WO2021075345A1 - Signal processing method, learning model generation method, signal processing device, radiation detection device, and computer program - Google Patents
Signal processing method, learning model generation method, signal processing device, radiation detection device, and computer program Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2021075345A1 WO2021075345A1 PCT/JP2020/038107 JP2020038107W WO2021075345A1 WO 2021075345 A1 WO2021075345 A1 WO 2021075345A1 JP 2020038107 W JP2020038107 W JP 2020038107W WO 2021075345 A1 WO2021075345 A1 WO 2021075345A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- wave
- signal
- pulse
- staircase
- waves
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N23/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00
- G01N23/22—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material
- G01N23/225—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material using electron or ion
- G01N23/2251—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of wave or particle radiation, e.g. X-rays or neutrons, not covered by groups G01N3/00 – G01N17/00, G01N21/00 or G01N22/00 by measuring secondary emission from the material using electron or ion using incident electron beams, e.g. scanning electron microscopy [SEM]
- G01N23/2252—Measuring emitted X-rays, e.g. electron probe microanalysis [EPMA]
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01T—MEASUREMENT OF NUCLEAR OR X-RADIATION
- G01T1/00—Measuring X-radiation, gamma radiation, corpuscular radiation, or cosmic radiation
- G01T1/16—Measuring radiation intensity
- G01T1/17—Circuit arrangements not adapted to a particular type of detector
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a signal processing method for processing a signal generated by detection of radiation, a learning model generation method, a signal processing device, a radiation detection device, and a computer program.
- the radiation detection device that detects radiation such as X-rays includes a radiation detector and a signal processing device that processes a signal output by the radiation detector.
- the radiation detector is configured by using a semiconductor radiation detection element or the like, and outputs a staircase wave each time radiation is detected.
- the signal processing device converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave and measures the height of the pulse wave. The height of the pulse wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation.
- the signal processing device detects the overlap of the pulse waves and suppresses the occurrence of the sum peak by not measuring the wave height of the overlapped pulse waves.
- a pulse wave is detected using a threshold value of wave height, and when the detection interval of a plurality of pulse waves is short, it is determined that overlap of pulse waves has occurred.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for determining that overlap of pulse waves has occurred when the differential waveform of a pulse wave changes from a negative value to a positive value.
- the signal processor may not be able to detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the detection interval is very short.
- the method based on the feature amount of the signal waveform such as the length of the base has a problem that it is vulnerable to noise because it focuses only on the feature amount.
- the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave is lowered, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves having a high wave height cannot be detected, and when the threshold value is raised, the pulse wave having a low wave height cannot be detected.
- the present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is a signal processing method, a learning model generation method, and a signal capable of improving the accuracy of elemental analysis based on a radiation spectrum.
- an object of the present invention is a signal processing method, a learning model generation method, and a signal capable of improving the accuracy of elemental analysis based on a radiation spectrum.
- the signal processing method is a signal processing method for counting a staircase wave corresponding to radiation detection or a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave by wave height, and is a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave. And, when at least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input, the signal including the step wave is configured in a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves. When at least one of the sequence of signal values and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input, and the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap according to the information output by the learning model. It is characterized by counting the staircase wave or the pulse wave.
- the overlap of pulse waves is detected by using a learning model.
- the training model outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. To do.
- the learning model it is possible to effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the signal processing method according to the present invention is characterized in that the staircase wave or the pulse wave when a plurality of the pulse waves overlap is not counted according to the information output by the learning model.
- counting is not performed according to the detection of radiation. It is possible to prevent erroneous measurement of radiation energy due to the overlap of pulse waves.
- the learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when a string of signal values constituting a signal including a wave obtained by shaping the pulse wave is further input, and the signal is used. It is characterized in that a sequence of constituent signal values is further input to the learning model.
- a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the wave formed by shaping the pulse wave is input to the learning model.
- the shape of the pulse wave shaped by a filter such as a differential filter differs depending on the presence or absence of a plurality of pulse waves. Therefore, by using a wave obtained by shaping a pulse wave, it is possible to more effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when at least one feature amount of the staircase wave and the pulse wave is further input, and the feature amount is the learning model. It is characterized by inputting to.
- the feature amount of the signal waveform such as the wave height or the time width is further input to the learning model. Since the feature amount of the signal waveform differs depending on the presence or absence of the plurality of pulse waves, the overlap of the plurality of pulse waves can be detected more effectively by using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
- the learning model generation method is composed of a single pulse wave, and generates a plurality of pulse wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise, and roundness of the single pulse wave is random.
- Each of the plurality of pulse waves is composed of a superposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped, and a plurality of superposed wave signals in which at least one of the interval, the wave height, the rising edge and the roundness of the plurality of pulse waves is random are generated, and the plurality of pulse waves
- a learning model is generated that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary pulse wave is input. It is characterized by that.
- a plurality of pulse wave signals each consisting of a single pulse wave and a plurality of superimposed wave signals each consisting of a superposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped are subjected to wave height, rising edge, and randomness. Generate by simulation so that at least one of the above is random.
- the learning model is trained using the generated plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals as teacher data. A learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlapping pulse waves can be generated. Further, by randomizing the bluntness of the pulse wave in the simulation, it is possible to generate a signal close to the actual signal.
- the learning model generation method is composed of a single staircase wave, and generates a plurality of staircase wave signals in which at least one of the wave height, rise and roundness of the single staircase wave is random.
- Each consists of a plurality of staircase waves, and a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting the plurality of staircase waves overlap each other, and at least one of the intervals, wave heights, rising edges, and rounds of the plurality of staircase waves is random.
- the plurality of staircase wave signals and the proximity staircase wave signal are used as teacher data and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary staircase wave is input, the plurality of staircase wave signals are generated. It is characterized by generating a learning model that outputs information on the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from.
- a plurality of staircase wave signals each consisting of a single staircase wave and a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals are simulated so that at least one of wave height, rise and roundness is random. Generated by.
- the learning model is trained using the generated plurality of staircase wave signals and a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals as teacher data.
- a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of pulse waves converted from staircase waves can be generated.
- the signal processing method converts a step wave corresponding to the detection of radiation into a pulse wave, and constitutes a signal including the pulse wave in a signal processing method for counting the pulse wave according to the height of the pulse wave.
- a product-sum calculation is performed between the sequence of signal values to be performed and the predetermined coefficient sequence, and the predetermined coefficient sequence is between the signal value sequence and the predetermined coefficient sequence constituting the signal including the plurality of overlapping pulse waves.
- the result of the product-sum calculation and the result of the product-sum calculation between the string of signal values constituting the signal including the single pulse wave and the predetermined coefficient sequence are larger than the predetermined value.
- a product-sum calculation is performed on a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and a predetermined coefficient sequence, and the overlap of pulse waves is detected based on the result of the product-sum calculation.
- the coefficient sequence is the result of the product-sum operation between the string of signal values and the coefficient sequence that compose the signal containing a single pulse wave, and the sequence and coefficient of the signal values that compose the signal containing multiple overlapping pulse waves. It is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation between columns is different. Also in this method, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves can be effectively detected.
- the signal processing device is a signal processing device that processes a signal including a staircase wave according to the detection of radiation, and is a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and a pulse obtained by converting the staircase wave. It is characterized by including a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when at least one of a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a wave is input.
- the radiation detection device comprises a radiation detector that outputs a staircase wave according to the energy of radiation at the time of radiation detection, a conversion unit that converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave, and a signal including the staircase wave.
- a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when at least one of the signal value sequence and the signal value sequence constituting the signal including the pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave is input.
- a counting unit that counts the staircase wave or the pulse wave when there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves, a wave height of the staircase wave or the pulse wave, and a count number according to the information output by the learning model. It is characterized by including a spectrum generation unit that generates a radiation spectrum according to the above.
- the computer program according to the present invention has at least one of a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave corresponding to the detection of radiation and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave.
- a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave and a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave are sent to a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when input. It is characterized in that a computer is made to execute a process of inputting at least one of them and outputting the information.
- the signal processing device uses a learning model to detect the overlap of pulse waves.
- the training model outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input.
- the radiation detector counts staircase waves or pulse waves when there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and generates a radiation spectrum.
- the signal processing device can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
- the present invention has excellent effects such as being able to effectively detect the overlap of pulse waves and improve the accuracy of elemental analysis.
- FIG. It is a block diagram which shows the functional structure of the radiation detection apparatus which concerns on Embodiment 1.
- FIG. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of a staircase wave and a pulse wave. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of a staircase wave and a pulse wave. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of the staircase wave and the pulse wave when the interval at which radiation is detected is short. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of the staircase wave and the pulse wave when the interval at which radiation is detected is short. It is a graph which shows typically the example of the signal input to a processing part. It is a conceptual diagram which shows the functional structure example of the learning model which concerns on Embodiment 1.
- FIG. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of a staircase wave and a pulse wave. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of a staircase wave and a pulse wave. It is a schematic characteristic diagram which shows the example of a staircase wave and a pulse wave. It is a schematic characteristic
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the first embodiment.
- the radiation detection device 10 includes a radiation detector 1, a signal processing device 2, and an analysis unit 3.
- the radiation detector 1 includes a radiation detection element 11 and a preamplifier 12.
- the radiation detection element 11 is a semiconductor radiation detection element such as an SDD (Silicon Drift Detector), which generates an electric charge according to the energy of the incident radiation and outputs a current signal according to the generated electric charge.
- SDD Silicon Drift Detector
- the preamplifier 12 converts the current signal output by the radiation detection element 11 into a voltage signal, and generates a step wave in which the signal value rises in a step-like manner at the time of radiation detection.
- the radiation detector 1 outputs a signal including a staircase wave generated by the preamplifier 12.
- the signal output by the radiation detector 1 is input to the signal processing device 2.
- the signal processing device 2 executes the signal processing method.
- the signal processing device 2 includes an A / D (analog / digital) conversion unit 21.
- the A / D conversion unit 21 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the radiation detector 1 and A / D-converts the signal including the staircase wave.
- a waveform shaping unit 22 is connected to the A / D conversion unit 21.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the A / D conversion unit 21.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 converts the signal including the staircase wave into the signal including the pulse wave by passing the signal including the staircase wave through a predetermined filter and shaping the waveform of the signal.
- the filter used by the waveform shaping unit 22 is, for example, a differential filter or a trapezoidal shaping filter.
- the staircase wave is converted into a pulse wave, the noise contained in the signal is reduced, and a predetermined amplification is performed.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 outputs a signal including a pulse wave.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 corresponds to the conversion unit.
- FIG. 2A and 2B are schematic characteristic diagrams showing examples of staircase waves and pulse waves.
- the horizontal axis in the figure shows time, and the vertical axis shows signal values.
- FIG. 2A shows a signal including a staircase wave output by the radiation detector 1.
- the radiation detector 1 outputs a step wave whose signal value rises in a step-like manner each time radiation is detected. In response to a single radiation detection, a step wave is generated in which the signal value rises in a step-like manner.
- a signal including a plurality of staircase waves is output. Each time radiation is detected, the signal value rises.
- the height of the step at which the signal value rises is defined as the wave height of the staircase wave.
- the height of the staircase wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation.
- the staircase wave is not completely stepped, and the signal waveform contains rising and rounding.
- the rising edge is the distortion of the signal waveform when the signal value rises from the reference value, and the rounding is the distortion of the signal waveform when the staircase wave ends.
- FIG. 2B shows a signal obtained by converting the signal shown in FIG. 2A by the waveform shaping unit 22.
- the staircase wave is converted into a pulse wave.
- a pulse wave is a signal in which a signal value rises from a predetermined signal reference at which the signal value becomes zero to a peak value and then falls to a signal reference.
- the signal reference is, for example, zero.
- the height from the signal reference to the peak value is defined as the wave height of the pulse wave.
- the height of the pulse wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation.
- the shape of the pulse wave includes rising and rounding.
- the rising edge is the distortion of the signal waveform when the signal value rises from the reference value, and the rounding is the distortion of the signal waveform when the pulse wave ends.
- FIG. 2B shows an example in which the radiation detector 1 detects radiation a plurality of times at long intervals and a plurality of pulse waves are not superimposed.
- FIG. 3A and 3B are schematic characteristic diagrams showing examples of staircase waves and pulse waves when the intervals at which radiation is detected are short.
- the horizontal axis in the figure shows time, and the vertical axis shows signal values.
- FIG. 3A shows a signal including a staircase wave output by the radiation detector 1. Compared to the example shown in FIG. 2A, the interval at which the radiation detector 1 detects radiation a plurality of times is short, and the interval between the plurality of staircase waves is short.
- FIG. 3B shows a signal obtained by converting the signal shown in FIG. 3A by the waveform shaping unit 22. The interval between the plurality of pulse waves is short, and a superposed wave in which the plurality of pulse waves overlap is formed. The wave height of the superimposed wave is different from the wave height of a single pulse wave, and the erroneous radiation energy is measured according to the wave height of the superimposed wave.
- the processing unit 23 and the pulse detection unit 24 are connected to the waveform shaping unit 22.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the processing unit 23 and the pulse detecting unit 24.
- the pulse detection unit 24 receives a signal from the waveform shaping unit 22 and detects a pulse wave contained in the signal. For example, the pulse detection unit 24 determines that a pulse wave has been detected when the signal value exceeds a predetermined threshold value.
- the pulse detection unit 24 is connected to the processing unit 23. When the pulse detection unit 24 detects the pulse wave, the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23.
- the processing unit 23 receives a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and an information indicating that the pulse wave is detected is input from the pulse detection unit 24.
- the processing unit 23 is configured by using an element that performs an operation.
- the processing unit 23 includes a buffer memory 231 and a learning model 232 for determining whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap.
- the learning model 232 is configured by using FPGA (field-programmable gate array).
- FPGA field-programmable gate array
- a wave height measuring unit 25 is connected to the waveform shaping unit 22 and the processing unit 23.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the signal input from the waveform shaping unit 22 when the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap. When there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height of the pulse wave included in the signal input from the waveform shaping unit 22.
- a counting unit 26 is connected to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26.
- the counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to wave height.
- the counting unit 26 is a multi-channel analyzer.
- the counting unit 26 may be in a form of counting pulse waves for all wave heights, or may be in a form of counting pulse waves only for a specific wave height.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26.
- the count number corresponds to the number of times that the radiation detector 1 detects radiation having energy corresponding to the wave height of the pulse wave.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 When there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height of the pulse waves, so that the signal processing device 2 does not count the overlapped pulse waves.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 may measure the wave height of the overlapping pulse waves, but may not input the measured wave height to the counting unit 26.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 may also input the wave heights of the overlapping pulse waves to the counting unit 26, and the counting unit 26 may be in a form in which the overlapping pulse waves are not counted.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 may also input the wave heights of the overlapping pulse waves to the counting unit 26, and the counting unit 26 may be in a form of distinguishing between the non-overlapping pulse waves and the overlapping pulse waves.
- the analysis unit 3 is composed of a computer such as a personal computer.
- the analysis unit 3 is input with the data output by the signal processing device 2.
- the analysis unit 3 performs a process of generating a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 from the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the count number.
- the analysis unit 3 corresponds to the spectrum generation unit.
- the analysis unit 3 may further perform further processing such as elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the generated spectrum of radiation. For example, the sample is irradiated with radiation, the characteristic X-rays generated from the sample are detected by the radiation detector 1, and qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis of the elements contained in the sample is performed based on the spectrum of the characteristic X-rays.
- the signal processing device 2 may also have a function of generating a radiation spectrum.
- the radiation spectrum will include the sum peak, which is the peak with the wrong energy.
- the sum peak may overlap the peak of an existing element, and the amount of the element may be excessively detected.
- the thumb peak overlaps the peak of the L line of Pb (lead), and the amount of Pb is excessively detected.
- the thumb peak overlaps the peak of the K line of Cd (cadmium), and the amount of Cd is excessively detected.
- FIG. 4 is a graph schematically showing an example of a signal input to the processing unit 23.
- the horizontal axis in the figure indicates time, and the vertical axis indicates signal value.
- the signal is composed of a time series of discrete signal values obtained at predetermined time intervals. That is, the signal is represented by one-dimensional data consisting of a sequence of signal values.
- a signal including a single pulse wave and a signal including a superimposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped have different signal shapes and different time changes in signal values.
- the learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input.
- FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the first embodiment.
- the learning model 232 uses a fully coupled neural network with an input layer, a plurality of intermediate layers, and an output layer, each having a plurality of nodes.
- the input layer has a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input.
- One signal value in the signal value sequence is input to one node 41, and each signal value is input to one of the nodes 41.
- the input layer includes m nodes 41, and m signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave are input to the input layer.
- the learning model 232 has an intermediate layer of n (n is a natural number) layer.
- the first intermediate layer has a plurality of nodes 421.
- Each node 41 of the input layer outputs a signal value to a plurality of nodes 421.
- the plurality of nodes 421 receive signal values from the nodes 41 of the input layer, calculate the signal values using parameters, and output the calculation result data to the plurality of nodes 422 included in the second intermediate layer.
- the nodes included in each intermediate layer receive data from a plurality of nodes in the previous intermediate layer, calculate the received data using parameters, and output the data to the nodes in the subsequent intermediate layer.
- the node has f ( ⁇ (w * x), where x is the value of the data received from each node in the previous layer, w is the weight corresponding to each node, b is the bias value, and f () is the activation function. ) + B) is performed, and the data of the calculation result is output to a plurality of nodes in the subsequent layer.
- the activation function is, for example, a relu function or a sigmoid function.
- the activation function may be another function generally used in machine learning.
- the output layer of the learning model 232 has a single node 43.
- the plurality of nodes 42n included in the nth intermediate layer output data to the node 43 included in the output layer.
- the node 43 of the output layer receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, calculates the received data using parameters, and outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves.
- the activation function at the node 43 is a function that outputs data indicating whether or not the calculation result of ( ⁇ (w * x) + b) is a positive value.
- the node 43 may output a value of 1 as data indicating a positive value and output a value of zero as data indicating a value of zero or less.
- the data showing a positive value is information indicating that there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves
- the data showing a value of zero or less is information indicating that there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the node 43 may output the probability that a plurality of pulse waves overlap each other as information indicating the presence or absence of the overlap of the pulse waves.
- a convolutional neural network CNN: Convolutional Neural Network
- RNN Recurrent Neural Network
- FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a learning device 5 that learns the learning model 232.
- the learning device 5 executes the learning model generation method.
- the learning device 5 is a computer such as a server device.
- the learning device 5 includes a calculation unit 51, a memory 52, a storage unit 53, a display unit 54, and an operation unit 55.
- the calculation unit 51 is configured by using, for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), or a multi-core CPU.
- the calculation unit 51 may be configured by using a quantum computer.
- the memory 52 stores temporary data generated by the calculation.
- the memory 52 is, for example, a RAM (Random Access Memory).
- the storage unit 53 is non-volatile, for example, a hard disk.
- the display unit 54 is, for example, a liquid crystal display or an EL display (Electroluminescent Display).
- the operation unit 55 accepts the input of information such as text by accepting the operation from the user.
- the operation unit 55 is, for example, a keyboard or a touch panel.
- the storage unit 53 stores the computer program 531.
- the calculation unit 51 executes the process according to the computer program 531.
- FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the process of generating the learning model 232.
- the step is abbreviated as S.
- the calculation unit 51 executes the following processing according to the computer program 531.
- the arithmetic unit 51 generates a plurality of pulse wave signals each consisting of a single pulse wave (S11).
- the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of pulse wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise, and roundness of the pulse wave is random by simulation.
- the height, rise and roundness of the pulse wave may all be random.
- a pulse wave signal is composed of a sequence of signal values. For example, the number of signal values included in the pulse wave signal is the same as the number of nodes 41 in the input layer of the learning model 232.
- the calculation unit 51 generates the wave height of the pulse wave, the rising time constant, and the rising start time from random numbers having a uniform distribution. As the random number, a random number having an exponential distribution or a Poisson distribution may be used. Further, the calculation unit 51 randomly generates a time constant of the bluntness of the pulse wave. The calculation unit 51 superimposes white noise on the pulse wave according to the generated parameter to generate a pulse wave signal. The noise superimposed on the pulse wave may be 1 / f noise, and the noise may not be superimposed. The noise superimposed on the pulse wave is preferably noise according to the characteristics of the radiation detector 1.
- the pulse wave signal is a signal as shown in FIG. 2B.
- the calculation unit 51 stores the pulse wave data 532 including the generated plurality of pulse wave signals in the storage unit 53.
- the roundness of the actually measured signal fluctuates greatly.
- randomizing the bluntness of the pulse wave in the simulation it is possible to generate a signal close to the actual signal.
- the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of superimposed wave signals composed of superimposed waves in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped with each other (S12).
- the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of superimposed wave signals in which two pulse waves having at least one of a wave height, a rising edge, and a randomness are random are overlapped with each other by simulation.
- the superimposed wave signal is also composed of a sequence of signal values.
- the calculation unit 51 generates the wave height, rise time constant, and rise start time of the first pulse wave, and the wave height, rise time constant, and rise start time of the second pulse wave from a uniformly distributed random number. Further, the calculation unit 51 randomly generates a time constant of the bluntness of the pulse wave.
- the time constant of the rounding may be the same for the two pulse waves.
- the calculation unit 51 superimposes noise on the superposed wave according to the generated parameter to generate a superposed wave signal.
- the superimposed wave signal is a signal as shown in FIG. 3B.
- the calculation unit 51 stores the superimposed wave data 533 including the generated plurality of superimposed wave signals in the storage unit 53.
- the calculation unit 51 performs processing for generating the learning model 232 by using the plurality of pulse wave signals included in the pulse wave data 532 and the plurality of superimposed wave signals included in the superimposed wave data 533 as teacher data ( S13).
- the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals to the input layer of the learning model 232, respectively.
- One signal value is input to each of the nodes 41 of the input layer.
- the calculation unit 51 associates the pulse wave signal with information indicating that the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap, and associates the superimposed wave signal with information indicating that the plurality of pulse waves overlap.
- the learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap from the node 43 of the output layer.
- the calculation unit 51 calculates the error of the information by the error function using the information associated with the input pulse wave signal or the superimposed wave signal and the information output from the node 43 as variables, and the error is calculated by the error back propagation method.
- the calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so as to be the minimum. That is, when a pulse wave signal is input, information close to the information indicating that there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves is output, and when a superimposed wave signal is input, information indicating that a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped is output. The parameters are adjusted so that close information is output.
- the calculation unit 51 performs machine learning of the learning model 232 by repeating the process using the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals and adjusting the parameters of each node of the learning model 232.
- the calculation unit 51 stores the learned data 534 in which the adjusted final parameters are recorded in the storage unit 53. In this way, the trained learning model 232 is generated. After the end of S13, the calculation unit 51 ends the process.
- the learning model 232 included in the processing unit 23 is manufactured based on the trained data 534. For example, the learning model 232 is manufactured by writing the parameters recorded in the trained data 534 to the FPGA included in the processing unit 23.
- the calculation unit 51 may perform machine learning of the learning model 232 using the actually measured pulse wave signal and the superimposed wave signal instead of using the pulse wave signal and the superimposed wave signal created by the simulation. ..
- FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a procedure of processing executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the first embodiment.
- the radiation detector 1 When radiation is incident on the radiation detection element 11, the radiation detector 1 generates a staircase wave according to the energy of the radiation and outputs a signal including the staircase wave.
- the signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the radiation detector 1 (S21).
- the A / D conversion unit 21 A / D converts the input signal (S22).
- the A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the waveform shaping unit 22.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 shapes the waveform of the input signal (S23).
- the waveform shaping unit 22 reduces the noise included in the signal and converts the staircase wave included in the signal into a pulse wave.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the processing unit 23, the pulse detecting unit 24, and the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the signal input to the processing unit 23 is composed of a time series of signal values.
- the processing unit 23 sequentially stores the signal values in the buffer memory 231 (S24).
- the processes S21 to S24 are individually and repeatedly executed, and the signal values are sequentially stored in the buffer memory 231.
- the buffer memory 231 is a first-in first-out memory, and stores a plurality of sequentially input signal values. When a new signal value is input while the amount of the plurality of signal values stored in the buffer memory 231 has reached the upper limit, the buffer memory 231 first stores the stored signal values. The signal value is erased and a new signal value is stored.
- the pulse detection unit 24 waits for the detection of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S25). In S25, for example, the pulse detection unit 24 determines that the pulse wave included in the signal has been detected when the signal value exceeds a predetermined threshold value. The threshold value is stored in the processing unit 23 in advance. If no pulse wave is detected (S25: NO), the pulse detection unit 24 repeats the process of S25.
- the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23, and the processing unit 23 inputs the pulse wave.
- a sequence of signal values constituting the including signal is input to the learning model 232 (S26).
- the processing unit 23 inputs a plurality of signal values stored in the buffer memory 231 to the learning model 232 at the time when the information indicating that the pulse wave is detected is input.
- the processing unit 23 may input the signal values constituting the signal to the learning model 232 after thinning out the signal values.
- the learning model 232 to which the signal including the pulse wave is input performs the calculation of the neural network and outputs the information indicating whether or not the plurality of pulse waves overlap.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating whether or not the plurality of pulse waves output by the learning model 232 overlap to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 identifies whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap each other based on the input information (S27). When information indicating that there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves is input and there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves (S27: NO), the wave height measuring unit 25 is the pulse wave included in the input signal. The wave height is measured (S28).
- the wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26.
- the counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to the wave height input from the wave height measuring unit 25 (S29), and ends the process.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height for the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. Is not performed, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves.
- the signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S21 to S29 individually.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26.
- the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data.
- FIG. 9 is a spectrum diagram showing the spectra of radiation obtained by a plurality of methods.
- the horizontal axis in the figure shows the energy of radiation in units of keV, and the vertical axis shows the number of counts of radiation.
- the spectrum shown in FIG. 9 includes a peak near 11.8 keV and a peak near 12.4 keV. However, all of these peaks are sum peaks obtained by measuring the heights of a plurality of overlapping pulse waves.
- the spectrum when the overlap of the pulse waves is not detected is shown by a broken line
- the spectrum when the overlap of the pulse waves is detected by the conventional technique is shown by a thin solid line.
- the spectrum when the overlap of pulse waves is detected according to this embodiment is shown by a thick solid line.
- the intensity of the thumb peak decreases.
- the intensity of the thumb peak is further reduced as compared with the prior art. Therefore, in the present embodiment, it is possible to effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, which has been difficult to detect in the past.
- By effectively detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves it is possible to suppress erroneous measurement of radiation energy due to the overlap of pulse waves.
- the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave is lowered, it is possible to detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves. Therefore, it is possible to lower the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave, and it becomes easy to detect an element having a low radiation energy such as a light element.
- the signal processing device 2 detects the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using the learning model 232.
- the learning model 232 outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input.
- the learning model 232 determines whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap from the entire signal waveform, it is less susceptible to noise than the conventional determination method based on the feature amount of the signal waveform, and is more reliable. The presence or absence of overlap of multiple pulse waves can be obtained.
- the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the radiation spectrum.
- the signal processing device 2 can execute the processing at a higher speed than the case of processing the image of the signal by processing the sequence of the signal values, and can detect the overlap of the pulse waves in almost real time. it can.
- FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the second embodiment.
- the configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- the processing unit 23 is connected to the waveform shaping unit 22 and the A / D conversion unit 21.
- the processing unit 23 inputs a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and inputs a signal including a step wave from the A / D conversion unit 21.
- the processing unit 23 stores the signal value constituting the signal including the pulse wave and the signal value constituting the signal including the staircase wave in the buffer memory 231.
- the learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap when a signal including a pulse wave and a signal including a staircase wave are input.
- the learning model 232 uses a fully connected neural network as in the first embodiment.
- the input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 in which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input, and a plurality of nodes 41 in which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. Includes node 41.
- the node 43 of the output layer of the learning model 232 outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlapping of the plurality of pulse waves, as in the first embodiment.
- the configuration of the parts other than the A / D conversion unit 21 and the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
- the learning of the learning model 232 is performed by the learning device 5 as in the first embodiment.
- the calculation unit 51 of the learning device 5 In addition to generating a plurality of pulse wave signals in S11, the calculation unit 51 of the learning device 5 generates a stair wave signal corresponding to the signal including the stair wave before the pulse wave is converted by the waveform shaping unit 22. ..
- the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of staircase wave signals including staircase waves by simulation, in which at least one of the wave height, rise and roundness of the staircase wave is random, and white noise is superimposed, and the staircase wave signal is generated.
- a pulse wave signal may be generated by differentiating.
- the noise superimposed on the signal may be 1 / f noise, and the noise may not be superimposed.
- the arithmetic unit 51 in addition to the generation of the plurality of superimposed wave signals in S12, the arithmetic unit 51 generates a proximity staircase wave signal corresponding to the signal including the plurality of staircase waves before the superimposed wave is converted by the waveform shaping unit 22. To do. On the contrary, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals including two proximity staircase waves in which at least one of the wave height, the rise and the roundness is random by simulation, and differentiates the proximity staircase wave signals. May generate a superimposed wave signal. The calculation unit 51 may use the actually measured staircase wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal instead of using the staircase wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal created by the simulation.
- the calculation unit 51 performs processing for generating the learning model 232 by using the plurality of pulse wave signals and staircase wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals and proximity staircase wave signals as teacher data.
- the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the pulse wave signal and the step wave signal to the input layer of the learning model 232. Further, the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the superimposed wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal to the input layer of the learning model 232.
- the calculation unit 51 adjusts the calculation parameters of each node of the learning model 232 by the error back propagation method.
- the calculation unit 51 repeats the process using the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals to perform machine learning of the learning model 232.
- the signal processing device 2 executes the processes of S21 to S25 as in the first embodiment.
- the processing unit 23 comprises a string of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave input from the waveform shaping unit 22, and a signal value constituting a signal including a staircase wave input from the A / D conversion unit 21.
- the column of is input to the training model 232.
- the learning model 232 performs a neural network operation and outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap.
- the signal processing device 2 executes the processes of S27 to S29 as in the first embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the number of counts, and the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2 and the radiation spectrum detected by the radiation detector 1. To generate.
- the analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation.
- the signal processing device 2 inputs a signal including a step wave before being converted into a pulse wave into the learning model 232 in addition to the signal including the pulse wave, and inputs the pulse wave. Detects overlap. When a plurality of pulse waves overlap, the interval between the staircase waves is short, and the waveform of the signal including the staircase wave is also different from that when the pulse waves do not overlap. Therefore, by using the signal including the staircase wave in addition to the signal including the pulse wave, it becomes easier to determine whether or not there is an overlap of the pulse waves.
- the signal processing device 2 can detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves more effectively as compared with the first embodiment, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. it can.
- the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using a signal including a staircase wave without using a signal including a pulse wave.
- the learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap when a signal including a staircase wave is input.
- the input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input.
- the learning device 5 generates a staircase wave signal and a proximity staircase wave signal, and performs machine learning of the learning model 232 using the plurality of staircase wave signals and the proximity staircase wave signal as teacher data.
- the signal processing device 2 does not input the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave to the learning model 232, but inputs the sequence of the signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave to the learning model 232.
- the learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Similar to the first embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the signal processing device 2 further inputs the signal including the shaped wave obtained by shaping the pulse wave by the waveform shaping unit 22 into the learning model 232. , It may be in the form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the shaped wave corresponds to, for example, the second derivative of the staircase wave.
- the learning model 232 a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave are input. In this case, it is learned in advance to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap.
- the input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave is input.
- the learning device 5 In the learning of the learning model 232, the learning device 5 generates a signal including a shaped wave and a signal obtained by shaping the superimposed wave signal, and generates a pulse wave signal and / or a staircase wave signal, a signal containing the shaped wave, and a superimposed wave.
- Machine learning is performed using the signal and / or the proximity step wave signal and the signal obtained by shaping the superimposed wave signal as training data.
- the signal processing device 2 includes a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave, and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave. Is input to the learning model 232.
- the learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Also in this form, the signal processing device 2 can more effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
- the signal processing device 2 is in the form of detecting the overlap of the pulse waves by further inputting the feature amount of the signal waveform into the learning model 232 in addition to the signal including the pulse wave and / or the signal including the step wave.
- the feature amount of the signal waveform is, for example, a wave height, a rising time constant, a time width of a signal wave, or the like.
- the learning model 232 receives a plurality of pulses when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a feature amount of a signal waveform are input. It has been learned in advance to output information indicating whether or not there is overlap of waves.
- the signal processing device 2 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a feature amount of a signal waveform into the learning model 232. To do.
- the learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Further, a signal including a shaping wave may also be used. Since the feature amount of the signal waveform is different between the single pulse wave and the superimposed wave, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves can be detected more effectively by using the feature amount of the signal waveform. Therefore, the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
- FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the third embodiment.
- the configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a waveform shaping unit 22, a processing unit 23, a wave height measuring unit 25, and a counting unit 26.
- the processing unit 23 does not have a buffer memory.
- the processing unit 23 is input with at least one of a signal including a staircase wave from the A / D conversion unit 21 and a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- FIG. 12 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the third embodiment.
- the learning model 232 outputs the probability of the number of overlapping pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. It has been learned in advance so as to do so.
- the output layer of the learning model 232 has a plurality of nodes 43. Each node 43 receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, calculates the received data using parameters, and outputs the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves included in the signal is a specific number.
- one node 43 outputs the probability that the signal does not contain a pulse wave
- the other node 43 outputs the probability that a plurality of pulse waves do not overlap and the number of pulse waves is one.
- the other node 43 outputs the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves is two.
- the node 43 may output the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves is a specific number as a real number of 0 to 1, or may output as a binary value of 0 or 1.
- the learning device 5 uses the signal not including the pulse wave and the staircase wave, the pulse wave signal and / or the staircase wave signal, and the superimposed wave signal and / or the proximity staircase wave signal as training data. Perform machine learning.
- the learning device 5 associates information that the probability that there is no pulse wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 with the signal that does not include the pulse wave and the step wave, and the pulse wave signal and / or the step wave signal is pulsed.
- the information that the probability of one wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 is associated, and the superimposed wave signal and / or the proximity staircase wave signal has a probability of having multiple pulse waves of 1 and other probabilities. Associate information that is 0.
- the learning device 5 calculates an error of information by an error function having each probability indicated by the information associated with the signal input to the input layer and each probability output from the output layer as variables, and back-propagates the information.
- the calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so that the error is minimized by the method.
- FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the third embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a step wave from the radiation detector 1 (S31), and the A / D conversion unit 21 converts the signal into A / D (S32).
- the A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the waveform shaping unit 22.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 shapes the waveform of the input signal (S33). Waveform shaping converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave.
- the waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the processing unit 23 receives a signal including a step wave from the A / D conversion unit 21 and / or a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and learns a sequence of signal values constituting the input signal. Input to model 232 (S34). As described above, the learning model 232 performs the operation of the neural network and outputs the probability of the number of overlapping pulse waves.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25. At this time, the processing unit 23 may input the probability output by the learning model 232 to the wave height measuring unit 25 as information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves.
- the processing unit 23 determines the number of overlapping pulse waves based on the probability, and even if the information indicating the determined number is input to the wave height measuring unit 25 as the information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves. Good. For example, the processing unit 23 determines that the number having the maximum probability or the number having the probability equal to or higher than a predetermined value is the number of overlapping pulse waves.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 identifies whether or not the number of pulse waves is one based on the input information (S35). When the number of pulse waves is one (S35: YES), the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S36). The wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26. The counting unit 26 counts the pulse wave according to the wave height (S37), and ends the process. When the number of pulse waves is other than one (S35: NO), the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S31 to S37.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26.
- the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data.
- the analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation. Also in this embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
- the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using a signal including a shaped wave obtained by further shaping the pulse wave by the waveform shaping unit 22. Further, the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
- FIG. 14 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the fourth embodiment.
- the configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a processing unit 23, and a counting unit 26.
- the A / D conversion unit 21 inputs a signal including a staircase wave to the processing unit 23.
- FIG. 15 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the fourth embodiment.
- the learning model 232 is pre-learned to output the probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal and the wave height of the staircase wave when a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave is input. ..
- the output layer of the learning model 232 has a plurality of nodes 43. Each node 43 receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, and calculates the received data using parameters. One node 43 outputs the height of the staircase wave included in the signal. The other node 43 outputs the probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal.
- a node 43 that outputs the probability that the signal does not include staircase waves a node 43 that outputs the probability that the number of staircase waves is one, and a node that outputs the probability that the number of staircase waves is two.
- the node 43 may output the probability that the number of staircase waves is a specific number as a real number from 0 to 1, or may output as a binary value of 0 or 1.
- the probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal is information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting a plurality of staircase waves.
- the learning device 5 performs machine learning using the signal not including the staircase wave, the staircase wave signal, and the proximity staircase wave signal as teacher data.
- the learning device 5 associates information indicating that the wave height is zero, the probability that there is no staircase wave is 1, and the other probabilities are 0 with the signal that does not include the staircase wave.
- the learning device 5 associates the wave height of the stair wave with the information indicating that the probability that there is one stair wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 in the stair wave signal.
- the learning device 5 associates the proximity staircase wave signal with the sum of the wave heights of the plurality of staircase waves and information indicating that the probability of having a plurality of staircase waves is 1 and the other probabilities are 0.
- the learning device 5 calculates an error of information by an error function having the wave height and each probability indicated by the information associated with the signal input to the input layer and each probability output from the output layer as variables, and the error.
- the calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so that the error is minimized by the back propagation method.
- FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the fourth embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a step wave from the radiation detector 1 (S41), and the A / D conversion unit 21 converts the signal into A / D (S42).
- the A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the processing unit 23.
- the processing unit 23 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the input signal to the learning model 232 (S43). As described above, the learning model 232 performs the calculation of the neural network and outputs the wave height of the staircase wave included in the signal and the probability of the number of staircase waves.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the wave height and the number of staircase waves to the counting unit 26. At this time, the processing unit 23 may input the probability output by the learning model 232 to the counting unit 26 as information indicating the number of staircase waves. Further, the processing unit 23 may determine the number of staircase waves based on the probability, and input the information indicating the determined number to the counting unit 26 as the information indicating the number of staircase waves. For example, the processing unit 23 determines that the number having the maximum probability or the number having the probability equal to or higher than a predetermined value is the number of staircase waves.
- the counting unit 26 specifies whether or not the number of staircase waves is one based on the input information (S44). When the number of staircase waves is one (S44: YES), the counting unit 26 counts the staircase waves according to the wave height (S45), and ends the process. As a result, the counting unit 26 counts the staircase waves when there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves converted from the plurality of staircase waves. When the number of staircase waves is other than one (S44: NO), the counting unit 26 does not count, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the staircase wave when the plurality of pulse waves converted from the plurality of staircase waves overlap. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S41 to S45.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the staircase wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26.
- the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data.
- the analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation.
- the signal processing device 2 can efficiently detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from a plurality of staircase waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. It can be improved further.
- the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by also using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
- FIG. 17 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the processing unit 23 according to the fifth embodiment.
- the processing unit 23 has a calculation unit 233 and a memory 234.
- the calculation unit 233 is configured by using, for example, a CPU, a GPU, or a multi-core CPU.
- the calculation unit 233 may be configured by using a quantum computer.
- the memory 234 is a non-volatile memory.
- the memory 234 stores the computer program 235.
- the calculation unit 233 executes the processing required for the processing unit 23 according to the computer program 235.
- the learning model 232 is realized by the arithmetic unit 233 executing information processing according to the computer program 235.
- the calculation unit 233 executes information processing according to the computer program 235 to execute the processing required for the processing units 23 in the first to fourth embodiments. In this way, the processing unit 23 in the first to fourth embodiments is realized.
- the configurations and functions of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first to fourth embodiments.
- the configuration and function of the parts other than the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 are the same as those of the first to fourth embodiments.
- the signal processing device 2 and the radiation detection device 10 perform the same processing as in the first to fourth embodiments. Also in this embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can efficiently detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from a plurality of staircase waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. It can be improved further.
- a part or all of the part other than the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 may also be realized by using a computer program.
- FIG. 18 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the sixth embodiment.
- the configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a waveform shaping unit 22, a processing unit 23, a pulse detection unit 24, a wave height measuring unit 25, a counting unit 26, and a storage unit 27.
- the processing unit 23 does not include the learning model.
- a storage unit 27 is connected to the processing unit 23.
- the storage unit 27 is non-volatile.
- the storage unit 27 is composed of a non-volatile semiconductor memory.
- the storage unit 27 stores a predetermined coefficient sequence.
- the configuration of the parts other than the processing unit 23 and the storage unit 27 of the signal processing device 2 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
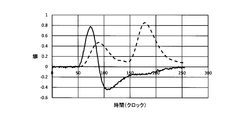
- 19 and 20 are graphs showing an example of a coefficient sequence.
- the horizontal axis in the figure indicates the time in units of clock, and the vertical axis indicates the coefficient value or signal value.
- the coefficient sequence is a one-dimensional array in which a plurality of coefficients are arranged.
- a signal including a single pulse wave is shown by a broken line
- a coefficient sequence is shown by a solid line.
- a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is shown side by side at clock intervals.
- a plurality of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence are shown in order at clock intervals.
- the plurality of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence are for performing a product-sum operation with a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave.
- m be the number of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence.
- the coefficient sequence be a 1 , a 2 , ..., Am
- the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave be x 1 , x 2 , ....
- Product-sum operation is represented by (a 1 * x 1 + a 2 * x 2 + ... + a m * x m + C).
- C is a constant value.
- the constant value C is stored in the storage unit 27.
- the coefficient sequence rises almost at the same time as the pulse wave, increases and decreases in a shorter period than the pulse wave, becomes almost zero near the peak of the pulse wave, and thereafter becomes a negative value. It slowly approaches the value of zero.
- the coefficient sequence is set so that the result of the product-sum operation with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including a single pulse wave becomes almost zero. As shown in FIG. 19, the value of the signal including the pulse wave becomes almost zero at the time of the clock 150, and the product-sum operation after that becomes almost zero.
- the result of the product-sum calculation of the signal value before the peak of the pulse wave and the positive coefficient is a positive value
- the product-sum calculation of the signal value after the peak of the pulse wave and the negative coefficient is performed.
- the change in the coefficient value is defined so that the result is a negative value and the total is almost zero. Therefore, the result of the product-sum calculation of the sequence of signal values and the coefficient sequence constituting the signal including a single pulse wave becomes almost zero. In this way, the coefficient sequence is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation with the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes almost zero.
- the signal including the superimposed wave is shown by a broken line, and the coefficient sequence is shown by a solid line.
- the coefficient sequences shown in FIGS. 19 and 20 are the same.
- the signal value of the signal including the superimposed wave keeps a positive value even after the time of the clock 150.
- the coefficient sequence has a negative value after the time of the clock 150. Therefore, the result of the product-sum calculation of the string of signal values and the coefficient string constituting the signal including the superimposed wave becomes a negative value after the time of the clock 150.
- the result of the product-sum operation is almost zero, as in the case of a single pulse wave.
- the result of the product-sum calculation of the string of signal values and the sequence of coefficients constituting the signal including the superimposed wave is a negative value.
- the coefficient sequence is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation with the signal including the superimposed wave becomes a negative value. That is, with a predetermined value less than zero as the reference value, the result of the product-sum calculation with the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes larger than the reference value in the coefficient sequence, and the product-sum calculation with the signal containing the superimposed wave is performed. The result is set to be smaller than the reference value.
- FIG. 21 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the sixth embodiment.
- the signal processing device 2 executes the processing of S51 to S55 similar to the processing of S21 to S25 in the first embodiment.
- the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23, and the processing unit 23 inputs the information.
- the product-sum calculation of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal and the sequence of coefficients stored in the storage unit 27 is performed (S56).
- the processing unit 23 determines whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap in the input signal according to the result of the product-sum calculation (S57). In S57, the processing unit 23 determines that there is overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the result of the product-sum calculation is less than the reference value of less than zero, and when the result of the product-sum calculation is greater than or equal to the reference value. , It is determined that there is no overlap of multiple pulse waves.
- the reference value is stored in advance in the processing unit 23 or the storage unit 27.
- the processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlapping of the plurality of pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S58), and inputs the measured wave height to the counting unit 26. ..
- the counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to the wave height input from the wave height measuring unit 25 (S59), and ends the process.
- the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height for the overlapping plurality of pulse waves, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves.
- the signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S51 to S59 individually.
- the signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts.
- the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data.
- the analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation.
- the result of the product-sum calculation with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including a single pulse wave is smaller than the reference value, and the product with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the superimposed wave. It may be set so that the result of the sum operation is larger than the reference value. For example, in the coefficient sequence, the result of the product-sum calculation of the signal value sequence and the coefficient sequence constituting the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes almost zero, and the result of the product-sum calculation with the signal including the superimposed wave is almost zero. It may be set to be a positive value.
- the processing unit 23 determines that there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the result of the product-sum calculation exceeds the reference value, using a predetermined value exceeding zero as a reference value. When the result of the product-sum operation is equal to or less than the reference value, it is determined that the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap.
- the signal processing device 2 performs a product-sum calculation of a string of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and a predetermined coefficient string, and is based on the result of the product-sum calculation. Then, the overlap of pulse waves is detected. Also in the sixth embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. Since the determination is performed by the product-sum calculation without using the learning model, the signal processing device 2 can execute the processing at a higher speed.
- the signal processing device 2 may be in a form in which both the method using the learning model 232 shown in the first or second embodiment and the method using the result of the product-sum calculation shown in the sixth embodiment are executed. For example, the signal processing device 2 determines whether or not there is overlap of pulse waves in both the method using the learning model 232 and the method using the result of the product-sum calculation, and the overlap of pulse waves is performed by either method. When it is determined that there is, it is determined that the overlap of pulse waves has occurred. In the first to sixth embodiments, the signal processing device 2 includes the counting unit 26, but the counting unit 26 may be provided outside the signal processing device 2.
- the radiation detection element 11 is a semiconductor radiation detection element
- the radiation detector 1 may have a form in which the radiation detection element 11 other than the semiconductor radiation detection element is used.
- the radiation detector 1 may be a scintillation detector.
- Radiation detector 10 Radiation detection device 11 Radiation detection element 2 Signal processing device 21 A / D conversion unit 22 Waveform shaping unit 23 Processing unit 232 Learning model 235 Computer program 25 Wave height measurement unit 26 Counting unit 27 Storage unit 3 Analysis unit 5 Learning apparatus
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Measurement Of Radiation (AREA)
Abstract
Provided are a signal processing method, a learning model generation method, a signal processing device, a radiation detection device, and a computer program which are capable of improving the accuracy of elemental analysis. In a signal processing method for counting, by wave height, a staircase wave corresponding to radiation detection or a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave, when at least one among a string of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave and a string of signal values constituting a signal including the pulse wave are input, at least one among the string of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave and the string of signal values constituting a signal including the pulse wave is input to a learning model that outputs information regarding whether a plurality of the pulse waves overlap or not, and the staircase wave or the pulse wave when the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap is counted in accordance with the information output by the learning model.
Description
本発明は、放射線の検出によって発生する信号を処理するための信号処理方法、学習モデル生成方法、信号処理装置、放射線検出装置及びコンピュータプログラムに関する。
The present invention relates to a signal processing method for processing a signal generated by detection of radiation, a learning model generation method, a signal processing device, a radiation detection device, and a computer program.
X線等の放射線を検出する放射線検出装置は、放射線検出器と、放射線検出器が出力する信号を処理する信号処理装置とを備えている。放射線検出器は、半導体放射線検出素子等を用いて構成されており、放射線が検出される都度、階段波を出力する。信号処理装置は、階段波をパルス波へ変換し、パルス波の波高を測定する。パルス波の波高は放射線のエネルギーに対応する。
The radiation detection device that detects radiation such as X-rays includes a radiation detector and a signal processing device that processes a signal output by the radiation detector. The radiation detector is configured by using a semiconductor radiation detection element or the like, and outputs a staircase wave each time radiation is detected. The signal processing device converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave and measures the height of the pulse wave. The height of the pulse wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation.
放射線が検出される間隔が短い場合、複数のパルス波が重なり、パルス波の波高が変化する所謂パイルアップが発生することがある。このとき、誤った放射線のエネルギーが測定され、放射線のスペクトルには、誤ったエネルギーを有するピーク、所謂サムピークが発生する。そこで、信号処理装置は、パルス波の重なりを検出し、重なったパルス波の波高の測定を行わないことにより、サムピークの発生を抑制する。従来、パルス波の重なりを検出する方法には、いくつかの方法がある。例えば、波高の閾値を用いてパルス波を検出し、複数のパルス波の検出間隔が短い場合に、パルス波の重なりが発生したと判定する。また、パルス波の底辺の長さ又はパルス波の立ち上がり速度等の信号波形の特徴量に基づいて、パルス波の重なりが発生したか否かを判定する方法がある。特許文献1には、パルス波の微分波形が負の値から正の値へ変化する場合に、パルス波の重なりが発生したと判定する技術が開示されている。
If the interval at which radiation is detected is short, multiple pulse waves may overlap, causing so-called pile-up in which the height of the pulse waves changes. At this time, the energy of erroneous radiation is measured, and a peak having erroneous energy, a so-called sum peak, is generated in the spectrum of radiation. Therefore, the signal processing device detects the overlap of the pulse waves and suppresses the occurrence of the sum peak by not measuring the wave height of the overlapped pulse waves. Conventionally, there are several methods for detecting the overlap of pulse waves. For example, a pulse wave is detected using a threshold value of wave height, and when the detection interval of a plurality of pulse waves is short, it is determined that overlap of pulse waves has occurred. Further, there is a method of determining whether or not the overlap of pulse waves has occurred based on the feature amount of the signal waveform such as the length of the base of the pulse wave or the rising speed of the pulse wave. Patent Document 1 discloses a technique for determining that overlap of pulse waves has occurred when the differential waveform of a pulse wave changes from a negative value to a positive value.
従来の何れの方法であっても、パルス波の重なりを検出できないことがある。パルス波の検出間隔に基づく方法では、検出間隔が非常に短い場合に、信号処理装置は、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出できないことがある。底辺の長さ等の信号波形の特徴量に基づく方法は、特徴量のみに着目するため、ノイズに弱いという問題がある。また、パルス波を検出するための閾値を低くした場合は、波高の高い複数のパルス波の重なりを検出できず、閾値を高くした場合は、波高の低いパルス波を検出できない。放射線のスペクトルに基づいて元素分析を行う際には、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出できない場合に、サムピークが発生し、存在しない元素を誤検出する虞がある。波高の低いパルス波を検出できない場合は、軽元素等、放射線のエネルギーの低い元素の検出が困難となる。
With any of the conventional methods, it may not be possible to detect the overlap of pulse waves. In the method based on the pulse wave detection interval, the signal processor may not be able to detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the detection interval is very short. The method based on the feature amount of the signal waveform such as the length of the base has a problem that it is vulnerable to noise because it focuses only on the feature amount. Further, when the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave is lowered, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves having a high wave height cannot be detected, and when the threshold value is raised, the pulse wave having a low wave height cannot be detected. When performing elemental analysis based on the radiation spectrum, if the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves cannot be detected, a sum peak may occur and an element that does not exist may be erroneously detected. If a pulse wave with a low wave height cannot be detected, it becomes difficult to detect an element having a low radiation energy such as a light element.
本発明は、斯かる事情に鑑みてなされたものであって、その目的とするところは、放射線のスペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度を向上させることができる信号処理方法、学習モデル生成方法、信号処理装置、放射線検出装置及びコンピュータプログラムを提供することにある。
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is a signal processing method, a learning model generation method, and a signal capable of improving the accuracy of elemental analysis based on a radiation spectrum. To provide processing equipment, radiation detection equipment and computer programs.
本発明に係る信号処理方法は、放射線の検出に応じた階段波又は前記階段波を変換したパルス波を、波高別にカウントする信号処理方法において、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルへ、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力し、前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりが無い場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントすることを特徴とする。
The signal processing method according to the present invention is a signal processing method for counting a staircase wave corresponding to radiation detection or a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave by wave height, and is a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave. And, when at least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input, the signal including the step wave is configured in a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves. When at least one of the sequence of signal values and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input, and the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap according to the information output by the learning model. It is characterized by counting the staircase wave or the pulse wave.
本発明の一形態においては、学習モデルを利用して、パルス波の重なりを検出する。学習モデルは、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する。学習モデルを用いることにより、複数のパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the overlap of pulse waves is detected by using a learning model. The training model outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. To do. By using the learning model, it is possible to effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
本発明に係る信号処理方法は、前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波が重なる場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントしないことを特徴とする。
The signal processing method according to the present invention is characterized in that the staircase wave or the pulse wave when a plurality of the pulse waves overlap is not counted according to the information output by the learning model.
本発明の一形態においては、複数のパルス波が重なる場合は、放射線の検出に応じたカウントを行わない。パルス波の重なりに起因して放射線のエネルギーを誤って測定することを防止することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, when a plurality of pulse waves overlap, counting is not performed according to the detection of radiation. It is possible to prevent erroneous measurement of radiation energy due to the overlap of pulse waves.
本発明に係る信号処理方法は、前記学習モデルは、前記パルス波を整形した波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を更に入力した場合に前記情報を出力する学習モデルであり、前記信号を構成する信号値の列を更に前記学習モデルへ入力することを特徴とする。
In the signal processing method according to the present invention, the learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when a string of signal values constituting a signal including a wave obtained by shaping the pulse wave is further input, and the signal is used. It is characterized in that a sequence of constituent signal values is further input to the learning model.
本発明の一形態においては、パルス波を含む信号及び/又は階段波を含む信号に加えて、パルス波を整形した波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を、学習モデルへ入力する。微分フィルタ等のフィルタによってパルス波を整形した波の形状は、複数のパルス波の有無に応じて異なる。このため、パルス波を整形した波を利用することにより、複数のパルス波の重なりをより効果的に検出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, in addition to the signal including the pulse wave and / or the signal including the step wave, a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the wave formed by shaping the pulse wave is input to the learning model. The shape of the pulse wave shaped by a filter such as a differential filter differs depending on the presence or absence of a plurality of pulse waves. Therefore, by using a wave obtained by shaping a pulse wave, it is possible to more effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
本発明に係る信号処理方法は、前記学習モデルは、前記階段波及び前記パルス波の少なくとも一方の特徴量を更に入力した場合に前記情報を出力する学習モデルであり、前記特徴量を前記学習モデルへ入力することを特徴とする。
In the signal processing method according to the present invention, the learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when at least one feature amount of the staircase wave and the pulse wave is further input, and the feature amount is the learning model. It is characterized by inputting to.
本発明の一形態においては、波高又は時間幅等の信号波形の特徴量を更に学習モデルへ入力する。信号波形の特徴量は、複数のパルス波の有無に応じて異なるので、信号波形の特徴量を用いることにより、複数のパルス波の重なりをより効果的に検出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the feature amount of the signal waveform such as the wave height or the time width is further input to the learning model. Since the feature amount of the signal waveform differs depending on the presence or absence of the plurality of pulse waves, the overlap of the plurality of pulse waves can be detected more effectively by using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
本発明に係る学習モデル生成方法は、夫々に単一のパルス波からなり、前記単一のパルス波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数のパルス波信号を生成し、夫々に複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波からなり、前記複数のパルス波の間隔、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の重畳波信号を生成し、前記複数のパルス波信号及び前記複数の重畳波信号を教師データとして、任意のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力した場合に複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを生成することを特徴とする。
The learning model generation method according to the present invention is composed of a single pulse wave, and generates a plurality of pulse wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise, and roundness of the single pulse wave is random. Each of the plurality of pulse waves is composed of a superposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped, and a plurality of superposed wave signals in which at least one of the interval, the wave height, the rising edge and the roundness of the plurality of pulse waves is random are generated, and the plurality of pulse waves Using the signal and the plurality of superimposed wave signals as training data, a learning model is generated that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary pulse wave is input. It is characterized by that.
本発明の一形態においては、夫々に単一のパルス波からなる複数のパルス波信号と、夫々に複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波からなる複数の重畳波信号とを、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムになるようにシミュレーションにより生成する。生成した複数のパルス波信号及び複数の重畳波信号を教師データとして、学習モデルの学習を行う。パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルが生成できる。また、シミュレーションにおいてパルス波のなまりをランダムにすることにより、実際の信号に近い信号を生成することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, a plurality of pulse wave signals each consisting of a single pulse wave and a plurality of superimposed wave signals each consisting of a superposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped are subjected to wave height, rising edge, and randomness. Generate by simulation so that at least one of the above is random. The learning model is trained using the generated plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals as teacher data. A learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlapping pulse waves can be generated. Further, by randomizing the bluntness of the pulse wave in the simulation, it is possible to generate a signal close to the actual signal.
本発明に係る学習モデル生成方法は、夫々に単一の階段波からなり、前記単一の階段波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の階段波信号を生成し、夫々に複数の階段波からなり、前記複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波が重なることになり、前記複数の階段波の間隔、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の近接階段波信号を生成し、前記複数の階段波信号及び前記近接階段波信号を教師データとして、任意の階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力した場合に前記複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを生成することを特徴とする。
The learning model generation method according to the present invention is composed of a single staircase wave, and generates a plurality of staircase wave signals in which at least one of the wave height, rise and roundness of the single staircase wave is random. Each consists of a plurality of staircase waves, and a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting the plurality of staircase waves overlap each other, and at least one of the intervals, wave heights, rising edges, and rounds of the plurality of staircase waves is random. When the plurality of staircase wave signals and the proximity staircase wave signal are used as teacher data and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary staircase wave is input, the plurality of staircase wave signals are generated. It is characterized by generating a learning model that outputs information on the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from.
本発明の一形態においては、夫々に単一の階段波からなる複数の階段波信号と、複数の近接階段波信号とを、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムになるようにシミュレーションにより生成する。生成した複数の階段波信号及び複数の近接階段波信号を教師データとして、学習モデルの学習を行う。階段波を変換したパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルが生成できる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, a plurality of staircase wave signals each consisting of a single staircase wave and a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals are simulated so that at least one of wave height, rise and roundness is random. Generated by. The learning model is trained using the generated plurality of staircase wave signals and a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals as teacher data. A learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of pulse waves converted from staircase waves can be generated.
本発明に係る信号処理方法は、放射線の検出に応じた階段波をパルス波へ変換し、前記パルス波の波高別に、前記パルス波をカウントする信号処理方法において、前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と所定の係数列との積和演算を行い、前記所定の係数列は、重なった複数の前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記所定の係数列の間の積和演算の結果と、単一の前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記所定の係数列の間の積和演算の結果とが、所定の値に対して大であるか小であるかについて異なるように、予め定められており、前記積和演算の結果に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定し、重なっていない前記パルス波をカウントすることを特徴とする。
The signal processing method according to the present invention converts a step wave corresponding to the detection of radiation into a pulse wave, and constitutes a signal including the pulse wave in a signal processing method for counting the pulse wave according to the height of the pulse wave. A product-sum calculation is performed between the sequence of signal values to be performed and the predetermined coefficient sequence, and the predetermined coefficient sequence is between the signal value sequence and the predetermined coefficient sequence constituting the signal including the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. The result of the product-sum calculation and the result of the product-sum calculation between the string of signal values constituting the signal including the single pulse wave and the predetermined coefficient sequence are larger than the predetermined value. It is predetermined to be different depending on whether it is small or small, and it is determined whether or not a plurality of the pulse waves are overlapped according to the result of the product-sum calculation, and the non-overlapping pulse waves are counted. It is characterized by doing.
本発明の一形態においては、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と所定の係数列との積和演算を行い、積和演算の結果に基づいて、パルス波の重なりを検出する。係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び係数列の間の積和演算の結果と、重なった複数のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び係数列の間の積和演算の結果とが異なるように、定められている。この方法においても、複数のパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, a product-sum calculation is performed on a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and a predetermined coefficient sequence, and the overlap of pulse waves is detected based on the result of the product-sum calculation. The coefficient sequence is the result of the product-sum operation between the string of signal values and the coefficient sequence that compose the signal containing a single pulse wave, and the sequence and coefficient of the signal values that compose the signal containing multiple overlapping pulse waves. It is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation between columns is different. Also in this method, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves can be effectively detected.
本発明に係る信号処理装置は、放射線の検出に応じた階段波を含む信号を処理する信号処理装置において、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に、複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを備えることを特徴とする。
The signal processing device according to the present invention is a signal processing device that processes a signal including a staircase wave according to the detection of radiation, and is a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and a pulse obtained by converting the staircase wave. It is characterized by including a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when at least one of a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a wave is input.
本発明に係る放射線検出装置は、放射線検出時に放射線のエネルギーに応じた階段波を出力する放射線検出器と、前記階段波をパルス波へ変換する変換部と、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列の少なくとも一方を入力した場合に、複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルと、前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりが無い場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントするカウント部と、前記階段波又は前記パルス波の波高、及びカウント数に応じて、放射線のスペクトルを生成するスペクトル生成部とを備えることを特徴とする。
The radiation detection device according to the present invention comprises a radiation detector that outputs a staircase wave according to the energy of radiation at the time of radiation detection, a conversion unit that converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave, and a signal including the staircase wave. A learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when at least one of the signal value sequence and the signal value sequence constituting the signal including the pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave is input. A counting unit that counts the staircase wave or the pulse wave when there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves, a wave height of the staircase wave or the pulse wave, and a count number according to the information output by the learning model. It is characterized by including a spectrum generation unit that generates a radiation spectrum according to the above.
本発明に係るコンピュータプログラムは、放射線の検出に応じた階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルへ、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列の少なくとも一方を入力して、前記情報を出力する処理をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とする。
The computer program according to the present invention has at least one of a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave corresponding to the detection of radiation and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave. A sequence of signal values constituting a signal including the staircase wave and a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave are sent to a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves when input. It is characterized in that a computer is made to execute a process of inputting at least one of them and outputting the information.
本発明の一形態においては、信号処理装置は、学習モデルを利用して、パルス波の重なりを検出する。学習モデルは、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する。放射線検出装置は、複数のパルス波の重なりが無い場合の階段波又はパルス波をカウントし、放射線のスペクトルを生成する。信号処理装置は、複数のパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出することができ、放射線検出装置は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度を向上させることができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the signal processing device uses a learning model to detect the overlap of pulse waves. The training model outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. To do. The radiation detector counts staircase waves or pulse waves when there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and generates a radiation spectrum. The signal processing device can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
本発明にあっては、パルス波の重なりを効果的に検出し、元素分析の精度を向上させることができる等、優れた効果を奏する。
The present invention has excellent effects such as being able to effectively detect the overlap of pulse waves and improve the accuracy of elemental analysis.
以下本発明をその実施の形態を示す図面に基づき具体的に説明する。
<実施形態1>
図1は、実施形態1に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出装置10は、放射線検出器1と、信号処理装置2と、分析部3とを備えている。放射線検出器1は、放射線検出素子11と、プリアンプ12とを備えている。放射線検出素子11は、SDD(Silicon Drift Detector)等の半導体放射線検出素子であり、入射した放射線のエネルギーに応じた電荷を発生し、発生した電荷に応じた電流信号を出力する。プリアンプ12は、放射線検出素子11が出力した電流信号を電圧信号へ変換し、放射線検出時に一段のステップ状に信号値が上昇する階段波を生成する。放射線検出器1は、プリアンプ12が生成した階段波を含む信号を出力する。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings showing the embodiments thereof.
<Embodiment 1>
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of theradiation detection device 10 according to the first embodiment. The radiation detection device 10 includes a radiation detector 1, a signal processing device 2, and an analysis unit 3. The radiation detector 1 includes a radiation detection element 11 and a preamplifier 12. The radiation detection element 11 is a semiconductor radiation detection element such as an SDD (Silicon Drift Detector), which generates an electric charge according to the energy of the incident radiation and outputs a current signal according to the generated electric charge. The preamplifier 12 converts the current signal output by the radiation detection element 11 into a voltage signal, and generates a step wave in which the signal value rises in a step-like manner at the time of radiation detection. The radiation detector 1 outputs a signal including a staircase wave generated by the preamplifier 12.
<実施形態1>
図1は、実施形態1に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出装置10は、放射線検出器1と、信号処理装置2と、分析部3とを備えている。放射線検出器1は、放射線検出素子11と、プリアンプ12とを備えている。放射線検出素子11は、SDD(Silicon Drift Detector)等の半導体放射線検出素子であり、入射した放射線のエネルギーに応じた電荷を発生し、発生した電荷に応じた電流信号を出力する。プリアンプ12は、放射線検出素子11が出力した電流信号を電圧信号へ変換し、放射線検出時に一段のステップ状に信号値が上昇する階段波を生成する。放射線検出器1は、プリアンプ12が生成した階段波を含む信号を出力する。 Hereinafter, the present invention will be specifically described with reference to the drawings showing the embodiments thereof.
<
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the
放射線検出器1が出力した信号は、信号処理装置2へ入力される。信号処理装置2は、信号処理方法を実行する。信号処理装置2は、A/D(アナログ/デジタル)変換部21を備えている。A/D変換部21は、放射線検出器1から階段波を含む信号を入力され、階段波を含む信号をA/D変換する。A/D変換部21には波形整形部22が接続されている。波形整形部22は、A/D変換部21から階段波を含む信号を入力される。波形整形部22は、階段波を含む信号を所定のフィルタに通して、信号の波形を整形することにより、階段波を含む信号をパルス波を含む信号へ変換する。波形整形部22が用いるフィルタは、例えば微分フィルタ又は台形整形フィルタである。波形整形部22での処理により、階段波がパルス波へ変換され、信号に含まれるノイズが低減され、所定の増幅が行われる。波形整形部22はパルス波を含む信号を出力する。波形整形部22は変換部に対応する。
The signal output by the radiation detector 1 is input to the signal processing device 2. The signal processing device 2 executes the signal processing method. The signal processing device 2 includes an A / D (analog / digital) conversion unit 21. The A / D conversion unit 21 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the radiation detector 1 and A / D-converts the signal including the staircase wave. A waveform shaping unit 22 is connected to the A / D conversion unit 21. The waveform shaping unit 22 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the A / D conversion unit 21. The waveform shaping unit 22 converts the signal including the staircase wave into the signal including the pulse wave by passing the signal including the staircase wave through a predetermined filter and shaping the waveform of the signal. The filter used by the waveform shaping unit 22 is, for example, a differential filter or a trapezoidal shaping filter. By the processing in the waveform shaping unit 22, the staircase wave is converted into a pulse wave, the noise contained in the signal is reduced, and a predetermined amplification is performed. The waveform shaping unit 22 outputs a signal including a pulse wave. The waveform shaping unit 22 corresponds to the conversion unit.
図2A及び図2Bは、階段波及びパルス波の例を示す模式的特性図である。図中の横軸は時間を示し、縦軸は信号値を示している。図2Aは放射線検出器1が出力する階段波を含む信号を示している。放射線検出器1は、放射線を検出する都度、一段のステップ状に信号値が上昇する階段波を出力する。一回の放射線検出に応じて、信号値が一段のステップ状に上昇する一つの階段波が生成される。放射線検出器1が放射線を複数回検出した場合、複数の階段波を含む信号が出力される。放射線が検出される都度、信号値は上昇していく。信号値が上昇するステップの高さを階段波の波高とする。階段波の波高は、放射線のエネルギーに対応する。実際には、階段波は完全なステップ状ではなく、信号波形に立ち上がり及びなまりが含まれている。立ち上がりは、信号値が基準値から立ち上がる際の信号波形の歪みであり、なまりは、階段波が終了する際の信号波形の歪みである。
2A and 2B are schematic characteristic diagrams showing examples of staircase waves and pulse waves. The horizontal axis in the figure shows time, and the vertical axis shows signal values. FIG. 2A shows a signal including a staircase wave output by the radiation detector 1. The radiation detector 1 outputs a step wave whose signal value rises in a step-like manner each time radiation is detected. In response to a single radiation detection, a step wave is generated in which the signal value rises in a step-like manner. When the radiation detector 1 detects radiation a plurality of times, a signal including a plurality of staircase waves is output. Each time radiation is detected, the signal value rises. The height of the step at which the signal value rises is defined as the wave height of the staircase wave. The height of the staircase wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation. In reality, the staircase wave is not completely stepped, and the signal waveform contains rising and rounding. The rising edge is the distortion of the signal waveform when the signal value rises from the reference value, and the rounding is the distortion of the signal waveform when the staircase wave ends.
図2Bは、図2Aに示す信号を波形整形部22で変換した信号を示す。階段波は、パルス波へ変換される。パルス波は、信号値がゼロになる所定の信号基準から信号値がピーク値まで上昇し、その後信号基準まで下降する信号である。信号基準は例えばゼロである。信号基準からピーク値までの高さをパルス波の波高とする。パルス波の波高は放射線のエネルギーに対応する。パルス波の形には、立ち上がり及びなまりが含まれている。立ち上がりは、信号値が基準値から立ち上がる際の信号波形の歪みであり、なまりは、パルス波が終了する際の信号波形の歪みである。図2Bには、放射線検出器1が放射線を複数回検出した間隔が長く、複数のパルス波が重畳していない例を示している。
FIG. 2B shows a signal obtained by converting the signal shown in FIG. 2A by the waveform shaping unit 22. The staircase wave is converted into a pulse wave. A pulse wave is a signal in which a signal value rises from a predetermined signal reference at which the signal value becomes zero to a peak value and then falls to a signal reference. The signal reference is, for example, zero. The height from the signal reference to the peak value is defined as the wave height of the pulse wave. The height of the pulse wave corresponds to the energy of the radiation. The shape of the pulse wave includes rising and rounding. The rising edge is the distortion of the signal waveform when the signal value rises from the reference value, and the rounding is the distortion of the signal waveform when the pulse wave ends. FIG. 2B shows an example in which the radiation detector 1 detects radiation a plurality of times at long intervals and a plurality of pulse waves are not superimposed.
図3A及び図3Bは、放射線の検出される間隔が短い場合の階段波及びパルス波の例を示す模式的特性図である。図中の横軸は時間を示し、縦軸は信号値を示している。図3Aは放射線検出器1が出力する階段波を含む信号を示している。図2Aに示した例に比べて、放射線検出器1が放射線を複数回検出した間隔が短く、複数の階段波の間隔が短い。図3Bは、図3Aに示す信号を波形整形部22で変換した信号を示す。複数のパルス波の間隔が短く、複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波が形成されている。重畳波の波高は、単独のパルス波の波高とは異なっており、重畳波の波高に応じて誤った放射線のエネルギーが測定される。
3A and 3B are schematic characteristic diagrams showing examples of staircase waves and pulse waves when the intervals at which radiation is detected are short. The horizontal axis in the figure shows time, and the vertical axis shows signal values. FIG. 3A shows a signal including a staircase wave output by the radiation detector 1. Compared to the example shown in FIG. 2A, the interval at which the radiation detector 1 detects radiation a plurality of times is short, and the interval between the plurality of staircase waves is short. FIG. 3B shows a signal obtained by converting the signal shown in FIG. 3A by the waveform shaping unit 22. The interval between the plurality of pulse waves is short, and a superposed wave in which the plurality of pulse waves overlap is formed. The wave height of the superimposed wave is different from the wave height of a single pulse wave, and the erroneous radiation energy is measured according to the wave height of the superimposed wave.
波形整形部22には、処理部23及びパルス検出部24が接続されている。波形整形部22は、処理部23及びパルス検出部24へ、パルス波を含む信号を入力する。パルス検出部24は、波形整形部22から信号を入力され、信号に含まれているパルス波を検出する。例えば、パルス検出部24は、信号値が所定の閾値を超過した場合に、パルス波を検出したと判定する。パルス検出部24は、処理部23に接続されている。パルス検出部24は、パルス波を検出した場合に、パルス波を検出したことを示す情報を処理部23へ入力する。
The processing unit 23 and the pulse detection unit 24 are connected to the waveform shaping unit 22. The waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the processing unit 23 and the pulse detecting unit 24. The pulse detection unit 24 receives a signal from the waveform shaping unit 22 and detects a pulse wave contained in the signal. For example, the pulse detection unit 24 determines that a pulse wave has been detected when the signal value exceeds a predetermined threshold value. The pulse detection unit 24 is connected to the processing unit 23. When the pulse detection unit 24 detects the pulse wave, the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23.
処理部23は、波形整形部22からパルス波を含む信号を入力され、パルス検出部24から、パルス波を検出したことを示す情報を入力される。処理部23は、演算を行う素子を用いて構成されている。処理部23は、バッファメモリ231と、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定するための学習モデル232とを含んでいる。例えば、学習モデル232は、FPGA(field-programmable gate array )を用いて構成されている。処理部23は、パルス波が検出された場合に、学習モデル232を用いて、信号に複数のパルス波の重なりが含まれるか否かを判定する。複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定する方法については、後述する。
The processing unit 23 receives a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and an information indicating that the pulse wave is detected is input from the pulse detection unit 24. The processing unit 23 is configured by using an element that performs an operation. The processing unit 23 includes a buffer memory 231 and a learning model 232 for determining whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. For example, the learning model 232 is configured by using FPGA (field-programmable gate array). When the pulse wave is detected, the processing unit 23 uses the learning model 232 to determine whether or not the signal includes the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves. A method for determining whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap will be described later.
波形整形部22及び処理部23には、波高測定部25が接続されている。波形整形部22は、波高測定部25へ、パルス波を含む信号を入力する。処理部23は、波高測定部25へ、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を入力する。波高測定部25は、複数のパルス波の重なりが無い場合に、波形整形部22から入力された信号に含まれるパルス波の波高を測定する。複数のパルス波の重なりがある場合は、波高測定部25は、波形整形部22から入力された信号に含まれるパルス波の波高を測定しない。
A wave height measuring unit 25 is connected to the waveform shaping unit 22 and the processing unit 23. The waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the wave height measuring unit 25. The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap to the wave height measuring unit 25. The wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the signal input from the waveform shaping unit 22 when the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap. When there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height of the pulse wave included in the signal input from the waveform shaping unit 22.
波高測定部25には、カウント部26が接続されている。波高測定部25は、測定したパルス波の波高をカウント部26へ入力する。カウント部26は、波高別にパルス波をカウントする。例えば、カウント部26は、マルチチャネルアナライザである。カウント部26は、全ての波高についてパルス波をカウントする形態であってもよく、又は特定の波高についてのみパルス波をカウントする形態であってもよい。信号処理装置2は、パルス波の波高とカウント部26がカウントしたカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力する。カウント数は、パルス波の波高に対応するエネルギーを有する放射線を放射線検出器1が検出した回数に対応する。
A counting unit 26 is connected to the wave height measuring unit 25. The wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26. The counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to wave height. For example, the counting unit 26 is a multi-channel analyzer. The counting unit 26 may be in a form of counting pulse waves for all wave heights, or may be in a form of counting pulse waves only for a specific wave height. The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26. The count number corresponds to the number of times that the radiation detector 1 detects radiation having energy corresponding to the wave height of the pulse wave.
複数のパルス波の重なりがある場合に波高測定部25がパルス波の波高を測定しないことにより、信号処理装置2は、重なったパルス波についてはカウントを行わない。なお、波高測定部25は、重なったパルス波については、波高の測定は行うものの、測定した波高をカウント部26へ入力しない形態であってもよい。波高測定部25は、重なったパルス波の波高をもカウント部26へ入力し、カウント部26は、重なったパルス波のカウントをしない形態であってもよい。波高測定部25は、重なったパルス波の波高をもカウント部26へ入力し、カウント部26は、重なっていないパルス波と重なったパルス波とを区別してカウントする形態であってもよい。
When there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height of the pulse waves, so that the signal processing device 2 does not count the overlapped pulse waves. The wave height measuring unit 25 may measure the wave height of the overlapping pulse waves, but may not input the measured wave height to the counting unit 26. The wave height measuring unit 25 may also input the wave heights of the overlapping pulse waves to the counting unit 26, and the counting unit 26 may be in a form in which the overlapping pulse waves are not counted. The wave height measuring unit 25 may also input the wave heights of the overlapping pulse waves to the counting unit 26, and the counting unit 26 may be in a form of distinguishing between the non-overlapping pulse waves and the overlapping pulse waves.
分析部3は、パーソナルコンピュータ等のコンピュータで構成されている。分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力される。分析部3は、パルス波の波高とカウント数との関係から、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する処理を行う。分析部3はスペクトル生成部に対応する。分析部3は、更に、生成した放射線のスペクトルに基づいて、放射線源の元素分析等の更なる処理を行ってもよい。例えば、試料へ放射線を照射し、試料から発生した特性X線を放射線検出器1で検出し、特性X線のスペクトルに基づいて、試料に含まれる元素の定性分析又は定量分析を行う。なお、信号処理装置2は、放射線のスペクトルを生成する機能をも有していてもよい。
The analysis unit 3 is composed of a computer such as a personal computer. The analysis unit 3 is input with the data output by the signal processing device 2. The analysis unit 3 performs a process of generating a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 from the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the count number. The analysis unit 3 corresponds to the spectrum generation unit. The analysis unit 3 may further perform further processing such as elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the generated spectrum of radiation. For example, the sample is irradiated with radiation, the characteristic X-rays generated from the sample are detected by the radiation detector 1, and qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis of the elements contained in the sample is performed based on the spectrum of the characteristic X-rays. The signal processing device 2 may also have a function of generating a radiation spectrum.
重なったパルス波が単独のパルス波と誤ってカウントされ、誤った放射線のエネルギーが測定された場合、放射線のスペクトルは、誤ったエネルギーを有するピークであるサムピークを含むことになる。サムピークを含むスペクトルに基づいて元素分析を行った場合は、サムピークに応じた存在しない元素を誤って検出する虞がある。或は、存在する元素のピークにサムピークが重なり、当該元素の量が過剰に検出される虞がある。例えば、Fe(鉄)のK線を検出したことにより発生する複数のパルス波が重なった場合、サムピークはPb(鉛)のL線のピークに重なり、Pbの量が過剰に検出される。Cu(銅)のK線を検出したことにより発生する複数のパルス波が重なった場合、サムピークはCd(カドミウム)のK線のピークに重なり、Cdの量が過剰に検出される。
If the overlapping pulse waves are erroneously counted as a single pulse wave and the wrong radiation energy is measured, the radiation spectrum will include the sum peak, which is the peak with the wrong energy. When elemental analysis is performed based on a spectrum including a sum peak, there is a risk of erroneously detecting an element that does not exist according to the sum peak. Alternatively, the sum peak may overlap the peak of an existing element, and the amount of the element may be excessively detected. For example, when a plurality of pulse waves generated by detecting the K line of Fe (iron) overlap, the thumb peak overlaps the peak of the L line of Pb (lead), and the amount of Pb is excessively detected. When a plurality of pulse waves generated by detecting the K line of Cu (copper) overlap, the thumb peak overlaps the peak of the K line of Cd (cadmium), and the amount of Cd is excessively detected.
処理部23における複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定する方法を説明する。図4は、処理部23へ入力される信号の例を模式的に示すグラフである。図中の横軸は時間を示し、縦軸は信号値を示す。信号は、所定の時間間隔で得られた離散的な信号値の時系列で構成される。即ち、信号は、信号値の列からなる一次元データで表される。
A method of determining whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap in the processing unit 23 will be described. FIG. 4 is a graph schematically showing an example of a signal input to the processing unit 23. The horizontal axis in the figure indicates time, and the vertical axis indicates signal value. The signal is composed of a time series of discrete signal values obtained at predetermined time intervals. That is, the signal is represented by one-dimensional data consisting of a sequence of signal values.
図2B及び図3Bに示すように、単一のパルス波を含む信号と、複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波を含む信号とでは、信号の形が異なり、信号値の時間変化も異なる。学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力するように、予め学習されている。
As shown in FIGS. 2B and 3B, a signal including a single pulse wave and a signal including a superimposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped have different signal shapes and different time changes in signal values. The learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input.
図5は、実施形態1に係る学習モデル232の機能構成例を示す概念図である。学習モデル232は、夫々に複数のノードを有する入力層、複数の中間層及び出力層を備えた全結合のニューラルネットワークを用いる。入力層は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列が入力される複数のノード41を有する。信号値の列の中の一つの信号値が一つのノード41へ入力され、夫々の信号値がいずれかのノード41へ入力される。例えば、入力層にはm個のノード41が含まれており、パルス波を含む信号を構成するm個の信号値が入力層へ入力される。
FIG. 5 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the first embodiment. The learning model 232 uses a fully coupled neural network with an input layer, a plurality of intermediate layers, and an output layer, each having a plurality of nodes. The input layer has a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input. One signal value in the signal value sequence is input to one node 41, and each signal value is input to one of the nodes 41. For example, the input layer includes m nodes 41, and m signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave are input to the input layer.
学習モデル232はn(nは自然数)層の中間層を有している。第1の中間層は、複数のノード421を有する。入力層の夫々のノード41は、複数のノード421へ信号値を出力する。複数のノード421は、入力層のノード41から信号値を受け付け、信号値にパラメータを用いて演算し、第2の中間層に含まれる複数のノード422へ演算結果のデータを出力する。各中間層に含まれるノードは、前の中間層の複数のノードからデータを受け付け、受け付けたデータにパラメータを用いて演算し、後の中間層のノードへデータを出力する。例えば、ノードは、前の層の各ノードから受け付けたデータの値をx、各ノードに対応する重みをw、バイアス値をb、活性化関数をf()として、f(Σ(w*x)+b)の演算を行い、演算結果のデータを後の層の複数のノードへ出力する。活性化関数は、例えば、relu関数又はシグモイド関数である。活性化関数は、一般的に機械学習で用いられるその他の関数であってもよい。
The learning model 232 has an intermediate layer of n (n is a natural number) layer. The first intermediate layer has a plurality of nodes 421. Each node 41 of the input layer outputs a signal value to a plurality of nodes 421. The plurality of nodes 421 receive signal values from the nodes 41 of the input layer, calculate the signal values using parameters, and output the calculation result data to the plurality of nodes 422 included in the second intermediate layer. The nodes included in each intermediate layer receive data from a plurality of nodes in the previous intermediate layer, calculate the received data using parameters, and output the data to the nodes in the subsequent intermediate layer. For example, the node has f (Σ (w * x), where x is the value of the data received from each node in the previous layer, w is the weight corresponding to each node, b is the bias value, and f () is the activation function. ) + B) is performed, and the data of the calculation result is output to a plurality of nodes in the subsequent layer. The activation function is, for example, a relu function or a sigmoid function. The activation function may be another function generally used in machine learning.
学習モデル232の出力層は、単一のノード43を有する。第nの中間層に含まれる複数のノード42nは、出力層に含まれるノード43へデータを出力する。出力層のノード43は、複数のノード42nからデータを受け付け、受け付けたデータにパラメータを用いて演算し、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を出力する。例えば、ノード43での活性化関数は、(Σ(w*x)+b)の演算結果が正の値であるか否かを示すデータを出力する関数である。例えば、ノード43は、正の値を示すデータとして1の値を出力し、ゼロ以下の値を示すデータとしてゼロの値を出力してもよい。例えば、正の値を示すデータは、複数のパルス波の重なりが無いことを示す情報であり、ゼロ以下の値を示すデータは、複数のパルス波の重なりがあることを示す情報である。なお、ノード43は、パルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報として、複数のパルス波の重なりが存在する確率を出力してもよい。学習モデル232は、ニューラルネットワークとして、畳みこみニューラルネットワーク(CNN:Convolutional Neural Network)、又は再帰型ニューラルネットワーク(RNN:Recurrent Neural Network)を用いてもよい。
The output layer of the learning model 232 has a single node 43. The plurality of nodes 42n included in the nth intermediate layer output data to the node 43 included in the output layer. The node 43 of the output layer receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, calculates the received data using parameters, and outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves. For example, the activation function at the node 43 is a function that outputs data indicating whether or not the calculation result of (Σ (w * x) + b) is a positive value. For example, the node 43 may output a value of 1 as data indicating a positive value and output a value of zero as data indicating a value of zero or less. For example, the data showing a positive value is information indicating that there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and the data showing a value of zero or less is information indicating that there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves. Note that the node 43 may output the probability that a plurality of pulse waves overlap each other as information indicating the presence or absence of the overlap of the pulse waves. As the learning model 232, a convolutional neural network (CNN: Convolutional Neural Network) or a recurrent neural network (RNN: Recurrent Neural Network) may be used as the neural network.
学習モデル232の学習は、コンピュータを用いて行われる。図6は、学習モデル232の学習を行う学習装置5の構成例を示すブロック図である。学習装置5は学習モデル生成方法を実行する。学習装置5は、サーバ装置等のコンピュータである。学習装置5は、演算部51と、メモリ52と、記憶部53と、表示部54と、操作部55とを備えている。演算部51は、例えばCPU(Central Processing Unit )、GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)、又はマルチコアCPUを用いて構成されている。演算部51は、量子コンピュータを用いて構成されていてもよい。メモリ52は、演算に伴って発生する一時的なデータを記憶する。メモリ52は、例えばRAM(Random Access Memory)である。記憶部53は、不揮発性であり、例えばハードディスクである。表示部54は、例えば液晶ディスプレイ又はELディスプレイ(Electroluminescent Display)である。操作部55は、使用者からの操作を受け付けることにより、テキスト等の情報の入力を受け付ける。操作部55は、例えばキーボード又はタッチパネルである。記憶部53は、コンピュータプログラム531を記憶している。演算部51は、コンピュータプログラム531に従って処理を実行する。
The learning of the learning model 232 is performed using a computer. FIG. 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of a learning device 5 that learns the learning model 232. The learning device 5 executes the learning model generation method. The learning device 5 is a computer such as a server device. The learning device 5 includes a calculation unit 51, a memory 52, a storage unit 53, a display unit 54, and an operation unit 55. The calculation unit 51 is configured by using, for example, a CPU (Central Processing Unit), a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), or a multi-core CPU. The calculation unit 51 may be configured by using a quantum computer. The memory 52 stores temporary data generated by the calculation. The memory 52 is, for example, a RAM (Random Access Memory). The storage unit 53 is non-volatile, for example, a hard disk. The display unit 54 is, for example, a liquid crystal display or an EL display (Electroluminescent Display). The operation unit 55 accepts the input of information such as text by accepting the operation from the user. The operation unit 55 is, for example, a keyboard or a touch panel. The storage unit 53 stores the computer program 531. The calculation unit 51 executes the process according to the computer program 531.
図7は、学習モデル232を生成する処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。以下、ステップをSと略す。演算部51は、コンピュータプログラム531に従って以下の処理を実行する。演算部51は、夫々に単一のパルス波からなる複数のパルス波信号を生成する(S11)。S11では、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより、パルス波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくとも一つがランダムである複数のパルス波信号を生成する。パルス波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの全てがランダムであってもよい。パルス波信号は信号値の列で構成される。例えば、パルス波信号に含まれる信号値の数は、学習モデル232の入力層のノード41の数と同じである。
FIG. 7 is a flowchart showing the procedure of the process of generating the learning model 232. Hereinafter, the step is abbreviated as S. The calculation unit 51 executes the following processing according to the computer program 531. The arithmetic unit 51 generates a plurality of pulse wave signals each consisting of a single pulse wave (S11). In S11, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of pulse wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise, and roundness of the pulse wave is random by simulation. The height, rise and roundness of the pulse wave may all be random. A pulse wave signal is composed of a sequence of signal values. For example, the number of signal values included in the pulse wave signal is the same as the number of nodes 41 in the input layer of the learning model 232.
演算部51は、パルス波の波高、立ち上がり時定数及び立ち上がり開始時刻を、一様分布の乱数により生成する。乱数として、指数分布又はポアソン分布の乱数を用いてもよい。また、演算部51は、パルス波のなまりの時定数をランダムに生成する。演算部51は、生成したパラメータに従ったパルス波にホワイトノイズを重畳して、パルス波信号を生成する。パルス波に重畳するノイズは1/fノイズであってもよく、ノイズを重畳しなくてもよい。パルス波に重畳するノイズは、放射線検出器1の特性に応じたノイズであることが望ましい。パルス波信号は、図2Bに示す如き信号である。演算部51は、生成した複数のパルス波信号を含んだパルス波データ532を記憶部53に記憶する。放射線検出器1のサイズが大きい場合、実際に測定される信号のなまりが大きく変動する。シミュレーションにおいてパルス波のなまりをランダムにすることにより、実際の信号に近い信号を生成することができる。
The calculation unit 51 generates the wave height of the pulse wave, the rising time constant, and the rising start time from random numbers having a uniform distribution. As the random number, a random number having an exponential distribution or a Poisson distribution may be used. Further, the calculation unit 51 randomly generates a time constant of the bluntness of the pulse wave. The calculation unit 51 superimposes white noise on the pulse wave according to the generated parameter to generate a pulse wave signal. The noise superimposed on the pulse wave may be 1 / f noise, and the noise may not be superimposed. The noise superimposed on the pulse wave is preferably noise according to the characteristics of the radiation detector 1. The pulse wave signal is a signal as shown in FIG. 2B. The calculation unit 51 stores the pulse wave data 532 including the generated plurality of pulse wave signals in the storage unit 53. When the size of the radiation detector 1 is large, the roundness of the actually measured signal fluctuates greatly. By randomizing the bluntness of the pulse wave in the simulation, it is possible to generate a signal close to the actual signal.
演算部51は、次に、夫々に複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波からなる複数の重畳波信号を生成する(S12)。S12では、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくとも一つがランダムである二つのパルス波が夫々に重なった複数の重畳波信号を生成する。重畳波信号も信号値の列で構成される。演算部51は、一つ目のパルス波の波高、立ち上がり時定数及び立ち上がり開始時刻、並びに二つ目のパルス波の波高、立ち上がり時定数及び立ち上がり開始時刻を、一様分布の乱数により生成する。また、演算部51は、パルス波のなまりの時定数をランダムに生成する。なまりの時定数は二つのパルス波で同一であってもよい。演算部51は、生成したパラメータに従った重畳波にノイズを重畳して、重畳波信号を生成する。重畳波信号は、図3Bに示す如き信号である。演算部51は、生成した複数の重畳波信号を含んだ重畳波データ533を記憶部53に記憶する。
Next, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of superimposed wave signals composed of superimposed waves in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped with each other (S12). In S12, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of superimposed wave signals in which two pulse waves having at least one of a wave height, a rising edge, and a randomness are random are overlapped with each other by simulation. The superimposed wave signal is also composed of a sequence of signal values. The calculation unit 51 generates the wave height, rise time constant, and rise start time of the first pulse wave, and the wave height, rise time constant, and rise start time of the second pulse wave from a uniformly distributed random number. Further, the calculation unit 51 randomly generates a time constant of the bluntness of the pulse wave. The time constant of the rounding may be the same for the two pulse waves. The calculation unit 51 superimposes noise on the superposed wave according to the generated parameter to generate a superposed wave signal. The superimposed wave signal is a signal as shown in FIG. 3B. The calculation unit 51 stores the superimposed wave data 533 including the generated plurality of superimposed wave signals in the storage unit 53.
演算部51は、次に、パルス波データ532に含まれる複数のパルス波信号及び重畳波データ533に含まれる複数の重畳波信号を教師データとして、学習モデル232を生成するための処理を行う(S13)。S13では、演算部51は、複数のパルス波信号及び複数の重畳波信号を構成する信号値の列を、夫々に学習モデル232の入力層へ入力する。入力層のノード41の夫々には、一つの信号値が入力される。演算部51は、パルス波信号には、複数のパルス波の重なりが無いことを示す情報を関連付け、重畳波信号には、複数のパルス波の重なりがあることを示す情報を関連付ける。学習モデル232によって、出力層のノード43から複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報が出力される。演算部51は、入力されたパルス波信号又は重畳波信号に関連付けられた情報とノード43から出力された情報とを変数とする誤差関数により情報の誤差を計算し、誤差逆伝播法によって誤差が最小となるように、学習モデル232の各ノードの演算のパラメータを調整する。即ち、パルス波信号が入力されたときには複数のパルス波の重なりが無いことを示す情報に近い情報が出力され、重畳波信号が入力されたときには複数のパルス波の重なりがあることを示す情報に近い情報が出力されるように、パラメータが調整される。
Next, the calculation unit 51 performs processing for generating the learning model 232 by using the plurality of pulse wave signals included in the pulse wave data 532 and the plurality of superimposed wave signals included in the superimposed wave data 533 as teacher data ( S13). In S13, the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals to the input layer of the learning model 232, respectively. One signal value is input to each of the nodes 41 of the input layer. The calculation unit 51 associates the pulse wave signal with information indicating that the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap, and associates the superimposed wave signal with information indicating that the plurality of pulse waves overlap. The learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap from the node 43 of the output layer. The calculation unit 51 calculates the error of the information by the error function using the information associated with the input pulse wave signal or the superimposed wave signal and the information output from the node 43 as variables, and the error is calculated by the error back propagation method. The calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so as to be the minimum. That is, when a pulse wave signal is input, information close to the information indicating that there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves is output, and when a superimposed wave signal is input, information indicating that a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped is output. The parameters are adjusted so that close information is output.
演算部51は、複数のパルス波信号及び複数の重畳波信号を用いて処理を繰り返して、学習モデル232の各ノードのパラメータを調整することにより、学習モデル232の機械学習を行う。演算部51は、調整された最終的なパラメータを記録した学習済データ534を記憶部53に記憶する。このようにして、学習された学習モデル232が生成される。S13が終了した後、演算部51は処理を終了する。処理部23に含まれる学習モデル232は、学習済データ534に基づいて製造される。例えば、処理部23に含まれるFPGAに学習済データ534に記録されたパラメータが書き込まれることにより、学習モデル232が製造される。なお、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより作成したパルス波信号及び重畳波信号を用いるのではなく、実際に測定されたパルス波信号及び重畳波信号を用いて学習モデル232の機械学習を行ってもよい。
The calculation unit 51 performs machine learning of the learning model 232 by repeating the process using the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals and adjusting the parameters of each node of the learning model 232. The calculation unit 51 stores the learned data 534 in which the adjusted final parameters are recorded in the storage unit 53. In this way, the trained learning model 232 is generated. After the end of S13, the calculation unit 51 ends the process. The learning model 232 included in the processing unit 23 is manufactured based on the trained data 534. For example, the learning model 232 is manufactured by writing the parameters recorded in the trained data 534 to the FPGA included in the processing unit 23. The calculation unit 51 may perform machine learning of the learning model 232 using the actually measured pulse wave signal and the superimposed wave signal instead of using the pulse wave signal and the superimposed wave signal created by the simulation. ..
次に、信号処理装置2が実行する処理を説明する。図8は、実施形態1に係る信号処理装置2が実行する処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。放射線検出素子11に放射線が入射した場合、放射線検出器1は、放射線のエネルギーに応じた階段波を生成し、階段波を含む信号を出力する。信号処理装置2は、放射線検出器1から階段波を含む信号が入力される(S21)。A/D変換部21は、入力された信号をA/D変換する(S22)。A/D変換部21は、A/D変換した信号を波形整形部22へ入力する。波形整形部22は、入力された信号の波形を整形する(S23)。波形整形により、波形整形部22は信号に含まれるノイズを低減し、信号に含まれる階段波をパルス波へ変換する。波形整形部22は、パルス波を含む信号を処理部23、パルス検出部24及び波高測定部25へ入力する。
Next, the processing executed by the signal processing device 2 will be described. FIG. 8 is a flowchart showing a procedure of processing executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the first embodiment. When radiation is incident on the radiation detection element 11, the radiation detector 1 generates a staircase wave according to the energy of the radiation and outputs a signal including the staircase wave. The signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a staircase wave from the radiation detector 1 (S21). The A / D conversion unit 21 A / D converts the input signal (S22). The A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the waveform shaping unit 22. The waveform shaping unit 22 shapes the waveform of the input signal (S23). By the waveform shaping, the waveform shaping unit 22 reduces the noise included in the signal and converts the staircase wave included in the signal into a pulse wave. The waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the processing unit 23, the pulse detecting unit 24, and the wave height measuring unit 25.
処理部23へ入力される信号は、信号値の時系列で構成される。処理部23は、信号値をバッファメモリ231に順次記憶する(S24)。S21~S24の処理は個々に繰り返し実行され、信号値はバッファメモリ231に順次記憶される。バッファメモリ231は、先入れ先出しメモリであり、順次的に入力された複数の信号値を記憶する。バッファメモリ231が記憶する複数の信号値の量が上限に達している状態で新たな信号値が入力された場合、バッファメモリ231は、記憶している複数の信号値の中で最初に記憶した信号値を消去し、新たな信号値を記憶する。
The signal input to the processing unit 23 is composed of a time series of signal values. The processing unit 23 sequentially stores the signal values in the buffer memory 231 (S24). The processes S21 to S24 are individually and repeatedly executed, and the signal values are sequentially stored in the buffer memory 231. The buffer memory 231 is a first-in first-out memory, and stores a plurality of sequentially input signal values. When a new signal value is input while the amount of the plurality of signal values stored in the buffer memory 231 has reached the upper limit, the buffer memory 231 first stores the stored signal values. The signal value is erased and a new signal value is stored.
パルス検出部24は、入力された信号に含まれているパルス波の検出を待ち受ける(S25)。S25では、例えば、パルス検出部24は、信号値が所定の閾値を超過した場合に、信号に含まれているパルス波を検出したと判定する。閾値は予め処理部23に記憶されている。パルス波の検出がない場合は(S25:NO)、パルス検出部24は、S25の処理を繰り返す。
The pulse detection unit 24 waits for the detection of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S25). In S25, for example, the pulse detection unit 24 determines that the pulse wave included in the signal has been detected when the signal value exceeds a predetermined threshold value. The threshold value is stored in the processing unit 23 in advance. If no pulse wave is detected (S25: NO), the pulse detection unit 24 repeats the process of S25.
信号に含まれているパルス波を検出した場合は(S25:YES)、パルス検出部24は、パルス波を検出したことを示す情報を処理部23へ入力し、処理部23は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232へ入力する(S26)。S26では、処理部23は、例えば、パルス波を検出したことを示す情報を入力された時点でバッファメモリ231に記憶されている複数の信号値を、学習モデル232へ入力する。処理部23は、信号を構成する信号値を、間引いた上で学習モデル232へ入力してもよい。パルス波を含む信号を入力された学習モデル232は、前述したように、ニューラルネットワークの演算を行い、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力する。
When the pulse wave included in the signal is detected (S25: YES), the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23, and the processing unit 23 inputs the pulse wave. A sequence of signal values constituting the including signal is input to the learning model 232 (S26). In S26, for example, the processing unit 23 inputs a plurality of signal values stored in the buffer memory 231 to the learning model 232 at the time when the information indicating that the pulse wave is detected is input. The processing unit 23 may input the signal values constituting the signal to the learning model 232 after thinning out the signal values. As described above, the learning model 232 to which the signal including the pulse wave is input performs the calculation of the neural network and outputs the information indicating whether or not the plurality of pulse waves overlap.
処理部23は、学習モデル232が出力した複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力する。波高測定部25は、入力された情報に基づいて、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを特定する(S27)。複数のパルス波の重なりが無いことを示す情報が入力されており、複数のパルス波の重なりが無い場合は(S27:NO)、波高測定部25は、入力された信号に含まれるパルス波の波高を測定する(S28)。波高測定部25は、測定したパルス波の波高をカウント部26へ入力する。カウント部26は、波高測定部25から入力された波高別に、パルス波をカウントし(S29)、処理を終了する。複数のパルス波の重なりがあることを示す情報が入力されており、複数のパルス波の重なりがある場合(S27:YES)、波高測定部25は、重なった複数のパルス波については波高の測定を行わず、信号処理装置2は処理を終了する。この結果、カウント部26は、重なった複数のパルス波をカウントしない。信号処理装置2は、S21~S29の処理を個々に繰り返し実行する。
The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating whether or not the plurality of pulse waves output by the learning model 232 overlap to the wave height measuring unit 25. The wave height measuring unit 25 identifies whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap each other based on the input information (S27). When information indicating that there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves is input and there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves (S27: NO), the wave height measuring unit 25 is the pulse wave included in the input signal. The wave height is measured (S28). The wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26. The counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to the wave height input from the wave height measuring unit 25 (S29), and ends the process. When information indicating that there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves is input and there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves (S27: YES), the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height for the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. Is not performed, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S21 to S29 individually.
信号処理装置2は、パルス波の波高とカウント部26がカウントしたカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力する。分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力され、データに基づいて、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する。
The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26. The analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data.
図9は、複数の方法で得られた放射線のスペクトルを示すスペクトル図である。図中の横軸は放射線のエネルギーをkeVの単位で示し、縦軸は放射線のカウント数を示す。図9に示すスペクトルには、11.8keV付近のピークと、12.4keV付近のピークとが含まれている。しかしながら、これらのピークはいずれも、重なった複数のパルス波の波高を測定したことによって得られるサムピークである。図9には、パルス波の重なりの検出を行わない場合のスペクトルを破線で示し、従来技術によってパルス波の重なりの検出を行った場合のスペクトルを細い実線で示す。また、本実施形態によってパルス波の重なりの検出を行った場合のスペクトルを太い実線で示す。
FIG. 9 is a spectrum diagram showing the spectra of radiation obtained by a plurality of methods. The horizontal axis in the figure shows the energy of radiation in units of keV, and the vertical axis shows the number of counts of radiation. The spectrum shown in FIG. 9 includes a peak near 11.8 keV and a peak near 12.4 keV. However, all of these peaks are sum peaks obtained by measuring the heights of a plurality of overlapping pulse waves. In FIG. 9, the spectrum when the overlap of the pulse waves is not detected is shown by a broken line, and the spectrum when the overlap of the pulse waves is detected by the conventional technique is shown by a thin solid line. In addition, the spectrum when the overlap of pulse waves is detected according to this embodiment is shown by a thick solid line.
図9に示すように、パルス波の重なりの検出を行った場合は、サムピークの強度が減少する。本実施形態では、従来技術に比べて、サムピークの強度がより減少している。このため、本実施形態では、従来検出が困難であった複数のパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出することができる。複数のパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出することにより、パルス波の重なりに起因して放射線のエネルギーを誤って測定することを抑制することができる。これにより、放射線のスペクトルにサムピークが発生することを抑制し、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度を向上させることができる。例えば、存在しない元素を誤って検出することを抑制することができる。また、パルス波を検出するための閾値を低くしたとしても、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することが可能となる。このため、パルス波を検出するための閾値を低くすることが可能となり、軽元素等、放射線のエネルギーの低い元素の検出が容易となる。
As shown in FIG. 9, when the overlap of pulse waves is detected, the intensity of the thumb peak decreases. In the present embodiment, the intensity of the thumb peak is further reduced as compared with the prior art. Therefore, in the present embodiment, it is possible to effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, which has been difficult to detect in the past. By effectively detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, it is possible to suppress erroneous measurement of radiation energy due to the overlap of pulse waves. As a result, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of thumb peaks in the radiation spectrum and improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. For example, it is possible to prevent erroneous detection of non-existent elements. Further, even if the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave is lowered, it is possible to detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves. Therefore, it is possible to lower the threshold value for detecting the pulse wave, and it becomes easy to detect an element having a low radiation energy such as a light element.
以上詳述した如く、信号処理装置2は、学習モデル232を用いて、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する。学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を出力する。学習モデル232を用いることにより、従来検出が困難であった複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することができる。学習モデル232は信号の波形の全体から複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を判定するので、信号波形の特徴量に基づいた従来の判定方法に比べて、ノイズの影響を受け難くなり、より確実に複数のパルス波の重なりの有無が得られる。これによって、放射線検出装置10は、放射線のスペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度を向上させることができる。また、信号処理装置2は、信号値の列を処理することによって、信号の画像を処理する場合に比べて高速に処理を実行することができ、ほぼリアルタイムにパルス波の重なりを検出することができる。
As described in detail above, the signal processing device 2 detects the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using the learning model 232. The learning model 232 outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input. By using the learning model 232, it is possible to detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, which has been difficult to detect in the past. Since the learning model 232 determines whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap from the entire signal waveform, it is less susceptible to noise than the conventional determination method based on the feature amount of the signal waveform, and is more reliable. The presence or absence of overlap of multiple pulse waves can be obtained. As a result, the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the radiation spectrum. Further, the signal processing device 2 can execute the processing at a higher speed than the case of processing the image of the signal by processing the sequence of the signal values, and can detect the overlap of the pulse waves in almost real time. it can.
<実施形態2>
図10は、実施形態2に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。処理部23は、波形整形部22及びA/D変換部21に接続されている。処理部23は、パルス波を含む信号を波形整形部22から入力され、階段波を含む信号をA/D変換部21から入力される。処理部23は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値と、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値を、バッファメモリ231に記憶する。 <Embodiment 2>
FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of theradiation detection device 10 according to the second embodiment. The configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The processing unit 23 is connected to the waveform shaping unit 22 and the A / D conversion unit 21. The processing unit 23 inputs a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and inputs a signal including a step wave from the A / D conversion unit 21. The processing unit 23 stores the signal value constituting the signal including the pulse wave and the signal value constituting the signal including the staircase wave in the buffer memory 231.
図10は、実施形態2に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。処理部23は、波形整形部22及びA/D変換部21に接続されている。処理部23は、パルス波を含む信号を波形整形部22から入力され、階段波を含む信号をA/D変換部21から入力される。処理部23は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値と、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値を、バッファメモリ231に記憶する。 <
FIG. 10 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the
学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号と階段波を含む信号とを入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力するように、予め学習されている。学習モデル232は、実施形態1と同様に、全結合のニューラルネットワークを用いる。学習モデル232の入力層は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列が入力される複数のノード41に加えて、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列が入力される複数のノード41を含んでいる。学習モデル232の出力層のノード43は、実施形態1と同様に、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を出力する。信号処理装置2のA/D変換部21及び処理部23以外の部分の構成は、実施形態1と同様である。
The learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap when a signal including a pulse wave and a signal including a staircase wave are input. The learning model 232 uses a fully connected neural network as in the first embodiment. The input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 in which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is input, and a plurality of nodes 41 in which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. Includes node 41. The node 43 of the output layer of the learning model 232 outputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlapping of the plurality of pulse waves, as in the first embodiment. The configuration of the parts other than the A / D conversion unit 21 and the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
学習モデル232の学習は、実施形態1と同様に、学習装置5によって行われる。学習装置5の演算部51は、S11での複数のパルス波信号の生成に加えて、パルス波が波形整形部22により変換される前の階段波を含む信号に対応する階段波信号を生成する。逆に、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより、階段波を含み、階段波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくとも一つがランダムであり、ホワイトノイズを重畳した複数の階段波信号を生成し、階段波信号を微分することによりパルス波信号を生成してもよい。信号に重畳するノイズは1/fノイズであってもよく、ノイズを重畳しなくてもよい。また、演算部51は、S12での複数の重畳波信号の生成に加えて、重畳波が波形整形部22により変換される前の複数の階段波を含む信号に対応する近接階段波信号を生成する。逆に、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくとも一つがランダムである二つの近接した階段波を含んだ複数の近接階段波信号を生成し、近接階段波信号を微分することにより重畳波信号を生成してもよい。なお、演算部51は、シミュレーションにより作成した階段波信号及び近接階段波信号を用いるのではなく、実際に測定された階段波信号及び近接階段波信号を用いてもよい。
The learning of the learning model 232 is performed by the learning device 5 as in the first embodiment. In addition to generating a plurality of pulse wave signals in S11, the calculation unit 51 of the learning device 5 generates a stair wave signal corresponding to the signal including the stair wave before the pulse wave is converted by the waveform shaping unit 22. .. On the contrary, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of staircase wave signals including staircase waves by simulation, in which at least one of the wave height, rise and roundness of the staircase wave is random, and white noise is superimposed, and the staircase wave signal is generated. A pulse wave signal may be generated by differentiating. The noise superimposed on the signal may be 1 / f noise, and the noise may not be superimposed. Further, in addition to the generation of the plurality of superimposed wave signals in S12, the arithmetic unit 51 generates a proximity staircase wave signal corresponding to the signal including the plurality of staircase waves before the superimposed wave is converted by the waveform shaping unit 22. To do. On the contrary, the calculation unit 51 generates a plurality of proximity staircase wave signals including two proximity staircase waves in which at least one of the wave height, the rise and the roundness is random by simulation, and differentiates the proximity staircase wave signals. May generate a superimposed wave signal. The calculation unit 51 may use the actually measured staircase wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal instead of using the staircase wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal created by the simulation.
演算部51は、S13で、複数のパルス波信号及び階段波信号と、複数の重畳波信号及び近接階段波信号とを教師データとして、学習モデル232を生成するための処理を行う。S13では、演算部51は、パルス波信号及び階段波信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232の入力層へ入力する。また、演算部51は、重畳波信号及び近接階段波信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232の入力層へ入力する。演算部51は、誤差逆伝播法により、学習モデル232の各ノードの演算のパラメータを調整する。演算部51は、複数のパルス波信号及び複数の重畳波信号を用いて処理を繰り返して、学習モデル232の機械学習を行う。
In S13, the calculation unit 51 performs processing for generating the learning model 232 by using the plurality of pulse wave signals and staircase wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals and proximity staircase wave signals as teacher data. In S13, the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the pulse wave signal and the step wave signal to the input layer of the learning model 232. Further, the calculation unit 51 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the superimposed wave signal and the proximity staircase wave signal to the input layer of the learning model 232. The calculation unit 51 adjusts the calculation parameters of each node of the learning model 232 by the error back propagation method. The calculation unit 51 repeats the process using the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals to perform machine learning of the learning model 232.
信号処理装置2は、実施形態1と同様に、S21~S25の処理を実行する。S26では、処理部23は、波形整形部22から入力されたパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、A/D変換部21から入力された階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列とを、学習モデル232へ入力する。学習モデル232は、ニューラルネットワークの演算を行い、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力する。信号処理装置2は、実施形態1と同様に、S27~S29の処理を実行する。信号処理装置2は、パルス波の波高とカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力し、分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力され、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する。分析部3は、放射線のスペクトルに基づいて、放射線源の元素分析を行ってもよい。
The signal processing device 2 executes the processes of S21 to S25 as in the first embodiment. In S26, the processing unit 23 comprises a string of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave input from the waveform shaping unit 22, and a signal value constituting a signal including a staircase wave input from the A / D conversion unit 21. The column of is input to the training model 232. The learning model 232 performs a neural network operation and outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. The signal processing device 2 executes the processes of S27 to S29 as in the first embodiment. The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the pulse wave and the number of counts, and the analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2 and the radiation spectrum detected by the radiation detector 1. To generate. The analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation.
以上詳述した如く、実施形態2においては、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を含む信号に加えて、パルス波に変換する前の階段波を含む信号を学習モデル232へ入力して、パルス波の重なりを検出する。複数のパルス波が重なっている場合は、階段波の間隔が短く、階段波を含む信号の波形も、パルス波が重なっていない場合と比べて異なる。このため、パルス波を含む信号に加えて、階段波を含む信号をも用いることにより、パルス波の重なりがあるか否かの判定がより容易となる。信号処理装置2は、実施形態1に比べて、より効果的に複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することができ、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。
As described in detail above, in the second embodiment, the signal processing device 2 inputs a signal including a step wave before being converted into a pulse wave into the learning model 232 in addition to the signal including the pulse wave, and inputs the pulse wave. Detects overlap. When a plurality of pulse waves overlap, the interval between the staircase waves is short, and the waveform of the signal including the staircase wave is also different from that when the pulse waves do not overlap. Therefore, by using the signal including the staircase wave in addition to the signal including the pulse wave, it becomes easier to determine whether or not there is an overlap of the pulse waves. The signal processing device 2 can detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves more effectively as compared with the first embodiment, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. it can.
なお、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を含んだ信号を用いずに、階段波を含んだ信号を用いて、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。この形態では、学習モデル232は、階段波を含む信号を入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力するように、予め学習されている。学習モデル232の入力層は、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列が入力される複数のノード41を含んでいる。学習モデル232の学習では、学習装置5は、階段波信号及び近接階段波信号を生成し、複数の階段波信号及び近接階段波信号を教師データとして、学習モデル232の機械学習を行う。信号処理装置2は、S26では、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列は学習モデル232へ入力せず、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232へ入力する。学習モデル232は、同様に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力する。信号処理装置2は、実施形態1と同様に、効果的に複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することができる。
Note that the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using a signal including a staircase wave without using a signal including a pulse wave. In this embodiment, the learning model 232 is trained in advance so as to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap when a signal including a staircase wave is input. The input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. In the learning of the learning model 232, the learning device 5 generates a staircase wave signal and a proximity staircase wave signal, and performs machine learning of the learning model 232 using the plurality of staircase wave signals and the proximity staircase wave signal as teacher data. In S26, the signal processing device 2 does not input the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave to the learning model 232, but inputs the sequence of the signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave to the learning model 232. Similarly, the learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Similar to the first embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
また、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を含む信号及び/又は階段波を含む信号に加えて、パルス波を更に波形整形部22で整形した整形波を含む信号を更に学習モデル232へ入力して、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。整形波は、例えば、階段波の二階微分に相当する。学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、整形波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列とを入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力するように、予め学習されている。学習モデル232の入力層は、整形波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列が入力される複数のノード41を含んでいる。学習モデル232の学習では、学習装置5は、整形波を含む信号、及び重畳波信号を整形した信号を生成し、パルス波信号及び/又は階段波信号と、整形波を含む信号と、重畳波信号及び/又は近接階段波信号と、重畳波信号を整形した信号とを教師データとして、機械学習を行う。信号処理装置2は、S26では、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、整形波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列とを学習モデル232へ入力する。学習モデル232は、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力する。この形態においても、信号処理装置2は、より効果的に複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することができる。
Further, in addition to the signal including the pulse wave and / or the signal including the staircase wave, the signal processing device 2 further inputs the signal including the shaped wave obtained by shaping the pulse wave by the waveform shaping unit 22 into the learning model 232. , It may be in the form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves. The shaped wave corresponds to, for example, the second derivative of the staircase wave. In the learning model 232, a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave are input. In this case, it is learned in advance to output information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. The input layer of the learning model 232 includes a plurality of nodes 41 into which a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave is input. In the learning of the learning model 232, the learning device 5 generates a signal including a shaped wave and a signal obtained by shaping the superimposed wave signal, and generates a pulse wave signal and / or a staircase wave signal, a signal containing the shaped wave, and a superimposed wave. Machine learning is performed using the signal and / or the proximity step wave signal and the signal obtained by shaping the superimposed wave signal as training data. In S26, the signal processing device 2 includes a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave, and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a shaping wave. Is input to the learning model 232. The learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Also in this form, the signal processing device 2 can more effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves.
また、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を含む信号及び/又は階段波を含む信号に加えて、信号波形の特徴量を更に学習モデル232へ入力して、パルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。信号波形の特徴量は、例えば、波高、立ち上がり時定数、又は信号波の時間幅等である。学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、信号波形の特徴量とを入力された場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力するように、予め学習されている。信号処理装置2は、S26で、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、信号波形の特徴量とを学習モデル232へ入力する。学習モデル232は、複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを示す情報を出力する。更に、整形波を含む信号をも用いてもよい。信号波形の特徴量は、単一のパルス波と重畳波とで異なるので、信号波形の特徴量を用いることにより、複数のパルス波の重なりをより効果的に検出することができる。このため、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。
Further, the signal processing device 2 is in the form of detecting the overlap of the pulse waves by further inputting the feature amount of the signal waveform into the learning model 232 in addition to the signal including the pulse wave and / or the signal including the step wave. You may. The feature amount of the signal waveform is, for example, a wave height, a rising time constant, a time width of a signal wave, or the like. The learning model 232 receives a plurality of pulses when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a feature amount of a signal waveform are input. It has been learned in advance to output information indicating whether or not there is overlap of waves. In S26, the signal processing device 2 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave and a feature amount of a signal waveform into the learning model 232. To do. The learning model 232 outputs information indicating whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap. Further, a signal including a shaping wave may also be used. Since the feature amount of the signal waveform is different between the single pulse wave and the superimposed wave, the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves can be detected more effectively by using the feature amount of the signal waveform. Therefore, the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
<実施形態3>
実施形態3においては、学習モデル232が重なっているパルス波の数を判定する形態を示す。図11は、実施形態3に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、波形整形部22と、処理部23と、波高測定部25と、カウント部26とを備える。処理部23は、バッファメモリを有していない。処理部23は、A/D変換部21からの階段波を含む信号と、波形整形部22からのパルス波を含む信号との少なくとも一方を入力される。処理部23は、重なっているパルス波の数を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力する。 <Embodiment 3>
In the third embodiment, a mode in which thelearning model 232 determines the number of overlapping pulse waves is shown. FIG. 11 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the third embodiment. The configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a waveform shaping unit 22, a processing unit 23, a wave height measuring unit 25, and a counting unit 26. The processing unit 23 does not have a buffer memory. The processing unit 23 is input with at least one of a signal including a staircase wave from the A / D conversion unit 21 and a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22. The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25.
実施形態3においては、学習モデル232が重なっているパルス波の数を判定する形態を示す。図11は、実施形態3に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、波形整形部22と、処理部23と、波高測定部25と、カウント部26とを備える。処理部23は、バッファメモリを有していない。処理部23は、A/D変換部21からの階段波を含む信号と、波形整形部22からのパルス波を含む信号との少なくとも一方を入力される。処理部23は、重なっているパルス波の数を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力する。 <
In the third embodiment, a mode in which the
図12は、実施形態3に係る学習モデル232の機能構成例を示す概念図である。学習モデル232は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び/又は階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、重なっているパルス波の数の確率を出力するように、予め学習されている。学習モデル232の出力層は、複数のノード43を有する。夫々のノード43は、複数のノード42nからデータを受け付け、受け付けたデータにパラメータを用いて演算し、信号に含まれるパルス波が重なっている数が特定の数である確率を出力する。例えば、一のノード43は、信号にパルス波が含まれていない確率を出力し、他のノード43は、複数のパルス波が重なっておらず、パルス波の数が一つである確率を出力し、更に他のノード43は、重なっているパルス波の数が二つである確率を出力する。ノード43は、パルス波が重なっている数が特定の数である確率を0~1の実数で出力してもよく、0又は1の二値で出力してもよい。
FIG. 12 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the third embodiment. The learning model 232 outputs the probability of the number of overlapping pulse waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and / or a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave is input. It has been learned in advance so as to do so. The output layer of the learning model 232 has a plurality of nodes 43. Each node 43 receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, calculates the received data using parameters, and outputs the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves included in the signal is a specific number. For example, one node 43 outputs the probability that the signal does not contain a pulse wave, and the other node 43 outputs the probability that a plurality of pulse waves do not overlap and the number of pulse waves is one. However, the other node 43 outputs the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves is two. The node 43 may output the probability that the number of overlapping pulse waves is a specific number as a real number of 0 to 1, or may output as a binary value of 0 or 1.
学習モデル232の学習では、学習装置5は、パルス波及び階段波を含まない信号と、パルス波信号及び/又は階段波信号と、重畳波信号及び/又は近接階段波信号とを教師データとして、機械学習を行う。学習装置5は、パルス波及び階段波を含まない信号には、パルス波が無い確率が1であり他の確率が0である情報を関連付け、パルス波信号及び/又は階段波信号には、パルス波が一つである確率が1であり他の確率が0である情報を関連付け、重畳波信号及び/又は近接階段波信号には、パルス波が複数である確率が1であり他の確率が0である情報を関連付ける。学習装置5は、入力層へ入力した信号に関連付けられた情報が示す夫々の確率と、出力層から出力された夫々の確率とを変数とする誤差関数により情報の誤差を計算し、誤差逆伝播法によって誤差が最小となるように、学習モデル232の各ノードの演算のパラメータを調整する。
In the training of the learning model 232, the learning device 5 uses the signal not including the pulse wave and the staircase wave, the pulse wave signal and / or the staircase wave signal, and the superimposed wave signal and / or the proximity staircase wave signal as training data. Perform machine learning. The learning device 5 associates information that the probability that there is no pulse wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 with the signal that does not include the pulse wave and the step wave, and the pulse wave signal and / or the step wave signal is pulsed. The information that the probability of one wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 is associated, and the superimposed wave signal and / or the proximity staircase wave signal has a probability of having multiple pulse waves of 1 and other probabilities. Associate information that is 0. The learning device 5 calculates an error of information by an error function having each probability indicated by the information associated with the signal input to the input layer and each probability output from the output layer as variables, and back-propagates the information. The calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so that the error is minimized by the method.
図13は、実施形態3に係る信号処理装置2が実行する処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。信号処理装置2は、放射線検出器1から階段波を含む信号が入力され(S31)、A/D変換部21は、信号をA/D変換する(S32)。A/D変換部21は、A/D変換した信号を波形整形部22へ入力する。波形整形部22は、入力された信号の波形を整形する(S33)。波形整形により、階段波はパルス波へ変換される。波形整形部22は、パルス波を含む信号を波高測定部25へ入力する。
FIG. 13 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the third embodiment. The signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a step wave from the radiation detector 1 (S31), and the A / D conversion unit 21 converts the signal into A / D (S32). The A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the waveform shaping unit 22. The waveform shaping unit 22 shapes the waveform of the input signal (S33). Waveform shaping converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave. The waveform shaping unit 22 inputs a signal including a pulse wave to the wave height measuring unit 25.
処理部23は、A/D変換部21からの階段波を含む信号、及び/又は波形整形部22からのパルス波を含む信号を入力され、入力された信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232へ入力する(S34)。学習モデル232は、前述したように、ニューラルネットワークの演算を行い、重なっているパルス波の数の確率を出力する。処理部23は、重なっているパルス波の数を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力する。このとき、処理部23は、重なっているパルス波の数を示す情報として、学習モデル232が出力した確率を波高測定部25へ入力してもよい。また、処理部23は、重なっているパルス波の数を確率に基づいて判定し、重なっているパルス波の数を示す情報として、判定した数を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力してもよい。例えば、処理部23は、確率が最大である数、又は確率が所定値以上である数を、重なっているパルス波の数であると判定する。
The processing unit 23 receives a signal including a step wave from the A / D conversion unit 21 and / or a signal including a pulse wave from the waveform shaping unit 22, and learns a sequence of signal values constituting the input signal. Input to model 232 (S34). As described above, the learning model 232 performs the operation of the neural network and outputs the probability of the number of overlapping pulse waves. The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25. At this time, the processing unit 23 may input the probability output by the learning model 232 to the wave height measuring unit 25 as information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves. Further, the processing unit 23 determines the number of overlapping pulse waves based on the probability, and even if the information indicating the determined number is input to the wave height measuring unit 25 as the information indicating the number of overlapping pulse waves. Good. For example, the processing unit 23 determines that the number having the maximum probability or the number having the probability equal to or higher than a predetermined value is the number of overlapping pulse waves.
波高測定部25は、入力された情報に基づいて、パルス波の数が一つであるか否かを特定する(S35)。パルス波の数が一つである場合は(S35:YES)、波高測定部25は、入力された信号に含まれるパルス波の波高を測定する(S36)。波高測定部25は、測定したパルス波の波高をカウント部26へ入力する。カウント部26は、波高別にパルス波をカウントし(S37)、処理を終了する。パルス波の数が一つ以外の数である場合は(S35:NO)、波高測定部25は波高の測定を行わず、信号処理装置2は処理を終了する。この結果、カウント部26は、重なった複数のパルス波をカウントしない。信号処理装置2は、S31~S37の処理を繰り返し実行する。
The wave height measuring unit 25 identifies whether or not the number of pulse waves is one based on the input information (S35). When the number of pulse waves is one (S35: YES), the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S36). The wave height measuring unit 25 inputs the measured pulse wave height to the counting unit 26. The counting unit 26 counts the pulse wave according to the wave height (S37), and ends the process. When the number of pulse waves is other than one (S35: NO), the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S31 to S37.
信号処理装置2は、パルス波の波高とカウント部26がカウントしたカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力する。分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力され、データに基づいて、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する。分析部3は、放射線のスペクトルに基づいて、放射線源の元素分析を行ってもよい。本実施形態においても、信号処理装置2は、効果的に複数のパルス波の重なりを検出することができ、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。
The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26. The analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data. The analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation. Also in this embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum.
なお、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を更に波形整形部22で整形した整形波を含む信号をも用いて、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。また、信号処理装置2は、信号波形の特徴量をも用いて、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。
Note that the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using a signal including a shaped wave obtained by further shaping the pulse wave by the waveform shaping unit 22. Further, the signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
<実施形態4>
実施形態4においては、学習モデル232が階段波の数と波高とを判定する形態を示す。図14は、実施形態4に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、処理部23と、カウント部26とを備える。A/D変換部21は、階段波を含む信号を処理部23へ入力する。 <Embodiment 4>
In the fourth embodiment, thelearning model 232 shows a mode in which the number of staircase waves and the wave height are determined. FIG. 14 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the fourth embodiment. The configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a processing unit 23, and a counting unit 26. The A / D conversion unit 21 inputs a signal including a staircase wave to the processing unit 23.
実施形態4においては、学習モデル232が階段波の数と波高とを判定する形態を示す。図14は、実施形態4に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、処理部23と、カウント部26とを備える。A/D変換部21は、階段波を含む信号を処理部23へ入力する。 <Embodiment 4>
In the fourth embodiment, the
図15は、実施形態4に係る学習モデル232の機能構成例を示す概念図である。学習モデル232は、階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力された場合に、信号に含まれる階段波の数の確率及び階段波の波高を出力するように、予め学習されている。学習モデル232の出力層は、複数のノード43を有する。夫々のノード43は、複数のノード42nからデータを受け付け、受け付けたデータにパラメータを用いて演算する。一のノード43は、信号に含まれている階段波の波高を出力する。他のノード43は、信号に含まれる階段波の数の確率を出力する。例えば、信号に階段波が含まれていない確率を出力するノード43と、階段波の数が一つである確率を出力するノード43と、階段波の数が二つである確率を出力するノード43とがある。ノード43は、階段波の数が特定の数である確率を0~1の実数で出力してもよく、0又は1の二値で出力してもよい。信号に含まれる階段波の数の確率は、複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報である。
FIG. 15 is a conceptual diagram showing a functional configuration example of the learning model 232 according to the fourth embodiment. The learning model 232 is pre-learned to output the probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal and the wave height of the staircase wave when a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave is input. .. The output layer of the learning model 232 has a plurality of nodes 43. Each node 43 receives data from a plurality of nodes 42n, and calculates the received data using parameters. One node 43 outputs the height of the staircase wave included in the signal. The other node 43 outputs the probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal. For example, a node 43 that outputs the probability that the signal does not include staircase waves, a node 43 that outputs the probability that the number of staircase waves is one, and a node that outputs the probability that the number of staircase waves is two. There is 43. The node 43 may output the probability that the number of staircase waves is a specific number as a real number from 0 to 1, or may output as a binary value of 0 or 1. The probability of the number of staircase waves included in the signal is information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting a plurality of staircase waves.
学習モデル232の学習では、学習装置5は、階段波を含まない信号と、階段波信号と、近接階段波信号とを教師データとして、機械学習を行う。学習装置5は、階段波を含まない信号には、波高がゼロであり、階段波が無い確率が1であり他の確率が0であることを示す情報を関連付ける。学習装置5は、階段波信号には、階段波の波高と、階段波が一つである確率が1であり他の確率が0であることとを示す情報を関連付ける。学習装置5は、近接階段波信号には、複数の階段波の波高の合計と、階段波が複数である確率が1であり他の確率が0であることを示す情報を関連付ける。学習装置5は、入力層へ入力した信号に関連付けられた情報が示す波高及び夫々の確率と、出力層から出力された夫々の確率とを変数とする誤差関数により情報の誤差を計算し、誤差逆伝播法によって誤差が最小となるように、学習モデル232の各ノードの演算のパラメータを調整する。
In the learning of the learning model 232, the learning device 5 performs machine learning using the signal not including the staircase wave, the staircase wave signal, and the proximity staircase wave signal as teacher data. The learning device 5 associates information indicating that the wave height is zero, the probability that there is no staircase wave is 1, and the other probabilities are 0 with the signal that does not include the staircase wave. The learning device 5 associates the wave height of the stair wave with the information indicating that the probability that there is one stair wave is 1 and the other probability is 0 in the stair wave signal. The learning device 5 associates the proximity staircase wave signal with the sum of the wave heights of the plurality of staircase waves and information indicating that the probability of having a plurality of staircase waves is 1 and the other probabilities are 0. The learning device 5 calculates an error of information by an error function having the wave height and each probability indicated by the information associated with the signal input to the input layer and each probability output from the output layer as variables, and the error. The calculation parameters of each node of the training model 232 are adjusted so that the error is minimized by the back propagation method.
図16は、実施形態4に係る信号処理装置2が実行する処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。信号処理装置2は、放射線検出器1から階段波を含む信号が入力され(S41)、A/D変換部21は、信号をA/D変換する(S42)。A/D変換部21は、A/D変換した信号を処理部23へ入力する。
FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the fourth embodiment. The signal processing device 2 receives a signal including a step wave from the radiation detector 1 (S41), and the A / D conversion unit 21 converts the signal into A / D (S42). The A / D conversion unit 21 inputs the A / D converted signal to the processing unit 23.
処理部23は、入力された信号を構成する信号値の列を学習モデル232へ入力する(S43)。学習モデル232は、前述したように、ニューラルネットワークの演算を行い、信号に含まれる階段波の波高、及び階段波の数の確率を出力する。処理部23は、波高及び階段波の数を示す情報をカウント部26へ入力する。このとき、処理部23は、階段波の数を示す情報として、学習モデル232が出力した確率をカウント部26へ入力してもよい。また、処理部23は、階段波の数を確率に基づいて判定し、階段波の数を示す情報として、判定した数を示す情報をカウント部26へ入力してもよい。例えば、処理部23は、確率が最大である数、又は確率が所定値以上である数を、階段波の数であると判定する。
The processing unit 23 inputs a sequence of signal values constituting the input signal to the learning model 232 (S43). As described above, the learning model 232 performs the calculation of the neural network and outputs the wave height of the staircase wave included in the signal and the probability of the number of staircase waves. The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the wave height and the number of staircase waves to the counting unit 26. At this time, the processing unit 23 may input the probability output by the learning model 232 to the counting unit 26 as information indicating the number of staircase waves. Further, the processing unit 23 may determine the number of staircase waves based on the probability, and input the information indicating the determined number to the counting unit 26 as the information indicating the number of staircase waves. For example, the processing unit 23 determines that the number having the maximum probability or the number having the probability equal to or higher than a predetermined value is the number of staircase waves.
カウント部26は、入力された情報に基づいて、階段波の数が一つであるか否かを特定する(S44)。階段波の数が一つである場合は(S44:YES)、カウント部26は、波高別に階段波をカウントし(S45)、処理を終了する。これにより、カウント部26は、複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりが無い場合の階段波をカウントする。階段波の数が一つ以外の数である場合は(S44:NO)、カウント部26はカウントを行わず、信号処理装置2は処理を終了する。この結果、カウント部26は、複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波が重なる場合の階段波をカウントしない。信号処理装置2は、S41~S45の処理を繰り返し実行する。
The counting unit 26 specifies whether or not the number of staircase waves is one based on the input information (S44). When the number of staircase waves is one (S44: YES), the counting unit 26 counts the staircase waves according to the wave height (S45), and ends the process. As a result, the counting unit 26 counts the staircase waves when there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves converted from the plurality of staircase waves. When the number of staircase waves is other than one (S44: NO), the counting unit 26 does not count, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the staircase wave when the plurality of pulse waves converted from the plurality of staircase waves overlap. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S41 to S45.
信号処理装置2は、階段波の波高とカウント部26がカウントしたカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力する。分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力され、データに基づいて、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する。分析部3は、放射線のスペクトルに基づいて、放射線源の元素分析を行ってもよい。本実施形態においても、信号処理装置2は、複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりを効率的に検出することができ、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。なお、信号処理装置2は、信号波形の特徴量をも用いて、複数のパルス波の重なりを検出する形態であってもよい。
The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the wave height of the staircase wave and the number of counts counted by the counting unit 26. The analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data. The analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation. Also in this embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can efficiently detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from a plurality of staircase waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. It can be improved further. The signal processing device 2 may be in a form of detecting the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves by also using the feature amount of the signal waveform.
<実施形態5>
図17は、実施形態5に係る処理部23の機能構成を示すブロック図である。処理部23は、演算部233及びメモリ234を有する。演算部233は、例えばCPU、GPU、又はマルチコアCPUを用いて構成されている。演算部233は、量子コンピュータを用いて構成されていてもよい。メモリ234は、不揮発性のメモリである。メモリ234は、コンピュータプログラム235を記憶している。演算部233は、コンピュータプログラム235に従って処理部23に必要な処理を実行する。学習モデル232は、コンピュータプログラム235に従って演算部233が情報処理を実行することにより実現される。 <Embodiment 5>
FIG. 17 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of theprocessing unit 23 according to the fifth embodiment. The processing unit 23 has a calculation unit 233 and a memory 234. The calculation unit 233 is configured by using, for example, a CPU, a GPU, or a multi-core CPU. The calculation unit 233 may be configured by using a quantum computer. The memory 234 is a non-volatile memory. The memory 234 stores the computer program 235. The calculation unit 233 executes the processing required for the processing unit 23 according to the computer program 235. The learning model 232 is realized by the arithmetic unit 233 executing information processing according to the computer program 235.
図17は、実施形態5に係る処理部23の機能構成を示すブロック図である。処理部23は、演算部233及びメモリ234を有する。演算部233は、例えばCPU、GPU、又はマルチコアCPUを用いて構成されている。演算部233は、量子コンピュータを用いて構成されていてもよい。メモリ234は、不揮発性のメモリである。メモリ234は、コンピュータプログラム235を記憶している。演算部233は、コンピュータプログラム235に従って処理部23に必要な処理を実行する。学習モデル232は、コンピュータプログラム235に従って演算部233が情報処理を実行することにより実現される。 <
FIG. 17 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the
演算部233は、コンピュータプログラム235に従って情報処理を実行することにより、実施形態1~4における処理部23に必要な処理を実行する。このようにして、実施形態1~4における処理部23が実現される。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1~4と同様である。信号処理装置2の処理部23以外の部分の構成及び機能は、実施形態1~4と同様である。信号処理装置2及び放射線検出装置10は、実施形態1~4と同様の処理を実行する。本実施形態においても、信号処理装置2は、複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりを効率的に検出することができ、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。なお、信号処理装置2の処理部23以外の部分の一部又は全部も、コンピュータプログラムを用いて実現されてもよい。
The calculation unit 233 executes information processing according to the computer program 235 to execute the processing required for the processing units 23 in the first to fourth embodiments. In this way, the processing unit 23 in the first to fourth embodiments is realized. The configurations and functions of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first to fourth embodiments. The configuration and function of the parts other than the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 are the same as those of the first to fourth embodiments. The signal processing device 2 and the radiation detection device 10 perform the same processing as in the first to fourth embodiments. Also in this embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can efficiently detect the overlap of a plurality of pulse waves converted from a plurality of staircase waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. It can be improved further. A part or all of the part other than the processing unit 23 of the signal processing device 2 may also be realized by using a computer program.
<実施形態6>
実施形態6では、信号処理装置2は、学習モデルを用いずにパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出する。図18は、実施形態6に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、波形整形部22と、処理部23と、パルス検出部24と、波高測定部25と、カウント部26と、記憶部27とを備える。処理部23は、学習モデルを含んでいない。処理部23には、記憶部27が接続されている。記憶部27は、不揮発性である。例えば、記憶部27は不揮発性の半導体メモリで構成されている。記憶部27は、所定の係数列を記憶している。信号処理装置2の処理部23及び記憶部27以外の部分の構成は、実施形態1と同様である。 <Embodiment 6>
In the sixth embodiment, thesignal processing device 2 effectively detects the overlap of pulse waves without using the learning model. FIG. 18 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the radiation detection device 10 according to the sixth embodiment. The configuration and function of the radiation detector 1 and the analysis unit 3 are the same as those in the first embodiment. The signal processing device 2 includes an A / D conversion unit 21, a waveform shaping unit 22, a processing unit 23, a pulse detection unit 24, a wave height measuring unit 25, a counting unit 26, and a storage unit 27. The processing unit 23 does not include the learning model. A storage unit 27 is connected to the processing unit 23. The storage unit 27 is non-volatile. For example, the storage unit 27 is composed of a non-volatile semiconductor memory. The storage unit 27 stores a predetermined coefficient sequence. The configuration of the parts other than the processing unit 23 and the storage unit 27 of the signal processing device 2 is the same as that of the first embodiment.
実施形態6では、信号処理装置2は、学習モデルを用いずにパルス波の重なりを効果的に検出する。図18は、実施形態6に係る放射線検出装置10の機能構成を示すブロック図である。放射線検出器1及び分析部3の構成及び機能は、実施形態1と同様である。信号処理装置2は、A/D変換部21と、波形整形部22と、処理部23と、パルス検出部24と、波高測定部25と、カウント部26と、記憶部27とを備える。処理部23は、学習モデルを含んでいない。処理部23には、記憶部27が接続されている。記憶部27は、不揮発性である。例えば、記憶部27は不揮発性の半導体メモリで構成されている。記憶部27は、所定の係数列を記憶している。信号処理装置2の処理部23及び記憶部27以外の部分の構成は、実施形態1と同様である。 <Embodiment 6>
In the sixth embodiment, the
図19及び図20は、係数列の例を示すグラフである。図中の横軸はクロックを単位にした時間を示し、縦軸は係数の値又は信号値を示す。係数列は、複数の係数が並んだ一次元の配列である。図19には、単一のパルス波を含む信号を破線で示し、係数列を実線で示している。パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列をクロックの間隔で並べて示している。また、係数列に含まれる複数の係数を順番にクロックの間隔で並べて示している。係数列に含まれる複数の係数は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と積和演算を行うためのものである。係数列に含まれる係数の数をmとする。係数列をa1 ,a2 ,…,am ,とし、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列をx1 ,x2 ,…とする。積和演算は、(a1 *x1 +a2 *x2 +…+am *xm +C)で表される。Cは定数値である。定数値Cは記憶部27に記憶されている。
19 and 20 are graphs showing an example of a coefficient sequence. The horizontal axis in the figure indicates the time in units of clock, and the vertical axis indicates the coefficient value or signal value. The coefficient sequence is a one-dimensional array in which a plurality of coefficients are arranged. In FIG. 19, a signal including a single pulse wave is shown by a broken line, and a coefficient sequence is shown by a solid line. A sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave is shown side by side at clock intervals. In addition, a plurality of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence are shown in order at clock intervals. The plurality of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence are for performing a product-sum operation with a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave. Let m be the number of coefficients included in the coefficient sequence. Let the coefficient sequence be a 1 , a 2 , ..., Am , and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave be x 1 , x 2 , .... Product-sum operation is represented by (a 1 * x 1 + a 2 * x 2 + ... + a m * x m + C). C is a constant value. The constant value C is stored in the storage unit 27.
図19に示すように、係数列は、パルス波とほぼ同時に立ち上がり、パルス波よりも短い期間で増大と減少とを行い、パルス波のピーク付近でほぼゼロになり、以後はマイナスの値となり、ゆっくりとゼロの値に近づく。係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との積和演算の結果が、ほぼゼロになるように設定されている。図19に示すように、クロック150の時点でパルス波を含む信号の値がほぼゼロとなり、これ以後の積和演算はほぼゼロとなる。クロック150の時点以前では、パルス波のピーク以前の信号値とプラスの係数との積和演算の結果はプラスの値となり、パルス波のピーク以後の信号値とマイナスの係数との積和演算の結果はマイナスの値となり、合計でほぼゼロとなるように、係数の値の変化が定められている。このため、単一のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と係数列との積和演算の結果は、ほぼゼロになる。このように、係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号との積和演算の結果がほぼゼロになるように定められている。
As shown in FIG. 19, the coefficient sequence rises almost at the same time as the pulse wave, increases and decreases in a shorter period than the pulse wave, becomes almost zero near the peak of the pulse wave, and thereafter becomes a negative value. It slowly approaches the value of zero. The coefficient sequence is set so that the result of the product-sum operation with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including a single pulse wave becomes almost zero. As shown in FIG. 19, the value of the signal including the pulse wave becomes almost zero at the time of the clock 150, and the product-sum operation after that becomes almost zero. Before the time of clock 150, the result of the product-sum calculation of the signal value before the peak of the pulse wave and the positive coefficient is a positive value, and the product-sum calculation of the signal value after the peak of the pulse wave and the negative coefficient is performed. The change in the coefficient value is defined so that the result is a negative value and the total is almost zero. Therefore, the result of the product-sum calculation of the sequence of signal values and the coefficient sequence constituting the signal including a single pulse wave becomes almost zero. In this way, the coefficient sequence is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation with the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes almost zero.
図20には、重畳波を含む信号を破線で示し、係数列を実線で示している。図19及び図20に示す係数列は同一である。図20に示すように、重畳波の時間幅は単一のパルス波よりも大きいので、重畳波を含む信号では、クロック150の時点以後でも、信号値はプラスの値を保っている。また、係数列は、クロック150の時点以後はマイナスの値となっている。このため、重畳波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と係数列との積和演算の結果は、クロック150の時点以後ではマイナスの値となる。クロック150の時点以前では、単一のパルス波と同様に、積和演算の結果はほぼゼロとなる。このため、重畳波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と係数列との積和演算の結果は、マイナスの値となる。このように、係数列は、重畳波を含む信号との積和演算の結果がマイナスの値になるように定められている。即ち、ゼロ未満の所定の値を基準値として、係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号との積和演算の結果が基準値より大となり、重畳波を含む信号との積和演算の結果が基準値より小となるように、定められている。
In FIG. 20, the signal including the superimposed wave is shown by a broken line, and the coefficient sequence is shown by a solid line. The coefficient sequences shown in FIGS. 19 and 20 are the same. As shown in FIG. 20, since the time width of the superimposed wave is larger than that of the single pulse wave, the signal value of the signal including the superimposed wave keeps a positive value even after the time of the clock 150. Further, the coefficient sequence has a negative value after the time of the clock 150. Therefore, the result of the product-sum calculation of the string of signal values and the coefficient string constituting the signal including the superimposed wave becomes a negative value after the time of the clock 150. Before the time of clock 150, the result of the product-sum operation is almost zero, as in the case of a single pulse wave. Therefore, the result of the product-sum calculation of the string of signal values and the sequence of coefficients constituting the signal including the superimposed wave is a negative value. In this way, the coefficient sequence is defined so that the result of the product-sum operation with the signal including the superimposed wave becomes a negative value. That is, with a predetermined value less than zero as the reference value, the result of the product-sum calculation with the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes larger than the reference value in the coefficient sequence, and the product-sum calculation with the signal containing the superimposed wave is performed. The result is set to be smaller than the reference value.
図21は、実施形態6に係る信号処理装置2が実行する処理の手順を示すフローチャートである。信号処理装置2は、実施形態1におけるS21~S25の処理と同様のS51~S55の処理を実行する。信号に含まれているパルス波を検出した場合は(S25:YES)、パルス検出部24は、パルス波を検出したことを示す情報を処理部23へ入力し、処理部23は、入力された信号を構成する信号値の列と記憶部27に記憶している係数列との積和演算を行う(S56)。
FIG. 21 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure executed by the signal processing device 2 according to the sixth embodiment. The signal processing device 2 executes the processing of S51 to S55 similar to the processing of S21 to S25 in the first embodiment. When the pulse wave included in the signal is detected (S25: YES), the pulse detection unit 24 inputs information indicating that the pulse wave is detected to the processing unit 23, and the processing unit 23 inputs the information. The product-sum calculation of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal and the sequence of coefficients stored in the storage unit 27 is performed (S56).
処理部23は、積和演算の結果に従って、入力された信号に複数のパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定する(S57)。S57では、処理部23は、積和演算の結果がゼロ未満の基準値未満である場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあると判定し、積和演算の結果が基準値以上である場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりは無いと判定する。基準値は予め処理部23又は記憶部27に記憶されている。処理部23は、複数のパルス波の重なりの有無を示す情報を波高測定部25へ入力する。複数のパルス波の重なりが無い場合は(S57:NO)、波高測定部25は、入力された信号に含まれるパルス波の波高を測定し(S58)、測定した波高をカウント部26へ入力する。カウント部26は、波高測定部25から入力された波高別に、パルス波をカウントし(S59)、処理を終了する。
The processing unit 23 determines whether or not a plurality of pulse waves overlap in the input signal according to the result of the product-sum calculation (S57). In S57, the processing unit 23 determines that there is overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the result of the product-sum calculation is less than the reference value of less than zero, and when the result of the product-sum calculation is greater than or equal to the reference value. , It is determined that there is no overlap of multiple pulse waves. The reference value is stored in advance in the processing unit 23 or the storage unit 27. The processing unit 23 inputs information indicating the presence or absence of overlapping of the plurality of pulse waves to the wave height measuring unit 25. When there is no overlap of a plurality of pulse waves (S57: NO), the wave height measuring unit 25 measures the wave height of the pulse wave included in the input signal (S58), and inputs the measured wave height to the counting unit 26. .. The counting unit 26 counts pulse waves according to the wave height input from the wave height measuring unit 25 (S59), and ends the process.
複数のパルス波の重なりがある場合(S57:YES)、波高測定部25は、重なった複数のパルス波については波高の測定を行わず、信号処理装置2は処理を終了する。この結果、カウント部26は、重なった複数のパルス波をカウントしない。信号処理装置2は、S51~S59の処理を個々に繰り返し実行する。信号処理装置2は、パルス波の波高とカウント数との関係を示すデータを出力する。分析部3は、信号処理装置2が出力したデータを入力され、データに基づいて、放射線検出器1が検出した放射線のスペクトルを生成する。分析部3は、放射線のスペクトルに基づいて、放射線源の元素分析を行ってもよい。
When there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves (S57: YES), the wave height measuring unit 25 does not measure the wave height for the overlapping plurality of pulse waves, and the signal processing device 2 ends the processing. As a result, the counting unit 26 does not count the plurality of overlapping pulse waves. The signal processing device 2 repeatedly executes the processes of S51 to S59 individually. The signal processing device 2 outputs data showing the relationship between the height of the pulse wave and the number of counts. The analysis unit 3 inputs the data output by the signal processing device 2, and generates a spectrum of the radiation detected by the radiation detector 1 based on the data. The analysis unit 3 may perform elemental analysis of the radiation source based on the spectrum of radiation.
なお、係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との積和演算の結果が基準値より小となり、重畳波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との積和演算の結果が基準値より大となるように、定められていてもよい。例えば、係数列は、単一のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と係数列との積和演算の結果がほぼゼロになり、重畳波を含む信号との積和演算の結果がプラスの値になるように定められていてもよい。この形態では、S57で、処理部23は、ゼロを超過する所定の値を基準値として、積和演算の結果が基準値を超過する場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりがあると判定し、積和演算の結果が基準値以下である場合に、複数のパルス波の重なりは無いと判定する。
In the coefficient sequence, the result of the product-sum calculation with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including a single pulse wave is smaller than the reference value, and the product with the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the superimposed wave. It may be set so that the result of the sum operation is larger than the reference value. For example, in the coefficient sequence, the result of the product-sum calculation of the signal value sequence and the coefficient sequence constituting the signal containing a single pulse wave becomes almost zero, and the result of the product-sum calculation with the signal including the superimposed wave is almost zero. It may be set to be a positive value. In this embodiment, in S57, the processing unit 23 determines that there is an overlap of a plurality of pulse waves when the result of the product-sum calculation exceeds the reference value, using a predetermined value exceeding zero as a reference value. When the result of the product-sum operation is equal to or less than the reference value, it is determined that the plurality of pulse waves do not overlap.
以上詳述した如く、実施形態6においては、信号処理装置2は、パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と所定の係数列との積和演算を行い、積和演算の結果に基づいて、パルス波の重なりを検出する。実施形態6においても、信号処理装置2は、効果的にパルス波の重なりを検出することができ、放射線検出装置10は、スペクトルに基づいた元素分析の精度をより向上させることができる。学習モデルを使用せずに積和演算によって判定を行うので、信号処理装置2は、より高速に処理を実行することができる。
As described in detail above, in the sixth embodiment, the signal processing device 2 performs a product-sum calculation of a string of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave and a predetermined coefficient string, and is based on the result of the product-sum calculation. Then, the overlap of pulse waves is detected. Also in the sixth embodiment, the signal processing device 2 can effectively detect the overlap of pulse waves, and the radiation detection device 10 can further improve the accuracy of elemental analysis based on the spectrum. Since the determination is performed by the product-sum calculation without using the learning model, the signal processing device 2 can execute the processing at a higher speed.
信号処理装置2は、実施形態1又は2に示した学習モデル232を用いる方法と、実施形態6に示した積和演算の結果を用いる方法とを両方実行する形態であってもよい。例えば、信号処理装置2は、学習モデル232を用いる方法と積和演算の結果を用いる方法との両方でパルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定し、何れか一方の方法でパルス波の重なりがあると判定した場合に、パルス波の重なりが発生したと判定する。実施形態1~6では、信号処理装置2がカウント部26を備える形態を示したが、カウント部26は信号処理装置2の外部に設けられていてもよい。また、実施形態1~6では、放射線検出素子11が半導体放射線検出素子である例を示したが、放射線検出器1は、半導体放射線検出素子以外の放射線検出素子11を用いた形態であってもよい。例えば、放射線検出器1は、シンチレーション検出器であってもよい。
The signal processing device 2 may be in a form in which both the method using the learning model 232 shown in the first or second embodiment and the method using the result of the product-sum calculation shown in the sixth embodiment are executed. For example, the signal processing device 2 determines whether or not there is overlap of pulse waves in both the method using the learning model 232 and the method using the result of the product-sum calculation, and the overlap of pulse waves is performed by either method. When it is determined that there is, it is determined that the overlap of pulse waves has occurred. In the first to sixth embodiments, the signal processing device 2 includes the counting unit 26, but the counting unit 26 may be provided outside the signal processing device 2. Further, in the first to sixth embodiments, an example in which the radiation detection element 11 is a semiconductor radiation detection element is shown, but the radiation detector 1 may have a form in which the radiation detection element 11 other than the semiconductor radiation detection element is used. Good. For example, the radiation detector 1 may be a scintillation detector.
本発明は上述した実施の形態の内容に限定されるものではなく、請求項に示した範囲で種々の変更が可能である。即ち、請求項に示した範囲で適宜変更した技術的手段を組み合わせて得られる実施形態も本発明の技術的範囲に含まれる。
The present invention is not limited to the contents of the above-described embodiment, and various modifications can be made within the scope of the claims. That is, an embodiment obtained by combining technical means appropriately modified within the scope of the claims is also included in the technical scope of the present invention.
1 放射線検出器
10 放射線検出装置
11 放射線検出素子
2 信号処理装置
21 A/D変換部
22 波形整形部
23 処理部
232 学習モデル
235 コンピュータプログラム
25 波高測定部
26 カウント部
27 記憶部
3 分析部
5 学習装置
1Radiation detector 10 Radiation detection device 11 Radiation detection element 2 Signal processing device 21 A / D conversion unit 22 Waveform shaping unit 23 Processing unit 232 Learning model 235 Computer program 25 Wave height measurement unit 26 Counting unit 27 Storage unit 3 Analysis unit 5 Learning apparatus
10 放射線検出装置
11 放射線検出素子
2 信号処理装置
21 A/D変換部
22 波形整形部
23 処理部
232 学習モデル
235 コンピュータプログラム
25 波高測定部
26 カウント部
27 記憶部
3 分析部
5 学習装置
1
Claims (10)
- 放射線の検出に応じた階段波又は前記階段波を変換したパルス波を、波高別にカウントする信号処理方法において、
前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルへ、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力し、
前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりが無い場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントすること
を特徴とする信号処理方法。 In a signal processing method that counts a staircase wave corresponding to radiation detection or a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave by wave height.
When at least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input, information regarding the presence or absence of overlapping of the plurality of pulse waves is output. At least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave are input to the learning model to be performed.
A signal processing method comprising counting the staircase wave or the pulse wave when there is no overlap of a plurality of the pulse waves according to the information output by the learning model. - 前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波が重なる場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントしないこと
を特徴とする請求項1に記載の信号処理方法。 The signal processing method according to claim 1, wherein the step wave or the pulse wave is not counted when a plurality of the pulse waves overlap according to the information output by the learning model. - 前記学習モデルは、前記パルス波を整形した波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を更に入力した場合に前記情報を出力する学習モデルであり、
前記信号を構成する信号値の列を更に前記学習モデルへ入力すること
を特徴とする請求項1又は2に記載の信号処理方法。 The learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a wave obtained by shaping the pulse wave is further input.
The signal processing method according to claim 1 or 2, wherein a sequence of signal values constituting the signal is further input to the learning model. - 前記学習モデルは、前記階段波及び前記パルス波の少なくとも一方の特徴量を更に入力した場合に前記情報を出力する学習モデルであり、
前記特徴量を前記学習モデルへ入力すること
を特徴とする請求項1乃至3のいずれか一つに記載の信号処理方法。 The learning model is a learning model that outputs the information when at least one feature amount of the staircase wave and the pulse wave is further input.
The signal processing method according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein the feature amount is input to the learning model. - 夫々に単一のパルス波からなり、前記単一のパルス波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数のパルス波信号を生成し、
夫々に複数のパルス波が重なった重畳波からなり、前記複数のパルス波の間隔、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の重畳波信号を生成し、
前記複数のパルス波信号及び前記複数の重畳波信号を教師データとして、任意のパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力した場合に複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを生成すること
を特徴とする学習モデル生成方法。 Each of them consists of a single pulse wave, and generates a plurality of pulse wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise and roundness of the single pulse wave is random.
Each of the plurality of pulse waves is composed of a superposed wave in which a plurality of pulse waves are overlapped, and a plurality of superposed wave signals in which at least one of the interval, wave height, rising edge, and rounding of the plurality of pulse waves is random are generated.
When the plurality of pulse wave signals and the plurality of superimposed wave signals are used as teacher data and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary pulse wave is input, information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves is output. A training model generation method characterized by generating a training model. - 夫々に単一の階段波からなり、前記単一の階段波の波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の階段波信号を生成し、
夫々に複数の階段波からなり、前記複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波が重なることになり、前記複数の階段波の間隔、波高、立ち上がり及びなまりの少なくともいずれか一つがランダムである複数の近接階段波信号を生成し、
前記複数の階段波信号及び前記近接階段波信号を教師データとして、任意の階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列を入力した場合に前記複数の階段波を変換した複数のパルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを生成すること
を特徴とする学習モデル生成方法。 Each staircase wave consists of a single staircase wave, generating multiple staircase wave signals in which at least one of the height, rise and roundness of the single staircase wave is random.
Each consists of a plurality of staircase waves, and a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting the plurality of staircase waves overlap each other, and at least one of the intervals, wave heights, rises, and rounds of the plurality of staircase waves is random. Generates a proximity staircase wave signal,
Overlapping of a plurality of pulse waves obtained by converting the plurality of staircase waves when a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including an arbitrary staircase wave is input using the plurality of staircase wave signals and the proximity staircase wave signal as training data. A learning model generation method characterized by generating a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of. - 放射線の検出に応じた階段波をパルス波へ変換し、前記パルス波の波高別に、前記パルス波をカウントする信号処理方法において、
前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と所定の係数列との積和演算を行い、
前記所定の係数列は、重なった複数の前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記所定の係数列の間の積和演算の結果と、単一の前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記所定の係数列の間の積和演算の結果とが、所定の値に対して大であるか小であるかについて異なるように、予め定められており、
前記積和演算の結果に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりがあるか否かを判定し、
重なっていない前記パルス波をカウントすること
を特徴とする信号処理方法。 In a signal processing method in which a staircase wave corresponding to radiation detection is converted into a pulse wave and the pulse wave is counted according to the height of the pulse wave.
A product-sum calculation is performed on a sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave and a predetermined sequence of coefficients.
The predetermined coefficient sequence includes a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a plurality of overlapping pulse waves, a result of a product-sum calculation between the predetermined coefficient sequences, and a signal including a single pulse wave. It is predetermined so that the result of the product-sum calculation between the constituent signal value sequence and the predetermined coefficient sequence differs depending on whether it is large or small with respect to the predetermined value.
Depending on the result of the product-sum calculation, it is determined whether or not the plurality of pulse waves overlap.
A signal processing method comprising counting the non-overlapping pulse waves. - 放射線の検出に応じた階段波を含む信号を処理する信号処理装置において、
前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と、前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に、複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルを備えること
を特徴とする信号処理装置。 In a signal processing device that processes a signal including staircase waves in response to radiation detection
When at least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave is input, a plurality of the pulse waves are overlapped. A signal processing device characterized by having a learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of a signal. - 放射線検出時に放射線のエネルギーに応じた階段波を出力する放射線検出器と、
前記階段波をパルス波へ変換する変換部と、
前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列の少なくとも一方を入力した場合に、複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルと、
前記学習モデルが出力する前記情報に応じて、複数の前記パルス波の重なりが無い場合の前記階段波又は前記パルス波をカウントするカウント部と、
前記階段波又は前記パルス波の波高、及びカウント数に応じて、放射線のスペクトルを生成するスペクトル生成部と
を備えることを特徴とする放射線検出装置。 A radiation detector that outputs staircase waves according to the energy of radiation when detecting radiation,
A conversion unit that converts the staircase wave into a pulse wave,
When at least one of the signal value sequence constituting the signal including the staircase wave and the signal value sequence constituting the signal including the pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave is input, the presence or absence of overlap of the plurality of pulse waves. A learning model that outputs information about
A counting unit that counts the staircase wave or the pulse wave when there is no overlap of the plurality of pulse waves according to the information output by the learning model.
A radiation detection device including a spectrum generation unit that generates a spectrum of radiation according to the wave height of the staircase wave or the pulse wave and the number of counts. - 放射線の検出に応じた階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列と前記階段波を変換したパルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列との少なくとも一方を入力した場合に複数の前記パルス波の重なりの有無に関する情報を出力する学習モデルへ、前記階段波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列及び前記パルス波を含む信号を構成する信号値の列の少なくとも一方を入力して、前記情報を出力する
処理をコンピュータに実行させることを特徴とするコンピュータプログラム。
When at least one of a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a staircase wave according to radiation detection and a sequence of signal values constituting a signal including a pulse wave obtained by converting the staircase wave is input, a plurality of the pulses are performed. At least one of the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the staircase wave and the sequence of signal values constituting the signal including the pulse wave is input to the learning model that outputs information regarding the presence or absence of overlap of the waves. A computer program characterized by having a computer execute a process that outputs information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021552358A JPWO2021075345A1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2020-10-08 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019-191446 | 2019-10-18 | ||
| JP2019191446 | 2019-10-18 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2021075345A1 true WO2021075345A1 (en) | 2021-04-22 |
Family
ID=75537989
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/038107 WO2021075345A1 (en) | 2019-10-18 | 2020-10-08 | Signal processing method, learning model generation method, signal processing device, radiation detection device, and computer program |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JPWO2021075345A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021075345A1 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7218958B1 (en) | 2021-08-24 | 2023-02-07 | 株式会社リガク | X-ray analyzer and peak value prediction program |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0829538A (en) * | 1994-07-13 | 1996-02-02 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Radiation detector |
| JP2007057356A (en) * | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Toshiba Corp | Radiation measuring device |
| JP2009229127A (en) * | 2008-03-19 | 2009-10-08 | Jeol Ltd | Pulse processor for radiation measurement |
| JP2011508201A (en) * | 2007-12-20 | 2011-03-10 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Counting type integrated detector |
| US10422896B1 (en) * | 2016-10-24 | 2019-09-24 | Triad National Security, Llc | High count rate thermal neutron detectors and electronics |
-
2020
- 2020-10-08 WO PCT/JP2020/038107 patent/WO2021075345A1/en active Application Filing
- 2020-10-08 JP JP2021552358A patent/JPWO2021075345A1/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0829538A (en) * | 1994-07-13 | 1996-02-02 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Radiation detector |
| JP2007057356A (en) * | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-08 | Toshiba Corp | Radiation measuring device |
| JP2011508201A (en) * | 2007-12-20 | 2011-03-10 | コーニンクレッカ フィリップス エレクトロニクス エヌ ヴィ | Counting type integrated detector |
| JP2009229127A (en) * | 2008-03-19 | 2009-10-08 | Jeol Ltd | Pulse processor for radiation measurement |
| US10422896B1 (en) * | 2016-10-24 | 2019-09-24 | Triad National Security, Llc | High count rate thermal neutron detectors and electronics |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7218958B1 (en) | 2021-08-24 | 2023-02-07 | 株式会社リガク | X-ray analyzer and peak value prediction program |
| WO2023026598A1 (en) * | 2021-08-24 | 2023-03-02 | 株式会社リガク | X-ray analysis device and wave height value prediction program |
| JP2023031101A (en) * | 2021-08-24 | 2023-03-08 | 株式会社リガク | X-ray analyzer and wave height prediction program |
| CN117836616A (en) * | 2021-08-24 | 2024-04-05 | 株式会社理学 | X-ray analysis device and peak prediction program |
| EP4394365A4 (en) * | 2021-08-24 | 2024-09-18 | Rigaku Denki Co Ltd | X-ray analysis device and wave height value prediction program |
| US12105035B2 (en) | 2021-08-24 | 2024-10-01 | Rigaku Corporation | X-ray spectrometer and pulse height prediction program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2021075345A1 (en) | 2021-04-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11686863B2 (en) | Neural network-based corrector for photon counting detectors | |
| US10325007B2 (en) | Noise and bound management for RPU array | |
| US20160196175A1 (en) | Information processing system, information processing method, and program | |
| Wielgosz et al. | The model of an anomaly detector for HiLumi LHC magnets based on Recurrent Neural Networks and adaptive quantization | |
| WO2019082166A1 (en) | Unit-level uncertainty and propagation | |
| US20220252744A1 (en) | Method and device for identifying atomic species emitting x- or gamma radiation | |
| CN106483550A (en) | A kind of simulation spectrum curve emulation mode | |
| JP5111105B2 (en) | Measurement method and analysis apparatus including signal processing including a chain of main impulses | |
| WO2021075345A1 (en) | Signal processing method, learning model generation method, signal processing device, radiation detection device, and computer program | |
| EP3812797B1 (en) | Processing apparatus, system, x-ray measurement method, and program | |
| US10156647B2 (en) | Method of spectral data detection and manipulation | |
| US11199638B2 (en) | Input count rate estimation in radiation pulse detectors | |
| JP7539975B2 (en) | Signal processing method, learning model generation method, signal processing device, radiation detection device, and computer program | |
| Lanchares et al. | Real-time evolvable pulse shaper for radiation measurements | |
| Lennox et al. | Assessing and minimizing contamination in time of flight basedvalidation data | |
| CN116432703B (en) | Pulse height estimation method, system and terminal based on composite neural network model | |
| Trigano et al. | Intensity estimation of spectroscopic signals with an improved sparse reconstruction algorithm | |
| WO2023026598A1 (en) | X-ray analysis device and wave height value prediction program | |
| WO2022224653A1 (en) | Signal processing method, computer program, signal processing device, and radiation detection device | |
| CN116203613A (en) | Processing method and device of scintillation pulse, digitizing equipment and storage medium | |
| McLean et al. | Limitations of decision based pile-up correction algorithms | |
| Trigano et al. | Deep Learning Based Method for Activity Estimation from Short-Duration Gamma Spectroscopy Recordings | |
| Theenhausen et al. | Neural-network-based level-1 trigger upgrade for the SuperCDMS experiment at SNOLAB | |
| CN116243359A (en) | Stacked signal reconstruction method and device, storage medium and electronic equipment | |
| Bobin et al. | Learning to unmix from Poisson measurements with application to γ-spectroscopy |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20876525 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2021552358 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20876525 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |