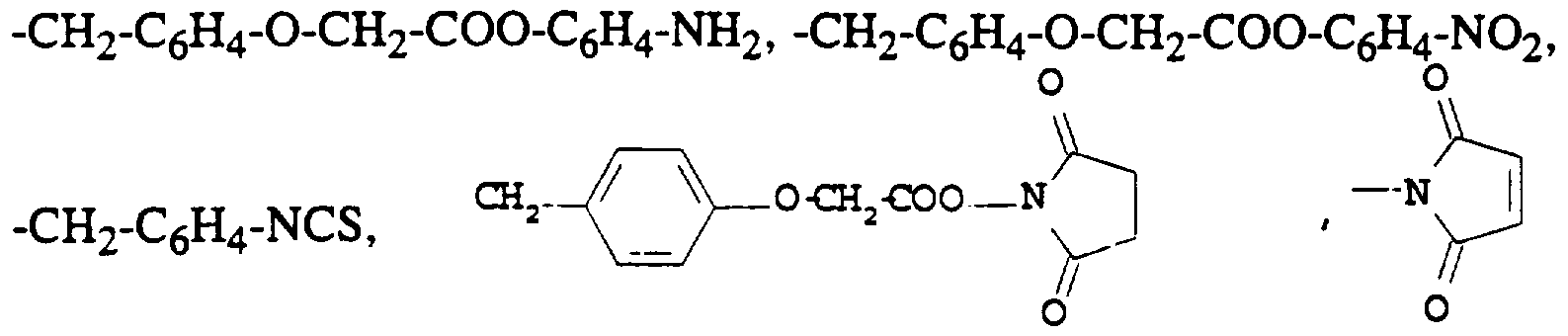WO1996002500A1 - Technetium-sulfonamid-komplexe, deren verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische mittel, sowie verfahren zur herstellung der komplexe und mittel - Google Patents
Technetium-sulfonamid-komplexe, deren verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische mittel, sowie verfahren zur herstellung der komplexe und mittel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO1996002500A1 WO1996002500A1 PCT/EP1995/002404 EP9502404W WO9602500A1 WO 1996002500 A1 WO1996002500 A1 WO 1996002500A1 EP 9502404 W EP9502404 W EP 9502404W WO 9602500 A1 WO9602500 A1 WO 9602500A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- mmol
- group
- yield
- solution
- found
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 12
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 title claims abstract description 7
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 title abstract description 10
- 239000008177 pharmaceutical agent Substances 0.000 title abstract 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 88
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000003745 diagnosis Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 259
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 245
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 212
- -1 Imino, phenylene, phenyleneoxy, phenylenamino, amide Chemical class 0.000 claims description 102
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 claims description 31
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000008139 complexing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 26
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 24
- 229910021645 metal ion Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 24
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 20
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000003446 ligand Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 16
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 claims description 14
- 230000002285 radioactive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052713 technetium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 claims description 9
- GKLVYJBZJHMRIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N technetium atom Chemical compound [Tc] GKLVYJBZJHMRIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000000350 glycoloyl group Chemical group O=C([*])C([H])([H])O[H] 0.000 claims description 8
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 8
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M thiocyanate group Chemical group [S-]C#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 7
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 6
- 150000004696 coordination complex Chemical group 0.000 claims description 6
- 102000040430 polynucleotide Human genes 0.000 claims description 6
- 108091033319 polynucleotide Proteins 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002157 polynucleotide Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen thiocyanate Natural products SC#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 125000000449 nitro group Chemical group [O-][N+](*)=O 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000003431 steroids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical group [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- KZBUYRJDOAKODT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine Chemical compound ClCl KZBUYRJDOAKODT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N [C]1=CC=CC=C1 Chemical class [C]1=CC=CC=C1 CIUQDSCDWFSTQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000003638 chemical reducing agent Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000000956 methoxy group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])O* 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 claims description 4
- MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dioxygen Chemical compound O=O MYMOFIZGZYHOMD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical compound [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Trifluoroacetate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001951 carbamoylamino group Chemical group C(N)(=O)N* 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000002843 carboxylic acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000004185 ester group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 3
- AEOCXXJPGCBFJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethionamide Chemical compound CCC1=CC(C(N)=S)=CC=N1 AEOCXXJPGCBFJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000001959 radiotherapy Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011593 sulfur Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 claims description 2
- PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Maleimide Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C=C1 PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VEQOALNAAJBPNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N antipyrine Chemical class CN1C(C)=CC(=O)N1C1=CC=CC=C1 VEQOALNAAJBPNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000012736 aqueous medium Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000003236 benzoyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C(*)=O 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000001447 alkali salts Chemical class 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 abstract description 12
- 102000004196 processed proteins & peptides Human genes 0.000 abstract description 6
- 238000002560 therapeutic procedure Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 125000000565 sulfonamide group Chemical group 0.000 abstract description 2
- 239000013522 chelant Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 261
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 150
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 109
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 104
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 86
- HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroform Chemical compound ClC(Cl)Cl HEDRZPFGACZZDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 78
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 78
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 73
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 57
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 50
- CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L Magnesium sulfate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-][S+2]([O-])([O-])[O-] CSNNHWWHGAXBCP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 49
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 48
- 239000000741 silica gel Substances 0.000 description 48
- 229910002027 silica gel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 48
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 47
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 46
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 42
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 40
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical compound CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 34
- 239000012074 organic phase Substances 0.000 description 33
- 235000019439 ethyl acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 32
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 32
- DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Trifluoroacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(F)(F)F DTQVDTLACAAQTR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 27
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 26
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 25
- CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetone Chemical compound CC(C)=O CSCPPACGZOOCGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- 229910052943 magnesium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 24
- 235000019341 magnesium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 24
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 22
- VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-Hexane Chemical compound CCCCCC VLKZOEOYAKHREP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylenediamine Chemical compound NCCN PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 20
- 239000000706 filtrate Substances 0.000 description 20
- 125000000022 2-aminoethyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])[H] 0.000 description 19
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 18
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 18
- 150000001408 amides Chemical class 0.000 description 16
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 16
- FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium chloride Chemical compound [Na+].[Cl-] FAPWRFPIFSIZLT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 15
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 15
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000002372 labelling Methods 0.000 description 14
- BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L potassium carbonate Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-]C([O-])=O BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 14
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 14
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-Dimethylaminopyridine Chemical compound CN(C)C1=CC=NC=C1 VHYFNPMBLIVWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Toluene Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1 YXFVVABEGXRONW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N citric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)(C(O)=O)CC(O)=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 12
- 239000002738 chelating agent Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 11
- RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,4-Dioxane Chemical compound C1COCCO1 RYHBNJHYFVUHQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicylcohexylcarbodiimide Chemical compound C1CCCCC1N=C=NC1CCCCC1 QOSSAOTZNIDXMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- GKLVYJBZJHMRIY-OUBTZVSYSA-N Technetium-99 Chemical compound [99Tc] GKLVYJBZJHMRIY-OUBTZVSYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 229960002449 glycine Drugs 0.000 description 10
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000008363 phosphate buffer Substances 0.000 description 10
- DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butoxycarbonyl anhydride Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)OC(=O)OC(C)(C)C DYHSDKLCOJIUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- HDECRAPHCDXMIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylbenzenesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1S(Cl)(=O)=O HDECRAPHCDXMIJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- VGCXGMAHQTYDJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chloroacetyl chloride Chemical compound ClCC(Cl)=O VGCXGMAHQTYDJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 9
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 9
- 239000012217 radiopharmaceutical Substances 0.000 description 9
- 229940121896 radiopharmaceutical Drugs 0.000 description 9
- 230000002799 radiopharmaceutical effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- AHTFMWCHTGEJHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N s-(2,5-dioxooxolan-3-yl) ethanethioate Chemical compound CC(=O)SC1CC(=O)OC1=O AHTFMWCHTGEJHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 229910000029 sodium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 9
- 229940056501 technetium 99m Drugs 0.000 description 9
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M D-gluconate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M 0.000 description 7
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 7
- MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N anhydrous diethylene glycol Natural products OCCOCCO MTHSVFCYNBDYFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 7
- 229940050410 gluconate Drugs 0.000 description 7
- 229910000027 potassium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 7
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 229910021626 Tin(II) chloride Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 235000004279 alanine Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 238000007098 aminolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 6
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N cholesterol Chemical compound C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-DPAQBDIFSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 description 6
- MWZPENIJLUWBSY-VIFPVBQESA-N methyl L-tyrosinate Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 MWZPENIJLUWBSY-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 6
- KQSSATDQUYCRGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl glycinate Chemical compound COC(=O)CN KQSSATDQUYCRGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 235000011150 stannous chloride Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 125000005931 tert-butyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(OC(*)=O)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 6
- ZWZVWGITAAIFPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N thiophosgene Chemical compound ClC(Cl)=S ZWZVWGITAAIFPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- AXZWODMDQAVCJE-UHFFFAOYSA-L tin(II) chloride (anhydrous) Chemical compound [Cl-].[Cl-].[Sn+2] AXZWODMDQAVCJE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 6
- 125000003143 4-hydroxybenzyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C(O[H])C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 5
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 5
- NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-Hydroxysuccinimide Chemical compound ON1C(=O)CCC1=O NQTADLQHYWFPDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- UIJGNTRUPZPVNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzenecarbothioic s-acid Chemical compound SC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 UIJGNTRUPZPVNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 5
- ADFXKUOMJKEIND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-dicyclohexylurea Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC(=O)NC1CCCCC1 ADFXKUOMJKEIND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dihydrogen disulfide Chemical compound SS BWGNESOTFCXPMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229960000583 acetic acid Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 4
- RDOXTESZEPMUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N anisole Chemical compound COC1=CC=CC=C1 RDOXTESZEPMUJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000012230 colorless oil Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- OOTFVKOQINZBBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cystamine Chemical compound CCSSCCN OOTFVKOQINZBBF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229940099500 cystamine Drugs 0.000 description 4
- 238000003818 flash chromatography Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000012362 glacial acetic acid Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000004677 hydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 4
- 150000004702 methyl esters Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910052702 rhenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhenium atom Chemical compound [Re] WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000001509 sodium citrate Substances 0.000 description 4
- HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K trisodium citrate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[Na+].[O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 4
- 229940038773 trisodium citrate Drugs 0.000 description 4
- VJRWULUDVUWCCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzoylsulfanylacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CSC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 VJRWULUDVUWCCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KLDLRDSRCMJKGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-[chloro-(2-oxo-1,3-oxazolidin-3-yl)phosphoryl]-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one Chemical compound C1COC(=O)N1P(=O)(Cl)N1CCOC1=O KLDLRDSRCMJKGM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- OEDJQRXNDRUGEU-SRVKXCTJSA-N Asp-Leu-His Chemical compound N[C@@H](CC(O)=O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CNC=N1)C(=O)O OEDJQRXNDRUGEU-SRVKXCTJSA-N 0.000 description 3
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethylene glycol Chemical compound OCCO LYCAIKOWRPUZTN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycine Natural products NCC(O)=O DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- PQFMNVGMJJMLAE-QMMMGPOBSA-N L-tyrosinamide Chemical compound NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 PQFMNVGMJJMLAE-QMMMGPOBSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 3
- 101100208721 Mus musculus Usp5 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- WFUWMDOCVRUDPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-(2-aminoethyl)-2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-ylmethylsulfanyl)acetamide Chemical compound C1OC2=C(O1)C=C(C=C2)CSCC(=O)NCCN WFUWMDOCVRUDPJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Potassium Chemical compound [K] ZLMJMSJWJFRBEC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YQVFPYAOCQOJGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N S-[2-(2-aminoethylamino)-2-oxoethyl] benzenecarbothioate Chemical compound C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)SCC(=O)NCCN YQVFPYAOCQOJGG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000012300 argon atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000037396 body weight Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000004744 butyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 235000012000 cholesterol Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000011097 chromatography purification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000536 complexating effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000037406 food intake Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 3
- DWKPPFQULDPWHX-VKHMYHEASA-N l-alanyl ester Chemical compound COC(=O)[C@H](C)N DWKPPFQULDPWHX-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 3
- ZGEGCLOFRBLKSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N methylene hexane Natural products CCCCCC=C ZGEGCLOFRBLKSE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 210000000056 organ Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenol group Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=C1)O ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000011591 potassium Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052700 potassium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 3
- KOUKXHPPRFNWPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrazine-2,5-dicarboxylic acid;hydrate Chemical compound O.OC(=O)C1=CN=C(C(O)=O)C=N1 KOUKXHPPRFNWPP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910000030 sodium bicarbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000003381 stabilizer Substances 0.000 description 3
- KZNICNPSHKQLFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N succinimide Chemical compound O=C1CCC(=O)N1 KZNICNPSHKQLFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229940124530 sulfonamide Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 3
- OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N tyrosine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 OUYCCCASQSFEME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- ANOOTOPTCJRUPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-iodohexane Chemical compound CCCCCCI ANOOTOPTCJRUPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BTJIUGUIPKRLHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-nitrophenol Chemical class OC1=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C1 BTJIUGUIPKRLHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YYROPELSRYBVMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-toluenesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(Cl)(=O)=O)C=C1 YYROPELSRYBVMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonia Chemical compound N QGZKDVFQNNGYKY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- BMTAFVWTTFSTOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylate Chemical compound CCSC(=O)N(CC(C)C)CC(C)C BMTAFVWTTFSTOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WCYPEANLNHLKEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(C(N)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CC)=O Chemical compound COC(C(N)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CC)=O WCYPEANLNHLKEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ANRSPZPXKYMMOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N COC(C(N)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CCCCCCCC)=O Chemical compound COC(C(N)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CCCCCCCC)=O ANRSPZPXKYMMOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004471 Glycine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 241000562429 Jamides Species 0.000 description 2
- BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methyl tert-butyl ether Chemical compound COC(C)(C)C BZLVMXJERCGZMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- IBIJSOUBYFMKST-UHFFFAOYSA-N S-[2-(2-aminoethylamino)-2-oxoethyl] ethanethioate Chemical compound CC(=O)SCC(=O)NCCN IBIJSOUBYFMKST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Sulfate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]S([O-])(=O)=O PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical class [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Urea Chemical compound NC(N)=O XSQUKJJJFZCRTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 150000001351 alkyl iodides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- JHVLLYQQQYIWKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl 2-bromoacetate Chemical compound BrCC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 JHVLLYQQQYIWKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- HSDAJNMJOMSNEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl chloroformate Chemical compound ClC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 HSDAJNMJOMSNEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000001584 benzyloxycarbonyl group Chemical group C(=O)(OCC1=CC=CC=C1)* 0.000 description 2
- 230000001588 bifunctional effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 description 2
- OVIISSOUXFJLSM-KPNWGBFJSA-N butanedioic acid;(3s,8s,9s,10r,13r,14s,17r)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2r)-6-methylheptan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1h-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC(O)=O.C1C=C2C[C@@H](O)CC[C@]2(C)[C@@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H]1CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)[C@@]1(C)CC2 OVIISSOUXFJLSM-KPNWGBFJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009918 complex formation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010668 complexation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- UKJLNMAFNRKWGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexatrienamine Chemical group NC1=CC=C=C[CH]1 UKJLNMAFNRKWGR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001914 filtration Methods 0.000 description 2
- NGAZZOYFWWSOGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N heptan-3-one Chemical compound CCCCC(=O)CC NGAZZOYFWWSOGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001990 intravenous administration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- ZBKFYXZXZJPWNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N isothiocyanate group Chemical group [N-]=C=S ZBKFYXZXZJPWNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 2
- UZKWTJUDCOPSNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N methoxybenzene Substances CCCCOC=C UZKWTJUDCOPSNM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000009206 nuclear medicine Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000000636 p-nitrophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(=C([H])C([H])=C1*)[N+]([O-])=O 0.000 description 2
- 230000001575 pathological effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 2
- NMHMNPHRMNGLLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N phloretic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 NMHMNPHRMNGLLB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000021317 phosphate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium benzoate Chemical compound [K+].[O-]C(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 XAEFZNCEHLXOMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N potassium tert-butoxide Chemical compound [K+].CC(C)(C)[O-] LPNYRYFBWFDTMA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000001556 precipitation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 2
- WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-IGMARMGPSA-N rhenium-186 Chemical compound [186Re] WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-IGMARMGPSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011780 sodium chloride Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052938 sodium sulfate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 235000011152 sodium sulphate Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000007790 solid phase Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003456 sulfonamides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- BNWCETAHAJSBFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl 2-bromoacetate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)CBr BNWCETAHAJSBFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrachloromethane Chemical compound ClC(Cl)(Cl)Cl VZGDMQKNWNREIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylphosphine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LJCWRJYVPJJTMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) 2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]acetate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NCC(=O)ON1C(=O)CCC1=O LJCWRJYVPJJTMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IKVJXWPRHDLPIA-INIZCTEOSA-N (2S)-2-[benzylsulfonyloxy(carboxymethyl)amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid Chemical compound C(C1=CC=CC=C1)S(=O)(=O)ON([C@@H](CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)C(=O)O)CC(=O)O IKVJXWPRHDLPIA-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BQHFYSWNHZMMDO-WDSKDSINSA-N (2r)-2-[2-[[(1r)-1-carboxy-2-sulfanylethyl]amino]ethylamino]-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](CS)NCCN[C@@H](CS)C(O)=O BQHFYSWNHZMMDO-WDSKDSINSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YGFLNRUFVZPRST-VIFPVBQESA-N (2s)-2-amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-n-methylsulfonylpropanamide Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)NC(=O)[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1 YGFLNRUFVZPRST-VIFPVBQESA-N 0.000 description 1
- JEJLGIQLPYYGEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,2-dipalmitoylglycerol Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(CO)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC JEJLGIQLPYYGEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AWNXKZVIZARMME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[[5-[2-[(2-chloropyridin-4-yl)amino]pyrimidin-4-yl]-4-(cyclopropylmethyl)pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]-2-methylpropan-2-ol Chemical compound N=1C(NCC(C)(O)C)=NC=C(C=2N=C(NC=3C=C(Cl)N=CC=3)N=CC=2)C=1CC1CC1 AWNXKZVIZARMME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XDFZUXHZXUFQOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chloro-2-(2-chloroethyldisulfanyl)ethane Chemical compound ClCCSSCCCl XDFZUXHZXUFQOS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GCDPERPXPREHJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-iodododecane Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCI GCDPERPXPREHJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BSOYWTITVKXHLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-phenylmethoxycarbonyl-2,3-dihydroindole-2-carboxylic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1CC2=CC=CC=C2N1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 BSOYWTITVKXHLM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBNGYFFABRKICK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,3,4,5,6-pentafluorophenol Chemical compound OC1=C(F)C(F)=C(F)C(F)=C1F XBNGYFFABRKICK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JYWKEVKEKOTYEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,6-dibromo-4-chloroiminocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one Chemical compound ClN=C1C=C(Br)C(=O)C(Br)=C1 JYWKEVKEKOTYEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QHQZEEGNGSZBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(aminomethyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)propane-1,3-diol Chemical compound NCC(CO)(CO)CO QHQZEEGNGSZBOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DLLMHEDYJQACRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(carboxymethyldisulfanyl)acetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CSSCC(O)=O DLLMHEDYJQACRM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VRPJIFMKZZEXLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxycarbonylamino]acetic acid Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)NCC(O)=O VRPJIFMKZZEXLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[2,4-di(pentan-2-yl)phenoxy]acetyl chloride Chemical compound CCCC(C)C1=CC=C(OCC(Cl)=O)C(C(C)CCC)=C1 NGNBDVOYPDDBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AIYSZVYTSYFSED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[4-[3-[2-(2-chloroethylamino)ethylamino]-2-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylamino]propyl]phenoxy]acetic acid Chemical compound ClCCNCCNCC(NS(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C)C=C1)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC(=O)O AIYSZVYTSYFSED-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YESGREFKORFTDE-IBGZPJMESA-N 2-[benzylsulfonyloxy-[(2S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-oxo-1-[2-[(2-sulfanylacetyl)amino]ethylamino]propan-2-yl]amino]acetic acid Chemical compound SCC(=O)NCCNC([C@@H](N(OS(=O)(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1)CC(=O)O)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)=O YESGREFKORFTDE-IBGZPJMESA-N 0.000 description 1
- PLVJDOHPOBQTSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-amino-N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-dodecan-4-yloxy-3-phenylpropanamide Chemical compound NCCNC(C(N)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CCCCCCCC)=O PLVJDOHPOBQTSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WPHUUIODWRNJLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound [O-][N+](=O)C1=CC=CC=C1S(Cl)(=O)=O WPHUUIODWRNJLO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZAGWQJWRWKULDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3,3,3-trifluoropropanethioic s-acid Chemical compound OC(=S)CC(F)(F)F ZAGWQJWRWKULDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-cholesterol Natural products C1C=C2CC(O)CCC2(C)C2C1C1CCC(C(C)CCCC(C)C)C1(C)CC2 HVYWMOMLDIMFJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JWMFYGXQPXQEEM-NUNROCCHSA-N 5β-pregnane Chemical compound C([C@H]1CC2)CCC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H](CC)[C@@]2(C)CC1 JWMFYGXQPXQEEM-NUNROCCHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PZASAAIJIFDWSB-CKPDSHCKSA-N 8-[(1S)-1-[8-(trifluoromethyl)-7-[4-(trifluoromethyl)cyclohexyl]oxynaphthalen-2-yl]ethyl]-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-3-carboxylic acid Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C=1C2=CC([C@@H](N3C4CCC3CC(C4)C(O)=O)C)=CC=C2C=CC=1OC1CCC(C(F)(F)F)CC1 PZASAAIJIFDWSB-CKPDSHCKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bicarbonate Chemical compound OC([O-])=O BVKZGUZCCUSVTD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- QJQDEALMHVUOJI-JTQLQIEISA-N C(=O)=CN[C@@H](CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)C(=O)O Chemical compound C(=O)=CN[C@@H](CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)C(=O)O QJQDEALMHVUOJI-JTQLQIEISA-N 0.000 description 1
- IXIKZPZCDLLVJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)SCC(=O)NCCNC(=O)CN Chemical compound C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)SCC(=O)NCCNC(=O)CN IXIKZPZCDLLVJW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RISPLBFGEFZFER-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC(C(=O)O)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CCCCCCCC Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)NC(C(=O)O)C(C1=CC=CC=C1)OC(CCC)CCCCCCCC RISPLBFGEFZFER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HFBANUSWIBDLTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N CS(=O)(=O)NC(CC1=CC=C(OCC(O)=O)C=C1)C(=O)NCCNC(=O)CCl Chemical compound CS(=O)(=O)NC(CC1=CC=C(OCC(O)=O)C=C1)C(=O)NCCNC(=O)CCl HFBANUSWIBDLTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JZCKXWVFOLYLJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ClCC(NCC(NS(=O)(=O)C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC1=CC=CC=C1)=O Chemical compound ClCC(NCC(NS(=O)(=O)C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)OCC1=CC=CC=C1)=O JZCKXWVFOLYLJE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000610640 Homo sapiens U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Prp3 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrazine Chemical compound NN OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Malonic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC(O)=O OFOBLEOULBTSOW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorous acid Chemical class OP(O)=O ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CNJHMIIVBJFYFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N S-[2-[2-[[2-[(3-aminophenyl)sulfonylamino]acetyl]amino]ethylamino]-2-oxoethyl] benzenecarbothioate Chemical compound C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)SCC(=O)NCCNC(=O)CNS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=CC(=C2)N CNJHMIIVBJFYFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101001110823 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) 60S ribosomal protein L6-A Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101000712176 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) 60S ribosomal protein L6-B Proteins 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102100040374 U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein Prp3 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229910052770 Uranium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000005856 abnormality Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021529 ammonia Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003098 androgen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940030486 androgens Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000427 antigen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 102000036639 antigens Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108091007433 antigens Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012062 aqueous buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001558 benzoic acid derivatives Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000012620 biological material Substances 0.000 description 1
- JCXGWMGPZLAOME-AKLPVKDBSA-N bismuth-212 Chemical compound [212Bi] JCXGWMGPZLAOME-AKLPVKDBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004202 carbamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- VXIVSQZSERGHQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N chloroacetamide Chemical compound NC(=O)CCl VXIVSQZSERGHQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940107161 cholesterol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000001841 cholesterols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-OELDTZBJSA-N cholic acid Chemical class C([C@H]1C[C@H]2O)[C@H](O)CC[C@]1(C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]2[C@@H]2CC[C@H]([C@@H](CCC(O)=O)C)[C@@]2(C)[C@@H](O)C1 BHQCQFFYRZLCQQ-OELDTZBJSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002812 cholic acid derivative Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000356 contaminant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007819 coupling partner Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000032 diagnostic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940039227 diagnostic agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- FHHZOYXKOICLGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichloromethane;ethanol Chemical compound CCO.ClCCl FHHZOYXKOICLGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SPWVRYZQLGQKGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichloromethane;hexane Chemical compound ClCCl.CCCCCC SPWVRYZQLGQKGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WGLUMOCWFMKWIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichloromethane;methanol Chemical compound OC.ClCCl WGLUMOCWFMKWIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FDSGHYHRLSWSLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N dichloromethane;propan-2-one Chemical compound ClCCl.CC(C)=O FDSGHYHRLSWSLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TWXWPPKDQOWNSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N dicyclohexylmethanone Chemical group C1CCCCC1C(=O)C1CCCCC1 TWXWPPKDQOWNSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003792 electrolyte Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003480 eluent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940011871 estrogen Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000262 estrogen Substances 0.000 description 1
- HWJHWSBFPPPIPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethoxyethane;propan-2-one Chemical compound CC(C)=O.CCOCC HWJHWSBFPPPIPD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005448 ethoxyethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 238000001704 evaporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008020 evaporation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000029142 excretion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005755 formation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 1
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N glycerol Substances OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003102 growth factor Substances 0.000 description 1
- ARBOVOVUTSQWSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexadecanoyl chloride Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(Cl)=O ARBOVOVUTSQWSS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940088597 hormone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000005556 hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004356 hydroxy functional group Chemical group O* 0.000 description 1
- 238000011503 in vivo imaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013067 intermediate product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001361 intraarterial administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002601 intratumoral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodomethane Chemical compound IC INQOMBQAUSQDDS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WABPQHHGFIMREM-BKFZFHPZSA-N lead-212 Chemical compound [212Pb] WABPQHHGFIMREM-BKFZFHPZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanesulfonyl chloride Chemical compound CS(Cl)(=O)=O QARBMVPHQWIHKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- AZXDUPQUGNUREG-JTQLQIEISA-N methyl (2S)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(methanesulfonamido)propanoate Chemical compound COC([C@@H](NS(=O)(=O)C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)=O AZXDUPQUGNUREG-JTQLQIEISA-N 0.000 description 1
- SLLMDHBKALJDBW-INIZCTEOSA-N methyl (2s)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)propanoate Chemical compound C([C@@H](C(=O)OC)NC(=O)OCC=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 SLLMDHBKALJDBW-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UXZGXNVSAQZJTL-INIZCTEOSA-N methyl (2s)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylamino]propanoate Chemical compound C([C@@H](C(=O)OC)NS(=O)(=O)C=1C=CC(C)=CC=1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1 UXZGXNVSAQZJTL-INIZCTEOSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000896 monocarboxylic acid group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- NWKYZYGOSPOKDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N n,n-dimethylformamide;pyridine Chemical compound CN(C)C=O.C1=CC=NC=C1 NWKYZYGOSPOKDY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000002829 nitrogen Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen Substances N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000957 no side effect Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-AKLPVKDBSA-N palladium-109 Chemical compound [109Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-AKLPVKDBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 231100000915 pathological change Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000036285 pathological change Effects 0.000 description 1
- IZUPBVBPLAPZRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentachloro-phenol Natural products OC1=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C1Cl IZUPBVBPLAPZRR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003013 phosphoric acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002504 physiological saline solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004540 pour-on Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000583 progesterone congener Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhodium atom Chemical compound [Rh] MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002603 single-photon emission computed tomography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- RBBWNXJFTBCLKT-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;ethanethioate Chemical compound [Na+].CC([S-])=O RBBWNXJFTBCLKT-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 239000008223 sterile water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003270 steroid hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960002317 succinimide Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003573 thiols Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- HPGGPRDJHPYFRM-UHFFFAOYSA-J tin(iv) chloride Chemical compound Cl[Sn](Cl)(Cl)Cl HPGGPRDJHPYFRM-UHFFFAOYSA-J 0.000 description 1
- 238000003325 tomography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007070 tosylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940055764 triaz Drugs 0.000 description 1
- YSCVYRUCAPMZFG-UHFFFAOYSA-K trichlorotin Chemical compound Cl[Sn](Cl)Cl YSCVYRUCAPMZFG-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000281 trometamol Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003313 weakening effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010626 work up procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C327/00—Thiocarboxylic acids
- C07C327/20—Esters of monothiocarboxylic acids
- C07C327/32—Esters of monothiocarboxylic acids having sulfur atoms of esterified thiocarboxyl groups bound to carbon atoms of hydrocarbon radicals substituted by carboxyl groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C331/00—Derivatives of thiocyanic acid or of isothiocyanic acid
- C07C331/16—Isothiocyanates
- C07C331/28—Isothiocyanates having isothiocyanate groups bound to carbon atoms of six-membered aromatic rings
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
- A61K51/0474—Organic compounds complexes or complex-forming compounds, i.e. wherein a radioactive metal (e.g. 111In3+) is complexed or chelated by, e.g. a N2S2, N3S, NS3, N4 chelating group
- A61K51/0478—Organic compounds complexes or complex-forming compounds, i.e. wherein a radioactive metal (e.g. 111In3+) is complexed or chelated by, e.g. a N2S2, N3S, NS3, N4 chelating group complexes from non-cyclic ligands, e.g. EDTA, MAG3
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K51/00—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo
- A61K51/02—Preparations containing radioactive substances for use in therapy or testing in vivo characterised by the carrier, i.e. characterised by the agent or material covalently linked or complexing the radioactive nucleus
- A61K51/04—Organic compounds
- A61K51/08—Peptides, e.g. proteins, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins
- A61K51/088—Peptides, e.g. proteins, carriers being peptides, polyamino acids, proteins conjugates with carriers being peptides, polyamino acids or proteins
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C323/00—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups
- C07C323/50—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton
- C07C323/51—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton
- C07C323/60—Thiols, sulfides, hydropolysulfides or polysulfides substituted by halogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms, or by sulfur atoms not being part of thio groups containing thio groups and carboxyl groups bound to the same carbon skeleton having the sulfur atoms of the thio groups bound to acyclic carbon atoms of the carbon skeleton with the carbon atom of at least one of the carboxyl groups bound to nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07F—ACYCLIC, CARBOCYCLIC OR HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING ELEMENTS OTHER THAN CARBON, HYDROGEN, HALOGEN, OXYGEN, NITROGEN, SULFUR, SELENIUM OR TELLURIUM
- C07F13/00—Compounds containing elements of Groups 7 or 17 of the Periodic Table
- C07F13/005—Compounds without a metal-carbon linkage
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J31/00—Normal steroids containing one or more sulfur atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
- C07J31/006—Normal steroids containing one or more sulfur atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J31/003
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
- C07J41/0033—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005
- C07J41/0055—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005 the 17-beta position being substituted by an uninterrupted chain of at least three carbon atoms which may or may not be branched, e.g. cholane or cholestane derivatives, optionally cyclised, e.g. 17-beta-phenyl or 17-beta-furyl derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J51/00—Normal steroids with unmodified cyclopenta(a)hydrophenanthrene skeleton not provided for in groups C07J1/00 - C07J43/00
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J9/00—Normal steroids containing carbon, hydrogen, halogen or oxygen substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of more than two carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, coprostane
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K7/00—Peptides having 5 to 20 amino acids in a fully defined sequence; Derivatives thereof
- C07K7/04—Linear peptides containing only normal peptide links
- C07K7/06—Linear peptides containing only normal peptide links having 5 to 11 amino acids
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2121/00—Preparations for use in therapy
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K2123/00—Preparations for testing in vivo
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K38/00—Medicinal preparations containing peptides
Definitions
- the invention relates to the subject matter characterized in the claims, that is to say new chelating agents containing sulfonamide groups, their metal complexes, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds, their use in radiodiagnostics and radiotherapy, methods for producing these compounds and compositions, and conjugates of these compounds with them in diseased tissue selectively enriching substances, especially peptides.
- radiopharmaceuticals for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes has long been known in the field of biological and medical research.
- radiopharmaceuticals are used to represent certain structures such as the skeleton, organs or tissues.
- the diagnostic application presupposes the use of such radioactive agents that, after application, accumulate specifically in the structures in the patient that are to be examined. These locally accumulating radioactive agents can then be tracked down, plotted or scintigraphed using suitable detectors, such as scintillation cameras or other suitable recording methods.
- suitable detectors such as scintillation cameras or other suitable recording methods.
- the distribution and relative intensity of the detected radioactive agent characterizes the location of a structure in which the radioactive agent is located and can represent the presence of abnormalities in structure and function, pathological changes etc.
- radiopharmaceuticals can be used as therapeutic agents to irradiate certain pathological tissues or areas.
- Such treatment requires the production of radioactive therapeutic agents that accumulate in certain structures, tissues or organs. By enriching these agents, the therapeutic radiation is carried directly to the pathological tissue.
- metallic radionuclides are used as diagnostics or therapeutic agents, it being possible for the metal to be present in free form, as an ion or in the form of a metal complex.
- Technetium-99m and various rhenium isotopes are examples of metallic radionuclides that can form complexes.
- the former is used in diagnostics, the latter in therapy.
- radiopharmaceuticals In addition to the metal (complex), radiopharmaceuticals generally also contain suitable carriers and additives which permit injection, inhalation or ingestion by the patient, such as physiological buffers, salts, etc.
- suitable carriers and additives which permit injection, inhalation or ingestion by the patient, such as physiological buffers, salts, etc.
- the most frequently used radionuclide for nuclear medicine questions is technetium-99m, which due to its favorable physical properties (no corpuscular radiation, 6 h physical half-life, 140 KeV gamma radiation) and the resulting low radiation exposure is particularly suitable as a radioisotope for in vivo Diagnostics are suitable.
- Technetium-99m can be easily obtained from nuclide generators as pertechnetate and can be used directly in this form for the production of kits for routine clinical needs.
- the production of radiopharmaceuticals first requires the synthesis of a suitable ligand.
- the complex is then produced in the clinic immediately before use from the respective complexing agent (hereinafter also referred to as ligand or chelator) and the desired radionuclide (labeling).
- the complexing agent which is always in the form of a lyophilized kit, is reacted with a solution containing the radionuclide under complexing conditions.
- the ligand produced is mixed with a pertechnetate solution with the addition of a suitable reducing agent and the corresponding technetium complex is produced under suitable reaction conditions.
- the solution containing the radionuclide can, as in the case of technetium-99m, be obtained from a commercially available Mo-99 / Tc-99m nuclide generator or, as in the case of rhenium-186, can be obtained directly from a manufacturer.
- the complex formation reaction is carried out under suitable temperatures (for example 20 ° -100 ° C.) within a few minutes to several hours. To ensure complete complex formation, a large excess (more than 100-fold excess) of the ligand produced and an amount of reducing agent (for example SnCl 2 , S 2 O 4 etc.) sufficient for a complete reduction of the radionuclide used are required.
- technetium can exist in a number of oxidation states (+7 to -1) that can change the pharmacological properties by changing the charge of a complex, it is necessary to provide chelators that can stably bind technetium in a defined oxidation state in order to prevent an in vivo redox processes or technetium releases from the corresponding radio diagnostics Biodistribution takes place, which complicates the safe diagnosis of corresponding diseases.
- radionuclides in in vivo diagnostics as well as therapy depends on the specificity and the selectivity of the labeled chelates to the target cell. These properties can be improved by coupling the chelates to biomolecules according to the "drug targeting" principle. Antibodies, their fragments, hormones, growth factors and substrates of receptors and enzymes are suitable biomolecules.
- the British patent application GB 2,109,407 describes the use of radioactively labeled monoclonal antibodies against tumor-associated antigens for tumor diagnosis in vivo.
- direct protein labels via donor groups (amino, amide, thiol, etc.) of the protein (Rhodes, BA et al., J. Nukl. Med. 1986, 27, 685-693) or by introducing complexing agents (US 4,479,930 and Fritzberg, AR et al., J. Nucl. Med. 1986, 27, 957) with Technetium-99m.
- Suitable complexing agents for technetium and rhenium isotopes are, for. B. cyclic amines, as described by Volkert et al. (Appl.Radiol.Isot. 1982, 33; 891) and Troutner et al. (J. Nucl. Med. 1980, 21; 443), which have the disadvantage, however, that they are only able to bind technetium-99m in good yields from a pH> 9.
- N2 ⁇ 2 systems are in clinical use, but have the disadvantage that the corresponding metal complexes are not very stable in vivo. According to studies by Pillai and Troutner, the complexes in the plasma lose up to 30% of the complexed metal after 1 hour (Pillai, MRA, Troutner, DE et al .; Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29; 1850).
- Non-cyclic N 4 systems such. B. the HM-PAO have a major disadvantage of their low complex stability. Tc-99m-HM-PAO must because of its instability (Ballinger, JR et al., Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991, 42; 315), Billinghurst, MW et al., Appl. Radiat. Isot. 1991, 42; 607) can be applied within 30 minutes after its labeling, so that the proportion of decay products that have a different pharmacokinetics and excretion can be kept low. Such radiochemical contaminants complicate the detection of diagnosing diseases. A coupling of these chelates or chelating agents to other substances that selectively accumulate in foci of disease cannot be solved with simple means, so that they are generally distributed nonspecifically in the organism.
- NS 2 chelators (Bormans, G. et al .; Nucl. Med. Biol. 1990, 17; 499), such as e.g. B. ethylenedicysteine (EC; Verbruggen, AM et al .; J. Nucl. Med. 1992, 33; 551) meet the requirement for sufficient stability of the corresponding technetium-99m complex, but only form from a pH value of the complexing medium > 9 radio diagnostics with a purity of more than 69%.
- B. ethylenedicysteine ethylenedicysteine
- NßS systems (Fritzburg, A.; EP 0 173 424 and EP 0 250 013) form stable technetium-99m complexes, but must be heated to temperatures of approximately 100 ° C. in order to form a uniform radiopharmaceutical.
- bifunctional complexing agents which carry both functional groups for binding the desired metal ion and one (other, several) functional group for binding the selectively enriching molecule.
- Such bifunctional ligands enable a specific, chemically defined binding of technetium or rhenium isotopes to a wide variety of biological materials, even if so-called pre-labeling is carried out.
- EP 0 247 866 EP 0 188 256 and EP 0 200 492 describe some chelating agents which are coupled to monoclonal antibodies or fatty acids.
- N2S2 systems are used as chelating agents, which are not very suitable due to their low stability. Since both the selectively enriching substances in their properties, as well as the mechanisms, after to which they are enriched are very different, it is still necessary to vary the couplable chelating agent and the physiological
- the invention is therefore based on the object of finding complexes or complexing agents which overcome the disadvantages of the prior art, i.e. the
- the corresponding complexing agent and the respective metal oxide / salt can be prepared at low temperatures, preferably at room temperature, from the corresponding complexing agent and the respective metal oxide / salt, show high complex stability even under in vivo conditions , - Show a high selectivity or tissue / organ specificity.
- the complexes must meet the requirements that are generally placed on pharmaceuticals, such as good tolerance (i.e. no side effects), good solubility and complete elimination.
- the object is achieved by the present invention.
- V 1 , V 2 , V 3 , V 4 independently of one another represent a carbonyl,> CH (COOH) or -CH2 group, ⁇ l for a hydrogen atom, one optionally with a
- Carboxyl an amino or a thiocyanate group substituted C 1 -C ⁇ alkyl radical or a metal ion equivalent of a radioactive metal ion of an element of atomic number 43, 45, 46, 75, 82 or 83,
- X 2 , X 3 independently of one another for a hydrogen atom or a
- U stands for a direct bond, a straight-chain or branched, saturated or unsaturated C 1 -C 2 -alkylene radical which, if desired, a maleimide, a succinimide, an optionally substituted by 1 to 5 fluorine atoms, an amino or nitro group
- Phenyl radical one or two imino, phenylene, phenyleneoxy, phenylenamino, amide, hydrazide, carbonyl, ureido, thiourido-, thioamide, ester group (s), 1 to 2 oxygen, sulfur and / or nitrogen atom (s) and optionally 1 to 5 hydroxy,
- R 2 a straight-chain or branched C ⁇ -C alkyl radical, which optionally contains a -COOH group, a C7-C12 - aralkyl radical or an aromatic, optionally substituted with one
- R 4 represents a hydrogen atom or a carboxyl group or in the event that R 1 represents a hydrogen atom or a
- Carboxyl group means additionally also represents a group -UZ, in which U and Z have the meanings given, R 3 represents a hydrogen atom, a metal ion equivalent of an element of the atomic numbers mentioned, a trifluoroacetate, acetate, benzoate, - acyl, a benzoyl, a hydroxyacetyl, an acetamidomethyl, if desired with a chlorine or bromine atom, a methyl, ethyl, carboxyl and / or methoxy group substituted benzoic acid residue, a p-methoxybenzyl, one
- R 4 have the meanings given, where at least one and at most two radicals V 1 , V 2 , V 3 , V 4 stand for a carbonyl group, are outstandingly suitable as or for the production of radiodiagnostics and therapeutics.
- complexing agents ie compounds of the general formula I with X 1 , X 2 , X 3 and R 3 in the meanings indicated, with the exception of one metal ion equivalent, meet the requirement profile mentioned. They are characterized in particular by the fact that they have the desired metal 3 complex quickly at physiological pH and low temperatures. They are therefore particularly suitable for routine use in the clinic.
- the dimeric chelators with R 3 as a radical of the general formula ⁇ become monomeric metal complexes of the formula I with R 3 as a metal ion equivalent.
- Radioactive metal ions of elements of atomic numbers 43, 45, 46, 75, 82 or 83 such as e.g. the radioisotopes technetium-99m, rhodium-103, palladium-109, rhenium-186, lead-212 and bismuth-212 use, the choice of the metal isotope depending on the desired field of application. According to the invention, metal complexes of the elements technetium and rhenium are preferred.
- ⁇ -radiation-emitting isotopes e.g. Tc-99m
- these can be used in single photon emission tomography (SPECT).
- SPECT single photon emission tomography
- ⁇ -particle-emitting isotopes such as e.g. Bi-211, Bi-212, Bi-213, Bi-214 or ß-emitting
- Isotopes such as Re-186 or Re-188, these can be used in radiotherapy.
- V 1 and V 4 each represent a carbonyl group
- V 2 and V 3 each represent a -CH group
- p represents the number 0.
- Suitable radicals R 1 are hydrogen or a carboxylic acid group and in particular a group -UZ in which Z is a hydrogen atom, but preferably for the rest of a biomolecule with tissue or structure-specific properties or a functional group which may be present in activated form via the desired such a biomolecule can be stands.
- biomolecules are residues of an amino acid, a peptide or a steroid, such as the known steroid hormones (androgens, gestagens, estrogens, cholesterol, cholic acid derivatives, Pregnane, etc.), and polynucleotides such as RNA or DNA.
- Examples of functional groups that can be used to bind a biomolecule are a -COOH, a -SCN, a -OH, a -Cl or an -NH 2 group.
- Such groups can also be present in their activated form, for example as succinimide esters or acid chloride.
- U can preferably represent a direct bond, however, a straight-chain or branched, saturated or unsaturated C 1 -C 2 o -alkylene radical which, if desired, a succimide, a phenyl radical which is optionally substituted by 1 to 5 fluorine atoms, an amino or a nitro group, one or two imino, phenylene, phenyleneoxy, phenylenamino, amide, hydrazide, carbonyl, ureido, thiourido-, thioamide, ester group (s), 1 to 2 oxygen, sulfur and / or nitrogen atom (e) and optionally 1 to 5 hydroxyl, mercapto, oxo, thioxo, carboxy, alkyl carboxylic acid, ester, thiocyanate and / or amino groups.
- a succimide a phenyl radical which is optionally substituted by 1 to 5 fluorine atoms, an amino or
- the radicals -UZ with Z in the meaning of hydrogen are -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -O-CH 2 -COO-C 6 F 5 , -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -O-CH 2 -C 6 H 5 , -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -O-CH 3 , -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -OC 6 H 3 , -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -OC 12 H 25 or a -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -O-CO-C 15 H 31 group.
- radicals -UZ with Z meaning an optionally activated functional group are -CH 2 - (CH 2 ) -NCS, -CH 2 -C 6 H 4 -O-CO- (CH 2 ) 2 -COOH,
- -COO-N ie Z stands for an -NCS, -COOH, -NH 2 , -NO 2 , -OH or an S ⁇ group
- radicals R 2 are a -C 6 H 4 -NCS - or a - C $ H 4 -COOH group, but in particular a -CH 3 group or a phenyl ring.
- R 3 may be mentioned as examples, a) in the case of the complexing agents: -SH protective groups, such as, for example, a -CO-CH 3 ,
- R 3 can also represent a metal ion equivalent of a radioactive metal ion of an element of the atomic numbers mentioned.
- X 2 , X 3 represent a hydrogen atom and X 1 represents a hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted C r C 12 alkyl radical; in the case of the complexes, depending on the oxidation state of the metal in the complex, at least 2 of the radicals X 1 , X 2 , X 3 or R 3 the meaning of a metal ion equivalent.
- R 4 represents hydrogen or a carboxyl group. However, R 4 can also stand for a group -UZ with U and Z in the meanings given above, it always being true that at most one of the two radicals R 1 or R 4 denotes a group -UZ. Compounds with R 4 in the meaning of hydrogen are preferred according to the invention.
- indices m and n stand for the digits 0 or 1. Since isomers can be obtained in the synthesis of the complexing agents according to the invention, the sum of m and n is always 1.
- the invention also relates to processes for the preparation of the complexing agents and complexes according to the invention, different reaction paths advantageously being followed in the synthesis of the complexing agent depending on the desired target structure.
- Some typical syntheses are described below by way of example.
- Further complexing agents can be prepared analogously to the synthetic routes described.
- ligands are to be prepared which contain an —O — CgH 4 —CH 2 - group in R 1 , then a tyrosine ester, whose II amino group is initially protected in a manner known to the person skilled in the art by reaction with a reagent Z 1 -Cl, in which Z 1 stands for any amino protective group, preferably for benzyloxycarbonyl group (hereinafter also referred to as Z group).
- Z 1 stands for any amino protective group, preferably for benzyloxycarbonyl group (hereinafter also referred to as Z group).
- the phenolic hydroxyl group is then alkylated with an alkyl iodide in a manner known per se, the amino protecting group is split off acidically and then tosylated, for example, with toluenesulfonyl chloride.
- T-butyl bromoacetate alkylated and the amino protecting group split off in a conventional manner The tosylation and aminolysis of the ester function with ethylenediamine is carried out as described under 1, but the reaction is then carried out with chloroacetyl chloride. Chlorine is substituted in a manner known per se by reaction with potassium or sodium thioacetate and the t-butyl ester is saponified with acid. If desired, the resulting carboxylic acid group can be activated with hydroxysuccinimide and then reacted with the desired biomolecule.
- Ligands according to the invention in which R 1 is an SCN-C 6 H -CH 2 radical can be obtained by first tosylating the amino group of a p-nitrophenylalanine ester in a manner known per se. The nitro group is then hydrogenated and the resulting aromatic amino group is protected, for example by reaction with benzyl chloroformate. As described in the preceding cases, this reaction step is followed by aminolysis of the ester function with ethylenediamine, followed by reaction with S-protected mercaptoacetic acid. This is followed by the elimination of the benzyloxycarbonyl group. The isothiocyanate group is introduced by reaction with thiophosgene.
- Toluene sulfonyl chloride is tosylated.
- the ester function is then reacted with ethylenediamine in an aminolysis.
- the resulting free amino group is identified with a tert-butoxycarbonyl group (hereinafter referred to as the BOC group protected and the nitrogen substituted with a tosyl radical is N-alkylated with an alkyl iodide in a manner known per se.
- the reaction with 2-acetylmercapto-succinic anhydride follows, again giving a mixture of isomers.
- Ligands according to the invention with R 1 in the meaning of an aminobutyl radical can be obtained by first tosylating the LOC sine ester protected on a nitrogen atom on the remaining unprotected primary amino group and then reacting it with ethylenediamine in an aminolysis. The reaction is then carried out with 2-acetylmercapto-succinic anhydride (forming an isomer mixture) and the amino protecting group is split off by known methods.
- the preparation of ligands according to the invention which contain an isomiocyanate phenyl radical as R 2 is carried out by reacting a glycine methyl ester with nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride, then reducing the nitro group and protecting the resulting amino group.
- the intermediate compound thus obtained is reacted in an aminolysis with ethylenediamine and then with S-protected mercaptoacetic acid.
- the (BOC) protective group is subsequently split off in a known manner.
- the free amino group is then reacted with thiophosgene to form the corresponding isothiocyanate group.
- the metal complexes of the general formula I according to the invention with at least two radicals X 1 , X 2 , X 3 and / or R 3 in the meaning of a metal ion equivalent are prepared in a manner known per se by the complexing agents according to the invention (which can be obtained as described above) ) with the addition of a reducing agent, preferably tin salts, such as tin chloride or tartrate - and optionally with the addition of the additives customary in galenics, such as physiologically acceptable buffers (e.g. tromethamine), small additions of electrolytes (e.g. sodium chloride), stabilizers (e.g. gluconate , Phosphates or phosphonates) etc.
- a reducing agent preferably tin salts, such as tin chloride or tartrate -
- the additives customary in galenics such as physiologically acceptable buffers (e.g. tromethamine), small additions of electrolytes (e.
- the complexing agent is generally added in at least a 100-fold excess, ie the agents according to the invention contain, in addition to the 3 desired metal complex additionally also the metal-free complexing agent, which is advantageously added in the form of its potassium salt.
- reaction solutions containing the metal complex described above can in principle be applied directly without further workup.
- auxiliary ligands are gluconheptonic acid, tartaric acid, citric acid (including the salts thereof) or other substances known to the person skilled in the art.
- the metal complexes obtained can be mixed with pharmacologically acceptable radiological carriers.
- This radiological carrier should have favorable properties for the application of the radiopharmaceutical in the form of an injection, inhalation or ingestion.
- excipients are HSA, aqueous buffer solutions such as tris (hydroxymethyl) aminoethane (or their salts), phosphate, citrate, bicarbonate etc., sterile water, physiological saline, isotonic chloride or dicarbonate ion solutions or normal plasma ions like Ca 2 +, Na +, K + ; and Mg +.
- the agents according to the invention are dosed in amounts of 10 " 5 to 5 x 10 4 nmol / kg body weight, preferably in amounts between 10" 3 to 5 x 10 2 nmol / kg body weight (based on the metal complex) .
- the radioactivity required for diagnostic applications is between 1.85 MBq and 1.85 GBq per application.
- the application is usually carried out by intravenous, intraarterial, peritoneal or intratumoral injection of 0.1 to 2 ml of a solution of the agent according to the invention. Intravenous administration is preferred.
- the metal complexes according to the invention with metal ions of the elements mentioned and the pharmaceutical compositions prepared from them are notable for good Compatibility and high stability in vivo.
- the complexing agents according to the invention are notable for easy labeling, ie they complex the desired metals in high yields at room temperature and neutral pH.
- Np-toluenesulfonyl-2 [(4-hexyloxy) benzyl] -2-aminoacetic acid methyl ester 8.38 g of the amine (30 mmol) prepared according to Example lc) are dissolved in 50 ml dichloromethane and at 0 ° C. with 5.72 g Toluene sulfonyl chloride in 30 ml dichloromethane. With intensive stirring, 3.0 g of triethylamine are added dropwise at 0 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. After the reaction is complete, ice water is added and the mixture is extracted several times with dichloromethane.
- the catalyst is filtered off and the solvent is stripped off.
- Np-toluenesulfonyl-2 [(4-methyloxy) benzyl] -2-aminoacetic acid methyl ester 6.28 g of the amine (30 mmol) prepared according to Example 2b) are dissolved in 50 ml of dichloromethane and at 0 ° C. with 5.72 g of toluenesulfonic acid chloride 30 ml dichloromethane added. With intensive stirring, 3.0 g of triethylamine are added dropwise at 0 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. After the reaction is complete, ice water is added and the mixture is extracted several times with dichloromethane. The combined organic extracts are washed 2x with cold 10% HCl, 3x with 10% NaHC03 and 2x with saturated NaCl solution. After drying, the solvent is removed. Yield: 76%
- Np-toluenesulfonyl-2 [(4-dodecyloxy) benzyl] -2-aminoacetic acid methyl ester 10.91 g of the amine (30 mmol) prepared according to Example 3b) are dissolved in 50 ml dichloromethane and at 0 ° C. with 5.72 g toluenesulfonic acid chloride added in 30 ml dichloromethane. With intensive stirring, 3.0 g of triethylamine are added dropwise at 0 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 1 hour.
- the thiophosgene was added dropwise in a little dichloromethane and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h.
- Np-toluenesulfonyl-2 [(4-cholesteryldiethylene glycolyl) benzyl] - 2-aminoacetic acid methyl ester 19.53 g of the amine (30 mmol) prepared according to Example 9d) are dissolved in 50 ml dichloromethane and at 0 ° C. with 5.72 g toluenesulfonyl chloride in 30 ml dichloromethane added. With intensive stirring, 3.0 g of triethylamine are added dropwise at 0 ° C. and the mixture is stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. After the reaction is complete, ice water is added and the mixture is extracted several times with dichloromethane.
- Np-toluenesulfonyl-2 [(4-cholesteryldiethylene glycolyl) benzylJ-2-aminoacetic acid [N- (2-aminoethyl)] amide.
- a solution slowly becomes a solution of 1.2 g of ethylenediamine (20 mmol) in 1 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane 806 mg of the tosylglycine ester (1 mmol) prepared according to Example 9e in 1 ml of anhydrous dichloromethane were added dropwise and the mixture was boiled under reflux. When the reaction is complete, the mixture is concentrated in vacuo and the residue is chromatographed (silica gel, MeOH). Yield: 85% Ber. : C 70.55% H 9.06% N 5.04% O 11.51% S 3.84%
- 50 ⁇ l of this solution are added to 250 ⁇ l of a 0.1 M phosphate buffer (pH 8.5) and then with 50 ⁇ l of a citrate solution (50 mg of trisodium citrate in 1.0 ml of water) and 2.5 ⁇ l of a tin (TI) chloride Solution (5.0 mg of tin (II) chloride in 1 ml of 0.1 N HCl) was added. 50 ⁇ l of a Tc-99m generator eluate are then added and the mixture is left to stand for 15 minutes. The labeling yield is determined by means of HPLC.
- a solution of 27 g (100 mmol) of the amino compound prepared according to Example 10a) in 500 ml of dioxane is mixed with 74 g of di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (340 mmol) in one portion.
- the solution is stirred for 3 hours at room temperature, then poured onto ice water and extracted 3 times with ethyl acetate.
- the combined organic phases are washed 3 times with water and once with saturated sodium chloride solution, dried (MgSO.j.), concentrated and recrystallized. There remain 27.9 g of white crystals.
- N-a-toluenesulfonyl-lysine [N- (2- (piperonylmercapto) acetylaminoethyl)] amide 651 mg N- ⁇ -toluenesulfonyl-N- ⁇ -tert-butyloxycarbonyllysine
- 50 ⁇ l of this solution are added to 250 ⁇ l of a 0.1 M phosphate buffer pH 8.5 and with 50 ⁇ l of a citrate solution (50 mg of trisodium citrate in 1.0 ml of water) and 2.5 ⁇ l of a tin (III) chloride Solution (5.0 mg of tin (II) chloride in 1.0 ml of 0.1 N HCl) was added. 50 ⁇ l of a Tc-99m generator eluate is then added and the mixture is left to stand for 15 minutes. The labeling yield is determined by HPLC (> 95%).
- Trifluoroacetic acid removed in vacuo, the residue taken up in tetrahydrofuran, concentrated and chromatographed.
- N-Toluenesulfonyl-0-t-butyloxycarbonylmethyltyrosine [N. (2- (benzoylmercapto) - acetylaminoethyl)] amide 2 mmol S-benzoyl-2-mercaptoacetic acid (394 mg) and 4 mmol NEt 3 (560 ⁇ l) and 2 5 ml of dichloromethane are added to mmol (982 mg) of the compound obtained according to Example 8d) and the mixture is cooled to 10 ° C.
- the precipitate is filtered off and washed with plenty of water. Then over
- Trißuoressigklad ⁇ 10 g (18.19 mmol) of the title compound from Example 25c) are stirred for 1 mouth in 100 ml of trifluoroacetic acid at room temperature. It is evaporated to dryness in a vacuum. 9.95 g of a glassy foam are obtained, which solidifies on standing. Yield: 97%
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Medicines Containing Antibodies Or Antigens For Use As Internal Diagnostic Agents (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
Abstract
Description
Claims
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP95924304A EP0770063A1 (de) | 1994-07-14 | 1995-06-22 | Technetium-sulfonamid-komplexe, deren verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische mittel, sowie verfahren zur herstellung der komplexe und mittel |
| JP8504625A JPH10502648A (ja) | 1994-07-14 | 1995-06-22 | テクネチウム−スルホンアミド−錯体、これらの利用、これらを含有する医薬、並びに錯体及び薬剤を製造する方法 |
| KR1019970700193A KR970704682A (ko) | 1994-07-14 | 1995-06-22 | 테크네튬-술폰아미드 착물, 이들의 용도, 이들을 함유하는 약제, 및 상기 착물 및 약제의 제조 방법(Technetium-Sulphonamide Complexes, Their Use, Pharmaceutical Agents Containing Them, and Process for Producing the Complexes and Agents) |
| AU28865/95A AU698824B2 (en) | 1994-07-14 | 1995-06-22 | Technetium-sulphonamide complexes, their use, pharmaceutical agents containing the latter, as well as process for the production of the complexes and agents |
| NO970140A NO970140L (no) | 1994-07-14 | 1997-01-13 | Technetium-sulfonamidkomplekser, deres anvendelse, farmasöytiske midler inneholdende disse, samt fremgangsmåte for fremstilling av kompleksene og midlene |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DEP4425781.3 | 1994-07-14 | ||
| DE4425781A DE4425781A1 (de) | 1994-07-14 | 1994-07-14 | Technetium-Sulfonamid-Komplexe, deren Verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische Mittel, sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung der Komplexe und Mittel |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO1996002500A1 true WO1996002500A1 (de) | 1996-02-01 |
Family
ID=6523740
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP1995/002404 WO1996002500A1 (de) | 1994-07-14 | 1995-06-22 | Technetium-sulfonamid-komplexe, deren verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische mittel, sowie verfahren zur herstellung der komplexe und mittel |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP0770063A1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JPH10502648A (de) |
| KR (1) | KR970704682A (de) |
| CN (1) | CN1152914A (de) |
| AU (1) | AU698824B2 (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2194561A1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE4425781A1 (de) |
| HU (1) | HUT76806A (de) |
| NO (1) | NO970140L (de) |
| WO (1) | WO1996002500A1 (de) |
| ZA (1) | ZA955896B (de) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5028422A (en) * | 1986-05-27 | 1991-07-02 | Schering Corporation | Treatment of basal cell carcinoma intralesionally with recombinant human alpha interferon |
| WO2002004412A2 (en) * | 2000-07-06 | 2002-01-17 | Array Biopharma Inc. | Tyrosine derivatives as phosphatase inhibitors |
| KR100445971B1 (ko) * | 2002-04-15 | 2004-08-25 | 한국원자력연구소 | 수소화붕소 교환수지를 이용한 테크네튬 또는 레늄의표지방법 |
| DK2258401T3 (da) * | 2002-05-06 | 2014-10-13 | Endocyte Inc | Folat-receptor targetede billeddannelsesmidler |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0173424A1 (de) * | 1984-06-25 | 1986-03-05 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | Radiomarkierte Technetium-Chelate für die Anwendung in der Bestimmung der Nierenfunktion |
| EP0250013A1 (de) * | 1986-05-28 | 1987-12-23 | MALLINCKRODT, INC.(a Missouri corporation) | Technetiumchelate für die Bestimmung der Nierenfunktion |
-
1994
- 1994-07-14 DE DE4425781A patent/DE4425781A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1995
- 1995-06-22 HU HU9700101A patent/HUT76806A/hu unknown
- 1995-06-22 CA CA002194561A patent/CA2194561A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 1995-06-22 JP JP8504625A patent/JPH10502648A/ja active Pending
- 1995-06-22 WO PCT/EP1995/002404 patent/WO1996002500A1/de not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1995-06-22 KR KR1019970700193A patent/KR970704682A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 1995-06-22 CN CN95194028A patent/CN1152914A/zh active Pending
- 1995-06-22 AU AU28865/95A patent/AU698824B2/en not_active Ceased
- 1995-06-22 EP EP95924304A patent/EP0770063A1/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1995-07-14 ZA ZA955896A patent/ZA955896B/xx unknown
-
1997
- 1997-01-13 NO NO970140A patent/NO970140L/no unknown
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0173424A1 (de) * | 1984-06-25 | 1986-03-05 | University Of Utah Research Foundation | Radiomarkierte Technetium-Chelate für die Anwendung in der Bestimmung der Nierenfunktion |
| EP0250013A1 (de) * | 1986-05-28 | 1987-12-23 | MALLINCKRODT, INC.(a Missouri corporation) | Technetiumchelate für die Bestimmung der Nierenfunktion |
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| A.M. EL-NAGGER, ET AL.:: "Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of some di-, tri- and tetrapeptides containing cysteine and cystine", JOURNAL OF THE INDIAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY, vol. 60, no. 8, CALCUTTA, IN, pages 762 - 765 * |
| J. RUDINGER, ET AL.:: "Synthetic studies in the oxytocin field. III. An alternative synthesis of oxytocin", COLLECTION OF CZECHOSLOVAK CHEMICAL COMMUNICATIONS, vol. 21, no. 1, PRAGUE, CS, pages 202 - 210 * |
| J.A. MACLAREN, ET AL.:: "Amino acids and peptides. IV. Intermediates for the synthesis of certain cysteine-containing peptide sequences in insulin", AUSTRALIAN JOURNAL OF CHEMISTRY, vol. 11, MELBOURNE, AU, pages 345 - 359 * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR970704682A (ko) | 1997-09-06 |
| HUT76806A (en) | 1997-11-28 |
| AU698824B2 (en) | 1998-11-05 |
| JPH10502648A (ja) | 1998-03-10 |
| NO970140D0 (no) | 1997-01-13 |
| DE4425781A1 (de) | 1996-01-18 |
| NO970140L (no) | 1997-03-13 |
| EP0770063A1 (de) | 1997-05-02 |
| ZA955896B (en) | 1996-02-19 |
| CN1152914A (zh) | 1997-06-25 |
| CA2194561A1 (en) | 1996-02-01 |
| AU2886595A (en) | 1996-02-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE68908273T2 (de) | Metal Radionukleid-Chelatverbindungen mit verbesserter Chelatierungskinetik. | |
| DE69738353T2 (de) | Radiometall-bindende peptide analoge | |
| DD297636A5 (de) | Chelatbildner zur komplexierung von radioaktiven isotopen, deren metallkomplexe sowie ihre verwendung in diagnostik und therapie | |
| EP0692976B1 (de) | Chelatbildner vom typ xn 1?s 1?o 1? für radioaktive isotope, deren metallkomplexe und ihre verwendung in diagnostik und therapie | |
| EP0851771A2 (de) | Bifunktionelle nicotinamid-chelatbildner vom typ n2s2 für radioaktive isotope | |
| WO1997010852A2 (de) | Bifunktionelle sulfidhaltige sulfonamid-chelatbildner vom typ xsns für radioaktive isotope | |
| EP0692979A1 (de) | Bifunktionelle chelatbildner und ihre anwendung in der radiopharmazeutik | |
| WO1997012636A2 (de) | Bifunktionelle sulfidhaltige sulfonamid-chelatbildner vom typ s2ny für radioaktive isotope | |
| DE19860289C2 (de) | Neue Chelatoren sowie deren Tricarbonyl-Komplexe mit Technetium und Rhenium | |
| DE69532965T2 (de) | Gegebenenfalls durch tc oder re radioaktiv markierte n3s2-chelate, geeignet für diagnostische oder therapeutische anwendungen | |
| EP0770063A1 (de) | Technetium-sulfonamid-komplexe, deren verwendung, diese enthaltende pharmazeutische mittel, sowie verfahren zur herstellung der komplexe und mittel | |
| EP0692981B1 (de) | Chelatbildner vom typ xn 1?s 1?x' für radioaktive isotope, deren metallkomplexe und ihre verwendung in diagnostik und therapie | |
| EP0692980B1 (de) | Chelatbildner vom typ s3n2 für radioaktive isotope, deren metallkomplexe und ihre verwendung in diagnostik und therapie | |
| DE69515302T2 (de) | Aromatische aminsubstituierte liganden mit verbrückten stickstoff-und schwefeldonatoratomen für bildformung | |
| EP0851847A2 (de) | Bifunktionelle sulfidhaltige sulfonamid-chelatbildner vom typ xsny für radioaktive isotope | |
| WO1996007629A1 (en) | Technetium chelates to be used for determining the renal function |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 95194028.7 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| AK | Designated states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AU CA CN HU JP KR NO NZ US |
|
| AL | Designated countries for regional patents |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| DFPE | Request for preliminary examination filed prior to expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed before 20040101) | ||
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application | ||
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1995924304 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 289120 Country of ref document: NZ |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2194561 Country of ref document: CA |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1019970700193 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 1995924304 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 1997 765291 Country of ref document: US Date of ref document: 19970605 Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWP | Wipo information: published in national office |
Ref document number: 1019970700193 Country of ref document: KR |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 1995924304 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWW | Wipo information: withdrawn in national office |
Ref document number: 1019970700193 Country of ref document: KR |