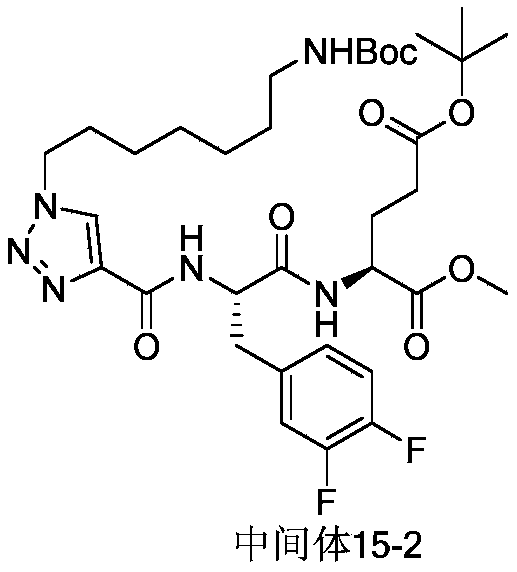
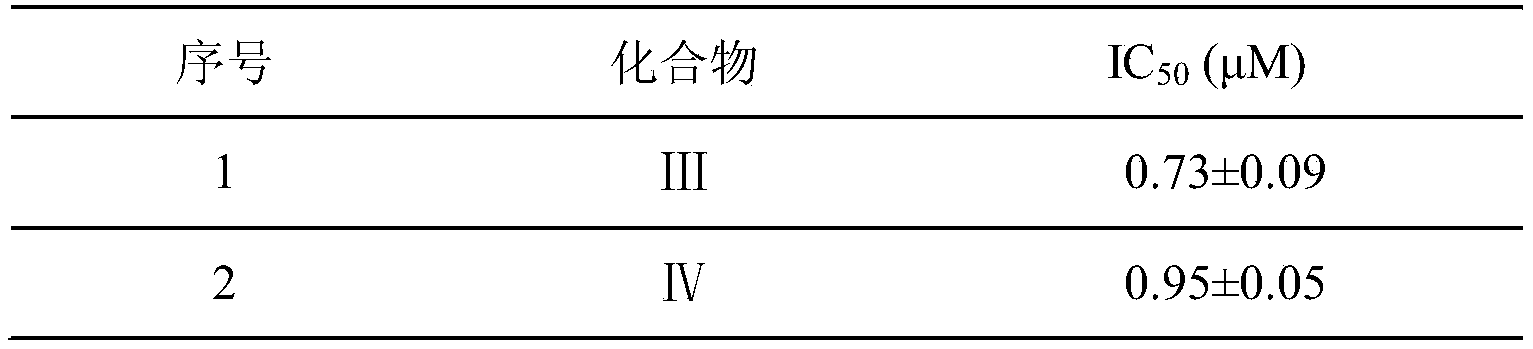
WO2022156692A1 - 一种环肽类病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,其制备方法,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 - Google Patents
一种环肽类病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,其制备方法,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2022156692A1 WO2022156692A1 PCT/CN2022/072680 CN2022072680W WO2022156692A1 WO 2022156692 A1 WO2022156692 A1 WO 2022156692A1 CN 2022072680 W CN2022072680 W CN 2022072680W WO 2022156692 A1 WO2022156692 A1 WO 2022156692A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- compound
- formula
- hcov
- cov
- pharmaceutically acceptable
- Prior art date
Links
- 108010069514 Cyclic Peptides Proteins 0.000 title claims abstract description 16
- 102000001189 Cyclic Peptides Human genes 0.000 title claims abstract description 16
- 239000003443 antiviral agent Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 230000003612 virological effect Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 11
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 title claims description 15
- 239000000137 peptide hydrolase inhibitor Substances 0.000 title claims description 11
- 229940124158 Protease/peptidase inhibitor Drugs 0.000 title claims description 6
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 161
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 53
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 108091005804 Peptidases Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 239000004365 Protease Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 40
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 39
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 102100037486 Reverse transcriptase/ribonuclease H Human genes 0.000 claims abstract description 30
- 241001529459 Enterovirus A71 Species 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 239000000651 prodrug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 229940002612 prodrug Drugs 0.000 claims abstract description 29
- 239000002207 metabolite Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 27
- 241000711573 Coronaviridae Species 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 241000709664 Picornaviridae Species 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 116
- -1 fluorine-substituted benzene rings Chemical group 0.000 claims description 44
- 241000430519 Human rhinovirus sp. Species 0.000 claims description 23
- 241000709721 Hepatovirus A Species 0.000 claims description 22
- WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lithium hydroxide Chemical compound [Li+].[OH-] WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 241000709687 Coxsackievirus Species 0.000 claims description 18
- 241000709661 Enterovirus Species 0.000 claims description 18
- 241000991587 Enterovirus C Species 0.000 claims description 18
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 241000315672 SARS coronavirus Species 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 241001678559 COVID-19 virus Species 0.000 claims description 11
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000005913 (C3-C6) cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 241001109669 Human coronavirus HKU1 Species 0.000 claims description 10
- 241000482741 Human coronavirus NL63 Species 0.000 claims description 10
- 241001428935 Human coronavirus OC43 Species 0.000 claims description 10
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000001559 cyclopropyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])* 0.000 claims description 8
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 8
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L sodium carbonate Substances [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 8
- 241000711467 Human coronavirus 229E Species 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 7
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 6
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000000113 cyclohexyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 5
- 229940042399 direct acting antivirals protease inhibitors Drugs 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000015181 infectious disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000009385 viral infection Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 241000988559 Enterovirus A Species 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000036142 Viral infection Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000006273 (C1-C3) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004180 3-fluorophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C(F)=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001255 4-fluorophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C([H])=C1F 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000006163 5-membered heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 208000025721 COVID-19 Diseases 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710132601 Capsid protein Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710197658 Capsid protein VP1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710118046 RNA-directed RNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 208000037847 SARS-CoV-2-infection Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 101710108545 Viral protein 1 Proteins 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002671 adjuvant Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229940121649 protein inhibitor Drugs 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012268 protein inhibitor Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 241000127282 Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus Species 0.000 claims 4
- 125000004169 (C1-C6) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims 2
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 abstract description 11
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 9
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000005496 eutectics Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 85
- 239000000543 intermediate Substances 0.000 description 53
- 238000002330 electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry Methods 0.000 description 43
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 42
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 38
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 33
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 30
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 30
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical compound [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 21
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 19
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N Dimethyl sulfoxide Chemical compound [2H]C([2H])([2H])S(=O)C([2H])([2H])[2H] IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-WFGJKAKNSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 18
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 18
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 17
- NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia chloride Chemical compound [NH4+].[Cl-] NLXLAEXVIDQMFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 14
- 238000010189 synthetic method Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 13
- HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;chloride;hydrate Chemical class O.[Na+].[Cl-] HPALAKNZSZLMCH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 13
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 102000035195 Peptidases Human genes 0.000 description 10
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 10
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 10
- 235000017557 sodium bicarbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 10
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 10
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 9
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 9
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 8
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 8
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Furan Chemical compound C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 8
- 241001493065 dsRNA viruses Species 0.000 description 8
- 239000011259 mixed solution Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 8
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N Trichloro(2H)methane Chemical compound [2H]C(Cl)(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-MICDWDOJSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 239000008346 aqueous phase Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000012467 final product Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229960002989 glutamic acid Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 7
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 6
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 description 6
- 235000019270 ammonium chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 6
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 6
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 6
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 201000003176 Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 5
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000012043 crude product Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 5
- 125000001501 propionyl group Chemical group O=C([*])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 5
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 5
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 4
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 description 4
- 108010076039 Polyproteins Proteins 0.000 description 4
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 description 4
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- UXOLDCOJRAMLTQ-UTCJRWHESA-N ethyl (2z)-2-chloro-2-hydroxyiminoacetate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)C(\Cl)=N\O UXOLDCOJRAMLTQ-UTCJRWHESA-N 0.000 description 4
- 125000002572 propoxy group Chemical group [*]OC([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 4
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2N(O)N=NC2=C1 ASOKPJOREAFHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 3
- XQFWQWUIBPUXLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-oct-7-ynylisoindole-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)N(CCCCCCC#C)C(=O)C2=C1 XQFWQWUIBPUXLG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(dimethylamino)propyliminomethylidene-ethylazanium;chloride Chemical compound Cl.CCN=C=NCCCN(C)C FPQQSJJWHUJYPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O Ammonium Chemical compound [NH4+] QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 3
- 241000283690 Bos taurus Species 0.000 description 3
- 241000282465 Canis Species 0.000 description 3
- 241000283073 Equus caballus Species 0.000 description 3
- 241000282324 Felis Species 0.000 description 3
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Methylmorpholine Chemical compound CN1CCOCC1 SJRJJKPEHAURKC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000288906 Primates Species 0.000 description 3
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Propanedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000283984 Rodentia Species 0.000 description 3
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 3
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229960005070 ascorbic acid Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 3
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 3
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000002243 precursor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000003826 tablet Substances 0.000 description 3
- VBICKXHEKHSIBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-monostearoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(O)CO VBICKXHEKHSIBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GQHTUMJGOHRCHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,6,7,8,9,10-octahydropyrimido[1,2-a]azepine Chemical compound C1CCCCN2CCCN=C21 GQHTUMJGOHRCHB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Aminoethan-1-ol Chemical compound NCCO HZAXFHJVJLSVMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol;hydron;chloride Chemical compound Cl.OCC(N)(CO)CO QKNYBSVHEMOAJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IZHVBANLECCAGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-hydroxy-3-(octadecanoyloxy)propyl octadecanoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(O)COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC IZHVBANLECCAGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Dimethylaminopyridine Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=NC=C1 VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 208000035473 Communicable disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N Deuterated methanol Chemical compound [2H]OC([2H])([2H])[2H] OKKJLVBELUTLKV-MZCSYVLQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylamine Chemical compound CNC ROSDSFDQCJNGOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylamine Chemical compound CCN QUSNBJAOOMFDIB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycolic acid Chemical compound OCC(O)=O AEMRFAOFKBGASW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 2
- UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron oxide Chemical compound [Fe]=O UQSXHKLRYXJYBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KJHKTHWMRKYKJE-SUGCFTRWSA-N Kaletra Chemical compound N1([C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC=2C=CC=CC=2)NC(=O)COC=2C(=CC=CC=2C)C)CC=2C=CC=CC=2)CCCNC1=O KJHKTHWMRKYKJE-SUGCFTRWSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 2
- BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methylamine Chemical compound NC BAVYZALUXZFZLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010035664 Pneumonia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 208000000474 Poliomyelitis Diseases 0.000 description 2
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrrole Chemical compound C=1C=CNC=1 KAESVJOAVNADME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ritonavir Natural products C=1C=CC=CC=1CC(NC(=O)OCC=1SC=NC=1)C(O)CC(CC=1C=CC=CC=1)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)N(C)CC1=CSC(C(C)C)=N1 NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PXIPVTKHYLBLMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium azide Chemical compound [Na+].[N-]=[N+]=[N-] PXIPVTKHYLBLMZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tert-Butanol Chemical compound CC(C)(C)O DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YTPLMLYBLZKORZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Thiophene Chemical compound C=1C=CSC=1 YTPLMLYBLZKORZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N adipic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCC(O)=O WNLRTRBMVRJNCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000012267 brine Substances 0.000 description 2
- RYYVLZVUVIJVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N caffeine Chemical compound CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1N=CN2C RYYVLZVUVIJVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- JZCCFEFSEZPSOG-UHFFFAOYSA-L copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate Chemical compound O.O.O.O.O.[Cu+2].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O JZCCFEFSEZPSOG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000001995 cyclobutyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 125000001511 cyclopentyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylselenoniopropionate Natural products CCC(O)=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003995 emulsifying agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- CAYJBRBGZBCZKO-BHGBQCOSSA-N ethyl (e,4s)-4-[[(2r,5s)-2-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-6-methyl-5-[(5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-3-carbonyl)amino]-4-oxoheptanoyl]amino]-5-[(3s)-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl]pent-2-enoate Chemical compound C([C@@H](/C=C/C(=O)OCC)NC(=O)[C@@H](CC(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)C1=NOC(C)=C1)C(C)C)CC=1C=CC(F)=CC=1)[C@@H]1CCNC1=O CAYJBRBGZBCZKO-BHGBQCOSSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012065 filter cake Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002866 fluorescence resonance energy transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000019000 fluorine Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000004220 glutamic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N lactic acid Chemical compound CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229960004525 lopinavir Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 239000006210 lotion Substances 0.000 description 2
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 229910052943 magnesium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000019341 magnesium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 2
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-VMNATFBRSA-N methanol-d1 Chemical compound [2H]OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-VMNATFBRSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001788 mono and diglycerides of fatty acids Substances 0.000 description 2
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007911 parenteral administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001436 propyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000023504 respiratory system disease Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 229960000311 ritonavir Drugs 0.000 description 2
- NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-XGKFQTDJSA-N ritonavir Chemical compound N([C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](C[C@H](O)[C@H](CC=1C=CC=CC=1)NC(=O)OCC=1SC=NC=1)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C(=O)N(C)CC1=CSC(C(C)C)=N1 NCDNCNXCDXHOMX-XGKFQTDJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N salicylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002914 sec-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000012265 solid product Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000829 suppository Substances 0.000 description 2
- DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butoxycarbonyl anhydride Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)OC(=O)OC(C)(C)C DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- YAPQBXQYLJRXSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N theobromine Chemical compound CN1C(=O)NC(=O)C2=C1N=CN2C YAPQBXQYLJRXSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethylamine Chemical compound CN(C)C GETQZCLCWQTVFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000029812 viral genome replication Effects 0.000 description 2
- NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N (2s)-2,6-diaminohexanoic acid;(2s)-2-hydroxybutanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O.NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O NWZSZGALRFJKBT-KNIFDHDWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FMCAFXHLMUOIGG-JTJHWIPRSA-N (2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-formamido-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethylphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid Chemical compound O=CN[C@@H](CS)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(O)=O)CC1=CC(C)=C(O)C=C1C FMCAFXHLMUOIGG-JTJHWIPRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FMCAFXHLMUOIGG-IWFBPKFRSA-N (2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-formamido-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethylphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid Chemical compound O=CN[C@@H](CS)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(O)=O)CC1=CC(C)=C(O)C=C1C FMCAFXHLMUOIGG-IWFBPKFRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VTESCYNPUGSWKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N (4-tert-butylphenyl)hydrazine;hydrochloride Chemical compound [Cl-].CC(C)(C)C1=CC=C(N[NH3+])C=C1 VTESCYNPUGSWKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N (S)-malic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)CC(O)=O BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108091032973 (ribonucleotides)n+m Proteins 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M .beta-Phenylacrylic acid Natural products [O-]C(=O)\C=C\C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-VOTSOKGWSA-M 0.000 description 1
- QWENRTYMTSOGBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1H-1,2,3-Triazole Chemical compound C=1C=NNN=1 QWENRTYMTSOGBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XNJVIJQATFJERB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4-trimethylbenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C(C)=C1C XNJVIJQATFJERB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OBTZDIRUQWFRFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)-n-(4-methylphenyl)quinoline-4-carboxamide Chemical compound O1C(C)=CC=C1C1=CC(C(=O)NC=2C=CC(C)=CC=2)=C(C=CC=C2)C2=N1 OBTZDIRUQWFRFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-IVMDWMLBSA-N 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucopyranose Chemical compound N[C@H]1C(O)O[C@H](CO)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-IVMDWMLBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YOETUEMZNOLGDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpropyl carbonochloridate Chemical compound CC(C)COC(Cl)=O YOETUEMZNOLGDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010091324 3C proteases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- HVBSAKJJOYLTQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-aminobenzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound NC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 HVBSAKJJOYLTQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000549 4-dimethylaminophenol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001279686 Allium moly Species 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N Alpha-Lactose Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](CO)O[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-XLOQQCSPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KLSJWNVTNUYHDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Amitrole Chemical group NC1=NC=NN1 KLSJWNVTNUYHDU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010002383 Angina Pectoris Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091032955 Bacterial small RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000005711 Benzoic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Betaine Natural products C[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- DRSHXJFUUPIBHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N COc1ccc(cc1)N1N=CC2C=NC(Nc3cc(OC)c(OC)c(OCCCN4CCN(C)CC4)c3)=NC12 Chemical compound COc1ccc(cc1)N1N=CC2C=NC(Nc3cc(OC)c(OC)c(OCCCN4CCN(C)CC4)c3)=NC12 DRSHXJFUUPIBHX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QAGYKUNXZHXKMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N CPD000469186 Natural products CC1=C(O)C=CC=C1C(=O)NC(C(O)CN1C(CC2CCCCC2C1)C(=O)NC(C)(C)C)CSC1=CC=CC=C1 QAGYKUNXZHXKMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium chloride Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Ca+2] UXVMQQNJUSDDNG-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-SREVYHEPSA-N Cinnamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-SREVYHEPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940126062 Compound A Drugs 0.000 description 1
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000001528 Coronaviridae Infections Diseases 0.000 description 1
- VMQMZMRVKUZKQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cu+ Chemical compound [Cu+] VMQMZMRVKUZKQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Cyclohexane Chemical compound C1CCCCC1 XDTMQSROBMDMFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010005843 Cysteine Proteases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000005927 Cysteine Proteases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N D-Mannitol Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO FBPFZTCFMRRESA-KVTDHHQDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N EDTA Chemical compound OC(=O)CN(CC(O)=O)CCN(CC(O)=O)CC(O)=O KCXVZYZYPLLWCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001856 Ethyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl cellulose Chemical compound CCOCC1OC(OC)C(OCC)C(OCC)C1OC1C(O)C(O)C(OC)C(CO)O1 ZZSNKZQZMQGXPY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCN PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000710831 Flavivirus Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000007212 Foot-and-Mouth Disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000710198 Foot-and-mouth disease virus Species 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007821 HATU Substances 0.000 description 1
- NLDMNSXOCDLTTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Heterophylliin A Natural products O1C2COC(=O)C3=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C3C3=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C=C3C(=O)OC2C(OC(=O)C=2C=C(O)C(O)=C(O)C=2)C(O)C1OC(=O)C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1 NLDMNSXOCDLTTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MAJYPBAJPNUFPV-BQBZGAKWSA-N His-Cys Chemical compound SC[C@@H](C(O)=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 MAJYPBAJPNUFPV-BQBZGAKWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LPHGQDQBBGAPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isocaffeine Natural products CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1N(C)C=N2 LPHGQDQBBGAPDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P L-argininium(2+) Chemical compound NC(=[NH2+])NCCC[C@H]([NH3+])C(O)=O ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-BYPYZUCNSA-P 0.000 description 1
- CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N L-aspartic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC(O)=O CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-histidine Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N L-lysine Chemical compound NCCCC[C@H](N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-YFKPBYRVSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N Lactose Natural products OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229930195725 Mannitol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl methacrylate Chemical compound COC(=O)C(C)=C VVQNEPGJFQJSBK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920000168 Microcrystalline cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 208000025370 Middle East respiratory syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 1
- HSHXDCVZWHOWCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N N'-hexadecylthiophene-2-carbohydrazide Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCNNC(=O)c1cccs1 HSHXDCVZWHOWCS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O N,N,N-trimethylglycinium Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- MBBZMMPHUWSWHV-BDVNFPICSA-N N-methylglucamine Chemical compound CNC[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)CO MBBZMMPHUWSWHV-BDVNFPICSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FIWILGQIZHDAQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N NC1=C(C(=O)NCC2=CC=C(C=C2)OCC(F)(F)F)C=C(C(=N1)N)N1N=C(N=C1)C1(CC1)C(F)(F)F Chemical compound NC1=C(C(=O)NCC2=CC=C(C=C2)OCC(F)(F)F)C=C(C(=N1)N)N1N=C(N=C1)C1(CC1)C(F)(F)F FIWILGQIZHDAQG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Niacin Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CN=C1 PVNIIMVLHYAWGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001292005 Nidovirales Species 0.000 description 1
- 101800000515 Non-structural protein 3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710188652 Non-structural protein 4a Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101800000508 Non-structural protein 5 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- ZCQWOFVYLHDMMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxazole Chemical compound C1=COC=N1 ZCQWOFVYLHDMMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WTKZEGDFNFYCGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyrazole Chemical compound C=1C=NNC=1 WTKZEGDFNFYCGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101710153041 Replicase polyprotein 1a Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101710151619 Replicase polyprotein 1ab Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 206010061494 Rhinovirus infection Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108091005532 SARS-CoV-2 main proteases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000012300 Sequence Analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sodium Chemical compound [Na] KEAYESYHFKHZAL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium laurylsulphate Chemical compound [Na+].CCCCCCCCCCCCOS([O-])(=O)=O DBMJMQXJHONAFJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Succinic acid Natural products OC(=O)CCC(O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FZWLAAWBMGSTSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Thiazole Chemical compound C1=CSC=N1 FZWLAAWBMGSTSO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108700022715 Viral Proteases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000726445 Viroids Species 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001361 adipic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011037 adipic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000783 alginic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010443 alginic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000615 alginic acid Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960001126 alginic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004781 alginic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000000172 allergic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N alpha-hydroxysuccinic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(O)CC(O)=O BJEPYKJPYRNKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009435 amidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007112 amidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229960001830 amprenavir Drugs 0.000 description 1
- YMARZQAQMVYCKC-OEMFJLHTSA-N amprenavir Chemical compound C([C@@H]([C@H](O)CN(CC(C)C)S(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC(N)=CC=1)NC(=O)O[C@@H]1COCC1)C1=CC=CC=C1 YMARZQAQMVYCKC-OEMFJLHTSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002259 anti human immunodeficiency virus agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000840 anti-viral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000006708 antioxidants Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007900 aqueous suspension Substances 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003121 arginine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000003704 aspartic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000010668 atopic eczema Diseases 0.000 description 1
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenesulfonic acid Chemical compound OS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940092714 benzenesulfonic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000010233 benzoic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-D-galactosamine Natural products NC1C(O)OC(CO)C(O)C1O MSWZFWKMSRAUBD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N beta-D-glucose Chemical compound OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N beta-carboxyaspartic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(N)C(C(O)=O)C(O)=O OQFSQFPPLPISGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003237 betaine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001222 biopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229960000517 boceprevir Drugs 0.000 description 1
- LHHCSNFAOIFYRV-DOVBMPENSA-N boceprevir Chemical compound O=C([C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H](C2(C)C)CN1C(=O)[C@@H](NC(=O)NC(C)(C)C)C(C)(C)C)NC(C(=O)C(N)=O)CC1CCC1 LHHCSNFAOIFYRV-DOVBMPENSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001246 bromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 description 1
- 239000007975 buffered saline Substances 0.000 description 1
- OTJZCIYGRUNXTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N but-3-yn-1-ol Chemical compound OCCC#C OTJZCIYGRUNXTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N butanedioic acid Chemical compound O[14C](=O)CC[14C](O)=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-NUQCWPJISA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001948 caffeine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- VJEONQKOZGKCAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N caffeine Natural products CN1C(=O)N(C)C(=O)C2=C1C=CN2C VJEONQKOZGKCAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001110 calcium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001628 calcium chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001768 cations Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000001913 cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010980 cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920002678 cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 1
- PJGJQVRXEUVAFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloroiodomethane Chemical compound ClCI PJGJQVRXEUVAFT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N choline Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CCO OEYIOHPDSNJKLS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001231 choline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000013985 cinnamic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229930016911 cinnamic acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001924 cycloalkanes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- IISBKOXJLDGGPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanamine 2-(2-hydroxyethylamino)ethanol Chemical compound N(CCO)CCO.C1(CCCCC1)N IISBKOXJLDGGPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000596 cyclohexenyl group Chemical group C1(=CCCCC1)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000006240 deamidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015961 delipidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000008121 dextrose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethylamine Chemical compound CCNCC HPNMFZURTQLUMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008298 dragée Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002651 drug therapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010410 dusting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007071 enzymatic hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006047 enzymatic hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZCRZCMUDOWDGOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethanesulfonimidic acid Chemical compound CCS(N)(=O)=O ZCRZCMUDOWDGOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001301 ethoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- NLFBCYMMUAKCPC-KQQUZDAGSA-N ethyl (e)-3-[3-amino-2-cyano-1-[(e)-3-ethoxy-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]sulfanyl-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]sulfanylprop-2-enoate Chemical compound CCOC(=O)\C=C\SC(=C(C#N)C(N)=O)S\C=C\C(=O)OCC NLFBCYMMUAKCPC-KQQUZDAGSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019325 ethyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001249 ethyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229940012017 ethylenediamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000003818 flash chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000796 flavoring agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012458 free base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940083124 ganglion-blocking antiadrenergic secondary and tertiary amines Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229960002442 glucosamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940074045 glyceryl distearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940075507 glyceryl monostearate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940093915 gynecological organic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 208000005252 hepatitis A Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004051 hexyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N histidine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CN=CN1 HNDVDQJCIGZPNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960002885 histidine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrazine monohydrate Substances O.NN IKDUDTNKRLTJSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001866 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010979 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920003088 hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002519 immonomodulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- CBVCZFGXHXORBI-PXQQMZJSSA-N indinavir Chemical compound C([C@H](N(CC1)C[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](CC=2C=CC=CC=2)C(=O)N[C@H]2C3=CC=CC=C3C[C@H]2O)C(=O)NC(C)(C)C)N1CC1=CC=CN=C1 CBVCZFGXHXORBI-PXQQMZJSSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960001936 indinavir Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000001802 infusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004615 ingredient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001023 inorganic pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- UEXQBEVWFZKHNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N intermediate 29 Natural products C1=CC(N)=CC=C1NC1=NC=CC=N1 UEXQBEVWFZKHNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000001361 intraarterial administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007918 intramuscular administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007912 intraperitoneal administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003456 ion exchange resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003303 ion-exchange polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002427 irreversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001972 isopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- JJWLVOIRVHMVIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N isopropylamine Chemical compound CC(C)N JJWLVOIRVHMVIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CTAPFRYPJLPFDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N isoxazole Chemical compound C=1C=NOC=1 CTAPFRYPJLPFDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004310 lactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014655 lactic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 description 1
- WMWSRIHFAVOHSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N lithium;ethane-1,2-diamine;ethyne Chemical compound [Li+].[C-]#C.NCCN WMWSRIHFAVOHSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003646 lysine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium carbonate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=O ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000001095 magnesium carbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000021 magnesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000014380 magnesium carbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 159000000003 magnesium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000011976 maleic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000001630 malic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011090 malic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N mandelic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1 IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000594 mannitol Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010355 mannitol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CS(Cl)(=O)=O QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 description 1
- AGJSNMGHAVDLRQ-HUUJSLGLSA-N methyl (2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethylphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoate Chemical compound SC[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)OC)CC1=CC=C(O)C(C)=C1C AGJSNMGHAVDLRQ-HUUJSLGLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AGJSNMGHAVDLRQ-IWFBPKFRSA-N methyl (2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2s)-2-[[(2r)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxy-2,3-dimethylphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylsulfanylbutanoate Chemical compound SC[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCSC)C(=O)OC)CC1=CC=C(O)C(C)=C1C AGJSNMGHAVDLRQ-IWFBPKFRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NCSHKOSBEYDZFY-VIFPVBQESA-N methyl (2s)-2-amino-3-(4-fluorophenyl)propanoate Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(F)C=C1 NCSHKOSBEYDZFY-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl p-hydroxycinnamate Natural products OC(=O)C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 WBYWAXJHAXSJNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IMAKHNTVDGLIRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl prop-2-ynoate Chemical compound COC(=O)C#C IMAKHNTVDGLIRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000019813 microcrystalline cellulose Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008108 microcrystalline cellulose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940016286 microcrystalline cellulose Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007923 nasal drop Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940100662 nasal drops Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 201000009240 nasopharyngitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 229960000884 nelfinavir Drugs 0.000 description 1
- QAGYKUNXZHXKMR-HKWSIXNMSA-N nelfinavir Chemical compound CC1=C(O)C=CC=C1C(=O)N[C@H]([C@H](O)CN1[C@@H](C[C@@H]2CCCC[C@@H]2C1)C(=O)NC(C)(C)C)CSC1=CC=CC=C1 QAGYKUNXZHXKMR-HKWSIXNMSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000001971 neopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000011664 nicotinic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960003512 nicotinic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000001968 nicotinic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 231100000344 non-irritating Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002674 ointment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000006408 oxalic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940116315 oxalic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000007800 oxidant agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006179 pH buffering agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N papa-hydroxy-benzoic acid Natural products OC(=O)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 FJKROLUGYXJWQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006072 paste Substances 0.000 description 1
- 244000052769 pathogen Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000001717 pathogenic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001814 pectin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000010987 pectin Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920001277 pectin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001147 pentyl group Chemical group C(CCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940124531 pharmaceutical excipient Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000825 pharmaceutical preparation Substances 0.000 description 1
- OXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N picric acid Chemical compound OC1=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1[N+]([O-])=O OXNIZHLAWKMVMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006187 pill Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001223 polyethylene glycol Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000012704 polymeric precursor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001184 polypeptide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000001267 polyvinylpyrrolidone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000036 polyvinylpyrrolidone Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000013855 polyvinylpyrrolidone Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000015320 potassium carbonate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- FYRHIOVKTDQVFC-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium phthalimide Chemical compound [K+].C1=CC=C2C(=O)[N-]C(=O)C2=C1 FYRHIOVKTDQVFC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 description 1
- BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N propan-1-ol Chemical compound CCCO BDERNNFJNOPAEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000000069 prophylactic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000019260 propionic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000002685 pulmonary effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000003856 quaternary ammonium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N quinbolone Chemical compound O([C@H]1CC[C@H]2[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@]4(C=CC(=O)C=C4CC3)C)CC[C@@]21C)C1=CCCC1 IUVKMZGDUIUOCP-BTNSXGMBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006722 reduction reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004007 reversed phase HPLC Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006413 ring segment Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229950007656 rupintrivir Drugs 0.000 description 1
- CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N saccharin Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(=O)NS(=O)(=O)C2=C1 CVHZOJJKTDOEJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004889 salicylic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002002 slurry Substances 0.000 description 1
- PPASLZSBLFJQEF-RKJRWTFHSA-M sodium ascorbate Substances [Na+].OC[C@@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1[O-] PPASLZSBLFJQEF-RKJRWTFHSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000010378 sodium ascorbate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229960005055 sodium ascorbate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000012279 sodium borohydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000033 sodium borohydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012312 sodium hydride Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000104 sodium hydride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000019333 sodium laurylsulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- PPASLZSBLFJQEF-RXSVEWSESA-M sodium-L-ascorbate Chemical compound [Na+].OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1[O-] PPASLZSBLFJQEF-RXSVEWSESA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960004274 stearic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000007920 subcutaneous administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007940 sugar coated tablet Substances 0.000 description 1
- IIACRCGMVDHOTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfamic acid group Chemical group S(N)(O)(=O)=O IIACRCGMVDHOTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229950000244 sulfanilic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003871 sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000013268 sustained release Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012730 sustained-release form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960001367 tartaric acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000006068 taste-masking agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- XDJCYKMWJCYQJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl n-(3-hydroxypropyl)carbamate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NCCCO XDJCYKMWJCYQJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDLPJHZUTLGFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl n-(6-hydroxyhexyl)carbamate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NCCCCCCO BDLPJHZUTLGFON-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004559 theobromine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229930192474 thiophene Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 230000000699 topical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003626 triacylglycerols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- IMFACGCPASFAPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N tributylamine Chemical compound CCCCN(CCCC)CCCC IMFACGCPASFAPR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trichloroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl YNJBWRMUSHSURL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YFTHZRPMJXBUME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tripropylamine Chemical compound CCCN(CCC)CCC YFTHZRPMJXBUME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000017613 viral reproduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009736 wetting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000080 wetting agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
- A61K38/04—Peptides having up to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- A61K38/12—Cyclic peptides, e.g. bacitracins; Polymyxins; Gramicidins S, C; Tyrocidins A, B or C
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
- A61P31/14—Antivirals for RNA viruses
Definitions
- the invention belongs to the field of medicine and chemical industry, and relates to a class of cyclic peptide compounds and their application as viral protease inhibitors in preparing antiviral drugs.
- the present invention relates to a class of cyclic peptide compounds, stereoisomers, tautomers or mixtures thereof, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, co-crystals or Solvates, alternatively, stable isotope derivatives, metabolites or prodrugs of the compounds, and viruses (mainly including but not limited to, which play an important role in inhibiting viral proteases, producing prophylactic and/or therapeutic proteases in the viral life cycle) Infectious diseases caused by picornaviruses and coronaviruses).
- the present invention also relates to methods and intermediates for synthesizing the cyclic peptide compounds.
- Picornaviruses and coronaviruses are single positive-stranded RNA viruses.
- the picornavirus family mainly includes enterovirus (coxsackie virus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enterovirus type 71, etc.], human rhinovirus (HRV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV) )Wait.
- Enterovirus 71 (EV71virus) and Coxsackievirus (Coxsackievirus) infection can cause herpetic angina and hand, foot and mouth disease in children, which can be life-threatening in severe cases.
- Poliovirus (PV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV) can cause polio (usually polio) and hepatitis A, respectively.
- RhV Human rhinovirus is a kind of rhinovirus (rhinovirus, RhV), which is the virus with the most serotypes among human viruses. Rhinovirus is the main pathogen that causes the common cold. The virus is the main culprit in causing acute respiratory disease, and nearly half of all acute respiratory disease infections are caused by rhinovirus infections.
- the coronavirus belongs to the genus Coronavirus in the family Coronaviridae of the order Nidovirales in the systematic taxonomy.
- coronaviruses that can infect humans.
- SARS-CoV-2 the 2019 novel coronavirus
- the remaining 6 coronaviruses that can infect humans are HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV (SARS virus, which causes severe acute respiratory syndrome) and MERS-CoV (which causes Middle East respiratory syndrome) sign).
- the genome of some viruses first encodes a large polymeric precursor protein, which is then hydrolyzed by the polyprotein to produce functional proteins. This hydrolysis process is mainly completed by proteases. Most of the precursor proteins produced by single-positive-strand RNA viruses can only undergo subsequent replication and encapsulation after being hydrolyzed by 3C or 3CL protease to form functional proteins. A core protease that plays a crucial role in the replication of single positive-stranded RNA viruses.
- the picornavirus first encodes a large multimeric precursor protein, which is then hydrolyzed by 3C protease, while the coronavirus first encodes two polyproteins (pp1a and pp1ab), and then the polyprotein
- the same hydrolysis produces functional protein, and the hydrolysis process is mainly completed by 3CL protease.
- the non-structural protein NS3/4A is mainly responsible for the hydrolysis of polyproteins. Similar proteases are also involved in the life cycle of non-single positive-stranded RNA viruses, such as human transcriptovirus (HIV).
- 3C or 3CL protease is an important target for single positive-stranded RNA viroid drug therapy research. Despite the diversity of single positive stranded RNA virus genes, the 3C and 3CL protease substrate binding sites are highly conserved and have similar catalytic mechanisms, which are highly similar proteases in single positive stranded RNA viruses. Therefore, the research on broad-spectrum anti-single positive-strand RNA virus inhibitors targeting 3C and 3CL proteases has received extensive attention.
- Both 3C and 3CL proteases are cysteine proteases with highly conserved three-dimensional structures. Although 3C and 3CL proteases have low sequence homology, structural-based sequence analysis found that the two types of proteases have a highly conserved Gly-X-Cys-Gly-Gly-Gly/Ser sequence structure, and the catalytic triad of 3C proteases has a highly conserved Gly-X-Cys-Gly-Gly-Gly/Ser sequence structure. His-Cys is almost identical to that of 3CL protease, indicating that the two types of proteases have highly conserved substrate binding sites and have similar catalytic mechanisms.
- Rupintrivir (AG7088, Rupintrivirvr) was originally developed by Agouton Pharmaceutical Company, it is an irreversible specific inhibitor of human rhinovirus, is a peptide drug, it has a similar spatial structure to 3C protease substrate Therefore, it can compete with the substrate to bind to 3C protease and exert its inhibitory effect on the enzyme.
- Lupintravir inhibited replication of 48 different HRV serotypes in H1-HeLA and MRC-5 cytoprotection assays with a mean EC50 of 0.023 ⁇ M. Lupintravir has immunomodulatory effects. Lupintravir has been reported in the literature to have a therapeutic effect on EV71-infected animals.
- anti-HIV drugs include nelfinavir, saquibonvir, indinavir, amprenavir, ritonavir, lopinavir Navir, etc.
- anti-HCV drugs include traprevir and boceprevir.
- ritonavir/lopinavir was tried to treat the new crown ("Diagnosis and Treatment Plan for Pneumonia Infected by Novel Coronavirus (Trial Fifth Edition)").
- the cyclic peptide compounds with the general formula M involved in the invention are effective viral protease inhibitors.
- Compounds with general formula M can be used to inhibit viral protease, and can be used to prevent and/or treat infectious diseases caused by viruses (mainly including but not limited to picornaviruses and coronaviruses) in which proteases play an important role in the virus life cycle.
- Another object of the present invention is to provide a preparation method of a cyclic peptide protease inhibitor with the general formula M and its synthetic intermediate, which is used to synthesize the compound of the general formula M and its intermediate.
- the present application provides a cyclic peptide compound represented by formula M, a stereoisomer, tautomer or a mixture thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt and polymorph of the compound , co-crystals or solvates, or, alternatively, stable isotope derivatives, metabolites or prodrugs of said compounds,
- R 1 is selected from wherein R' is C 1 -C 6 alkyl or C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl,
- R 2 is C 1 -C 6 alkyl or C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl, or aryl substituted with one or more (eg 2, 3, 4) substituents selected from fluorine, Chlorine, bromine, iodine, C 1 -C 6 alkyl, C 1 -C 6 alkoxy, cyano, nitro;
- Ring A is selected from substituted or unsubstituted five- or six-membered aryl, substituted or unsubstituted five- or six-membered heteroaryl.
- R' is C 1 -C 3 alkyl or C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl
- R 2 is C 1 -C 6 alkyl or C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl, or one or more (eg 2, 3, 4) fluorine-substituted benzene rings,
- Ring A is a benzene ring or a five-membered heteroaryl group preferably containing 1, 2 or 3 nitrogen atoms and/or 1, 2 or 3 oxygen atoms.
- R 1 is selected from wherein R' is methyl, ethyl or cyclopropyl,
- R 2 is selected from cyclopropyl, cyclohexyl, isopropyl, 4-fluorophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl,
- Ring A is selected from the following 5-membered heteroaryl groups
- R 1 is selected from
- R' is C1 - C4 alkyl, eg, methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl, tert-butyl.
- R' is selected from cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl.
- R 1 is selected from wherein R' is selected from methyl, ethyl, cyclopropyl.
- R 2 is phenyl substituted with one or more (eg, 2, 3, 4) substituents selected from fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, C 1 -C 6 Alkyl (eg C 1 -C 4 alkyl or C 1 -C 3 alkyl), C 1 -C 6 alkoxy (eg methoxy or ethoxy), cyano, nitro.
- substituents selected from fluoro, chloro, bromo, iodo, C 1 -C 6 Alkyl (eg C 1 -C 4 alkyl or C 1 -C 3 alkyl), C 1 -C 6 alkoxy (eg methoxy or ethoxy), cyano, nitro.
- R 2 is phenyl substituted with one or more (eg, 2, 3, 4) substituents selected from fluoro, chloro, bromo.
- R 2 is phenyl substituted with one or more (eg, 2, 3, 4) fluorines.
- R 2 is C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl.
- R2 is selected from cyclopropyl, cyclohexyl, isopropyl, 4 -fluorophenyl, 3-fluorophenyl, 3,4-difluorophenyl.
- Y is C or O.
- n+m 5, 6 or 7.
- Ring A is a benzene ring or a five-membered heteroaryl group containing 1, 2, or 3 nitrogen atoms and/or 1, 2, or 3 oxygen atoms.
- Ring A is selected from the following 5-membered heteroaryl groups
- the compounds of the present invention may have structures selected from the group consisting of:
- the application provides the preparation of a compound of the present invention, a stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal of the compound compound or solvate, or a method for a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound, the method comprising: synthesizing the compound of formula 5 (intermediate 5) through the following reaction scheme:
- reaction conditions a and b are inorganic bases, including but not limited to sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, lithium hydroxide.
- the compound of the present invention has the structure shown in formula 6, and its synthesis method can adopt the following reaction scheme:
- the compound of the present invention has the structure shown in formula 7, and its synthesis method can adopt the following reaction scheme:
- reaction condition c is an inorganic base, including but not limited to sodium hydroxide, sodium carbonate, and lithium hydroxide.
- the compound of formula 2 has the structure shown in formula 2-1, and the compound of formula 2-1 is prepared by the following reaction scheme:
- the reaction can be carried out in the presence of Cu(I), for example in the presence of ascorbic acid and copper sulfate pentahydrate.
- the compound of formula 2 has the structure shown in formula 2-2, and the compound of formula 2-2 is prepared by the following reaction scheme:
- the reaction can be carried out in the presence of an inorganic base such as sodium bicarbonate.
- the compound of formula 2 has the structure shown in formula 2-3, and the compound of formula 2-3 is prepared by the following reaction scheme:
- the present application also provides a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising at least one compound of the present invention, a stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof of the compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the compound, a poly A crystalline form, co-crystal or solvate, or a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound; optionally, the pharmaceutical composition further comprises at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient , carrier, medium or adjuvant.
- the pharmaceutical composition further comprises an EV71 antiviral agent; in certain embodiments, the EV71 antiviral agent is an antiviral agent selected from the group consisting of 3D protease inhibitors and VP1 protein inhibitors.
- the pharmaceutical composition is for preventing/treating a disease in a subject associated with a viral infection selected from the group consisting of picornaviruses (eg, Enteroviruses, Human Rhinoviruses (HRV) and Hepatitis A virus (HAV)), as well as coronaviruses.
- a viral infection selected from the group consisting of picornaviruses (eg, Enteroviruses, Human Rhinoviruses (HRV) and Hepatitis A virus (HAV)), as well as coronaviruses.
- the enteroviruses include but are not limited to enterovirus 71 (EV71), poliovirus, coxsackievirus A, coxsackievirus B, and the coronaviruses include but are not limited to SARS-CoV-2, HCoV- 229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
- the pharmaceutical composition is used to prevent/treat a disease associated with enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection or a disease associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in a subject.
- the subject is a mammal, eg, bovine, equine, porcine, canine, feline, rodent, primate. Among them, particularly preferred subjects are humans.
- the application also provides a compound of the present invention, a stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof of said compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal or solvate of said compound, or , the use of a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound in the preparation of a drug, the drug being a viral protease inhibitor.
- the virus is selected from the group consisting of picornaviruses (eg, enteroviruses (eg, coxsackievirus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enterovirus type 71), human rhinoviruses (HRV) and Hepatitis A virus (HAV)), as well as coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV.
- picornaviruses eg, enteroviruses (eg, coxsackievirus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enterovirus type 71), human rhinoviruses (HRV) and Hepatitis A virus (HAV)
- coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-
- the protease is a 3C/3CL protease.
- the application also provides a compound of the present invention, a stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof of said compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal or solvate of said compound, or , the use of a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound in the preparation of a drug, the drug being an antiviral drug;
- the virus against which the antiviral drug is directed is selected from picornaviruses (eg, enteroviruses (eg, coxsackievirus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enterovirus type 71), human rhinoviruses genus (HRV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV), as well as coronaviruses (e.g. SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV) .
- enteroviruses eg, coxsackievirus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enterovirus type 71
- HRV human rhinoviruses genus
- HAV hepatitis A virus
- coronaviruses e.g. SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-
- the application also provides a compound of the present invention, a stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof of said compound, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal or solvate of said compound, or , the use of a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound in the preparation of a medicine, the medicine is used for the prevention/treatment of a subject's disease related to viral infection, and the virus is selected from a small RNA virus ( Examples include enteroviruses, human rhinoviruses (HRV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV), and coronaviruses.
- HRV human rhinoviruses
- HAV hepatitis A virus
- the enteroviruses include but are not limited to enterovirus 71 (EV71), poliovirus, coxsackievirus A, coxsackievirus B, and the coronaviruses include but are not limited to SARS-CoV-2, HCoV- 229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63, HCoV-HKU1, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV.
- the subject is a mammal, eg, bovine, equine, porcine, canine, feline, rodent, primate. Among them, particularly preferred subjects are humans.
- the present invention provides a method of preventing/treating a disease associated with a viral infection in a subject, comprising the steps of: adding a prophylactically/therapeutic effective amount of a compound of the present invention, the stereoisomer of the compound A isomer, tautomer or mixture thereof, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal or solvate of the compound, or a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound , or the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention is administered to the subject, and the virus is selected from the group consisting of picornaviruses (such as enteroviruses (such as coxsackievirus (CV), poliovirus (PV), enteroviruses virus type 71), human rhinovirus (HRV) and hepatitis A virus (HAV), as well as coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV-2, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63,
- the subject is a mammal, eg, bovine, equine, porcine, canine, feline, rodent, primate. Among them, particularly preferred subjects are humans.
- the present application also provides a compound having the structure shown in formula 5 and the compound thereof as an intermediate to prepare the cyclic peptide compound of the present invention, the stereoisomer, tautomer or mixture thereof, Use of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, polymorph, co-crystal or solvate of the compound, or a stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of the compound:
- C1 - C6 alkyl refers to straight or branched chain alkyl groups having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl, n-butyl, sec-butyl group, tert-butyl group, pentyl group, 2-pentyl group, isopentyl group, neopentyl group, hexyl group, 2-hexyl group, 3-hexyl group, etc.; C1-C3 alkyl group can also be similarly understood. Preferred are C1 - C3 alkyl groups.
- C 1 -C 6 alkoxy refers to a straight or branched chain alkoxy group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms, such as methoxy, ethoxy, propoxy, isopropoxy, n-butoxy, sec-butoxy, tert-butoxy, pentyloxy, 2-pentyloxy, isopentyloxy, neopentyloxy, hexyloxy, 2-hexyloxy, 3-oxyhexyl, etc. ; C 1 -C 3 alkoxy can also be understood similarly. Preferred are C 1 -C 3 alkoxy groups.
- aryl means an aromatic monocyclic ring system containing 6 carbon atoms, or an aromatic bicyclic ring system containing 10 atoms, such as phenyl and naphthyl-ring systems.
- heteroaryl as used herein, alone or in combination with another substituent, means a radical attached through a ring carbon atom or a heterocyclic atom (eg, a nitrogen atom) having, for example, 1, 2, or 3 atoms selected from the group consisting of A monovalent substituent derived from a five-membered, six-membered or seven-membered unsaturated heterocycle of N,0,S heteroatoms by removing hydrogen.
- suitable heteroaryl groups are: thiophene, furan, pyrrole, imidazole, pyrazole, thiazole, oxazole, isoxazole, 1,2,3-triazole.
- C 3 -C 6 cycloalkyl refers to a saturated or partially saturated and non-aromatic monocyclic cyclic group containing 3-6 ring atoms, including “3-6 membered saturated cycloalkane” and “3-6 membered partially saturated cycloalkyl", such as “5-6 membered cycloalkyl", “5-6 membered saturated cycloalkyl” and the like. Examples include, but are not limited to, cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl, cyclohexyl, or cyclohexenyl, and the like.
- stereoisomer refers to isomers formed due to at least one asymmetric center. In compounds having one or more (eg, one, two, three or four) asymmetric centers, it may give rise to racemic mixtures, single enantiomers, diastereomeric mixtures and individual of diastereomers. Certain individual molecules can also exist as geometric isomers (cis/trans). Similarly, the compounds of the present invention may exist as mixtures of two or more structurally distinct forms in rapid equilibrium (often referred to as tautomers). Representative examples of tautomers include keto-enol tautomers, phenol-ketone tautomers, nitroso-oxime tautomers, imine-enamine tautomers Wait.
- the present invention encompasses all possible crystalline forms or polymorphs of the compounds of the present invention, which may be a single polymorph or a mixture of more than one polymorph in any ratio.
- compositions of the present invention may exist in free form for use in therapy, or, where appropriate, in the form of their pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives.
- pharmaceutically acceptable derivatives include, but are not limited to, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates, metabolites or prodrugs, which directly or indirectly provide the present invention after administration to a patient in need thereof compounds or their metabolites or residues.
- pharmaceutically acceptable salts refers to salts of compounds of formula (M) which are non-toxic, non-irritating, non-allergic, etc. suitable for tissue contact in humans and animals under normal medical treatment. Generally water- or oil-soluble, or readily dispersible, and effective in their use. This term includes pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts and pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts.
- pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts refers to maintaining biological activity and the properties of a free base, and being non-biologically or otherwise undesirable, which interact with inorganic acids such as sulfuric, nitric, phosphoric, hydrochloric, sulfamic Acids, etc., and organic acids such as acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, cinnamic acid, citric acid, maleic acid, adipic acid, alginic acid, ascorbic acid, aspartic acid, benzoic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, glycolic acid , malic acid, lactic acid, malonic acid, oxalic acid, niacin, succinic acid, salicylic acid, stearic acid, tartaric acid, p-aminobenzenesulfonic acid, trimethylbenzenesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, almond Acid, pectin
- pharmaceutically acceptable base addition salts refers to maintaining biological activity and properties of a free acid, and being abiotic or otherwise undesirable, which are formed with inorganic bases such as ammonia or ammonium or metal cations such as sodium, Among the salts formed of sulfonates of magnesium, copper, zinc, calcium, potassium, aluminum, etc., ammonium, potassium, sodium, calcium, and magnesium salts are particularly preferred.
- Salts derived from pharmaceutically acceptable organic non-toxic bases include primary, secondary and tertiary amines, quaternary ammonium compounds, substituted amines including natural substituted amines, cyclic amines and base ion exchange resins, Such as methylamine, dimethylamine, trimethylamine, ethylamine, diethylamine, triethylamine, tripropylamine, isopropylamine, tributylamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, diethanolamine Cyclohexylamine, Lysine, Arginine, Histidine, Caffeine, Choline, Betaine, Ethylenediamine, Glucosamine, Methylglucamine, Theobromine.
- methylamine dimethylamine, trimethylamine, ethylamine, diethylamine, triethylamine, tripropylamine, isopropylamine, tributylamine, ethanolamine, diethanolamine, diethanolamine Cyclohe
- solvate refers to a substance formed by the association of a compound with a solvent molecule.
- the solvent may be water or an organic solvent (eg methanol, ethanol, propanol, acetonitrile, etc.) and the like.
- metabolites of the compounds of the present invention ie substances formed in the body upon administration of the compounds of the present invention. Such products may result from, for example, oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, amidation, deamidation, esterification, delipidation, enzymatic hydrolysis, and the like, of the administered compound. Accordingly, the present invention includes metabolites of the compounds of the present invention, including compounds prepared by methods of contacting a compound of the present invention with a mammal for a time sufficient to produce the metabolites thereof.
- the present invention further includes within its scope prodrugs of the compounds of the present invention.
- prodrugs will be functional derivatives of the compound that are readily converted in vivo to the desired therapeutically active compound.
- the term "administering" as used in the methods of treatment of the present invention shall include the treatment of various diseases or conditions with prodrug forms of one or more of the claimed compounds, but in the The prodrug forms are converted in vivo to the compounds described above following administration to a subject.
- “Design of Prodrug” ed. H. Bundgaard, Elsevier, 1985, conventional methods for selecting and preparing suitable prodrug derivatives are described.
- the present invention further includes within its scope stable isotope derivatives of the compounds of the present invention, which are identical to the compounds of the present invention except that one or more atoms are replaced with the same atomic number but an atomic mass or mass number different from that which predominates in nature atomic substitution of atomic mass or mass number.
- the present invention also encompasses compounds of the present invention that contain protecting groups.
- protecting groups In any process for preparing the compounds of the present invention, it may be necessary and/or desirable to protect sensitive or reactive groups on any relevant molecule, thereby forming chemically protected forms of the compounds of the present invention. This can be accomplished by conventional protecting groups, such as those described in Protective Groups in Organic Chemistry, ed.J.F.W.McOmie, Plenum Press, 1973; and T.W.Greene & P.G.M. Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, 1991 protecting groups, these references are incorporated herein by reference. Protecting groups can be removed at an appropriate subsequent stage using methods known in the art.
- the present invention comprises a pharmaceutical composition
- a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutic amount of a compound of the present invention, and one or more pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and/or excipients.
- Carriers include, for example, saline, buffered saline, dextrose, water, glycerol, ethanol, and combinations thereof.
- the carrier or excipient may also include time delay materials known in the art, such as glyceryl monostearate or glyceryl distearate, and may also include waxes, ethyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, Methyl methacrylate, etc.
- the composition may also contain minor amounts of wetting or emulsifying agents, or pH buffering agents, if desired.
- the composition may be a liquid, suspension, emulsion, tablet, pill, capsule, sustained release formulation or powder.
- the composition can be formulated as a suppository with traditional binders and carriers such as triglycerides.
- Oral formulations can include standard carriers such as pharmaceutical grades of mannitol, lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, sodium saccharin, cellulose, magnesium carbonate, and the like. Formulations can be designed to mix, granulate and compress or dissolve the ingredients, depending on the desired formulation. In another approach, the composition can be formulated as nanoparticles.
- the active ingredients of the pharmaceutical compositions encompassed by the present invention may have systemic and/or local effects and, therefore, may be administered by appropriate routes such as oral, parenteral, pulmonary, nasal, sublingual, Tongue, buccal, rectal, transdermal, conjunctival, topical or in the form of implants.
- the active ingredient can also be administered in administration forms suitable for these routes of administration.
- Suitable for oral administration are the well-known forms of administration which deliver the active ingredient rapidly and/or in a modified manner, such as tablets (uncoated or coated, eg enteric- or moly-coated) dosage), capsules, sugar-coated tablets, granules, pellets, powders, emulsions, suspensions and aerosols.
- parenteral administration it is possible to avoid the absorption step (intravenous, intraarterial, intracardiac, intraspinal or lumbar intramedullary administration) or to include absorption (intramuscular, subcutaneous, intradermal, transdermal or intraperitoneal administration) .
- Administration forms suitable for parenteral administration are especially formulations in the form of solutions, suspensions, emulsions, lyophilisates and sterile powders for injection and infusion.
- Suitable for other routes of administration are, for example, medicaments for inhalation (especially powder inhalation, spray), nasal drops/solutions, sprays; tablets or capsules for lingual, sublingual or buccal administration, suppositories, for Ear and eye preparations, vaginal capsules, aqueous suspensions (lotions, shaker mixtures), lipophilic suspensions, ointments, creams, lotions, pastes, dusting powders, or implants such as stents mold.
- the active ingredient can be converted into the said administration form by methods known per se. This can be accomplished with inert nontoxic suitable pharmaceutical excipients.
- the active ingredient may be in microencapsulated form in one or more of the aforementioned carriers.
- the above-mentioned pharmaceutical preparations may also contain other pharmaceutically active ingredients.
- the present invention also relates to the preparation of compounds of formula M of the present invention, stereoisomers, tautomers or mixtures thereof, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, co-crystals or solvates of said compounds , or, the synthetic method of the stable isotope derivative, metabolite or prodrug of described compound, comprising:
- lithium acetylide ethylenediamine complex (11.2 g, 130 mmol) was added to 100 mL of anhydrous dimethyl sulfoxide, stirred to dissolve, and protected with nitrogen. The temperature was lowered to 0°C, 1-chloro-6-bromo (11.2 g, 130 mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and the reaction solution was stirred at room temperature for 20 hours. After the reaction was completed, 50 mL of saturated aqueous ammonium chloride solution was added dropwise to the reaction solution in an ice bath to quench the reaction. Saturated brine and ether were added for separation, the aqueous phase was extracted with ether, and the organic phases were combined.
- intermediate 1 (11.2 g, 130 mmol) was added to a mixed solution of ethanol and water, stirred to dissolve, hydrazine hydrate (11.2 g, 130 mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and then the reaction solution was stirred at 75 ° C for 2 Hour. After the reaction was completed, 12N aqueous hydrochloric acid solution was added dropwise to the reaction solution in an ice bath until the pH of the reaction solution was 2. Filter and collect the filtrate.
- intermediate 2 (1.83 g, 6 mmol) was added to 10 mL of tetrahydrofuran, and stirred to dissolve.
- lithium hydroxide 0.4 g, 9.6 mmol
- the reaction was then stirred at room temperature for 4 hours.
- the pH value of the reaction solution was adjusted to 7 with saturated citric acid solution.
- the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was added to 10 ml of ice water, and the aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 2 with saturated citric acid solution.
- intermediate 4 (1.83 g, 6 mmol) was added to 10 mL of tetrahydrofuran, and stirred to dissolve.
- lithium hydroxide 0.4 g, 9.6 mmol
- the reaction was then stirred at room temperature for 4 hours.
- the pH value of the reaction solution was adjusted to 7 with saturated citric acid solution.
- the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, the residue was added to 10 ml of ice water, and the aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 2 with saturated citric acid solution.
- intermediate 5 was added to 8 mL of dichloromethane, and stirred to dissolve. The temperature was lowered to 0°C, and 8 mL of trifluoroacetic acid was added dropwise to the reaction solution. The reaction was carried out at room temperature for 12h. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was spin-dried, the residue was added to 15 ml of DMF, cooled to 0° C., and 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (4.70 g, 24 mmol), 1-hydroxybenzotriazole (3.20 g, 24 mmol).
- tert-Butyl (6-hydroxyhexyl)carbamate (1.83 g, 6 mmol) was added to 60 ml of DCM and dissolved by stirring. The temperature was lowered to 0° C., triethylamine (1.83 g, 6 mmol) was added dropwise, and methylsulfonyl chloride (0.4 g, 9.6 mmol) was added dropwise to the reaction solution within 1 h. The reaction solution was then stirred at 0°C for 2 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction was concentrated, the residue was added to 30 ml of DMF, stirred uniformly, sodium azide (0.4 g, 9.6 mmol) was added to the reaction solution, and the reaction solution was stirred at 80° C.
- the yellow solid product (14.46 g, 57.07 mmol) was dissolved in a small amount of toluene, 3-butyn-1-ol (8.0 g, 0.11 mol) was dissolved in toluene, heated to 60 ° C, and tetrabutyl bromide was added after 15 minutes Ammonium (917.2 mg, 2.85 mmol) was stirred for 15 minutes. Then solid sodium hydroxide (2.97 g, 74.19 mmol) was added and the temperature was raised to 75°C. After 30 minutes, the toluene solution of the yellow solid product was added dropwise, and the temperature was raised to 85° C. after the addition was completed, and stirring was continued for 8 hours.
- This white solid was added to a mixed solution of DCM and DMF, Dess Martin's oxidizing agent (0.4 g, 9.6 mmol) was added, and the reaction solution was stirred at 20°C for 10 hours. After the reaction was completed, saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution was added to the reaction solution to quench the reaction. The reaction solution was spin-dried, and the residue was added to 10 ml of water, slurried, filtered, and dried. A crude white solid was obtained. Column chromatography gave a white solid.
- This white solid was added to a mixed solution of dichloromethane and DMF, and stirred to dissolve. The temperature was lowered to 0°C, and HATU (4.70 g, 24 mmol) and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) (7.8 g, 60 mmol) were added to the reaction solution. After stirring for 30 min, ethylsulfonamide, DMAP and DBU were added successively. React at room temperature for 12h.
- DIPEA N,N-diisopropylethylamine
- reaction system was spin-dried, dissolved in dichloromethane, the organic phase was washed with 1 mol/L citric acid solution and saturated sodium chloride solution, and the crude product was purified by column chromatography to obtain a white solid.
- the final product XX is synthesized with the intermediate 17-2 as the raw material.
- the enzyme activity of the inhibitor against SARS-Cov-2 3CL protease was determined by fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) technology, and the substrate was designed according to the recognition site of Nsp5 protease: MCA-AVLQSGFR-Lys(Dnp)-Lys -NH2, the final concentrations of the inhibitor were 2uM, 1uM, 500nM, 250nM, 125nM, 62.5nM, 31.25nM, 15.625nM, 7.8nM, 3.9nM, 1.95nM, and a negative control was set at the same time. 96-well plate was used to measure the enzymatic activity.
- FRET fluorescence resonance energy transfer
- the 100 ⁇ L reaction system included: 50 mM Tris-HCl pH7.3, 1 mM EDTA, 150 nM SARS-Cov-2-3CLpro, 20 ⁇ M fluorescent substrate and different concentrations of inhibitors.
- the reaction was carried out at 30°C, the fluorescence intensity was detected by a microplate reader, and the obtained data were processed by the software GraphPad Prism 5 to obtain the IC 50 of the inhibitor.
- the experimental results are shown in Table 1.
- the enzymatic activity of the inhibitor against EV71 3C protease was determined by reverse-phase-HPLC.
- the peptide enzyme activity detection substrate (LEVLFQGPSK) was designed according to the 3C protease recognition site, and the final concentrations of the inhibitors were: 9uM, 3uM, 1uM, 333nM, 111nM, and a negative control was set at the same time.
- the enzyme activity was measured by 96-well plate, and the 100ul reaction system included: 50mM Tris-HCl pH7.5, 4uM EV71 3C protein, 2g/L polypeptide substrate and inhibitors of different concentrations.
- the reaction was carried out at 30°C, the fluorescence intensity was detected by a microplate reader, and the obtained data were processed by the software GraphPad Prism 5 to obtain the IC 50 of the inhibitor.
- Table 2 The experimental results are shown in Table 2.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Oncology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
属于医药化工领域,涉及如式M所示的环肽化合物或所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药。还涉及合成所述环肽类化合物的方法和中间体。提供的环肽类化合物对冠状病毒3CL蛋白酶和小RNA病毒(例如肠病毒属EV71病毒)3C蛋白酶有强抑制作用,经过细胞水平活性测试,提供的环肽类化合物对EV71病毒和冠状病毒等有明显的抑制作用,提示,如式M所示的环肽类化合物可以通过抑制病毒蛋白酶活性,在细胞水平上产生病毒抑制效果,具有良好的抗病毒药物应用前景。
Description
本发明属于医药化工领域,涉及一类环肽类化合物,及其作为病毒蛋白酶抑制剂、在制备抗病毒药物中的应用。具体地,本发明涉及一类环肽类化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药,以及它们在抑制病毒蛋白酶、制备预防和/或治疗蛋白酶在病毒生命周期中起重要作用的病毒(主要包括但不限于小RNA病毒和冠状病毒)引起的感染性疾病中的应用。本发明还涉及合成所述环肽类化合物的方法和中间体。
小RNA病毒和冠状病毒属于单正链RNA病毒。小RNA病毒家族主要包括肠道病毒属〔柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型等〕、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)等。肠道病毒71型(EV71virus)和柯萨奇病毒(Coxsackievirus)感染后会引起疱疹性咽峡炎,和儿童手足口病,严重的可以危及生命。脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)可以分别引起脊髓灰质炎(通常表现为小儿麻痹)和甲型肝炎。人鼻病毒是鼻病毒(rhinovirus,RhV)属的一种,是人类病毒中血清型最多的病毒,鼻病毒是引起普通感冒的主要病原体。该病毒是引起急性呼吸道疾病的罪魁祸首,将近半数的急性呼吸道疾病感染是由鼻病毒感染引起。
冠状病毒在系统分类上属套式病毒目(Nidovirales)冠状病毒科(Coronaviridae)冠状病毒属(Coronavirus)。目前已知有7种可以感染人的冠状病毒。其中危害最重的2019年爆发的新型冠状病毒(SARS-CoV-2),可引发新型冠状病毒肺炎COVID-19和并发症,已经引起全球大流行。其余6种可以感染人的冠状病毒分别是HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV(SARS病毒,引发重症急性呼吸综合征)和MERS-CoV(引发中东呼吸综合征)。
在病毒复制过程中,有些病毒的基因组首先编码一个大的多聚前体蛋白,之后由多聚蛋白水解产生功能蛋白,这一水解过程主要由蛋白酶完成。大部分单正链RNA病毒产生的前体蛋白只有在3C或3CL蛋白酶水解后形成功能蛋白,才能进行后续的复制、封装,因此3C和3CL蛋白酶是单正链RNA病毒前体多聚蛋白水解的核心蛋白酶,在单正链RNA病毒复制过程中起着至关重要的作用。例如,小RNA病毒首先编码一个大的多聚前体蛋白, 然后由3C蛋白酶完成多聚前体蛋白的水解,冠状病毒的则首先编码2个多聚蛋白(pp1a和pp1ab),之后多聚蛋白同样水解产生功能蛋白,水解过程主要由3CL蛋白酶完成。在黄病毒属(Flavivirus)中,主要由非结构蛋白NS3/4A完成多聚蛋白的水解任务。在非单正链RNA病毒,例如人转录病毒(HIV)的生命周期中,也有类似蛋白酶的参与。
因为人体中没有与此结构和功能其相似的蛋白酶,抑制病毒蛋白酶的催化功能就可有效抑制病毒前体蛋白的切割,阻断病毒复制。3C或3CL蛋白酶是单正链RNA类病毒药物治疗研究的重要靶点。尽管单正链RNA病毒基因具有多样性,但3C和3CL蛋白酶底物结合位点高度保守且具有相似的催化机制,是单正链RNA病毒中高度相似的蛋白酶。因此以3C和3CL蛋白酶为靶点的广谱抗单正链RNA病毒抑制剂研究获得了广泛的关注。3C和3CL蛋白酶都属于半胱氨酸蛋白酶,具有高度保守的三维结构。虽然3C和3CL蛋白酶序列同源性低,但基于结构基础的序列分析发现两类蛋白酶存在高度保守的Gly-X-Cys-Gly-Gly-Gly/Ser序列结构,并且3C蛋白酶的催化三联体中His-Cys与3CL蛋白酶的His-Cys几乎完全一致,说明两类蛋白酶与底物的结合位点高度保守且具有相似的催化机制。
芦平曲韦(AG7088,Rupintrivirvr)最初是由Agouton Pharmaceutical公司开发的,它是一种不可逆的人类鼻病毒的特异性抑制剂,是一种肽类药物,它具有与3C蛋白酶底物相似的空间构型,因而能够同底物竞争性地与3C蛋白酶结合,发挥对酶的抑制作用。芦平曲韦在H1-HeLA和MRC-5细胞保护试验中抑制48种不同HRV血清型的复制,其平均EC50为0.023μM。芦平曲韦具有免疫调节作用。有文献报到芦平曲韦对EV71感染的动物有治疗作用。另有文献报道,芦平曲韦对可以通过抑制SARS冠状病毒3CL蛋白酶抑抑制SARS冠状病毒,上述事实说明一种化合物可以对病毒3C蛋白酶或3CL蛋白酶有广谱的抗病毒作用。
目前已经上市的病毒蛋白酶抑制剂主要是治疗HIV和HCV感染的药物,其中抗HIV药物有奈非那韦、沙奎邦韦、茚地那韦、安泼那韦、利托那韦、洛匹那韦等,抗HCV药物有特拉普韦和博赛泼韦。在2020年新冠爆发早期,曾经尝试使用利托那韦/洛匹那韦治疗新冠(《新型冠状病毒感染的肺炎诊疗方案(试行第五版)》)。
发明内容
发明所涉及的具有通式M的环肽类化合物是有效的病毒蛋白酶抑制剂。具有通式M的化合物可用于抑制病毒蛋白酶,可用于预防和/或治疗蛋白酶在病毒生命周期中起重要作用的病毒(主要包括但不限于小RNA病毒和冠状病毒)引起的感染性疾病。本发明另一个目的是要提供具有通式M所描述的环肽类蛋白酶抑制剂及其合成中间体的制备方法,用于合成通式M化合物及其中间体。
在一个方面,本申请提供了式M所示的环肽类化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药,
R
2为C
1-C
6烷基或C
3-C
6环烷基,或被一个或多个(例如2、3、4个)取代基取代的芳基,所述取代基选自氟、氯、溴、碘、C
1-C
6烷基、C
1-C
6烷氧基、氰基、硝基;
Y选自C,N,O;n+m=4,5,6,7或8;
R
2为C
1-C
6烷基或C
3-C
6环烷基,或一个或多个(例如2、3、4个)氟取代的苯环,
Y选自C,N,O;n+m=5,6或7,
A环为苯环或五元杂芳基,所述杂芳基优选地含1、2或3个氮原子和/或1、2或3个氧原子。
R
2选自环丙基,环己基、异丙基,4-氟苯基,3-氟苯基,3,4-二氟苯基,
Y选自,C,O;n+m=5,6,7或8
A环选自如下5元杂芳基
在某些实施方案中,R'为C
1-C
4烷基,例如甲基、乙基、丙基、异丙基、正丁基、仲丁基、叔丁基。
在某些实施方案中,R'选自环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基。
在某些实施方案中,R
2为被一个或多个(例如2、3、4个)取代基取代的苯基,所述取代基选自氟、氯、溴、碘、C
1-C
6烷基(例如C
1-C
4烷基或C
1-C
3烷基)、C
1-C
6烷氧基(例如甲氧基或乙氧基)、氰基、硝基。
在某些实施方案中,R
2为被一个或多个(例如2、3、4个)取代基取代的苯基,所述取代基选自氟、氯、溴。
在某些实施方案中,R
2为被一个或多个(例如2、3、4个)氟取代的苯基。
在某些实施方案中,R
2为C
3-C
6环烷基。
在某些实施方案中,R
2选自环丙基,环己基、异丙基,4-氟苯基,3-氟苯基,3,4-二氟苯基。
在某些实施方案中,Y为C或O。
在某些实施方案中,n+m=5,6或7。
在某些实施方案中,A环为苯环或五元杂芳基,所述杂芳基含1、2或3个氮原子和/或1、2或3个氧原子。
在某些实施方案中,A环选自如下5元杂芳基
本发明的化合物可以具有选自下面的结构:
在另一方面,本申请提供了制备本发明的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药的方法,所述方法包括:通过如下反应路线合成式5化合物(中间体5):
其中A,R2,m和n如上文所述,反应条件a和b为无机碱,包括但不限于氢氧化钠,碳酸钠,氢氧化锂。
在某些实施方案中,本发明的化合物具有如式6所示的结构,其合成方法可以采用如下的反应路线:
式5化合物可以采用如上文所述的路线制备。
在某些实施方案中,本发明的化合物具有如式7所示的结构,其合成方法可以采用如下的反应路线:
其中反应条件c为无机碱,包括但不限于氢氧化钠,碳酸钠,氢氧化锂。
式5化合物可以采用如上文所述的路线制备。
在某些实施方案中,式2化合物具有式2-1所示的结构,并且式2-1化合物通过如下反应路线制备:
所述反应可以在Cu(I)存在的条件下进行,例如在抗坏血酸和五水合硫酸铜存在的条件下进行。
在某些实施方案中,式2化合物具有式2-2所示的结构,并且式2-2化合物通过如下反应路线制备:
所述反应可以在无机碱(例如碳酸氢钠)存在的条件下进行。
在某些实施方案中,式2化合物具有式2-3所示的结构,并且式2-3化合物通过如下反应路线制备:
本申请还提供了一种药物组合物,其包含至少一种本发明的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药;任选地,所述药物组合物还包含至少一种药学上可接受的赋形剂、载体、介质或助剂。
任选地,所述药物组合物还包含EV71抗病毒剂;在某些实施方案中,所述EV71抗病毒剂是选自3D蛋白酶抑制剂和VP1蛋白抑制剂的抗病毒制剂。
在某些实施方案中,所述药物组合物用于预防/治疗受试者的与病毒感染相关的疾病,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒。其中,所述肠病毒包括但不限于肠病毒71(EV71)、脊髓灰质炎病毒、柯萨奇病毒A、柯萨奇病毒B,所述冠状病毒包括但不限于SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV。在某些实施方案中,所述药物组合物用于预防/治疗受试者的与肠病毒71(EV71)感染相关的疾病或与SARS-CoV-2感染相关的疾病。在某些实施方案中,所述受试者为哺乳动物,例如牛科动物、马科动物、猪科动物、犬科动物、猫科动物、啮齿类动物、灵长类动物。其中,特别优选的受试者为人。
本申请还提供了本发明化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物为病毒蛋白酶抑制剂。
在某些实施方案中,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属(例如柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型)、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒(例如SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV)。
在某些实施方案中,所述蛋白酶为3C/3CL蛋白酶。
本申请还提供了本发明化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物为抗病毒药物;
优选地,所述抗病毒药物针对的病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属(例如柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型)、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒(例如SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV)。
本申请还提供了本发明化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物用于预防/治疗受试者的与病毒感染相关的疾病,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒。其中,所述肠 病毒包括但不限于肠病毒71(EV71)、脊髓灰质炎病毒、柯萨奇病毒A、柯萨奇病毒B,所述冠状病毒包括但不限于SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV。在某些实施方案中,所述受试者为哺乳动物,例如牛科动物、马科动物、猪科动物、犬科动物、猫科动物、啮齿类动物、灵长类动物。其中,特别优选的受试者为人。
在另一个方面,本发明提供了一种预防/治疗受试者的与病毒感染相关的疾病的方法,其包括下列步骤:将预防/治疗有效量的本发明的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药,或者本发明的药物组合物施用于所述受试者,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属(例如柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型)、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒(例如SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV)。在某些实施方案中,所述受试者为哺乳动物,例如牛科动物、马科动物、猪科动物、犬科动物、猫科动物、啮齿类动物、灵长类动物。其中,特别优选的受试者为人。在又一个方面,本申请还提供了具有式5所示结构的化合物及其作为中间体制备本发明的环肽类化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药的用途:
其中A,R2,m和n如上文所述。
术语定义
在本发明中,除非另有说明,否则本文中使用的科学和技术名词具有本领域技术人员通常理解的含义,然而为了更好地理解本发明,下面提供了部分术语的定义。当本发明所提供的术语的定义和解释与本领域技术人员所通常理解的含义不符的时候,以本发明所提供的术语的定义和解释为准。在述及各实例时,(R)或(S)用于指明不对称 中心的绝对构型,这指明是用于整个化合物的说明而不是单独取代基的说明。
本文所用的“C
1-C
6烷基”是指具有1-6个碳原子的直链或支链烷基,例如甲基、乙基、丙基、异丙基、正丁基、仲丁基、叔丁基、戊基、2-戊基、异戊基、新戊基、己基、2-己基、3-己基等;C1-C3烷基也可做类似理解。优选的是C
1-C
3烷基。
本文所用的“C
1-C
6烷氧基”是指具有1-6个碳原子的直链或支链烷氧基,例如甲氧基、乙氧基、丙氧基、异丙氧基、正丁氧基、仲丁氧基、叔丁氧基、戊氧基、2-戊氧基、异戊氧基、新戊氧基、己氧基、2-己氧基、3-氧己基等;C
1-C
3烷氧基也可做类似理解。优选的是C
1-C
3烷氧基。
本文所用的“芳基”一词,意指含有6个碳原子的芳香族单环系统,或含有10个原子的芳香族双环系统,例如苯基和萘基-环系统。
本文所用的“杂芳基”一词,单独使用或与另一取代基组合使用时,意指通过环碳原子或杂环原子(例如氮原子)连接的具有例如1,2或3个选自N,0,S的杂原子的五元,六元或七元不饱和的杂环移除氢而衍生的单价取代基。适当的杂芳基实例如:噻吩,呋喃,吡咯,咪唑,吡唑,噻唑,噁唑,异噁唑,1,2,3-三唑。
本文所用的“C
3-C
6环烷基”是指含有3-6个环原子的饱和或部分饱和的且不具有芳香性的单环环状基团,包括“3-6元饱和环烷基”和“3-6元部分饱和环烷基”,例如“5-6元环烷基”、“5-6元饱和环烷基”等。其实例包括但不限于:环丙基、环丁基、环戊基、环己基或环己烯基等。
本文所用的术语“立体异构体”表示由于至少一个不对称中心形成的异构体。在具有一个或多个(例如一个、两个、三个或四个)不对称中心的化合物中,其可产生外消旋混合物、单一对映异构体、非对映异构体混合物和单独的非对映异构体。特定个别分子也可以几何异构体(顺式/反式)存在。类似地,本发明的化合物可以两种或更多种处于快速平衡的结构不同的形式的混合物(通常称作互变异构体)存在。互变异构体的代表性实例包括酮-烯醇互变异构体、苯酚-酮互变异构体、亚硝基-肟互变异构体、亚胺-烯胺互变异构体等。要理解,本申请的范围涵盖所有这样的以任意比例(例如60%、65%、70%、75%、80%、85%、90%、95%、96%、97%、98%或99%)的异构体或其混合物。
本发明涵盖本发明的化合物的所有可能的结晶形式或多晶型物,其可为单一多晶型物或多于一种多晶型物的任意比例的混合物。
还应当理解,本发明的某些化合物可以游离形式存在用于治疗,或适当时,以其药学上可接受的衍生物形式存在。在本发明中,药学上可接受的衍生物包括但不限于, 可药用盐、溶剂化物、代谢物或前药,在将它们向需要其的患者给药后,能够直接或间接提供本发明的化合物或其代谢物或残余物。
本文中“药物上可接受的盐”一词是指式(M)化合物的盐,其在正常医学治疗中,适用于人及动物的组织接触而无毒性,无刺激性,无过敏反应等。一般是水溶性或油溶性,或是易分散的,并在其使用上是有效的。此词包括药物上可接受的酸加成盐和药物上可接受的碱加成盐。
“药物上可接受的酸加成盐”一词是指保持生物活性及游离态碱的性质,并且是非生物上或其他方面不需要的,其与无机酸如硫酸、硝酸、磷酸、盐酸、氨基磺酸等,及有机酸如醋酸、三氟醋酸、三氯醋酸、肉桂酸、柠檬酸、马来酸、己二酸、藻酸、抗坏血酸、天冬氨酸、苯甲酸、苯磺酸、乙醇酸、苹果酸、乳酸、丙二酸、草酸、烟酸、丁二酸、水杨酸、硬脂酸、酒石酸、对氨基苯磺酸、三甲基苯磺酸、对甲基苯磺酸、扁桃酸、果胶酯酸、苦味酸、丙酸等所形成的盐。
“药物上可接受的碱加成盐”一词是指保持生物活性及游离态酸的性质,并且是非生物上或其他方面不需要的,其是与无机碱如氨或铵或金属阳离子如钠、镁、铜、锌、钙、钾、铝等的磺酸盐所形成的盐,特别优选的是铵、钾、钠、钙、镁盐。由药物上可接受的有机的非毒性的碱衍生的盐包括伯胺、仲胺及叔胺、季铵化合物,经取代的胺,包括天然的经取代的胺,环胺以及碱离子交换树脂,如甲基胺、二甲基胺、三甲基胺、乙基胺、二乙基胺、三乙基胺、三丙基胺、异丙基胺、三丁基胺、乙醇胺、二乙醇胺、二环己基胺、赖氨酸、精氨酸、组氨酸、咖啡因、胆碱、甜菜碱、亚乙基二胺、葡糖胺、甲基葡糖胺、可可碱。
本文所用的术语“溶剂化物”是指化合物与溶剂分子缔合形成的物质。所述溶剂可以是水或有机溶剂(例如甲醇、乙醇、丙醇、乙腈等)等。
在本发明的范围内还包括本发明的化合物的代谢物,即在给药本发明的化合物时体内形成的物质。这样的产物可由例如被给药的化合物的氧化、还原、水解、酰胺化、脱酰胺化、酯化、脱脂化、酶解等产生。因此,本发明包括本发明的化合物的代谢物,包括通过使本发明的化合物与哺乳动物接触足以产生其代谢产物的时间的方法制得的化合物。
本发明在其范围内进一步包括本发明的化合物的前药。通常这样的前药会是所述化合物的官能团衍生物,其易于在体内转化成期望的治疗活性化合物。因此,在这些情况中,用于本发明的治疗方法的术语“给药”应包括用所要求保护的化合物中的一种或多种的前药形式来治疗各种疾病或病症,但是在向个体给药后所述前药形式在体内转化成上述化合物。例如,在“Design of Prodrug”,ed.H.Bundgaard,Elsevier,1985中,描述了选择和制备适 合的前药衍生物的常规方法。
本发明在其范围内进一步包括本发明的化合物的稳定同位素衍生物,其与本发明的化合物相同,除了一个或多个原子被具有相同原子序数但原子质量或质量数不同于在自然界中占优势的原子质量或质量数的原子替代。
本发明还涵盖含有保护基的本发明的化合物。在制备本发明的化合物的任何过程中,保护在任何有关分子上的敏感基团或反应基团可能是必需的和/或期望的,由此形成本发明的化合物的化学保护的形式。这可以通过常规的保护基实现,例如,在Protective Groups in Organic Chemistry,ed.J.F.W.McOmie,Plenum Press,1973;和T.W.Greene&P.G.M.Wuts,Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis,John Wiley&Sons,1991中所述的那些保护基,这些参考文献通过援引加入本文。使用本领域已知的方法,在适当的后续阶段可以移除保护基。
本发明包含有治疗量本发明化合物的药物,和一种或多种药学上可接受载体和/或赋形剂的药物组合物。载体包括如盐水、缓冲盐水、葡萄糖、水、甘油、乙醇和它们的结合物。载体或赋形剂还可以包括本领域已知的时间延迟材料,如单硬脂酸甘油酯或二硬脂酸甘油酯,还可包括蜡、乙基纤维素、羟丙基甲基纤维素、异丁烯酸甲酯等等。如果需要,该组合物还可以包含较小量的润湿剂或乳化剂,或pH缓冲剂。该组合物可以是液体、悬浮液、乳剂、片剂、丸剂、胶囊、持续释放制剂或粉末。该组合物可以用传统的黏合剂和载体如三酸甘油酯配制成栓剂。口服制剂可以包括标准载体如药物品级的甘露糖醇、乳糖、淀粉、硬脂酸镁、糖精钠、纤维素和碳酸镁等等。视需要制剂而定,配制可以设计混合,制粒和压缩或溶解成分。在另一个途径中,该组合物可以配制成纳米颗粒。
本发明包含的药物组合物的活性成分可以具有全身和/或局部作用,因此,其可以以适宜的途径进行给药,所说的适宜途径如口服、胃肠外、肺、鼻、舌下、舌、颊、直肠、经皮、结膜、局部给药或以植入物的形式给药。该活性成分还可以以适于这些给药途径的给药形式进行给药。适于口服给药的有可以迅速和/或以改变的方式传递活性成分的公知的给药形式,如片剂(未包衣片或包衣片,如具有肠包衣或莫包衣的片剂)、胶囊、糖衣片、颗粒、小药丸、粉剂、乳剂、混悬液和气雾剂。采用胃肠外给药可能可避免吸收步骤(静脉内、动脉内、心内、脊柱内或腰髓内给药)或者包含吸收(肌内、皮下、皮内、经皮或腹膜内给药)。适于胃肠外给药的给药形式特别是用于注射和输入的溶液、混悬液、乳剂、冷冻干燥物和无菌粉末形式的制剂。适于其他给药途径的有例如吸入(特别是粉末吸入、喷雾)的药物、鼻滴剂/溶液、喷雾剂;用于舌、舌下或颊给药的片剂或胶囊、栓剂、用于耳朵和眼睛的制剂、阴道胶囊、水性混悬液(洗剂、振摇混合物)、亲脂性混悬液、软膏、乳膏、乳液、糊剂、撒粉或植入物,如斯腾特固定模。可以用本身已知的方法将该活性成 分转化成所述的给药形式。其可以用惰性无毒的适宜药用赋形剂来实现。其特别是包括载体(例如微晶纤维素)、溶剂(例如液体聚乙二醇)、乳化剂(例如十二烷基硫酸钠)、分散剂(例如聚乙烯吡咯烷酮)、合成和天然生物聚合物(例如蛋白质)、稳定剂(例如抗氧剂和抗坏血酸)、着色剂(例如无机颜料如氧化铁)或矫味剂和/或掩味剂。在适宜的情况中,所说的活性成分可以以微囊包封的形式存在于一种或多种上述载体中。除本发明式M的化合物外,上述药物制剂还可以包含其他药物活性成分。
制备方法
本发明还涉及制备本发明式M化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药的合成方法,包括:
工艺流程Ⅰ:中间体1~6的合成
工艺流程Ⅱ:
中间体7~9、13-1、13-2、14-1、14-2、15、16-1、16-2、17-1、17-2、18-1、18-2的合成
工艺流程Ⅲ:
中间体19~25的合成
工艺流程Ⅳ:
中间体26~29的合成
下述实施例中所使用的实验方法如无特殊说明,均为常规方法。
下述实施例中所用的材料、试剂等,如无特殊说明,均可从商业途径得到。
下面的实施例是本发明优选的说明性优选方案,对本发明不构成任何限制。
实施例1 2-(辛-7-炔-1-基)异二氢吲哚-1,3-二酮(1)的合成
室温下,将乙炔锂乙二胺复合物(11.2g,130mmol)加入至100mL无水二甲亚砜中,搅拌溶解,氮气保护。降温至0℃,向反应液中滴加1-氯-6-溴(11.2g,130mmol),然后将反应液在室温搅拌20小时。反应完毕,将反应液于冰浴下滴加50mL饱和氯化铵水溶液以淬灭反应。加入饱和食盐水和乙醚分液,水相用乙醚萃取,合并有机相。有机相用饱 和柠檬酸洗涤,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩,得无色澄清液体。将此无色澄清液体加入至DMF中,再加入酞酰亚胺钾(20g,110mmol)。然后将反应液在80℃搅拌18小时。TLC监测反应完全,减压蒸发除去溶剂,将残余物溶于60mL乙酸乙酯中,加入水30mL分液,收集有机相,减压蒸发除去溶剂,干燥,得到粗品。向粗品中加入100ml石油醚,打浆过滤。收集滤液,减压蒸发除去溶剂,得白色固体。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ7.87–7.65(m,4H),2.68(s,1H),2.08(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),1.52(d,J=6.3Hz,2H),1.45–1.15(m,6H).
实施例2 5-(6-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)己基)异恶唑-3-羧酸甲酯(2)的合成
室温下,将中间体1(11.2g,130mmol)加入至乙醇和水的混合溶液中,搅拌溶解,向反应液中滴加水合肼(11.2g,130mmol),然后将反应液在75℃搅拌2小时。反应完毕,将反应液于冰浴下滴加12N盐酸水溶液至反应液ph=2。过滤,收集滤液。减压蒸发除去溶剂,将残余物溶于0.1N盐酸水溶液,DCM萃取水相,收集水相,将水相用NaOH固体调ph=14,乙醚萃取水相,收集有机相,减压蒸发除去溶剂得无色澄清液体。将此无色澄清液体加入至DCM中,再依次滴加Boc酸酐(20g,110mmol),TEA,然后将反应液在室温搅拌18小时.反应完毕,用饱和氯化铵水溶液淬灭反应,加入水,分液收集有机相。有机相用饱和柠檬酸洗涤,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩,得无色液体。将此无色液体加入至乙酸乙酯和水的混合溶液中,搅拌溶解,然后加入碳酸氢钠。降温至0℃,向反应液中滴加氯代肟基乙酸乙酯(11.2g,130mmol)的乙酸乙酯溶液,然后将反应液室温搅拌10小时。分批次滴加氯代肟基乙酸乙酯(11.2g,130mmol)的乙酸乙酯溶液,室温搅拌8小时。反应完毕,向反应液中加入水,分液,收集有机相,有机相用饱和柠檬酸洗涤,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩,得无色澄清液体。柱色谱分离得白色固体。
1H NMR(400MHz,Chloroform-d)δ4.40(d,J=14.5Hz,2H),3.08(s,2H),2.79(d,J=7.4Hz,2H),1.42-1.40(m,11H),1.37(d,J=9.1Hz,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):326.18[M+H]
+
实施例3(S)-2-(5-(6-((叔丁氧羰基羰基)氨基)己基)异恶唑-3-羧酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苯基)丙酸甲酯(3)的合成
0℃下,将中间体2(1.83g,6mmol)加入至10mL四氢呋喃中,搅拌溶解。向反应液中分批次加入氢氧化锂(0.4g,9.6mmol)的10ml水溶液中。然后将反应液在室温搅拌4小时。反应完毕,反应液用饱和柠檬酸溶液调pH值为7。减压除去溶剂,将残余物加入10ml冰水中,水相用饱和柠檬酸溶液调pH值为2。二氯甲烷(10mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,0.01N盐酸洗,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩得到白色固体。将此白色固体加入至50mL无水二氯甲烷中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,向反应液中加入1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐(4.70g,24mmol)、1-羟基苯并三唑(3.20g,24mmol)。于0℃下反应1h。向反应液中加入L-4-氟苯丙氨酸一甲酯(4.70g,24mmol)。再向反应液中滴加N,N-二异丙基乙胺(DIPEA)(7.8g,60mmol)。然后将反应液在室温搅拌8小时。反应完毕,向反应液中加入20mL饱和氯化铵水溶液以淬灭反应。分层收集有机层,有机层用饱和柠檬酸水溶液洗涤,饱和碳酸氢钠水溶液洗涤,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩得到白色固体4粗品。柱色谱分离得到白色固体(3),
1H NMR(400MHz,Chloroform-d)δ7.22–7.15(m,1H),7.12(s,2H),6.96(s,2H),6.39(s,1H),4.99(s,1H),3.72(s,3H),3.10(s,4H),2.78(s,2H),1.69(s,2H),1.43(s,11H),1.35(s,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):491.24[M+H]
+
实施例4 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(5-(6-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)己基)异恶唑-3-羧酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苯基)丙酰基)-谷氨酸(4)的合成
0℃下,将中间体4(1.83g,6mmol)加入至10mL四氢呋喃中,搅拌溶解。向反应液中分批次加入氢氧化锂(0.4g,9.6mmol)的10ml水溶液中。然后将反应液在室温搅拌4小时。反应完毕,反应液用饱和柠檬酸溶液调pH值为7。减压除去溶剂,将残余物加入10ml冰水中,水相用饱和柠檬酸溶液调pH值为2。二氯甲烷(10mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,0.01N盐酸洗,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩得到白色固体。将此白色固体加入至50mL无水二氯甲烷中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,向反应液中加入1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳 二亚胺盐酸盐(4.70g,24mmol)、1-羟基苯并三唑(3.20g,24mmol)。于0℃下反应1h。向反应液中加入叔丁基-L-谷氨酸甲酯盐酸盐(4.70g,24mmol)。再向反应液中滴加N,N-二异丙基乙胺(DIPEA)(7.8g,60mmol)。然后将反应液在室温搅拌8小时。反应完毕,向反应液中加入20mL饱和氯化铵水溶液以淬灭反应。分层收集有机层,有机层用饱和柠檬酸水溶液洗涤,饱和碳酸氢钠水溶液洗涤,饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩得到白色固体4粗品。加入50ml石油醚打浆,过滤固体,得到白色固体(4),
1H NMR(400MHz,Chloroform-d)δ7.33(s,1H),7.18(s,2H),6.96(s,2H),6.80(s,1H),6.70(s,1H),6.38(s,1H),4.80(s,1H),4.50(s,2H),3.68(s,3H),3.08(s,4H),2.75(s,2H),2.14(d,J=40.5Hz,4H),1.67(s,2H),1.42(s,24H).ESI-MS(m/z):676.35[M+H]
+
实施例5 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酸甲酯(5)的合成
室温下,将中间体5加入至8mL二氯甲烷中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,向反应液中滴加8mL三氟乙酸。室温反应12h。反应完毕,将反应液旋干,将残余物加入至15mlDMF中,降温至0℃,加入1-(3-二甲氨基丙基)-3-乙基碳二亚胺盐酸盐(4.70g,24mmol)、1-羟基苯并三唑(3.20g,24mmol)。0℃下搅拌1h,将反应液滴加至-40℃预冷的DCM与DIPEA混合溶液中(600ml/10ml)。自然升温至室温,缓慢搅拌12h。反应完毕,向反应液中加入20mL饱和氯化铵水溶液以淬灭反应。分层收集有机层,有机层用饱和柠檬酸水溶液洗涤,饱和碳酸氢钠水溶液洗涤,收集有机层旋干,将残余物溶于20mlEA中,用水洗,用饱和食盐水洗涤、干燥。浓缩得到白色固体4粗品。柱色谱分离得到白色固体(5)
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.94(d,J=12.1Hz,2H),7.87(s,1H),7.34(s,2H),7.06(s,2H),6.67(s,1H),4.44(s,1H),4.20(s,1H),3.65(s,3H),3.28–2.67(m,6H),2.13(s,2H),1.87(d,J=10.9Hz,2H),1.62(s,2H),1.24(s,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):502.22[M+H]
+
实施例6 (4S,7S,Z)-7-(2-氯乙酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-2,5,10-三酮(6)的合成
室温下向三口瓶中加入中间体5(10g,35mmol),THF(200mL)和氯碘甲烷(10.2mL,140mmol),氮气保护,并将溶液冷却至-77℃。滴加LDA(140mL,210mmol,在环己烷中的1.5M单-THF络合物)是通过均压滴液漏斗添加的速率保持内部温度低于-70℃。完成添加后,将反应搅拌另外1小时,并用NaHCO 3淬灭。添加速率的AcOH(33mL)和THF(200mL)的混合物调节温度以保持内部温度低于-65℃。后完全添加后,将深色悬浮液搅拌10分钟并然后加热到环境温度。反应被稀释用乙酸乙酯(500mL)洗涤,并将有机物用水洗涤(250mL),饱和。将NaHCO3(250毫升)和盐水(250毫升)干燥用硫酸镁干燥,过滤,并真空除去溶剂,得到硫酸钠。粗产物,为黑油,经急骤纯化层析,用乙酸乙酯洗脱。所得固体为用乙醚研磨,得到标题化合物,为浅色黄色固体。
ESI-MS(m/z):520.19[M+H]
+
实施例7 1-(6-(((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)己基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-羧酸乙酯(7)的合成
将(6-羟基己基)氨基甲酸叔丁酯(1.83g,6mmol)加入至60mlDCM中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,滴加三乙胺(1.83g,6mmol)后于1h内向反应液中滴加甲基磺酰氯(0.4g,9.6mmol)。然后将反应液在0℃下搅拌2小时。反应完毕,将反应浓缩,残余物加入30mlDMF中,搅拌均匀,向反应液中加入叠氮化钠(0.4g,9.6mmol),然后将反应液在80℃搅拌18小时。反应完毕,减压蒸发除去溶剂,将残余物溶于50mlDCM溶液中,分别用水,饱和氯化铵水溶液洗有机相。旋干有机相,溶于50ml正己烷中,用水洗,用饱和食盐水洗涤、无水硫酸钠除水,浓缩得到无色液体。将此无色液体加入至叔丁醇和水的混合溶液中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃依次加入丙炔酸甲酯(1.83g,6mmol),抗坏血酸钠(1.83g,6mmol),五水合硫酸铜(1.83g,6mmol),然后将反应液在室温下搅拌12小时。反应完毕,减压蒸 发除去溶剂,残余物溶于100mlDCM中,用水洗,饱和碳酸氢钠溶液洗,用饱和食盐水洗涤、无水硫酸钠除水,减压蒸发除去溶剂,将残余物加入100ml石油醚打浆过滤的白色固体。
1H NMR(400MHz,Chloroform-d)δ8.07(s,1H),4.38(s,2H),3.92(s,3H),3.04(s,2H),1.91(s,2H),1.40(s,11H),1.31(s,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):340.21[M+H]
+
实施例8 1-(7-(((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)庚基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-羧酸甲酯(11)的合成
按照中间体7的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,Chloroform-d)δ8.07(s,1H),4.41(t,J=7.2Hz,2H),3.96(s,3H),3.09(s,2H),1.93(p,J=7.2Hz,2H),1.44(s,12H),1.38–1.27(m,7H).ESI-MS(m/z):363.19[M+Na]
+
实施例9 (S)-2-(1-(6-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)己基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-羧酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苯基)丙酸甲酯(8)的合成
按照合成中间体3的方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.78(s,1H),8.55(s,1H),7.29(s,2H),7.07(s,2H),6.77(s,1H),4.69(s,1H),4.37(s,2H),3.64(s,3H),3.16(s,2H),2.86(s,2H),1.80(s,2H),1.36(s,11H),1.23(s,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):491.25[M+H]
+
实施例10 (S)-2-(1-(7-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)庚基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苄基)丙酸甲酯(13-1)的合成
按照中间体3的合成方法。1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.74(d,J=8.2Hz,1H), 8.55(s,1H),7.38–7.22(m,2H),7.18–6.97(m,2H),6.75(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),4.79–4.63(m,1H),4.38(t,J=7.1Hz,2H),3.64(s,2H),3.20–3.07(m,2H),2.87(q,J=6.6Hz,2H),1.85–1.76(m,2H),1.36(s,11H),1.28–1.16(m,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):506.27[M+H]
+
实施例11 (S)-2-(1-(7-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)庚基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酸甲酯(13-2)的合成
按照中间体3的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.82(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),8.54(s,1H),7.39–7.34(m,1H),7.32–7.26(m,1H),7.11(s,1H),6.74(s,1H),4.75–4.71(m,1H),4.37(t,J=7.1Hz,2H),3.65(s,3H),3.21–3.11(m,2H),2.87(d,J=6.4Hz,2H),1.84–1.78(m,2H),1.35(s,11H),1.22(d,J=33.2Hz,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):524.27[M+H]
+
实施例12 (S)-2-(1-(8-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)辛基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酸甲酯(14-2)的合成
按照合成中间体3的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.82(d,J=8.3Hz,1H),8.54(s,1H),7.38–7.34(m,1H),7.33–7.26(m,1H),7.10(s,1H),6.74(t,J=5.4Hz,1H),4.77–4.71(m,1H),4.37(t,J=7.1Hz,2H),3.65(s,3H),3.21–3.10(m,2H),2.90–2.85(m,2H),1.84–1.78(m,2H),1.36(s,11H),1.22(d,J=17.8Hz,8H).ESI-MS(m/z):538.28[M+H]
+
实施例13 5-(叔丁基)-1-甲基((s)-2-(1-(6-(叔丁氧羰基)氨基)己基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-羧氨基)-3-(4-氟苄基)丙酰基-谷氨酸(9)的合成
按照合成中间体4的方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.53(s,2H),8.26(s,1H),7.27(t,J=8.4Hz,2H),7.03(s,2H),6.75(s,1H),5.72(s,0H),4.72(d,J=12.5Hz,1H),4.34(s,3H),3.60(s,3H),3.02(s,2H),2.84(s,2H),2.21(d,J=42.3Hz,2H),1.84(d,J=63.0Hz,4H),1.34(s,20H),1.18(s,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):577.28[M+H]
+
实施例14 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(1-(7-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)庚基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苄基)丙酰基)-L-谷氨酸(15-1)的合成
按照中间体4的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.53(d,J=12.0Hz,2H),8.27(s,1H),7.30(dd,J=8.6,5.7Hz,2H),7.06(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.74(s,1H),4.76(td,J=9.0,4.7Hz,1H),4.40–4.31(m,3H),3.64(s,3H),3.11–3.00(m,2H),2.87(d,J=6.5Hz,2H),2.29(td,J=7.1,6.5,2.1Hz,2H),2.03–1.94(m,1H),1.81(dd,J=9.4,5.1Hz,3H),1.37(d,J=13.2Hz,20H),1.27–1.17(m,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):713.34[M+Na]
+
实施例15 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(1-(7-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)庚基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酰基)-L-谷氨酸(15-2)的合成
按照中间体4的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.54(s,1H),8.52(d,J=7.6 Hz,1H),8.34(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),7.36–7.26(m,2H),7.11(s,1H),6.74(t,J=5.4Hz,1H),4.77(q,J=4.2Hz,1H),4.37(t,J=7.0Hz,2H),4.34(s,1H),3.63(s,3H),3.11–3.00(m,2H),2.87(q,J=6.6Hz,2H),2.69(s,1H),2.29(t,J=8.0Hz,2H),1.96(d,J=5.6Hz,1H),1.85–1.77(m,3H),1.39–1.31(m,20H),1.22(dt,J=33.3,7.0Hz,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):709.37[M+H]
+
实施例16 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(1-(8-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)辛基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-甲酰胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酰基)-L-谷氨酸(16-2)的合成
按照中间体4的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.54(s,1H),8.51(s,1H),8.33(s,1H),7.36–7.26(m,2H),7.12(s,1H),6.74(s,1H),4.76(td,J=9.0,4.7Hz,1H),4.45–4.30(m,3H),3.63(s,3H),3.11–3.00(m,2H),2.87(q,J=6.7Hz,2H),2.31–2.26(m,2H),2.00–1.94(m,1H),1.81(q,J=7.1Hz,3H),1.37(t,J=10.0Hz,20H),1.28–1.14(m,8H).ESI-MS(m/z):745.37[M+Na]
+
实施例17 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十七烷-7-羧酸甲酯(10)的合成
按照合成中间体5的方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.87–8.58(m,3H),8.54(s,1H),7.59(d,J=37.5Hz,1H),7.35–7.15(m,2H),7.10–6.94(m,2H),4.55–4.26(m,3H),4.17–4.03(m,1H),3.59(s,3H),3.16–3.02(m,1H),2.90–2.67(m,1H),2.72–2.57(m,1H),2.15–1.89(m,2H),1.88–1.64(m,3H),1.38–0.87(m,6H)..ESI-MS(m/z):502.23[M+H]
+
实施例18 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十八烷-7-羧酸甲酯(17-1)的合成
按照合成中间体5的方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.76(s,1H),8.60(d,J=10.4Hz,2H),7.46(s,1H),7.33–7.28(m,2H),7.05(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.64(ddd,J=10.1,8.5,4.6Hz,1H),4.47(ddd,J=11.6,7.4,3.8Hz,1H),4.39(ddd,J=13.4,7.3,4.1Hz,1H),4.25(ddd,J=10.4,6.9,3.9Hz,1H),3.62(s,3H),3.17(dd,J=14.0,4.6Hz,1H),3.03(dd,J=14.1,10.2Hz,1H),2.75(dt,J=21.1,8.0Hz,2H),2.16–2.08(m,2H),1.94(ddd,J=13.0,6.2,2.6Hz,1H),1.83(s,2H),1.76(tt,J=9.0,5.7Hz,1H),1.24(s,2H),1.08(t,J=7.0Hz,4H),0.96(s,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):517.25[M+H]
+
实施例19 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十八烷-7-羧酸甲酯(17-2)的合成
按照合成中间体5的方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d6)δ8.76(d,J=6.8Hz,1H),8.67(d,J=8.6Hz,1H),8.59(s,1H),7.47(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),7.37–7.31(m,1H),7.27(d,J=10.8Hz,1H),7.11(s,1H),4.66(td,J=8.9,4.8Hz,1H),4.47(td,J=8.3,7.3,3.8Hz,1H),4.42–4.36(m,1H),4.24(dt,J=6.1,2.9Hz,1H),3.62(s,3H),3.18(dd,J=13.9,4.7Hz,1H),3.06–3.00(m,1H),2.80–2.68(m,2H),2.12(q,J=5.9Hz,2H),1.98–1.90(m,1H),1.83(s,2H),1.79–1.71(m,1H),1.13–0.91(m,8H).ESI-MS(m/z):535.25[M+H]
+
实施例20 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十九烷-7-羧酸甲酯(18-2)的合成
按照合成中间体5的方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.65(s,1H),8.41(s,1H),7.40–7.29(m,2H),7.21(s,1H),7.13(s,1H),4.63(ddd,J=9.1,5.5,3.9Hz,1H),4.53–4.45(m,1H),4.41–4.30(m,2H),3.62(s,3H),3.07(qd,J=13.9,7.5Hz,2H),2.97(dd,J=13.3,6.4Hz,1H),2.83–2.76(m,1H),2.15–1.97(m,3H),1.89–1.78(m,2H),1.77–1.68(m,1H),1.24–0.91(m,10H).ESI-MS(m/z):549.25[M+H]
+
实施例21 5-(2-(3-((叔丁氧基羰基)氨基)丙氧基)乙基)异恶唑-3-羧酸乙酯(19)的合成
将(3-羟丙基)氨基甲酸叔丁酯(10g,57.1mmol)在0℃下溶解于二氯甲烷,缓慢滴加三乙胺(14.44g,0.14mol),将反应液置于0℃下搅拌1小时,然后缓慢滴加MSC(8.5g,74.19mmol),继续搅拌反应8小时。反应完毕,将反应液依次用水、饱和柠檬酸溶液和饱和氯化钠溶液萃取,旋干有机相,得到黄色透明固体。将黄色固体产物(14.46g,57.07mmol)溶于少量甲苯,将3-丁炔-1-醇(8.0g,0.11mol)溶于甲苯,加热至60℃,15分钟后加入四丁基溴化铵(917.2mg,2.85mmol)搅拌15分钟。然后加入氢氧化钠固体(2.97g,74.19mmol),升温至75℃。30分钟后,滴加黄色固体产物的甲苯溶液,加入完毕后升温至85℃,继续搅拌8小时。反应结束,用饱和氯化铵溶液洗涤反应体系,旋干有机相,得到黄色液体。将产物黄色液体(9.640g,57.07mmol)和碳酸氢钠固体(3.12g,37.09mmol)溶于乙酸乙酯与水(100:1)混合溶液中,降温至0℃。(Z)-2-氯-2-(羟基亚氨基)乙酸乙酯(5.62g,37.09mmol)溶于50ml乙酸乙酯,控制温度15~20℃,加入至上述反应体系。2小时后,将剩余的碳酸氢钠固体(3.12g,37.02mmol)和(Z)-2-氯-2-(羟基亚氨基)乙酸乙 酯(5.62g,37.09mmol)的乙酸乙酯溶液加入至反应体系,控温15~20℃搅拌反应。反应结束后,依次用水、饱和柠檬酸水溶液和饱和氯化钠溶液洗涤有机相,旋干有机相,经柱层析纯化后,得到中间体19(9.710g,45%)。
1H NMR(400MHz,Chloroform-d)δ6.49(s,1H),4.75(s,1H),4.50–4.33(m,2H),3.71(t,J=6.3Hz,2H),3.49(d,J=12.0Hz,2H),3.16(q,J=8.0,7.0Hz,4H),3.11–3.00(m,2H),1.79–1.65(m,2H),1.41–1.37(m,12H),ESI-MS(m/z):243.13[M+H]
+
实施例22 (S)-2-(5-(2-(4-((叔丁氧羰基)氨基)丙氧基)乙基)异恶唑-3-羧酸胺基)-3-(4-氟苄基)丙酸甲酯(20)的合成
按照中间体3的合成方法。1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ9.10(d,J=8.1Hz,1H),7.30(dd,J=8.8,5.6Hz,2H),7.08(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.79(t,J=5.5Hz,1H),6.55(s,1H),4.67(ddd,J=10.1,8.1,5.2Hz,1H),3.64-3.67(m,5H),3.39(t,J=6.3Hz,2H),3.21–3.07(m,2H),3.03(t,J=6.2Hz,2H),2.93(q,J=6.7Hz,2H),1.57(p,J=6.5Hz,2H),1.36(s,9H)。ESI-MS(m/z):516.20[M+Na]+
实施例23 (S)-2-(5-(2-(4-((叔丁氧羰基)氨基)丙氧基)乙基)异恶唑-3-羧酸胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酸甲酯(21)的合成
按照中间体3的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,Chloroform-d)δ7.08(s,1H),6.98(s,1H),6.87(s,1H),6.51(s,1H),5.00(s,1H),3.76(s,3H),3.74(s,2H),3.51(s,2H),3.24–3.10(m,4H),3.06(s,2H),1.74(s,2H),1.44(s,6H),1.25(s,3H).ESI-MS(m/z):534.20[M+Na]
+
实施例24 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(5-(2-(4-((叔丁氧羰基羰基)氨基)丙氧基)乙基异恶唑-3-羧酰胺基)-3-(4-氟苄基)丙酰基)-L-谷氨酸(22)的合成
按照中间体4的合成方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d4)δ7.27(dd,J=8.7,5.4Hz,2H),7.02–6.93(m,2H),6.48(s,1H),4.80(dd,J=8.6,5.8Hz,1H),4.50–4.42(m,1H),3.70(d,J=9.9Hz,5H),3.51–3.43(m,2H),3.20(dd,J=13.9,5.8Hz,1H),3.10–2.94(m,5H),2.30(d,J=14.9Hz,2H),2.15–2.05(m,1H),1.92–1.82(m,1H),1.72–1.63(m,2H),1.40(s,17H).ESI-MS(m/z):679.33[M+H]
+
实施例25 5-(叔丁基)1-甲基((S)-2-(5-(2-(4-((叔丁氧羰基羰基)氨基)丙氧基)乙基异恶唑-3-羧酰胺基)-3-(3,4-二氟苄基)丙酰基)-L-谷氨酸(23)的合成
按照中间体4的合成方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.70(s,1H),8.54(s,1H),7.34(s,2H),7.13(s,1H),6.77(s,1H),6.56(s,1H),4.75(s,1H),4.35(dt,J=8.4,4.3Hz,1H),3.66(d,J=8.4Hz,5H),3.42(s,2H),2.98(d,J=45.0Hz,6H),2.29(s,2H),1.97(s,1H),1.84(s,1H),1.61(s,2H),1.40(s,9H),1.38(s,9H).ESI-MS(m/z):697.32[M+H]
+
实施例26 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酸甲酯(24)的合成
按照中间体6的合成方法。
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d4)δ7.25(s,2H),7.00–6.92(m,2H),6.64(s,1H),4.81(s,1H),4.26(s,1H),3.69(s,5H),3.37(s,2H),2.95(d,J=58.0Hz,6H),2.23(s,2H),1.99(s,2H),1.50(s,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):505.21[M+H]
+
实施例27 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酸甲酯(25)的合成
按照中间体6的合成方法。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.47(d,J=5.2Hz,1H),8.91(d,J=9.1Hz,1H),7.88(t,J=5.7Hz,1H),7.38–7.22(m,2H),7.08(t,J=6.7Hz,1H),6.68(s,1H),4.67–4.62(m,1H),4.14(dt,J=9.2,4.7Hz,1H),3.66(q,J=5.4Hz,2H),3.62(s,3H),3.04–2.76(m,4H),2.20(qdd,J=16.7,7.5,3.6Hz,2H),1.93–1.79(m,2H),1.43(dddd,J=16.0,13.0,8.1,5.5Hz,2H),1.23(d,J=6.2Hz,2H),0.85–0.73(m,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):523.19[M+H]
+
实施例28 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-甲醛(Ⅰ)的合成
室温下,将中间体5(1.83g,6mmol)加入至四氢呋喃和乙醇混合溶液中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,向反应液中依次加入氯化钙(0.4g,9.6mmol)、硼氢化钠(0.4g,9.6mmol)。 然后将反应液于20℃搅拌6小时。反应完毕,反应液用饱和氯化铵淬灭。减压除去溶剂,将残余物加入10ml水打浆过滤,干燥。得到白色固体。将此白色固体加入至DCM和DMF的混合溶液中,加入戴斯马丁氧化剂(0.4g,9.6mmol),然后将反应液于20℃搅拌10小时。反应完毕,向反应液中加入饱和碳酸氢钠水溶液淬灭反应。将反应液旋干,将残余物加入10ml水打浆过滤,干燥。得到白色固体粗品。柱色谱分离得白色固体。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.08(s,1H),8.94(d,J=12.1Hz,2H),7.87(s,1H),7.34(s,2H),7.06(s,2H),6.67(s,1H),4.44(s,1H),4.20(s,1H),3.65(s,3H),3.28–2.67(m,6H),2.13(s,2H),1.87(d,J=10.9Hz,2H),1.62-1.56(m,2H),1.24-1.20(m,6H).ESI-MS(m/z):472.21[M+H]
+
实施例29 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十七烷-7-甲醛(Ⅱ)
按照化合物Ⅰ的合成方法,以中间体10为原料合成化合物Ⅱ。
1H NMR(500MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.38(d,J=6.5Hz,1H),8.92–8.66(m,2H),8.63(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),7.74–7.56(m,1H),7.34(dt,J=13.6,6.9Hz,3H),7.08(q,J=8.5Hz,3H),4.71–4.50(m,1H),4.49–4.32(m,4H),4.22–3.94(m,1H),3.27–3.06(m,3H),2.96–2.57(m,2H),2.23–1.93(m,2H),1.91–1.66(m,9H),1.24(t,J=20.7Hz,3H),1.13–0.91(m,4H).ESI-MS(m/z):472.22[M+H]
+
实施例30 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑并环十九烷-7-甲醛(Ⅲ)
按照化合物Ⅰ的合成方法,以中间体18-1为原料合成化合物Ⅲ。
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d
4)δ9.30(d,J=70.5Hz,1H),8.42(s,1H),8.37(d,J=21.3Hz,1H),7.30(s,2H),7.00(s,2H),4.61–4.51(m,1H),4.46–4.36(m,1H),3.82(s,2H),2.86(s,4H),1.90(s,6H),1.64(s,2H),1.22(s,8H).ESI-MS(m/z):500.25[M+H]
+
实施例31 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-甲醛(Ⅳ)
按照化合物Ⅰ的合成方法,以中间体24为原料合成化合物Ⅳ。
1H NMR(500MHz,DMSO-d6)δ9.39(s,1H),9.16–8.76(m,1H),7.96(s,1H),7.33(s,2H),7.08(s,2H),6.78(s,1H),4.57(s,1H),4.22(d,J=242.3Hz,1H),3.66(s,2H),3.20(s,3H),3.00(s,3H),2.83(s,2H),2.02(d,J=191.1Hz,4H),1.47(s,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):474.19[M+H]
+
实施例32 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异噁唑杂环十八烷-7-甲醛(Ⅴ)
按照化合物Ⅰ的合成方法,以中间体29为原料合成化合物Ⅴ。
1H NMR(500MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.07(s,1H),7.30(dd,J=8.7,5.6Hz,3H),7.12(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.46(s,1H),6.38(d,J=5.0Hz,1H),4.55(td,J=10.3,5.4Hz,1H),4.30(s,1H),4.07(dd,J=8.0,4.4Hz,1H),3.55(s,1H),3.40(ddd,J=9.4,6.4,2.9Hz,2H),3.33–3.25(m,1H),3.06(s,3H),3.02–2.95(m,1H),2.86(s,2H),2.44(ddd,J=21.5,13.2,5.6Hz,2H),2.29–2.15(m,2H),1.98–1.81(m,2H),1.68–1.42(m,1H),1.38–1.29(m,1H),1.60–1.50(m,1H).ESI-MS(m/z):488.21[M+H]
+
实施例33 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(乙基磺酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑并环十七烷-7-羧酰胺(Ⅵ)
将中间体9(1.83g,6mmol)加入至10mL四氢呋喃中,搅拌溶解。控温于15℃-20℃之间,于1h内向反应液中滴加氢氧化锂(0.4g,9.6mmol)的10ml水溶液。然后将反应液在20℃以下搅拌1小时。反应完毕,反应液用饱和柠檬酸溶液调pH值为2。乙酸乙酯(10mL×2)萃取,合并有机相,减压除去溶剂,将残余物加入10ml水中,打浆过滤,干燥滤饼,得到白色固体。将此白色固体加入至二氯甲烷和DMF混合溶液中,搅拌溶解。降温至0℃,向反应液中加入HATU(4.70g,24mmol)、N,N-二异丙基乙胺(DIPEA)(7.8g,60mmol)。搅拌30min,依次加入乙基磺酰胺、DMAP、DBU。于室温反应12h。反应完毕,向反应液中加入饱和柠檬酸水溶液调pH值为2,减压除去溶剂,将残余物加入10ml水中,打浆过滤,干燥滤饼,柱色谱分离得白色固体。
1H NMR(400MHz,Methanol-d
4)δ8.35(s,1H),7.32(s,2H),6.95(s,2H),4.72(s,1H),4.46(d,J=28.1Hz,2H),4.20(s,1H),3.12(d,J=60.5Hz,3H),2.88–2.61(m,2H),1.97(q,J=44.8,38.5Hz,8H),1.22(d,J=40.6Hz,7H).ESI-MS(m/z):579.23[M+H]
+
实施例34 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(环丙基磺酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-1
1H-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(4,1)-三唑环十九烷-7-羧酰胺(Ⅶ)的合成
按照化合物Ⅵ的合成方法,以中间体18-1为原料合成化合物Ⅶ。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.92(s,1H),8.64(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),8.06(s,1H),7.46–7.36(m,2H),7.34(dd,J=8.5,5.7Hz,3H),7.06(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.73–4.61(m,2H),4.54–4.35(m,2H),4.43–4.32(m,3H),4.22(s,1H),3.16–2.79(m,5H),2.34–1.56(m,4H),1.22–0.86(m,3H).
实施例35 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(乙基磺酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酰胺(Ⅷ)
按照化合物Ⅵ的合成方法,以中间体24为原料合成化合物Ⅷ。
1H NMR(400MHz,DMSO-d6)δ9.10(s,1H),7.96(d,J=7.1Hz,1H),7.45(t,J=5.3Hz,1H),7.29(s,2H),7.05(s,2H),6.76(s,1H),4.64(s,1H),4.03(s,1H),3.63-3.40(m,4H),3.29(s,3H),2.96(s,4H),2.68(s,1H),1.94(td,J=13.9,11.5,7.4Hz,2H),1.81(t,J=6.4Hz,2H),1.47(s,2H),1.23(t,3H).ESI-MS(m/z):581.20[M+H]
+
实施例36 (4S,7S,Z)-7-(2-羟基乙酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)-异恶唑环十七烷-2,5,10-三酮(Ⅸ)
室温下,将中间体6(1.35g,2.67mmol)加入至DMF(25mL)中,然后加入苯甲酰基甲酸(521mg,3.47mmol),加入新鲜研磨的CsF(933mg,6.14mmol),将得到的悬浮液置于65 0℃的预热油浴中4小时。将反应冷却至环境温度,用乙酸乙酯(200mL)稀释,并用水(3×50mL),盐水(50mL)洗涤,经MgSO
4干燥,过滤并真空除去溶剂。将残余物放入甲醇(120mL)中,加入K
2CO
3(38mg,0.27mmol),并将悬浮液在环境温度下搅拌1小时。通过加入1M盐酸中和反应,并真空除去溶剂。粗产物通过柱色谱分离得白色固体。ESI-MS(m/z):502.22[M+H]
+
实施例37 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酸胺(ⅩⅠ)的合成
将氢化钠溶解于0℃的5ml四氢呋喃溶液,加入甲基磺酸胺(78mg,0.82mmol)至反应液,然后移至25℃搅拌4小时,得到混合体系A。在-20℃下,将N-甲基吗啉溶于6ml四氢呋喃,加入中间体22(200mg,0.41mmol)搅拌10分钟,加入氯甲酸异丁酯(111.4mg,0.82mmol)搅拌45分钟,然后在0℃下将反应体系加入至混合体系A中,30分钟后移至25℃搅拌18小时。反应结束,旋干反应体系,用二氯甲烷溶解,1mol/L柠檬酸溶液和饱和氯化钠溶液洗涤有机相,粗产物经柱层析纯化后得到白色固体。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.07(s,1H),8.21(s,1H),7.93(s,1H),7.35(ddd,J=12.1,7.9,2.2Hz,2H),7.28(dd,J=11.0,8.4Hz,1H),7.11(s,1H),6.72(s,1H),4.65(td,J=9.5,5.0Hz,1H),4.51–4.30(m,2H),4.00(dt,J=7.3,4.7Hz,1H),3.72–3.65(m,2H),3.03–2.94(m,4H),2.94–2.83(m,2H),2.75(s,3H),2.02–1.81(m,4H),1.50–1.45(m,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):586.21[M+H]
+
实施例38 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-4-(4-氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)异恶唑环十七烷-7-羧酸胺(Ⅹ)的合成
按照化合物Ⅵ的合成方法,以中间体24为原料合成化合物Ⅹ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.05(s,1H),8.22(s,1H),7.83(s,1H),7.37–7.23(m,3H),7.05(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),6.72(s,1H),4.62(td,J=9.3,5.1Hz,1H),3.99(ddd,J=7.5,5.5,3.8Hz,1H),3.77–3.60(m,2H),3.17(dd,J=13.8,5.2Hz,2H),2.99(dt,J=11.9,4.3Hz,2H),2.96–2.92(m,1H),2.86(dd,J=13.0,6.2Hz,1H),2.73(s,3H),1.99–1.75(m,4H),1.48(p,J=6.5Hz,2H),1.23(s,2H).ESI-MS(m/z):568.19[M+H]
+
实施例39 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(乙基磺酰基)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)异恶唑环十八烷-7-羧酸胺(ⅩⅡ)的合成
按照化合物Ⅵ的合成方法,以中间体25为原料合成化合物ⅩⅡ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ9.08(s,1H),7.97(s,1H),7.42(s,1H),7.38–7.20(m,3H),7.11(s,1H),6.76(s,1H),4.65(td,J=9.7,4.8Hz,1H),3.99(d,J=6.1Hz,1H),3.67(ddd,J=16.6,9.2,4.5Hz,2H),2.99(s,2H),2.90(d,J=12.0Hz,2H),2.62–2.61(m,2H),2.39(t,J=1.9Hz,2H),2.03–1.92(m,2H),1.83(dt,J=14.3,7.2Hz,2H),1.51–1.45(m,2H),1.24(s,2H),1.05(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).ESI-MS(m/z):600.19[M+H]
+
实施例40 (4S,7S,Z)-N-(环丙基磺酰基)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-2,5,10-三氧代-15-氧杂-3,6,11-三氮杂-1(3,5)异恶唑环十八烷-7-羧酸胺(ⅩⅢ)的合成
按照化合物Ⅵ的合成方法,以中间体25为原料合成化合物ⅩⅢ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.93(s,1H),7.90(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.73(d,J=7.5Hz,2H),7.42(t,J=7.4Hz,2H),7.34(td,J=7.5,1.1Hz,2H),4.30(dd,J=7.1,5.3Hz,2H),4.23(t,J=7.1Hz,1H),4.09–4.02(m,1H),3.23(s,3H),2.26(ddd,J=9.7,6.4,3.5Hz,2H),1.95–1.70(m,2H),1.40(s,9H).ESI-MS(m/z):612.18[M+H]
+
实施例41 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十九烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅣ)的合成
按照化合物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体18-1为原料合成化合物ⅩⅣ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.65(s,1H),7.36(s,2H),7.06(t,J=8.8Hz,2H),4.70–4.64(m,1H),4.51–4.33(m,2H),4.12(s,1H),3.17(d,J=4.5Hz,1H),3.06(s,2H),2.99–2.89(m,2H),2.62(s,1H),1.89(d,J=83.3Hz,5H),1.37–0.90(m,12H).ESI-MS(m/z):594.23[M+H]
+
实施例42 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-N-(乙基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十九烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅤ)的合成
按照化合物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体18-1为原料合成化合物ⅩⅤ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ8.61(s,1H),8.54(s,1H),7.36(d,J=7.1Hz,2H),7.32(s,1H),7.07–7.04(m,2H),4.68(d,J=6.3Hz,1H),4.53–4.43(m,2H),4.39–4.35(m,1H),3.13–2.87(m,6H),1.98–1.79(m,6H),1.24–1.08(m,10H),0.98(d,J=12.1Hz,3H).ESI-MS(m/z):608.27[M+H]
+
实施例43 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十九烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅥ)的合成
按照终产物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体18-2为原料,合成化合物ⅩⅥ。
1H NMR(600 MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.93(s,1H),8.68(d,J=8.2Hz,1H),8.60(s,1H),8.22(d,J=7.7Hz,1H),7.42–7.32(m,2H),7.28(dt,J=10.9,8.5Hz,1H),7.13–7.08(m,1H),4.67(ddd,J=9.8,8.1,5.2Hz,1H),4.47(dt,J=13.7,5.6Hz,1H),4.38(dt,J=13.8,5.6Hz,1H),4.33(ddd,J=10.8,7.7,3.6Hz,1H),3.13–3.03(m,2H),2.99(dq,J=12.7,6.2Hz,1H),2.85(dq,J=12.3,5.9Hz,1H),2.02(dd,J=8.9,6.7Hz,2H),1.90(dtd,J=16.5,8.4,7.9,3.6Hz,1H),1.81(p,J=6.5Hz,2H),1.74(ddt,J=13.8,10.0,7.1Hz,1H),1.20–1.08(m,5H),1.07–0.93(m,5H).ESI-MS(m/z):612.24[M+H]
+
实施例44 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十八烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅦ)的合成
按照终产物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体17-1为原料合成化合物ⅩⅦ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.87(s,1H),8.66(d,J=8.8Hz,2H),8.56(s,1H),7.61(t,J=5.8Hz,1H),7.31–7.26(m,2H),7.05–7.01(m,2H),4.66(ddd,J=10.5,8.7,4.3Hz,1H),4.46(dt,J=13.6,5.5Hz,1H),4.39(dt,J=13.7,5.3Hz,1H),4.21(ddd,J=8.6,6.3,4.0Hz,1H),3.23(s,4H),3.02(dd,J=14.0,10.6Hz,1H),2.76(q,J=6.8Hz,2H),2.09(t,J=6.9Hz,2H),1.90–1.73(m,4H),1.17–0.93(m,8H).ESI-MS(m/z):580.24[M+H]
+
实施例45 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-N-(乙基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十八烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅧ)的合成
按照终产物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体17-1为原料合成终产物ⅩⅧ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.74(s,1H),8.74(s,1H),8.65(d,J=8.8Hz,1H),8.55(s,1H),7.64(s,1H),7.32–7.26(m,2H),7.02(t,J=8.7Hz,2H),4.65(t,J=11.7Hz,1H),4.48–4.42(m,1H),4.42–4.36(m,1H),4.19(s,1H),3.23(d,J=14.0Hz,1H),3.05–2.98(m,1H),2.80–2.68(m, 2H),2.10(s,2H),1.90–1.75(m,4H),1.23(t,J=7.1Hz,4H),1.18–0.87(m,9H).ESI-MS(m/z):594.25[M+H]
+
实施例46 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(4-氟苄基)-N-(环丙基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十八烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅨ)的合成
按照终产物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体18-1为原料合成化合物ⅩⅨ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d
6)δ11.80(s,1H),8.66(d,J=8.7Hz,2H),8.56(s,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.32–7.26(m,2H),7.03(t,J=8.9Hz,2H),4.66(ddd,J=10.5,8.7,4.3Hz,1H),4.48–4.41(m,1H),4.42–4.35(m,1H),4.23(s,1H),3.22(d,J=18.0Hz,1H),3.05–3.00(m,1H),2.94(s,1H),2.76(d,J=6.0Hz,2H),2.09(t,J=6.8Hz,2H),1.84(d,J=6.5Hz,4H),1.08(s,11H).ESI-MS(m/z):606.27[M+H]
+
实施例47 (4S,7S,Z)-4-(3,4-二氟苄基)-N-(甲基磺酰基)-2,5,10-三氧代-11H-3,6,11-三氧杂-1(4,1)-三氮唑环十八烷基-7-羧酰胺(ⅩⅩ)的合成
按照终产物ⅩⅠ的合成方法,以中间体17-2为原料合成终产物ⅩⅩ。
1H NMR(600MHz,DMSO-d6)δ11.88(s,1H),8.72(d,J=8.7Hz,1H),8.57(s,1H),7.59(s,1H),7.39–7.31(m,1H),7.26(q,J=8.6Hz,1H),7.10(s,1H),4.72–4.66(m,1H),4.49–4.43(m,1H),4.43–4.36(m,1H),4.20(s,1H),3.22(d,J=14.9Hz,3H),3.06–2.99(m,1H),2.77(s,2H),2.08(s,2H),1.81(d,J=38.3Hz,4H),1.09(s,8H).
实施例48 SARS-Cov-2 3CL蛋白酶抑制剂体外酶活实验
利用荧光共振能量转移(fluorescence resonance energy transfer,FRET)技术测定针对SARS-Cov-2 3CL蛋白酶的抑制剂的酶活,根据Nsp5蛋白酶识别位点设计底物: MCA-AVLQSGFR-Lys(Dnp)-Lys-NH2,抑制剂最终浓度分别为2uM,1uM,500nM,250nM,125nM,62.5nM,31.25nM,15.625nM,7.8nM,3.9nM,1.95nM,同时设阴性对照。利用96孔板测定酶活,100μL反应体系包括:50mM Tris-HCl PH7.3,1mM EDTA,150nM SARS-Cov-2-3CLpro,20μM荧光底物和不同浓度的抑制剂。30℃反应,通过酶标仪检测荧光强度,所得数据利用软件GraphPad Prism 5处理得到抑制剂的IC
50。实验结果如表1所示。
结果表明,化合物I-IX对SARS-Cov-2 3CL蛋白酶具有良好的抑制活性,其IC
50为32-275nM。
表1 化合物抑制SARS-Cov-2 3CL蛋白酶IC
50
实施例21 EV71 3C蛋白酶抑制剂体外酶活实验
利用反相-HPLC法测定针对EV71 3C蛋白酶的抑制剂的酶活。根据3C蛋白酶识别位点设计多肽酶活性检测底物(LEVLFQGPSK),抑制剂最终浓度分别为:9uM,3uM,1uM,333nM,111nM,同时设阴性对照。利用96孔板测定酶活,100ul反应体系包括:50mM Tris-HCl pH7.5,4uM EV71 3C蛋白,2g/L多肽底物和不同浓度的抑制剂。30℃反应,通过酶标仪检测荧光强度,所得数据利用软件GraphPad Prism 5处理得到抑制剂的IC
50。实验结果如表2所示。
结果表明,化合物I-IX的IC
50为0.45-6.28μM。其中化合物Ⅲ、Ⅳ、Ⅷ的酶抑制活性均为阳性药芦平曲韦的两倍左右,化合物IX的酶抑制活性为阳性药芦平曲韦的至少三倍。结果表明,上述化合物对EV71 3C蛋白酶具有良好的抑制活性。
表2 化合物抑制EV71 3C蛋白酶IC
50
尽管本发明的具体实施方式已经得到详细的描述,本领域技术人员将会理解,根据已经公开的所有教导,可以对那些细节进行各种修改和替换,这些改变均在本发明的保护范围之内。本发明的全部范围由所附权利要求及其任何等同物给出。
Claims (18)
- 一种药物组合物,其包含至少一种权利要求1~4任一项所定义的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药;任选地,所述药物组合物还包含至少一种药学上可接受的赋形剂、载体、介质或助剂。
- 权利要求11的药物组合物,其还包含EV71抗病毒剂;优选地,所述EV71抗病毒剂是选自3D蛋白酶抑制剂和VP1蛋白抑制剂的抗病毒制剂。
- 权利要求11或12的药物组合物,其用于预防/治疗受试者的与病毒感染相关的疾病,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒。其中,所述肠病毒包括但不限于肠病毒71(EV71)、脊髓灰质炎病毒、柯萨奇病毒A、柯萨奇病毒B,所述冠状病毒包括但不限于SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV;优选地,所述药物组合物用于预防/治疗受试者的肠病毒71(EV71)感染疾病或SARS-CoV-2感染疾病。
- 如权利要求1~4任一项所定义的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物为病毒蛋白酶抑制剂;优选地,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属(例如柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型)、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒(例如SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV);优选地,所述蛋白酶为3C/3CL蛋白酶。
- 如权利要求1~4任一项所定义的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物为抗病毒药物;优选地,所述抗病毒药物针对的病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属(例如柯萨奇病毒(CV)、脊髓灰质炎病毒(PV)、肠道病毒71型)、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒(例如SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV)。
- 如权利要求1~4任一项所定义的化合物,所述化合物的立体异构体、互变异构体或其混合物,所述化合物药学上可接受的盐、多晶型物、共晶物或溶剂化物,或者,所述化合物的稳定同位素衍生物、代谢物或前药在制备药物中的用途,所述药物用于预防/治疗受试者的与病毒感染相关的疾病,所述病毒选自小RNA病毒(例如肠道病毒属、人类鼻病毒属(HRV)和甲型肝炎病毒属(HAV)),以及冠状病毒;优选地,所述肠病毒选自肠病毒71(EV71)、脊髓灰质炎病毒、柯萨奇病毒A、柯萨奇病毒B;优选地,所述冠状病毒选自SARS-CoV-2、HCoV-229E、HCoV-OC43、HCoV-NL63、HCoV-HKU1、SARS-CoV和MERS-CoV。
- 权利要求17所述的具有式5所示结构的化合物作为中间体制备环肽类化合物的用途,所述环肽类化合物如权利要求1~4任一项所述。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202280008015.5A CN116648240A (zh) | 2021-01-22 | 2022-01-19 | 一种环肽类病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,其制备方法,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN202110089818.5 | 2021-01-22 | ||
| CN202110089818 | 2021-01-22 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2022156692A1 true WO2022156692A1 (zh) | 2022-07-28 |
Family
ID=82549299
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2022/072680 WO2022156692A1 (zh) | 2021-01-22 | 2022-01-19 | 一种环肽类病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,其制备方法,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN116648240A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2022156692A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN116987152B (zh) * | 2023-09-27 | 2024-01-02 | 中国科学院微生物研究所 | 一种结合沙贝冠状病毒s蛋白rbd结构域的环肽及其应用 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1997043305A1 (en) * | 1996-05-14 | 1997-11-20 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Inhibitors of picornavirus 3c proteases and methods for their use and preparation |
| WO1999031122A1 (en) * | 1997-12-16 | 1999-06-24 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Antipicornaviral compounds and methods for their use and preparation |
| CN1311793A (zh) * | 1998-04-30 | 2001-09-05 | 阿格罗尼制药公司 | 抗小rna病毒化合物及其制备方法和用途 |
| WO2001090095A1 (en) * | 2000-05-23 | 2001-11-29 | Apotex Inc. | Thiadiazole compounds useful as inhibitors of cysteine activity dependent enzymes |
| CN1431995A (zh) * | 2000-04-14 | 2003-07-23 | 阿格罗尼制药公司 | 抗细小rna病毒的化合物与组合物,它们的药物用途,以及用于其合成的物质 |
| WO2004093860A1 (en) * | 2003-04-21 | 2004-11-04 | Pfizer Inc. | Inhibitors of sars related coronavirus proteinase |
-
2022
- 2022-01-19 CN CN202280008015.5A patent/CN116648240A/zh active Pending
- 2022-01-19 WO PCT/CN2022/072680 patent/WO2022156692A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO1997043305A1 (en) * | 1996-05-14 | 1997-11-20 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Inhibitors of picornavirus 3c proteases and methods for their use and preparation |
| WO1999031122A1 (en) * | 1997-12-16 | 1999-06-24 | Agouron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Antipicornaviral compounds and methods for their use and preparation |
| CN1311793A (zh) * | 1998-04-30 | 2001-09-05 | 阿格罗尼制药公司 | 抗小rna病毒化合物及其制备方法和用途 |
| CN1431995A (zh) * | 2000-04-14 | 2003-07-23 | 阿格罗尼制药公司 | 抗细小rna病毒的化合物与组合物,它们的药物用途,以及用于其合成的物质 |
| WO2001090095A1 (en) * | 2000-05-23 | 2001-11-29 | Apotex Inc. | Thiadiazole compounds useful as inhibitors of cysteine activity dependent enzymes |
| WO2004093860A1 (en) * | 2003-04-21 | 2004-11-04 | Pfizer Inc. | Inhibitors of sars related coronavirus proteinase |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| P. S. DRAGOVICH ET AL.: "STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN, SYNTHESIS, AND BIOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF IRREVERSIBLE HUMAN RHINOVIRUS 3C PROTEASE INHIBITORS. 4. INCORPORATION OF P1 LACTAM MOIEITES AS L-GLUTAMINE REPLACEMENTS.", JOURNAL OF MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY, AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, US, vol. 42, no. 7, 8 April 1999 (1999-04-08), US , pages 1213 - 1224, XP002153221, ISSN: 0022-2623, DOI: 10.1021/jm9805384 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN116648240A (zh) | 2023-08-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8044080B2 (en) | Isoxazoline derivative and novel process for its preparation | |
| CA2845127C (en) | Pyrazole compound and pharmaceutical use thereof for inhibiting sglt1 | |
| IL104748A (en) | History of isoxalil sulfonamide and pharmaceutical preparations containing them | |
| TW201249782A (en) | Substituted 1-benzylcycloalkylcarboxylic acids and the use thereof | |
| TW200831513A (en) | Anti-viral compounds | |
| KR20050099525A (ko) | 피롤로트리아진 키나제 억제제의 제조 방법 | |
| CN105873919A (zh) | 作为类糜蛋白酶抑制剂的取代的尿嘧啶 | |
| AU2024203286A1 (en) | Antiviral 1,3-di-oxo-indene compounds | |
| JP5815542B2 (ja) | Dpp−1阻害剤として有用なアルキニル誘導体 | |
| WO2022156692A1 (zh) | 一种环肽类病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,其制备方法,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 | |
| AU2024204863A1 (en) | Antiviral 1,3-di-oxo-indene compounds | |
| JP3215850B2 (ja) | ハロアルコキシ基を含有するピロロ[3,2―c]キノリン誘導体及び薬学的に許容されるその塩 | |
| WO2021093172A1 (zh) | Hbv抑制剂及其用途 | |
| CA2647163C (en) | Modified macrophage migration inhibitory factor inhibitors | |
| JP4881532B2 (ja) | ナフトアミジン系ウロキナーゼ阻害薬 | |
| US6495562B1 (en) | Naphthamidine urokinase inhibitors | |
| WO2022156693A1 (zh) | 含有n-(取代磺酰基)乙酰胺结构的病毒蛋白酶抑制剂,及其在抗病毒药物中的应用 | |
| JP2004507539A (ja) | ピロリジン誘導体及びそのキマーゼ阻害剤としての使用 | |
| CN113004284B (zh) | 作为血浆激肽释放酶抑制剂的四环类化合物及其用途 | |
| WO2017173960A1 (zh) | 一类抑制丙肝病毒的大环状杂环化合物及其制备和用途 | |
| CN118026948A (zh) | 三联芳环类化合物及其制备方法、药物组合物和应用 | |
| WO2022092141A1 (ja) | 抗ウイルス活性を有するアミド誘導体 | |
| KR100747002B1 (ko) | 이소옥사졸린 유도체 및 그의 제조 방법 | |
| CN103059042B (zh) | 噻吩类衍生物及其在药学中的用途 | |
| NZ523134A (en) | Antipicornaviral compounds and compositions, their pharmaceutical uses, and materials for their synthesis |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 22742171 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 202280008015.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 22742171 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |