WO2006127550A1 - Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists - Google Patents
Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2006127550A1 WO2006127550A1 PCT/US2006/019649 US2006019649W WO2006127550A1 WO 2006127550 A1 WO2006127550 A1 WO 2006127550A1 US 2006019649 W US2006019649 W US 2006019649W WO 2006127550 A1 WO2006127550 A1 WO 2006127550A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- prolinamide
- benzimidazol
- phenyl
- methyl
- propanoyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 CC(CCC(**)(CC(C)(*)CC1)N)C1NCC(*(CCC1)[C@@]1C(*C1=CC=CC=*=C1)=O)=O Chemical compound CC(CCC(**)(CC(C)(*)CC1)N)C1NCC(*(CCC1)[C@@]1C(*C1=CC=CC=*=C1)=O)=O 0.000 description 6
- VDJVABHVVXVKHP-SFHVURJKSA-N C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(Nc(cccc1)c1OS(C(F)(F)F)(=O)=O)=O)=O Chemical compound C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(Nc(cccc1)c1OS(C(F)(F)F)(=O)=O)=O)=O VDJVABHVVXVKHP-SFHVURJKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GGMLECMFIKXOFE-ZDUSSCGKSA-N C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(O)=O)=O Chemical compound C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(O)=O)=O GGMLECMFIKXOFE-ZDUSSCGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CLDLUXZUWPYXNF-AWEZNQCLSA-N C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(OC)=O)=O Chemical compound C[n]1c(cccc2)c2nc1CCC(N(CCC1)[C@@H]1C(OC)=O)=O CLDLUXZUWPYXNF-AWEZNQCLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DYKGDAUEEKXLNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N NC(C(F)F)c1ccccc1 Chemical compound NC(C(F)F)c1ccccc1 DYKGDAUEEKXLNO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CDAWCLOXVUBKRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nc(cccc1)c1O Chemical compound Nc(cccc1)c1O CDAWCLOXVUBKRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PLPVLSBYYOWFKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nc(cccc1)c1OCc1ccccc1 Chemical compound Nc(cccc1)c1OCc1ccccc1 PLPVLSBYYOWFKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XYWJNTOURDMTPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N OC(CCc1nc(cccc2)c2[nH]1)=O Chemical compound OC(CCc1nc(cccc2)c2[nH]1)=O XYWJNTOURDMTPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FXAKWJBLHHNRPR-NSHDSACASA-N OC([C@H](CCC1)N1C(CSc1nc(cccc2)c2[nH]1)=O)=O Chemical compound OC([C@H](CCC1)N1C(CSc1nc(cccc2)c2[nH]1)=O)=O FXAKWJBLHHNRPR-NSHDSACASA-N 0.000 description 1
- XQYPHQUCUSQDQK-AJZOCDQUSA-N OC([C@H](CCC1)N1C(CSc1nc2ccccc2[nH]1)=O)Oc(cccc1)c1N1C=CCC1 Chemical compound OC([C@H](CCC1)N1C(CSc1nc2ccccc2[nH]1)=O)Oc(cccc1)c1N1C=CCC1 XQYPHQUCUSQDQK-AJZOCDQUSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/12—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings linked by a chain containing hetero atoms as chain links
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/04—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system for ulcers, gastritis or reflux esophagitis, e.g. antacids, inhibitors of acid secretion, mucosal protectants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P1/00—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system
- A61P1/08—Drugs for disorders of the alimentary tract or the digestive system for nausea, cinetosis or vertigo; Antiemetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P11/00—Drugs for disorders of the respiratory system
- A61P11/06—Antiasthmatics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/02—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of urine or of the urinary tract, e.g. urine acidifiers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/08—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of the prostate
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P13/00—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system
- A61P13/12—Drugs for disorders of the urinary system of the kidneys
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P15/00—Drugs for genital or sexual disorders; Contraceptives
- A61P15/08—Drugs for genital or sexual disorders; Contraceptives for gonadal disorders or for enhancing fertility, e.g. inducers of ovulation or of spermatogenesis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P19/00—Drugs for skeletal disorders
- A61P19/08—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease
- A61P19/10—Drugs for skeletal disorders for bone diseases, e.g. rachitism, Paget's disease for osteoporosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/06—Antimigraine agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/08—Antiepileptics; Anticonvulsants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/14—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abnormal movements, e.g. chorea, dyskinesia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/14—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating abnormal movements, e.g. chorea, dyskinesia
- A61P25/16—Anti-Parkinson drugs
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/18—Antipsychotics, i.e. neuroleptics; Drugs for mania or schizophrenia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/20—Hypnotics; Sedatives
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/22—Anxiolytics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/24—Antidepressants
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P25/00—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system
- A61P25/28—Drugs for disorders of the nervous system for treating neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system, e.g. nootropic agents, cognition enhancers, drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease or other forms of dementia
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P29/00—Non-central analgesic, antipyretic or antiinflammatory agents, e.g. antirheumatic agents; Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs [NSAID]
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P31/00—Antiinfectives, i.e. antibiotics, antiseptics, chemotherapeutics
- A61P31/12—Antivirals
- A61P31/14—Antivirals for RNA viruses
- A61P31/18—Antivirals for RNA viruses for HIV
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P35/00—Antineoplastic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P37/00—Drugs for immunological or allergic disorders
- A61P37/08—Antiallergic agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P43/00—Drugs for specific purposes, not provided for in groups A61P1/00-A61P41/00
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/02—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the hypothalamic hormones, e.g. TRH, GnRH, CRH, GRH, somatostatin
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/02—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the hypothalamic hormones, e.g. TRH, GnRH, CRH, GRH, somatostatin
- A61P5/04—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the hypothalamic hormones, e.g. TRH, GnRH, CRH, GRH, somatostatin for decreasing, blocking or antagonising the activity of the hypothalamic hormones
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/10—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the posterior pituitary hormones, e.g. oxytocin, ADH
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P5/00—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system
- A61P5/14—Drugs for disorders of the endocrine system of the thyroid hormones, e.g. T3, T4
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/04—Inotropic agents, i.e. stimulants of cardiac contraction; Drugs for heart failure
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/12—Antihypertensives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings
- C07D403/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D403/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00
- C07D403/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D401/00 containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D405/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D405/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing both one or more hetero rings having oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, and one or more rings having nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D413/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D413/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D417/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D415/00
- C07D417/14—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for by group C07D415/00 containing three or more hetero rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D471/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00
- C07D471/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with one nitrogen atom, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D463/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D471/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D487/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00
- C07D487/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms in the condensed system, not provided for by groups C07D451/00 - C07D477/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D487/04—Ortho-condensed systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D513/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for in groups C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D499/00 - C07D507/00
- C07D513/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing in the condensed system at least one hetero ring having nitrogen and sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, not provided for in groups C07D463/00, C07D477/00 or C07D499/00 - C07D507/00 in which the condensed system contains two hetero rings
- C07D513/04—Ortho-condensed systems
Definitions
- the orexins (hypocretins) comprise two neuropeptides produced in the hypothalamus: the orexin A (OX-A) (a 33 amino acid peptide) and the orexin B (OX-B) (a 28 amino acid peptide) (Sakurai T. et al., Cell, 1998, 92, 573-585). Orexins are found to stimulate food consumption in rats suggesting a physiological role for these peptides as mediators in the central feedback mechanism that regulates feeding behaviour (Sakurai T. et al., Cell, 1998, 92, 573-585).
- Orexins also regulate states of sleep and wakefulness opening potentially novel therapeutic approaches for narcoleptic or insomniac patients (Chemelli R.M. et al., Cell, 1999, 98, 437-451).
- Two orexin receptors have been cloned and characterized in mammals. They belong to the super family of G-protein coupled receptors (Sakurai T. et al., Cell, 1998, 92, 573-585): the orexin-1 receptor (OX or OXlR) is selective for OX-A and the orexin-2 receptor (0X2 or OX2R) is capable to bind OX-A as well as OX-B.
- the physiological actions in which orexins are presumed to participate are thought to be expressed via one or both of OX 1 receptor and OX 2 receptor as the two subtypes of orexin receptors.
- Orexin receptors are found in the mammalian brain and may have numerous implications in pathologies such as depression; anxiety; addictions; obsessive compulsive disorder; affective neurosis; depressive neurosis; anxiety neurosis; dysthymic disorder; behaviour disorder; mood disorder; sexual dysfunction; psychosexual dysfunction; sex disorder; schizophrenia; manic depression; delirium; dementia; severe mental retardation and dyskinesias such as Huntington's disease and Tourette syndrome; eating disorders such as anorexia, bulimia, cachexia, and obesity; cardiovascular diseases; diabetes; appetite/taste disorders; vomiting/nausea; asthma; cancer; Parkinson's disease; Cushing's syndrome/disease; basophile adenoma; prolactinoma; hyperprolactinemia; hypophysis tumour/adenoma; hypothalamic diseases; inflammatory bowel disease; gastric diskinesia; gastric ulcers; Froehlich's syndrome; adrenohypophysis disease
- HTV post- chemotherapy pain; post-stroke pain; post-operative pain; neuralgia; conditions associated with visceral pain such as irritable bowel syndrome, and angina; urinary bladder incontinence e.g. urge incontinence; tolerance to narcotics or withdrawal from narcotics; sleep disorders; migraine; sleep apnea; narcolepsy; insomnia; parasomnia; jet lag syndrome; and neurodegenerative disorders including nosological entities such as disinhibition-dementia-parkinsomsm-amyotrophy complex; pallido-ponto-nigral degeneration epilepsy; seizure disorders and other diseases related to general orexin system dysfunction.
- Certain orexin receptor antagonists are disclosed in PCT patent publications WO
- 2-Amino- methylpiperidine derivatives (WO 01/96302), 3-aminomethyl morpholine derivatives (WO 02/44172) and N-aroyl cyclic amines (WO 02/090355, WO 02/089800 and WO 03/051368) are disclosed as orexin receptor antagonists.
- the present invention is directed to proline bis-amide compounds which are antagonists of orexin receptors, and which are useful in the treatment or prevention of neurological and psychiatric disorders and diseases in which orexin receptors are involved.
- the invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds and the use of these compounds and compositions in the prevention or treatment of such diseases in which orexin receptors are involved.
- the present invention is directed to compounds of the formula I:
- A is selected from the group consisting of phenyl, napthyl and heteroaryl
- Z is selected from O and H,H; p is O, 1, 2 or 3;
- Rl a , Rib and Rl° may be absent if the valency of A does not permit such substitution and are independently selected from the group consisting of: (1) hydrogen,
- R2 is selected from the group consisting of:
- Ci_6alkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted with one or more substituents selected from Rl3, and
- C3_6cycloalkyl which may be fused to a phenyl ring and which is unsubstituted or substituted with one or more substituents selected from Rl 3;
- R7a, R.7b an d R7C ma y be absent if the valency of the group to which they are attached does not permit such substitution and are independently selected from the group consisting of:
- Rl 3 is selected from the group consisting of:
- R14 is selected from the group consisting of:
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds of the formula Ia:
- Rl a , Rib, Rl c ; R7a ; R7b an( j R7C are defined herein; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or an individual enantiomer or diastereomer thereof.
- Rl a , Rib, Rlc 3 R7a ? R7b a nd R7C are defined herein; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or an individual enantiomer or diastereomer thereof.
- Rl a , RIb 3 RIc 5 R7a ; R7b and R7 C are defined herein; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or an individual enantiomer or diastereomer thereof.
- X, Rl a , Rib and Rl° are defined herein; or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or an individual enantiomer or diastereomer thereof.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein p is 1.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein X is -S-CH2- or -CH2CH2-.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein Y is -NH-.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein Z is -O-.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein A is selected from the group consisting of benzimidazole, N-methylbenzimidazole, benzthiazole and benzoxazole.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein A is benzimidazole , Rl a is hydrogen or Ci-6alkyl, Rib is hydrogen and Rl° is hydrogen.
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein R2 is phenyl or pyridyl which is substituted with R7a, R7b and R7c.
- R7a, R7b and R7C are independently selected from the group consisting of:
- Ci_6alkyl which is unsubstituted or substituted with halogen, hydroxyl or phenyl or napthyl,
- heteroaryl wherein heteroaryl is selected from pyrrolyl, imidazolyl, indolyl, pyridyl, and pyrimidinyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted with halogen, hydroxyl, Ci_6alkyl, -O- Ci-6alkyl or-NO2, (7) phenyl, which is unsubstituted or substituted with halogen, hydroxyl, Ci_6alkyl, -O-Ci_
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein R7b Js hydrogen, R7c is hydrogen and R7a is selected from the group consisting of:
- An embodiment of the present invention includes compounds wherein R2 is phenyl which is substituted with pyrrolyl.
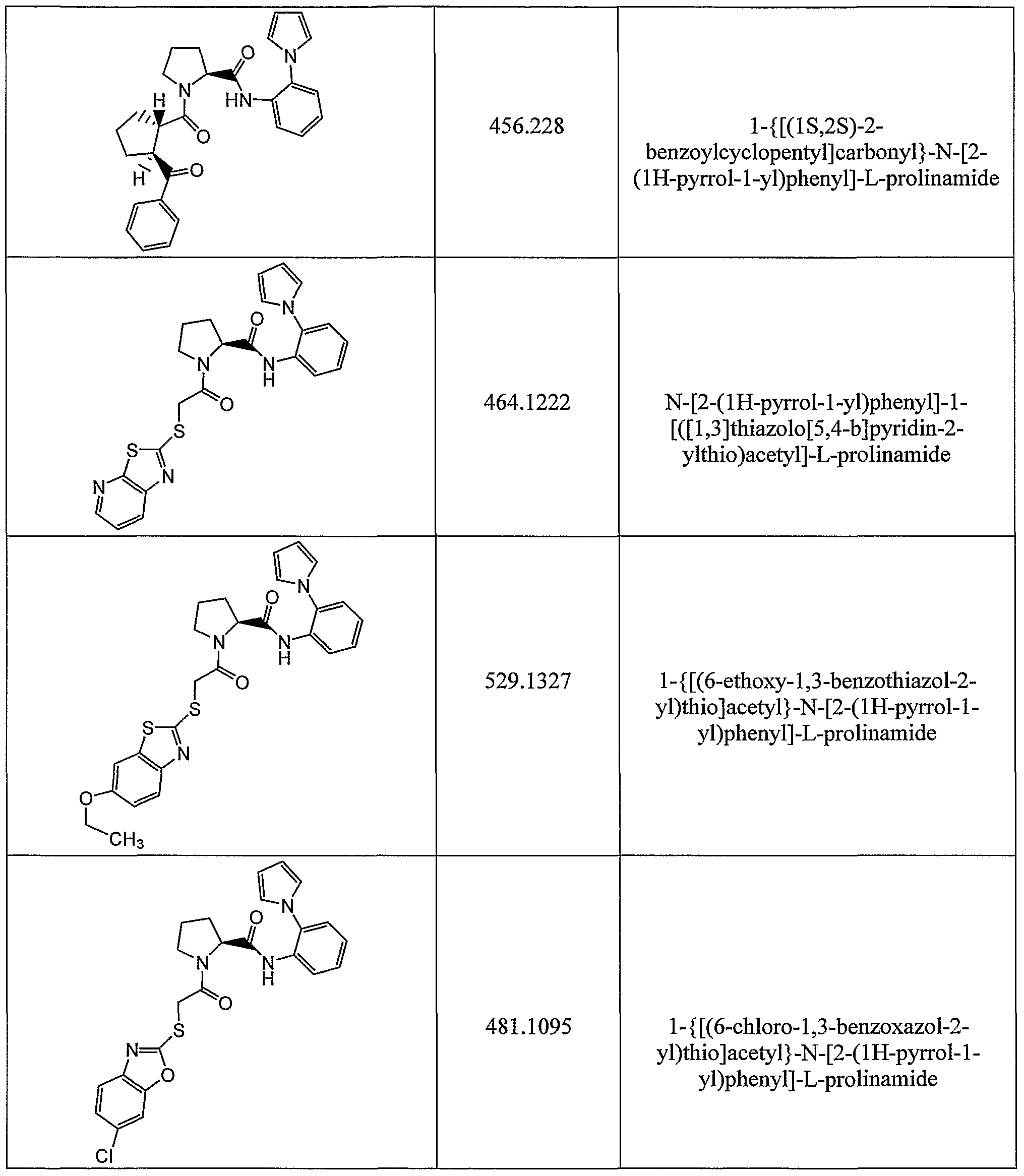
- Specific embodiments of the present invention include a compound which is selected from the group consisting of the subject compounds of the Examples herein or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
- the compounds of the present invention may contain one or more asymmetric centers and can thus occur as racemates and racemic mixtures, single enantiomers, diastereomeric mixtures and individual diastereomers. Additional asymmetric centers may be present depending upon the nature of the various substituents on the molecule. Each such asymmetric center will independently produce two optical isomers and it is intended that all of the possible optical isomers and diastereomers in mixtures and as pure or partially purified compounds are included within the ambit of this invention. The present invention is meant to comprehend all such isomeric forms of these compounds.
- Formula I shows the structure of the class of compounds without preferred stereochemistry.
- racemic mixtures of the compounds may be separated so that the individual enantiomers are isolated.
- the separation can be carried out by methods well known in the art, such as the coupling of a racemic mixture of compounds to an enantiomerically pure compound to form a diastereomeric mixture, followed by separation of the individual diastereomers by standard methods, such as fractional crystallization or chromatography.
- the coupling reaction is often the formation of salts using an enantiomerically pure acid or base.
- the diasteromeric derivatives may then be converted to the pure enantiomers by cleavage of the added chiral residue.
- the racemic mixture of the compounds can also be separated directly by chromatographic methods utilizing chiral stationary phases, which methods are well known in the art.
- any enantiomer of a compound may be obtained by stereoselective synthesis using optically pure starting materials or reagents of known configuration by methods well known in the art.
- Ci_6alkyl is defined to identify the group as having 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6 carbons in a linear or branched arrangement, such that Ci_8alkyl specifically includes methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, iso-propyl, n-butyl, iso-butyl, tert-butyl, pentyl, and hexyl.
- a group which is designated as being independently substituted with substituents may be independently substituted with multiple numbers of such substituents.
- heterocycle includes both unsaturated and saturated heterocyclic moieties, wherein the unsaturated heterocyclic moieties (i.e. "heteroaryl”) include benzoimidazolyl, benzimidazolonyl, benzofuranyl, benzofurazanyl, benzopyrazolyl, benzotriazolyl, benzothiophenyl, benzoxazolyl, carbazolyl, carbolinyl, cinnolinyl, furanyl, imidazolyl, indolinyl, indolyl, indolazinyl, indazolyl, isobenzofuranyl, isoindolyl, isoquinolyl, isothiazolyl, isoxazolyl, naphthpyridinyl, oxadiazolyl, oxazolyl, oxazoline, isoxazoline, oxetanyl, pyrazinyl, pyr
- salts refers to salts prepared from pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic bases or acids including inorganic or organic bases and inorganic or organic acids.
- Salts derived from inorganic bases include aluminum, ammonium, calcium, copper, ferric, ferrous, lithium, magnesium, manganic salts, manganous, potassium, sodium, zinc, and the like. Particularly preferred are the ammonium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium salts. Salts in the solid form may exist in more than one crystal structure, and may also be in the form of hydrates.
- Salts derived from pharmaceutically acceptable organic non-toxic bases include salts of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines, substituted amines including naturally occurring substituted amines, cyclic amines, and basic ion exchange resins, such as arginine, betaine, caffeine, choline, N,N'-dibenzylethylene- diamine, diethylamine, 2-diethylaminoethanol, 2-dimethylaminoethanol, ethanolamine, ethylenediamine, N-ethyl-morpholine, N-ethylpiperidine, glucamine, glucosamine, histidine, hydrabamine, isopropylamine, lysine, methylglucamine, morpholine, piperazine, piperidine, polyamine resins, procaine, purines, theobromine, triethylamine, trimethylamine, tripropylamine, tromethamine, and the like.
- basic ion exchange resins such as
- salts may be prepared from pharmaceutically acceptable non-toxic acids, including inorganic and organic acids.
- acids include acetic, benzenesulfonic, benzoic, camphorsulfonic, citric, ethanesulfonic, fumaric, gluconic, glutamic, hydrobromic, hydrochloric, isethionic, lactic, maleic, malic, mandelic, methanesulfonic, mucic, nitric, pamoic, pantothenic, phosphoric, succinic, sulfuric, tartaric, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and the like.
- Exemplifying the invention is the use of the compounds disclosed in the Examples and herein.
- Specific compounds within the present invention include a compound which selected from the group consisting of the compounds disclosed in the following Examples and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof and individual diastereomers thereof.
- the subject compounds are useful in a method of antagonizing orexin receptor activity in a patient such as a mammal in need of such inhibition comprising the administration of an effective amount of the compound.
- the present invention is directed to the use of the compounds disclosed herein as antagonists of orexin receptor activity.
- primates, especially humans a variety of other mammals can be treated according to the method of the present invention.
- the present invention is further directed to a method for the manufacture of a medicament for antagonizing orexin receptor activity or treating the disorders and diseases noted herein in humans and animals comprising combining a compound of the present invention or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof with a pharmaceutical carrier or diluent.
- the subject treated in the present methods is generally a mammal, preferably a human being, male or female.
- the term "therapeutically effective amount” means the amount of the subject compound that will elicit the biological or medical response of a tissue, system, animal or human that is being sought by the researcher, veterinarian, medical doctor or other clinician. It is recognized that one skilled in the art may affect the neurological and psychiatric disorders by treating a patient presently afflicted with the disorders or by prophylactically treating a patient afflicted with the disorders with an effective amount of the compound of the present invention.
- treatment and “treating” refer to all processes wherein there may be a slowing, interrupting, arresting, controlling, or stopping of the progression of the neurological and psychiatric disorders described herein, but does not necessarily indicate a total elimination of all disorder symptoms, as well as the prophylactic therapy of the mentioned conditions, particularly in a patient who is predisposed to such disease or disorder.
- administration of and or “administering a” compound should be understood to mean providing a compound of the invention or a prodrug of a compound of the invention to the individual in need thereof.
- composition as used herein is intended to encompass a product comprising the specified ingredients in the specified amounts, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from combination of the specified ingredients in the specified amounts.
- Such term in relation to pharmaceutical composition is intended to encompass a product comprising the active ingredient(s), and the inert ingredient(s) that make up the carrier, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from combination, complexation or aggregation of any two or more of the ingredients, or from dissociation of one or more of the ingredients, or from other types of reactions or interactions of one or more of the ingredients.
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention encompass any composition made by admixing a compound of the present invention and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
- pharmaceutically acceptable it is meant the carrier, diluent or excipient must be compatible with the other ingredients of the formulation and not deleterious to the recipient thereof.
- CHO cells expressing the rat orexin-1 receptor or the human orexin-2 receptor, are grown in Iscove's modified DMEM containing 2 mM L-glutamine, 0.5 g/ml G418, 1% hypoxanthine-thymidine supplement, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 ug/ml streptomycin and 10 % heat-inactivated fetal calf serum (FCS).
- FCS heat-inactivated fetal calf serum
- the cells are seeded at 20,000 cells / well into Becton-Dickinson black 384-well clear bottom sterile plates coated with poly-D-lysine. All reagents were from GEBCO-Invitrogen Corp.
- Ala 6 ' 12 human orexin-A as the agonist is prepared as a 1 mM stock solution in 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) and diluted in assay buffer (HBSS containing 20 mM HEPES, 0.1% BSA and 2.5mM probenecid, pH7.4) for use in the assay at a final concentration of 7OpM.
- Test compounds are prepared as 10 mM stock solution in DMSO, then diluted in 384-well plates, first in DMSO, then assay buffer.
- Fluorescence is measured for each well at 1 second intervals for 5 minutes and the height of each fluorescence peak is compared to the height of the fluorescence peak induced by 70 pM Ala 6 ' 12 orexin-A with buffer in place of antagonist.
- IC50 value the concentration of compound needed to inhibit 50 % of the agonist response
- the intrinsic orexin receptor antagonist activity of a compound which may be used in the present invention may be determined by these assays.
- the compounds of the following examples had activity in antagonizing the rat orexin-1 receptor and/or the human orexin-2 receptor in the aforementioned assays, generally with an IC50 of less than about 50 ⁇ M.
- Preferred compounds within the present invention had activity in antagonizing the rat orexin-1 receptor and/or the human orexin-2 receptor in the aforementioned assays with an IC50 of less than about 100 nM.
- Such a result is indicative of the intrinsic activity of the compounds in use as antagonists of orexin-1 receptor and/or the orexin-2 receptor.
- the present invention also includes compounds within the generic scope of the invention which possess activity as agonists of the orexin-1 receptor and/or the orexin-2 receptor.
- the orexin receptors have been implicated in a wide range of biological functions. This has suggested a potential role for these receptors in a variety of disease processes in humans or other species.
- the compounds of the present invention have utility in treating, preventing, ameliorating, controlling or reducing the risk of a variety of neurological and psychiatric disorders associated with orexin receptors, including one or more of the following conditions or diseases: sleep disorders, sleep disturbances, including enhancing sleep quality, improving sleep quality, increasing sleep efficiency, augmenting sleep maintenance; increasing the value which is calculated from the time that a subject sleeps divided by the time that a subject is attempting to sleep; improving sleep initiation; decreasing sleep latency or onset (the time it takes to fall asleep); decreasing difficulties in falling asleep; increasing sleep continuity; decreasing the number of awakenings during sleep; decreasing intermittent wakings during sleep; decreasing nocturnal arousals; decreasing the time spent awake following the initial onset of sleep; increasing the total amount of sleep; reducing the fragmentation of sleep; altering the timing, frequency or duration of REM sleep bout
- the present invention provides methods for: enhancing the quality of sleep; augmenting sleep maintenance; increasing REM sleep; increasing stage 2 sleep; decreasing fragmentation of sleep patterns; treating insomnia; enhancing cognition; increasing memory retention; treating or controlling obesity; treating or controlling depression; treating, controlling, ameliorating or reducing the risk of epilepsy, including absence epilepsy; treating or controlling pain, including neuropathic pain; treating or controlling Parkinson's disease; treating or controlling psychosis; or treating, controlling, ameliorating or reducing the risk of schizophrenia, in a mammalian patient in need thereof which comprises administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of the present invention.
- the subject compounds are further useful in a method for the prevention, treatment, control, amelioration, or reducation of risk of the diseases, disorders and conditions noted herein.
- the dosage of active ingredient in the compositions of this invention may be varied, however, it is necessary that the amount of the active ingredient be such that a suitable dosage form is obtained.
- the active ingredient may be administered to patients (animals and human) in need of such treatment in dosages that will provide optimal pharmaceutical efficacy.
- the selected dosage depends upon the desired therapeutic effect, on the route of administration, and on the duration of the treatment.
- the dose will vary from patient to patient depending upon the nature and severity of disease, the patient's weight, special diets then being followed by a patient, concurrent medication, and other factors which those skilled in the art will recognize.
- dosage levels of between 0.0001 to 10 mg/kg. of body weight daily are administered to the patient, e.g., humans and elderly humans, to obtain effective antagonism of orexin receptors.
- the dosage range will generally be about 0.5 mg to 1.0 g. per patient per day which may be administered in single or multiple doses.
- the dosage range will be about 0.5 mg to 500 mg per patient per day; more preferably about 0.5 mg to 200 mg per patient per day; and even more preferably about 5 mg to 50 mg per patient per day.
- Pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention may be provided in a solid dosage formulation preferably comprising about 0.5 mg to 500 mg active ingredient, more preferably comprising about 1 mg to 250 mg active ingredient.
- the pharmaceutical composition is preferably provided in a solid dosage formulation comprising about 1 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg, 200 mg or 250 mg active ingredient.
- the compositions are preferably provided in the form of tablets containing 1.0 to 1000 milligrams of the active ingredient, particularly 1, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 50, 75, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 400, 500, 600, 750, 800, 900, and 1000 milligrams of the active ingredient for the symptomatic adjustment of the dosage to the patient to be treated.
- the compounds may be administered on a regimen of 1 to 4 times per day, preferably once or twice per day.
- the compounds of the present invention may be used in combination with one or more other drugs in the treatment, prevention, control, amelioration, or reduction of risk of diseases or conditions for which compounds of the present invention or the other drugs may have utility, where the combination of the drugs together are safer or more effective than either drug alone.
- Such other drug(s) may be administered, by a route and in an amount commonly used therefor, contemporaneously or sequentially with a compound of the present invention.
- a pharmaceutical composition in unit dosage form containing such other drugs and the compound of the present invention is preferred.
- the combination therapy may also includes therapies in which the compound of the present invention and one or more other drugs are administered on different overlapping schedules.
- the compounds of the present invention and the other active ingredients may be used in lower doses than when each is used singly.
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention include those that contain one or more other active ingredients, in addition to a compound of the present invention.
- the above combinations include combinations of a compound of the present invention not only with one other active compound, but also with two or more other active compounds.
- compounds of the present invention may be used in combination with other drugs that are used in the prevention, treatment, control, amelioration, or reduction of risk of the diseases or conditions for which compounds of the present invention are useful.
- Such other drugs may be administered, by a route and in an amount commonly used therefor, contemporaneously or sequentially with a compound of the present invention.
- a pharmaceutical composition containing such other drugs in addition to the compound of the present invention is preferred.
- the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention include those that also contain one or more other active ingredients, in addition to a compound of the present invention.
- the weight ratio of the compound of the compound of the present invention to the second active ingredient may be varied and will depend upon the effective dose of each ingredient. Generally, an effective dose of each will be used. Thus, for example, when a compound of the present invention is combined with another agent, the weight ratio of the compound of the present invention to the other agent will generally range from about 1000:1 to about 1:1000, preferably about 200:1 to about 1 :200. Combinations of a compound of the present invention and other active ingredients will generally also be within the aforementioned range, but in each case, an effective dose of each active ingredient should be used. In such combinations the compound of the present invention and other active agents may be administered separately or in conjunction. In addition, the administration of one element may be prior to, concurrent to, or subsequent to the administration of other agent(s).
- the compounds of the present invention may be administered in conbination with other compounds which are known in the art to be useful for enhancing sleep quality and preventing and treating sleep disorders and sleep disturbances, including e.g., sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, antihistamines, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, cyclopyrrolones, GABA agonists, 5HT-2 antagonists including 5HT-2A antagonists and 5HT-2A/2C antagonists, histamine antagonists including histamine H3 antagonists, histamine H3 inverse agonists, imidazopyridines, minor tranquilizers, melatonin agonists and antagonists, melatonergic agents, other orexin antagonists, orexin agonists, prokineticin agonists and antagonists, pyrazolopyrimidines, T-type calcium channel antagonists, triazolopyridines, and the like, such as: adinazolam, allobar
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with other compounds which are known in the art, either administered separately or in the same pharmaceutical compositions, include, but are not limited to: insulin sensitizers including (i) PPAR ⁇ antagonists such as glitazones (e.g.
- ciglitazone darglitazone; englitazone; isaglitazone (MCC-555); pioglitazone; rosiglitazone; troglitazone; tularik; BRL49653; CLX-0921; 5-BTZD), GW-0207, LG- 100641, and LY-300512, and the like);
- biguanides such as metformin and phenformin
- insulin or insulin mimetics such as biota, LP-100, novarapid, insulin detemir, insulin lispro, insulin glargine, insulin zinc suspension (lente and ultralente); Lys-Pro insulin, GLP-I (73-7) (insulintropin); and GLP-I (7-36)-NH2)
- sulfonylureas such as acetohexamide; chlorpropamide; diabinese; glibenclamide; glipizide; gly
- CNTF Central neurotrophic factors
- GI-181771 Gaxo-SmithKline
- SR146131 Sanof ⁇ Synthelabo
- butabindide PD 170,292, and PD 149164 (Pfizer)
- CNTF derivatives such as axokine (Regeneron);
- monoamine reuptake inhibitors such as sibutramine;
- UCP-I uncoupling protein-1
- activators such as phytanic acid, 4-[(E)-2-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-2-napthalenyl)-l-propenyl]benzoic acid (TTNPB), retinoic acid;
- thyroid hormone ⁇ agonists such as KB-2611 (KaroBioBMS)
- FAS fatty acid synthase inhibitors, such as Cerulenin
- dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP-rV) inhibitors such as isoleucine thiazolidide, valine pyrrolidide, NVP-DPP728, LAF237, MK-431, P93/01, TSL 225, TMC-2A/2B/2C, FE 999011, P9310/K364, VIP 0177, SDZ 274-444; (46) dicarboxylate transporter inhibitors; (47) glucose transporter inhibitors; (48) phosphate transporter inhibitors; (49) Metformin (Glucophage®); and (50) Topiramate (Topimax®); and (50) peptide YY,
- DP-rV dipeptidyl peptidase IV
- PYY 3-36 peptide YY analogs, derivatives, and fragments such as BHVI-43073D, BIM-43004C (Olitvak, D.A. et al., Dig. Dis. Sci. 44(3):643-48 (1999));
- Neuropeptide Y2 (NPY2) receptor agonists such NPY3-36, N acetyl [Leu(28,31)] NPY 24-36, TASP-V, and cyclo-(28/32)-Ac-[Lys28-Glu32]-(25-36)- pNPY;
- Neuropeptide Y4 (NPY4) agonists such as pancreatic peptide (PP), and other Y4 agonists such as 1229U91;
- cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors such as etoricoxib, celecoxib, valdecoxib, parecoxib, lumiracoxib, BMS347070, tiracoxib or JTE522,
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with an anti-depressant or anti-anxiety agent, including norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (including tertiary amine tricyclics and secondary amine tricyclics), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase (RIMAs), serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) antagonists, ⁇ - adrenoreceptor antagonists, neurokinin- 1 receptor antagonists, atypical anti-depressants, benzodiazepines, 5-HTi A agonists or antagonists, especially 5-HTi A partial agonists, and corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) antagonists.
- norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors including tertiary amine tricyclics and secondary amine tricyclics
- Specific agents include: amitriptyline, clomipramine, doxepin, imipramine and trimipramine; amoxapine, desipramine, maprotiline, nortriptyline and protriptyline; fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine and sertraline; isocarboxazid, phenelzine, tranylcypromine and selegiline; moclobemide: venlafaxine; aprepitant; bupropion, lithium, nefazodone, trazodone and viloxazine; alprazolam, chlordiazepoxide, clonazepam, chlorazepate, diazepam, halazepam, lorazepam, oxazepam and prazepam; buspirone, flesinoxan, gepirone and ipsapirone, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with anti-Alzheimer's agents; beta-secretase inhibitors; gamma-secretase inhibitors; growth hormone secretagogues; recombinant growth hormone; HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors; NSAID's including ibuprofen; vitamin E; anti-amyloid antibodies; CB-I receptor antagonists or CB-I receptor inverse agonists; antibiotics such as doxycycline and rifampin; N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists, such as memantine; cholinesterase inhibitors such as galantamine, rivastigmine, donepezil, and tacrine; growth hormone secretagogues such as ibutamoren, ibutamoren mesylate, and capromorelin; histamine H3 antagonists; AMPA agonists; PDE IV inhibitors; GABAA inverse agonists; or neuronal nicotin
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, cyclopyrrolones, imidazopyridines, pyrazolopyrimidines, minor tranquilizers, melatonin agonists and antagonists, melatonergic agents, benzodiazepines, barbiturates, 5HT-2 antagonists, and the like, such as: adinazolam, allobarbital, alonimid, alprazolam, amitriptyline, amobarbital, amoxapine, bentazepam, benzoctamine, brotizolam, bupropion, busprione, butabarbital, butalbital, capuride, carbocloral, chloral betaine, chloral hydrate, chlordiazepoxide, clomipramine, clonazepam, cloperidone, clorazepate, clorethate
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with levodopa (with or without a selective extracerebral decarboxylase inhibitor such as carbidopa or benserazide), anticholinergics such as biperiden (optionally as its hydrochloride or lactate salt) and trihexyphenidyl (benzhexol) hydrochloride, COMT inhibitors such as entacapone, MOA-B inhibitors, antioxidants, A2a adenosine receptor antagonists, cholinergic agonists, NMDA receptor antagonists, serotonin receptor antagonists and dopamine receptor agonists such as alentemol, bromocriptine, fenoldopam, lisuride, naxagolide, pergolide and pramipexole.
- levodopa with or without a selective extracerebral decarboxylase inhibitor such as carbidopa or benserazide
- anticholinergics such as biperi
- the dopamine agonist may be in the form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, for example, alentemol hydrobromide, bromocriptine mesylate, fenoldopam mesylate, naxagolide hydrochloride and pergolide mesylate.
- a pharmaceutically acceptable salt for example, alentemol hydrobromide, bromocriptine mesylate, fenoldopam mesylate, naxagolide hydrochloride and pergolide mesylate.
- Lisuride and pramipexol are commonly used in a non-salt form.
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with acetophenazine, alentemol, benzhexol, bromocriptine, biperiden, chlorpromazine, chlorprothixene, clozapine, diazepam, fenoldopam, fluphenazine, haloperidol, levodopa, levodopa with benserazide, levodopa with carbidopa, lisuride, loxapine, mesoridazine, molindolone, naxagolide, olanzapine, pergolide, perphenazine, pimozide, pramipexole, risperidone, sulpiride, tetrabenazine, trihexyphenidyl, thioridazine, thiothixene or trifluoperazine.
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with a compound from the phenothiazine, thioxanthene, heterocyclic dibenzazepine, butyrophenone, diphenylbutylpiperidine and indolone classes of neuroleptic agent.
- phenothiazines include chlorpromazine, mesoridazine, thioridazine, acetophenazine, fluphenazine, perphenazine and trifluoperazine.
- Suitable examples of thioxanthenes include chlorprothixene and thiothixene.
- An example of a dibenzazepine is clozapine.
- An example of a butyrophenone is haloperidol.
- An example of a diphenylbutylpiperidine is pimozide.
- An example of an indolone is molindolone.
- Other neuroleptic agents include loxapine, sulpiride and risperidone.
- the neuroleptic agents when used in combination with thesubject compound may be in the form of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, for example, chlorpromazine hydrochloride, mesoridazine besylate, thioridazine hydrochloride, acetophenazine maleate, fluphenazine hydrochloride, flurphenazine enathate, fluphenazine decanoate, trifluoperazine hydrochloride, thiothixene hydrochloride, haloperidol decanoate, loxapine succinate and molindone hydrochloride.
- a pharmaceutically acceptable salt for example, chlorpromazine hydrochloride, mesoridazine besylate, thioridazine hydrochloride, acetophenazine maleate, fluphenazine hydrochloride, flurphenazine enathate, fluphenazine decanoate, trifluoperazine hydrochloride, thiothix
- Perphenazine, chlorprothixene, clozapine, haloperidol, pimozide and risperidone are commonly used in a non-salt form.
- the subject compound may be employed in combination with an anoretic agent such as aminorex, amphechloral, amphetamine, benzphetamine, chlorphentermine, clobenzorex, cloforex, clominorex, clortermine, cyclexedrine, dexfenfluramine, dextroamphetamine, diethylpropion, diphemethoxidine, N-ethylamphetamine, fenbutrazate, fenfluramine, fenisorex, fenproporex, fludorex, fluminorex, furfurylmethylamphetamine, levamfetamine, levophacetoperane, mazindol, mefenorex, metamfepramone, methamphetamine
- the subject compound may be administered with a pain reliever; a potentiator such as caffeine, an H2-antagonist, simethicone, aluminum or magnesium hydroxide; a decongestant such as phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, pseudophedrine, oxymetazoline, ephinephrine, naphazoline, xylometazoline, propylhexedrine, or levo-desoxy-ephedrine; an antiitussive such as codeine, hydrocodone, caramiphen, carbetapentane, or dextramethorphan; a diuretic; and a sedating or non-sedating antihistamine.
- a pain reliever such as caffeine, an H2-antagonist, simethicone, aluminum or magnesium hydroxide
- a decongestant such as phenylephrine, phenylpropanolamine, pseudophedrine, oxymetazoline, ephinep
- the compounds of the present invention may be administered by oral, parenteral (e.g., intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intravenous, ICV, intracisternal injection or infusion, subcutaneous injection, or implant), by inhalation spray, nasal, vaginal, rectal, sublingual, or topical routes of administration and may be formulated, alone or together, in suitable dosage unit formulations containing conventional non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, adjuvants and vehicles appropriate for each route of administration.
- parenteral e.g., intramuscular, intraperitoneal, intravenous, ICV, intracisternal injection or infusion, subcutaneous injection, or implant
- inhalation spray nasal, vaginal, rectal, sublingual, or topical routes of administration
- nasal, vaginal, rectal, sublingual, or topical routes of administration may be formulated, alone or together, in suitable dosage unit formulations containing conventional non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable carriers, adjuvants and vehicles appropriate for each route of administration.
- the compounds of the invention are effective for
- compositions for the administration of the compounds of this invention may conveniently be presented in dosage unit form and may be prepared by any of the methods well known in the art of pharmacy. All methods include the step of bringing the active ingredient into association with the carrier which constitutes one or more accessory ingredients.
- the pharmaceutical compositions are prepared by uniformly and intimately bringing the active ingredient into association with a liquid carrier or a finely divided solid carrier or both, and then, if necessary, shaping the product into the desired formulation.
- the active object compound is included in an amount sufficient to produce the desired effect upon the process or condition of diseases.
- composition is intended to encompass a product comprising the specified ingredients in the specified amounts, as well as any product which results, directly or indirectly, from combination of the specified ingredients in the specified amounts.
- compositions intended for oral use may be prepared according to any method known to the art for the manufacture of pharmaceutical compositions and such compositions may contain one or more agents selected from the group consisting of sweetening agents, flavoring agents, coloring agents and preserving agents in order to provide pharmaceutically elegant and palatable preparations.
- Tablets contain the active ingredient in admixture with non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable excipients which are suitable for the manufacture of tablets.
- excipients may be for example, inert diluents, such as calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate, lactose, calcium phosphate or sodium phosphate; granulating and disintegrating agents, for example, corn starch, or alginic acid; binding agents, for example starch, gelatin or acacia, and lubricating agents, for example magnesium stearate, stearic acid or talc.
- the tablets may be uncoated or they may be coated by known techniques to delay disintegration and absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and thereby provide a sustained action over a longer period.
- compositions for oral use may also be presented as hard gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with an inert solid diluent, for example, calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate or kaolin, or as soft gelatin capsules wherein the active ingredient is mixed with water or an oil medium, for example peanut oil, liquid paraffin, or olive oil.
- Aqueous suspensions contain the active materials in admixture with excipients suitable for the manufacture of aqueous suspensions.
- Oily suspensions may be formulated by suspending the active ingredient in a suitable oil. Oil-in-water emulsions may also be employed.
- Dispersible powders and granules suitable for preparation of an aqueous suspension by the addition of water provide the active ingredient in admixture with a dispersing or wetting agent, suspending agent and one or more preservatives.
- Pharmaceutical compositions of the present compounds may be in the form of a sterile injectable aqueous or oleagenous suspension.
- the compounds of the present invention may also be administered in the form of suppositories for rectal administration.
- creams, ointments, jellies, solutions or suspensions, etc., containing the compounds of the present invention may be employed.
- the compounds of the present invention may also be formulated for administered by inhalation.
- the compounds of the present invention may also be administered by a transdermal patch by methods known in the art.
- L-proline can be acylated under EDC-mediated coupling conditions to afford acyl- proline esters (A-2). These esters can be hydrolyzed and further functionalized using phosphorous oxychloride to couple aromatic amines to generate the desired proline bis-amides (A-4).
- L-proline can be acylated under EDC-mediated coupling conditions to afford acyl- proline esters (B2). These esters can be hydrolyzed and further functionalized using a second EDC coupling using non-aromatic amines to generate the desired proline bis-amides (B-4).
- C-I Acylated proline carboxylic acids
- 2-benzyloxyaniline can be coupled with phosphorous oxychloride to afford the anilide, C-2.
- This anilide can be deprotected under Standard hydrogenolysis conditions and converted to the aryl triflate under the action of trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride.
- Various boronic acids can be used in the subsequent Suzuki reaction to afford the desired proline bis-amides (C-4).
- Boc-L-proline can be reacted with an aromatic amine under the action of phosphorous oxychloride to afford protected anilides, D-2.
- These coupled products can be deprotected with gaseous hydrogen chloride and the resulting amine can be coupled with various acids under the action of PyBrop to give proline bis-amides, D-4.
- Proline mono-amides (E-I) can be reacted with triphosgene to afford an intermediate carbamoyl chloride which when treated with various amines can give ureas (E-2).
- Proline mono-amides (F-I) can be reacted with alpha-bromoacetylbromide and then subsequently treated with thiols to afford proline bis-amides containing thioether functionality (F-2).
- Proline mono-amides (G-I) can be treated under standard reductive animation conditions using various aldehydes to afford N-alkylated products (G-2).
- REACTION SCHEME H
- Keto-prolines (1-2) can be transformed into arylated keto-prolines via palladium catalyzed arylation conditions and then modified under standard amide coupling conditions to afford compounds (1-4).
- the final product may be further modified, for example, by manipulation of substituents.
- substituents may include, but are not limited to, reduction, oxidation, alkylation, acylation, and hydrolysis reactions which are commonly known to those skilled in the art.
- the order of carrying out the foregoing reaction schemes may be varied to facilitate the reaction or to avoid unwanted reaction products.
- the following examples are provided so that the invention might be more fully understood. These examples are illustrative only and should not be construed as limiting the invention in any way.
- ester i_7 (4.3 g, 13.6 mmol) in THF (30 mL) was added NaOH (0.82 g, 20.5 mmol) in water (1.5mL) at 25 0 C.
- the reaction was stirred for 2 h and acidified to pH 5 with concentrated HCl and the solvent was evaporated to dryness. The residue was azeotroped with toluene (3 x 150 mL) to afford a white solid (1 ⁇ 8) which was used without further purification.
- N-(2-hvdroxyphenyl)-l-[3-(l-methyl-lH-benzimidazol-2-yl)propanoyll-L-prolinamide (1-11; step 1)
- N-[2-(benzyloxy)phenyl]-l-[3-(l-methyl-lH-benzimidazol-2- yl)propanoyl]-L-prolinamide (2.60 g, 5.38 mmol)
- 20 wt% Pd(OH) 2 1.3 g, 1.80 mmol
- the system was cooled to room temperature, extracted with EtOAc, washed with water and dried over sodium sulfate.
- the crude reaction mixture was purified using reverse phase conditions (5% ⁇ 95% 0.1% TFA in water: 0.1% TFA in ACN) followed by free base extraction with saturated sodium carbonate to afford the title compound (1-12) as a white semi-solid.
- Phosporus oxychloride (468 ⁇ L, 5.11 mmol) was added to a stirring a solution of L- BOC-proline (Ig, 4.65 mmol) and l-(2-aminophenyl)pyrrole (735mg, 4.65 mmol) in dry pyridine (15mL). After 20 minutes the reaction was complete and quenched by slow addition of ice/water (5OmL). The reaction was extracted with EtOAc, washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine. The combined organics were dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated in vacuo.
- the amine salt (145) (lOOmg, 0.343 mmol), the acid (1-16) (114 mg, 0.514 mmol), PyBrOP (240mg, 0.514 mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (198 ⁇ L, 1.2 mmol) were stirred in DMF (3 mL) at room temperature for 20 minutes. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc, washed with water, saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine. The combined organics were dried over Na 2 S ⁇ 4 and concentrated in vacuo.
- Methyl Iodide (839 ⁇ L, 13.48 mmol) was added to a mixture of the 3-(lH-benzimidazol- 2-yl)propan-l-ol (2.5g, 14.19 mmol) and Et 3 N (2.16mL, 15.6 mmol) in DCM (100 mL) at O 0 C. The reaction stirred for 40 minutes, was warmed to room temperature and stirred 1 hour. DMF (50 mL) was added and continued stirring for 1 hour. Cesium carbonate (4.62g, 14.19 mmol) and methyl iodide (839 ⁇ L, 13.48 mmol) were added and the reaction stirred overnight.
- the aldehyde (1-21) (53mg, 0.282 mmol), the amine salt (1-15) (82mg, 0.282 mmol), sodium triacetoxyborohydride (90mg, 0.422 mmol) and powdered 4A sieves (lOOmg) were combined in dichloroethane (2 niL) and stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. Additional aldehyde (40mg, 0.21 mmol) in dichloroethane (0.5 mL) was added and the reaction stirred 20 minutes more. The reaction was diluted with EtOAc, washed with water, saturated sodium bicarbonate and brine. The combined organics were dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated in vacuo.
- Phosporus oxychloride (14.0 mL, 153 mmol) was added to a stirred solution of L-BOC- proline (30 g, 139 mmol)) and 2-aminobiphenyl (25.9 g, 153 mmol) in dry pyridine (200 mL). After 30 minutes the reaction was complete and quenched by slow addition of ice/water (200 mL). The reaction was diluted with EtOAc and washed with water once. The combined organics were dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated. The crude product was purified on silica by normal phase chromatography (0 to 100% ethyl acetate in hexanes) to give the titled compound (1-24) as an oil. ESI+ MS: 367.1[M+H] + . N-r2-aminobiphenyl]-L-prolinamide hydrochloride (1-25)
- the amine salt (1-25) (18.8 g, 62.1 mmol), the acid (1-26) (19.0 g, 68.3 mmol), EDC (15.5 g, 81.0 mmol), ⁇ OBT (12.4 g, 81.0 mmol), and triethylamine (87.0 mL, 621 mmol) were stirred in DMF (300 mL) at 90 0 C for 3h.
- the reaction was diluted with EtOAc (1000 mL), washed with water (2 x 500 mL), saturated sodium bicarbonate (3 x 500 mL) and brine (500 mL). The combined organics were dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated.
- the mixture was diluted with EtOAc (400 mL) and washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate (3 x 100 mL), water (3 x 100 mL), and brine (1 x 100 mL). The combined organics were dried over Na 2 SO 4 and concentrated.
- the crude oil was then diluted in THF (80 mL) and cooled to 0 0 C. To the reaction was added methylmagnesium bromide (8.9 g, 74.5 mmol, 3M solution in THF) and the reaction was stirred for 2h. The reaction was then quenched with brine (10OmL) and extracted with EtOAc (3 x 100 mL). The combined organics were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated.
- the amine salt (1-29) (30mg, 0.099 mmol), the acid (1-26) (55 mg, 0.248 mmol), EDC (48mg, 0.248 mmol), ⁇ OBT (34 mg, 0.248 mmol), and triethylamine (0.070 mL, 0.50 mmol) were stirred in DMF (2 mL) at 90 0 C for 3h.
- the reaction was diluted with EtOAc (10 mL), washed with water (10 mL), saturated sodium bicarbonate (2 x 20 mL) and brine (10 mL).
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Neurosurgery (AREA)
- Neurology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Pain & Pain Management (AREA)
- Pulmonology (AREA)
- Physical Education & Sports Medicine (AREA)
- Psychiatry (AREA)
- Hospice & Palliative Care (AREA)
- Rheumatology (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Orthopedic Medicine & Surgery (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Reproductive Health (AREA)
- Psychology (AREA)
- Anesthesiology (AREA)
- Pregnancy & Childbirth (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- AIDS & HIV (AREA)
- Communicable Diseases (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AU2006251590A AU2006251590A1 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| JP2008513571A JP2008542276A (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bisamidoorexin receptor antagonist |
| CA002609203A CA2609203A1 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| EP06760249A EP1888563A1 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| US11/920,596 US20090118200A1 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US68369005P | 2005-05-23 | 2005-05-23 | |
| US60/683,690 | 2005-05-23 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2006127550A1 true WO2006127550A1 (en) | 2006-11-30 |
Family
ID=37452344
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/US2006/019649 WO2006127550A1 (en) | 2005-05-23 | 2006-05-22 | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20090118200A1 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP1888563A1 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2008542276A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2006251590A1 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA2609203A1 (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2006127550A1 (en) |
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008008517A2 (en) | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-17 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Bridged diazepan orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008008551A2 (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-17 | Merck & Co., Inc. | 2-substituted proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008069997A1 (en) | 2006-12-01 | 2008-06-12 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Substituted diazepan compounds as orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008147518A1 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2008-12-04 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Pyridyl piperidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008150364A1 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2008-12-11 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Cyclopropyl pyrrolidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| JP2010514713A (en) * | 2006-12-27 | 2010-05-06 | サノフィ−アベンティス | Heteroaryl substituted carboxamides and their use to stimulate the expression of NO synthase |
| JP2010540429A (en) * | 2007-09-24 | 2010-12-24 | アクテリオン ファーマシューティカルズ リミテッド | Pyrrolidines and piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2010131192A3 (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2011-02-03 | Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd | Novel oxazolidinone derivatives and their use as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US20110098287A1 (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2011-04-28 | Bayer Cropscience Ag | Novel Heteroaromatic Amides And Thioamides As Pesticides |
| JP2011528016A (en) * | 2008-07-15 | 2011-11-10 | ノバルティス アーゲー | Heteroaryl derivatives as DGAT1 inhibitors |
| JP2012530137A (en) * | 2009-06-16 | 2012-11-29 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Azetidine 2-carboxamide derivative that modulates CB2 receptor |
| CN103201261A (en) * | 2010-11-10 | 2013-07-10 | 埃科特莱茵药品有限公司 | Lactam derivatives useful as orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2013139730A1 (en) | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-26 | Rottapharm Spa | Chemical compounds |
| EP2771346A4 (en) * | 2011-10-25 | 2015-06-03 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Isoxazolopyridine orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9085555B2 (en) | 2011-01-04 | 2015-07-21 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9156819B2 (en) | 2011-10-19 | 2015-10-13 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | 2-pyridyloxy-4-nitrile orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9388199B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-07-12 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9440982B2 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2016-09-13 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Substituted prolines/piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9464081B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-10-11 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9468661B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9487483B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-11-08 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9499517B2 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2016-11-22 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Substituted prolines / piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9505749B2 (en) | 2012-08-29 | 2016-11-29 | Amgen Inc. | Quinazolinone compounds and derivatives thereof |
| US9550755B2 (en) | 2012-07-12 | 2017-01-24 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9815819B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2017-11-14 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| WO2017194548A1 (en) | 2016-05-10 | 2017-11-16 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases |
| US10221170B2 (en) | 2014-08-13 | 2019-03-05 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Difluoropyrrolidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| US10894789B2 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2021-01-19 | Astrazeneca Ab | Halo-substituted piperidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| US11814367B2 (en) | 2021-03-15 | 2023-11-14 | Maze Therapeutics, Inc. | Inhibitors of glycogen synthase 1 (GYS1) and methods of use thereof |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101229603B1 (en) * | 2008-02-12 | 2013-02-04 | 에프. 호프만-라 로슈 아게 | Piperidine sulfonamide derivatives |
| WO2011053522A1 (en) * | 2009-10-29 | 2011-05-05 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Tertiary amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| PT3929196T (en) | 2013-09-24 | 2023-09-11 | Fujifilm Corp | Novel nitrogen-containing compound or salt thereof, or metal complex thereof |
| GB201318222D0 (en) * | 2013-10-15 | 2013-11-27 | Takeda Pharmaceutical | Novel compounds |
| TW201613864A (en) * | 2014-02-20 | 2016-04-16 | Takeda Pharmaceutical | Novel compounds |
| MA44474A (en) | 2015-10-23 | 2019-01-30 | Vifor Int Ag | NEW FERROPORTINE INHIBITORS |
| JOP20180036A1 (en) | 2017-04-18 | 2019-01-30 | Vifor Int Ag | Novel ferroportin-inhibitor salts |
| AU2021267373A1 (en) | 2020-05-06 | 2022-12-08 | Ajax Therapeutics, Inc. | 6-heteroaryloxy benzimidazoles and azabenzimidazoles as JAK2 inhibitors |
| EP4267574A1 (en) | 2020-12-23 | 2023-11-01 | Ajax Therapeutics, Inc. | 6-heteroaryloxy benzimidazoles and azabenzimidazoles as jak2 inhibitors |
| WO2022250108A1 (en) * | 2021-05-26 | 2022-12-01 | 住友ファーマ株式会社 | Phenyl urea derivative |
| JP2024540292A (en) | 2021-11-09 | 2024-10-31 | エイジャックス セラピューティクス, インコーポレイテッド | 6-Heteroaryloxybenzimidazoles and azabenzimidazoles as JAK2 inhibitors |
-
2006
- 2006-05-22 CA CA002609203A patent/CA2609203A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2006-05-22 AU AU2006251590A patent/AU2006251590A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2006-05-22 EP EP06760249A patent/EP1888563A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2006-05-22 WO PCT/US2006/019649 patent/WO2006127550A1/en active Application Filing
- 2006-05-22 US US11/920,596 patent/US20090118200A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2006-05-22 JP JP2008513571A patent/JP2008542276A/en not_active Withdrawn
Non-Patent Citations (2)
| Title |
|---|
| CARCINOGENESIS, vol. 15, no. 11, 1994, pages 2547 - 2552 * |
| DATABASE CAS REISTAD ET AL.: "In vitro formation and degradation of 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (PhlP) protein adducts", XP003003960 * |
Cited By (46)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008008551A2 (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-17 | Merck & Co., Inc. | 2-substituted proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008008551A3 (en) * | 2006-07-14 | 2008-02-28 | Merck & Co Inc | 2-substituted proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008008517A2 (en) | 2006-07-14 | 2008-01-17 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Bridged diazepan orexin receptor antagonists |
| US7951797B2 (en) | 2006-12-01 | 2011-05-31 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Substituted diazepan orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008069997A1 (en) | 2006-12-01 | 2008-06-12 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Substituted diazepan compounds as orexin receptor antagonists |
| EP2392572A1 (en) | 2006-12-01 | 2011-12-07 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Substituted diazepan compounds as orexin receptor antagonists |
| JP2010514713A (en) * | 2006-12-27 | 2010-05-06 | サノフィ−アベンティス | Heteroaryl substituted carboxamides and their use to stimulate the expression of NO synthase |
| WO2008147518A1 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2008-12-04 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Pyridyl piperidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2008150364A1 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2008-12-11 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Cyclopropyl pyrrolidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| US8569311B2 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2013-10-29 | Merch Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Pyridyl piperidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| US8242121B2 (en) | 2007-05-23 | 2012-08-14 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Pyridyl piperidine orexin receptor antagonists |
| JP2010540429A (en) * | 2007-09-24 | 2010-12-24 | アクテリオン ファーマシューティカルズ リミテッド | Pyrrolidines and piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9428487B2 (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2016-08-30 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | Heteroaromatic amides and thioamides as pesticides |
| US20110098287A1 (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2011-04-28 | Bayer Cropscience Ag | Novel Heteroaromatic Amides And Thioamides As Pesticides |
| JP2015205902A (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2015-11-19 | バイエル・クロップサイエンス・アクチェンゲゼルシャフト | Novel hetero-aromatic amide and thioamide as pest-cidal agent |
| JP2014224128A (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2014-12-04 | バイエル・クロップサイエンス・アーゲーBayer Cropscience Ag | Novel heteroaromatic amides and thioamides as pesticides |
| EP2725020A1 (en) * | 2008-06-13 | 2014-04-30 | Bayer CropScience AG | New heteroaromatic amides and thioamides as pest control agents |
| JP2011528016A (en) * | 2008-07-15 | 2011-11-10 | ノバルティス アーゲー | Heteroaryl derivatives as DGAT1 inhibitors |
| US8703761B2 (en) | 2008-07-15 | 2014-04-22 | Novartis Ag | Organic compounds |
| CN102414184A (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2012-04-11 | 埃科特莱茵药品有限公司 | Novel oxazolidinone derivatives and their use as orexin receptor antagonists |
| WO2010131192A3 (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2011-02-03 | Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd | Novel oxazolidinone derivatives and their use as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US8329706B2 (en) | 2009-05-12 | 2012-12-11 | Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd. | Oxazolidinone derivatives |
| KR101727764B1 (en) | 2009-05-12 | 2017-05-02 | 액테리온 파마슈티칼 리미티드 | Novel oxazolidinone derivatives |
| JP2012530137A (en) * | 2009-06-16 | 2012-11-29 | ベーリンガー インゲルハイム インターナショナル ゲゼルシャフト ミット ベシュレンクテル ハフツング | Azetidine 2-carboxamide derivative that modulates CB2 receptor |
| CN103201261A (en) * | 2010-11-10 | 2013-07-10 | 埃科特莱茵药品有限公司 | Lactam derivatives useful as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9085555B2 (en) | 2011-01-04 | 2015-07-21 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9156819B2 (en) | 2011-10-19 | 2015-10-13 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | 2-pyridyloxy-4-nitrile orexin receptor antagonists |
| EP2771346A4 (en) * | 2011-10-25 | 2015-06-03 | Merck Sharp & Dohme | Isoxazolopyridine orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9896452B2 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2018-02-20 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Substituted prolines/piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9499517B2 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2016-11-22 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Substituted prolines / piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9440982B2 (en) | 2012-02-07 | 2016-09-13 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Substituted prolines/piperidines as orexin receptor antagonists |
| US9174977B2 (en) | 2012-03-19 | 2015-11-03 | Rottapharm Biotech S.R.L. | 2-azabicyclo[4.1.0]heptane derivatives as orexin receptor antagonists for the treatment of certain disorders |
| WO2013139730A1 (en) | 2012-03-19 | 2013-09-26 | Rottapharm Spa | Chemical compounds |
| US9468661B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-10-18 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9487483B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-11-08 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9464081B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-10-11 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9815819B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2017-11-14 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9388199B2 (en) | 2012-06-28 | 2016-07-12 | Novartis Ag | Pyrrolidine derivatives and their use as complement pathway modulators |
| US9550755B2 (en) | 2012-07-12 | 2017-01-24 | Novartis Ag | Complement pathway modulators and uses thereof |
| US9505749B2 (en) | 2012-08-29 | 2016-11-29 | Amgen Inc. | Quinazolinone compounds and derivatives thereof |
| US10221170B2 (en) | 2014-08-13 | 2019-03-05 | Eolas Therapeutics, Inc. | Difluoropyrrolidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| US10894789B2 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2021-01-19 | Astrazeneca Ab | Halo-substituted piperidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| US11434236B2 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2022-09-06 | Astrazeneca Ab | Halo-substituted piperidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| US12084437B2 (en) | 2016-02-12 | 2024-09-10 | Astrazeneca Ab | Halo-substituted piperidines as orexin receptor modulators |
| WO2017194548A1 (en) | 2016-05-10 | 2017-11-16 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases |
| US11814367B2 (en) | 2021-03-15 | 2023-11-14 | Maze Therapeutics, Inc. | Inhibitors of glycogen synthase 1 (GYS1) and methods of use thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1888563A1 (en) | 2008-02-20 |
| JP2008542276A (en) | 2008-11-27 |
| CA2609203A1 (en) | 2006-11-30 |
| AU2006251590A1 (en) | 2006-11-30 |
| US20090118200A1 (en) | 2009-05-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2001485B1 (en) | Diazepan orexin receptor antagonists | |
| US8669272B2 (en) | 2,5-disubstituted piperidine orexin receptor antagonists | |
| EP2150115B1 (en) | Cyclopropyl pyrrolidine orexin receptor antagonists | |
| US8710076B2 (en) | 2,5-disubstituted piperidine orexin receptor antagonists | |
| AU2007272855B2 (en) | Substituted diazepan orexin receptor antagonists | |
| US20090118200A1 (en) | Proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists | |
| US20100029736A1 (en) | 2-substituted proline bis-amide orexin receptor antagonists | |
| EP1922071A2 (en) | Diazaspirodecane orexin receptor antagonists | |
| CA2739927A1 (en) | Disubstituted azepan orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2007126934A2 (en) | Amidoethylthioether orexin receptor antagonists | |
| EP2349270A1 (en) | 2,5-disubstituted morpholine orexin receptor antagonists | |
| EP1871752A1 (en) | Amidopropoxyphenyl orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2007061763A2 (en) | Indole orexin receptor antagonists | |
| CA2687321A1 (en) | Pyridyl piperidine orexin receptor antagonists | |
| CA2679817A1 (en) | Bipyridine carboxamide orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2016065586A1 (en) | Pyrazole, triazole and tetrazole orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2016069515A1 (en) | Oxazole orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2007019234A2 (en) | Aminoethane sulfonamide orexin receptor antagonists | |
| WO2009011775A1 (en) | Amidoethyl alkylamino orexin receptor antagonists |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2006251590 Country of ref document: AU |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 11920596 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2609203 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2006760249 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2008513571 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2006251590 Country of ref document: AU Date of ref document: 20060522 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: RU |