US3287821A - Conveying and treating apparatus - Google Patents
Conveying and treating apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- US3287821A US3287821A US312586A US31258663A US3287821A US 3287821 A US3287821 A US 3287821A US 312586 A US312586 A US 312586A US 31258663 A US31258663 A US 31258663A US 3287821 A US3287821 A US 3287821A
- Authority
- US
- United States
- Prior art keywords
- web
- air
- plenum
- gaseous medium
- plenums
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 230000008093 supporting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 208000027418 Wounds and injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007373 indentation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000014674 injury Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002035 prolonged effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000153 supplemental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F26—DRYING
- F26B—DRYING SOLID MATERIALS OR OBJECTS BY REMOVING LIQUID THEREFROM
- F26B13/00—Machines and apparatus for drying fabrics, fibres, yarns, or other materials in long lengths, with progressive movement
- F26B13/10—Arrangements for feeding, heating or supporting materials; Controlling movement, tension or position of materials
- F26B13/101—Supporting materials without tension, e.g. on or between foraminous belts
- F26B13/104—Supporting materials without tension, e.g. on or between foraminous belts supported by fluid jets only; Fluid blowing arrangements for flotation dryers, e.g. coanda nozzles
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D21—PAPER-MAKING; PRODUCTION OF CELLULOSE
- D21F—PAPER-MAKING MACHINES; METHODS OF PRODUCING PAPER THEREON
- D21F5/00—Dryer section of machines for making continuous webs of paper
Definitions
- FIG 6 45 4 5n INVENTOR.
- This invention relates to an apparatus for the treatment of web materials while being air-borne therethrough and, more particularly, to apparatus having a plenum of simplified construction adapted to heating, cooling or otherwise processing of previously wet treated, coated and/ or printed materials for an interval of time during which they are supported by a cushion of flowing gaseous fluid such as air, the air being supplied for treatment and returned to the same plenum.
- a web material that has been air-conveyed and simultaneously treated during its travel through such an apparatus is generally more uniformly and thoroughly treated than by methods requiring physical support. And whatever shrinkage or change in size that will occur while being air floated and conveyed will be in all directions; the final result is a totally relaxed and stable web product.
- the present invention provides for an improved treating and air-conveying apparatus wherein the web is floated or supported by a great many air jet streams at points occurring at a frequency so as to minimize undulation or possible vibration that may injure the web material or a surface applied treatment.
- the air support is provided in the direction of travel of the web urging it forwardly and, where the air is heated and used for drying, or heating, it is substantially recovered and reused. The recovery of once used air is simply and automatically effected by the terminal structure of the surface of the plenum.
- the plenum interior is open and clear for its entire length, simulating a rectangular unobstructed conduit for the continuous flow of a gaseous fluid therethrough.
- support for the web moving through the apparatus can be one-sided or it can be two-sided depending on web treatment as to whether a single or opposing plenum is required. Air emitted from each plenum is returned thereto only to be emitted again in the direction of travel of the web.
- the outward surfaces of the opposing plenums advantageously are flat and continuous, the plenum air openings for impingement or web support and for return being positioned flush therein.
- the flush con struction is advantageous in that the web material will not meet any obstruction which could keep it confined in the event of a break.
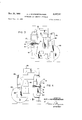
- FIGURE 1 is a view in side elevation, in partial section, of the web conveying apparatus
- FIGURE 2 is a plan view of the air treating and conveying apparatus
- FIGURE 3 is a schematic end view of the web inlet side of the apparatus of FIGURE 1 taken along lines 3--3 thereof;
- FIGURE 4 is, likewise, an end view of the web exit end of the apparatus of FIGURE 1, taken along lines 44 thereof;
- FIGURES 5 and 6 are sectional details, in elevation and transverse planes, of the air inlets and exhausts of the opposing plenum surfaces taken on lines 55 of FIG- URE 2 and 6-6 of FIGURE 1;
- FIGURE 7 is a sectional plan view of the surface of a plenum, showing the indented air inlets and exhausts taken on line 77 of FIGURE 1;
- FIGURE 8 is an end section of a plenum at the web exit showing air re-entry into the air pump system, taken on line 88 of FIGURE 2.
- Web advancing and treating air is supplied through an air supply system having an air fan 25, itself being supplied from the surrounding area, from recovered air from within the apparatus itself and through dampers in the system.
- the supply fan forces such air into an initial common conduit 26 then to split take-off conduits 17, 18 supplying upper and lower plenums 15, 16.
- the air which may be heated to a desirable temperature by an interposed heater 27 positioned in conduit 26 for a specific drying or fixing treatment is being passed on through a regulating damper 30 thence through volume regulating dampers 32 and 33 in connecting diverging plenum supply conduits 17, 18, each separately supplying their respective plenums 15, 16.
- the additional dampers 32, 33 are provided to control the volume of the flowing air and to regulate velocities to the respective plenums 15, 16.
- Damper 28, located in conduit 26 between the fan 25 and damper 30, serves to exhaust a controlled amount of the air to keep the concentration of the vapors added to the air during the treating process at a desired level.
- the dampers control the supplemental air to.
- the fan for admixture with recovered air in accordance with requirements for recirculation.
- the air circulating system as shown in FIGURES 1-4 contains one central blower or fan 25 which generally will prove suflicient for the treatment of a web of paper or other material for over a distance of about 20 feet or so. Beyond such a nominal distance another blower desirably would have to be interposed.
- FIGURES 1-4 also is advantageously economical, being designed about the improved plenum chambers 15, 16.
- the plenums are simple, elongated, rectangular chambers with their are part of the same and continuing plenum surface. This construction is shown in detail in FIGURES 5, 6 and 7. Air in the plenums flows outwardly over inward indentations or scoops 44, through apertures 45 formed when the metal was die-cut, to impinge against the traveling web 21 maintaining it aloft, and over scoops 46 and through apertures 47 also against the web 21 of the plenums and 16 respectively.
- the air in the plenums 15 and 16 moves at a relatively high velocity from the entering end, conduits 17 and 18, toward the leaving end, conduits 19 and 20, a suction develops downstream of the directional lips 49 and 51 effecting the removal of the air from the web into plenums 15 and 16 through openings 48 and 50 to join the flow therein to be again forced out through further similar outlets, and back in through inlets.
- the flow of Web supporting air is in the form of an undulating stream, the frequency of web impingement being based on the number of air outlets and inlets in the plenum surfaces.
- the lower terminal plenum face as Well as the opposing upper plenum face, has several air return openings 55, 56, 57 and return scoops 58, 59, 60 for pulling in air.
- Opposing plenum faces at about the exit end, containing said return openings, are inclined at a shallow angle away from the web, effecting an increasingly higher static pressure between the web and the plenum faces due to a decreasing air velocity parallel to the web and effecting a decreasingly lower static pressure in the plenums 15 and 16 due to an increasing air velocity inside said plenums.
- Apparatus for supporting, conveying and meanwhile treating a web passing therethrough by a gaseous medium comprising, a circulating gas system including a blower, conduit means for the gaseous medium from said blower, conduit means returning said gaseous medium to said blower, opposing plenums positioned in said system between said conduits through which said gaseous medium flows dividedly and uninterruptedly, said web passing between the faces of said opposing plenums, a plurality of openings in the faces of said plenums made by perforation thereof each having the perforated sections angled as directing deflectors for directing the flow of said gaseous medium against said Web in the direction of its travel, and a further plurality of perforate openings in the same plenum face and each also having the perforate sections angled as deflectors for redirecting Web deflecting gaseous medium into said plenum and into said gas supply system for recirculation.
- Apparatus for supporting, conveying and meanwhile treating a web passing therethrough by a gaseous medium comprising, a circulating gas supply system including a blower, conduit means for the gaseous medium from said blower, conduit means returning said gaseous medium to said blower, a plenum positioned in said system between said conduits through which said gaseous medium flows uninterruptedly, said web passing through the apparatus over said plenum, a plurality of openings in the face of the plenum having deflectors for directing the flow of said gaseous medium against said web in the direction of its travel, and a further plurality of openings in the same plenum face also having deflectors for redirecting web deflected gaseous medium into said plenum and into said gas supply system, the directing and redirecting deflectors are within the plenum interior and are part of the plenum face being angled upwardly for directing gas flow against a running web and angled downwardly into the plenum interior for redirecting gas flow into said plenum
- the plenum has an additional consecutive plurality of openings having downwardly angled deflectors for redirecting gas into the plenum interior at about its end.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Drying Of Solid Materials (AREA)
- Paper (AREA)
Description
N V- 1966 A. J. SCHREGENBERGER 3,287,821
CONVEYING AND TREATING APPARATUS Filed Sept. 30, 1963 4 SheetsSheet l FIG.
INVENTOR. ALEX J. SCHREGENBERGER ATTORNEY 1 A. J. SCHREGENBERGER 3,287,821
CONVEYING AND TREATING APPARATUS 4 Sheets-Sheet 2 Filed Sept. 30, 1963 INVENTOR. ALEX J. SCHREGENBERGER v fmd/ ,4 gym ATTORNEY 1966 A. J. SCHREGENBERGER 4 3,287,321
CONVEYING AND TREATING APPARATUS Filed Sept. 30, 1963 4 Sheets-Sheet 5 INVENTOR. ALEX J. SCHREGENBERGER ATTORNEY N v- 1966 A. J. SCHREGENBERGER 3,
CONVEYING AND TREATING APPARATUS Filed Sept. 30, 1963 4 Sheets-Sheet 4 M W. v
IV n FIG 6 45 4 5n INVENTOR. ALEX J. SCHREGENBERGER ATTO R NEY United States Patent 3,287,821 CONVEYING AND TREATING APPARATUS Alex J. Schregenberger, Milltown, N.J., assignor to Midland-Ross Corporation, Cleveland, Ohio, a corporation of Ohio Filed Sept. 30, 1963, Ser. No. 312,586 3 Claims. (Cl. 34-156) This invention relates to an apparatus for the treatment of web materials while being air-borne therethrough and, more particularly, to apparatus having a plenum of simplified construction adapted to heating, cooling or otherwise processing of previously wet treated, coated and/ or printed materials for an interval of time during which they are supported by a cushion of flowing gaseous fluid such as air, the air being supplied for treatment and returned to the same plenum.
It is advantageous and desirable to dry, fix, set or reduce a treated or coated web of paper or of a textile material, or of lightweight metal without injury to the web or to an applied treatment. This is generally done by airconveying the material for over a necessary or required distance without frictional support or any physical contact that would tend to injure the web or the applied treatment. A web material that has been air-conveyed and simultaneously treated during its travel through such an apparatus is generally more uniformly and thoroughly treated than by methods requiring physical support. And whatever shrinkage or change in size that will occur while being air floated and conveyed will be in all directions; the final result is a totally relaxed and stable web product.
The present invention provides for an improved treating and air-conveying apparatus wherein the web is floated or supported by a great many air jet streams at points occurring at a frequency so as to minimize undulation or possible vibration that may injure the web material or a surface applied treatment. The air support is provided in the direction of travel of the web urging it forwardly and, where the air is heated and used for drying, or heating, it is substantially recovered and reused. The recovery of once used air is simply and automatically effected by the terminal structure of the surface of the plenum. Advantageously, the plenum interior is open and clear for its entire length, simulating a rectangular unobstructed conduit for the continuous flow of a gaseous fluid therethrough.
Furthermore, support for the web moving through the apparatus can be one-sided or it can be two-sided depending on web treatment as to whether a single or opposing plenum is required. Air emitted from each plenum is returned thereto only to be emitted again in the direction of travel of the web. The outward surfaces of the opposing plenums advantageously are flat and continuous, the plenum air openings for impingement or web support and for return being positioned flush therein. The flush con struction is advantageous in that the web material will not meet any obstruction which could keep it confined in the event of a break.
The mentioned improvements and further embodiments are fully described hereinafter, illustrated in detail in the accompanying drawings in which:
FIGURE 1 is a view in side elevation, in partial section, of the web conveying apparatus;
FIGURE 2 is a plan view of the air treating and conveying apparatus;
FIGURE 3 is a schematic end view of the web inlet side of the apparatus of FIGURE 1 taken along lines 3--3 thereof;
FIGURE 4 is, likewise, an end view of the web exit end of the apparatus of FIGURE 1, taken along lines 44 thereof;
3,287,821 Patented Nov. 29, 1966 'ice FIGURES 5 and 6 are sectional details, in elevation and transverse planes, of the air inlets and exhausts of the opposing plenum surfaces taken on lines 55 of FIG- URE 2 and 6-6 of FIGURE 1;
FIGURE 7 is a sectional plan view of the surface of a plenum, showing the indented air inlets and exhausts taken on line 77 of FIGURE 1; and
FIGURE 8 is an end section of a plenum at the web exit showing air re-entry into the air pump system, taken on line 88 of FIGURE 2.
Referring now to the drawings and to FIGURES 1 to 4 thereof, a longitudinally extending rectangular chamber 10 having a web inlet 11 and exit end 12 has positioned therein two opposing box- like plenums 15, 16. Each is connected at, their ends to divided air supply inlets 17, 18, upper and lower respectively, and air exhaust returns 19 and 20 also upper and lower respectively of an air supply system. A web 21 is introduced into the inlet 11 then it is urged forwardly between the plenum faces 15, 16 toward its exit 12 by air coming from within each opposing plenum through a plurality of equi-spaced, semi-circular apertures, the angle of the impinging air jets and their return being in the direction of web 21 travel.
Web advancing and treating air is supplied through an air supply system having an air fan 25, itself being supplied from the surrounding area, from recovered air from within the apparatus itself and through dampers in the system. The supply fan forces such air into an initial common conduit 26 then to split take- off conduits 17, 18 supplying upper and lower plenums 15, 16. The air which may be heated to a desirable temperature by an interposed heater 27 positioned in conduit 26 for a specific drying or fixing treatment is being passed on through a regulating damper 30 thence through volume regulating dampers 32 and 33 in connecting diverging plenum supply conduits 17, 18, each separately supplying their respective plenums 15, 16. The additional dampers 32, 33 are provided to control the volume of the flowing air and to regulate velocities to the respective plenums 15, 16. Damper 28, located in conduit 26 between the fan 25 and damper 30, serves to exhaust a controlled amount of the air to keep the concentration of the vapors added to the air during the treating process at a desired level.
While some air is lost with the web 21 emerging out from between the plenums 15, 16 yet a substantial portion of it is recovered at about the exit 12 being returned by separate conduits 35, 36 joined to the plenum exhaust terminals to a common conduit 37 thence back to the air fan or blower 25 for recirculation. Again, the volume of recovered air for admixture is controlled by individual. dampers 38, 39 in the respective recovery conduits 35, 36. Fresh air may be added through a damper 40 and the mixture fed to the fan 25 through inlet damper 41. As
indicated, the dampers control the supplemental air to.
the fan for admixture with recovered air in accordance with requirements for recirculation.
The air circulating system as shown in FIGURES 1-4 contains one central blower or fan 25 which generally will prove suflicient for the treatment of a web of paper or other material for over a distance of about 20 feet or so. Beyond such a nominal distance another blower desirably would have to be interposed.
The compact arrangement shown in FIGURES 1-4 also is advantageously economical, being designed about the improved plenum chambers 15, 16. The plenums are simple, elongated, rectangular chambers with their are part of the same and continuing plenum surface. This construction is shown in detail in FIGURES 5, 6 and 7. Air in the plenums flows outwardly over inward indentations or scoops 44, through apertures 45 formed when the metal was die-cut, to impinge against the traveling web 21 maintaining it aloft, and over scoops 46 and through apertures 47 also against the web 21 of the plenums and 16 respectively. Since only a portion of the plenum air is being forced out through openings 45, 47, the air in the plenums themselves is flowing therethrough being at all times supplemented by external air and by the return of plenum air upon its deflection by the Web, through plenum return openings 48, directional lip 49, return openings 50 and directional scoops 51 of ple nums 15 and 16. Since the air in the plenums 15 and 16 moves at a relatively high velocity from the entering end, conduits 17 and 18, toward the leaving end, conduits 19 and 20, a suction develops downstream of the directional lips 49 and 51 effecting the removal of the air from the web into plenums 15 and 16 through openings 48 and 50 to join the flow therein to be again forced out through further similar outlets, and back in through inlets. Thus, the flow of Web supporting air is in the form of an undulating stream, the frequency of web impingement being based on the number of air outlets and inlets in the plenum surfaces.
Some of the air of necessity is exhausted to the atmosphere but a substantial portion is recovered and returned to the blower for reuse. Recovery is further assisted by a terminal consecutive plurality of plenum air return inlets. Referring to FIGURE 8, the lower terminal plenum face, as Well as the opposing upper plenum face, has several air return openings 55, 56, 57 and return scoops 58, 59, 60 for pulling in air. Opposing plenum faces at about the exit end, containing said return openings, are inclined at a shallow angle away from the web, effecting an increasingly higher static pressure between the web and the plenum faces due to a decreasing air velocity parallel to the web and effecting a decreasingly lower static pressure in the plenums 15 and 16 due to an increasing air velocity inside said plenums. The flowing air (indicated by arrows) upon supporting the moving web 21 partly escapes to the atmosphere along the web 21 but a substantial portion is pulled back into the plenum through the mentioned openings 56, 57, 58 due to the steadily increasing pressure difference betweenthe exterior and the interior of the plenum. If the web treating air was heated to effect drying, or ink fixing on the web, its return for recirculation reduces the heat input into the system. Upon prolonged operation the system becomes stabilized, additional air and heating requirements becoming nominal. For longer treating by floating requirements, an additional air supply system of the nature herein described can be added, the two being coordinated to maintain stable floating conditions.
What is claimed is:
1. Apparatus for supporting, conveying and meanwhile treating a web passing therethrough by a gaseous medium comprising, a circulating gas system including a blower, conduit means for the gaseous medium from said blower, conduit means returning said gaseous medium to said blower, opposing plenums positioned in said system between said conduits through which said gaseous medium flows dividedly and uninterruptedly, said web passing between the faces of said opposing plenums, a plurality of openings in the faces of said plenums made by perforation thereof each having the perforated sections angled as directing deflectors for directing the flow of said gaseous medium against said Web in the direction of its travel, and a further plurality of perforate openings in the same plenum face and each also having the perforate sections angled as deflectors for redirecting Web deflecting gaseous medium into said plenum and into said gas supply system for recirculation.
2. Apparatus for supporting, conveying and meanwhile treating a web passing therethrough by a gaseous medium comprising, a circulating gas supply system including a blower, conduit means for the gaseous medium from said blower, conduit means returning said gaseous medium to said blower, a plenum positioned in said system between said conduits through which said gaseous medium flows uninterruptedly, said web passing through the apparatus over said plenum, a plurality of openings in the face of the plenum having deflectors for directing the flow of said gaseous medium against said web in the direction of its travel, and a further plurality of openings in the same plenum face also having deflectors for redirecting web deflected gaseous medium into said plenum and into said gas supply system, the directing and redirecting deflectors are within the plenum interior and are part of the plenum face being angled upwardly for directing gas flow against a running web and angled downwardly into the plenum interior for redirecting gas flow into said plenum thence into said gas circulating system.
3. In apparatus characterized in claim 2 where the plenum has an additional consecutive plurality of openings having downwardly angled deflectors for redirecting gas into the plenum interior at about its end.
References Cited by the Examiner UNITED STATES PATENTS 2,144,919 1/1939 Gautreau 34-156 FOREIGN PATENTS 211,745 7/ 1909 Germany.
FREDERICK L. MA'I'I'ESON, JR., Primary Examiner.
'- JOHN J. CAMBY, Examiner.
Claims (1)
1. APPARATUS FOR SUPPORTING, CONVEYING AND MEANWHILE TREATING A WEB PASSING THERETHROUGH BY A GASEOUS MEDIUM COMPRISING, A CIRCULATING GAS SYSTEM INCLUDING A BLOWER, CONDUIT MEANS FOR GASEOUS MEDIUM FROM SAID BLOWER, CONDUIT MEANS RETURNING SAID GASEOUS MEDIUM TO SAID BLOWER, OPPOSING PLENUMS POSITIONED IN SAID SYSTEM BETWEEN SAID CONDUITS THROUGH WHICH SAID GASEOUS MEDIUM FLOWS DIVIDEDLY AND UNINTERRUPTEDLY, SAID WEB PASSING BETWEEN THE FACES OF SAID OPPOSING PLENUMS, A PLURALITY OF OPENINGS IN THE FACES OF SAID PLENUMS MADE TO PERFORATION THEREOF EACH HAVING THE PERFORATED SECTIONS ANGLED AS DIRECTING DEFLECTORS FOR DIRECTING THE FLOW OF SAID GASEOUS MEDIUM AGAINST SAID WEB IN THE DIRECTION OF ITS TRAVEL, AND A FURTHER PLURALITY OF PERFORATE OPENINGS IN THE SAME PLENUM FACE AND EACH ALSO HAVING THE PERFORATE SECTIONS ANGLED AS DEFLECTORS FOR REDIRECTING WEB DEFLECTING GASEOUS MEDIUM INTO SAID PLENUM AND INTO SAID GAS SUPPLY SYSTEM FOR RECIRCULATION.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US312586A US3287821A (en) | 1963-09-30 | 1963-09-30 | Conveying and treating apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US312586A US3287821A (en) | 1963-09-30 | 1963-09-30 | Conveying and treating apparatus |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| US3287821A true US3287821A (en) | 1966-11-29 |
Family
ID=23212140
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US312586A Expired - Lifetime US3287821A (en) | 1963-09-30 | 1963-09-30 | Conveying and treating apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US3287821A (en) |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3384282A (en) * | 1964-09-03 | 1968-05-21 | Vits G M B H Maschf | Pneumatic conveyor for strip materials |
| US3577653A (en) * | 1970-01-20 | 1971-05-04 | Beloit Corp | Web drying tunnel |
| US3622058A (en) * | 1966-11-23 | 1971-11-23 | Vits Gmbh Maschf | Contact-free holding of a web of sheet material guided in a floating manner |
| US3867085A (en) * | 1974-01-03 | 1975-02-18 | Nrm Corp | Thermoforming apparatus with web support means |
| US3907480A (en) * | 1973-01-08 | 1975-09-23 | Robert A Renoux | Apparatus for processing thin plastics film |
| WO1999036615A1 (en) * | 1998-01-15 | 1999-07-22 | ABB Fläkt AB | Method of reducing the power consumption in a plant for drying a material web |
| US6751889B2 (en) * | 2001-09-29 | 2004-06-22 | Eastman Kodak Company | Photographic media dryer |
| US20140237848A1 (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2014-08-28 | Casey E. Walker | Force-balancing gas flow in dryers for printing systems |
| WO2016173671A1 (en) * | 2015-04-30 | 2016-11-03 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Dryers for printed media |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE211745C (en) * | ||||
| US2144919A (en) * | 1937-06-24 | 1939-01-24 | Andrews And Goodrich Inc | Apparatus for and method of drying web material |
-
1963
- 1963-09-30 US US312586A patent/US3287821A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE211745C (en) * | ||||
| US2144919A (en) * | 1937-06-24 | 1939-01-24 | Andrews And Goodrich Inc | Apparatus for and method of drying web material |
Cited By (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3384282A (en) * | 1964-09-03 | 1968-05-21 | Vits G M B H Maschf | Pneumatic conveyor for strip materials |
| US3622058A (en) * | 1966-11-23 | 1971-11-23 | Vits Gmbh Maschf | Contact-free holding of a web of sheet material guided in a floating manner |
| US3577653A (en) * | 1970-01-20 | 1971-05-04 | Beloit Corp | Web drying tunnel |
| US3907480A (en) * | 1973-01-08 | 1975-09-23 | Robert A Renoux | Apparatus for processing thin plastics film |
| US3867085A (en) * | 1974-01-03 | 1975-02-18 | Nrm Corp | Thermoforming apparatus with web support means |
| WO1999036615A1 (en) * | 1998-01-15 | 1999-07-22 | ABB Fläkt AB | Method of reducing the power consumption in a plant for drying a material web |
| US6751889B2 (en) * | 2001-09-29 | 2004-06-22 | Eastman Kodak Company | Photographic media dryer |
| US20140237848A1 (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2014-08-28 | Casey E. Walker | Force-balancing gas flow in dryers for printing systems |
| US9423177B2 (en) * | 2013-02-22 | 2016-08-23 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Force-balancing gas flow in dryers for printing systems |
| WO2016173671A1 (en) * | 2015-04-30 | 2016-11-03 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Dryers for printed media |
| CN107206782A (en) * | 2015-04-30 | 2017-09-26 | 惠普发展公司,有限责任合伙企业 | Drier for print media |
| US10442184B2 (en) | 2015-04-30 | 2019-10-15 | Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. | Dryers for printed media |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4274210A (en) | Gas nozzle for use in treating material webs | |
| US3324570A (en) | Float dryer | |
| US4575952A (en) | Hot air dryer structure | |
| US4467537A (en) | Equipment for heat-treating flat, band-like lengths of material | |
| US3287821A (en) | Conveying and treating apparatus | |
| US2389586A (en) | Drying apparatus | |
| US4085522A (en) | Method and apparatus for freely suspending moving webs of material | |
| US1847915A (en) | Apparatus for drying paper and the like | |
| ES295582A1 (en) | Apparatus for stabilized transport of web-or sheet-like materials | |
| JPS5844945B2 (en) | Air column device that supports floating continuous moving strips | |
| GB1269826A (en) | Air flotation system for conveying web materials | |
| GB1207827A (en) | Apparatus for treating a layer of material | |
| US3405627A (en) | Film processor | |
| US4843731A (en) | Device for floatably guiding webs of material by means of a gaseous or liquid medium | |
| GB1244392A (en) | Method and apparatus for heat-treating planar material | |
| US3279091A (en) | Apparatus for drying a moving web over a non-rotating shell | |
| US3060595A (en) | Jet dryer | |
| US3398466A (en) | Slot apparatus for high velocity gas treatment of moving webs | |
| US4295284A (en) | Dryer range | |
| US2976794A (en) | High-velocity primary air nozzle | |
| US2071015A (en) | Method of and apparatus for drying material in sheet or web form | |
| US5074278A (en) | Pocket ventilator | |
| US3403454A (en) | Heat treating apparatus for web and sheet material | |
| US3096162A (en) | Gaseous restraint of conveyed articles | |
| US4050885A (en) | Method of drying gypsum wallboard and apparatus therefor |