US3820594A - Tube support system for heat exchanger - Google Patents
Tube support system for heat exchanger Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US3820594A US3820594A US00315708A US31570872A US3820594A US 3820594 A US3820594 A US 3820594A US 00315708 A US00315708 A US 00315708A US 31570872 A US31570872 A US 31570872A US 3820594 A US3820594 A US 3820594A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- strips
- tubes
- group
- support system
- bent
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F28—HEAT EXCHANGE IN GENERAL
- F28F—DETAILS OF HEAT-EXCHANGE AND HEAT-TRANSFER APPARATUS, OF GENERAL APPLICATION
- F28F9/00—Casings; Header boxes; Auxiliary supports for elements; Auxiliary members within casings
- F28F9/007—Auxiliary supports for elements
- F28F9/013—Auxiliary supports for elements for tubes or tube-assemblies
- F28F9/0135—Auxiliary supports for elements for tubes or tube-assemblies formed by grids having only one tube per closed grid opening
- F28F9/0136—Auxiliary supports for elements for tubes or tube-assemblies formed by grids having only one tube per closed grid opening formed by intersecting strips
Definitions
- ABSTRACT Two groups of parallel flat bars disposed on an angle with respect to each other form a lattice which engages four sides of each tube to reduce the vibrations; the ends of the flat bars are bent and fastened to end bars which provide rigidity necessary to produce an economical vibration dampening support system which can be easily installed in an assembled heat exchanger.
- a tube support system for a heat exchanger having a plurality of rows of tubes forming a tube bundle when made in accordance with this invention, comprises a first group of strips disposed generally parallelto each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, and a second group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes.
- the first group of strips is disposed at an angle withrespect to the second group of strips forming a latticewhich generally surrounds the tubes.
- the strips have terminal ends which are generally disposed at the periphery of the tube bundles and a bar for interconnecting the strips to add rigidity to the lattice, to reduce vibration and to prevent the strips from sliding through the tube bundles.
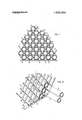
- FIG. 1 is a partial sectional view of a heat exchanger with a tube support system made in accordance with this invention.
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view description the heat exchanger and tube support system.
- DESCRIPTIONM OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT strips 7 disposed generally parallel to each other between adjacent rows 5 of tubes 3.
- the strips 7 have ends 8 which are bent to form an obtuse angle with respect to the strips 7 and terminate adjacent the periphery of the tube bundle.
- a second group of strips 9 disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes 3 are also disposed at an angle with respect to the first group of strips 7, forming a lattice which generally surrounds the tubes 3 so that each tube is engaged on four sides by the strips 7 and 9.
- the strips 9 have ends 10 which are bent to form an obtuse angle with respect to the strips 9 and terminate at the periphery of the tube bundle.
- bent portions 8 and 10 of the strips 7 and 9 engage a flat bar 15 and are fastened thereto by tack welding or other means.
- the group of strips 7 and 9 being disposed at an angle with respect to each other form a lattice which surrounds the tubes and engages four sides thereof. Since the ends of the strips are fastened to the flat bars 15, the lattice has sufficient rigidity to reduce vibration of the tubes 3.
- the strips 7 and 9 are generally the thickness of the spacing between rows of tubes so that the strips can be slipped between the rows of tubes. The ends of the strips 7 and 9 are then bent to retain the strips within the row of tubes thus facilitating fabrication of this tube support system in an assembled heat exchanger to provide an economical tube support system, which can be installed in an assembled heat exchanger to reduce the vibration of the tubes and to prevent their premature failure.
- a tube support system for a heat exchanger having a plurality of rows of tubes forming a tube bundle, said tube support system comprising a first group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, a second group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, said first group of strips being disposed at an angle with respect to said second group of strips and arranged to cooperate with each other to exclusively form a lattice which generally surrounds the tubes, said strips having terminal ends which are bent at an oblique angle with respect to the strip, and are generally disposed at the periphery of the tube bundle, the ends of the first group of strips being bent in one direction and the ends of the second group of strips being bent in the opposite direction, said bent ends of said second group of strips overlapping with said bent ends of said first group of strips, and a flat bar fastened to the overlapping bent ends of the strips to add rigidity to the lattice, to reduce vibration between the tubes, and to prevent the strips from sliding through the rows of tubes.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Heat-Exchange Devices With Radiators And Conduit Assemblies (AREA)
Abstract
Two groups of parallel flat bars disposed on an angle with respect to each other form a lattice which engages four sides of each tube to reduce the vibrations; the ends of the flat bars are bent and fastened to end bars which provide rigidity necessary to produce an economical vibration dampening support system which can be easily installed in an assembled heat exchanger.
Description
United States Patent 1191 Ritland et al.
[ 1 June 28, 1974 TUBE SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR HEAT EXCHANGER [75] Inventors: Paul D. Ritland, Secane; Rollin W.
V Ache, New Town Square, both of [73] Assignee: Westinghouse Electric Corporation,
Pittsburgh, Pa.
[22] Filed: Dec. 15, 1972 [21] Appl. No.: 315,708
52 us. (:1 165/69, 165/162, 165/172 [51] Int. Cl F281 l/00 [58] Field of Search 165/69, 172, 67, 162;
[56] References Cited UNITED STATES PATENTS 1,967,961 7/1934 Metten 165/162 3,104,218 9/1963 Speidel et a1. 165/162 X 3,163,208 12/1964 Cuzzone et al. 165/69 3,260,649 7/1966 Jens ct al. 176/76 X 3,420,297 1/1969 Romanos 165/162 FOREIGN PATENTS OR APPLICATIONS 367,842 4/1963 Switzerland 165/162 Primary Examiner-Albert W. Davis, Jr. Assistant Examiner-Sheldon .1. Richter Attorney, Agent, or Firm-F. .1. Baehr, Jr.
[ 5 7] ABSTRACT Two groups of parallel flat bars disposed on an angle with respect to each other form a lattice which engages four sides of each tube to reduce the vibrations; the ends of the flat bars are bent and fastened to end bars which provide rigidity necessary to produce an economical vibration dampening support system which can be easily installed in an assembled heat exchanger.
4 Claims, 2 Drawing Figures TUBE SUPPORT SYSTEM FOR HEAT EXCHANGER BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION This invention relates to heat exchangers, and more particularly, to a tube support system which can be easily installed in an assembled heat exchanger to reduce vibration in the tubes.
As fluid flows over heat exchanger tubes it produces dynamic forces which act upon the tubes causing the tubes to vibrate. The amplitude and frequency of the vibrations are affected by such facts as the span between the tube supports, the stiffness of the tubes and the velocity and density of the fluid. Reducing the length of the span between supports in the most expedient method of reducing vibration of the tubes, however, if the heat exchanger is assembled, it is impossible to utilize additional conventional tube support plates, which consist of plates having a plurality of holes through which the tubes pass. Therefore, an economical support system is needed to facilitate field installation of an additional support to reduce vibrations which were not apparent until the heat exchanger has been in service.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In general, a tube support system for a heat exchanger having a plurality of rows of tubes forming a tube bundle, when made in accordance with this invention, comprises a first group of strips disposed generally parallelto each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, and a second group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes. The first group of strips is disposed at an angle withrespect to the second group of strips forming a latticewhich generally surrounds the tubes. The strips have terminal ends which are generally disposed at the periphery of the tube bundles and a bar for interconnecting the strips to add rigidity to the lattice, to reduce vibration and to prevent the strips from sliding through the tube bundles.
' BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The objects and advantages of this invention will become more apparent from reading the following detailed description in connection with the accompanying drawings, in which:
FIG. 1 is a partial sectional view of a heat exchanger with a tube support system made in accordance with this invention; and
FIG. 2 is a perspective view description the heat exchanger and tube support system.
DESCRIPTIONM OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENT strips 7 disposed generally parallel to each other between adjacent rows 5 of tubes 3. The strips 7 have ends 8 which are bent to form an obtuse angle with respect to the strips 7 and terminate adjacent the periphery of the tube bundle.
A second group of strips 9 disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes 3 are also disposed at an angle with respect to the first group of strips 7, forming a lattice which generally surrounds the tubes 3 so that each tube is engaged on four sides by the strips 7 and 9. The strips 9 have ends 10 which are bent to form an obtuse angle with respect to the strips 9 and terminate at the periphery of the tube bundle. I
The bent portions 8 and 10 of the strips 7 and 9 engage a flat bar 15 and are fastened thereto by tack welding or other means.
The group of strips 7 and 9 being disposed at an angle with respect to each other form a lattice which surrounds the tubes and engages four sides thereof. Since the ends of the strips are fastened to the flat bars 15, the lattice has sufficient rigidity to reduce vibration of the tubes 3. The strips 7 and 9 are generally the thickness of the spacing between rows of tubes so that the strips can be slipped between the rows of tubes. The ends of the strips 7 and 9 are then bent to retain the strips within the row of tubes thus facilitating fabrication of this tube support system in an assembled heat exchanger to provide an economical tube support system, which can be installed in an assembled heat exchanger to reduce the vibration of the tubes and to prevent their premature failure.
What is claimed is:
l. A tube support system for a heat exchanger having a plurality of rows of tubes forming a tube bundle, said tube support system comprising a first group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, a second group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, said first group of strips being disposed at an angle with respect to said second group of strips and arranged to cooperate with each other to exclusively form a lattice which generally surrounds the tubes, said strips having terminal ends which are bent at an oblique angle with respect to the strip, and are generally disposed at the periphery of the tube bundle, the ends of the first group of strips being bent in one direction and the ends of the second group of strips being bent in the opposite direction, said bent ends of said second group of strips overlapping with said bent ends of said first group of strips, and a flat bar fastened to the overlapping bent ends of the strips to add rigidity to the lattice, to reduce vibration between the tubes, and to prevent the strips from sliding through the rows of tubes.
2. A tube support system as set forth in claim 1, wherein the bent portion of the strips are fastened to the bar by tack welding.
3. A tube support system as set forth in claim 1, wherein the thickness of the strip is such that the strips engage the tubes in adjacent rows.
4. A tube support system as set forth in claim 3,
wherein the tubes are disposed on a triangular pitch.
Claims (4)
1. A tube support system for a heat exchanger having a plurality of rows of tubes forming a tube bundle, said tube support system comprising a first group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, a second group of strips disposed generally parallel to each other and between adjacent rows of tubes, said first group of strips being disposed at an angle with respect to said second group of strips and arranged to cooperate with each other to exclusively form a lattice which generally surrounds the tubes, said strips having terminal ends which are bent at an oblique angle with respect to the strip, and are generally disposed at the periphery of the tube bundle, the ends of the first group of strips being bent in one direction and the ends of the second group of strips being bent in the opposite direction, said bent ends of said second group of strips overlapping with said bent ends of said first group of strips, and a flat bar fastened to the overlapping bent ends of the strips to add rigidity to the lattice, to reduce vibration between the tubes, and to prevent the strips from sliding through the rows of tubes.
2. A tube support system as set forth in claim 1, wherein the bent portion of the strips are fastened to the bar by tack welding.
3. A tube support system as set forth in claim 1, wherein the thickness of the strip is such that the strips engage the tubes in adjacent rows.
4. A tube support system as set forth in claim 3, wherein the tubes are disposed on a triangular pitch.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US00315708A US3820594A (en) | 1972-12-15 | 1972-12-15 | Tube support system for heat exchanger |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US00315708A US3820594A (en) | 1972-12-15 | 1972-12-15 | Tube support system for heat exchanger |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US3820594A true US3820594A (en) | 1974-06-28 |
Family
ID=23225695
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US00315708A Expired - Lifetime US3820594A (en) | 1972-12-15 | 1972-12-15 | Tube support system for heat exchanger |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US3820594A (en) |
Cited By (23)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3937277A (en) * | 1973-03-17 | 1976-02-10 | Gutehoffnungshutte Sterkrade Aktiengesellschaft | Tubular apparatus, in particular a steam generator |
| US3964146A (en) * | 1973-04-10 | 1976-06-22 | Norsk Hydro A.S. | Means for assembly of tube banks in heat exchangers |
| US4143709A (en) * | 1977-03-15 | 1979-03-13 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Tube support system |
| FR2430588A1 (en) * | 1978-07-06 | 1980-02-01 | Sulzer Ag | Helicoidal tube bundle structure for heat exchangers - has damping device which does not complicate erecting operations |
| DE2840146A1 (en) * | 1978-09-15 | 1980-03-27 | Balcke Duerr Ag | Holder grid for heat exchanger tube nest - has members with ends bent at tube pitch providing grid for vertical parallel tubes |
| EP0027092A1 (en) * | 1979-10-08 | 1981-04-15 | Framatome | Spacing grid for tubular bundles |
| DE3136865A1 (en) * | 1981-09-17 | 1983-03-31 | Schwelmer Eisenwerk Müller & Co GmbH, 5830 Schwelm | Tubular heat exchanger with flow-guiding internals arranged in the flow chamber |
| US4552292A (en) * | 1982-11-12 | 1985-11-12 | General Electric Company | Heat exchanger |
| US4579304A (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1986-04-01 | Williams George J | Tube bundle support |
| US4595161A (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1986-06-17 | Williams George J | Tube bundle support |
| US4637455A (en) * | 1984-09-28 | 1987-01-20 | Combustion Engineering, Inc. | Support rack for tubes immersed in a fluidized bed |
| US4648442A (en) * | 1985-12-10 | 1987-03-10 | Williams George J | Stake for a tube bundle |
| US4697637A (en) * | 1981-12-02 | 1987-10-06 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Tube support and flow director |
| US4787440A (en) * | 1981-12-02 | 1988-11-29 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Spiral flow in a shell and tube heat exchanger |
| US4828021A (en) * | 1976-04-29 | 1989-05-09 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Heat exchanger baffle |
| US4893671A (en) * | 1988-06-20 | 1990-01-16 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Steam generator tube antivibration apparatus and method |
| US4991645A (en) * | 1988-06-20 | 1991-02-12 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Steam generator tube antivibration apparatus |
| US5158162A (en) * | 1989-09-15 | 1992-10-27 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Tube vibration dampener and stiffener apparatus and method |
| US5570739A (en) * | 1994-12-07 | 1996-11-05 | Foster Wheeler Development Corporation | Anti-vibration spacers used in tubular type heat exchangers |
| US20080315047A1 (en) * | 2007-06-20 | 2008-12-25 | Exxonmobil Research And Engineering Company | Anti-vibration tube support with locking assembly |
| JP2015094482A (en) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-05-18 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Fin tube heat exchanger |
| US20170321971A1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2017-11-09 | Joint Stock Company "Akme-Engineering" | Heat Exchanger Tube Spacing Device (Varinats) |
| WO2019203300A1 (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2019-10-24 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Heat-transfer-tube support structure, and method for supporting heat transfer tube |
-
1972
- 1972-12-15 US US00315708A patent/US3820594A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (29)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3937277A (en) * | 1973-03-17 | 1976-02-10 | Gutehoffnungshutte Sterkrade Aktiengesellschaft | Tubular apparatus, in particular a steam generator |
| US3964146A (en) * | 1973-04-10 | 1976-06-22 | Norsk Hydro A.S. | Means for assembly of tube banks in heat exchangers |
| US4828021A (en) * | 1976-04-29 | 1989-05-09 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Heat exchanger baffle |
| US4143709A (en) * | 1977-03-15 | 1979-03-13 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Tube support system |
| FR2430588A1 (en) * | 1978-07-06 | 1980-02-01 | Sulzer Ag | Helicoidal tube bundle structure for heat exchangers - has damping device which does not complicate erecting operations |
| DE2840146A1 (en) * | 1978-09-15 | 1980-03-27 | Balcke Duerr Ag | Holder grid for heat exchanger tube nest - has members with ends bent at tube pitch providing grid for vertical parallel tubes |
| EP0027092A1 (en) * | 1979-10-08 | 1981-04-15 | Framatome | Spacing grid for tubular bundles |
| FR2467371A1 (en) * | 1979-10-08 | 1981-04-17 | Framatome Sa | SPACER GRID FOR TUBULAR BEAMS |
| DE3136865A1 (en) * | 1981-09-17 | 1983-03-31 | Schwelmer Eisenwerk Müller & Co GmbH, 5830 Schwelm | Tubular heat exchanger with flow-guiding internals arranged in the flow chamber |
| US4787440A (en) * | 1981-12-02 | 1988-11-29 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Spiral flow in a shell and tube heat exchanger |
| US4697637A (en) * | 1981-12-02 | 1987-10-06 | Phillips Petroleum Company | Tube support and flow director |
| US4552292A (en) * | 1982-11-12 | 1985-11-12 | General Electric Company | Heat exchanger |
| US4595161A (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1986-06-17 | Williams George J | Tube bundle support |
| US4579304A (en) * | 1983-06-01 | 1986-04-01 | Williams George J | Tube bundle support |
| US4637455A (en) * | 1984-09-28 | 1987-01-20 | Combustion Engineering, Inc. | Support rack for tubes immersed in a fluidized bed |
| US4648442A (en) * | 1985-12-10 | 1987-03-10 | Williams George J | Stake for a tube bundle |
| US4893671A (en) * | 1988-06-20 | 1990-01-16 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Steam generator tube antivibration apparatus and method |
| US4991645A (en) * | 1988-06-20 | 1991-02-12 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Steam generator tube antivibration apparatus |
| US5158162A (en) * | 1989-09-15 | 1992-10-27 | Westinghouse Electric Corp. | Tube vibration dampener and stiffener apparatus and method |
| US5570739A (en) * | 1994-12-07 | 1996-11-05 | Foster Wheeler Development Corporation | Anti-vibration spacers used in tubular type heat exchangers |
| US20080315047A1 (en) * | 2007-06-20 | 2008-12-25 | Exxonmobil Research And Engineering Company | Anti-vibration tube support with locking assembly |
| US7506684B2 (en) | 2007-06-20 | 2009-03-24 | Exxonmobil Research & Engineering Company | Anti-vibration tube support with locking assembly |
| JP2015094482A (en) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-05-18 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Fin tube heat exchanger |
| US20170321971A1 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2017-11-09 | Joint Stock Company "Akme-Engineering" | Heat Exchanger Tube Spacing Device (Varinats) |
| US10563929B2 (en) * | 2014-12-30 | 2020-02-18 | Joint Stock Company “Akme-Engineering” | Heat exchanger tube spacing device (varinats) |
| WO2019203300A1 (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2019-10-24 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Heat-transfer-tube support structure, and method for supporting heat transfer tube |
| JP2019190672A (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2019-10-31 | 三菱日立パワーシステムズ株式会社 | Heat transfer pipe support structure and heat transfer pipe support method |
| CN111989531A (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2020-11-24 | 三菱动力株式会社 | Heat transfer tube support structure and heat transfer tube support method |
| CN111989531B (en) * | 2018-04-18 | 2022-01-14 | 三菱动力株式会社 | Heat transfer tube support structure and heat transfer tube support method |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US3820594A (en) | Tube support system for heat exchanger | |
| US3967677A (en) | Heat exchanger baffles | |
| US3286767A (en) | Tube support arrangement | |
| US7219718B2 (en) | Reduced vibration tube bundle device | |
| US3854529A (en) | Tube support system for a heat exchanger | |
| US3720259A (en) | Tubular heat exchanger supporting and spacer structure | |
| US4398595A (en) | Vortex generators | |
| US4160477A (en) | Spacer grid for parallel cylindrical tubes | |
| US3896874A (en) | Support system for serpentine tubes of a heat exchanger | |
| CA1135684A (en) | Vortex generators | |
| EP0268147B1 (en) | Heat exchanger u-bend tube support | |
| JP2010506128A (en) | Low vibration tube bundle device with slotted baffle | |
| US3326282A (en) | Arrangement for fastening spiral wire spacers in tubular heat exchangers | |
| US4589618A (en) | Holding device for a tube bundle | |
| EP1815202B1 (en) | Fluid-handling equipment with anti-vibration tube supports | |
| US4706614A (en) | Device for suspending a bundle of horizontal tubes in a vertical plane and method of fabricating the device | |
| US3850235A (en) | Heat exchanger | |
| US5158134A (en) | Fully floating tube bundle | |
| EP0757219A2 (en) | Pack of heat exchanger plates for regenerative heat exchanger | |
| US4413394A (en) | Method of constructing a tube bundle | |
| US3360039A (en) | Damping device for heat exchangers | |
| JPH05240592A (en) | Heat exchanger having u-shaped pipe provided with elutriation-proof support device | |
| US3277958A (en) | Heat exchangers | |
| JPH025275Y2 (en) | ||
| US3361197A (en) | Tube support |