dimethylformamide, water or mixture thereof.
12. The pharmaceutical composition as claimed in claim 1 is tablet comprising: a. 5 to 10 wt.% of regorafenib, b. about 0.1 wt.% to about 5 wt.% of poloxamer, c. 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of diluents, d. 5 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of disintegrants,
e. 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more lubricant, f. 0.1 wt.% to 5 wt.% of one or more glidant, and g. 10 wt.% to 50 wt.% of one or more of recrystallization inhibitor, wherein the poloxamer is present in coating.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| TR2023002705 | 2023-03-10 | ||
| TR2023/002705 TR2023002705A2 (en) | 2023-03-10 | A PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING REGORAFENIB |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2024191390A1 true WO2024191390A1 (en) | 2024-09-19 |
Family
ID=92756208
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/TR2024/050230 WO2024191390A1 (en) | 2023-03-10 | 2024-03-08 | A pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| WO (1) | WO2024191390A1 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2005065653A1 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-21 | E.I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Intimate coating of ibuprofen with poloxamers to enhance aqueous dissolution |
| WO2019241504A1 (en) * | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Handa Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Kinase inhibitor salts and compositions thereof |
| CN112842998A (en) * | 2021-01-19 | 2021-05-28 | 深圳市简一生物科技有限公司 | Regorafenib dispersant and preparation method thereof |
| EP3861989A1 (en) * | 2020-02-07 | 2021-08-11 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Pharmaceutical composition containing regorafenib and a stabilizing agent |
-
2024
- 2024-03-08 WO PCT/TR2024/050230 patent/WO2024191390A1/en unknown
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2005065653A1 (en) * | 2003-12-19 | 2005-07-21 | E.I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Intimate coating of ibuprofen with poloxamers to enhance aqueous dissolution |
| WO2019241504A1 (en) * | 2018-06-15 | 2019-12-19 | Handa Pharmaceuticals, Llc | Kinase inhibitor salts and compositions thereof |
| EP3861989A1 (en) * | 2020-02-07 | 2021-08-11 | Bayer Aktiengesellschaft | Pharmaceutical composition containing regorafenib and a stabilizing agent |
| CN112842998A (en) * | 2021-01-19 | 2021-05-28 | 深圳市简一生物科技有限公司 | Regorafenib dispersant and preparation method thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US20200163882A1 (en) | Solid Pharmaceutical Compositions Of Androgen Receptor Antagonists | |
| US10874671B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions of nilotinib | |
| US10034854B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition with improved bioavailability | |
| NZ576987A (en) | Pharmaceutical formulation comprising neurokinin antagonist | |
| CN103068372B (en) | The pharmaceutical composition of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (MGLU5) antagonist | |
| WO2024096838A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition comprising solid dispersion of empagliflozin | |
| JP6113203B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition of metabotropic glutamate 5 receptor (mGlu5) antagonist | |
| US20220265633A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions of cabozantinib | |
| JP2016512845A (en) | Sobaprevir tablets | |
| JP7428356B2 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions of sorafenib with high bioavailability, oral solid preparations of sorafenib, and uses thereof | |
| US20210085611A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical formulation | |
| WO2013008253A2 (en) | Imatinib formulations | |
| WO2024191390A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib | |
| WO2024191389A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition of regorafenib | |
| TR2023002705A2 (en) | A PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION CONTAINING REGORAFENIB | |
| TR2023002707A2 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition containing regorafenib. | |
| WO2021106004A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical composition of s-adenosylmethionine | |
| KR20190120094A (en) | Pharmaceutical composition comprising lenalidomide | |
| WO2024096839A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition comprising solid dispersion of empagliflozin | |
| WO2020048449A1 (en) | Solid pharmaceutical composition containing 1,3,5-triazine derivative or salt thereof | |
| JP2022113343A (en) | Pharmaceutical tablet containing axitinib as active ingredient | |
| WO2022162687A1 (en) | Pharmaceutical compositions comprising nilotinib | |
| WO2023239336A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition comprising palbociclib | |
| WO2023239337A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition comprising palbociclib | |
| TR2022009480A1 (en) | A pharmaceutical composition comprising palbociclib. |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 24771309 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |