TWI718245B - Integrated circuits, computer-implemented method of manufacturing the same, and standard cell defining the same - Google Patents
Integrated circuits, computer-implemented method of manufacturing the same, and standard cell defining the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- TWI718245B TWI718245B TW106104007A TW106104007A TWI718245B TW I718245 B TWI718245 B TW I718245B TW 106104007 A TW106104007 A TW 106104007A TW 106104007 A TW106104007 A TW 106104007A TW I718245 B TWI718245 B TW I718245B
- Authority
- TW
- Taiwan
- Prior art keywords
- conductive pattern
- air gap
- pattern
- timing
- integrated circuit
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/768—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics
- H01L21/76801—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics characterised by the formation and the after-treatment of the dielectrics, e.g. smoothing
- H01L21/7682—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics characterised by the formation and the after-treatment of the dielectrics, e.g. smoothing the dielectric comprising air gaps
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Design And Manufacture Of Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Evolutionary Computation (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本申請案主張於2016年2月11日提出申請的韓國專利申請案第10-2016-0015820號及於2016年8月5日提出申請的韓國專利申請案第10-2016-0100122號的優先權,所述申請案的揭露內容併入本案供參考。 This application claims the priority of Korean Patent Application No. 10-2016-0015820 filed on February 11, 2016 and Korean Patent Application No. 10-2016-0100122 filed on August 5, 2016 , The disclosed content of the application case is incorporated into this case for reference.
本發明概念的示例性實施例是有關於一種積體電路,且更具體而言,是有關於一種包括空氣間隙層的積體電路及製造其的電腦實施方法。 The exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept relates to an integrated circuit, and more specifically, to an integrated circuit including an air gap layer and a computer-implemented method for manufacturing the integrated circuit.
隨著半導體製程技術的進步,製程變得越來越精細。因此,寄生電容可隨著導電圖案之間的間隔減小而增大。為減小寄生電容,正實施其中在導電圖案之間放置空氣間隙圖案的空氣間隙技術。由於空氣具有小的介電常數,因此寄生電容可因空氣間隙圖案而減小,且半導體晶片的運作速度可得到提高。 With the advancement of semiconductor process technology, the process has become more and more sophisticated. Therefore, the parasitic capacitance may increase as the interval between the conductive patterns decreases. In order to reduce parasitic capacitance, air gap technology in which air gap patterns are placed between conductive patterns is being implemented. Since air has a small dielectric constant, the parasitic capacitance can be reduced due to the air gap pattern, and the operating speed of the semiconductor chip can be increased.
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,一種製造積體電路的電腦實施方法包括:放置多個標準元件,多個標準元件定義所述積體電路;自包含於所放置的標準元件中的多個定時路徑中選擇定時緊要路徑(timing critical path);自包含於定時緊要路徑中的多個網路中選擇至少一個網路作為至少一個定時緊要網路(timing critical net);以空氣間隙層對至少一個定時緊要網路進行預路由(pre-routing);對未選擇的網路進行路由;使用被預路由的至少一個定時緊要網路及被路由的未選擇的網路來產生佈局;以及基於佈局來製造積體電路。According to an exemplary embodiment of the concept of the present invention, a computer-implemented method for manufacturing an integrated circuit includes: placing a plurality of standard components, and the plurality of standard components define the integrated circuit; Select the timing critical path from the timing path; select at least one of the multiple networks contained in the timing critical path as at least one timing critical net; use the air gap layer to at least A timing critical network is pre-routing; the unselected network is routed; at least one timing critical network that is pre-routed and the routed unselected network are used to generate a layout; and based on the layout To manufacture integrated circuits.
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,一種積體電路包括:第一導電圖案,在第一方向上延伸;第二導電圖案,在不同於第一方向的第二方向上延伸;第一介層窗,電性連接第一導電圖案與第二導電圖案;以及第一空氣間隙圖案至第四空氣間隙圖案。第一空氣間隙圖案在第一方向上延伸且安置於第一導電圖案的第一側上。第二空氣間隙圖案在第一方向上延伸且安置於第一導電圖案的第二側上。第一導電圖案的第一側與所述第一導電圖案的第二側相對。第三空氣間隙圖案在第二方向上延伸且安置於第二導電圖案的第一側上。第四空氣間隙圖案在第二方向上延伸且安置於第二導電圖案的第二側上。第二導電圖案的第一側與第二導電圖案的第二側相對。According to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, an integrated circuit includes: a first conductive pattern extending in a first direction; a second conductive pattern extending in a second direction different from the first direction; and a first interlayer The window is electrically connected to the first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern; and the first air gap pattern to the fourth air gap pattern. The first air gap pattern extends in the first direction and is disposed on the first side of the first conductive pattern. The second air gap pattern extends in the first direction and is disposed on the second side of the first conductive pattern. The first side of the first conductive pattern is opposite to the second side of the first conductive pattern. The third air gap pattern extends in the second direction and is disposed on the first side of the second conductive pattern. The fourth air gap pattern extends in the second direction and is disposed on the second side of the second conductive pattern. The first side of the second conductive pattern is opposite to the second side of the second conductive pattern.
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,一種積體電路包括:第一導電圖案,在第一方向上延伸;第二導電圖案,在不同於第一方向的第二方向上延伸;第一介層窗,電性連接第一導電圖案與第二導電圖案;第一空氣間隙圖案,在第一方向上延伸且安置於第一導電圖案的第一側上;以及第二空氣間隙圖案,在第二方向上延伸且安置於第二導電圖案的第一側上。According to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, an integrated circuit includes: a first conductive pattern extending in a first direction; a second conductive pattern extending in a second direction different from the first direction; and a first interlayer The window electrically connects the first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern; the first air gap pattern extends in the first direction and is disposed on the first side of the first conductive pattern; and the second air gap pattern is in the second It extends in the direction and is arranged on the first side of the second conductive pattern.
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,一種積體電路包括:第一導電圖案,在第一方向上延伸;第二導電圖案,在不同於第一方向的第二方向上延伸;第三導電圖案,在第一方向上延伸;以及第一空氣間隙圖案至第三空氣間隙圖案。第一空氣間隙圖案在第一方向上延伸且安置於第一導電圖案的第一側上。第二空氣間隙圖案在第二方向上延伸且安置於第二導電圖案的第一側上。第三空氣間隙圖案在第一方向上延伸且安置於第三導電圖案的第一側上。第一導電圖案、第二導電圖案、第三導電圖案、第一空氣間隙圖案、第二空氣間隙圖案及第三空氣間隙圖案安置於同一層中。According to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, an integrated circuit includes: a first conductive pattern extending in a first direction; a second conductive pattern extending in a second direction different from the first direction; and a third conductive pattern , Extending in the first direction; and the first air gap pattern to the third air gap pattern. The first air gap pattern extends in the first direction and is disposed on the first side of the first conductive pattern. The second air gap pattern extends in the second direction and is disposed on the first side of the second conductive pattern. The third air gap pattern extends in the first direction and is disposed on the first side of the third conductive pattern. The first conductive pattern, the second conductive pattern, the third conductive pattern, the first air gap pattern, the second air gap pattern, and the third air gap pattern are arranged in the same layer.
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,一種定義積體電路的標準元件包括:第一主動區域;第二主動區域;多個鰭,在第一方向上延伸;多個第一金屬線,在與第一方向交叉的第二方向上延伸;以及第二金屬線,在第一方向上延伸。多個第一金屬線及第二金屬線安置於第一主動區域與第二主動區域之間。標準元件更包括:多個第一空氣間隙圖案,在第二方向上延伸且安置於多個第一金屬線之間;以及第二空氣間隙圖案,在第一方向上延伸且安置於第二金屬線的第一側上。According to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, a standard component defining an integrated circuit includes: a first active area; a second active area; a plurality of fins extending in a first direction; a plurality of first metal lines in and Extending in a second direction intersecting the first direction; and a second metal wire extending in the first direction. A plurality of first metal wires and second metal wires are arranged between the first active area and the second active area. The standard element further includes: a plurality of first air gap patterns extending in the second direction and disposed between the plurality of first metal lines; and a second air gap pattern extending in the first direction and disposed on the second metal On the first side of the line.
以下將參考附圖更充分地闡述本發明概念的示例性實施例。在附圖中,相同參考編號可自始至終指代相同組件。Hereinafter, exemplary embodiments of the inventive concept will be explained more fully with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the drawings, the same reference numbers may refer to the same components throughout.
應理解,在本文中使用用語「第一」、「第二」、「第三」等來區分各個組件,且所述組件並非受限於該些用語。因此,在一示例性實施例中的「第一」組件可在另一示例性實施例中被闡述為「第二」組件。更應理解,當兩個部件或方向被闡述為實質上彼此平行或彼此垂直延伸時,所述兩個部件或方向則精確地彼此平行或彼此垂直延伸,抑或近似彼此平行或彼此垂直延伸,如此項技術中具有通常知識者將理解。It should be understood that the terms "first", "second", "third", etc. are used herein to distinguish various components, and the components are not limited to these terms. Therefore, the “first” component in one exemplary embodiment may be described as the “second” component in another exemplary embodiment. It should be further understood that when two parts or directions are described as extending substantially parallel to each other or perpendicular to each other, the two parts or directions are exactly parallel to each other or extend perpendicular to each other, or approximately parallel to each other or extend perpendicular to each other, so Those who have general knowledge in this technology will understand.
圖1是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種製造積體電路的方法的流程圖。FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
參考圖1,根據示例性實施例,一種製造積體電路的方法可包括積體電路設計操作S10及積體電路製造製程S20。積體電路設計操作S10可包括其中使用用於設計積體電路的工具來設計積體電路的佈局的操作S110至操作S130。在此種情形中,用於設計積體電路的工具可為包括由處理器執行的多個指令的程式。所述程式可儲存於記憶體上。因此,積體電路設計操作S10可被稱為可由處理器執行的設計積體電路的電腦實施方法。積體電路製造製程S20對應於根據基於所設計佈局的積體電路來製造半導體裝置的操作,且可由半導體製程裝置來實行。1, according to an exemplary embodiment, a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit may include an integrated circuit design operation S10 and an integrated circuit manufacturing process S20. The integrated circuit design operation S10 may include operations S110 to S130 in which a tool for designing an integrated circuit is used to design the layout of the integrated circuit. In this case, the tool for designing the integrated circuit may be a program including multiple instructions executed by the processor. The program can be stored on the memory. Therefore, the integrated circuit design operation S10 can be referred to as a computer-implemented method for designing an integrated circuit that can be executed by a processor. The integrated circuit manufacturing process S20 corresponds to an operation of manufacturing a semiconductor device based on an integrated circuit based on the designed layout, and can be performed by a semiconductor manufacturing process device.
積體電路可由多個元件來定義。舉例而言,可使用包括所述多個元件的特徵資訊的元件庫來設計積體電路。舉例而言,在元件庫中,可定義元件的元件名稱、尺寸、閘極寬度、引腳、延遲特性、漏電流、臨限電壓、及功能。在示例性實施例中,元件庫可為標準元件庫。標準元件庫可包括例如(舉例而言)多個標準元件的佈局資訊及定時資訊等資訊。包括標準元件庫的元件庫可儲存於電腦可讀取儲存媒體中。The integrated circuit can be defined by multiple components. For example, a component library including characteristic information of the plurality of components can be used to design an integrated circuit. For example, in the component library, the component name, size, gate width, pin, delay characteristic, leakage current, threshold voltage, and function of the component can be defined. In an exemplary embodiment, the component library may be a standard component library. The standard component library may include, for example, information such as layout information and timing information of a plurality of standard components. The component library including the standard component library can be stored in a computer-readable storage medium.
在操作S110中,可例如由處理器使用放置及路由(placement and routing,P/R)工具來實行操作S110。首先,接收定義積體電路的輸入資料。此處,可藉由使用標準元件庫對以積體電路行為的摘要形式所定義的資料(例如,在暫存器轉移層次(register transfer level,RTL)中定義的資料)進行合成來產生輸入資料。輸入資料可為例如藉由對由甚高速積體電路(very high speed integrated circuit,VHSIC)硬體描述語言(hardware description language,VHDL)及硬體描述語言(hardware description language,HDL)(例如,舉例而言,VERILOG)定義的積體電路進行合成而產生的位元流或網路連線表(netlist)。隨後,對儲存有標準元件庫的儲存媒體進行存取,且放置根據輸入資料而自儲存於標準元件庫中的多個標準元件中選出的標準元件。In operation S110, operation S110 may be performed by a processor using a placement and routing (P/R) tool, for example. First, receive the input data defining the integrated circuit. Here, the input data can be generated by synthesizing the data defined in the summary form of the integrated circuit behavior (for example, the data defined in the register transfer level (RTL)) using the standard component library . The input data can be, for example, by comparing very high speed integrated circuit (VHSIC) hardware description language (VHDL) and hardware description language (hardware description language, HDL) (for example, for example, In other words, the bit stream or netlist generated by the synthesis of integrated circuits defined by VERILOG. Subsequently, the storage medium storing the standard component library is accessed, and the standard component selected from the plurality of standard components stored in the standard component library is placed according to the input data.
在操作S120中,以空氣間隙層對自所放置標準元件中選擇的網路進行預路由,如下文進一步所述。在操作S130中,對未自所放置標準元件中選擇的網路進行路由(例如,在無空氣間隙層的情況下)。本文中,空氣間隙層指代包括空氣間隙或空氣間隙圖案的層。舉例而言,可選擇包含於所放置標準元件中的所述多個網路中的至少一者,且可將所述被選擇的至少一個網路分配給空氣間隙層。在示例性實施例中,所述至少一個網路可對應於定時緊要路徑的一個網路,如下文進一步所述。In operation S120, the air gap layer is used to pre-route the network selected from the placed standard components, as described further below. In operation S130, a network that is not selected from the placed standard components is routed (for example, in the case of no air gap layer). Here, the air gap layer refers to a layer including air gaps or air gap patterns. For example, at least one of the plurality of nets included in the placed standard element may be selected, and the selected at least one net may be allocated to the air gap layer. In an exemplary embodiment, the at least one network may correspond to one network of the timing critical path, as described further below.
本文中,網路可表示積體電路的等效電路圖中的等電位(equipotential)。一個網路可對應於積體電路的佈局中的一個互連。互連可對應於例如包括彼此電性連接的多個佈線層及介層窗的佈線結構。佈線層中的每一者可包括例如多個導電圖案。形成於可安置於不同層次上的佈線層中的導電圖案可藉由由導電材料形成的介層窗而彼此電性連接。在示例性實施例中,佈線層可包含金屬作為導電材料,且可被稱為金屬層。在示例性實施例中,佈線層可包含除金屬外的導電材料。In this article, the net can represent the equipotential in the equivalent circuit diagram of an integrated circuit. One net can correspond to one interconnection in the layout of the integrated circuit. The interconnection may correspond to, for example, a wiring structure including a plurality of wiring layers and vias electrically connected to each other. Each of the wiring layers may include, for example, a plurality of conductive patterns. The conductive patterns formed in the wiring layers that can be arranged on different levels can be electrically connected to each other through the vias formed of conductive materials. In an exemplary embodiment, the wiring layer may include metal as a conductive material, and may be referred to as a metal layer. In an exemplary embodiment, the wiring layer may include conductive materials other than metals.
根據示例性實施例,網路可包括:第一導電圖案,包含於第一佈線層中;第二導電圖案,包含於第二佈線層中;以及介層窗,安置於所述第一導電圖案與所述第二導電圖案之間且電性連接所述第一導電圖案與所述第二導電圖案。所述第一佈線層與所述第二佈線層可安置於不同層次處。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,網路可包括包含於同一佈線層中的導電圖案。此外,在示例性實施例中,網路可包括包含於第一佈線層中的多個第一導電圖案以及包含於第二佈線層中的多個第二導電圖案。According to an exemplary embodiment, the net may include: a first conductive pattern included in the first wiring layer; a second conductive pattern included in the second wiring layer; and a via window disposed in the first conductive pattern The first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern are electrically connected to the second conductive pattern. The first wiring layer and the second wiring layer may be arranged at different levels. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the net may include conductive patterns included in the same wiring layer. In addition, in an exemplary embodiment, the net may include a plurality of first conductive patterns included in the first wiring layer and a plurality of second conductive patterns included in the second wiring layer.
根據示例性實施例,由於空氣間隙圖案鄰近(例如,緊鄰)與被選擇的網路對應的導電圖案安置,因此可以空氣間隙層對被選擇的網路進行預路由。在示例性實施例中,空氣間隙層可由雙向空氣間隙層來實施。舉例而言,包含於空氣間隙層中的空氣間隙圖案可在第一方向上延伸,或可在實質上垂直於所述第一方向的第二方向上延伸。以下,將參考圖2A來闡述根據示例性實施例的空氣間隙層。According to an exemplary embodiment, since the air gap pattern is disposed adjacent (for example, next to) the conductive pattern corresponding to the selected net, the selected net may be pre-routed by the air gap layer. In an exemplary embodiment, the air gap layer may be implemented by a bidirectional air gap layer. For example, the air gap pattern included in the air gap layer may extend in a first direction, or may extend in a second direction substantially perpendicular to the first direction. Hereinafter, an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment will be explained with reference to FIG. 2A.
圖2A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的包括空氣間隙層的積體電路IC的剖視圖。2A is a cross-sectional view illustrating an integrated circuit IC including an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
參考圖2A,積體電路IC可包括第一佈線層至第三佈線層M1、M2及M3、第一絕緣層ILD1及第二絕緣層ILD2、以及第一障壁層BM1及第二障壁層BM2。積體電路IC可例如根據圖1所示製程S10來設計,且可例如根據圖1所示製程S20來製造。2A, the integrated circuit IC may include first to third wiring layers M1, M2, and M3, a first insulating layer ILD1 and a second insulating layer ILD2, and a first barrier layer BM1 and a second barrier layer BM2. The integrated circuit IC can be designed, for example, according to the process S10 shown in FIG. 1, and can be manufactured, for example, according to the process S20 shown in FIG.
第一佈線層M1可在X方向上延伸,第一障壁層BM1可包括安置於第一佈線層M1上的多個障壁層,且第一絕緣層ILD1可安置於第一障壁層BM1上。第二佈線層M2可安置於第一絕緣層ILD1上且在Y方向上延伸,第二障壁層BM2可包括安置於第二佈線層M2上的多個障壁層,且第二絕緣層ILD2可安置於第二障壁層BM2上。第一絕緣層ILD1及第二絕緣層ILD2可被稱為層間介電質。第三佈線層M3安置於第二絕緣層ILD2上且在X方向上延伸。The first wiring layer M1 may extend in the X direction, the first barrier layer BM1 may include a plurality of barrier layers disposed on the first wiring layer M1, and the first insulating layer ILD1 may be disposed on the first barrier layer BM1. The second wiring layer M2 may be disposed on the first insulating layer ILD1 and extending in the Y direction, the second barrier layer BM2 may include a plurality of barrier layers disposed on the second wiring layer M2, and the second insulating layer ILD2 may be disposed On the second barrier layer BM2. The first insulating layer ILD1 and the second insulating layer ILD2 can be referred to as interlayer dielectric. The third wiring layer M3 is disposed on the second insulating layer ILD2 and extends in the X direction.
在示例性實施例中,可預先選擇第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3中的欲分配給空氣間隙層AGL的一者。在示例性實施例中,可基於第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3的高度及/或寬度來選擇欲分配給空氣間隙層AGL的佈線層。舉例而言,第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3中具有相對大的高度及/或寬度的佈線層可具有相對低的電阻。此佈線層可被選擇為空氣間隙層。舉例而言,例如第一佈線層M1等較低層次的佈線層的電阻可高於例如第三佈線層M3等較高層次的佈線層的電阻。在示例性實施例中,可基於連接第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3的介層窗的高度及/或寬度來選擇欲分配給空氣間隙層AGL的佈線層。舉例而言,例如第一佈線層M1等較低層次的佈線層的介層窗的電阻可低於例如第三佈線層M3等較高層次的佈線層的介層窗的電阻。在示例性實施例中,可基於第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3的高度及/或寬度以及連接第一佈線層M1至第三佈線層M3的介層窗的高度及/或寬度來選擇欲分配的佈線層作為空氣間隙層AGL。In an exemplary embodiment, one of the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3 to be allocated to the air gap layer AGL may be selected in advance. In an exemplary embodiment, the wiring layer to be allocated to the air gap layer AGL may be selected based on the height and/or width of the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3. For example, a wiring layer having a relatively large height and/or width among the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3 may have a relatively low resistance. This wiring layer can be selected as an air gap layer. For example, the resistance of a lower-level wiring layer such as the first wiring layer M1 may be higher than the resistance of a higher-level wiring layer such as the third wiring layer M3. In an exemplary embodiment, the wiring layer to be allocated to the air gap layer AGL may be selected based on the height and/or width of the via window connecting the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3. For example, the resistance of a via of a lower-level wiring layer such as the first wiring layer M1 may be lower than the resistance of a via of a higher-level wiring layer such as the third wiring layer M3. In an exemplary embodiment, it may be based on the height and/or width of the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3 and the height and/or width of the via window connecting the first wiring layer M1 to the third wiring layer M3. The wiring layer to be allocated is selected as the air gap layer AGL.
在示例性實施例中,第二佈線層M2可分配給包括空氣間隙圖案AGP的空氣間隙層AGL,而第一佈線層M1及第三佈線層M3可分配給不包括空氣間隙圖案AGP的正常層,如在圖2A中所示。在示例性實施例中,可以空氣間隙層AGL對第二佈線層M2進行預路由,且可以正常層對第一佈線層M1及第三佈線層M3進行路由。因此,可藉由兩階段佈線方案(two-stage wiring scheme)而對第一佈線層至第三佈線層M1、M2、及M3進行路由。在示例性實施例中,在以正常層對其他層進行路由之前或在以正常層對其他層進行路由之後,可以空氣間隙層AGL對以空氣間隙層AGL進行預路由的佈線層進行預路由。 In an exemplary embodiment, the second wiring layer M2 may be allocated to the air gap layer AGL including the air gap pattern AGP, and the first wiring layer M1 and the third wiring layer M3 may be allocated to the normal layer not including the air gap pattern AGP , As shown in Figure 2A. In an exemplary embodiment, the second wiring layer M2 may be pre-routed by the air gap layer AGL, and the first wiring layer M1 and the third wiring layer M3 may be routed in the normal layer. Therefore, a two-stage wiring scheme can be used to route the first wiring layer to the third wiring layer M1, M2, and M3. In an exemplary embodiment, before routing other layers with the normal layer or after routing other layers with the normal layer, the wiring layer pre-routed with the air gap layer AGL may be pre-routed with the air gap layer AGL.
根據示例性實施例,第二佈線層M2可包括在Y方向上延伸的導電圖案CPT以及安置於各導電圖案CPT之間的空氣間隙圖案AGP。可藉由以空氣置換各導電圖案CPT之間的金屬間介電質(inter-metal dielectric,IMD)材料來產生空氣間隙圖案AGP。由於空氣的介電係數為低的值1,因此空氣間隙圖案AGP可減小各導電圖案CPT之間的寄生電容,且因此可提高包括積體電路IC的半導體晶片的運作速度。然而,由於在產生空氣間隙圖案AGP時例如遮罩成本等製程成本增加,因此在包含於積體電路IC中的所有第一佈線層至第三佈線層M1、M2、及M3均使用空氣間隙層來實施時,晶片的製造成本顯著增加。 According to an exemplary embodiment, the second wiring layer M2 may include conductive patterns CPT extending in the Y direction and air gap patterns AGP disposed between the respective conductive patterns CPT. The air gap pattern AGP can be generated by replacing the inter-metal dielectric (IMD) material between the conductive patterns CPT with air. Since the dielectric constant of air is a low value of 1, the air gap pattern AGP can reduce the parasitic capacitance between the conductive patterns CPT, and thus can increase the operating speed of the semiconductor chip including the integrated circuit IC. However, due to the increase in process costs such as mask cost when generating the air gap pattern AGP, air gap layers are used in all the first wiring layers to the third wiring layers M1, M2, and M3 included in the integrated circuit IC. When it comes to implementation, the manufacturing cost of the wafer increases significantly.
因此,根據示例性實施例,包含於積體電路IC中的所有層(例如,圖2A中所示的示例性實施例中的第一佈線層至第三佈線層M1、M2、及M3)均不使用空氣間隙層來實施。而是,僅某些層(例如,與定時緊要路徑的網路對應的層)-例如(舉例而言)僅圖2A所示示例性實施例中的第二佈線層M2-可使用空氣間隙層來實施。因此,可在不顯著增加製造成本的情況下改良積體電路IC的效能。舉例而言,根據示例性實施例,可將其中實施有積體電路IC的晶片的運作速度提高至與其中使用空氣間隙層來實施其所有層的積體電路的水準實質上等效的水準。 Therefore, according to the exemplary embodiment, all layers included in the integrated circuit IC (for example, the first to third wiring layers M1, M2, and M3 in the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 2A) are It is implemented without using an air gap layer. Rather, only certain layers (for example, the layer corresponding to the network of the timing critical path)-for example (for example) only the second wiring layer M2 in the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 2A may use an air gap layer To implement. Therefore, the performance of the integrated circuit IC can be improved without significantly increasing the manufacturing cost. For example, according to the exemplary embodiment, the operating speed of the chip in which the integrated circuit IC is implemented can be increased to a level that is substantially equivalent to the level of the integrated circuit in which all layers of the integrated circuit are implemented using an air gap layer.
圖2B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的包括空氣間隙層的積體電路IC'的剖視圖。2B is a cross-sectional view illustrating an integrated circuit IC′ including an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
參考圖2B,積體電路IC'可包括第一佈線層至第三佈線層M1、M2'、及M3、第一絕緣層ILD1及第二絕緣層ILD2、以及第一障壁層BM1及第二障壁層BM2。圖2B中所示的示例性實施例包括與圖2A所示示例性實施例的某些相似之處。為便於闡釋,在本文中可省略先前參考圖2A所述的組件及配置的進一步詳細說明。在示例性實施例中,第二佈線層M2'可分配給包括空氣間隙圖案AGP的空氣間隙層AGL,而第一佈線層M1及第三佈線層M3可分配給不包括空氣間隙圖案AGP的一般層。2B, the integrated circuit IC' may include first to third wiring layers M1, M2', and M3, a first insulating layer ILD1 and a second insulating layer ILD2, and a first barrier layer BM1 and a second barrier. Layer BM2. The exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 2B includes certain similarities to the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 2A. For ease of explanation, further detailed description of the components and configurations previously described with reference to FIG. 2A may be omitted herein. In an exemplary embodiment, the second wiring layer M2' may be allocated to the air gap layer AGL including the air gap pattern AGP, and the first wiring layer M1 and the third wiring layer M3 may be allocated to the general air gap layer M1 and M3 that do not include the air gap pattern AGP. Floor.
根據示例性實施例,第二佈線層M2'可包括在Y方向上延伸的導電圖案CPT。舉例而言,導電圖案CPT可包括:第一導電圖案CPT1,具有安置於第一導電圖案CPT1的相對側表面上的空氣間隙圖案AGP;第二導電圖案CPT2,具有安置於第二導電圖案CPT2的一個側表面上的空氣間隙圖案AGP;以及第三導電圖案CPT3,不具有安置於第三導電圖案CPT3的任一相對側表面上的空氣間隙圖案AGP。因此,第一導電圖案CPT1及第二導電圖案CPT2可被稱為空氣間隙導電圖案,而第三導電圖案CPT3可被稱為正常導電圖案。因此,在示例性實施例中,包含於空氣間隙層AGL(例如,圖2B所示示例性實施例中的第二佈線層M2')中的導電圖案CPT中的一者可使用空氣間隙導電圖案來實施。According to an exemplary embodiment, the second wiring layer M2' may include a conductive pattern CPT extending in the Y direction. For example, the conductive pattern CPT may include: a first conductive pattern CPT1 having an air gap pattern AGP disposed on opposite side surfaces of the first conductive pattern CPT1; a second conductive pattern CPT2 having an air gap pattern disposed on the second conductive pattern CPT2 The air gap pattern AGP on one side surface; and the third conductive pattern CPT3 does not have the air gap pattern AGP disposed on either opposite side surface of the third conductive pattern CPT3. Therefore, the first conductive pattern CPT1 and the second conductive pattern CPT2 may be referred to as an air gap conductive pattern, and the third conductive pattern CPT3 may be referred to as a normal conductive pattern. Therefore, in an exemplary embodiment, one of the conductive patterns CPT included in the air gap layer AGL (for example, the second wiring layer M2' in the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 2B) may use the air gap conductive pattern To implement.
返回參考圖1,在操作S130之後,可將定義積體電路的輸出資料提供至半導體製程裝置。此處,輸出資料可具有包括標準元件的所有佈局資訊的格式。舉例而言,輸出資料可包括所有層的圖案資訊,且可具有例如圖形設計系統(graphic design system,GDS)II格式。此外,輸出資料可具有包括標準元件的外部資訊(例如,舉例而言,標準元件的引腳)的格式。舉例而言,輸出資料可具有庫交換格式(Library Exchange Format,LEF)或銀河(MILKYWAY)格式。Referring back to FIG. 1, after operation S130, the output data defining the integrated circuit may be provided to the semiconductor process device. Here, the output data may have a format including all layout information of standard components. For example, the output data may include pattern information of all layers, and may have, for example, a graphic design system (GDS) II format. In addition, the output data may have a format including external information of standard components (for example, pins of standard components). For example, the output data may have a library exchange format (LEF) or a Milky Way (MILKYWAY) format.
如上所述,根據示例性實施例,可藉由對所排列標準元件應用兩階段佈線方案而實行路由。舉例而言,所排列標準元件的路由可包括第一路由操作(例如操作S120)及第二路由操作(例如操作S130)。舉例而言,所排列標準元件中的多個定時緊要路徑中的定時緊要路徑的至少一個網路可分配給空氣間隙層,且其餘網路可分配給正常層。因此,可藉由使用少量空氣間隙層來製造高效能積體電路。As described above, according to the exemplary embodiment, routing can be performed by applying a two-stage wiring scheme to the arranged standard components. For example, the routing of the arranged standard elements may include a first routing operation (for example, operation S120) and a second routing operation (for example, operation S130). For example, at least one net of the timing critical path among the plurality of timing critical paths in the arranged standard components may be allocated to the air gap layer, and the remaining nets may be allocated to the normal layer. Therefore, a high-performance integrated circuit can be manufactured by using a small number of air gap layers.
設計積體電路的操作S10可包括上述操作S110至操作S130。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,操作S10可包括與設計積體電路相關的各種操作,例如(舉例而言)標準元件庫的產生、標準元件庫的校正、及佈局的驗證。此外,在示例性實施例中,操作S110至操作S130可對應於積體電路設計過程的後端設計過程,且可在操作S110之前實行前端設計過程。前端設計過程可包括例如設計規範的確定、動作層次(act level)的建模及驗證、暫存器轉移層次(register-transfer level,RTL)的設計、功能的驗證、邏輯的合成、及閘層次的驗證(或預先佈局的模擬)。The operation S10 of designing an integrated circuit may include the above-mentioned operations S110 to S130. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the operation S10 may include various operations related to designing an integrated circuit, such as, for example, the generation of a standard component library, the calibration of the standard component library, and the verification of the layout. In addition, in an exemplary embodiment, operations S110 to S130 may correspond to a back-end design process of an integrated circuit design process, and the front-end design process may be performed before operation S110. The front-end design process can include, for example, the determination of design specifications, the modeling and verification of the act level, the design of register-transfer level (RTL), the verification of functions, the synthesis of logic, and the gate level Verification (or pre-layout simulation).
在操作S140中,基於佈局來產生遮罩。舉例而言,首先,可基於所述佈局來實行光學鄰近校正(optical proximity correction,OPC)。光學鄰近校正是指根據光學鄰近效應而在反映錯誤的同時改變佈局的過程。隨後,可根據基於光學鄰近校正效能結果而改變的佈局來製造所述遮罩。然後,可使用反映光學鄰近校正的佈局(例如,舉例而言,反映光學鄰近校正的圖形資料系統(graphic data system,GDS))來製造所述遮罩。In operation S140, a mask is generated based on the layout. For example, first, optical proximity correction (OPC) can be implemented based on the layout. Optical proximity correction refers to the process of changing the layout while reflecting errors based on the optical proximity effect. Subsequently, the mask may be manufactured according to the layout changed based on the result of the optical proximity correction performance. Then, a layout that reflects optical proximity correction (eg, for example, a graphic data system (GDS) that reflects optical proximity correction) can be used to manufacture the mask.
在操作S150中,使用所述遮罩來製造積體電路。舉例而言,藉由使用所述遮罩對例如晶圓等半導體基板實行各種半導體製程而形成其中實施有積體電路的半導體裝置。使用所述遮罩的製程可指代例如藉由微影製程而進行的圖案化製程。可藉由圖案化製程而在半導體基板或材料層上形成所需圖案。半導體製程可包括例如沈積製程、蝕刻製程、離子化製程、及清潔製程。半導體製程可更包括例如包括以下操作的封裝製程:在印刷電路板(printed circuit board,PCB)上安裝半導體裝置及以密封劑來密封半導體。半導體製程可更包括例如測試半導體裝置或封裝的測試製程。In operation S150, the mask is used to manufacture an integrated circuit. For example, by using the mask to perform various semiconductor processes on a semiconductor substrate such as a wafer, a semiconductor device in which an integrated circuit is implemented is formed. The process using the mask may refer to, for example, a patterning process performed by a photolithography process. The desired pattern can be formed on the semiconductor substrate or material layer through a patterning process. The semiconductor process may include, for example, a deposition process, an etching process, an ionization process, and a cleaning process. The semiconductor manufacturing process may further include, for example, a packaging process including the following operations: mounting a semiconductor device on a printed circuit board (PCB) and sealing the semiconductor with an encapsulant. The semiconductor manufacturing process may further include a testing process such as testing semiconductor devices or packaging.
圖3是根據本發明概念示例性實施例的積體電路設計系統10。FIG. 3 is an integrated
參考圖3,積體電路設計系統10可包括處理器11、工作記憶體13、輸入/輸出裝置15、輔助儲存器17、及匯流排19。積體電路設計系統10可實行圖1所示積體電路設計過程。在示例性實施例中,積體電路設計系統10可由積體裝置來實施,且因此,可被稱為積體電路設計設備。積體電路設計系統10可被提供作為用於設計半導體裝置的積體電路的專用設備,且可為用於驅動各種模擬工具或設計工具的電腦。Referring to FIG. 3, the integrated
處理器11可用以執行用於實行各種積體電路設計操作中的至少一者的指令。處理器11可藉由匯流排19而實行與工作記憶體13、輸入/輸出(input/output,I/O)裝置15、及輔助儲存器17的通訊。處理器11可執行藉由驅動被加載於工作記憶體13中的放置及路由(placement and routing,P&R)模組13a及定時分析模組13b而設計積體電路的操作。舉例而言,處理器11可執行藉由執行儲存於記憶體中且與放置及路由以及定時分析相關的指令而設計積體電路的操作。The
工作記憶體13可儲存放置及路由模組13a(例如,與放置及路由相關的指令)及定時分析模組13b(例如,與定時分析相關的指令)。放置及路由模組13a及定時分析模組13b可自輔助儲存器17加載至工作記憶體13。工作記憶體13可為揮發性記憶體,例如(舉例而言)靜態隨機存取記憶體(static random access memory,SRAM)或動態隨機存取記憶體(dynamic random access memory,DRAM),抑或可為非揮發性記憶體,例如(舉例而言)相變隨機存取記憶體(phase change random access memory,PRAM)、磁阻式隨機存取記憶體(magneto-resistive random access memory,MRAM)、基於電阻的隨機存取記憶體(resistance based random access memory,ReRAM)、或反或快閃記憶體。The working
放置及路由模組13a可為例如包括用於根據圖1所示操作S110而實行排列操作以及根據圖1所示操作S120及操作S130而實行佈線操作的指令的程式。定時分析模組13b可為例如包括用於判斷是否滿足定時限制條件(timing constraint)的指令的程式。判斷是否滿足定時限制條件可包括例如對所排列標準元件中的所有定時路徑實行定時分析。定時分析模組13b可指代例如靜態定時分析(static timing analysis,STA)工具。The placement and
輸入/輸出裝置15可控制來自使用者介面裝置的使用者輸入以及輸出。輸入/輸出裝置15可包括例如(舉例而言)鍵盤、滑鼠、或觸摸板等輸入裝置,且可接收定義積體電路的輸入資料。輸入/輸出裝置15可包括例如(舉例而言)顯示器或揚聲器等輸出裝置,且可顯示例如排列結果、佈線結果、或定時分析結果。The input/
輔助儲存器17可儲存與放置及路由模組13a及定時分析模組13b相關的各種資料。輔助儲存器17可包括例如記憶卡(例如,多媒體卡(multimedia card,MMC)、嵌式多媒體卡(embedded multimedia card,eMMC)、安全數位(secure digital,SD)卡、微安全數位卡等)、固態驅動機、及硬碟驅動機。The
圖4是根據本發明概念示例性實施例的積體電路設計系統20。FIG. 4 is an integrated
參考圖4,積體電路設計系統20可包括使用者裝置21、積體電路設計平台22、及輔助儲存器23。積體電路設計系統20可實行圖1所示積體電路設計操作S10。在示例性實施例中,使用者裝置21、積體電路設計平台22、及輔助儲存器23中的至少一者可為單獨的裝置,且使用者裝置21、積體電路設計平台22、及輔助儲存器23可藉由網路經由有線/無線通訊而彼此通訊。在示例性實施例中,使用者裝置21、積體電路設計平台22、及輔助儲存器23中的至少一者可安置於與其他部件不同的位置處。Referring to FIG. 4, the integrated
使用者裝置21可包括處理器21a及使用者介面(user interface,UI)21b。處理器21a可根據經由使用者介面21b而輸入的使用者輸入來驅動積體電路設計平台22。積體電路設計平台22為一組用於設計積體電路的電腦可讀取指令,且可包括放置及路由模組22a(例如,對應於與放置及路由相關的指令)及定時分析模組22b(例如,對應於與定時分析相關的指令)。輔助儲存器23可包括元件庫資料庫(database,DB)23a及佈局資料庫23b。元件庫資料庫23a儲存與用於產生積體電路的佈局的元件相關的資訊,且佈局資料庫23b儲存與由放置及路由模組22a產生的佈局相關的資訊(例如,佈局的物理資訊)。The
圖5是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種設計積體電路的方法S10A的流程圖。FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a method S10A for designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the concept of the present invention.
參考圖5,根據示例性實施例的設計積體電路的方法S10A可對應於圖1所示積體電路設計操作S10的實施。可例如由圖3所示積體電路設計系統10的處理器11或圖4所示積體電路設計系統20的處理器21a來實行設計積體電路的方法S10A。Referring to FIG. 5, a method S10A for designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment may correspond to the implementation of the integrated circuit design operation S10 shown in FIG. 1. The method S10A of designing an integrated circuit can be implemented, for example, by the
在操作S210中,實行基楚規劃(floor planning)。基楚規劃是放置規劃階段,且指代簡要地規劃標準元件及巨集元件(macro cell)的放置/佈線方式的操作。舉例而言,基楚規劃可包括例如(舉例而言)將輸入/輸出墊、標準元件、隨機存取記憶體(random access memory,RAM)等放置於晶片中等操作。In operation S210, floor planning is implemented. Base Chu planning is the placement planning stage, and refers to the operation of briefly planning the placement/wiring methods of standard components and macro cells. For example, the infrastructure planning may include, for example, operations such as placing input/output pads, standard components, random access memory (RAM), etc. on the chip.
在操作S220中,放置定義積體電路的標準元件。之後,可實行放置後最佳化。在操作S230中,實行時脈樹合成。時脈樹合成指代當產生電路的佈局時自動地產生時脈網路以及在合適的位置處插入緩衝器的操作。一旦在操作S220及操作S230中放置標準元件且實行時脈樹合成之後,標準元件的放置便已完成。In operation S220, a standard component defining an integrated circuit is placed. After that, optimization after placement can be performed. In operation S230, clock tree synthesis is performed. Clock tree synthesis refers to the operation of automatically generating a clock network when generating the circuit layout and inserting a buffer at an appropriate position. Once the standard components are placed in operations S220 and S230 and the clock tree synthesis is performed, the placement of the standard components is completed.
在操作S240中,選擇空氣間隙層。在示例性實施例中,可選擇包含於所放置標準元件中的多個定時路徑中的定時緊要路徑,且可將所述定時緊要路徑分配給空氣間隙層。在操作S250中,選擇定時緊要路徑上的網路(以下亦被稱為定時緊要網路)。在示例性實施例中,可將包含於定時緊要路徑範圍內的網路選擇為定時緊要網路。在示例性實施例中,可在放置操作S220期間實行操作S240及/或操作S250。在示例性實施例中,可在預路由操作S260及路由操作S270期間實行操作S240及/或操作S250。In operation S240, an air gap layer is selected. In an exemplary embodiment, a timing critical path among a plurality of timing paths included in the placed standard element may be selected, and the timing critical path may be assigned to the air gap layer. In operation S250, a network on the timing critical path (hereinafter also referred to as a timing critical network) is selected. In an exemplary embodiment, the network included in the timing critical path range may be selected as the timing critical network. In an exemplary embodiment, operation S240 and/or operation S250 may be performed during the placing operation S220. In an exemplary embodiment, operation S240 and/or operation S250 may be performed during pre-routing operation S260 and routing operation S270.
在示例性實施例中,積體電路設計方法可更包括在操作S250之後重新選擇定時緊要網路的操作。舉例而言,可基於例如定時緊要網路的延遲、與定時緊要網路對應的佈線層的物理條件等而自空氣間隙層目標網路排除定時緊要網路中的某些。可經由重新選擇操作來排除該些先前被選擇的定時緊要網路。In an exemplary embodiment, the integrated circuit design method may further include an operation of reselecting the timing critical network after operation S250. For example, some of the timing critical networks can be excluded from the air gap layer target network based on, for example, the delay of the timing critical network, the physical condition of the wiring layer corresponding to the timing critical network, and the like. The previously selected timing critical networks can be excluded through the reselection operation.
在示例性實施例中,可比較與其中使用空氣間隙導電圖案(例如,圖2B所示CPT1或CPT2)對定時緊要網路進行路由的情形對應的延遲(例如,空氣間隙導電圖案路由的延遲)和與其中使用正常導電圖案(例如,圖2B所示CPT3)對定時緊要網路進行路由的情形對應的延遲(例如,正常導電圖案路由的延遲),且可基於比較結果來重新選擇定時緊要網路。舉例而言,當被選擇的定時緊要網路中的第一網路的長度為小時(例如,當第一網路連接同一佈線層的兩個連接點時),所述第一網路的空氣間隙導電圖案的延遲可大於正常導電圖案路由的延遲。因此,可自被選擇的定時緊要網路(例如,經由重新選擇操作)排除所述第一網路。In an exemplary embodiment, the delay (for example, the delay of the air gap conductive pattern routing) corresponding to the case where the air gap conductive pattern (for example, CPT1 or CPT2 shown in FIG. 2B) is used to route the timing critical network can be compared And the delay corresponding to the situation in which the normal conductive pattern (for example, CPT3 shown in FIG. 2B) is used to route the timing critical network (for example, the delay of the normal conductive pattern routing), and the timing critical network can be reselected based on the comparison result road. For example, when the length of the first net in the selected timing critical net is small (for example, when the first net connects two connection points of the same wiring layer), the air of the first net The delay of the gap conductive pattern may be greater than the delay of the routing of the normal conductive pattern. Therefore, the first network can be excluded from the selected timing critical network (for example, via a reselection operation).
在示例性實施例中,可判斷與定時緊要網路對應的導電圖案與鄰近導電圖案之間的空間是否小於臨限值,且可基於所述判斷結果來重新選擇定時緊要網路。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,若與被選擇的定時緊要網路中的第一網路對應的導電圖案附近的空間不小於臨限值,則可自被選擇的定時緊要網路(例如,經由重新選擇操作)排除所述第一網路。In an exemplary embodiment, it may be determined whether the space between the conductive pattern corresponding to the timing critical network and the adjacent conductive pattern is less than the threshold value, and the timing critical network may be reselected based on the determination result. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, if the space near the conductive pattern corresponding to the first network in the selected timing critical network is not less than the threshold value, the selected timing critical network ( For example, through a reselection operation) exclude the first network.
此外,在示例性實施例中,可確定與定時緊要網路對應的導電圖案的位置,且可基於所述確定結果來重新選擇定時緊要網路。舉例而言,當與被選擇的定時緊要網路的第一網路對應的導電圖案位於佈線層的遠端處時,可自被選擇的定時緊要網路(例如,經由重新選擇操作)排除第一網路。In addition, in an exemplary embodiment, the position of the conductive pattern corresponding to the timing critical net may be determined, and the timing critical net may be reselected based on the determination result. For example, when the conductive pattern corresponding to the first net of the selected timing critical net is located at the far end of the wiring layer, the first net can be excluded from the selected timing critical net (for example, through a reselection operation). One network.
在操作S260中,在空氣間隙層上以高優先級對定時緊要網路進行預路由。在操作S270中,對所放置標準元件中的定時路徑中的非緊要路徑的網路(以下亦被稱為未選擇的網路)進行路由。以此種方式,根據示例性實施例,在設計積體電路的方法S10A中,可藉由使用少量空氣間隙層且藉由應用兩階段佈線方案來實施高效能積體電路,其中在空氣間隙層上以相對高的優先級對包含於定時緊要路徑中的網路進行預路由,且其中在無空氣間隙層的情況下以相對低的優先級對非緊要路徑的網路進行路由。In operation S260, the timing critical network is pre-routed on the air gap layer with high priority. In operation S270, the non-critical path network (hereinafter also referred to as the unselected network) among the timing paths in the placed standard components is routed. In this way, according to an exemplary embodiment, in the method S10A of designing an integrated circuit, a high-performance integrated circuit can be implemented by using a small number of air gap layers and by applying a two-stage wiring scheme, in which the air gap layer In the above, the network included in the timing critical path is pre-routed with a relatively high priority, and the network of the non-critical path is routed with a relatively low priority without an air gap layer.
圖6是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種設計積體電路的方法S10B的流程圖。FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a method S10B for designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the concept of the present invention.
參考圖6,根據示例性實施例的設計積體電路的方法S10B可對應於圖5所示積體電路設計製程S10A的實施。可例如由圖3所示積體電路設計系統10的處理器11或圖4所示積體電路設計系統20的處理器21a來實行設計積體電路的方法S10B。Referring to FIG. 6, the method S10B for designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment may correspond to the implementation of the integrated circuit design process S10A shown in FIG. 5. The method S10B of designing an integrated circuit can be implemented, for example, by the
在操作S310中,放置定義積體電路的多個標準元件。可例如使用放置工具及路由工具(例如,圖3所示部件13a或圖4所示部件22a)來實行操作S310。在示例性實施例中,操作S310可對應於圖5所示操作S220。此外,在示例性實施例中,操作S310可對應於圖5所示操作S220及操作S230。In operation S310, a plurality of standard components defining an integrated circuit are placed. Operation S310 may be performed, for example, using a placement tool and a routing tool (for example, the
在操作S320中,可對所放置標準元件進行嘗試路由(trial-routing)。此處,嘗試路由指代用於將定時緊要路徑進行分類的路由。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中可省略操作S320。舉例而言,當僅藉由操作S310的標準元件的放置資訊來啟用定時分析時,可省略操作S320。在操作S330中,實行定時分析。舉例而言,可實行定時分析以選擇所放置標準元件中的多個定時路徑中的定時緊要路徑,且可提供定時分析結果資料。舉例而言,在操作S330中,可基於藉由實行定時分析所獲得的定時分析結果資料而自包含於所放置標準元件中的多個定時路徑中選擇定時緊要路徑。此外,可基於所述定時分析結果資料而選擇至少一個網路作為定時緊要網路。In operation S320, trial-routing may be performed on the placed standard components. Here, the attempted route refers to a route used to classify timing critical paths. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, operation S320 may be omitted in an exemplary embodiment. For example, when the timing analysis is enabled only by the placement information of the standard components in operation S310, operation S320 may be omitted. In operation S330, timing analysis is performed. For example, timing analysis can be performed to select a timing critical path among multiple timing paths in the placed standard component, and timing analysis result data can be provided. For example, in operation S330, the timing critical path may be selected from a plurality of timing paths included in the placed standard component based on the timing analysis result data obtained by performing the timing analysis. In addition, at least one network can be selected as the timing critical network based on the timing analysis result data.
定時路徑可被劃分成例如資料路徑、時脈路徑、時脈閘控路徑、及異步路徑。各定時路徑中的每一者具有起點及終點。定時路徑可指代例如積體電路的各零件之間(例如,舉例而言,輸入墊與輸出墊之間、輸入墊與正反器的資料輸入之間、正反器的資料輸出與另一正反器的資料輸入之間、以及正反器的資料輸出與輸出墊之間)的組合邏輯及互連。經過定時路徑的延遲可對積體電路的運作速度產生重大影響。The timing path can be divided into, for example, a data path, a clock path, a clock gating path, and an asynchronous path. Each of the timing paths has a start point and an end point. The timing path can refer to, for example, between the various parts of the integrated circuit (for example, between the input pad and the output pad, between the input pad and the data input of the flip-flop, the data output of the flip-flop and another Combination logic and interconnection between the data input of the flip-flop, and between the data output of the flip-flop and the output pad. The delay through the timing path can have a significant impact on the operating speed of the integrated circuit.
定時緊要路徑可指代其中自輸入(例如,起點)至輸出(例如,終點)的總定時延遲超過定時限制條件的定時路徑。其中自輸入(例如,起點)至輸出(例如,終點)的總定時延遲不超過定時限制條件的定時路徑可被稱為非緊要路徑。在示例性實施例中,定時緊要路徑可指代具有最大延遲的定時路徑。以下,將參考圖7更詳細地闡述定時分析。A timing critical path may refer to a timing path in which the total timing delay from input (eg, start point) to output (eg, end point) exceeds timing constraints. The timing path in which the total timing delay from the input (for example, the start point) to the output (for example, the end point) does not exceed the timing limit may be referred to as a non-critical path. In an exemplary embodiment, the timing critical path may refer to the timing path with the greatest delay. Hereinafter, the timing analysis will be explained in more detail with reference to FIG. 7.
圖7是繪示根據本發明概念示例性實施例的定時分析結果的曲線圖。FIG. 7 is a graph showing a timing analysis result according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
參考圖7,橫軸表示遲緩時間(slack)而縱軸表示定時路徑的數目。此處,遲緩時間表示定時要求所需要的時間與實際到達時間之間的差,且可藉由定時分析器或定時分析模組(例如,圖3所示定時分析模組13b或圖4所示定時分析模組22b)來量測。正的遲緩時間說明尚未發生定時違規(timing violation)(例如,滿足定時要求),而負的遲緩時間說明已發生定時違規(例如,不滿足定時要求)。因此,與圖7中的負遲緩時間對應的定時路徑可對應於定時緊要路徑(timing critical path,TCP)。Referring to FIG. 7, the horizontal axis represents slack and the vertical axis represents the number of timing paths. Here, the lag time represents the difference between the time required for the timing request and the actual arrival time, and can be determined by a timing analyzer or a timing analysis module (for example, the
返回參考圖6,在操作S340中,選擇定時緊要路徑的網路。舉例而言,可藉由對在操作S310中所放置的標準元件應用在操作S330中所獲取的分析資料(例如,藉由對實行操作S320的嘗試路由之前的狀態應用所述分析資料)來選擇包含於定時緊要路徑中的多個網路中的至少一者。舉例而言,可選擇與定時緊要路徑的特定範圍對應的網路。因此,在操作S340中,可自包含於定時緊要路徑中的多個網路中選擇至少一個網路。此被選擇的至少一個網路可被稱為定時緊要路徑的至少一個定時緊要網路。Referring back to FIG. 6, in operation S340, the network of the timing critical path is selected. For example, it can be selected by applying the analysis data obtained in operation S330 to the standard components placed in operation S310 (for example, by applying the analysis data to the state before the attempted routing of operation S320 is performed). At least one of the multiple networks included in the timing critical path. For example, the network corresponding to the specific range of the timing critical path can be selected. Therefore, in operation S340, at least one network may be selected from a plurality of networks included in the timing critical path. The selected at least one network may be referred to as at least one timing critical network of the timing critical path.
在操作S350中,以空氣間隙層對被選擇的網路進行預路由。在示例性實施例中,被選擇的網路可對應於包含於第一佈線層中的第一導電圖案、電性連接至所述第一導電圖案的介層窗、及包含於第二佈線層中且電性連接至所述介層窗的第二導電圖案。在示例性實施例中,可藉由在第一導電圖案的相對側上安置空氣間隙圖案以及藉由在第二導電圖案的相對側上安置空氣間隙圖案而以兩個空氣間隙層來對被選擇的網路進行路由。以下,將參考圖8以及圖9A至圖9C更詳細地闡述操作S350。In operation S350, the selected network is pre-routed with the air gap layer. In an exemplary embodiment, the selected net may correspond to a first conductive pattern included in the first wiring layer, a via window electrically connected to the first conductive pattern, and a second wiring layer included In and electrically connected to the second conductive pattern of the via. In an exemplary embodiment, two air gap layers can be selected by disposing an air gap pattern on the opposite side of the first conductive pattern and by disposing an air gap pattern on the opposite side of the second conductive pattern. Network for routing. Hereinafter, operation S350 will be explained in more detail with reference to FIG. 8 and FIGS. 9A to 9C.
圖8說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的使用空氣間隙層AGL進行路由的佈線結構81。FIG. 8 illustrates a
參考圖8,佈線結構81對應於定時緊要路徑。在佈線結構81中,以空氣間隙層AGL僅對與佈線結構81的某些區域對應的第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6進行路由。第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6可對應於定時緊要路徑的被選擇的網路(例如,定時緊要網路)。第一佈線層M1可包括第一引腳P1及第二引腳P2。第一引腳P1及第二引腳P2可對應於例如定時緊要路徑的輸入引腳(例如,起點)及輸出引腳(例如,終點)。Referring to FIG. 8, the
定時緊要路徑為所放置標準元件中的定時路徑中不滿足定時限制條件的一者。因此,定時緊要路徑的各導電圖案之間的寄生電容可顯著地影響積體電路以及包括積體電路的晶片的效能(例如,運作速度)。根據示例性實施例,以空氣間隙層對包含於定時緊要路徑中的被選擇的網路(例如,定時緊要網路)進行預路由。以空氣間隙層對被選擇的網路進行預路由包括例如在與被選擇的網路對應的佈線層的相對側上安置空氣間隙圖案。The critical timing path is one of the timing paths in the placed standard components that does not meet the timing restriction conditions. Therefore, the parasitic capacitance between the conductive patterns in the critical path of timing can significantly affect the performance (for example, the operating speed) of the integrated circuit and the chip including the integrated circuit. According to an exemplary embodiment, the air gap layer is used to pre-route the selected network included in the timing critical path (for example, the timing critical network). Pre-routing the selected net with the air gap layer includes, for example, placing an air gap pattern on the opposite side of the wiring layer corresponding to the selected net.
根據示例性實施例,由於以空氣間隙層對定時緊要路徑的被選擇的網路進行預路由,因此與定時緊要路徑的被選擇的網路對應的各導電圖案之間的寄生電容可減小。因此,定時緊要路徑的定時延遲可減小,從而使得定時緊要路徑滿足定時限制條件。因此,可提高積體電路及包括積體電路的晶片的運作速度。According to an exemplary embodiment, since the selected network of the timing critical path is pre-routed with the air gap layer, the parasitic capacitance between the conductive patterns corresponding to the selected network of the timing critical path can be reduced. Therefore, the timing delay of the timing critical path can be reduced, so that the timing critical path meets the timing constraints. Therefore, the operating speed of the integrated circuit and the chip including the integrated circuit can be increased.
圖9A至圖9E是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的以空氣間隙層進行路由的定時緊要網路的立體圖。在圖9A以及圖9C至圖9E中例示的定時緊要網路可例如對應於圖8所示第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6。在圖9B中例示的定時緊要網路可包括第五佈線層M5及第八佈線層M8,如下文進一步所述。9A to 9E are perspective views illustrating a timing critical network routed with an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept. The timing critical net illustrated in FIGS. 9A and 9C to 9E may correspond to, for example, the fifth wiring layer M5 and the sixth wiring layer M6 shown in FIG. 8. The timing critical net illustrated in FIG. 9B may include a fifth wiring layer M5 and an eighth wiring layer M8, as described further below.
參考圖9A,可在連續金屬層(例如,連續佈線層)上安置雙向空氣間隙層。舉例而言,可在連續第五佈線層M5及連續第六佈線層M6上安置包括空氣間隙圖案AGP1、空氣間隙圖案AGP1’、 空氣間隙圖案AGP2、及空氣間隙圖案AGP2’的雙向空氣間隙層。在圖9A中,定時緊要網路100可為連接第一連接點CP1與第二連接點CP2的網路。定時緊要網路100可包括:第五佈線層M5,電性連接至第一連接點CP1;介層窗V5,安置於第五佈線層M5上且電性連接至第五佈線層M5;以及第六佈線層M6,安置於介層窗V5上且電性連接至介層窗V5及第二連接點CP2。第五佈線層M5可在Y方向上延伸,而第六佈線層M6可在X方向上延伸。在所有各圖中,X方向與Y方向可實質上彼此垂直。第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6可分別對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6。Referring to FIG. 9A, a bidirectional air gap layer may be disposed on a continuous metal layer (for example, a continuous wiring layer). For example, a bidirectional air gap layer including air gap pattern AGP1, air gap pattern AGP1', air gap pattern AGP2, and air gap pattern AGP2' can be disposed on the continuous fifth wiring layer M5 and the continuous sixth wiring layer M6. In FIG. 9A, the timing-
在圖9A所示示例性實施例中,第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6兩者可由空氣間隙層來實施。舉例而言,可在第五佈線層M5的相對兩側上安置空氣間隙圖案AGP1及空氣間隙圖案AGP1’,且可在第六佈線層M6的相對兩側上安置空氣間隙圖案AGP2及AGP2’。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,可在第五佈線層M5的僅一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案,且可在第五佈線層M5的相對的側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質。相似地,可在第六佈線層M6的僅一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案,且可在第六佈線層M6的相對的側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質。In the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 9A, both the fifth wiring layer M5 and the sixth wiring layer M6 may be implemented by an air gap layer. For example, the air gap pattern AGP1 and the air gap pattern AGP1' may be arranged on the opposite sides of the fifth wiring layer M5, and the air gap patterns AGP2 and AGP2' may be arranged on the opposite sides of the sixth wiring layer M6. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, an air gap pattern may be disposed on only one side of the fifth wiring layer M5, and an intermetallic containing a general dielectric material may be disposed on the opposite side of the fifth wiring layer M5. Dielectric. Similarly, an air gap pattern may be disposed on only one side of the sixth wiring layer M6, and an intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the opposite side of the sixth wiring layer M6.
在示例性實施例中,空氣間隙圖案AGP1及空氣間隙圖案AGP1’可在Y方向上延伸,而空氣間隙圖案AGP2及AGP2’可在X方向上延伸。根據示例性實施例,定時緊要網路100可如9A中所示由包括空氣間隙圖案且在在兩個不同方向上延伸的雙向空氣間隙層來實施。此外,根據示例性實施例,可如圖9A以及圖9C至圖9E中所示在Z方向上的兩個連續佈線層上抑或如圖9B中所示在Z方向上的兩個非連續佈線層上安置空氣間隙圖案。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6為如圖9A以及圖9C至圖9E中所示在Z方向上鄰近(例如,緊鄰)彼此的兩個連續佈線層,且由空氣間隙層實施。因此,根據示例性實施例,由於利用雙向空氣間隙層,因此可增大空氣間隙體積,而無論定時緊要網路100的第一連接點CP1及第二連接點CP2的位置如何。因此,可增大積體電路的效能增益。在示例性實施例中,空氣間隙體積可因利用雙向空氣間隙層而變為約100%,而無論定時緊要網路100的第一連接點CP1及第二連接點CP2的位置如何。In an exemplary embodiment, the air gap pattern AGP1 and the air gap pattern AGP1' may extend in the Y direction, and the air gap patterns AGP2 and AGP2' may extend in the X direction. According to an exemplary embodiment, the timing critical net 100 may be implemented by a bidirectional air gap layer that includes an air gap pattern and extends in two different directions as shown in 9A. In addition, according to an exemplary embodiment, it may be on two continuous wiring layers in the Z direction as shown in FIG. 9A and FIGS. 9C to 9E or on two non-continuous wiring layers in the Z direction as shown in FIG. 9B Place an air gap pattern on it. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the fifth wiring layer M5 and the sixth wiring layer M6 are two consecutive layers that are adjacent (for example, next to each other) in the Z direction as shown in FIGS. 9A and 9C to 9E. The wiring layer is implemented by the air gap layer. Therefore, according to the exemplary embodiment, due to the use of the bidirectional air gap layer, the air gap volume can be increased regardless of the positions of the first connection point CP1 and the second connection point CP2 of the timing
參考圖9B,可在非連續金屬層(例如,非連續佈線層)上安置雙向空氣間隙層。舉例而言,可在非連續的第五佈線層M5及第八佈線層M8上安置包括空氣間隙圖案AGP1、空氣間隙圖案AGP1’、 空氣間隙圖案AGP2、及空氣間隙圖案AGP2’的雙向空氣間隙層。可在非連續的第五佈線層M5與第八佈線層M8之間安置中間佈線層M6及中間佈線層M7。在圖9B中,定時緊要網路100可為連接第一連接點CP1與第二連接點CP2的網路。定時緊要網路100可包括:第五佈線層M5,電性連接至第一連接點CP1;介層窗V5,安置於第五佈線層M5上且電性連接至第五佈線層M5;第六佈線層M6,安置於介層窗V5上且電性連接至介層窗V5;介層窗V6,安置於第六佈線層M6上且電性連接至第六佈線層M6;第七佈線層M7,安置於介層窗V6上且電性連接至介層窗V6;介層窗V7,安置於第七佈線層M7上且電性連接至第七佈線層M7;以及第八佈線層M8,安置於介層窗V7上且電性連接至介層窗V7及第二連接點CP2。第五佈線層M5及第七佈線層M7可在Y方向上延伸,而第六佈線層M6及第八佈線層M8可在X方向上延伸。在所有各圖中,X方向與Y方向可實質上彼此垂直。Referring to FIG. 9B, a bidirectional air gap layer may be disposed on a discontinuous metal layer (for example, a discontinuous wiring layer). For example, a bidirectional air gap layer including an air gap pattern AGP1, an air gap pattern AGP1', an air gap pattern AGP2, and an air gap pattern AGP2' can be arranged on the discontinuous fifth wiring layer M5 and the eighth wiring layer M8. . The intermediate wiring layer M6 and the intermediate wiring layer M7 may be disposed between the discontinuous fifth wiring layer M5 and the eighth wiring layer M8. In FIG. 9B, the timing
在圖9B所示示例性實施例中,作為非連續佈線層的第五佈線層M5與第八佈線層M8可由空氣間隙層實施。舉例而言,可在第五佈線層M5的相對兩側上安置空氣間隙圖案AGP1及空氣間隙圖案AGP1’,且可在第八佈線層M8的相對兩側上安置空氣間隙層AGP2及空氣間隙圖案AGP2’。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,可在第五佈線層M5的僅一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案,且可在第五佈線層M5的相對的側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質。相似地,可在第八佈線層M8的僅一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案,且可在第八佈線層M8的相對的側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質。在示例性實施例中,空氣間隙圖案AGP1及空氣間隙圖案AGP1’可在Y方向上延伸,而空氣間隙圖案AGP2及空氣間隙圖案AGP2’可在X方向上延伸。根據示例性實施例,可如圖9B所示在Z方向上的兩個非連續佈線層上安置空氣間隙圖案。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,第五佈線層M5及第八佈線層M8如圖9B中所示為在Z方向上不鄰近(例如,不緊鄰)彼此的兩個非連續佈線層,且可由空氣間隙層來實施。In the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 9B, the fifth wiring layer M5 and the eighth wiring layer M8, which are discontinuous wiring layers, may be implemented by air gap layers. For example, the air gap pattern AGP1 and the air gap pattern AGP1' may be arranged on opposite sides of the fifth wiring layer M5, and the air gap layer AGP2 and the air gap pattern may be arranged on opposite sides of the eighth wiring layer M8 AGP2'. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, an air gap pattern may be disposed on only one side of the fifth wiring layer M5, and an intermetallic containing a general dielectric material may be disposed on the opposite side of the fifth wiring layer M5. Dielectric. Similarly, an air gap pattern may be disposed on only one side of the eighth wiring layer M8, and an intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the opposite side of the eighth wiring layer M8. In an exemplary embodiment, the air gap pattern AGP1 and the air gap pattern AGP1' may extend in the Y direction, and the air gap pattern AGP2 and the air gap pattern AGP2' may extend in the X direction. According to an exemplary embodiment, an air gap pattern may be arranged on two discontinuous wiring layers in the Z direction as shown in FIG. 9B. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the fifth wiring layer M5 and the eighth wiring layer M8 are two non-contiguous wiring layers that are not adjacent (for example, not immediately adjacent) to each other in the Z direction as shown in FIG. 9B, And can be implemented by an air gap layer.
參考圖9C至圖9E,可在第五佈線層M5及/或第六佈線層M6的僅一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案。可在僅在其一個側上安置空氣間隙圖案的第五佈線層M5及/或第六佈線層M6的相對的側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質。舉例而言,在圖9C所示示例性實施例中,雙向空氣間隙層可包括安置於第五佈線層M5的相對兩側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP1及空氣間隙圖案AGP1’以及安置於第六佈線層M6的僅一個側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP2。包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質可安置於第六佈線層M6的不包括鄰近其安置的空氣間隙圖案的一側上。在圖9D所示示例性實施例中,雙向空氣間隙層可包括安置於第六佈線層M6的相對兩側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP2及空氣間隙圖案AGP2’以及安置於第五佈線層M5的僅一個側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP1。包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質可安置於第五佈線層的不包括鄰近其安置的空氣間隙圖案的一側上。在圖9E所示示例性實施例中,雙向空氣間隙層可包括安置於第五佈線層M5的僅一個側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP1以及安置於第六佈線層M6的僅一個側上的空氣間隙圖案AGP2。包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質可安置於第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6的不包括鄰近其安置的空氣間隙圖案的一側上。Referring to FIGS. 9C to 9E, an air gap pattern may be disposed on only one side of the fifth wiring layer M5 and/or the sixth wiring layer M6. An intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the opposite side of the fifth wiring layer M5 and/or the sixth wiring layer M6 on which the air gap pattern is disposed only on one side. For example, in the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 9C, the bidirectional air gap layer may include air gap patterns AGP1 and AGP1' disposed on opposite sides of the fifth wiring layer M5, and the sixth wiring layer M5. The air gap pattern AGP2 on only one side of the layer M6. An intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the side of the sixth wiring layer M6 that does not include the air gap pattern disposed adjacent thereto. In the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 9D, the bidirectional air gap layer may include the air gap pattern AGP2 and the air gap pattern AGP2' disposed on opposite sides of the sixth wiring layer M6, and only the air gap pattern AGP2' disposed on the fifth wiring layer M5. Air gap pattern AGP1 on one side. An intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the side of the fifth wiring layer that does not include the air gap pattern disposed adjacent thereto. In the exemplary embodiment shown in FIG. 9E, the bidirectional air gap layer may include an air gap pattern AGP1 disposed on only one side of the fifth wiring layer M5 and an air gap disposed on only one side of the sixth wiring layer M6 Pattern AGP2. An intermetal dielectric including a general dielectric material may be disposed on the side of the fifth wiring layer M5 and the sixth wiring layer M6 that does not include the air gap pattern disposed adjacent thereto.
如參考圖9A至圖9E所述,可以各種方式實行對被選擇的網路(例如,定時緊要網路)的預路由。舉例而言,可基於定時分析結果而根據遲緩時間的大小來可變地確定空氣間隙層的數目及/或空氣間隙圖案的數目。此外,可鑒於其他限制條件(例如,舉例而言,功率限制條件或面積限制條件以及定時限制條件)來可變地確定空氣間隙層的數目及/或空氣間隙圖案的數目。可以上述方式利用空氣間隙層對多個被選擇的網路(例如,定時緊要網路)進行預路由。As described with reference to FIGS. 9A to 9E, the pre-routing of the selected network (for example, the timing critical network) can be implemented in various ways. For example, the number of air gap layers and/or the number of air gap patterns can be variably determined according to the size of the lag time based on the timing analysis result. In addition, the number of air gap layers and/or the number of air gap patterns can be variably determined in view of other constraints (for example, power constraints or area constraints, and timing constraints). The air gap layer can be used to pre-route multiple selected networks (for example, timing critical networks) in the above-mentioned manner.
返回參考圖6,在操作S360中,對未選擇的網路進行路由。在示例性實施例中,未選擇的網路可包括在標準元件中的所述多個定時路徑中的非緊要路徑中所包含的網路。此外,未選擇的網路可包括在定時緊要路徑中所包含的除在操作S340中所選擇的網路外的網路。舉例而言,在定時緊要路徑內,某些網路可被選擇為定時緊要網路且可以空氣間隙層來進行預路由,而其他網路可不被選擇且可在無空氣間隙層的情況下進行路由(例如,以不包括空氣間隙圖案的層進行路由)。未選擇的網路亦可被稱為非緊要網路。Referring back to FIG. 6, in operation S360, the unselected network is routed. In an exemplary embodiment, the unselected network may include a network included in a non-critical path among the plurality of timing paths in the standard element. In addition, the unselected network may include the network included in the timing critical path other than the network selected in operation S340. For example, in the timing critical path, certain networks can be selected as timing critical networks and can be pre-routed with an air gap layer, while other networks can be unselected and can be performed without an air gap layer. Routing (for example, routing in a layer that does not include an air gap pattern). The unselected network can also be called a non-critical network.
在示例性實施例中,未選擇的網路可對應於包含於第一佈線層中的第一導電圖案、電性連接至所述第一導電圖案的介層窗、以及包含於第二佈線層中且電性連接至所述介層窗的第二導電圖案。未選擇的網路可在無空氣間隙層的情況下進行路由。舉例而言,可藉由在第一導電圖案及第二導電圖案中的每一者的相對兩側上安置一般介電材料而非在第一導電圖案及第二導電圖案中的每一者的相對兩側上安置空氣間隙圖案來對未選擇的網路進行路由。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,可以空氣間隙層對未選擇的網路中的至少一者進行路由。舉例而言,定時緊要路徑的數目或長度可相對小(例如,小於預定臨限值),且包含於定時緊要路徑中的網路的數目亦可相對小(例如,小於預定臨限值)。因此,在操作S340中所選擇的網路的數目可為小的。在此種情形中,當空氣間隙層的資源剩餘時,可以空氣間隙層對操作S360中未選擇的網路中的至少一者進行路由。In an exemplary embodiment, the unselected net may correspond to a first conductive pattern included in the first wiring layer, a via window electrically connected to the first conductive pattern, and a second wiring layer included In and electrically connected to the second conductive pattern of the via. Unselected networks can be routed without an air gap layer. For example, it is possible to arrange a general dielectric material on opposite sides of each of the first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern instead of each of the first conductive pattern and the second conductive pattern. Air gap patterns are placed on opposite sides to route unselected nets. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, at least one of the unselected networks may be routed through an air gap layer. For example, the number or length of critical timing paths may be relatively small (for example, less than a predetermined threshold), and the number of networks included in critical timing paths may also be relatively small (for example, less than a predetermined threshold). Therefore, the number of networks selected in operation S340 may be small. In this case, when the resources of the air gap layer remain, the air gap layer may route at least one of the networks not selected in operation S360.
以下,將參考圖10來更詳細地闡述操作S360。Hereinafter, operation S360 will be explained in more detail with reference to FIG. 10.
圖10說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的使用正常層而進行路由的佈線結構101。FIG. 10 illustrates a
參考圖10,佈線結構101可對應於非緊要路徑,且包含於佈線結構101中的第一佈線層M1至第六佈線層M6可以正常層來進行路由(例如,在無空氣間隙層的情況下進行路由)。第一佈線層M1可包括第一引腳P1及第二引腳P2。第一引腳P1及第二引腳P2可分別對應於例如非緊要路徑的輸入引腳(例如,起點)以及輸出引腳(例如,終點)。10, the
非緊要路徑為所放置標準元件中的定時路徑中滿足定時限制條件的一者。因此,非緊要路徑的各導電圖案之間的寄生電容可不會顯著影響積體電路及包括積體電路的晶片的效能(例如,運作速度)。因此,根據示例性實施例,可由正常層替代空氣間隙層來對包含於非緊要路徑中的網路進行路由。舉例而言,可在佈線層的與包含於非緊要路徑中的網路對應的相對兩側上安置包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質(例如,而非在其相對兩側上安置空氣間隙圖案)。The non-critical path is one of the timing paths in the placed standard components that meets the timing restriction conditions. Therefore, the parasitic capacitance between the conductive patterns of the non-critical path may not significantly affect the performance (for example, the operating speed) of the integrated circuit and the chip including the integrated circuit. Therefore, according to an exemplary embodiment, the air gap layer may be replaced by the normal layer to route the network included in the non-critical path. For example, an intermetallic dielectric containing a general dielectric material can be placed on opposite sides of the wiring layer corresponding to the net included in the non-critical path (for example, instead of placing air on opposite sides thereof) Gap pattern).
根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,可藉由以下方式來減少在製造包括空氣間隙層的積體電路時使用的空氣間隙層的數目:以空氣間隙層對定時緊要路徑的被選擇的網路進行預路由,以及以正常層(例如,使用包含一般介電材料的金屬間介電質)而非空氣間隙層來對未選擇的網路(例如,非緊要路徑的網路及/或定時緊要路徑的未選擇的網路)進行路由。因此,可降低積體電路的製造成本,且可提高積體電路及包括積體電路的晶片的運作速度。According to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, the number of air gap layers used when manufacturing an integrated circuit including an air gap layer can be reduced by the following ways: the air gap layer is used to select the network of the critical path for timing Perform pre-routing, and use normal layers (for example, using intermetallic dielectrics containing general dielectric materials) instead of air gap layers for unselected networks (for example, non-critical path networks and/or timing critical Path of the unselected network) for routing. Therefore, the manufacturing cost of the integrated circuit can be reduced, and the operating speed of the integrated circuit and the chip including the integrated circuit can be increased.
返回參考圖6,在操作S370中,實行路由後最佳化。路由後最佳化會糾正在路由完成之後可能存在的定時及/或設計規則的違規。在路由後最佳化之後,可藉由實行工程設計變更命令(engineering change order,ECO)路由並在網路連線表中反映任何改變而產生最終佈局。Referring back to FIG. 6, in operation S370, post-routing optimization is performed. Post-routing optimization will correct timing and/or design rule violations that may exist after routing is completed. After the post-routing optimization, the final layout can be generated by implementing engineering change order (ECO) routing and reflecting any changes in the network connection table.
圖11A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路200的平面圖。圖11B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖11A所示積體電路200的立體圖。FIG. 11A is a plan view illustrating an
參考圖11A及圖11B,積體電路200可對應於包括第一連接點210及第二連接點215(在圖11A及圖11B中由CP標示)以及導電圖案220(在圖11A及圖11B中由Mb標示)的一個網路。第一連接點210與第二連接點215可安置於同一層中,且第一連接點210與第二連接點215的Y座標可為相同的而第一連接點210與第二連接點215的X座標可為不同的。積體電路200可包括例如安置於第一連接點210與第二連接點215之間的導電圖案220以及安置於導電圖案220的相對兩側上的空氣間隙圖案230及235(在圖11A及圖11B中由AGPb標示)。Referring to FIGS. 11A and 11B, the
在示例性實施例中,導電圖案220可對應於定時緊要路徑。因此,空氣間隙圖案230及空氣間隙圖案235可安置於導電圖案220的相對兩側上。導電圖案220可在X方向上延伸,且因此,空氣間隙圖案230及空氣間隙圖案235亦可在X方向上延伸。導電圖案220可對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5或第六佈線層M6。In an exemplary embodiment, the
圖12是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路300的平面圖。圖12B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖12A所示積體電路300的立體圖。FIG. 12 is a plan view illustrating an
參考圖12A及圖12B,積體電路300可對應於包括第一連接點310及第二連接點315(在圖12A及圖12B中由CP標示)以及第一導電圖案320及第二導電圖案350(在圖12A及圖12B中分別由Ma及Mb標示)的一個網路。第一連接點310與第二連接點315可安置於不同層中,且第一連接點310與第二連接點315的Y座標可為相同的而第一連接點310與第二連接點315的X座標可為不同的。積體電路300可包括例如:第一導電圖案320,連接至第一連接點310;第一介層窗340及第二介層窗345,安置於第一導電圖案320上;第二導電圖案350,安置於第二介層窗345上;第一空氣間隙圖案330及第一空氣間隙圖案335(在圖12A及圖12B中由AGPa標示),安置於第一導電圖案320的相對兩側上;以及第二空氣間隙圖案360及第二空氣間隙圖案365(在圖12A及圖12B中由AGPb標示),安置於第二導電圖案350的相對兩側上。Referring to FIGS. 12A and 12B, the
在示例性實施例中,第一導電圖案320及第二導電圖案350可對應於定時緊要路徑。因此,第一空氣間隙圖案330及第一空氣間隙圖案335可安置於第一導電圖案320的相對兩側上,且第二空氣間隙圖案360及第二空氣間隙圖案365可安置於第二導電圖案350的相對兩側上。第一導電圖案320可在X方向上延伸,且因此,第一空氣間隙圖案330及第一空氣間隙圖案335亦可在X方向上延伸。第二導電圖案350可在X方向上延伸,且因此,第二空氣間隙圖案360及第二空氣間隙圖案365亦可在X方向上延伸。第一導電圖案320及第二導電圖案350可分別對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6。In an exemplary embodiment, the first
圖13A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路400的平面圖。圖13B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖13A所示積體電路400的立體圖。FIG. 13A is a plan view illustrating an
參考圖13A及圖13B,積體電路400可對應於包括第一連接點410及第二連接點415(在圖13A及圖13B中由CP標示)以及導電圖案420(在圖13A及圖13B中由Ma標示)的一個網路。第一連接點410與第二連接點415可安置於同一層中,且第一連接點410與第二連接點415的X座標可為相同的而第一連接點410與第二連接點415的Y座標可為不同的。積體電路400可包括例如安置於第一連接點410與第二連接點415之間的導電圖案420以及安置於導電圖案420的相對側上的空氣間隙圖案430及空氣間隙圖案435。Referring to FIGS. 13A and 13B, the
在示例性實施例中,導電圖案420可對應於定時緊要路徑。因此,空氣間隙圖案430及空氣間隙圖案435(在圖13A及圖13B中由AGPa標示)可安置於導電圖案420的相對側上。導電圖案420可在Y方向上延伸,且因此,空氣間隙圖案430及空氣間隙圖案435亦可在Y方向上延伸。導電圖案420可對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5或第六佈線層M6。In an exemplary embodiment, the
圖14A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路600的平面圖。圖14B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖14A所示積體電路600的立體圖。14A is a plan view illustrating an
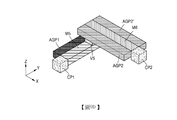
參考圖14A及圖14B,積體電路600可對應於包括第一連接點610及第二連接點615(在圖14A及圖14B中由CP標示)以及第一導電圖案620及第二導電圖案650(在圖14A及圖14B中分別由Ma及Mb標示)的一個網路。第一連接點610與第二連接點615可安置於不同層中,且第一連接點610與第二連接點615的X座標及Y座標可為不同的。積體電路600可包括例如:第一導電圖案620,連接至第一連接點610;介層窗640,安置於第一導電圖案620上;第二導電圖案650,安置於介層窗640上;第一空氣間隙圖案630及第一空氣間隙圖案635(在圖14A及圖14B中由AGPa標示),安置於第一導電圖案620的相對側上;以及第二空氣間隙圖案660及第二空氣間隙圖案665(在圖14A及圖14B中由AGPb標示),安置於第二導電圖案650的相對兩側上。Referring to FIGS. 14A and 14B, the
在示例性實施例中,第一導電圖案620及第二導電圖案650可對應於定時緊要路徑。因此,第一空氣間隙圖案630及第一空氣間隙圖案635可安置於第一導電圖案620的相對兩側上,且第二空氣間隙圖案660及第二空氣間隙圖案665可安置於第二導電圖案650的相對兩側上。第一導電圖案620可在Y方向上延伸,且因此,第一空氣間隙圖案630及第一空氣間隙圖案635亦可在Y方向上延伸。第二導電圖案650可在X方向上延伸,且因此,第二空氣間隙圖案660及第二空氣間隙圖案665亦可在X方向上延伸。第一導電圖案620及第二導電圖案650可分別對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6。In an exemplary embodiment, the first
以此種方式,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,第一空氣間隙圖案630及第一空氣間隙圖案635可被安置成在Y方向上延伸,而第二空氣間隙圖案660及第二空氣間隙圖案665可被安置成在X方向上延伸。因此,第一空氣間隙圖案630、第一空氣間隙圖案635、以及第二空氣間隙圖案660、第二空氣間隙圖案665由雙向空氣間隙圖案來實施。因此,在Z方向上鄰近(例如,緊鄰)彼此的兩個連續層可由空氣間隙層來實施(例如,每一連續層均可包括空氣間隙圖案)。舉例而言,當僅利用單向空氣間隙圖案時,兩個鄰近(例如,緊鄰)層可不由空氣間隙層實施,而僅交替排列的層可由空氣間隙層來實施。在本發明概念的示例性實施例中,利用雙向空氣間隙圖案來容許在Z方向上鄰近(例如,緊鄰)彼此的兩個連續層由空氣間隙層來實施。舉例而言,根據示例性實施例,鄰近(例如,緊鄰)彼此的兩個層可分別包括空氣間隙圖案。因此,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,可減小與定時緊要路徑的網路對應的各導電圖案之間的寄生電容,且可提高積體電路及包括積體電路的晶片的運作速度。In this way, according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, the first
圖15是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路700的立體圖。15 is a perspective view illustrating an
參考圖15,積體電路700可對應於包括第一連接點710及第二連接點715(在圖15中由CP標示)以及第一導電圖案720a至第三導電圖案720c(在圖15中由Mx標示)的一個網路。第一連接點710與第二連接點715可安置於同一層中,且第一連接點710與第二連接點715的X座標及Y座標可為不同的。第一導電圖案720a至第三導電圖案720c可安置於同一層中。第一導電圖案720a至第三導電圖案720c可對應於例如圖8所示第五佈線層M5或第六佈線層M6。15, the
在示例性實施例中,安置於同一層中的第一導電圖案720a至第三導電圖案720c可對應於定時緊要路徑。因此,第一導電圖案720a至第三導電圖案720c可由空氣間隙導電圖案來實施。舉例而言,第一空氣間隙圖案730a及第一空氣間隙圖案735a(在圖15中由AGPx標示)可安置於第一導電圖案720a的相對兩側上。第一導電圖案720a以及第一空氣間隙圖案730a及第一空氣間隙圖案735a可在X方向上延伸。第二空氣間隙圖案730b及第二空氣間隙圖案735b(在圖15中由AGPx標示)可安置於第二導電圖案720b的相對兩側上。第二導電圖案720b以及第二空氣間隙圖案730b及第二空氣間隙圖案735b可在Y方向上延伸。第三空氣間隙圖案730c及第三空氣間隙圖案735c(在圖15中由AGPx標示)可安置於第三導電圖案720c的相對兩側上。第三導電圖案720c以及第三空氣間隙圖案730c及第三空氣間隙圖案735c可在X方向上延伸。In an exemplary embodiment, the first to third
第二空氣間隙圖案730b及第二空氣間隙圖案735b可在Y方向上延伸,而第一空氣間隙圖案730a及第一空氣間隙圖案735a以及第三空氣間隙圖案730c及第三空氣間隙圖案735c可在X方向上延伸。因此,在示例性實施例中,安置於同一層中的第一空氣間隙圖案730a至第三空氣間隙圖案735c可由雙向空氣間隙圖案實施。因此,在示例性實施例中,在不同方向上延伸且安置於同一層中的導電圖案可由空氣間隙導電圖案來實施。The second
圖16是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路800的立體圖。FIG. 16 is a perspective view illustrating an
參考圖16,積體電路800可對應於包括第一連接點810及第二連接點815(在圖16中由CP標示)以及第一導電圖案820至第四導電圖案850(在圖16中由Ma、Ma+2、及Mb、Mb+2標示)的一個網路。第一連接點810與第二連接點815可安置於不同層中,且第一連接點810與第二連接點815的X座標及Y座標可為不同的。第一導電圖案820至第四導電圖案850可安置於不同層中。第一導電圖案820及第二導電圖案830可分別對應於圖8所示第五佈線層M5及第六佈線層M6,且第三導電圖案840及第四導電圖案850可對應於安置於第六佈線層M6上方的第七佈線層及第八佈線層。Referring to FIG. 16, the
積體電路800可包括例如:第一導電圖案820,連接至第一連接點810;介層窗880,安置於第一導電圖案820上;第二導電圖案830,安置於介層窗880上;介層窗885,安置於第二導電圖案830上;第三導電圖案840,安置於介層窗885上;介層窗890,安置於第三導電圖案840上;以及第四導電圖案850,安置於介層窗890上。積體電路800可更包括安置於第一導電圖案820的相對兩側上的第一空氣間隙圖案860及第一空氣間隙圖案865(在圖16中由AGPa標示)以及安置於第四導電圖案850的相對兩側上的第二空氣間隙圖案870及第二空氣間隙圖案875(在圖16中由AGPb標示)。The
在示例性實施例中,安置於不同層中的第一導電圖案820至第四導電圖案850可對應於定時緊要路徑。在示例性實施例中,第一導電圖案820及第四導電圖案850可由空氣間隙導電圖案來實施。舉例而言,第一空氣間隙圖案860及第一空氣間隙圖案865可安置於第一導電圖案820的相對兩側上。第一導電圖案820以及第一空氣間隙圖案860及第一空氣間隙圖案865可在Y方向上延伸。第二空氣間隙圖案870及第二空氣間隙圖案875可安置於第四導電圖案850的相對兩側上。第四導電圖案850以及第二空氣間隙圖案870及第二空氣間隙圖案875可在X方向上延伸。In an exemplary embodiment, the first to fourth
因此,根據示例性實施例,第一空氣間隙圖案860及第一空氣間隙圖案865可在Y方向上延伸,而第二空氣間隙圖案870及第二空氣間隙圖案875可在X方向上延伸。因此,在示例性實施例中,第一空氣間隙圖案860、第一空氣間隙圖案865以及第二空氣間隙圖案870、第二空氣間隙圖案875可由雙向空氣間隙圖案來實施。因此,在示例性實施例中,在Z方向上不鄰近(例如,不緊鄰)的兩個不連續層可由空氣間隙層來實施。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,不緊鄰彼此的兩個層(例如,在其之間安置有中間層的兩個層)可由空氣間隙層來實施,而中間層可不由空氣間隙層來實施(例如,中間層可包括含有一般介電材料且安置於其至少一個側上的金屬間介電質)。Therefore, according to an exemplary embodiment, the first
圖17是根據本發明概念示例性實施例的包含於積體電路中的標準元件900的佈局。FIG. 17 is a layout of a
參考圖17,標準元件900可由元件邊界CB來定義,且可包括多個鰭FN、第一主動區域AR1及第二主動區域AR2、多個閘極線GLa、GLb、及GLc(GL)、多個第一金屬線M1a、M1b、及M1c(M1)、以及第二金屬線M2。標準元件900可更包括第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1a及第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1b以及第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2a及第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2b。第一金屬線M1a、安置於第一金屬線M1a上的第二介層窗V1、以及第二金屬線M2可對應於定時緊要網路。Referring to FIG. 17, a
元件邊界CB為定義標準元件900的輪廓。放置工具及路由工具(例如,圖3所示放置及路由模組13a或圖4所示放置及路由模組22a)可利用元件邊界CB來識別標準元件900。元件邊界CB包括四條邊界線。The component boundary CB defines the outline of the
所述多個鰭FN可在X方向上延伸,且可沿實質上垂直於X方向的Y方向實質上彼此平行地安置。第一主動區域AR1與第二主動區域AR2可實質上彼此平行地安置,且可具有不同的導電類型。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,可在第一主動區域AR1及第二主動區域AR2中的每一者中安置三個鰭FN。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,安置於第一主動區域AR1及第二主動區域AR2中的每一者中的鰭的數目可有所改變。The plurality of fins FN may extend in the X direction, and may be arranged substantially parallel to each other along the Y direction that is substantially perpendicular to the X direction. The first active area AR1 and the second active area AR2 may be arranged substantially parallel to each other, and may have different conductivity types. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, three fins FN may be disposed in each of the first active area AR1 and the second active area AR2. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the number of fins disposed in each of the first active area AR1 and the second active area AR2 may be changed.
安置於第一主動區域AR1及第二主動區域AR2中的所述多個鰭FN可被稱為主動鰭。儘管圖17僅說明主動鰭,但本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,標準元件900可更包括安置於元件邊界CB與第一主動區域AR1之間的區域中、第一主動區域AR1與第二主動區域AR2之間的區域中、或第二主動區域AR2與元件邊界CB之間的區域中的虛設鰭。The plurality of fins FN arranged in the first active area AR1 and the second active area AR2 may be referred to as active fins. Although FIG. 17 only illustrates the active fin, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, the
所述多個閘極線GL可在Y方向上延伸,且可沿X方向實質上彼此平行地安置。閘極線GL可包含例如(舉例而言)多晶矽、金屬、或金屬合金等導電材料。為便於說明,圖17說明標準元件900包括三個閘極線GL。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,根據示例性實施例,標準元件900可包括在Y方向上延伸且在X方向上彼此平行地安置的四或更多個閘極線GL。The plurality of gate lines GL may extend in the Y direction, and may be arranged substantially parallel to each other in the X direction. The gate line GL may include conductive materials such as, for example, polysilicon, metal, or metal alloy. For ease of description, FIG. 17 illustrates that the
第一介層窗V0可分別安置於所述多個閘極線GLa、GLb、及GLc上,且可分別電性連接所述多個閘極線GLa、GLb、及GLc與所述多個第一金屬線M1a、M1b、及M1c。第一介層窗V0可包含例如(舉例而言)多晶矽、金屬、或金屬合金等導電材料。The first via V0 may be respectively disposed on the plurality of gate lines GLa, GLb, and GLc, and may be electrically connected to the plurality of gate lines GLa, GLb, and GLc and the plurality of first A metal wire M1a, M1b, and M1c. The first via V0 may include conductive materials such as, for example, polysilicon, metal, or metal alloy.
所述多個第一金屬線M1可形成安置於所述多個閘極線GL上的一個層。第一金屬線M1a可對應於例如圖14B所示第一導電圖案620。第一金屬線M1可包含例如(舉例而言)多晶矽、金屬、或金屬合金等導電材料。The plurality of first metal lines M1 may form a layer disposed on the plurality of gate lines GL. The first metal line M1a may correspond to, for example, the first
在示例性實施例中,第一金屬線M1可僅在Y方向上延伸,且可沿X方向實質上彼此平行地安置。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,第一金屬線M1中的一第一金屬線的一部分可在Y方向上延伸,而所述第一金屬線的另一部分可形成在X方向上延伸的L形狀。為便於說明,圖17說明標準元件900包括三個第一金屬線M1。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,根據示例性實施例,標準元件900可包括四或更多個第一金屬線M1。In an exemplary embodiment, the first metal wires M1 may only extend in the Y direction, and may be arranged substantially parallel to each other along the X direction. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, a part of a first metal line in the first metal line M1 may extend in the Y direction, and another part of the first metal line may be formed to extend in the X direction. L shape. For ease of description, FIG. 17 illustrates that the
第二介層窗V1可分別安置於所述多個第一金屬線M1a及M1c上,且可連接所述多個第一金屬線M1a及M1c與第二金屬線M2。安置於第一金屬線M1a上的第二介層窗V1可對應於圖14B所示介層窗640。第二介層窗V1可包含例如(舉例而言)多晶矽、金屬、或金屬合金等導電材料。The second via V1 can be respectively disposed on the plurality of first metal wires M1a and M1c, and can connect the plurality of first metal wires M1a and M1c and the second metal wire M2. The second via V1 disposed on the first metal line M1a may correspond to the via 640 shown in FIG. 14B. The second via V1 may include conductive materials such as, for example, polysilicon, metal, or metal alloy.
第二金屬線M2可形成安置於所述多個第一金屬線M1上的一個層。第二金屬線M2可對應於例如圖14B所示第二導電圖案650。第二金屬線M2可包含例如(舉例而言)多晶矽、金屬、或金屬合金等導電材料。The second metal line M2 may form a layer disposed on the plurality of first metal lines M1. The second metal line M2 may correspond to, for example, the second
第二金屬線M2可僅在X方向上延伸。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,在示例性實施例中,第二金屬線M2的一部分可在X方向上延伸,而第二金屬線M2的另一部分可形成在Y方向上延伸的L形狀。為便於說明,圖17說明標準元件900包括一個第二金屬線M2。然而,本發明概念並非僅限於此。舉例而言,根據示例性示例性,標準元件900可包括二或更多個第二金屬線M2。The second metal wire M2 may only extend in the X direction. However, the concept of the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in an exemplary embodiment, a part of the second metal line M2 may extend in the X direction, and another part of the second metal line M2 may be formed in an L shape extending in the Y direction. For ease of description, FIG. 17 illustrates that the
根據示例性實施例,第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1a及第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1b可安置於所述多個第一金屬線M1a至M1c之間。第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1a及AGP1b可在Y方向上延伸。所述多個第一金屬線M1a至M1c與第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1a及第一空氣間隙圖案AGP1b可形成第一空氣間隙層。因此,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,所述多個第一金屬線M1a至M1c之間的寄生電容可減小。According to an exemplary embodiment, the first air gap pattern AGP1a and the first air gap pattern AGP1b may be disposed between the plurality of first metal lines M1a to M1c. The first air gap patterns AGP1a and AGP1b may extend in the Y direction. The plurality of first metal lines M1a to M1c and the first air gap pattern AGP1a and the first air gap pattern AGP1b may form a first air gap layer. Therefore, according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, the parasitic capacitance between the plurality of first metal lines M1a to M1c may be reduced.
根據示例性實施例,第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2a及第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2b可安置於第二金屬線M2的相對兩側上。第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2a及第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2b可在X方向上延伸。第二金屬線M2與第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2a及第二空氣間隙圖案AGP2b可形成第二空氣間隙層。因此,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,第二金屬線M2與鄰近金屬線之間的寄生電容可減小。 According to an exemplary embodiment, the second air gap pattern AGP2a and the second air gap pattern AGP2b may be disposed on opposite sides of the second metal line M2. The second air gap pattern AGP2a and the second air gap pattern AGP2b may extend in the X direction. The second metal line M2 and the second air gap pattern AGP2a and the second air gap pattern AGP2b may form a second air gap layer. Therefore, according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, the parasitic capacitance between the second metal line M2 and the adjacent metal line can be reduced.
如參考圖1至圖17所述,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,在設計積體電路的佈局的過程中,可自所放置標準元件中的多個定時路徑中選擇定時緊要路徑,且可自被選擇的定時緊要路徑的網路中選擇至少一個網路。隨後,可以空氣間隙層對所述被選擇的至少一個網路進行預路由,且可以正常層(例如,在無空氣間隙層的情況下)對非緊要路徑的網路及/或定時緊要路徑的未選擇的網路進行路由。因此,根據本發明概念的示例性實施例,可藉由使用少量空氣間隙層而以低成本實施高效能積體電路。 As described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 17, according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept, in the process of designing the layout of an integrated circuit, a timing critical path can be selected from a plurality of timing paths in the placed standard components, and At least one network can be selected from the networks of the selected timing critical path. Subsequently, the selected at least one network can be pre-routed at the air gap layer, and the non-critical path network and/or the timing critical path can be pre-routed at the normal layer (for example, in the case of no air gap layer). The unselected network is routed. Therefore, according to exemplary embodiments of the inventive concept, a high-performance integrated circuit can be implemented at low cost by using a small amount of air gap layers.
圖18是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的儲存媒體1000的方塊圖。
FIG. 18 is a block diagram illustrating a
本發明概念的示例性實施例可直接實施於硬體中、實施於由處理器執行的軟體中、或實施於所述硬體與所述軟體的組合中。軟體模組可有形地實施於非暫時性程式儲存裝置(例如圖18所示儲存媒體1000)上。
The exemplary embodiments of the inventive concept may be directly implemented in hardware, implemented in software executed by a processor, or implemented in a combination of the hardware and the software. The software module can be tangibly implemented on a non-temporary program storage device (such as the
參考圖18,儲存媒體1000可儲存元件庫1100、佈局資料1200、放置及路由程式(P&R program)1300、及定時分析程式1400。儲存媒體1000為電腦可讀取儲存媒體(例如,非暫時性電腦可讀取儲存媒體),且可包括可由電腦讀取以將指令及/或資料提供至所述電腦的儲存媒體。所述指令可由電腦的處理器執行。電腦可讀取儲存媒體1000可包括例如磁性媒體或光學媒體(例如,磁碟、磁帶、光碟唯讀記憶體(Compact Disc Read-Only Memory,CD-ROM)、數位多功能光碟唯讀記憶體(digital versatile disk-ROM,DVD-ROM)、可記錄光碟(Compact Disk-Recordable,CD-R)、可重寫光碟(CD-Rewritable,CD-RW)、可記錄數位多功能光碟(DVD-Recordable,DVD-R)、或可重寫數位多功能光碟(DVD- Rewritable,DVD-RW))、揮發性記憶體或非揮發性記憶體(例如隨機存取記憶體、唯讀記憶體、或快閃記憶體)、可經由通用串列匯流排(Universal Serial Bus,USB)介面而進行存取的非揮發性記憶體、及微機電系統(microelectromechanical system,MEMS)。然而,電腦可讀取儲存媒體1000並非僅限於此。電腦可讀取儲存媒體可插入電腦中,可整合於電腦中,或可藉由例如有線網路或無線網路等通訊媒體而與電腦加以組合。Referring to FIG. 18, the
元件庫1100可為標準元件庫,且可包括關於作為構成積體電路的單元的標準元件的資訊。在示例性實施例中,關於標準元件的資訊可包括為產生佈局而需要的佈局資訊。在示例性實施例中,關於標準元件的資訊可包括例如為對佈局進行驗證或模擬而需要的定時資訊。The
佈局資料1200可包括關於藉由放置及路由操作而產生的佈局的物理資訊。在示例性實施例中,佈局資料1200可包括例如導電圖案的寬度及間距值以及排列於各導電圖案之間的空氣間隙圖案的數目及大小。The
放置及路由程式1300可包括多個指令,所述指令用以實行根據示例性實施例藉由使用標準元件庫來產生積體電路的佈局的方法。舉例而言,放置及路由程式1300可用於實行圖1所示操作S110及操作S130、圖5所示操作S210、操作S260、及操作S270、或圖6所示操作S310、操作S320、操作S350、及操作S360。The placement and
定時分析程式1400可為例如靜態定時分析(static timing analysis,STA)程式。靜態定時分析可對應於對數位電路的預期定時進行計算的模擬方法。可對所放置標準元件的所有定時路徑實行定時分析,且可輸出定時分析結果。可使用定時分析程式1400來實行例如圖1所示操作S120、圖5所示操作S240及操作S250、或圖6所示操作S330。The
在示例性實施例中,儲存媒體1000可更儲存分析程式。分析程式可包括多個指令,所述多個指令用於實行基於定義積體電路的輸入資料而分析積體電路的方法。在示例性實施例中,儲存媒體1000可更儲存資料結構。資料結構可包括用於自元件庫1100提取特定資訊或管理在利用分析程式來分析積體電路特性的過程中所產生的資料的儲存空間。In an exemplary embodiment, the
儘管已參考本發明概念的示例性實施例具體示出及闡述了本發明概念,然而熟習此項技術者應理解,在不背離由以下申請專利範圍界定的本發明概念的精神及範圍的條件下,可作出各種形式及細節上的改變。Although the concept of the invention has been specifically illustrated and explained with reference to the exemplary embodiments of the concept of the invention, those skilled in the art should understand that without departing from the spirit and scope of the concept of the invention defined by the scope of the following patent applications , Can make various changes in form and details.
10、20‧‧‧積體電路設計系統11、21a‧‧‧處理器13‧‧‧工作記憶體13a、22a‧‧‧放置及路由模組/部件13b、22b‧‧‧定時分析模組15‧‧‧輸入/輸出裝置17、23‧‧‧輔助儲存器19‧‧‧匯流排21‧‧‧使用者裝置21b‧‧‧使用者介面22‧‧‧積體電路設計平台23a‧‧‧元件庫資料庫23b‧‧‧佈局資料庫81、101‧‧‧佈線結構100‧‧‧定時緊要網路200、300、400、600、700、800、IC、IC’‧‧‧積體電路210、310、410、610、710、810、CP1‧‧‧第一連接點215、315、415、615、715、815、CP2‧‧‧第二連接點220、420、CPT‧‧‧導電圖案230、235、430、435、AGP、AGP1、AGP1’、AGP2、AGP2’‧‧‧空氣間隙圖案320、620、720a、820、CPT1、Ma‧‧‧第一導電圖案330、335、630、635、730a、735a、860、865、AGP1a、AGP1b‧‧‧第一空氣間隙圖案340、V0‧‧‧第一介層窗345、V1‧‧‧第二介層窗350、650、720b、830、CPT2、Ma+2‧‧‧第二導電圖案360、365、660、665、730b、735b、870、875、AGP2a、AGP2b‧‧‧第二空氣間隙圖案640、V5、V6、V7、880、885、890‧‧‧介層窗720c、840、CPT3、Mb、Mx‧‧‧第三導電圖案730c、735c‧‧‧第三空氣間隙圖案850、Mb+2‧‧‧第四導電圖案900‧‧‧標準元件1000‧‧‧儲存媒體/電腦可讀取儲存媒體1100‧‧‧元件庫1200‧‧‧佈局資料1300‧‧‧放置及路由程式1400‧‧‧定時分析程式AGL‧‧‧空氣間隙層AGPa‧‧‧第一空氣間隙圖案/空氣間隙圖案AGPb‧‧‧空氣間隙圖案/第二空氣間隙圖案AGPx‧‧‧第一空氣間隙圖案/第二空氣間隙圖案/第三空氣間隙圖案AR1‧‧‧第一主動區域AR2‧‧‧第二主動區域BM1‧‧‧第一障壁層BM2‧‧‧第二障壁層CB‧‧‧元件邊界CP‧‧‧第一連接點/第二連接點FN‧‧‧鰭GL、GLa、GLb、GLc‧‧‧閘極線ILD1‧‧‧第一絕緣層ILD2‧‧‧第二絕緣層M1‧‧‧第一佈線層/第一金屬線M1a、M1b、M1c‧‧‧第一金屬線M2‧‧‧第二佈線層/第二金屬線M2¢‧‧‧第二佈線層M3‧‧‧第三佈線層M5‧‧‧第五佈線層/非連續第五佈線層M6‧‧‧第六佈線層/中間佈線層M7‧‧‧第七佈線層/中間佈線層M8‧‧‧非連續第八佈線層/第八佈線層P1‧‧‧第一引腳P2‧‧‧第二引腳S10‧‧‧積體電路設計操作/製程/操作S10A、S10B‧‧‧方法S20‧‧‧積體電路製造製程/製程S110、S120、S130、S140、S150、S210、S230、S240、S250、S310、S320、S330、S340、S350、S360、S370‧‧‧操作S220‧‧‧放置操作/操作S260、S270‧‧‧預路由操作/操作TCP‧‧‧定時緊要路徑X、Y、Z‧‧‧方向10, 20‧‧‧Integrated circuit design system 11, 21a‧‧‧Processor 13‧‧‧Working memory 13a, 22a‧‧‧Placement and routing module/component 13b, 22b‧‧‧ Timing analysis module 15 ‧‧‧Input/Output Device 17, 23‧‧‧Auxiliary Storage 19‧‧‧Bus 21‧‧‧User Device 21b‧‧‧User Interface 22‧‧‧Integrated Circuit Design Platform 23a‧‧‧Component Library database 23b‧‧‧Layout database 81, 101‧‧‧Wiring structure 100‧‧‧Time critical network 200, 300, 400, 600, 700, 800, IC, IC'‧‧‧Integrated circuit 210, 310, 410, 610, 710, 810, CP1‧‧‧First connection point 215,315,415,615,715,815, CP2‧‧‧Second connection point 220,420, CPT‧‧‧Conductive pattern 230, 235, 430, 435, AGP, AGP1, AGP1', AGP2, AGP2'‧‧‧Air gap pattern 320, 620, 720a, 820, CPT1, Ma‧‧‧First conductive pattern 330, 335, 630, 635, 730a , 735a, 860, 865, AGP1a, AGP1b‧‧‧First air gap pattern 340, V0‧‧‧First via 345, V1‧‧‧Second via 350, 650, 720b, 830, CPT2 Ma+2‧‧‧Second conductive pattern 360, 365, 660, 665, 730b, 735b, 870, 875, AGP2a, AGP2b‧‧‧Second air gap pattern 640, V5, V6, V7, 880, 885, 890 ‧‧‧Interlayer windows 720c, 840, CPT3, Mb, Mx‧‧‧The third conductive pattern 730c, 735c‧‧‧The third air gap pattern 850, Mb+2‧‧‧The fourth conductive pattern 900‧‧‧Standard Component 1000‧‧‧Storage media/computer readable storage media 1100‧‧‧Component library 1200‧‧‧Layout data 1300‧‧‧Placement and routing program 1400‧‧‧Timing analysis program AGL‧‧‧Air gap layer AGPa‧ ‧‧First Air Gap Pattern/Air Gap Pattern AGPb‧‧‧Air Gap Pattern/Second Air Gap Pattern AGPx‧‧‧First Air Gap Pattern/Second Air Gap Pattern/Third Air Gap Pattern AR1‧‧‧第An active area AR2‧‧‧The second active area BM1‧‧‧First barrier layer BM2‧‧‧Second barrier layer CB‧‧‧Component boundary CP‧‧‧First connection point/second connection point FN‧‧‧ Fins GL, GLa, GLb, GLc‧‧‧Gate line ILD1‧‧‧First insulating layer ILD2‧‧‧Second insulating layer M1‧‧‧First wiring layer/first metal line M1a, M1b, M1c‧‧ ‧First metal wire M2‧‧‧Second wiring layer /Second metal wire M2¢‧‧‧Second wiring layer M3‧‧‧Third wiring layer M5‧‧‧Fifth wiring layer/Discontinuous fifth wiring layer M6‧‧‧Sixth wiring layer/Middle wiring layer M7 ‧‧‧Seventh wiring layer/Middle wiring layer M8‧‧‧Discontinuous eighth wiring layer/Eighth wiring layer P1‧‧‧First pin P2‧‧‧Second pin S10‧‧‧Integrated circuit design Operation/Process/Operation S10A, S10B‧‧‧Method S20‧‧‧Integrated circuit manufacturing process/Process S110, S120, S130, S140, S150, S210, S230, S240, S250, S310, S320, S330, S340, S350 , S360, S370‧‧‧Operation S220‧‧‧Placement operation/Operation S260, S270‧‧‧Pre-routing operation/Operation TCP‧‧‧Timing critical path X, Y, Z‧‧‧Direction
藉由參考附圖詳細闡述本發明概念的示例性實施例,本發明概念的以上及其他特徵將變得更顯而易見,在附圖中:The above and other features of the inventive concept will become more apparent by describing in detail the exemplary embodiments of the inventive concept with reference to the accompanying drawings. In the accompanying drawings:
圖1是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種製造積體電路的方法的流程圖。FIG. 1 is a flowchart illustrating a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖2A及圖2B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的分別包括空氣間隙層的各積體電路的剖視圖。2A and 2B are cross-sectional views illustrating integrated circuits each including an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖3及圖4說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的積體電路設計系統。3 and 4 illustrate an integrated circuit design system according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖5是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種設計積體電路的方法的流程圖。FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a method of designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the concept of the present invention.
圖6是根據本發明概念示例性實施例的一種設計積體電路的方法的流程圖。Fig. 6 is a flowchart of a method of designing an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the concept of the present invention.
圖7是繪示根據本發明概念示例性實施例的定時分析結果的曲線圖。FIG. 7 is a graph showing a timing analysis result according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖8說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的使用空氣間隙層而進行路由的佈線結構。FIG. 8 illustrates a wiring structure for routing using an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖9A至圖9E是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的以空氣間隙層而進行路由的定時緊要網路的立體圖。9A to 9E are perspective views illustrating a timing critical network for routing with an air gap layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖10說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的使用正常層而進行路由的佈線結構。FIG. 10 illustrates a wiring structure for routing using a normal layer according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖11A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的平面圖。FIG. 11A is a plan view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖11B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖11A所示積體電路的立體圖。FIG. 11B is a perspective view illustrating the integrated circuit shown in FIG. 11A according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖12A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的平面圖。FIG. 12A is a plan view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖12B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖12A所示積體電路的立體圖。FIG. 12B is a perspective view illustrating the integrated circuit shown in FIG. 12A according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖13A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的平面圖。FIG. 13A is a plan view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖13B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖13A所示積體電路的立體圖。FIG. 13B is a perspective view illustrating the integrated circuit shown in FIG. 13A according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖14A是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的平面圖。14A is a plan view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖14B是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的圖14A所示積體電路的立體圖。FIG. 14B is a perspective view illustrating the integrated circuit shown in FIG. 14A according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖15是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的立體圖。15 is a perspective view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖16是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的藉由應用空氣間隙圖案而進行路由的積體電路的立體圖。FIG. 16 is a perspective view illustrating an integrated circuit for routing by applying an air gap pattern according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖17是根據本發明概念示例性實施例的包含於積體電路中的標準元件的佈局。FIG. 17 is a layout of standard components included in an integrated circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
圖18是說明根據本發明概念示例性實施例的儲存媒體的方塊圖。FIG. 18 is a block diagram illustrating a storage medium according to an exemplary embodiment of the inventive concept.
S10‧‧‧積體電路設計操作/製程/操作 S10‧‧‧Integrated circuit design operation/process/operation
S20‧‧‧積體電路製造製程/製程 S20‧‧‧Integrated circuit manufacturing process/process
S110、S120、S130、S140、S150‧‧‧操作 S110, S120, S130, S140, S150‧‧‧Operation
Claims (25)
Applications Claiming Priority (8)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| ??10-2016-0015820 | 2016-02-11 | ||
| KR20160015820 | 2016-02-11 | ||
| KR10-2016-0015820 | 2016-02-11 | ||
| KR1020160100122A KR102717096B1 (en) | 2016-02-11 | 2016-08-05 | Integrated circuit and computer-implemented method for manufacturing the same |
| KR10-2016-0100122 | 2016-08-05 | ||
| ??10-2016-0100122 | 2016-08-05 | ||
| US15/420,514 US9991249B2 (en) | 2016-02-11 | 2017-01-31 | Integrated circuit and computer-implemented method of manufacturing the same |
| US15/420,514 | 2017-01-31 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| TW201826155A TW201826155A (en) | 2018-07-16 |
| TWI718245B true TWI718245B (en) | 2021-02-11 |
Family
ID=59757519
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW106104007A TWI718245B (en) | 2016-02-11 | 2017-02-08 | Integrated circuits, computer-implemented method of manufacturing the same, and standard cell defining the same |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR102717096B1 (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI718245B (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR102596609B1 (en) * | 2018-11-16 | 2023-10-31 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Method for fabricating semiconductor device and layout design system |
| TWI714039B (en) * | 2019-03-27 | 2020-12-21 | 創意電子股份有限公司 | Timing model, method for building timing model, and related method for performing top-level analysis |
| DE102020100001B4 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2022-05-25 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. Ltd. | Integrated circuit with a plurality of memory test structures and method of manufacturing the same and memory test structure of an embedded memory device |
| US11069695B2 (en) | 2019-05-31 | 2021-07-20 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Floating gate test structure for embedded memory device |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080097641A1 (en) * | 2006-10-20 | 2008-04-24 | Hirofumi Miyashita | Interconnect structure of semiconductor integrated circuit, and design method and device therefor |
| CN101887469A (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2010-11-17 | 台湾积体电路制造股份有限公司 | Method of designing integrated circuit and computer system with the method |
| US20130256758A1 (en) * | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Integrated circuit structure having air-gap trench isolation and related design structure |
| US20140167219A1 (en) * | 2012-01-06 | 2014-06-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Thick On-Chip High-Performance Wiring Structures |
| US20150021738A1 (en) * | 2013-07-19 | 2015-01-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Bipolar junction transistors with an air gap in the shallow trench isolation |
| TW201523313A (en) * | 2013-12-05 | 2015-06-16 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | Layout design system and semiconductor device fabricated using the system |
| US20150206800A1 (en) * | 2013-07-12 | 2015-07-23 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor device with air gap and method for fabricating the same |
| US20150287628A1 (en) * | 2014-04-07 | 2015-10-08 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating the same |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07326670A (en) * | 1994-05-31 | 1995-12-12 | Texas Instr Inc <Ti> | Semiconductor integrated circuit device |
| KR101098920B1 (en) * | 2004-12-07 | 2011-12-27 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | Method for manufacturing semicondoctor device |
| US10140407B2 (en) * | 2014-11-26 | 2018-11-27 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method, device and computer program product for integrated circuit layout generation |
-
2016
- 2016-08-05 KR KR1020160100122A patent/KR102717096B1/en active IP Right Grant
-
2017
- 2017-02-08 TW TW106104007A patent/TWI718245B/en active
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20080097641A1 (en) * | 2006-10-20 | 2008-04-24 | Hirofumi Miyashita | Interconnect structure of semiconductor integrated circuit, and design method and device therefor |
| CN101887469A (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2010-11-17 | 台湾积体电路制造股份有限公司 | Method of designing integrated circuit and computer system with the method |
| US20140167219A1 (en) * | 2012-01-06 | 2014-06-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Thick On-Chip High-Performance Wiring Structures |
| US20130256758A1 (en) * | 2012-03-30 | 2013-10-03 | International Business Machines Corporation | Integrated circuit structure having air-gap trench isolation and related design structure |
| US20150206800A1 (en) * | 2013-07-12 | 2015-07-23 | SK Hynix Inc. | Semiconductor device with air gap and method for fabricating the same |
| US20150021738A1 (en) * | 2013-07-19 | 2015-01-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Bipolar junction transistors with an air gap in the shallow trench isolation |
| TW201523313A (en) * | 2013-12-05 | 2015-06-16 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | Layout design system and semiconductor device fabricated using the system |
| US20150287628A1 (en) * | 2014-04-07 | 2015-10-08 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor devices and methods of fabricating the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20170094744A (en) | 2017-08-21 |
| KR102717096B1 (en) | 2024-10-15 |
| TW201826155A (en) | 2018-07-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN107066681B (en) | Integrated circuit and computer-implemented method of manufacturing an integrated circuit | |
| US10997346B2 (en) | Conception of a 3D circuit comprising macros | |
| TWI788345B (en) | Method and system for designing integrated circuit | |
| Kahng et al. | VLSI physical design: from graph partitioning to timing closure | |
| US10553574B2 (en) | Standard cell for removing routing interference between adjacent pins and device including the same | |
| TWI718245B (en) | Integrated circuits, computer-implemented method of manufacturing the same, and standard cell defining the same | |
| KR101776385B1 (en) | Method, device and computer program product for integrated circuit layout generation | |
| US10424518B2 (en) | Integrated circuit designing system and a method of manufacturing an integrated circuit | |
| TW201729133A (en) | Layout modification method and system | |
| US10796060B2 (en) | Method and system for pin layout | |
| US11030383B2 (en) | Integrated device and method of forming the same | |
| US9213793B1 (en) | Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for implementing electronic designs using flexible routing tracks | |
| US20180231604A1 (en) | Computer implemented methods and computing systems for designing integrated circuits by considering back-end-of-line | |
| JP4141322B2 (en) | Semiconductor integrated circuit automatic wiring method and semiconductor integrated circuit design program | |
| US20220129614A1 (en) | Method and system of forming semiconductor device | |
| US20150278421A1 (en) | Ir-aware sneak routing | |
| US9292648B1 (en) | Activity-driven capacitance reduction to reduce dynamic power consumption in an integrated circuit | |
| US10977415B2 (en) | Integrated device and method of forming the same | |
| US9183343B1 (en) | Methods, systems, and articles of manufacture for implementing high current carrying interconnects in electronic designs | |
| KR20180070321A (en) | Integrated circuit for triple patterning lithography, computing system and computer-implemented method for designing integrated circuit | |
| Lu et al. | A metal-only-ECO solver for input-slew and output-loading violations | |
| Murali et al. | Heterogeneous 3d ics: Current status and future directions for physical design technologies | |
| US9454632B1 (en) | Context specific spare cell determination during physical design | |
| KR20190037046A (en) | Semiconductor device design method and sysyem | |
| US8972910B1 (en) | Routing method |