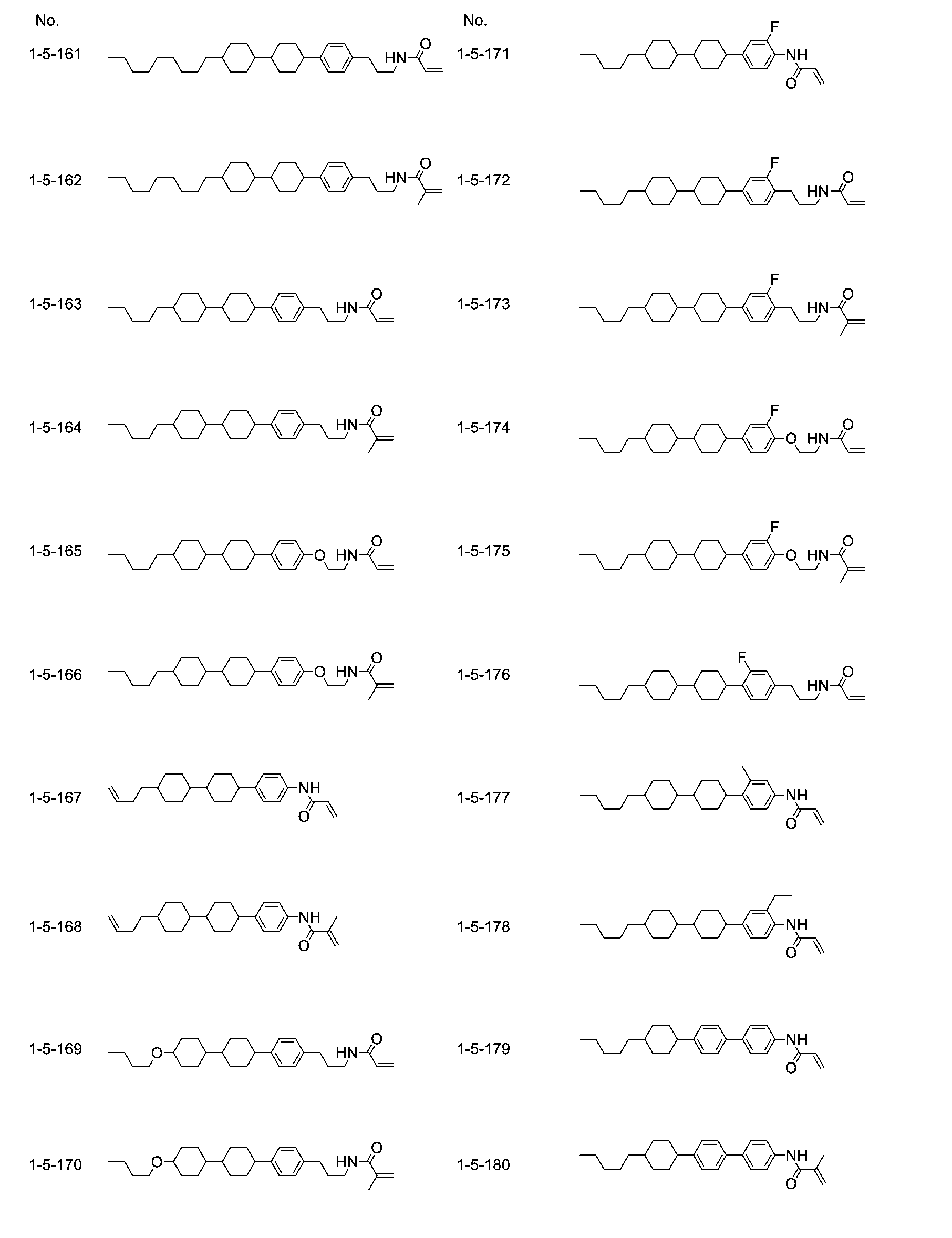TWI694140B - 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 - Google Patents
聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- TWI694140B TWI694140B TW105119246A TW105119246A TWI694140B TW I694140 B TWI694140 B TW I694140B TW 105119246 A TW105119246 A TW 105119246A TW 105119246 A TW105119246 A TW 105119246A TW I694140 B TWI694140 B TW I694140B
- Authority
- TW
- Taiwan
- Prior art keywords
- substituted
- formula
- diyl
- hydrogen
- group
- Prior art date
Links
- 0 *CCC(CC1)CCC1C1CCC(*)CC1 Chemical compound *CCC(CC1)CCC1C1CCC(*)CC1 0.000 description 9
- ZWJMKDWSBGLFEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N CC(C(Oc(cc1)ccc1-c(cc1)cc(F)c1OC(C(C)=C)=O)=O)=C Chemical compound CC(C(Oc(cc1)ccc1-c(cc1)cc(F)c1OC(C(C)=C)=O)=O)=C ZWJMKDWSBGLFEL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BRVTWQPRCYYCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N CCCCCc(cc1)cc2c1cc(cc(cc1)OCCNC(C=C)=O)c1c2 Chemical compound CCCCCc(cc1)cc2c1cc(cc(cc1)OCCNC(C=C)=O)c1c2 BRVTWQPRCYYCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/52—Liquid crystal materials characterised by components which are not liquid crystals, e.g. additives with special physical aspect: solvents, solid particles
- C09K19/54—Additives having no specific mesophase characterised by their chemical composition
- C09K19/56—Aligning agents
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/02—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals
- C07C233/09—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having nitrogen atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to carbon atoms of unsubstituted hydrocarbon radicals with carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to carbon atoms of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/12—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C233/13—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/12—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups
- C07C233/15—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by halogen atoms or by nitro or nitroso groups with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/16—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms
- C07C233/17—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom
- C07C233/20—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by an acyclic carbon atom having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/16—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms
- C07C233/23—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/16—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms
- C07C233/24—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
- C07C233/25—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a hydrogen atom or to a carbon atom of an acyclic saturated carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/16—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms
- C07C233/24—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring
- C07C233/27—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by singly-bound oxygen atoms with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a six-membered aromatic ring having the carbon atom of the carboxamide group bound to a carbon atom of an acyclic unsaturated carbon skeleton
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C233/00—Carboxylic acid amides
- C07C233/01—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms
- C07C233/45—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups
- C07C233/52—Carboxylic acid amides having carbon atoms of carboxamide groups bound to hydrogen atoms or to acyclic carbon atoms having the nitrogen atom of at least one of the carboxamide groups bound to a carbon atom of a hydrocarbon radical substituted by carboxyl groups with the substituted hydrocarbon radical bound to the nitrogen atom of the carboxamide group by a carbon atom of a ring other than a six-membered aromatic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D213/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D213/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom
- C07D213/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings, not condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom and three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having three double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members having no bond between the ring nitrogen atom and a non-ring member or having only hydrogen or carbon atoms directly attached to the ring nitrogen atom with substituted hydrocarbon radicals attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D213/28—Radicals substituted by singly-bound oxygen or sulphur atoms
- C07D213/30—Oxygen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having one double bond between ring members or between a ring member and a non-ring member
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D239/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings
- C07D239/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings
- C07D239/24—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D239/26—Heterocyclic compounds containing 1,3-diazine or hydrogenated 1,3-diazine rings not condensed with other rings having three or more double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D309/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings
- C07D309/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D309/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D309/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings
- C07D309/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members
- C07D309/04—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having one oxygen atom as the only ring hetero atom, not condensed with other rings having no double bonds between ring members or between ring members and non-ring members with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to ring carbon atoms
- C07D309/06—Radicals substituted by oxygen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D319/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing six-membered rings having two oxygen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D319/04—1,3-Dioxanes; Hydrogenated 1,3-dioxanes
- C07D319/06—1,3-Dioxanes; Hydrogenated 1,3-dioxanes not condensed with other rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J41/00—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring
- C07J41/0033—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005
- C07J41/0055—Normal steroids containing one or more nitrogen atoms not belonging to a hetero ring not covered by C07J41/0005 the 17-beta position being substituted by an uninterrupted chain of at least three carbon atoms which may or may not be branched, e.g. cholane or cholestane derivatives, optionally cyclised, e.g. 17-beta-phenyl or 17-beta-furyl derivatives
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07J—STEROIDS
- C07J9/00—Normal steroids containing carbon, hydrogen, halogen or oxygen substituted in position 17 beta by a chain of more than two carbon atoms, e.g. cholane, cholestane, coprostane
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/10—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings
- C09K19/12—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings at least two benzene rings directly linked, e.g. biphenyls
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/10—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings
- C09K19/20—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms as chain links, e.g. esters or ethers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3028—Cyclohexane rings in which at least two rings are linked by a carbon chain containing carbon to carbon single bonds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3048—Cyclohexane rings in which at least two rings are linked by a carbon chain containing carbon to carbon double bonds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3059—Cyclohexane rings in which at least two rings are linked by a carbon chain containing carbon to carbon triple bonds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3066—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers
- C09K19/3068—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers chain containing -COO- or -OCO- groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3098—Unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexene rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/32—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing condensed ring systems, i.e. fused, bridged or spiro ring systems
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/32—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing condensed ring systems, i.e. fused, bridged or spiro ring systems
- C09K19/322—Compounds containing a naphthalene ring or a completely or partially hydrogenated naphthalene ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/34—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/34—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring
- C09K19/3402—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring having oxygen as hetero atom
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/34—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring
- C09K19/3441—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring having nitrogen as hetero atom
- C09K19/345—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring having nitrogen as hetero atom the heterocyclic ring being a six-membered aromatic ring containing two nitrogen atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/36—Steroidal liquid crystal compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/38—Polymers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/52—Liquid crystal materials characterised by components which are not liquid crystals, e.g. additives with special physical aspect: solvents, solid particles
- C09K19/54—Additives having no specific mesophase characterised by their chemical composition
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1337—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers
- G02F1/13378—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers by treatment of the surface, e.g. embossing, rubbing or light irradiation
- G02F1/133788—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers by treatment of the surface, e.g. embossing, rubbing or light irradiation by light irradiation, e.g. linearly polarised light photo-polymerisation
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2601/00—Systems containing only non-condensed rings
- C07C2601/12—Systems containing only non-condensed rings with a six-membered ring
- C07C2601/14—The ring being saturated
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2601/00—Systems containing only non-condensed rings
- C07C2601/12—Systems containing only non-condensed rings with a six-membered ring
- C07C2601/16—Systems containing only non-condensed rings with a six-membered ring the ring being unsaturated
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2602/00—Systems containing two condensed rings
- C07C2602/02—Systems containing two condensed rings the rings having only two atoms in common
- C07C2602/04—One of the condensed rings being a six-membered aromatic ring
- C07C2602/10—One of the condensed rings being a six-membered aromatic ring the other ring being six-membered, e.g. tetraline
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2602/00—Systems containing two condensed rings
- C07C2602/02—Systems containing two condensed rings the rings having only two atoms in common
- C07C2602/14—All rings being cycloaliphatic
- C07C2602/26—All rings being cycloaliphatic the ring system containing ten carbon atoms
- C07C2602/28—Hydrogenated naphthalenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2603/00—Systems containing at least three condensed rings
- C07C2603/02—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems
- C07C2603/04—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings
- C07C2603/06—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members
- C07C2603/10—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members containing five-membered rings
- C07C2603/12—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing at least one ring with less than six ring members containing five-membered rings only one five-membered ring
- C07C2603/18—Fluorenes; Hydrogenated fluorenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2603/00—Systems containing at least three condensed rings
- C07C2603/02—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems
- C07C2603/04—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings
- C07C2603/22—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing only six-membered rings
- C07C2603/24—Anthracenes; Hydrogenated anthracenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2603/00—Systems containing at least three condensed rings
- C07C2603/02—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems
- C07C2603/04—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings
- C07C2603/22—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing three rings containing only six-membered rings
- C07C2603/26—Phenanthrenes; Hydrogenated phenanthrenes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07C—ACYCLIC OR CARBOCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07C2603/00—Systems containing at least three condensed rings
- C07C2603/02—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems
- C07C2603/40—Ortho- or ortho- and peri-condensed systems containing four condensed rings
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K2019/0444—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit characterized by a linking chain between rings or ring systems, a bridging chain between extensive mesogenic moieties or an end chain group
- C09K2019/0466—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit characterized by a linking chain between rings or ring systems, a bridging chain between extensive mesogenic moieties or an end chain group the linking chain being a -CF2O- chain
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/10—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings
- C09K19/12—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing at least two benzene rings at least two benzene rings directly linked, e.g. biphenyls
- C09K2019/121—Compounds containing phenylene-1,4-diyl (-Ph-)
- C09K2019/123—Ph-Ph-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
- C09K2019/3004—Cy-Cy
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
- C09K2019/3009—Cy-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
- C09K2019/301—Cy-Cy-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
- C09K2019/3016—Cy-Ph-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3003—Compounds containing at least two rings in which the different rings are directly linked (covalent bond)
- C09K2019/3019—Cy-Cy-Ph-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3066—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers
- C09K19/3068—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers chain containing -COO- or -OCO- groups
- C09K2019/3071—Cy-Cy-COO-Cy
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3066—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers
- C09K19/3068—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers chain containing -COO- or -OCO- groups
- C09K2019/3077—Cy-Cy-COO-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3066—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers
- C09K19/3068—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers chain containing -COO- or -OCO- groups
- C09K2019/308—Cy-Cy-COO-Ph-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/08—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings
- C09K19/30—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least two non-condensed rings containing saturated or unsaturated non-aromatic rings, e.g. cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3001—Cyclohexane rings
- C09K19/3066—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers
- C09K19/3068—Cyclohexane rings in which the rings are linked by a chain containing carbon and oxygen atoms, e.g. esters or ethers chain containing -COO- or -OCO- groups
- C09K2019/3083—Cy-Ph-COO-Ph
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09K—MATERIALS FOR MISCELLANEOUS APPLICATIONS, NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE
- C09K19/00—Liquid crystal materials
- C09K19/04—Liquid crystal materials characterised by the chemical structure of the liquid crystal components, e.g. by a specific unit
- C09K19/06—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds
- C09K19/34—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring
- C09K19/3402—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring having oxygen as hetero atom
- C09K2019/3422—Non-steroidal liquid crystal compounds containing at least one heterocyclic ring having oxygen as hetero atom the heterocyclic ring being a six-membered ring
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1337—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers
- G02F1/133703—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers by introducing organic surfactant additives into the liquid crystal material
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1337—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers
- G02F1/133742—Surface-induced orientation of the liquid crystal molecules, e.g. by alignment layers for homeotropic alignment
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/137—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells characterised by the electro-optical or magneto-optical effect, e.g. field-induced phase transition, orientation effect, guest-host interaction or dynamic scattering
- G02F1/13775—Polymer-stabilized liquid crystal layers
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal Substances (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
- Heterocyclic Carbon Compounds Containing A Hetero Ring Having Oxygen Or Sulfur (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本發明是有關於一種聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件。更詳細而言,是有關於一種具有丙烯醯胺基等極性基的聚合性化合物、含有該化合物且介電異向性為正或負的液晶組成物、及含有該組成物的液晶顯示元件。
液晶顯示元件根據液晶分子的動作模式而被分類為相變(phase change,PC)、扭轉向列(twisted nematic,TN)、超扭轉向列(super twisted nematic,STN)、電控雙折射(electrically controlled birefringence,ECB)、光學補償彎曲(optically compensated bend,OCB)、共面切換(in-plane switching,IPS)、垂直配向(vertical alignment,VA)、邊緣場切換(fringe field switching,FFS)、電場感應光反應配向(field-induced photo-reactive alignment,FPA)等模式。根據元件的驅動方式而被分類為被動式矩陣(passive matrix,PM)與主動式矩陣(active matrix,AM)。PM被分類為靜態式(static)、多工式(multiplex)等,AM被分類為薄膜電晶體(thin film transistor,TFT)、金屬-絕緣體-金屬(metal insulator metal,MIM)等。TFT被分類為非晶矽(amorphous
silicon)及多晶矽(polycrystal silicon)。後者依製造步驟而被分類為高溫型與低溫型。根據光源而被分類為利用自然光的反射型、利用背光的透射型、以及利用自然光與背光兩者的半透射型。
液晶顯示元件含有具有向列相的液晶組成物。該組成物具有適當的特性。藉由使該組成物的特性提高,可獲得具有良好特性的AM元件。將兩者的特性的關聯匯總於下述表1中。根據市售的AM元件來對組成物的特性進一步加以說明。向列相的溫度範圍與元件的可使用的溫度範圍有關。向列相的較佳上限溫度為約70℃以上,而且向列相的較佳下限溫度為約-10℃以下。組成物的黏度與元件的響應時間有關。為了以元件顯示動態影像,較佳為響應時間短。理想的是響應時間短於1毫秒。因此,較佳為組成物的黏度小。更佳為低溫下的黏度小。
組成物的光學異向性與元件的對比度有關。根據元件的
模式,需要大的光學異向性或小的光學異向性、即適當的光學異向性。組成物的光學異向性(Δn)與元件的單元間隙(d)之積(Δn×d)是以使對比度成為最大的方式設計。適當的積的值依存於動作模式的種類。於TN般的模式的元件中,所述值為約0.45μm。於VA模式的元件中,所述值為約0.30μm~約0.40μm的範圍,於IPS模式或FFS模式的元件中,所述值為約0.20μm~約0.30μm的範圍。該些情形時,對於單元間隙小的元件而言,較佳為具有大的光學異向性的組成物。組成物的大的介電異向性有助於使元件的臨限電壓低、消耗電力小及對比度大。因此,較佳為正或負的介電異向性大。組成物的大的比電阻有助於使元件的電壓保持率大及對比度大。因此,較佳為在初期階段中不僅於室溫下而且於接近向列相的上限溫度的溫度下亦具有大的比電阻的組成物。且較佳為於長時間使用後,不僅於室溫下而且於接近向列相的上限溫度的溫度下亦具有大的比電阻的組成物。組成物對紫外線及熱的穩定性與元件的壽命有關。於該穩定性高時,元件的壽命長。此種特性對於液晶投影儀(liquid crystal projector)、液晶電視等中所用的AM元件而言較佳。
於聚合物穩定配向(polymer sustained alignment,PSA)型的液晶顯示元件中,使用含有聚合物的液晶組成物。首先,將添加有少量的聚合性化合物的組成物注入至元件中。繼而,一面於該元件的基板間施加電壓,一面對組成物照射紫外線。聚合性化合物進行聚合,於組成物中生成聚合物的網眼結構。對於該組
成物而言,因可藉由聚合物來控制液晶分子的配向,故元件的響應時間縮短,圖像的殘像得以改善。於具有TN、ECB、OCB、IPS、VA、FFS、FPA般的模式的元件中,可期待聚合物的此種效果。
通用的液晶顯示元件中,液晶分子的垂直配向是藉由聚醯亞胺配向膜來達成。另一方面,作為不具有配向膜的液晶顯示元件,提出有將極性化合物添加至液晶組成物中,而使液晶分子配向的模式。首先,將添加有少量的極性化合物及少量的聚合性化合物的組成物注入至元件中。此處,藉由極性化合物的作用使液晶分子配向。繼而,一面於該元件的基板間施加電壓,一面對組成物照射紫外線。此處,聚合性化合物聚合,使液晶分子的配向變穩定。對於該組成物而言,因可藉由極性化合物及聚合物來控制液晶分子的配向,故元件的響應時間縮短,圖像的殘像得以改善。進而,不具有配向膜的元件無需形成配向膜的步驟。因不存在配向膜,故不會發生因配向膜與組成物的相互作用而元件的電阻降低的情況。於具有TN、ECB、OCB、IPS、VA、FFS、FPA般的模式的元件中,可期待由極性化合物與聚合物的組合所得的此種效果。
迄今為止,作為可於不具有配向膜的液晶顯示元件中使液晶分子垂直配向的化合物,已合成了各種於末端具有-OH基的化合物。於專利文獻1中記載有一種於末端具有-OH基的聯苯化合物(S-1)。然而,關於該化合物,雖然使液晶分子垂直配向的能力高,但於用於液晶顯示元件中的情形時的電壓保持率不夠大。
[現有技術文獻]
[專利文獻]
[專利文獻1]國際公開第2014/090362號
[專利文獻2]國際公開第2014/094959號
[專利文獻3]國際公開第2013/004372號
[專利文獻4]國際公開第2012/104008號
[專利文獻5]國際公開第2012/038026號
[專利文獻6]日本專利特開昭50-35076號公報
本發明的第一課題在於提供一種極性化合物,其具有高的化學穩定性、高的使液晶分子配向的能力及於液晶組成物中的高溶解度,而且於用於液晶顯示元件中的情形時的電壓保持率大。本發明的第二課題在於提供一種液晶組成物,其含有所述化合物,而且充分滿足如下特性中的至少一個:向列相的上限溫度高、向列相的下限溫度低、黏度小、光學異向性適當、正或負的介電異向性大、比電阻大、對紫外線的穩定性高、對熱的穩定性高、彈性常數大等。本發明的第三課題在於提供一種液晶顯示元件,其
含有所述組成物,而且具有如下特性:可使用元件的溫度範圍廣、響應時間短、電壓保持率高、臨限電壓低、對比度大、壽命長。
本發明是有關於式(1)所表示的化合物、含有該化合物的液晶組成物及含有該組成物的液晶顯示元件。
式(1)中,R1為碳數1~15的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;MES為具有至少一個環的液晶原基;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;R2、M1、M2及M3獨立地為氫、鹵素或碳數1~10的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
本發明的第一優點為提供一種極性化合物,其具有高的化學穩定性、高的使液晶分子配向的能力及於液晶組成物中的高溶解度,而且於用於液晶顯示元件中的情形時的電壓保持率大。本發明的第二優點為提供一種液晶組成物,其含有所述化合物,而且充分滿足如下特性的至少一個:向列相的上限溫度高、向列相的下限溫度低、黏度小、光學異向性適當、正或負的介電異向性大、比電阻大、對紫外線的穩定性高、對熱的穩定性高、彈性常數大等。本發明的第三優點為提供一種液晶顯示元件,其含有所述組成物,而且具有如下特性:可使用元件的溫度範圍廣、響應時間短、電壓保持率高、臨限電壓低、對比度大、壽命長。
本說明書中的術語的使用方法如下。有時將「液晶組成物」及「液晶顯示元件」的術語分別簡稱為「組成物」及「元件」。「液晶顯示元件」為液晶顯示面板及液晶顯示模組的總稱。「液晶性化合物」為具有向列相、層列相等液晶相的化合物以及雖不具有液晶相但以調節向列相的溫度範圍、黏度、介電異向性般的特性為目的而混合至組成物中的化合物的總稱。該化合物例如具有1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基般的六員環,且其分子結構為棒狀(rod like)。「聚合性化合物」是以使組成物中生成聚合物為目的而添加
的化合物。「極性化合物」藉由極性基與基板表面相互作用而幫助液晶分子排列。
液晶組成物是藉由將多種液晶性化合物混合而製備。液晶性化合物的比例(含量)是由以該液晶組成物的重量為基準的重量百分率(重量%)來表示。於該液晶組成物中,視需要而添加光學活性化合物、抗氧化劑、紫外線吸收劑、色素、消泡劑、聚合性化合物、聚合起始劑、聚合抑制劑、極性化合物般的添加物。與液晶性化合物的比例同樣地,添加物的比例(添加量)是由以液晶組成物的重量為基準的重量百分率(重量%)來表示。有時亦使用重量百萬分率(ppm)。例外地,聚合起始劑及聚合抑制劑的比例是以聚合性化合物的重量為基準來表示。
有時將式(1)所表示的化合物簡稱為「化合物(1)」。化合物(1)是指式(1)所表示的一種化合物、兩種化合物的混合物、或三種以上的化合物的混合物。該規則(rule)亦適用於選自式(2)所表示的化合物的群組中的至少一種化合物等。由六邊形包圍的B1、C1、F等記號分別對應於環B1、環C1、環F等。六邊形表示環己烷環或苯環般的六員環或萘環般的稠環。橫穿該六邊形的斜線表示環上的任意的氫可經-Sp1-P1等基團取代。e等下標表示經取代的基團的個數。於下標為0時,不存在此種取代。
將末端基R11的記號用於多種成分化合物。該些化合物中,任意兩個R11所表示的兩個基團可相同或亦可不同。例如存在化合物(2)的R11為乙基、化合物(3)的R11為乙基的情況。亦
存在化合物(2)的R11為乙基、化合物(3)的R11為丙基的情況。該規則亦適用於其他末端基、環、鍵結基等記號。式(8)中,於i為2時,存在兩個環D1。該化合物中,兩個環D1所表示的兩個基團可相同或亦可不同。該規則亦適用於i大於2時的任意兩個環D1。該規則亦適用於其他環、鍵結基等記號。
「至少一個‘A’」的表述是指‘A’的個數為任意。關於「至少一個‘A’可經‘B’取代」的表述,於‘A’的個數為一個時,‘A’的位置為任意,於‘A’的個數為兩個以上時,亦可無限制地選擇該些‘A’的位置。該規則亦適用於「至少一個‘A’經‘B’取代」的表述。「至少一個A可經B、C或D取代」的表述是指包括至少一個A經B取代的情形、至少一個A經C取代的情形及至少一個A經D取代的情形,進而包括多個A經B、C、D的至少兩個取代的情形。例如至少一個-CH2-(或-CH2CH2-)可經-O-(或-CH=CH-)取代的烷基中,包括烷基、烯基、烷氧基、烷氧基烷基、烷氧基烯基、烯氧基烷基。此外,連續的兩個-CH2-經-O-取代而成為-O-O-般的情況欠佳。烷基等中,甲基部分(-CH2-H)的-CH2-經-O-取代而成為-O-H的情況亦欠佳。
鹵素是指氟、氯、溴或碘。較佳的鹵素為氟或氯。進而佳的鹵素為氟。烷基為直鏈狀或分支狀,不包括環狀烷基。直鏈狀烷基通常較分支狀烷基更佳。該些情況對於烷氧基、烯基等末端基而言亦相同。關於與1,4-伸環己基有關的立體構型,為了提高向列相的上限溫度,反式構型較順式構型更佳。2-氟-1,4-伸苯基
是指下述兩個二價基。化學式中,氟可向左(L),亦可向右(R)。該規則亦適用於如四氫吡喃-2,5-二基般藉由自環中去除兩個氫而生成的非對稱的二價基。
本發明包含下述項等。
式(1)中,R1為碳數1~15的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;MES為具有至少一個環的液晶原基;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可
經鹵素取代;R2、M1、M2及M3獨立地為氫、鹵素或碳數1~10的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
式(1-1)中,R1為碳數1~15的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;環A1及環A4獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、萘-2,6-二基、十氫萘-2,6-二基、1,2,3,4-四氫萘-2,6-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、嘧啶-2,5-二基、吡啶-2,5-二基、茀-2,7-二基、菲-2,7-二基、蒽-2,6-二基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經氟、氯、碳數1~12的烷基、碳數2~12的烯基、碳數1~11的烷氧基或碳數2~11的烯氧基取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代;
Z1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;R2、M1、M2及M3獨立地為氫、鹵素或碳數1~8的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;a為0、1、2、3或4;於a為0且環A4為1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基時,R1為碳數5~15的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代;於a為0且環A4為全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基時,M1為鹵素或碳數1~8的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
式(1-3)~式(1-6)中,R1為碳數1~15的烷基、碳數2~15的烯基、碳數1~14的烷氧基或碳數2~14的烯氧基,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟取代;環A1、環A2、環A3及環A4獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、萘-2,6-二基、十氫萘-2,6-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少-個氫可經氟、氯、碳數1~7的烷基、碳數
2~7的烯基或碳數1~6的烷氧基取代;Z1、Z2及Z3獨立地為單鍵、-(CH2)2-、-CH=CH-、-C≡C-、-COO-、-OCO-、-CF2O-、-OCF2-、-CH2O-、-OCH2-或-CF=CF-;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~7的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-COO-或-OCO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟取代;R2、M1、M2及M3獨立地為氫或碳數1~8的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代;式(1-3)中,於環A4為1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基時,R1為碳數5~15的烷基、碳數5~15的烯基、碳數4~14的烷氧基或碳數4~14的烯氧基,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟取代;式(1-3)中,於環A4為全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基時,M1為碳數1~8的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代。
式(1-3)~式(1-6)中,M2及M3為氫;R1為碳數1~10的烷基、碳數2~10的烯基或碳數1~9的烷氧基;環A1、環A2、環A3及環A4獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸苯基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經氟或碳數1~5的烷基取代;Z1、Z2及Z3獨立地為單鍵或-(CH2)2-;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~5的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代;M1及R2獨立地為氫或碳數1~5的烷基,該烷基中,至少一
個-CH2-可經-O-取代;式(1-3)中,於環A4為1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基時,R1為碳數5~10的烷基、碳數5~10的烯基或碳數4~9的烷氧基;式(1-3)中,於環A4為全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基時,M1為碳數1~5的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代。
式(1-7)~式(1-20)中,R1為碳數1~10的烷基、碳數2~10的烯基或碳數1~9的烷氧基;Z1、Z2及Z3獨立地為單鍵或-(CH2)2-;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~5的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代;L1、L2、L3、L4、L5、L6、L7、L8、L9、L10、L11、L12、L13及L14獨立地為氫、氟、甲基或乙基;
Y1、Y2、Y3及Y4獨立地為氫或甲基;M1為氫或碳數1~5的烷基;M4為碳數1~5的烷基;R2為氫、甲基或乙基。
式(1-21)~式(1-29)中,R1為碳數1~10的烷基;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~5的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代;L1、L2、L3、L4、L5、L6、L7、L8、L9、L10、L11及L12獨立地為氫、氟、甲基或乙基;Y1及Y2獨立地為氫或甲基;M1為氫、甲基或乙基;M4為甲基或乙基;R2為氫或甲基。
式(1-30)~式(1-36)中,R1為碳數1~10的烷基;Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~3的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代;L1、L2、L3、L4及L5獨立地為氫、氟、甲基或乙基;Y1及Y2獨立地為氫或甲基;
R2為氫或甲基。
項8. 一種液晶組成物,其含有如項1~項7中任一項所記載的化合物的至少一種。
式(2)~式(4)中,R11及R12獨立地為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;環B1、環B2、環B3及環B4獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸苯基、2-氟-1,4-伸苯基、2,5-二氟-1,4-伸苯基或嘧啶-2,5-二基;Z11、Z12及Z13獨立地為單鍵、-CH2CH2-、-CH=CH-、-C≡C-或-COO-。
式(5)~式(7)中,R13為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;X11為氟、氯、-OCF3、-OCHF2、-CF3、-CHF2、-CH2F、-OCF2CHF2或-OCF2CHFCF3;環C1、環C2及環C3獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、至少一個氫可經氟取代的1,4-伸苯基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基或嘧啶-2,5-二基;Z14、Z15及Z16獨立地為單鍵、-CH2CH2-、-CH=CH-、-C≡C-、-COO-、-CF2O-、-OCF2-、-CH2O-或-(CH2)4-;L11及L12獨立地為氫或氟。
式(8)中,R14為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;X12為-C≡N或-C≡C-C≡N;環D1為1,4-伸環己基、至少一個氫可經氟取代的1,4-伸苯基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基或嘧啶-2,5-二基;Z17為單鍵、-CH2CH2-、-C≡C-、-COO-、-CF2O-、-OCF2-或-CH2O-;L13及L14獨立地為氫或氟;i為1、2、3或4。
式(9)~式(15)中,R15及R16獨立地為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;R17為氫、氟、碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;環E1、環E2、環E3及環E4獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸
環己烯基、至少一個氫可經氟取代的1,4-伸苯基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基或十氫萘-2,6-二基;環E5及環E6獨立地為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基或十氫萘-2,6-二基;Z18、Z19、Z20及Z21獨立地為單鍵、-CH2CH2-、-COO-、-CH2O-、-OCF2-或-OCF2CH2CH2-;L15及L16獨立地為氟或氯;S11為氫或甲基;X為-CHF-或-CF2-;j、k、m、n、p、q、r及s獨立地為0或1,k、m、n及p之和為1或2,q、r及s之和為0、1、2或3,t為1、2或3。
式(16)中,環F及環I獨立地為環己基、環己烯基、苯基、1-萘基、2-萘基、四氫吡喃-2-基、1,3-二噁烷-2-基、嘧啶-2-基或吡啶-2-基,
該些環中,至少一個氫可經鹵素、碳數1~12的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~12的烷基取代;環G為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、萘-1,2-二基、萘-1,3-二基、萘-1,4-二基、萘-1,5-二基、萘-1,6-二基、萘-1,7-二基、萘-1,8-二基、萘-2,3-二基、萘-2,6-二基、萘-2,7-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、嘧啶-2,5-二基或吡啶-2,5-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經鹵素、碳數1~12的烷基、碳數1~12的烷氧基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~12的烷基取代;Z22及Z23獨立地為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-或-OCO-取代,至少一個-CH2CH2-可經-CH=CH-、-C(CH3)=CH-、-CH=C(CH3)-或-C(CH3)=C(CH3)-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代;P11、P12及P13獨立地為聚合性基;Sp11、Sp12及Sp13獨立地為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-CH2CH2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代;u為0、1或2;f、g及h獨立地為0、1、2、3或4,而且f、g及h之和為2以上。
式(P-1)~式(P-5)中,M11、M12及M13獨立地為氫、氟、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基。
式(16-1)~式(16-7)中,P4、P5及P6獨立地為選自式(P-1)~式(P-3)所表示的基團的群組中的聚合性基,此處,M11、M12
及M13獨立地為氫、氟、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基;
L21、L22、L23、L24、L25、L26、L27及L28獨立地為氫、氟或甲基;Sp1、Sp2及Sp3獨立地為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-CH2CH2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代。
項16. 如項8~項15中任一項所記載的液晶組成物,其更含有選自由式(1)及式(16)以外的聚合性化合物、聚合起始劑、聚合抑制劑、光學活性化合物、抗氧化劑、紫外線吸收劑、光穩定劑、熱穩定劑及消泡劑所組成的群組中的至少一種。
項17. 一種液晶顯示元件,其含有至少一種如項8~項16中任一項所記載的液晶組成物。
本發明亦包括以下項。(a)更含有聚合性化合物、聚合起始劑、聚合抑制劑、光學活性化合物、抗氧化劑、紫外線吸收劑、光穩定劑、熱穩定劑、消泡劑般的添加物的至少兩種的所述液晶組成物。(b)藉由在所述液晶組成物中添加與化合物(1)或
化合物(16)不同的聚合性化合物而製備的聚合性組成物。(c)藉由在所述液晶組成物中添加化合物(1)及化合物(16)而製備的聚合性組成物。(d)藉由使聚合性組成物聚合而製備的液晶複合物。(e)含有所述液晶複合物的聚合物穩定配向型的元件。(f)藉由在所述液晶組成物中添加化合物(1)及化合物(16)、以及與化合物(1)或化合物(16)不同的聚合性化合物而製備聚合性組成物,藉由使用所製備的聚合性組成物而製作的聚合物穩定配向型的元件。
依序對化合物(1)的態樣、化合物(1)的合成、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件加以說明。
1.化合物(1)的態樣
本發明的化合物(1)的特徵在於具有由至少一個環構成的液晶原部位、與丙烯醯胺基。化合物(1)由於極性基與玻璃(或金屬氧化物)的基板表面以非共價鍵的方式相互作用,故而有用。用途之一為液晶顯示元件中使用的液晶組成物用的添加物。化合物(1)是以控制液晶分子的配向為目的而添加。此種添加物較佳為在密閉於元件中的條件下化學穩定,具有於液晶組成物中的高溶解度,而且於用於液晶顯示元件中的情形時的電壓保持率大。化合物(1)以相當大的程度充分滿足此種特性。
對化合物(1)的較佳例加以說明。化合物(1)中的R1、MES、Sp1、M1、R2、M2或M3的較佳例亦適用於化合物(1)的下位式。化合物(1)中,藉由將該些基團的種類適當組合,可
任意調整特性。由於化合物的特性並無大的差異,因此化合物(1)亦可含有較天然存在比之量更多的2H(氘)、13C等同位素。
式(1)中,R1為碳數1~15的烷基,該烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-或-S-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
較佳的R1為碳數1~15的烷基、碳數2~15的烯基、碳數1~14的烷氧基或碳數2~14的烯氧基。進而佳的R1為碳數1~10的烷基、碳數2~10的烯基或碳數1~9的烷氧基。特佳的R1為碳數1~10的烷基。
式(1)中,MES為具有至少一個環的液晶原基。液晶原基為本領域技術人員眾所周知。液晶原基是指於化合物具有液晶相(中間相)時,有助於形成液晶相的部分。化合物(1)的較佳例為化合物(1-1)。
較佳的環A1或環A4為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、萘-2,6-二基、十氫萘-2,6-二基、1,2,3,4-四氫萘-2,6-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、嘧啶-2,5-二基、吡啶-2,5-二基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經氟、氯、碳數1~12的烷基、碳數2~12的烯基、碳數1~11的烷氧基或碳數2~11的烯氧基取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代。進而佳的環A1或環A4為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸苯基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經氟或碳數1~5的烷基取代。特佳的環A1或環A4為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸苯基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫亦可經氟、甲基或乙基取代。
式(1-1)中,Z1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
較佳的Z1為單鍵、-(CH2)2-、-CH=CH-、-C≡C-、-COO-、-OCO-、-CF2O-、-OCF2-、-CH2O-、-OCH2-或-CF=CF-。進而佳的Z1為單鍵、-(CH2)2-或-CH=CH-。特佳的Z1為單鍵。
式(1-1)中,a為0、1、2、3或4。較佳的a為0、1、2或3。進而佳的a為0、1或2。
式(1)中,Sp1為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-(CH2)2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經鹵素取代。
較佳的Sp1為單鍵、碳數1~5的伸烷基或一個-CH2-經-O-取代的碳數1~5的伸烷基。進而佳的Sp1為單鍵、碳數1~3的伸烷基或一個-CH2-經-O-取代的碳數1~3的伸烷基。
式(1)中,M2及M3獨立地為氫、鹵素、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基。較佳的M2或M3為氫、氟、甲基、乙基或三氟甲基。進而佳的M2或M3為氫。
R2為氫、鹵素、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基。較佳的R2為氫、甲基、乙基。進而佳的R2為氫。
式(1)中,M1為氫、鹵素、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基。較佳的M1為氫、氟、甲基、乙基或三氟甲基。進而佳的M1為甲基。
式(2)~式(15)表示液晶組成物的成分化合物。化合物(2)~化合物(4)具有小的介電異向性。化合物(5)~化合物(7)具有正的大的介電異向性。化合物(8)具有氰基,故具有正的更大的介電異向性。化合物(9)~化合物(15)具有負的大的介電異向性。該些化合物的具體例將於後述。
式(16)中,P11、P12及P13獨立地為聚合性基。較佳的
P11、P12或P13為選自式(P-1)~式(P-5)所表示的基團的群組中的聚合性基。進而佳的P11、P12或P13為基團(P-1)、基團(P-2)或基團(P-3)。特佳的基團(P-1)為-OCO-CH=CH2或-OCO-C(CH3)=CH2。基團(P-1)~基團(P-5)的波浪線表示鍵結的部位。
基團(P-1)~基團(P-5)中,M11、M12及M13獨立地為氫、氟、碳數1~5的烷基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~5的烷基。為了提高反應性,較佳的M11、M12或M13為氫或甲基。進而佳的M11為甲基,進而佳的M12或M13為氫。
Sp11、Sp12及Sp13獨立地為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-COO-、-OCO-或-OCOO-取代,至少一個-CH2CH2-可經-CH=CH-或-C≡C-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代。較佳的Sp11、Sp12或Sp13為單鍵。
環F及環I獨立地為環己基、環己烯基、苯基、1-萘基、2-萘基、四氫吡喃-2-基、1,3-二噁烷-2-基、嘧啶-2-基或吡啶-2-基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經鹵素、碳數1~17的烷基、碳數1~12
的烷氧基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~12的烷基取代。較佳的環F或環I為苯基。環G為1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、萘-1,2-二基、萘-1,3-二基、萘-1,4-二基、萘-1,5-二基、萘-1,6-二基、萘-1,7-二基、萘-1,8-二基、萘-2,3-二基、萘-2,6-二基、萘-2,7-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、嘧啶-2,5-二基或吡啶-2,5-二基,該些環中,至少一個氫可經鹵素、碳數1~12的烷基、碳數1~12的烷氧基或至少一個氫經鹵素取代的碳數1~12的烷基取代。特佳的環G為1,4-伸苯基或2-氟-1,4-伸苯基。
Z22及Z23獨立地為單鍵或碳數1~10的伸烷基,該伸烷基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-、-CO-、-COO-或-OCO-取代,至少一個-CH2CH2-可經-CH=CH-、-C(CH3)=CH-、-CH=C(CH3)-或-C(CH3)=C(CH3)-取代,該些基團中,至少一個氫可經氟或氯取代。較佳的Z22或Z23為單鍵、-CH2CH2-、-CH2O-、-OCH2-、-COO-或-OCO-。進而佳的Z22或Z22為單鍵。
u為0、1或2。較佳的u為0或1。f、g及h獨立地為0、1、2、3或4,而且,f、g及h之和為1以上。較佳的f、g或h為1或2。
2.化合物(1)的合成
對化合物(1)的合成法加以說明。化合物(1)可藉由將有機合成化學的方法適當組合而合成。未記載合成法的化合物可藉由「有機合成(Organic Syntheses)」(約翰.威利父子出版公司(John
Wiley & Sons,Inc))、「有機反應(Organic Reactions)」(約翰.威利父子出版公司(John Wiley & Sons,Inc))、「綜合有機合成(Comprehensive Organic Synthesis)」(培格曼出版社(Pergamon Press))、「新實驗化學講座」(丸善)等書籍中記載的方法來合成。
2-1.鍵結基的生成
生成化合物(1)中的鍵結基的方法的例子如下述流程所述。該流程中,MSG1(或MSG2)為具有至少一個環的一價有機基。多個MSG1(或MSG2)所表示的一價有機基可相同或亦可不同。化合物(1A)~化合物(1H)相當於化合物(1)或化合物(1)的中間體。
(1)單鍵的生成
使芳基硼酸(21)與化合物(22)於碳酸鹽、四(三苯基膦)鈀觸媒的存在下反應,合成化合物(1A)。亦可使正丁基鋰、繼而使氯化鋅與化合物(23)反應,於二氯雙(三苯基膦)鈀觸媒的存在下使化合物(22)反應而合成該化合物(1A)。
(II)-COO-及-OCO-的生成
使正丁基鋰、繼而使二氧化碳與化合物(23)反應,獲得羧酸(24)。使該羧酸(24)與由化合物(21)所衍生的酚(25)於1,3-二環己基碳二醯亞胺(1,3-dicyclohexyl carbodiimide,DCC)及4-二甲基胺基吡啶(4-dimethylaminopyridine,DMAP)的存在下脫水,合成具有-COO-的化合物(1B)。藉由該方法亦合成具有-OCO-的化合物。
(III)-CF2O-及-OCF2-的生成
利用勞森試劑將化合物(1B)硫化,獲得化合物(26)。利用氟化氫吡啶錯合物及N-溴琥珀醯亞胺(N-bromosuccinimide,NBS)將化合物(26)氟化,合成具有-CF2O-的化合物(1C)。參照M.黑星(M.Kuroboshi)等人的「化學通訊(Chem.Lett.)」(1992,827.)。利用(二乙基胺基)三氟化硫((diethylamino)sulphur trifluoride,DAST)將化合物(26)氟化而亦合成化合物(1C)。參照W.H.邦奈拉(W.H.Bunnelle)等人的「有機化學期刊(J.Org.Chem.)」(1990,55,768.)。利用該方法而亦合成具有-OCF2-的化合物。
(IV)-CH=CH-的生成
使正丁基鋰、繼而使N,N-二甲基甲醯胺(N,N-dimethyl formamide,DMF)與化合物(22)反應而獲得醛(27)。使鏻鹽(28)與第三丁醇鉀反應而產生磷內鎓鹽(phosphorus ylide),使所得的磷內鎓鹽與醛(27)反應而合成化合物(1D)。視反應條件不同,有時生成順式體,故視需要藉由公知的方法將順式體異構化為反式體。
(V)-CH2CH2-的生成
於鈀碳觸媒的存在下將化合物(1D)氫化,合成化合物(1E)。
(VI)-C≡C-的生成
於二氯鈀及碘化銅的觸媒存在下,使2-甲基-3-丁炔-2-醇與化合物(23)反應後,於鹼性條件下脫保護而獲得化合物(29)。於
二氯雙(三苯基膦)鈀及鹵化銅的觸媒存在下,使化合物(29)與化合物(22)反應,合成化合物(1F)。
(VII)-CH2O-及-OCH2-的生成
利用硼氫化鈉將化合物(27)還原而獲得化合物(30)。利用氫溴酸將其溴化而獲得化合物(31)。於碳酸鉀的存在下,使化合物(25)與化合物(31)反應,合成化合物(1G)。藉由該方法而亦合成具有-OCH2-的化合物。
(VIII)-CF=CF-的生成
利用正丁基鋰對化合物(23)進行處理後,使四氟乙烯反應而獲得化合物(32)。利用正丁基鋰對化合物(22)進行處理後,與化合物(32)反應,合成化合物(1H)。
2-2.環A1及環A2的生成
關於1,4-伸環己基、1,4-伸環己烯基、1,4-伸苯基、2-氟-1,4-伸苯基、2-甲基-1,4-伸苯基、2-乙基-1,4-伸苯基、萘-2,6-二基、十氫萘-2,6-二基、1,2,3,4-四氫萘-2,6-二基、四氫吡喃-2,5-二基、1,3-二噁烷-2,5-二基、嘧啶-2,5-二基、吡啶-2,5-二基、全氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基或2,3,4,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-十四氫環戊并[a]菲-3,17-二基等環,其起始原料有市售,或合成法廣為人知。
2-3.合成例
合成化合物(1)的方法的例子如下。該些化合物中,R1、MES、M1及M2的定義與上文所述相同。
M1為甲基且R2、M2及M3為氫的化合物(1-51)可利
用以下方法來合成。使化合物(51)與丙烯醯氯於三乙基胺的存在下反應,獲得化合物(52)。使化合物(52)於NaH、CH3I的存在下反應,藉此可導出化合物(1-51)。
3.液晶組成物
本發明的液晶組成物含有化合物(1)作為成分A。化合物(1)可藉由與元件的基板的非共價鍵結方式的相互作用而控制液晶分子的配向。該組成物較佳為含有化合物(1)作為成分A,且更含有選自以下所示的成分B、成分C、成分D及成分E中的液晶性化合物。成分B為化合物(2)~化合物(4)。成分C為化合物(5)~化合物(7)。成分D為化合物(8)。成分E為化合物(9)~化合物(15)。該組成物亦可含有與化合物(2)~化合物(15)不同的其他液晶性化合物。於製備該組成物時,較佳為考慮到正或負的介電異向性的大小等而選擇成分B、成分C、成分D及成分E。適當選擇了成分的組成物具有高的上限溫度、低的下限溫度、小的黏度、適當的光學異向性(即,大的光學異向性或小的光學異向性)、正或負的大的介電異向性、大的比電阻、對熱或紫外線的穩定性、及適當的彈性常數(即,大的彈性常數或小的彈性常數)。
關於化合物(1)的較佳比例,為了維持對紫外線的高穩定性而為約0.01重量%以上,為了使其溶解於液晶組成物中而為約5重量%以下。進而佳的比例為約0.05重量%~約2重量%的範圍。最佳的比例為約0.05重量%~約1重量%的範圍。
成分B是兩個末端基為烷基等的化合物。成分B的較佳例可列舉化合物(2-1)~化合物(2-11)、化合物(3-1)~化合物(3-19)及化合物(4-1)~化合物(4-7)。成分B的化合物中,R11及R12獨立地為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基或烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代。
成分B由於介電異向性的絕對值小,故為接近中性的化合物。化合物(2)主要在減小黏度或調整光學異向性的方面有效果。化合物(3)及化合物(4)有藉由提高上限溫度而擴大向列相的溫度範圍的效果,或在調整光學異向性的方面有效果。
隨著使成分B的含量增加,組成物的介電異向性變小,但黏度變小。因此,只要滿足元件的臨限電壓的要求值,則含量
以多為佳。於製備IPS、VA等模式用的組成物的情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分B的含量較佳為30重量%以上,進而佳為40重量%以上。
成分C為於右末端具有鹵素或含氟基團的化合物。成分C的較佳例可列舉化合物(5-1)~化合物(5-16)、化合物(6-1)~化合物(6-113)、化合物(7-1)~化合物(7-57)。成分C的化合物中,R13為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;X11為氟、氯、-OCF3、-OCHF2、-CF3、-CHF2、-CH2F、-OCF2CHF2或-OCF2CHFCF3。
成分C的介電異向性為正,且對熱、光等的穩定性非常優異,因此可用於製備IPS、FFS、OCB等模式用的組成物的情形。以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分C的含量合適的是1重量%~99重量%的範圍,較佳為10重量%~97重量%的範圍,進而佳為40重量%~95重量%的範圍。於將成分C添加至介電異向性為負的組成物中的情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分C的含量較佳為30重量%以下。藉由添加成分C,可調整組成物的彈性常數,調整元件的電壓-透過率曲線。
成分D是右末端基為-C≡N或-C≡C-C≡N的化合物(8)。成分D的較佳例可列舉化合物(8-1)~化合物(8-64)。成分D的化合物中,R14為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;-X12為-C≡N或-C≡C-C≡N。
成分D的介電異向性為正,且其值大,因此主要可用於製備TN等模式用的組成物的情形。藉由添加該成分D,可增大組成物的介電異向性。成分D有擴大液晶相的溫度範圍、調整黏度或調整光學異向性的效果。成分D對於元件的電壓-透過率曲線的調整亦有用。
於製備TN等模式用的組成物的情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分D的含量合適的是1重量%~99重量%的範圍,較佳為10重量%~97重量%的範圍,進而佳為40重量%~95重量%的範圍。於將成分D添加至介電異向性為負的組成物中的
情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分D的含量較佳為30重量%以下。藉由添加成分D,可調整組成物的彈性常數,調整元件的電壓-透過率曲線。
成分E為化合物(9)~化合物(15)。該些化合物具有如2,3-二氟-1,4-伸苯基般側位經兩個鹵素取代的伸苯基。成分E的較佳例可列舉化合物(9-1)~化合物(9-8)、化合物(10-1)~化合物(10-17)、化合物(11-1)、化合物(12-1)~化合物(12-3)、化合物(13-1)~化合物(13-11)、化合物(14-1)~化合物(14-3)及化合物(15-1)~化合物(15-3)。成分E的化合物中,R15及R16獨立地為碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代;R17為氫、氟、碳數1~10的烷基或碳數2~10的烯基,該烷基及烯基中,至少一個-CH2-可經-O-取代,至少一個氫可經氟取代。
成分E的介電異向性為負且大。成分E可用於製備IPS、VA、PSA等模式用的組成物的情形。隨著使成分E的含量增加,組成物的介電異向性為負且增大,但黏度變大。因此,只要滿足元件的臨限電壓的要求值,則含量以少為佳。若考慮到介電異向性為-5左右,則為了進行充分的電壓驅動,較佳為含量為40重量%以上。
成分E中,化合物(9)為二環化合物,故主要在減小黏度、調整光學異向性或增加介電異向性的方面有效果。化合物(10)及化合物(11)為三環化合物,故有提高上限溫度、增大光學異向性或增大介電異向性的效果。化合物(12)~化合物(15)有增大介電異向性的效果。
於製備IPS、VA、PSA等模式用的組成物的情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分E的含量較佳為40重量%以上,進而佳為50重量%~95重量%的範圍。於將成分E添加至介電異
向性為正的組成物中的情形時,以液晶組成物的重量為基準,成分E的含量較佳為30重量%以下。藉由添加成分E,可調整組成物的彈性常數,調整元件的電壓-透過率曲線。
藉由將以上所述的成分B、成分C、成分D及成分E適當組合,可製備充分滿足如下特性的至少一個的液晶組成物:上限溫度高、下限溫度低、黏度小、光學異向性適當、正或負的介電異向性大、比電阻大、對紫外線的穩定性高、對熱的穩定性高、彈性常數大等。視需要亦可添加與成分B、成分C、成分D及成分E不同的液晶性化合物。
液晶組成物是藉由公知的方法而製備。例如將成分化合物混合,繼而藉由加熱使其彼此溶解。亦可根據用途而於該組成物中添加添加物。添加物的例子為式(1)及式(16)以外的聚合性化合物、聚合起始劑、聚合抑制劑、光學活性化合物、抗氧化劑、紫外線吸收劑、光穩定劑、熱穩定劑、消泡劑等。此種添加物已為本領域技術人員所熟知,且已記載於文獻中。
聚合性化合物是以使液晶組成物中生成聚合物為目的而添加。於對電極間施加電壓的狀態下照射紫外線,使聚合性化合物與化合物(1)進行共聚合,藉此使液晶組成物中生成聚合物。此時,化合物(1)於極性基與玻璃(或金屬氧化物)的基板表面以非共價鍵結的方式相互作用的狀態下經固定化。藉此,控制液晶分子的配向的能力進一步提高,同時不會發生極性化合物於液晶組成物中漏出的情況。另外,於玻璃(或金屬氧化物)的基板
表面亦可獲得適當的預傾角,故可獲得響應時間縮短、且電壓保持率大的液晶顯示元件。聚合性化合物的較佳例為丙烯酸酯、甲基丙烯酸酯、乙烯基化合物、乙烯氧基化合物、丙烯基醚、環氧化合物(氧雜環丙烷、氧雜環丁烷)及乙烯基酮。進而佳的例子為具有至少一個丙烯醯氧基的化合物及具有至少一個甲基丙烯醯氧基的化合物。進而佳的例子中亦包括具有丙烯醯氧基與甲基丙烯醯氧基兩者的化合物。
進而佳的例子為以下所示的化合物。該些化合物中,R25~R31獨立地為氫或甲基;v及x獨立地為0或1;t及u獨立地為1~10的整數;L31~L36獨立地為氫或氟,L37及L38獨立地為氫、氟或甲基。
聚合性化合物可藉由添加聚合起始劑而迅速聚合。藉由使反應溫度最適化,可減少殘存的聚合性化合物的量。光自由基聚合起始劑的例子為巴斯夫(BASF)公司的達羅固(Darocur)系列中的TPO、1173及4265以及豔佳固(Irgacure)系列中的184、
369、500、651、784、819、907、1300、1700、1800、1850及2959。
光自由基聚合起始劑的追加例為4-甲氧基苯基-2,4-雙(三氯甲基)三嗪、2-(4-丁氧基苯乙烯基)-5-三氯甲基-1,3,4-噁二唑、9-苯基吖啶、9,10-苯并啡嗪、二苯甲酮/米其勒酮混合物、六芳基聯咪唑/巰基苯并咪唑混合物、1-(4-異丙基苯基)-2-羥基-2-甲基丙烷-1-酮、苄基二甲基縮酮、2-甲基-1-[4-(甲硫基)苯基]-2-嗎啉基丙烷-1-酮、2,4-二乙基氧雜蒽酮/對二甲基胺基苯甲酸甲酯混合物、二苯甲酮/甲基三乙醇胺混合物。
於液晶組成物中添加光自由基聚合起始劑後,於施加電場的狀態下照射紫外線,藉此可進行聚合。然而,未反應的聚合起始劑或聚合起始劑的分解產物可能對元件引起圖像的殘像等顯示不良。為了防止該情況,亦可於不添加聚合起始劑的狀態下進行光聚合。所照射的光的較佳波長為150nm~500nm的範圍。進而佳的波長為250nm~450nm的範圍,最佳的波長為300nm~400nm的範圍。
於保管聚合性化合物時,亦可為了防止聚合而添加聚合抑制劑。聚合性化合物通常是以不去除聚合抑制劑的狀態而添加至組成物中。聚合抑制劑的例子為對苯二酚、甲基對苯二酚般的對苯二酚衍生物、4-第三丁基鄰苯二酚、4-甲氧基苯酚、啡噻嗪等。
光學活性化合物具有如下效果:對液晶分子誘發螺旋結構而賦予必要的扭轉角,藉此防止反向扭轉等。藉由添加光學活性化合物,可調整螺旋節距。以調整螺旋節距的溫度依存性為目
的而亦可添加兩種以上的光學活性化合物。光學活性化合物的較佳例可列舉下述化合物(Op-1)~化合物(Op-18)。化合物(Op-18)中,環J為1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基,R28為碳數1~10的烷基。
為了維持大的電壓保持率,抗氧化劑有效。抗氧化劑的較佳例可列舉:下述化合物(AO-1)及化合物(AO-2);豔佳諾(IRGANOX)415、豔佳諾(IRGANOX)565、豔佳諾(IRGANOX)
1010、豔佳諾(IRGANOX)1035、豔佳諾(IRGANOX)3114、及豔佳諾(IRGANOX)1098(商品名:巴斯夫(BASF)公司)。為了防止上限溫度的降低,紫外線吸收劑有效。紫外線吸收劑的較佳例為二苯甲酮衍生物、苯甲酸酯衍生物、三唑衍生物等。具體例可列舉:下述化合物(AO-3)及化合物(AO-4);地奴彬(TINUVIN)329、地奴彬(TINUVIN)P、地奴彬(TINUVIN)326、地奴彬(TINUVIN)234、地奴彬(TINUVIN)213、地奴彬(TINUVIN)400、地奴彬(TINUVIN)328及地奴彬(TINUVIN)99-2(商品名:巴斯夫(BASF)公司);及1,4-二氮雜雙環[2.2.2]辛烷(DABCO)。
為了維持大的電壓保持率,較佳為具有立體阻礙的胺般的光穩定劑。光穩定劑的較佳例可列舉:下述化合物(AO-5)及化合物(AO-6);地奴彬(TINUVIN)144、地奴彬(TINUVIN)765、及地奴彬(TINUVIN)770DF(商品名:巴斯夫(BASF)公司)。為了維持大的電壓保持率,熱穩定劑亦有效,較佳例可列舉豔佳富(IRGAFOS)168(商品名:巴斯夫(BASF)公司)。為了防止起泡,消泡劑有效。消泡劑的較佳例為二甲基矽油、甲基苯基矽油等。
化合物(AO-1)中,R40為碳數1~20的烷基、碳數1~20的烷氧基、-COOR41或-CH2CH2COOR41,此處,R41為碳數1~20的烷基。化合物(AO-2)及化合物(AO-5)中,R42為碳數1~20的烷基。化合物(AO-5)中,R43為氫、甲基或O.(氧自由基),環G為1,4-伸環己基或1,4-伸苯基,z為1、2或3。
4.液晶顯示元件
液晶組成物可用於具有PC、TN、STN、OCB、PSA等動作模式且以主動式矩陣方式驅動的液晶顯示元件。該組成物亦可用於具有PC、TN、STN、OCB、VA、IPS等動作模式且以被動式矩陣方式驅動的液晶顯示元件。該些元件亦可應用於反射型、透射型、半透射型的任一類型。
該組成物亦可用於將向列液晶微膠囊化而製作的向列曲線排列相(nematic curvilinear aligned phase,NCAP)元件、於液晶中形成三維網狀聚合物而製作的聚合物分散型液晶顯示元件(polymer dispersed liquid crystal display,PDLCD)、以及聚合物網絡液晶顯示元件(polymer net liquid crystal display,PNLCD)。
於以液晶組成物的重量為基準而聚合性化合物的添加量為約10重量%以下時,製作PSA模式的液晶顯示元件。較佳的比例為約0.1重量%~約2重量%的範圍。進而佳的比例為約0.2重量%~約1.0重量%的範圍。PSA模式的元件能以如主動式矩陣、被動式矩陣般的驅動方式來驅動。此種元件亦可應用於反射型、透射型、半透射型的任一類型。藉由增加聚合性化合物的添加量,亦可製作聚合物分散(polymer dispersed)模式的元件。
於聚合物穩定配向型的元件中,組成物所含的聚合物使液晶分子配向。極性化合物幫助液晶分子排列。即,極性化合物可代替配向膜而使用。製造此種元件的方法的一例如下。準備具有被稱為陣列基板與彩色濾光片基板的兩片基板的元件。該基板不具有配向膜。該基板的至少一片具有電極層。將液晶性化合物混合而製備液晶組成物。於該組成物中添加聚合性化合物及極性化合物。視需要亦可進一步添加添加物。將該組成物注入至元件中。於對該元件施加電壓的狀態下進行光照射。較佳為紫外線。藉由光照射使聚合性化合物聚合。藉由該聚合而生成含有聚合物的組成物,製作具有PSA模式的元件。
該順序中,極性化合物由於極性基與基板表面相互作用,故於基板上排列。該極性化合物使液晶分子配向。於施加電壓時,藉由電場的作用來進一步促進液晶分子的配向。聚合性化合物亦依照該配向而進行配向。於該狀態下聚合性化合物藉由紫外線而聚合,故生成維持所述配向的聚合物。藉由該聚合物的效
果,液晶分子的配向進一步變穩定,故元件的響應時間縮短。由於圖像的殘像為液晶分子的動作不良,故藉由該聚合物的效果而亦同時改善殘像。尤其本發明的化合物(1)為聚合性極性化合物,故使液晶分子配向,並且與其他聚合性化合物共聚合。藉此不會發生極性化合物於液晶組成物中漏出的情況,故可獲得電壓保持率大的液晶顯示元件。
[實施例]
藉由實施例(包括合成例、使用例)對本發明加以更詳細說明。本發明不受該些實施例的限制。本發明包括使用例1的組成物與使用例2的組成物的混合物。本發明亦包括藉由將使用例的組成物的至少兩種混合而製備的混合物。
1.化合物(1)的實施例
只要無特別記載,則反應是在氮氣環境下進行。化合物(1)是依照實施例1等所示的順序而合成。所合成的化合物是藉由核磁共振(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance,NMR)分析等方法而鑑定。化合物(1)、液晶性化合物、組成物、元件的特性是藉由下述方法來測定。
NMR分析:於測定時,使用布魯克拜厄斯賓(Bruker BioSpin)公司製造的DRX-500。於1H-NMR的測定中,使試樣溶解於CDCl3等氘化溶劑中,於室溫下以500MHz、累計次數16次的條件進行測定。使用四甲基矽烷作為內部標準。於19F-NMR的測定中,使用CFCl3作為內部標準,以累計次數24次進行測定。
核磁共振光譜的說明中,s是指單峰,d是指雙重峰,t是指三重峰,q是指四重峰,quin是指五重峰,sex是指六重峰,m是指多重峰,br是指寬峰。
氣相層析分析:於測定時,使用島津製作所製造的GC-2010型氣相層析儀。管柱是使用安捷倫科技公司(Agilent Technologies Inc.)製造的毛細管柱DB-1(長度60m、內徑0.25mm、膜厚0.25μm)。使用氦氣(1ml/min)作為載氣。將試樣氣化室的溫度設定為300℃,將檢測器(火焰離子化檢測器(flame ionization detector,FID))部分的溫度設定為300℃。試樣是溶解於丙酮中並以成為1重量%的溶液的方式製備,將1μl的所得的溶液注入至試樣氣化室中。記錄計是使用島津製作所製造的GC溶解(GC Solution)系統等。
高效液相層析(High Performance Liquid Chromatography,HPLC)分析:於測定時,使用島津製作所製造的普羅米納斯(Prominence)(LC-20AD;SPD-20A)。管柱是使用維美希(YMC)製造的YMC-填充(YMC-Pack)ODS-A(長度150mm、內徑4.6mm、粒徑5μm)。溶出液是將乙腈與水適當混合而使用。檢測器是適當使用紫外線(Ultraviolet,UV)檢測器、折射率(Reflective Index,RI)檢測器、科羅娜(CORONA)檢測器等。於使用UV檢測器的情形時,將檢測波長設定為254nm。試樣是溶解於乙腈中並以成為0.1重量%的溶液的方式製備,將1μL的該溶液導入至試樣室中。記錄計是使用島津製作所製造的
C-R7A加(C-R7A plus)。
紫外可見分光分析:於測定時,使用島津製作所製造的法碼思拜(PharmaSpec)UV-1700。將檢測波長設定為190nm~700nm。試樣是溶解於乙腈中並以成為0.01mmol/L的溶液的方式製備,並放入至石英池(光路長1cm)中進行測定。
測定試樣:於測定相結構及轉變溫度(透明點、熔點、聚合起始溫度等)時,將化合物本身用作試樣。
測定方法:特性的測定是利用下述方法來進行。該些方法大多為社團法人電子資訊技術產業協會(Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association,JEITA)審議製定的JEITA標準(JEITA.ED-2521B)中記載的方法或將其加以修飾的方法。用於測定的TN元件中,未安裝薄膜電晶體(TFT)。
(1)相結構
將試樣放置於具備偏光顯微鏡的熔點測定裝置的加熱板(梅特勒(Mettler)公司的FP-52型熱平台(hot stage))上。對該試樣一面以3℃/min的速度加熱一面利用偏光顯微鏡觀察相狀態及其變化,確定相的種類。
(2)轉變溫度(℃)
於測定時,使用帕金艾爾瑪(Perkin Elmer)公司製造的掃描熱量計、金剛石(Diamond)示差掃描熱量計(Differential Scanning Calorimeter,DSC)系統或SSI奈米科技(SSI Nanotechnology)公司製造的高感度示差掃描熱量計X-DSC7000。對試樣以3℃/min
的速度進行升降溫,藉由外推而求出伴隨著試樣的相變化的吸熱波峰或發熱波峰的起始點,確定轉變溫度。化合物的熔點、聚合起始溫度亦是使用該裝置來測定。有時將化合物由固體轉變為層列相、向列相等液晶相的溫度簡稱為「液晶相的下限溫度」。有時將化合物由液晶相轉變為液體的溫度簡稱為「透明點」。
將結晶表示作C。於區分結晶的種類的情形時,分別如C1、C2般表示。將層列相表示作S,將向列相表示作N。層列相中,於區分層列A相、層列B相、層列C相或層列F相的情形時,分別表示作SA、SB、SC或SF。將液體(等向性)表示作I。轉變溫度例如是如「C 50.0 N 100.0 I」般表述。其表示由結晶轉變為向列相的溫度為50.0℃,由向列相轉變為液體的溫度為100.0℃。
(3)向列相的上限溫度(TNI或NI;℃)
將試樣放置於具備偏光顯微鏡的熔點測定裝置的加熱板上,以1℃/min的速度進行加熱。對試樣的一部分由向列相變化為等向性液體時的溫度進行測定。有時將向列相的上限溫度簡稱為「上限溫度」。於試樣為化合物(1)與母液晶的混合物時,以TNI的記號表示。於試樣為化合物(1)與成分B、成分C、成分D般的化合物的混合物時,以NI的記號表示。
(4)向列相的下限溫度(TC;℃)
將具有向列相的試樣於0℃、-10℃、-20℃、-30℃及-40℃的冷凍器中保管10天後,觀察液晶相。例如當試樣於-20℃下保持
向列相、且於-30℃下變化為結晶或層列相時,將TC記載為≦-20℃。有時將向列相的下限溫度簡稱為「下限溫度」。
(5)黏度(體積黏度(bulk viscosity);η;於20℃下測定;mPa.s)
於測定時,使用東京計器股份有限公司製造的E型旋轉黏度計。
(6)光學異向性(折射率異向性;於25℃下測定;Δn)
使用波長589nm的光,藉由在接目鏡上安裝有偏光板的阿貝折射計來進行測定。對主稜鏡的表面朝一個方向摩擦後,將試樣滴加至主稜鏡上。折射率(n∥)是於偏光的方向與摩擦的方向平行時測定。折射率(n⊥)是於偏光的方向與摩擦的方向垂直時測定。光學異向性(Δn)的值是由Δn=n∥-n⊥的式子來計算。
(7)比電阻(ρ;於25℃下測定;Ωcm)
於具備電極的容器中注入1.0mL試樣。對該容器施加直流電壓(10V),測定10秒後的直流電流。比電阻是由下式來算出。
(比電阻)={(電壓)×(容器的電容)}/{(直流電流)×(真空的介電常數)}。
對於介電異向性為正的試樣與介電異向性為負的試樣,有時特性的測定法不同。於介電異向性為正時的測定法是記載於項(8a)~項(12a)中。於介電異向性為負的情形時,測定
法是記載於項(8b)~項(12b)中。
(8a)黏度(旋轉黏度;γ1;於25℃下測定;mPa.s)
正的介電異向性:測定是依照M.今井(M.Imai)等人的「分子晶體及液晶(Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals)」(Vol.259,37(1995))中記載的方法。於扭轉角為0度、而且兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為5μm的TN元件中放入試樣。對該元件於16V~19.5V的範圍內以0.5V為單位階段性地施加電壓。不施加電壓0.2秒後,以僅一個矩形波(矩形脈衝;0.2秒)與不施加(2秒)的條件反覆施加電壓。對因該施加而產生的暫態電流(transient current)的峰值電流(peak current)及峰值時間(peak time)進行測定。根據該些測定值及M.今井(M.Imai)等人的論文40頁的計算式(8)而獲得旋轉黏度的值。該計算所必需的介電異向性的值是使用測定了該旋轉黏度的元件利用以下記載的方法而求出。
(8b)黏度(旋轉黏度;γ1;於25℃下測定;mPa.s)
負的介電異向性:測定是依照M.今井(M.Imai)等人的「分子晶體及液晶(Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals)」(Vol.259,37(1995))中記載的方法。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為20μm的VA元件中放入試樣。對該元件於39伏特~50伏特的範圍內以1伏特為單位階段性地施加電壓。不施加電壓0.2秒後,以僅一個矩形波(矩形脈衝;0.2秒)與不施加(2秒)的條件反覆施加電壓。對因該施加而產生的暫態電流(transient current)的
峰值電流(peak current)及峰值時間(peak time)進行測定。根據該些測定值及M.今井(M.Imai)等人的論文40頁的計算式(8)而獲得旋轉黏度的值。該計算所必需的介電異向性是使用下述介電異向性的項中測定的值。
(9a)介電異向性(Δε;於25℃下測定)
正的介電異向性:於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為9μm、而且扭轉角為80度的TN元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加正弦波(10V、1kHz),2秒後測定液晶分子的長軸方向上的介電常數(ε∥)。對該元件施加正弦波(0.5V、1kHz),2秒後測定液晶分子的短軸方向上的介電常數(ε⊥)。介電異向性的值是由Δε=ε∥-ε⊥的式子來計算。
(9b)介電異向性(Δε;於25℃下測定)
負的介電異向性:介電異向性的值是由Δε=ε∥-ε⊥的式子來計算。介電常數(ε∥及ε⊥)是如下般測定。
1)介電常數(ε∥)的測定:於經充分清洗的玻璃基板上塗佈十八烷基三乙氧基矽烷(0.16mL)的乙醇(20mL)溶液。利用旋轉器使玻璃基板旋轉後,於150℃下加熱1小時。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為4μm的VA元件中放入試樣,藉由利用紫外線進行硬化的接著劑將該元件密閉。對該元件施加正弦波(0.5V、1kHz),2秒後測定液晶分子的長軸方向上的介電常數(ε∥)。
2)介電常數(ε⊥)的測定:於經充分清洗的玻璃基板上塗
佈聚醯亞胺溶液。將該玻璃基板煅燒後,對所得的配向膜實施摩擦處理。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為9μm、扭轉角為80度的TN元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加正弦波(0.5V、1kHz),2秒後測定液晶分子的短軸方向上的介電常數(ε⊥)。
(10a)彈性常數(K;於25℃下測定;pN)
正的介電異向性:於測定時使用橫河.惠普(Yokogawa-Hewlett Packard)股份有限公司製造的HP4284A型電感-電容-電阻(Inductance-Capacitance-Resistance,LCR)計。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為20μm的水平配向元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加0伏特~20伏特電荷,測定靜電電容及施加電壓。使用「液晶元件手冊」(日刊工業報社)75頁中的式(2.98)、式(2.101)對所測定的靜電電容(C)及施加電壓(V)的值進行擬合,由式(2.99)獲得K11及K33的值。繼而,於171頁中的式(3.18)中,使用先求出的K11及K33的值算出K22。彈性常數K是以如此般求出的K11、K22及K33的平均值表示。
(10b)彈性常數(K11及K33;於25℃下測定;pN)
負的介電異向性:於測定時使用東陽技術(TOYO Corporation)股份有限公司製造的EC-1型彈性常數測定器。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為20μm的垂直配向元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加20伏特~0伏特電荷,測定靜電電容及施加電壓。使用「液晶元件手冊」(日刊工業報社)75頁中的式(2.98)、式(2.101)對靜電電容(C)及施加電壓(V)的值進行擬合,由
式(2.100)獲得彈性常數的值。
(11a)臨限電壓(Vth;於25℃下測定;V)
正的介電異向性:於測定時使用大塚電子股份有限公司製造的LCD5100型亮度計。光源為鹵素燈。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為0.45/Δn(μm)、扭轉角為80度的常白模式(normally white mode)的TN元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加的電壓(32Hz、矩形波)是自0V起以0.02V為單位階段性地增加至10V為止。此時,對元件自垂直方向照射光,對透過元件的光量進行測定。製作該光量達到最大時為透過率100%、該光量最小時為透過率0%的電壓-透過率曲線。臨限電壓是以透過率成為90%時的電壓表示。
(11b)臨限電壓(Vth;於25℃下測定;V)
負的介電異向性:於測定時使用大塚電子股份有限公司製造的LCD5100型亮度計。光源為鹵素燈。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為4μm、摩擦方向為反平行的常黑模式(normally black mode)的VA元件中放入試樣,使用利用紫外線進行硬化的接著劑將該元件密閉。對該元件施加的電壓(60Hz、矩形波)是自0V起以0.02V為單位階段性地增加至20V。此時,對元件自垂直方向照射光,測定透過元件的光量。製作該光量達到最大時為透過率100%、該光量最小時為透過率0%的電壓-透過率曲線。臨限電壓是以透過率成為10%時的電壓表示。
(12a)響應時間(τ;於25℃下測定;ms)
正的介電異向性:於測定時使用大塚電子股份有限公司製造
的LCD5100型亮度計。光源為鹵素燈。低通濾波器(Low-pass filter)是設定為5kHz。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為5.0μm、扭轉角為80度的常白模式(normally white mode)的TN元件中放入試樣。對該元件施加矩形波(60Hz、5V、0.5秒)。此時,對元件自垂直方向照射光,測定透過元件的光量。將該光量達到最大時視為透過率100%,該光量最小時視為透過率0%。上升時間(τr:rise time;毫秒)為透過率由90%變化為10%所需要的時間。下降時間(τf:fall time;毫秒)為透過率由10%變化為90%所需要的時間。響應時間是以如此般求出的上升時間與下降時間之和表示。
(12b)響應時間(τ;於25℃下測定;ms)
負的介電異向性:於測定時使用大塚電子股份有限公司製造的LCD5100型亮度計。光源為鹵素燈。低通濾波器(Low-pass filter)是設定為5kHz。於兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為3.2μm、摩擦方向為反平行的常黑模式(normally black mode)的PVA元件中放入試樣。使用利用紫外線進行硬化的接著劑將該元件密閉。對該元件施加稍許超過臨限電壓的程度的電壓1分鐘,繼而一面施加5.6V的電壓一面照射23.5mW/cm2的紫外線8分鐘。對該元件施加矩形波(60Hz、10V、0.5秒)。此時,對元件自垂直方向照射光,測定透過元件的光量。將該光量達到最大時視為透過率100%,該光量最小時視為透過率0%。響應時間是以透過率由90%變化為10%所需要的時間(下降時間;fall time;毫
秒)來表示。
原料
索爾米(solmix)(註冊商標)A-11為乙醇(85.5%)、甲醇(13.4%)及異丙醇(1.1%)的混合物,是自日本醇銷售(股)獲取。
[合成例1]
化合物(1-4-3)的合成
第1步驟
將化合物(T-1)(25.0g)、三乙基胺(16.65ml)及四氫呋喃(tetrahydrofuran,THF)(300ml)放入至反應器中,冷卻至0℃。向其中緩慢滴加丙烯醯氯(9.7ml),恢復至室溫並且攪拌6小時。將不溶物過濾分離後,將反應混合物注入至水中,以甲苯萃取水層。以水清洗同時形成的有機層,以無水硫酸鎂進行乾燥。將該溶液於減壓下濃縮,以矽膠層析法(體積比,甲苯:乙酸乙酯=9:
1)將殘渣純化,獲得化合物(T-2)(16.4g;54%)。
第2步驟
將氫化鈉(2.57g)與THF(300ml)放入至反應器中,冷卻至0℃。向其中緩慢滴加化合物(T-2)(16.4g)的THF溶液(100ml),並且攪拌1小時。向其中緩慢滴加碘代甲烷(3.7ml),恢復至室溫並且攪拌3小時。將不溶物過濾分離後,將反應混合物注入至水中,以甲苯萃取水層。以水清洗同時形成的有機層,以無水硫酸鎂進行乾燥。將該溶液於減壓下濃縮,以矽膠層析法(體積比,甲苯:乙酸乙酯=4:1)將殘渣純化。進而藉由自庚烷的再結晶而進行純化,獲得化合物(1-4-3)(14.2g;83%)。
所得的化合物(1-4-3)的NMR分析值如下。
1H-NMR:化學位移δ(ppm;CDCl3):6.56(m,1H),6.27(t,1H),5.65(t,1H),4.45(m,1H),2.90(s,3H),1.83-1.52(m,8H),1.43-1.20(m,8H),1.18-0.92(m,9H),0.89-0.80(m,5H).
化合物(1-4-3)的物性如下。
轉變溫度:C 56.9 I.
[合成例2]
化合物(1-4-45)的合成
第1步驟
將化合物(T-3)(25.0g)、三乙基胺(16.0ml)及THF(300ml)放入至反應器中,冷卻至0℃。向其中緩慢滴加丙烯醯氯(9.28ml),恢復至室溫並且攪拌6小時。將不溶物過濾分離後,將反應混合物注入至水中,以甲苯萃取水層。以水清洗同時形成的有機層,以無水硫酸鎂進行乾燥。將該溶液於減壓下濃縮,以矽膠層析法(體積比,甲苯:乙酸乙酯=9:1)將殘渣純化,獲得化合物(T-4)(15.6g;51%)。
第2步驟
將氫化鈉(2.55g)與THF(300ml)放入至反應器中,冷卻至0℃。向其中緩慢滴加化合物(T-4)(15.6g)的THF溶液(100ml),並且攪拌1小時。向其中緩慢滴加碘代甲烷(3.6ml),恢復至室溫並且攪拌3小時。將不溶物過濾分離後,將反應混合物注入至水中,以甲苯萃取水層。以水清洗同時形成的有機層,以無水硫酸鎂進行乾燥。將該溶液於減壓下濃縮,以矽膠層析法(體積比,甲苯:乙酸乙酯=4:1)將殘渣純化。進而藉由自庚烷的再
結晶而進行純化,獲得化合物(1-4-45)(13.0g;80%)。
所得的化合物(1-4-45)的NMR分析值如下。
1H-NMR:化學位移δ(ppm;CDCl3):7.51(m,4H),7.23(m,4H),6.54(m,1H),6.25(t,1H),5.63(t,1H),2.95(s,3H),2.62(t,2H),1.67-1.62(m,2H),1.37-1.33(m,4H),0.90(s,3H).
化合物(1-4-45)的物性如下。
轉變溫度:C 58.0 I.
[比較例1]
合成化合物(S-1)作為比較化合物,測定特性。其原因在於,該化合物記載於國際公開第2014/090362號手冊中且與本發明的化合物類似。
所得的比較化合物(S-1)的NMR分析值如下。
1H-NMR:化學位移δ(ppm;CDCl3):7.57-7.52(m,2H),7.45-7.42(m,2H),7.36-7.30(m,1H),7.04-6.95(m,2H),4.75(d,6.0Hz,2H),2.62(t,J=7.8Hz,2H),1.75-1.64(m,3H),0.98(t,J=7.4Hz,3H).
將化合物(1-4-3)與比較化合物(S-1)的垂直配向性及電壓保持率(VHR)進行比較。再者,評價中使用組成物(i)
及聚合性化合物(M-1-1)。
以重量%表示組成物(i)的成分的比例。
以下示出聚合性化合物(M-1-1)。
.垂直配向性
於組成物(i)中以0.4重量%的比例添加聚合性化合物(M-1-1)。於其中以3.0重量%的比例添加化合物(1-4-3)或比較化合物(S-1)。將該混合物注入至兩片玻璃基板的間隔(單元間隙)為3.5μm的不具有配向膜的元件中。將該元件設置於偏光顯微鏡中,自下方對元件照射光,觀察有無漏光。於液晶分子充分配向、光不通過元件的情形時,將垂直配向性判斷為「良好」。於觀察到通過元件的光的情形時,表示作「不良」。
.電壓保持率(VHR)
對所述製作的元件於60℃下施加脈衝電壓(1V且60微秒)而進行充電。利用高速電壓計於0.0167秒的期間中測定衰減的電壓,求出單位週期的電壓曲線與橫軸之間的面積A。面積B為未衰減時的面積。電壓保持率是以面積A相對於面積B之百分率來表示。
將合成例2的化合物(1-4-3)與比較化合物(S-1)的
物性匯總於表2中。兩種化合物均於不具有配向膜的元件中顯示出良好的垂直配向性。另一方面,於使用化合物(1-4-3)的情形時,電壓保持率高於使用比較化合物(S-1)的情形。其原因在於:雖然如比較化合物(S-1)般的具有-OH基的極性化合物大幅度地降低元件的電壓保持率,但丙烯醯胺基不會引起電壓保持率的降低。因此,化合物(1-4-3)可謂為顯示出良好的垂直配向性而不使元件的電壓保持率降低的優異化合物。
可依據實施例1中記載的合成法,合成以下的化合物(1-3-1)~化合物(1-3-82)、化合物(1-4-1)~化合物(1-4-244)、化合物(1-5-1)~化合物(1-5-296)及化合物(1-6-1)~化合物(1-6-258)。
2.組成物的實施例
實施例的化合物是根據下述表3的定義由記號來表示。表3中,與1,4-伸環己基有關的立體構型為反式構型。記號後的括弧內的編號與化合物的編號相對應。(-)記號是指其他液晶性化合物。液晶性化合物的比例(百分率)為以液晶組成物的重量為基準的重量百分率(重量%)。最後,匯總液晶組成物的特性值。特
性是依照上文記載的方法來測定,(不進行外推而)直接記載測定值。
[使用例1]
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-125)。
NI=116.7℃;η=20.6mPa.s;Δn=0.093;Δε=4.0.
[使用例2]
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-3)。
進而以0.3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(RM-1)。
NI=85.3℃;η=24.9mPa.s;Δn=0.116;Δε=5.8.
[使用例3]
於所述組成物中以1重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-5-62)。
NI=97.2℃;η=34.9mPa.s;Δn=0.116;Δε=9.1.
[使用例4]
於所述組成物中以3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-85)。
NI=100.7℃;η=17.9mPa.s;Δn=0.101;Δε=4.8.
[使用例5]
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-3-1)。
NI=71.0℃;η=13.7mPa.s;Δn=0.073;Δε=2.8.
[使用例6]
5-HB-CL (5-1) 3%
於所述組成物中以2重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-4)。
NI=78.7℃;η=19.9mPa.s;Δn=0.064;Δε=5.8.
[使用例7]
於所述組成物中以0.5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-125)。
NI=80.3℃;η=12.1mPa.s;Δn=0.130;Δε=7.2.
[使用例8]
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-3)。
NI=85.9℃;η=14.7mPa.s;Δn=0.092;Δε=4.4.
[使用例9]
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-5-62)。
NI=98.5℃;η=39.6mPa.s;Δn=0.190;Δε=8.1.
[使用例10]
於所述組成物中以4重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-85)。
NI=70.1℃;η=25.3mPa.s;Δn=0.097;Δε=8.3.
[使用例11]
於所述組成物中以2重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-4)。
進而以0.3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(RM-2)。
NI=81.5℃;η=23.6mPa.s;Δn=0.102;Δε=9.1.
[使用例12]
於所述組成物中以1重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-259)。
[使用例13]
於所述組成物中以7重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-260)。
[使用例14]
1O1-HBBH-5 (4-1) 4%
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-261)。
[使用例15]
於所述組成物中以3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-262)。
此外,進而以0.3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(RM-1)。
[使用例16]
於所述組成物中以10重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-263)。
[使用例17]
3-HHBB(F,F)-F (7-6) 3%
於所述組成物中以1重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-259)。
[使用例18]
5-HBBH-3 (4-1) 3%
於所述組成物中以5重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-260)。
此外,進而以0.3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(RM-2)。
[使用例19]
於所述組成物中以3重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-261)。
[使用例20]
於所述組成物中以10重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-262)。
[使用例21]
3-HHBB(F,F)-F (7-6) 3%
於所述組成物中以6重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-6-263)。
[使用例22]
3-HHBB(F,F)-F (7-6) 3%
於所述組成物中以8重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-125)。
[使用例23]
於所述組成物中以4重量%的比例添加下述化合物(1-4-3)。
[產業上之可利用性]
化合物(1)具有高的化學穩定性、高的使液晶分子配向的能力及於液晶組成物中的高溶解度,而且於用於液晶顯示元件中的情形時的電壓保持率大。含有化合物(1)的液晶組成物充分滿足如下特性中的至少一個:上限溫度高、下限溫度低、黏度小、光學異向性適當、正或負的介電異向性大、比電阻大、對紫外線的穩定性高、對熱的穩定性高、彈性常數大等。含有該組成物的液晶顯示元件具有可使用元件的溫度範圍廣、響應時間短、電壓保持率大、臨限電壓低、對比度大、壽命長等特性,故可用於液晶投影儀、液晶電視等。
Claims (16)
- 一種式(1-1)所表示的化合物,
- 如申請專利範圍第1項所述的化合物,其是由式(1-4)~式(1-6)的任一個所表示,
- 如申請專利範圍第1項所述的化合物,其是由式(1-4)~式(1-6)的任一個所表示,
- 一種液晶組成物,其含有如申請專利範圍第1項所述 的化合物的至少一種。
- 如申請專利範圍第7項所述的液晶組成物,其更含有選自式(5)~式(7)所表示的化合物的群組中的至少一種化合物,
- 如申請專利範圍第7項所述的液晶組成物,其更含有選自式(9)~式(15)所表示的化合物的群組中的至少一種化合物,
- 如申請專利範圍第7項所述的液晶組成物,其更含有選自式(16)所表示的化合物的群組中的至少一種聚合性化合物,
- 如申請專利範圍第7項所述的液晶組成物,其含有選自式(16-1)~式(16-7)所表示的化合物的群組中的至少一種聚合性化合物,
- 如申請專利範圍第12項所述的液晶組成物,其更含有選自由式(1-1)及式(16)以外的聚合性化合物、聚合起始劑、聚合抑制劑、光學活性化合物、抗氧化劑、紫外線吸收劑、光穩定劑、熱穩定劑及消泡劑所組成的群組中的至少一種。
- 一種液晶顯示元件,其含有至少一種如申請專利範圍第7項所述的液晶組成物。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015142788 | 2015-07-17 | ||
| JP2015-142788 | 2015-07-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| TW201704455A TW201704455A (zh) | 2017-02-01 |
| TWI694140B true TWI694140B (zh) | 2020-05-21 |
Family
ID=57834011
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| TW105119246A TWI694140B (zh) | 2015-07-17 | 2016-06-20 | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10662379B2 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP6879207B2 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN107848955A (zh) |
| TW (1) | TWI694140B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2017014013A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109476998A (zh) * | 2016-07-27 | 2019-03-15 | 捷恩智株式会社 | 液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 |
| JPWO2018025974A1 (ja) * | 2016-08-03 | 2019-06-06 | Jnc株式会社 | 液晶表示素子、表示装置 |
| JPWO2018168721A1 (ja) * | 2017-03-17 | 2020-01-16 | Jnc株式会社 | 液晶組成物および液晶表示素子 |
| JP7225736B2 (ja) * | 2018-05-15 | 2023-02-21 | Jnc株式会社 | 化合物、液晶組成物、および液晶表示素子 |
| WO2020217710A1 (ja) * | 2019-04-25 | 2020-10-29 | Jnc株式会社 | 化合物、液晶組成物および液晶表示素子 |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5035076A (zh) | 1973-08-01 | 1975-04-03 | ||
| DE4437999A1 (de) * | 1994-10-25 | 1996-05-02 | Thomae Gmbh Dr K | N.N-disubstituierte Arylcycloalkylamine, ihre Salze mit physiologisch verträglichen organischen oder anorganischen Säuren, Verfahren zur Herstellung dieser Verbindungen und diese enthaltende Arzneimittel |
| JP4255204B2 (ja) * | 1999-08-23 | 2009-04-15 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 液晶配向膜、その製造方法、光学補償シート、stn型液晶表示装置およびディスコティック液晶性分子を配向させる方法 |
| EP1079244A3 (en) | 1999-08-23 | 2001-10-04 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Orientation layer containing (meth)acrylic copolymer having hydrophobic repeating units |
| JP4320128B2 (ja) * | 2000-03-29 | 2009-08-26 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | ディスコティック液晶性分子を配向させる方法 |
| JP2002294240A (ja) | 2001-03-30 | 2002-10-09 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 棒状液晶性分子の配向方法および光学異方性素子 |
| JP3993143B2 (ja) | 2003-08-25 | 2007-10-17 | 独立行政法人科学技術振興機構 | セミipn型複合体およびその製造方法、並びに防汚塗料 |
| JP2005275083A (ja) * | 2004-03-25 | 2005-10-06 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | 配向膜、位相差膜及び液晶表示装置 |
| JP2006169294A (ja) * | 2004-12-13 | 2006-06-29 | Fuji Photo Film Co Ltd | インク組成物及びこれを用いた画像形成方法 |
| CN101903345A (zh) * | 2007-11-06 | 2010-12-01 | Hcf合伙人股份两合公司 | 用在电子器件中的空穴传输聚合物 |
| JP5573011B2 (ja) * | 2009-06-10 | 2014-08-20 | Dic株式会社 | 重合性化合物を含有する液晶組成物及びそれを使用した液晶表示素子 |
| DE102011108708A1 (de) | 2010-09-25 | 2012-03-29 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Flüssigkristallanzeigen und flüssigkristalline Medien mit homöotroper Ausrichtung |
| EP2670818B1 (de) | 2011-02-05 | 2016-10-05 | Merck Patent GmbH | Flüssigkristallanzeigen mit homöotroper ausrichtung |
| US9493588B2 (en) | 2011-04-22 | 2016-11-15 | Lg Chem, Ltd. | Diblock copolymer, preparation method thereof, and method of forming nano pattern using the same |
| CN103619993B (zh) | 2011-07-07 | 2016-10-12 | 默克专利股份有限公司 | 液晶介质 |
| WO2014090362A1 (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-06-19 | Merck Patent Gmbh | Liquid-crystalline medium |
| CN104870612B (zh) | 2012-12-17 | 2017-09-12 | 默克专利股份有限公司 | 液晶显示器和具有垂面配向的液晶介质 |
| JP6213553B2 (ja) | 2013-02-13 | 2017-10-18 | Jnc株式会社 | ジフルオロメチレンオキシを有する液晶性化合物、液晶組成物および液晶表示素子 |
| EP2990424B1 (en) * | 2013-04-25 | 2019-01-30 | JNC Corporation | Polymerizable compound and polymerizable composition |
| KR20170116006A (ko) * | 2015-02-09 | 2017-10-18 | 제이엔씨 주식회사 | 중합성 극성 화합물, 액정 조성물 및 액정 표시 소자 |
-
2016
- 2016-06-20 TW TW105119246A patent/TWI694140B/zh active
- 2016-06-29 WO PCT/JP2016/069192 patent/WO2017014013A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2016-06-29 US US15/741,765 patent/US10662379B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-06-29 CN CN201680040933.0A patent/CN107848955A/zh active Pending
- 2016-06-29 JP JP2017529524A patent/JP6879207B2/ja active Active
Non-Patent Citations (3)
| Title |
|---|
| Zhang et al., "Amide as Terminal Groups: Synthesis and Properties as New Tolane‐Type Liquid Crystals", Chinese Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 33, Issue 7, 12 Jun., 2015, page 771-776. |
| Zhang et al., "Amide as Terminal Groups: Synthesis and Properties as New Tolane‐Type Liquid Crystals", Chinese Journal of Chemistry, Vol. 33, Issue 7, 12 Jun., 2015, page 771-776. Zhou Dong et al., "Copper‐Catalysed Alkylarylation of Activated Alkenes Using AIBN and Beyond: An Access to Cyano‐Containing Oxindoles", European Journal of Organic Chemistry, Vol. 7, 27 Jan., 2015, page 1606-1612. * |
| Zhou Dong et al., "Copper‐Catalysed Alkylarylation of Activated Alkenes Using AIBN and Beyond: An Access to Cyano‐Containing Oxindoles", European Journal of Organic Chemistry, Vol. 7, 27 Jan., 2015, page 1606-1612. |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TW201704455A (zh) | 2017-02-01 |
| WO2017014013A1 (ja) | 2017-01-26 |
| JP6879207B2 (ja) | 2021-06-02 |
| US10662379B2 (en) | 2020-05-26 |
| JPWO2017014013A1 (ja) | 2018-04-26 |
| US20180195005A1 (en) | 2018-07-12 |
| CN107848955A (zh) | 2018-03-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI744235B (zh) | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI704173B (zh) | 具有聚合性基的化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI744458B (zh) | 具有二苯并呋喃環的化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI583777B (zh) | 聚合性化合物與其用途、聚合物、液晶組成物以及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI682022B (zh) | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI619801B (zh) | 具有四個聚合性基的化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TW201816080A (zh) | 液晶顯示元件、顯示裝置 | |
| TWI694068B (zh) | 具有苯並噻吩的液晶性化合物、液晶組成物和液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI708770B (zh) | 具有苯并噻吩的液晶性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| JP6460089B2 (ja) | 1,1,3,3−テトラフルオロアリルオキシ基を有する液晶性化合物、液晶組成物、および液晶表示素子 | |
| CN111465592B (zh) | 化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 | |
| TWI694140B (zh) | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| TWI744302B (zh) | 聚合性組成物、液晶複合體、光學各向異性體、液晶顯示元件及其用途 | |
| TWI722120B (zh) | 使液晶介質均勻配向的低分子極性化合物及含有其的液晶介質 | |
| JP6299969B2 (ja) | 共役結合を有する重合性化合物、液晶組成物および液晶表示素子 | |
| TWI550074B (zh) | 聚合性化合物、組成物、聚合物與其用途、以及液晶顯示元件 | |
| CN113166035A (zh) | 化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 | |
| TWI722119B (zh) | 使液晶介質均勻配向的低分子極性化合物及含有其的液晶介質 | |
| TWI728101B (zh) | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| CN112334441B (zh) | 聚合性极性化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 | |
| CN110914233B (zh) | 聚合性极性化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 | |
| JP6115303B2 (ja) | 隣接基としてカルボニル基を有するフェノール化合物およびその用途 | |
| CN107868665B (zh) | 液晶性化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 | |
| TWI759568B (zh) | 聚合性極性化合物、液晶組成物及液晶顯示元件 | |
| CN113717147A (zh) | 化合物、液晶组合物及液晶显示元件 |