KR20230031322A - Compositions of Compounds that Modulate Cellular Metabolism and Methods of Use - Google Patents
Compositions of Compounds that Modulate Cellular Metabolism and Methods of Use Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20230031322A KR20230031322A KR1020237003178A KR20237003178A KR20230031322A KR 20230031322 A KR20230031322 A KR 20230031322A KR 1020237003178 A KR1020237003178 A KR 1020237003178A KR 20237003178 A KR20237003178 A KR 20237003178A KR 20230031322 A KR20230031322 A KR 20230031322A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- methyl
- carboxylic acid
- indole
- cyclohepta
- hexyl
- Prior art date
Links
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 title claims abstract description 155
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 56
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 title description 28
- 230000019522 cellular metabolic process Effects 0.000 title 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 37
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 claims abstract description 35
- 239000008194 pharmaceutical composition Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 12
- 102100030431 Fatty acid-binding protein, adipocyte Human genes 0.000 claims abstract description 11
- 239000003814 drug Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 9
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 6
- 239000013543 active substance Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 101001062864 Homo sapiens Fatty acid-binding protein, adipocyte Proteins 0.000 claims abstract 10
- -1 2-cyanophenyl Chemical group 0.000 claims description 44
- 125000000217 alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 43
- 125000004432 carbon atom Chemical group C* 0.000 claims description 38
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 claims description 38
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 claims description 34
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 claims description 33
- 125000002496 methyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 claims description 27
- 125000003178 carboxy group Chemical group [H]OC(*)=O 0.000 claims description 25
- RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethyl ether Chemical class CCOCC RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 24
- 125000003118 aryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 24
- 125000006297 carbonyl amino group Chemical group [H]N([*:2])C([*:1])=O 0.000 claims description 24
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 21
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 125000001072 heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 20
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 17
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetic acid Chemical compound CC(O)=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 14
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 125000000753 cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 125000000623 heterocyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 11
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000002619 bicyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 125000004122 cyclic group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052717 sulfur Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 241000124008 Mammalia Species 0.000 claims description 9
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen group Chemical group [N] QJGQUHMNIGDVPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 208000001072 type 2 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 claims description 9
- 201000001421 hyperglycemia Diseases 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 201000001320 Atherosclerosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 206010028980 Neoplasm Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000008589 Obesity Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000006673 asthma Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003143 atherosclerotic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 201000011510 cancer Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000001684 chronic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000002401 inhibitory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 235000020824 obesity Nutrition 0.000 claims description 6
- 201000010065 polycystic ovary syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 201000011461 pre-eclampsia Diseases 0.000 claims description 6
- 208000024827 Alzheimer disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000023275 Autoimmune disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000001145 Metabolic Syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 201000004810 Vascular dementia Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 201000000690 abdominal obesity-metabolic syndrome Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000019622 heart disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000027866 inflammatory disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007917 intracranial administration Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 201000006417 multiple sclerosis Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 208000008338 non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- 206010053219 non-alcoholic steatohepatitis Diseases 0.000 claims description 5
- LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N teixobactin Chemical compound C([C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H](CCC(N)=O)C(=O)N[C@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](CO)C(=O)N[C@H]1C(N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C[C@@H]2NC(=N)NC2)C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@H]1C)[C@@H](C)CC)=O)NC)C1=CC=CC=C1 LMBFAGIMSUYTBN-MPZNNTNKSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
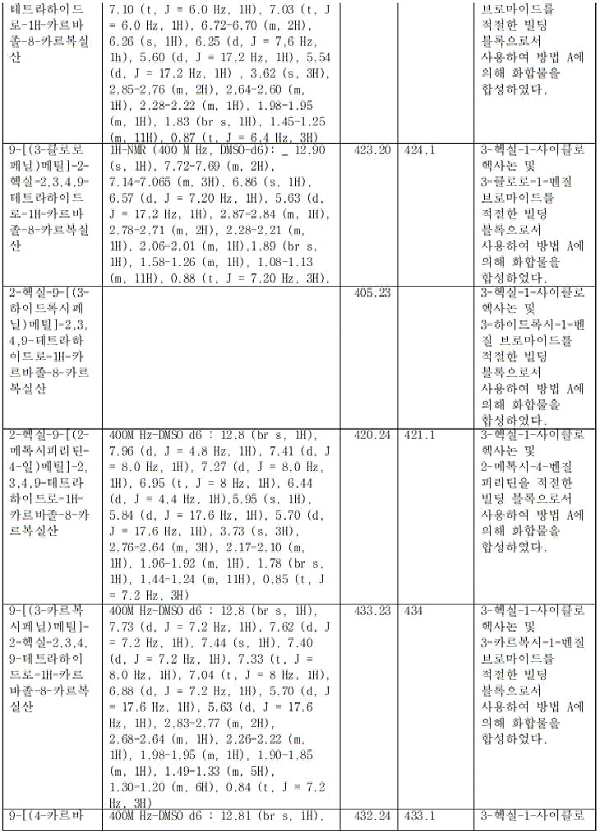
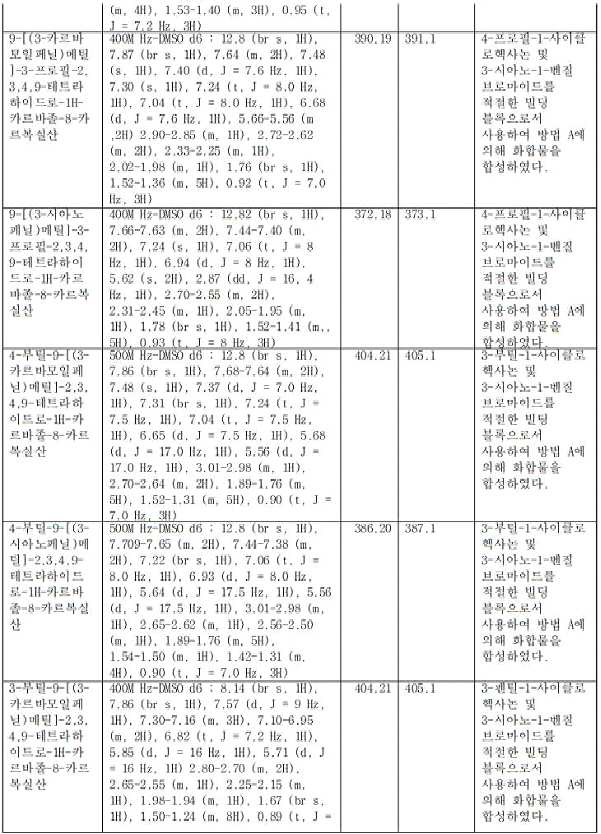
- YYZSBFGKQDRWNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 YYZSBFGKQDRWNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- MXVYQVKIYQRWLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C1 MXVYQVKIYQRWLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000004480 active ingredient Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000037976 chronic inflammation Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 208000037893 chronic inflammatory disorder Diseases 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002170 ethers Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 150000002431 hydrogen Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000001997 phenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(*)C([H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 4
- KPPVNWGJXFMGAM-UUILKARUSA-N (e)-2-methyl-1-(6-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2h-quinolin-1-yl)but-2-en-1-one Chemical compound CC1=CC=C2N(C(=O)C(/C)=C/C)CCCC2=C1 KPPVNWGJXFMGAM-UUILKARUSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- PZFBQDQAOBEYCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 PZFBQDQAOBEYCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- INWMTWALMSUOGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 INWMTWALMSUOGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000002757 inflammatory effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- LOTBYPQQWICYBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N methyl n-hexyl-n-[2-(hexylamino)ethyl]carbamate Chemical compound CCCCCCNCCN(C(=O)OC)CCCCCC LOTBYPQQWICYBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- GZUUXAYZUIYLMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 10-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O GZUUXAYZUIYLMR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- UCYAFVNAKKYATH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-[[7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carbonyl]amino]acetic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(NCC(O)=O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 UCYAFVNAKKYATH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JPNPUGXNXDWEJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-butyl-4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(C1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 JPNPUGXNXDWEJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OKAFDTVAPFCWQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-butyl-4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(C1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 OKAFDTVAPFCWQJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OOUKMRXMEYGLOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-butyl-4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 OOUKMRXMEYGLOA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BDPWWGDKRXWQRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-butyl-4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 BDPWWGDKRXWQRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004207 3-methoxyphenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(*)=C([H])C(OC([H])([H])[H])=C1[H] 0.000 claims description 2
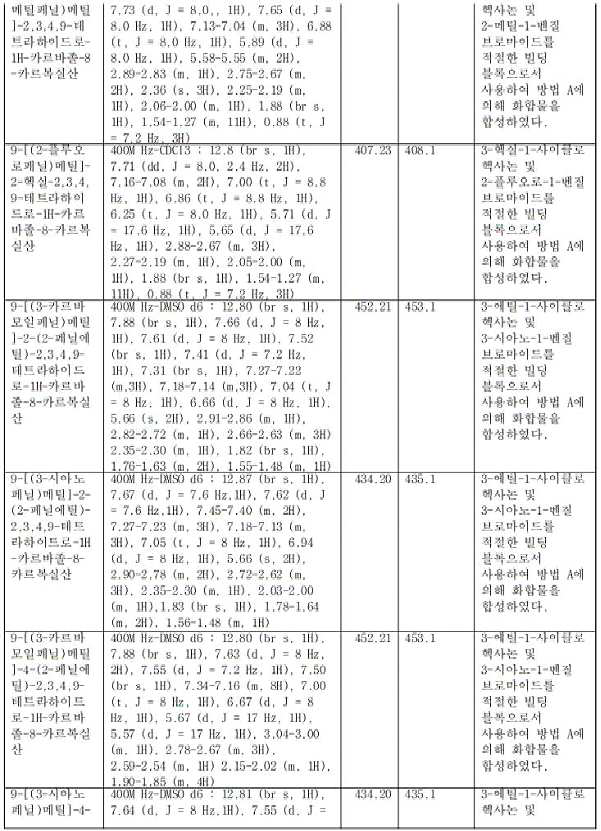
- SUFIOZISEOHGQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(C1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 SUFIOZISEOHGQW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VDJLTLOBOBTESP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-ethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 VDJLTLOBOBTESP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JJEAIYYWDWNNID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 JJEAIYYWDWNNID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NZWIGFGVIMJOLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(C1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 NZWIGFGVIMJOLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RBBXJFNTXRIQOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3-ethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 RBBXJFNTXRIQOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AFUCITXWOAEVQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 AFUCITXWOAEVQM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 125000004801 4-cyanophenyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C(C#N)=C([H])C([H])=C1* 0.000 claims description 2
- YKASTBHMLNMFOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5,6,7,8,9,10-hexahydrocyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C1CCCCC2=C1C(C=CC=C1C(=O)O)=C1N2 YKASTBHMLNMFOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JOULTSNVGQIWGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(1,3-benzoxazol-5-ylmethyl)-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC2=C1OC=N2 JOULTSNVGQIWGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XPIWUEOIDSKMAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(1,3-benzoxazol-6-ylmethyl)-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC2=C1N=CO2 XPIWUEOIDSKMAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KVYUQZYDKHPFTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(1,3-benzoxazol-7-ylmethyl)-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=CC2=C1OC=N2 KVYUQZYDKHPFTF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
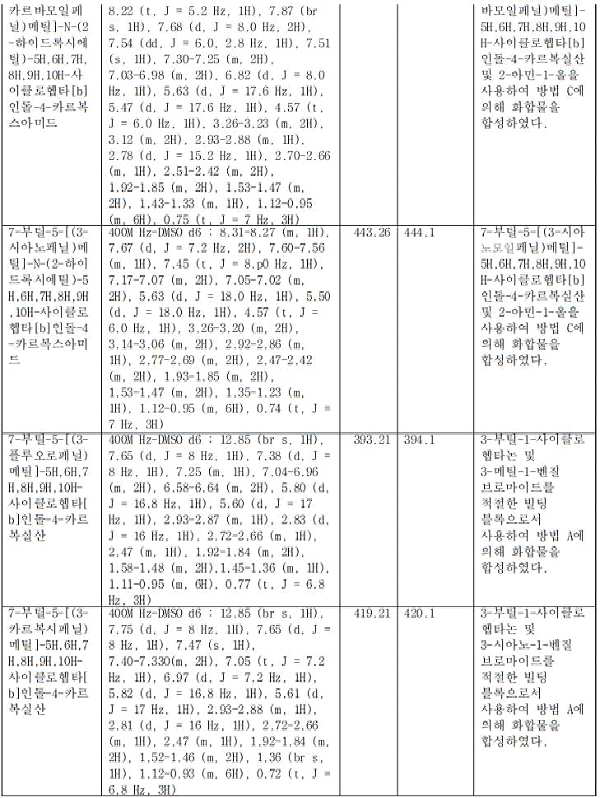
- XDNHERUANGTDQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1C(N)=O XDNHERUANGTDQI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LAXVFNPLXFIRMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1F LAXVFNPLXFIRMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- APINOAIRKDOEEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(2-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(F)=NC=C1 APINOAIRKDOEEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HJZSIJREGABIAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=C(C)ON=C1C HJZSIJREGABIAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MPMKUACQYJMWTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-ethyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O MPMKUACQYJMWTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LCQUMBMRHSXEFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-pentyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O LCQUMBMRHSXEFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GYBOTYSHCFCPHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-propyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O GYBOTYSHCFCPHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
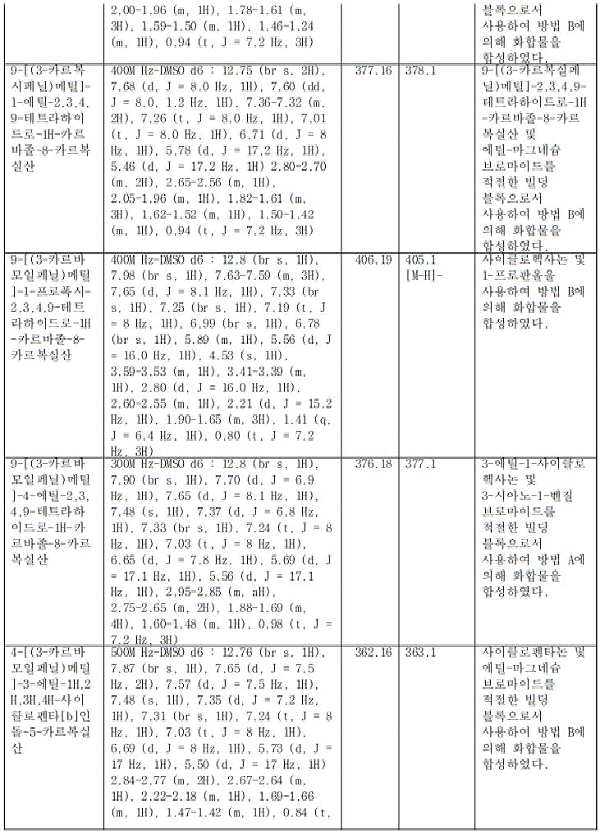
- VVVLHAFSZZNLEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound NC(C1=CC=CC(CN(C(CC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)CCC2)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1)=O VVVLHAFSZZNLEV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XRNDCQCJARZULV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 XRNDCQCJARZULV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WSFGUCRJUPWKHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 WSFGUCRJUPWKHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LQJUDFMTSBJKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-octyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 LQJUDFMTSBJKLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HERBNVUNOVXBFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 HERBNVUNOVXBFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IEFFPRAKUNINMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-propyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 IEFFPRAKUNINMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HDJIDOFZHFCAIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C1 HDJIDOFZHFCAIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- CHWBLPKXYQXQRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1 CHWBLPKXYQXQRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YVDGAVCUUBWVRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyano-2-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1C#N)=C1F YVDGAVCUUBWVRE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XPTHMOOKDZRBEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-ethyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O XPTHMOOKDZRBEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- QLLIDDHFABRTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-pentyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O QLLIDDHFABRTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ICZYLXLFLSGLJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-propyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CCCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O ICZYLXLFLSGLJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YRZQKEALVBXRRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-fluoro-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC(F)=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 YRZQKEALVBXRRJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HDPOERVMNOEXJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound N#CC1=CC=CC(CN(C(CC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)CCC2)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1 HDPOERVMNOEXJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IEZBWNOIBNYINI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 IEZBWNOIBNYINI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RNJGWGSCCNCUKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 RNJGWGSCCNCUKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YNPPVZGYXKDSDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-octyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 YNPPVZGYXKDSDM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GIEBDODJPCMLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 GIEBDODJPCMLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PDBOQBCRHMTXJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(3-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(F)=CC=C1 PDBOQBCRHMTXJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZYBOWQOTMYEVAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C(N)=O ZYBOWQOTMYEVAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FYXSSOLMWQOVDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C#N FYXSSOLMWQOVDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
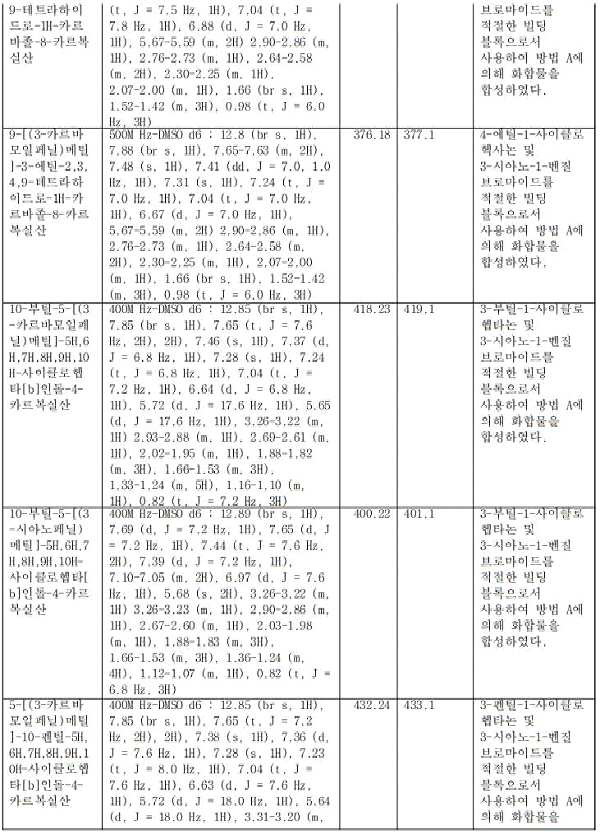
- JFDDQRBCBUUNNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(4-cyanothiophen-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CS1 JFDDQRBCBUUNNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FVTAGCDHVWQIMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC=C1F FVTAGCDHVWQIMU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VRNYIWGUWGVYAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(5-cyanofuran-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=C(C#N)O1 VRNYIWGUWGVYAO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BWAAKEWLJKTYTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(5-cyanopyridin-3-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CN=C1 BWAAKEWLJKTYTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XFMBZZSTVNCBAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(5-cyanothiophen-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=C(C#N)S1 XFMBZZSTVNCBAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YPJAUJRKYLZMLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(5-cyanothiophen-3-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CSC(C#N)=C1 YPJAUJRKYLZMLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MQGBKWNFGYDGEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(6-carboxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=N1 MQGBKWNFGYDGEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XNTGYHDLVMWWIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(6-cyanopyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=NC(C#N)=CC=C1 XNTGYHDLVMWWIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FBLXUVLQTOQIPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-[(6-fluoropyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=NC(F)=CC=C1 FBLXUVLQTOQIPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XNFAPKBWDLOPAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O XNFAPKBWDLOPAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DVJRPKMXYPKSTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-butyl-9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O DVJRPKMXYPKSTJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- POBJTDRFZSKTBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5h-carbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound C1CCCC2=C1C(C=CC=C1C(=O)O)=C1N2 POBJTDRFZSKTBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AUVHVIWZSZZSDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 AUVHVIWZSZZSDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AWLCFQCWCRBHLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 AWLCFQCWCRBHLZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RTJRJERWSCLRKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O RTJRJERWSCLRKU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JONMFQPYKKRNKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=CN=C1 JONMFQPYKKRNKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LYLMHCLYDCLKMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1C(N)=O LYLMHCLYDCLKMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- AYQJBTQUQUESOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(2-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1C#N AYQJBTQUQUESOM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SYBMSBXSGRMZOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(OC)=NC=C1 SYBMSBXSGRMZOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NVNXDSJAJCQOFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=C(C)C=CC=C1 NVNXDSJAJCQOFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IPGFCNWRPFSBDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxamide Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(NCCO)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 IPGFCNWRPFSBDH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JOAZNULWVNHRRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1 JOAZNULWVNHRRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- UIRNYKYLMISFNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxamide Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(NCCO)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 UIRNYKYLMISFNH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- QHZWFTRMJGEZNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(F)=CC=C1 QHZWFTRMJGEZNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- IMDVOEQGZHMYLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(O)=CC=C1 IMDVOEQGZHMYLP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BCYBDAFPFBSUNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(OC)=CC=C1 BCYBDAFPFBSUNI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OETSCNSYNUABQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1 OETSCNSYNUABQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- RCWSVEVCQJXNIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C(N)=O RCWSVEVCQJXNIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MACBAMVWRKPQRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-5-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 MACBAMVWRKPQRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- UYNCEERWSYORCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 UYNCEERWSYORCF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MKWBAOWDLHWEPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-(1H-indol-4-ylmethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=C(C=CN2)C2=CC=C1 MKWBAOWDLHWEPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YHNKOPVOMAQANR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=CN=C1 YHNKOPVOMAQANR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NXAFGMFGAZGDMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(OC)=NC=C1 NXAFGMFGAZGDMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FYMUSEBGDSWCKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=C(C)C=CC=C1 FYMUSEBGDSWCKG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PMBMAXBYPQGQJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(OC)=CC=C1 PMBMAXBYPQGQJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LXGIGZDMRANHMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1 LXGIGZDMRANHMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YMJBQEUHXPOONL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 YMJBQEUHXPOONL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LKUAVKXFNABRIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(F)(F)F)=NC=C1 LKUAVKXFNABRIN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YSQBGEXGPBMPDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-5-[[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]methyl]-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-6H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CCC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=NC(C(F)(F)F)=CC=C1 YSQBGEXGPBMPDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- JLJBDZJCXMTLJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=CN=C1 JLJBDZJCXMTLJZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KVZBOVDTAVQZNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-[(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(OC)=NC=C1 KVZBOVDTAVQZNA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- CNOHKKKCUPWXFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=C(C)C=CC=C1 CNOHKKKCUPWXFS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FYPJQDDYKYJHFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(O)=CC=C1 FYPJQDDYKYJHFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SFEVEDNMFPUAFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C)=CC=C1 SFEVEDNMFPUAFN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- MXIVWNWSVVBELS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-hexyl-9-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 MXIVWNWSVVBELS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HQMCMJCZVAYJNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 HQMCMJCZVAYJNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GEZKIGBYKQFZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-butyl-9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 GEZKIGBYKQFZJY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PTMQTCCLNVKCAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1C(N)=O PTMQTCCLNVKCAZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OVRNTBPNFZKEOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(2-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1C#N OVRNTBPNFZKEOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- UJZRSIWJQSTSDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=CC=C1)=C1F UJZRSIWJQSTSDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DOEKDCGDKZTAQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound NC(C1=CC=CC(CN(C(CCCC2CCC3=CC=CC=C3)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1)=O DOEKDCGDKZTAQF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BITTXIYOTBGLRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O BITTXIYOTBGLRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SSUVRHMLWZOTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O SSUVRHMLWZOTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- POFXRQUEVYHEDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5-propyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O POFXRQUEVYHEDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DBEMQUREWYUQBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-6-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O DBEMQUREWYUQBP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- LGADWSAZEZHAKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-6-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O LGADWSAZEZHAKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ACLSPNZYQMJXDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-6-propyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O ACLSPNZYQMJXDB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- URAREGGRKJNBDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound NC(C1=CC=CC(CN(C(CC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)CC2)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1)=O URAREGGRKJNBDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- ZFDCEXPRCXFHBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 ZFDCEXPRCXFHBQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BLVSVODJWVGUSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 BLVSVODJWVGUSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PSLGLCGEWSFCJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-propyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 PSLGLCGEWSFCJX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- GCXTUISDOBLUIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-8-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 GCXTUISDOBLUIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- KEPIBTRRADOFMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-8-pentoxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCOC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 KEPIBTRRADOFMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- YUVYFCLETXNTCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-8-propoxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCOC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(N)=O)=CC=C1 YUVYFCLETXNTCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SYAPNJOODKYYLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-5-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O SYAPNJOODKYYLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FZCVTAJZNVBCOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C1 FZCVTAJZNVBCOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NQWLGOREXJHSNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-8-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C(O)=O)=CC=C1 NQWLGOREXJHSNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HXNRJPQIPKEFRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(Cl)=CC=C1 HXNRJPQIPKEFRN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HCHTVURDWSSZQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound N#CC1=CC=CC(CN(C(CCCC2CCC3=CC=CC=C3)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1 HCHTVURDWSSZQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XTZJEWJDHNDLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CCC1)C(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O XTZJEWJDHNDLEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BUDOGVINGFNIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-6-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O BUDOGVINGFNIMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- BZSRKOHOSWGMGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-6-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O BZSRKOHOSWGMGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DLQBKCPJYNOZKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-6-propyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCC(CC1)CC(C2=CC=C3)=C1N(CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1)C2=C3C(O)=O DLQBKCPJYNOZKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- VTPVJHOQPJYMBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound N#CC1=CC=CC(CN(C(CC(CCC2=CC=CC=C2)CC2)=C2C2=CC=C3)C2=C3C(O)=O)=C1 VTPVJHOQPJYMBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- OJMXHQMEVBTHAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 OJMXHQMEVBTHAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- SBQWIFPOUKXBKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 SBQWIFPOUKXBKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- FDFPTRSZBLTKAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-8-ethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 FDFPTRSZBLTKAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- DTQHPDQTIMIMJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-8-pentoxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCOC(CCC1)C2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC1=CC(C#N)=CC=C1 DTQHPDQTIMIMJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- XZBIDDFDZINHTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 9-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrocarbazole-1-carboxylic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCC(CC1)CC2=C1C1=CC=CC(C(O)=O)=C1N2CC(C=C1)=CC=C1C(N)=O XZBIDDFDZINHTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 206010036049 Polycystic ovaries Diseases 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000001363 autoimmune Effects 0.000 claims 4
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 claims 4
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 abstract description 3
- XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethyl acetate Chemical compound CCOC(C)=O XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 33
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 31
- 102000013948 Fatty acid-binding protein 4 Human genes 0.000 description 29
- 108050003772 Fatty acid-binding protein 4 Proteins 0.000 description 29
- SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Indole Chemical compound C1=CC=C2NC=CC2=C1 SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 20
- 239000000651 prodrug Substances 0.000 description 20
- 229940002612 prodrug Drugs 0.000 description 20
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 19
- 235000019439 ethyl acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 16
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 15
- 239000012453 solvate Substances 0.000 description 15
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 14
- PZOUSPYUWWUPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N indole Natural products CC1=CC=CC2=C1C=CN2 PZOUSPYUWWUPPK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- RKJUIXBNRJVNHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N indolenine Natural products C1=CC=C2CC=NC2=C1 RKJUIXBNRJVNHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 14
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 239000008103 glucose Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 13
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 12
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 12
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 11
- 208000024891 symptom Diseases 0.000 description 11
- HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 8-[3-(1-cyclopropylpyrazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazolo[4,3-d]pyrimidin-5-yl]-3-methyl-3,8-diazabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-2-one Chemical class C1(CC1)N1N=CC(=C1)C1=NNC2=C1N=C(N=C2)N1C2C(N(CC1CC2)C)=O HBAQYPYDRFILMT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 10
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N nitrogen Substances N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 210000001789 adipocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 8
- 125000004429 atom Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 229920006395 saturated elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 8
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 7
- 238000004440 column chromatography Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000002609 medium Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000003208 petroleum Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000002390 rotary evaporation Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 7
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical group [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 102000030914 Fatty Acid-Binding Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 238000004587 chromatography analysis Methods 0.000 description 6
- 150000002148 esters Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 108091022862 fatty acid binding Proteins 0.000 description 6
- NOESYZHRGYRDHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N insulin Chemical compound N1C(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(CCC(O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)CN)C(C)CC)CSSCC(C(NC(CO)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)C(=O)NC(CCC(N)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(N)=O)C(=O)NC(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)C(=O)NC(CSSCC(NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC=2C=CC(O)=CC=2)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC=2NC=NC=2)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)CNC2=O)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCC(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(N)=N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC=CC=3)C(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC=CC=3)C(=O)NC(CC=3C=CC(O)=CC=3)C(=O)NC(C(C)O)C(=O)N3C(CCC3)C(=O)NC(CCCCN)C(=O)NC(C)C(O)=O)C(=O)NC(CC(N)=O)C(O)=O)=O)NC(=O)C(C(C)CC)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C1CSSCC2NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(CCC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(CC(N)=O)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C(N)CC=1C=CC=CC=1)C(C)C)CC1=CN=CN1 NOESYZHRGYRDHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000007858 starting material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Formic acid Chemical compound OC=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrochloric acid Chemical compound Cl VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 5
- NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfur Chemical group [S] NINIDFKCEFEMDL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000002585 base Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 229940079593 drug Drugs 0.000 description 5
- 238000009472 formulation Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000005764 inhibitory process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 5
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 125000004169 (C1-C6) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N Ascorbic acid Chemical compound OC[C@H](O)[C@H]1OC(=O)C(O)=C1O CIWBSHSKHKDKBQ-JLAZNSOCSA-N 0.000 description 4
- OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrazine Chemical compound NN OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 4
- UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium bicarbonate Chemical class [Na+].OC([O-])=O UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 4
- 230000002378 acidificating effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 125000000266 alpha-aminoacyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 125000001797 benzyl group Chemical group [H]C1=C([H])C([H])=C(C([H])=C1[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 4
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000001963 growth medium Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000004435 hydrogen atom Chemical group [H]* 0.000 description 4
- 238000006460 hydrolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000002503 metabolic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000004060 metabolic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000002207 metabolite Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 4
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 description 4
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 239000011593 sulfur Chemical group 0.000 description 4
- 230000009885 systemic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N trans-butenedioic acid Natural products OC(=O)C=CC(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K Citrate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CC(O)(CC([O-])=O)C([O-])=O KRKNYBCHXYNGOX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 3
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N Dextrotartaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-JCYAYHJZSA-N 0.000 description 3
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 241000282412 Homo Species 0.000 description 3
- 206010061218 Inflammation Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 102000004877 Insulin Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108090001061 Insulin Proteins 0.000 description 3
- AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanesulfonic acid Chemical compound CS(O)(=O)=O AFVFQIVMOAPDHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 150000001204 N-oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000005481 NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 230000029936 alkylation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005804 alkylation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000001732 carboxylic acid derivatives Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 150000001735 carboxylic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 239000003937 drug carrier Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000032050 esterification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000005886 esterification reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 3
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000001640 fractional crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000000592 heterocycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000004128 high performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 3
- XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen iodide Chemical compound I XMBWDFGMSWQBCA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000007062 hydrolysis Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 3
- RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N imidazole Natural products C1=CNC=N1 RAXXELZNTBOGNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000004054 inflammatory process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229940125396 insulin Drugs 0.000 description 3
- 239000000543 intermediate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 3
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 125000006413 ring segment Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000004704 ultra performance liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000003981 vehicle Substances 0.000 description 3
- KWGRBVOPPLSCSI-WPRPVWTQSA-N (-)-ephedrine Chemical compound CN[C@@H](C)[C@H](O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KWGRBVOPPLSCSI-WPRPVWTQSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000004178 (C1-C4) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- UZOBCRQUEAWJQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-benzyl-1h-indole Chemical compound C=1C2=CC=CC=C2NC=1CC1=CC=CC=C1 UZOBCRQUEAWJQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- CVKOOKPNCVYHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(bromomethyl)benzonitrile Chemical compound BrCC1=CC=CC(C#N)=C1 CVKOOKPNCVYHNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102100029470 Apolipoprotein E Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 101710095339 Apolipoprotein E Proteins 0.000 description 2
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M Bromide Chemical compound [Br-] CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YZCKVEUIGOORGS-OUBTZVSYSA-N Deuterium Chemical compound [2H] YZCKVEUIGOORGS-OUBTZVSYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N Fumaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C\C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010022489 Insulin Resistance Diseases 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M Lactate Chemical compound CC(O)C([O-])=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229910002651 NO3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nitrate Chemical compound [O-][N+]([O-])=O NHNBFGGVMKEFGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Oxalic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)=O MUBZPKHOEPUJKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 102000001708 Protein Isoforms Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 108010029485 Protein Isoforms Proteins 0.000 description 2
- JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Pyridine Chemical compound C1=CC=NC=C1 JUJWROOIHBZHMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LOUPRKONTZGTKE-WZBLMQSHSA-N Quinine Chemical compound C([C@H]([C@H](C1)C=C)C2)C[N@@]1[C@@H]2[C@H](O)C1=CC=NC2=CC=C(OC)C=C21 LOUPRKONTZGTKE-WZBLMQSHSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YASAKCUCGLMORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Rosiglitazone Chemical compound C=1C=CC=NC=1N(C)CCOC(C=C1)=CC=C1CC1SC(=O)NC1=O YASAKCUCGLMORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sulfate Chemical compound [O-]S([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 125000002777 acetyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)=O 0.000 description 2
- 239000000443 aerosol Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000003158 alcohol group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 150000001298 alcohols Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000001447 alkali salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000003545 alkoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N anthracene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC3=CC=CC=C3C=C21 MWPLVEDNUUSJAV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229940072107 ascorbate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 235000010323 ascorbic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 239000011668 ascorbic acid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 2
- SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M benzenesulfonate Chemical compound [O-]S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 SRSXLGNVWSONIS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229940077388 benzenesulfonate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzoic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1 WPYMKLBDIGXBTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000001246 bromo group Chemical group Br* 0.000 description 2
- 239000002775 capsule Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001721 carbon Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 125000001309 chloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 2
- 150000003997 cyclic ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052805 deuterium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 208000035475 disorder Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 238000004821 distillation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000009510 drug design Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001495 ethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000001153 fluoro group Chemical group F* 0.000 description 2
- 239000012737 fresh medium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000000524 functional group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 230000014101 glucose homeostasis Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 125000005842 heteroatom Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M hydrogensulfate Chemical compound OS([O-])(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000000959 isobutyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 125000001972 isopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 150000002576 ketones Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N lactic acid Chemical compound CC(O)C(O)=O JVTAAEKCZFNVCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000002632 lipids Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 210000002540 macrophage Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium stearate Chemical compound [Mg+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O HQKMJHAJHXVSDF-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N maleic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)\C=C/C(O)=O VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000004123 n-propyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 2
- 125000004433 nitrogen atom Chemical group N* 0.000 description 2
- 231100000252 nontoxic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000003000 nontoxic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000007530 organic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 150000002894 organic compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 125000004043 oxo group Chemical group O=* 0.000 description 2
- 125000004430 oxygen atom Chemical group O* 0.000 description 2
- 230000037361 pathway Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940067157 phenylhydrazine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 210000002826 placenta Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000002600 positron emission tomography Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000069 prophylactic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 125000006239 protecting group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 239000011541 reaction mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006722 reduction reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M salicylate Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1C([O-])=O YGSDEFSMJLZEOE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 2
- 229960001860 salicylate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 238000002603 single-photon emission computed tomography Methods 0.000 description 2
- UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N streptomycin Chemical compound CN[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@](C=O)(O)[C@H](C)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000000859 sublimation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008022 sublimation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 2
- KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L succinate(2-) Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)CCC([O-])=O KDYFGRWQOYBRFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 150000003460 sulfonic acids Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000001308 synthesis method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940095064 tartrate Drugs 0.000 description 2
- 125000000999 tert-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C(*)(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 2
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N toluene-4-sulfonic acid Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(S(O)(=O)=O)C=C1 JOXIMZWYDAKGHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000844 transformation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 125000001425 triazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- QAEDZJGFFMLHHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N trifluoroacetic anhydride Chemical compound FC(F)(F)C(=O)OC(=O)C(F)(F)F QAEDZJGFFMLHHQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N (+/-)-Camphoric acid Chemical compound CC1(C)C(C(O)=O)CCC1(C)C(O)=O LSPHULWDVZXLIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QBYIENPQHBMVBV-HFEGYEGKSA-N (2R)-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid Chemical compound O[C@@H](C(O)=O)c1ccccc1.O[C@@H](C(O)=O)c1ccccc1 QBYIENPQHBMVBV-HFEGYEGKSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KIUPCUCGVCGPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N (5-methyl-2-propan-2-ylcyclohexyl) carbonochloridate Chemical compound CC(C)C1CCC(C)CC1OC(Cl)=O KIUPCUCGVCGPPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000000008 (C1-C10) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005862 (C1-C6)alkanoyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005859 (C1-C6)alkanoyloxymethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004209 (C1-C8) alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000006272 (C3-C7) cycloalkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-ZETCQYMHSA-N (D)-(+)-Pantothenic acid Chemical compound OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(O)=O GHOKWGTUZJEAQD-ZETCQYMHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N (S)-camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1C[C@@]2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)C[C@@H]1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-GMSGAONNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003088 (fluoren-9-ylmethoxy)carbonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005860 1-((C1-C6)alkanoyloxy)ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005851 1-(N-(alkoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005846 1-(alkanoyloxy)ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005848 1-(alkoxycarbonyloxy)ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chlorobutane Chemical compound CCCCCl VFWCMGCRMGJXDK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VUQPJRPDRDVQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-chlorooctadecane Chemical class CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCl VUQPJRPDRDVQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005847 1-methyl-1-(alkanoyloxy)-ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005849 1-methyl-1-(alkoxycarbonyloxy)ethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004214 1-pyrrolidinyl group Chemical group [H]C1([H])N(*)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 238000005160 1H NMR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004918 2-methyl-2-pentyl group Chemical group CC(C)(CCC)* 0.000 description 1
- LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 2-methylbenzenesulfonate Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1S([O-])(=O)=O LBLYYCQCTBFVLH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000004493 2-methylbut-1-yl group Chemical group CC(C*)CC 0.000 description 1
- WMPPDTMATNBGJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-phenylethylbromide Chemical class BrCCC1=CC=CC=C1 WMPPDTMATNBGJN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 3-carboxy-2,3-dihydroxypropanoate Chemical compound OC(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000004919 3-methyl-2-pentyl group Chemical group CC(C(C)*)CC 0.000 description 1
- UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4,4'-Diphenylmethane Diisocyanate Chemical compound C1=CC(N=C=O)=CC=C1CC1=CC=C(N=C=O)C=C1 UPMLOUAZCHDJJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004920 4-methyl-2-pentyl group Chemical group CC(CC(C)*)C 0.000 description 1
- 125000006163 5-membered heteroaryl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7553-56-2 Chemical compound [I] ZCYVEMRRCGMTRW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000251468 Actinopterygii Species 0.000 description 1
- USFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ammonium acetate Chemical compound N.CC(O)=O USFZMSVCRYTOJT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005695 Ammonium acetate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004475 Arginine Substances 0.000 description 1
- BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Borate Chemical compound [O-]B([O-])[O-] BTBUEUYNUDRHOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000283690 Bos taurus Species 0.000 description 1
- WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Bromine atom Chemical compound [Br] WKBOTKDWSSQWDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M Butyrate Chemical compound CCCC([O-])=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyric acid Natural products CCCC(O)=O FERIUCNNQQJTOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000282472 Canis lupus familiaris Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283707 Capra Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000024172 Cardiovascular disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000014914 Carrier Proteins Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 241000700198 Cavia Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282693 Cercopithecidae Species 0.000 description 1
- VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M Chloride anion Chemical compound [Cl-] VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 235000001258 Cinchona calisaya Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-LLEIAEIESA-N D-glucaric acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O DSLZVSRJTYRBFB-LLEIAEIESA-N 0.000 description 1
- RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M D-gluconate Chemical compound OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C([O-])=O RGHNJXZEOKUKBD-SQOUGZDYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-AQKNRBDQSA-N D-glucopyranuronic acid Chemical compound OC1O[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O AEMOLEFTQBMNLQ-AQKNRBDQSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dicyclohexylamine Chemical compound C1CCCCC1NC1CCCCC1 XBPCUCUWBYBCDP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010061818 Disease progression Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000006144 Dulbecco’s modified Eagle's medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000283086 Equidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 101150018889 FABP4 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000282326 Felis catus Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000006783 Fischer indole synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M Formate Chemical compound [O-]C=O BDAGIHXWWSANSR-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 230000005526 G1 to G0 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 101100226596 Gallus gallus FABP gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108700039691 Genetic Promoter Regions Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001272567 Hominoidea Species 0.000 description 1
- CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen bromide Chemical compound Br CPELXLSAUQHCOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004566 IR spectroscopy Methods 0.000 description 1
- DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M Ilexoside XXIX Chemical compound C[C@@H]1CC[C@@]2(CC[C@@]3(C(=CC[C@H]4[C@]3(CC[C@@H]5[C@@]4(CC[C@@H](C5(C)C)OS(=O)(=O)[O-])C)C)[C@@H]2[C@]1(C)O)C)C(=O)O[C@H]6[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O6)CO)O)O)O.[Na+] DGAQECJNVWCQMB-PUAWFVPOSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 150000008575 L-amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N L-glutamic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)[C@@H](N)CCC(O)=O WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002061 L-isoleucyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)[*])[C@](C([H])([H])[H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000003580 L-valyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)[*])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N Lactose Natural products OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O GUBGYTABKSRVRQ-QKKXKWKRSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005684 Liebig rearrangement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lithium Chemical compound [Li] WHXSMMKQMYFTQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Lysine Natural products NCCCCC(N)C(O)=O KDXKERNSBIXSRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004472 Lysine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003820 Medium-pressure liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241000699666 Mus <mouse, genus> Species 0.000 description 1
- 125000005855 N,N-di(C1-C2)alkylcarbamoyl-(C1-C2)alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005850 N-(alkoxycarbonyl)aminomethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- FNVIDJPETWCVJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N NC(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1.C1(=CC=CC=C1)CCN Chemical compound NC(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1.C1(=CC=CC=C1)CCN FNVIDJPETWCVJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QMGVPVSNSZLJIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nux Vomica Natural products C1C2C3C4N(C=5C6=CC=CC=5)C(=O)CC3OCC=C2CN2C1C46CC2 QMGVPVSNSZLJIA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000283973 Oryctolagus cuniculus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282579 Pan Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001494479 Pecora Species 0.000 description 1
- 229930182555 Penicillin Natural products 0.000 description 1
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N Penicillin G Chemical compound N([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorous acid Chemical class OP(O)=O ABLZXFCXXLZCGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 206010035664 Pneumonia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 208000023146 Pre-existing disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M Propionate Chemical compound CCC([O-])=O XBDQKXXYIPTUBI-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- YZCKVEUIGOORGS-IGMARMGPSA-N Protium Chemical compound [1H] YZCKVEUIGOORGS-IGMARMGPSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N R-2-phenyl-2-hydroxyacetic acid Natural products OC(=O)C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1 IWYDHOAUDWTVEP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000700159 Rattus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283984 Rodentia Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000282887 Suidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 229920002253 Tannate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tartaric acid Natural products [H+].[H+].[O-]C(=O)C(O)C(O)C([O-])=O FEWJPZIEWOKRBE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052771 Terbium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Thiocyanate anion Chemical compound [S-]C#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 108091036066 Three prime untranslated region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 208000003721 Triple Negative Breast Neoplasms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000007983 Tris buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108091023045 Untranslated Region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940022663 acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- IPBVNPXQWQGGJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N acetic acid phenyl ester Natural products CC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1 IPBVNPXQWQGGJP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000008043 acidic salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004423 acyloxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000010014 adipocyte dysfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009815 adipogenic differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000577 adipose tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000003463 adsorbent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000001552 airway epithelial cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229910052783 alkali metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052784 alkaline earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000004183 alkoxy alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005206 alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000278 alkyl amino alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001347 alkyl bromides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000001350 alkyl halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004390 alkyl sulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005466 alkylenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000000172 allergic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004202 aminomethyl group Chemical group [H]N([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 229940043376 ammonium acetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019257 ammonium acetate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003863 ammonium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010171 animal model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000843 anti-fungal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940121375 antifungal agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012736 aqueous medium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000005140 aralkylsulfonyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N arginine Natural products OC(=O)C(N)CCCNC(N)=N ODKSFYDXXFIFQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005251 aryl acyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003710 aryl alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000005160 aryl oxy alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000012131 assay buffer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003149 assay kit Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000010668 atopic eczema Diseases 0.000 description 1
- DCBDOYDVQJVXOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N azane;1h-indole Chemical compound N.C1=CC=C2NC=CC2=C1 DCBDOYDVQJVXOH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003785 benzimidazolyl group Chemical group N1=C(NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940050390 benzoate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000499 benzofuranyl group Chemical group O1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004601 benzofurazanyl group Chemical group N1=C2C(=NO1)C(=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001164 benzothiazolyl group Chemical group S1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004196 benzothienyl group Chemical group S1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000004541 benzoxazolyl group Chemical group O1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 108091008324 binding proteins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000004071 biological effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N bromine Substances BrBr GDTBXPJZTBHREO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001649 bromium compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- RRKTZKIUPZVBMF-IBTVXLQLSA-N brucine Chemical compound O([C@@H]1[C@H]([C@H]2C3)[C@@H]4N(C(C1)=O)C=1C=C(C(=CC=11)OC)OC)CC=C2CN2[C@@H]3[C@]41CC2 RRKTZKIUPZVBMF-IBTVXLQLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RRKTZKIUPZVBMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N brucine Natural products C1=2C=C(OC)C(OC)=CC=2N(C(C2)=O)C3C(C4C5)C2OCC=C4CN2C5C31CC2 RRKTZKIUPZVBMF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229940038926 butyl chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000000484 butyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000006227 byproduct Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N camphorsulfonic acid Chemical compound C1CC2(CS(O)(=O)=O)C(=O)CC1C2(C)C MIOPJNTWMNEORI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005854 carbamoyl-(C1-C2)alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000001720 carbohydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000002915 carbonyl group Chemical group [*:2]C([*:1])=O 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002738 chelating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000005829 chemical entities Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000007795 chemical reaction product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004296 chiral HPLC Methods 0.000 description 1
- LOUPRKONTZGTKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N cinchonine Natural products C1C(C(C2)C=C)CCN2C1C(O)C1=CC=NC2=CC=C(OC)C=C21 LOUPRKONTZGTKE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000002983 circular dichroism Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940001468 citrate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011260 co-administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007398 colorimetric assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 208000029078 coronary artery disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 239000006071 cream Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003983 crown ethers Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000004093 cyano group Chemical group *C#N 0.000 description 1
- KWGRBVOPPLSCSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N d-ephedrine Natural products CNC(C)C(O)C1=CC=CC=C1 KWGRBVOPPLSCSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 125000002704 decyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010511 deprotection reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001212 derivatisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011033 desalting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N dexamethasone Chemical compound C1CC2=CC(=O)C=C[C@]2(C)[C@]2(F)[C@@H]1[C@@H]1C[C@@H](C)[C@@](C(=O)CO)(O)[C@@]1(C)C[C@@H]2O UREBDLICKHMUKA-CXSFZGCWSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960003957 dexamethasone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000005852 di-N,N—(C1-C2)alkylamino(C2-C3)alkyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 206010012601 diabetes mellitus Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 150000008050 dialkyl sulfates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- LMEDOLJKVASKTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N dibutyl sulfate Chemical compound CCCCOS(=O)(=O)OCCCC LMEDOLJKVASKTP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004177 diethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000118 dimethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 230000006806 disease prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005750 disease progression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003438 dodecyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 239000002552 dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001647 drug administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009509 drug development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002066 eicosanoids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000002124 endocrine Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003248 enzyme activator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229960002179 ephedrine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000004185 ester group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010931 ester hydrolysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M ethanesulfonate Chemical compound CCS([O-])(=O)=O CCIVGXIOQKPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229960003750 ethyl chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007717 exclusion Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000284 extract Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003818 flash chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- RFHAOTPXVQNOHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N fluconazole Chemical compound C1=NC=NN1CC(C=1C(=CC(F)=CC=1)F)(O)CN1C=NC=N1 RFHAOTPXVQNOHP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960004884 fluconazole Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000003599 food sweetener Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012458 free base Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000021588 free fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000004108 freeze drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940050411 fumarate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000003838 furazanyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004612 furopyridinyl group Chemical group O1C(=CC2=C1C=CC=N2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000002541 furyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 108010074605 gamma-Globulins Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 125000005643 gamma-butyrolacton-4-yl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940050410 gluconate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000002791 glucosyl group Chemical group C1([C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O1)CO)* 0.000 description 1
- 229940097042 glucuronate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229930195712 glutamate Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 235000011187 glycerol Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 125000003147 glycosyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000008187 granular material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000002503 granulosa cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002373 hemiacetals Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003187 heptyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 235000009200 high fat diet Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000005556 hormone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940088597 hormone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000004677 hydrates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N hydrogen thiocyanate Natural products SC#N ZMZDMBWJUHKJPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005457 ice water Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000002883 imidazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004857 imidazopyridinyl group Chemical group N1C(=NC2=C1C=CC=N2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003453 indazolyl group Chemical group N1N=C(C2=C1C=CC=C2)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003406 indolizinyl group Chemical group C=1(C=CN2C=CC=CC12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001041 indolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000003112 inhibitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007529 inorganic bases Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 150000004694 iodide salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N iodine Chemical compound II PNDPGZBMCMUPRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011630 iodine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000002346 iodo group Chemical group I* 0.000 description 1
- 238000005342 ion exchange Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004255 ion exchange chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012500 ion exchange media Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- TWBYWOBDOCUKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-M isonicotinate Chemical compound [O-]C(=O)C1=CC=NC=C1 TWBYWOBDOCUKOW-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000001449 isopropyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])(*)C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 125000002183 isoquinolinyl group Chemical group C1(=NC=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001786 isothiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000842 isoxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000011813 knockout mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004310 lactic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000014655 lactic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008101 lactose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000013190 lipid storage Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004811 liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012669 liquid formulation Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052744 lithium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006210 lotion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003819 low-pressure liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium carbonate Chemical compound [Mg+2].[O-]C([O-])=O ZLNQQNXFFQJAID-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000001095 magnesium carbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000021 magnesium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 159000000003 magnesium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000019359 magnesium stearate Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- FRIJBUGBVQZNTB-UHFFFAOYSA-M magnesium;ethane;bromide Chemical compound [Mg+2].[Br-].[CH2-]C FRIJBUGBVQZNTB-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 229960002510 mandelic acid Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006609 metabolic stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- HRDXJKGNWSUIBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N methoxybenzene Chemical group [CH2]OC1=CC=CC=C1 HRDXJKGNWSUIBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004184 methoxymethyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])OC([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 229940050176 methyl chloride Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000004170 methylsulfonyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])S(*)(=O)=O 0.000 description 1
- 150000007522 mineralic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002808 molecular sieve Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010172 mouse model Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035772 mutation Effects 0.000 description 1
- SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[4-(1,3-benzoxazol-2-yl)phenyl]-4-nitrobenzenesulfonamide Chemical class C1=CC([N+](=O)[O-])=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)NC1=CC=C(C=2OC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C=C1 SYSQUGFVNFXIIT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004108 n-butyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001280 n-hexyl group Chemical group C(CCCCC)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000740 n-pentyl group Chemical group [H]C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])* 0.000 description 1
- PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-M naphthalene-1-sulfonate Chemical compound C1=CC=C2C(S(=O)(=O)[O-])=CC=CC2=C1 PSZYNBSKGUBXEH-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 125000004593 naphthyridinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CN=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001971 neopentyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 239000012038 nucleophile Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002773 nucleotide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002347 octyl group Chemical group [H]C([*])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] 0.000 description 1
- 229940049964 oleate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(O)=O ZQPPMHVWECSIRJ-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003605 opacifier Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007524 organic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 235000005985 organic acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000012044 organic layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005416 organic matter Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001715 oxadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002971 oxazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940014662 pantothenate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019161 pantothenic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011713 pantothenic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007911 parenteral administration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008506 pathogenesis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007170 pathology Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940049954 penicillin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000000546 pharmaceutical excipient Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000144 pharmacologic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229940049953 phenylacetate Drugs 0.000 description 1
- WLJVXDMOQOGPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenylacetic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 WLJVXDMOQOGPHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000003014 phosphoric acid esters Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000004592 phthalazinyl group Chemical group C1(=NN=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 230000004962 physiological condition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000035790 physiological processes and functions Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 159000000001 potassium salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000000229 preadipocyte Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- ALDITMKAAPLVJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N prop-1-ene;hydrate Chemical group O.CC=C ALDITMKAAPLVJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N propylene glycol Substances CC(O)CO DNIAPMSPPWPWGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000425 proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000001042 pteridinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=CC2=NC=CN=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000000561 purinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=C2N=CNC2=C1)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000003373 pyrazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000003226 pyrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000002098 pyridazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyridine Natural products COC1=CC=CN=C1 UMJSCPRVCHMLSP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000004076 pyridyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000714 pyrimidinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000168 pyrrolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- WVIICGIFSIBFOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N pyrylium Chemical compound C1=CC=[O+]C=C1 WVIICGIFSIBFOG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000002294 quinazolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(N=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 229960000948 quinine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000002943 quinolinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=CC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 125000001567 quinoxalinyl group Chemical group N1=C(C=NC2=CC=CC=C12)* 0.000 description 1
- 150000003254 radicals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000001959 radiotherapy Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006268 reductive amination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010992 reflux Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004366 reverse phase liquid chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960004586 rosiglitazone Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000011664 signaling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011734 sodium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052708 sodium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- URGAHOPLAPQHLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N sodium aluminosilicate Chemical compound [Na+].[Al+3].[O-][Si]([O-])=O.[O-][Si]([O-])=O URGAHOPLAPQHLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007909 solid dosage form Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007790 solid phase Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011877 solvent mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003797 solvolysis reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000003003 spiro group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001954 sterilising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004659 sterilization and disinfection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960005322 streptomycin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 150000003871 sulfonates Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 125000004434 sulfur atom Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000006228 supernatant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000013589 supplement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000829 suppository Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004083 survival effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003765 sweetening agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011975 tartaric acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000002906 tartaric acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- GZCRRIHWUXGPOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N terbium atom Chemical compound [Tb] GZCRRIHWUXGPOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- YBRBMKDOPFTVDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butylamine Chemical compound CC(C)(C)N YBRBMKDOPFTVDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000003831 tetrazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229940124597 therapeutic agent Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 125000001113 thiadiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000000335 thiazolyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000001544 thienyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000004809 thin layer chromatography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003354 tissue distribution assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000004306 triazinyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 125000004044 trifluoroacetyl group Chemical group FC(C(=O)*)(F)F 0.000 description 1
- UNXRWKVEANCORM-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphosphoric acid Chemical class OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OP(O)(O)=O UNXRWKVEANCORM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 208000022679 triple-negative breast carcinoma Diseases 0.000 description 1
- LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tris Chemical compound OCC(N)(CO)CO LENZDBCJOHFCAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000005853 β-dimethylaminoethyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/56—Ring systems containing three or more rings
- C07D209/80—[b, c]- or [b, d]-condensed
- C07D209/82—Carbazoles; Hydrogenated carbazoles
- C07D209/86—Carbazoles; Hydrogenated carbazoles with only hydrogen atoms, hydrocarbon or substituted hydrocarbon radicals, directly attached to carbon atoms of the ring system
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K31/00—Medicinal preparations containing organic active ingredients
- A61K31/33—Heterocyclic compounds
- A61K31/395—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins
- A61K31/40—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil
- A61K31/403—Heterocyclic compounds having nitrogen as a ring hetero atom, e.g. guanethidine or rifamycins having five-membered rings with one nitrogen as the only ring hetero atom, e.g. sulpiride, succinimide, tolmetin, buflomedil condensed with carbocyclic rings, e.g. carbazole
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61K—PREPARATIONS FOR MEDICAL, DENTAL OR TOILETRY PURPOSES
- A61K45/00—Medicinal preparations containing active ingredients not provided for in groups A61K31/00 - A61K41/00
- A61K45/06—Mixtures of active ingredients without chemical characterisation, e.g. antiphlogistics and cardiaca
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/04—Anorexiants; Antiobesity agents
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P3/00—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism
- A61P3/08—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis
- A61P3/10—Drugs for disorders of the metabolism for glucose homeostasis for hyperglycaemia, e.g. antidiabetics
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61P—SPECIFIC THERAPEUTIC ACTIVITY OF CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS OR MEDICINAL PREPARATIONS
- A61P9/00—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system
- A61P9/10—Drugs for disorders of the cardiovascular system for treating ischaemic or atherosclerotic diseases, e.g. antianginal drugs, coronary vasodilators, drugs for myocardial infarction, retinopathy, cerebrovascula insufficiency, renal arteriosclerosis
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D209/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing five-membered rings, condensed with other rings, with one nitrogen atom as the only ring hetero atom
- C07D209/56—Ring systems containing three or more rings
- C07D209/80—[b, c]- or [b, d]-condensed
- C07D209/94—[b, c]- or [b, d]-condensed containing carbocyclic rings other than six-membered
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D401/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom
- C07D401/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings
- C07D401/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, having nitrogen atoms as the only ring hetero atoms, at least one ring being a six-membered ring with only one nitrogen atom containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07D—HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS
- C07D409/00—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms
- C07D409/02—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings
- C07D409/06—Heterocyclic compounds containing two or more hetero rings, at least one ring having sulfur atoms as the only ring hetero atoms containing two hetero rings linked by a carbon chain containing only aliphatic carbon atoms
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07B—GENERAL METHODS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY; APPARATUS THEREFOR
- C07B2200/00—Indexing scheme relating to specific properties of organic compounds
- C07B2200/07—Optical isomers
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Pharmacology & Pharmacy (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Diabetes (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nuclear Medicine, Radiotherapy & Molecular Imaging (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Hematology (AREA)
- Obesity (AREA)
- Endocrinology (AREA)
- Emergency Medicine (AREA)
- Urology & Nephrology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Child & Adolescent Psychology (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Indole Compounds (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Medicines That Contain Protein Lipid Enzymes And Other Medicines (AREA)
- Plural Heterocyclic Compounds (AREA)
- Organic Low-Molecular-Weight Compounds And Preparation Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
지방산 결합 단백질 FABP4에 결합하고 지방세포 물질대사를 조정하여 글루코오스 이용 증가를 조장하는 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 신규한 부류의 화합물(여기서, W1 내지 W4, Z1 내지 Z4, Z1 내지 Z5, X, Y, n 및 R1 내지 R8은 청구범위 및 실시형태의 설명에 정의된 바와 같음)뿐만 아니라, 이 부류의 화합물을 약학적으로 허용 가능한 희석제 또는 담체와 조합하여, 그리고 선택적으로 치료적 활성제와 추가로 조합하여 포함하는 약학 조성물, 및 FABP4에 작용하는 질병의 치료 시에 약제의 제조를 위한, 그리고 의료계에서의 이들 화합물의 용도가 개시되어 있다. 실시예에서, 고리 Z는 Z1-Z4를 함유한다. 기타 실시예에서, 고리 Z는 Z1-Z5를 함유한다.
[화학식 I]
A novel class of compounds according to Formula I, Formula II or Formula III, wherein W 1 to W 4 , Z 1 to Z 4 , Z 1 to Z 5 , X, Y, n and R 1 to R 8 are as defined in the claims and description of the embodiments), as well as combining compounds of this class with pharmaceutically acceptable diluents or carriers , and pharmaceutical compositions comprising, optionally in further combination with a therapeutically active agent, and the use of these compounds in the medical community and for the manufacture of medicaments in the treatment of diseases acting on FABP4. In an embodiment, ring Z contains Z 1 -Z 4 . In other embodiments, ring Z contains Z 1 -Z 5 .
[Formula I]
Description
관련 출원 분야에 대한 상호 참조Cross reference to related fields of application
본 출원은 2020년 6월 27일자로 출원된 미국 특허 가출원 일련번호 제63/045,079호의 우선권을 주장하고, 이의 전문은 본원에 그 전체가 참고로 포함된다.This application claims priority from US Provisional Patent Application Serial No. 63/045,079, filed on June 27, 2020, the entirety of which is incorporated herein by reference in its entirety.
실시형태의 분야FIELD OF EMBODIMENT
본 발명은 물질대사 및 염증과 관련된 질환(2형 당뇨병, 비만, 심혈관 질환, 천식, 암 및 기타 질환을 포함하지만, 이에 제한되지 않음)을 치료 또는 예방하기 위한 신규한 화합물에 관한 것이다. 본 발명에서 화합물은 특히 지방산 결합 단백질(FABP) 4와 상호작용을 하고, 지방세포에서 글루코오스 소비를 개선시킨다.The present invention relates to novel compounds for the treatment or prevention of diseases associated with metabolism and inflammation, including but not limited to type 2 diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular disease, asthma, cancer and other diseases. The compounds of the invention specifically interact with fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 and improve glucose consumption in adipocytes.
FABP는 유리 지방산 및 기타 지질 분자와 가역적으로 결합하고, 세포에서 이들의 수송을 용이하게 하는 단백질의 패밀리이다. 현재까지, 9개의 상이한 FABP 동형이 포유동물에서 식별되었다. FABP 동형은 상이한 조직에서 차등 발현 패턴을 보인다. 문헌에서 aP2로도 지칭되는 지방산 결합 단백질 4(FABP4)는 지방세포 및 대식세포에서 주로 발현되며, 이들 세포에서의 주요 대사성 및 염증성 경로, 예를 들어 지질 저장 및 분해, 신호전달 및 에이코사노이드 생성을 매개한다. 게다가, FABP4는 혈장으로 또한 분비되며, 전신성 글루코오스 항상성을 조절하는 지방-유래 인자로서 작용하는 것으로 제안되어 있다.FABPs are a family of proteins that reversibly bind free fatty acids and other lipid molecules and facilitate their transport in cells. To date, nine different FABP isoforms have been identified in mammals. FABP isoforms show differential expression patterns in different tissues. Fatty acid binding protein 4 (FABP4), also referred to as aP2 in the literature, is expressed predominantly in adipocytes and macrophages and plays key metabolic and inflammatory pathways in these cells, such as lipid storage and degradation, signaling and eicosanoid production. mediate Moreover, FABP4 is also secreted into plasma and has been proposed to act as an adipose-derived factor regulating systemic glucose homeostasis.
마우스에서의 유전적 녹아웃 연구는 FABP4의 조직-특이적 및 전신 기능에 대한 통찰력을 제공하였다. 중요하게도, FABP4 유전자의 동형 접합성 결실을 보유한 마우스가 장기간의 고지방 식이를 하는 경우, 이들은 야생형에 필적하게 체중이 늘고, 고혈당증 및 인슐린 저항성으로부터 보호되었다(Hotamisligil et al., Science. 1996 Nov 22; 274(5291): 1377-9). 또한, FABP4 결핍은 죽상동맥경화증으로부터 아포 지질단백질 E(ApoE) 녹아웃 마우스를 유의하게 보호하였으며, 이러한 표현형은 대식세포에서의 염증성 경로의 FABP4 조정에 기인한 것이다(문헌[Makowski et al., Nat Med. 2001 June; 7(6): 699-705]). FABP4 발현은 기도 상피 세포에서 또한 검출되었으며, FABP4 결핍은 알레르기성 폐 염증의 마우스 모델에서 보호적인 것으로 증명되었다(문헌[Shum et al., J Clin Invest. 2006 Aug; 116(8): 2183-2192]).Genetic knockout studies in mice have provided insight into the tissue-specific and systemic functions of FABP4. Importantly, when mice carrying a homozygous deletion of the FABP4 gene were fed a high-fat diet for a long period of time, they gained weight comparable to wild-type and were protected from hyperglycemia and insulin resistance (Hotamisligil et al. , Science. 1996 Nov 22; 274 (5291): 1377-9). In addition, FABP4 deficiency significantly protected apolipoprotein E (ApoE) knockout mice from atherosclerosis, a phenotype attributable to FABP4 modulation of inflammatory pathways in macrophages (Makowski et al. , Nat Med. 2001 June;7(6): 699-705]). FABP4 expression was also detected in airway epithelial cells, and FABP4 deficiency was demonstrated to be protective in a mouse model of allergic lung inflammation (Shum et al. , J Clin Invest. 2006 Aug; 116(8): 2183-2192 ]).
FABP4 발현 수준 및 기능을 인간에서의 다수의 병리현상과 연관시키는 여러 보고서가 문헌에 공개된 바 있다. 예를 들어, 2형 당뇨병 및 관상동맥성 심장 질환의 위험성 감소가 이러한 유전자의 발현 감소를 초래하는 FABP4(rs77878271)의 프로모터 영역에서의 유전적 변이를 보유한 개인에서 관찰되었다(문헌[Tuncman et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 May 2; 103(18): 6970-5]). 또한, 동일한 다형성은 독립적인 연구에서 죽상동맥경화 질환 징후의 감소와 연관이 있었다(문헌[Saksi et al., Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014 Oct; 7(5): 588-98]). 게다가, FAB4 발현 감소를 또한 초래하는 FABP4(rs1054135-GG 유전자형)의 3' 비번역 영역(UTR)에 단일 뉴클레오타이드 다형성을 갖는 삼중 음성 유방암 환자는 질환의 진행 위험성 감소 및 장기간 무질환 생존 시간과 연관이 있었다(문헌[Wang et al., Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5; 7(14): 18984-98]). FABP4의 발현 증가는 전자간증 태반(preeclamptic placenta)에서 관찰되었으며, 전자간증(preeclampsia)의 발병에서 역할을 하는 것으로 제안되었다(문헌[Yan et al., Placenta. 2016 Mar; 39: 94-100]). 유사하게, 다낭성 난소 증후군 환자의 과립막 세포는 FABP4 발현 증가를 보이며, 이는 질환의 임상적 특성분석과 관련이 있었다(문헌[Hu and Qiao, Endocrine. 2011 Oct; 40(2): 196-202]). 종합적으로, 이들 연구는 전신성 물질대사 및 염증을 조절하는 데 있어서 FAPB4의 적극적인 역할을 증명하였으며, FABP4의 약리학적 표적화는 FABP4 기능과 연관된 다양한 질환의 치료를 위한 전략으로서 사용될 수 있다는 것을 시사하였다.Several reports have been published in the literature linking FABP4 expression levels and functions with a number of pathologies in humans. For example, a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease has been observed in individuals carrying a genetic mutation in the promoter region of FABP4 (rs77878271) that results in reduced expression of these genes (Tuncman et al. , Proc Natl Acad Sci US A. 2006 May 2; 103(18): 6970-5]). In addition, the same polymorphism was associated with reduced atherosclerotic disease symptoms in an independent study (Saksi et al. , Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014 Oct; 7(5): 588-98). Moreover, triple-negative breast cancer patients with a single nucleotide polymorphism in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of FABP4 (rs1054135-GG genotype) that also resulted in decreased FAB4 expression were associated with reduced risk of disease progression and long-term disease-free survival time. (Wang et al. , Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5; 7(14): 18984-98). Increased expression of FABP4 has been observed in preeclamptic placenta and has been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia (Yan et al. , Placenta. 2016 Mar; 39: 94-100). . Similarly, granulosa cells from patients with polycystic ovary syndrome show increased expression of FABP4, which has been associated with clinical characterization of the disease (Hu and Qiao, Endocrine. 2011 Oct; 40(2): 196-202). ). Collectively, these studies demonstrated an active role of FAPB4 in regulating systemic metabolism and inflammation, and suggested that pharmacological targeting of FABP4 could be used as a strategy for the treatment of various diseases associated with FABP4 function.
지방세포는 전신성 글루코오스 항상성에서 중심적인 역할을 한다. 이들 주요 역할 중 하나는 혈장에서 과량의 글루코오스를 흡수하고 이를 지질의 형태로 저장하는 것이다. 대사성 스트레스 및 염증으로 인한 지방세포 기능 장애는 종종 고혈당증 및 인슐린 저항성과 같은 합병증을 초래한다. 주목할 점은, FABP4-결핍 마우스가 지방 조직에 대한 글루코오스의 침착 증가를 나타냈다는 것이다. 이들 동물로부터 단리된 지방세포는 이들의 야생형 대응물과 비교하여 지방산으로의 글루코오스의 전환율의 유의한 증가를 나타냈다(문헌[Shaughnessy et al., Diabetes 2000 Jun; 49(6): 904-911]). 따라서, 지방세포에서의 글루코오스 소비의 증가는 FABP4를 표적화함으로써 달성될 수 있다.Adipocytes play a central role in systemic glucose homeostasis. One of these major roles is to absorb excess glucose from plasma and store it in the form of lipids. Adipocyte dysfunction due to metabolic stress and inflammation often leads to complications such as hyperglycemia and insulin resistance. Of note, FABP4-deficient mice showed increased deposition of glucose to adipose tissue. Adipocytes isolated from these animals showed a significant increase in the conversion of glucose to fatty acids compared to their wild-type counterparts (Shaughnessy et al. , Diabetes Jun 2000; 49(6): 904-911). . Thus, increasing glucose consumption in adipocytes can be achieved by targeting FABP4.
문헌 및 특정 선행 특허 출원(예를 들어, WO 00/47734, WO 00/15229, WO 00/15230, WO 02/40448, WO 01/54694, WO 00/59506 및 WO 2004/063156)이 일반적으로 FABP의 저해 개념, 및 특히 FABP4의 저해 개념에 대한 다양한 설명을 제공하고 있지만, 이들 선행 문헌에서의 어떠한 논의에서도 충족되지 않은 모든 요구에 대해 본 발명과 같은 해결책(들)이 제공되지 않는다. 구체적으로, 본 발명에는 FABP4에 결합하고 지방세포 물질대사를 조정하여 글루코오스 이용 증가를 조장하는 신규한 부류의 화합물이 기술되어 있다.The literature and certain prior patent applications (e.g. WO 00/47734, WO 00/15229, WO 00/15230, WO 02/40448, WO 01/54694, WO 00/59506 and WO 2004/063156) generally refer to FABP Although various explanations are provided for the concept of inhibition of FABP4, and in particular inhibition of FABP4, no solution(s) such as the present invention are provided for all unmet needs in any discussion in these prior documents. Specifically, the present invention describes a new class of compounds that bind to FABP4 and modulate adipocyte metabolism to promote increased glucose utilization.
본 발명은, 이의 실시형태 중 하나에서, 화학식 I의 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염 또는 입체 이성질체에 관한 것이다:The present invention, in one of its embodiments, relates to a compound of Formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof:
[화학식 I][Formula I]
(상기 식에서,(In the above formula,
W1-4 및 Z1-Z5는 각각 독립적으로 -C, -CH, CH2, O, S 또는 N이고;W 1-4 and Z 1 -Z 5 are each independently -C, -CH, CH 2 , O, S or N;
X는 독립적으로 CH2, N 또는 CHR4이고;X is independently CH 2 , N or CHR 4 ;
Y는 독립적으로 CH2 또는 CHR5이고;Y is independently CH 2 or CHR 5 ;
n은 0 내지 3의 숫자이고;n is a number from 0 to 3;
고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체(acid isostere), 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되며, 이때 치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴은 수소, CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴, SO2NH2로 치환될 수 있고;At least one R 1 on ring Z is CN, OH, COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isostere, substituted amine, ether and independently selected from the group consisting of halogen, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted cyclic or heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl, wherein the substituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl is hydrogen , CN, OH, COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isomers, substituted amines, ethers and halogens, substituted or unsubstituted alkyls, substituted or may be substituted with unsubstituted cyclic or heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl, SO 2 NH 2 ;
고리(W) 상의 하나 이상의 R2는 CN, OH, CHF2, CH2F, CF3, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 할로겐 및 이환형 헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되고;At least one R 2 on ring (W) is CN, OH, CHF 2 , CH 2 F, CF 3 , COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isostere, halogen and bicyclic independently selected from the group consisting of heteroaryl;
R7은 수소 또는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;R 7 is hydrogen or CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R은 알킬이고;R is alkyl;
R3, R4, R5 또는 R8, 또는 n이 0인 아닌 경우의 R6은,R 3 , R 4 , R 5 or R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0,
(1) 수소;(1) hydrogen;
(2) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬 또는 에테르,(2) an alkyl or ether having 1 to 12 carbon atoms;
(3) 치환된 아민, 또는(3) a substituted amine, or
(4) --(CH2)mG로부터 각각 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,(4) --(CH 2 ) m G, wherein m is 1 to 12, and G is,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬,(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) 아릴 또는 헤테로아릴,(b) aryl or heteroaryl;
(c) CF3, CF2H 또는 CFH2, 또는(c) CF 3 , CF 2 H or CFH 2 , or
(d) 헤테로사이클로부터 독립적으로 선택되고,(d) independently selected from heterocycles;
단, R3, R4, R5, R8 또는 R6은 모두 수소가 아님).provided that none of R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 or R 6 are hydrogen.
본 발명의 목적은, 지방산 결합 단백질(FABP4)에 작용하는 질병의 치료에 사용하기 위한 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 화합물이다.An object of the present invention is a compound according to formula I, formula II or formula III for use in the treatment of diseases which act on fatty acid binding protein (FABP4).
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 약학적으로 허용 가능한 희석제 또는 담체와 조합하여 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 화합물을 유효성분으로서 포함하는, FABP4에 작용하는 질병의 치료에 사용하기 위한 약학 조성물이다. 여기서, 약학 조성물은 추가적인 치료적 활성제를 추가로 포함할 수 있다.Another object of the present invention is a pharmaceutical composition for use in the treatment of diseases acting on FABP4, comprising as an active ingredient a compound according to Formula I, Formula II or Formula III in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable diluent or carrier. am. Here, the pharmaceutical composition may further comprise additional therapeutically active agents.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, FABP4에 작용하는 질병을 치료하기 위한 방법으로, 이 방법은 이 같은 치료를 필요로 하는 개체(바람직하게는, 인간)에게 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 화합물을 유효량으로 투여하는 단계(선택적으로, 기타 치료제를 1회(또는 수회) 투여로서, 동시에 또는 순차적으로 공동 투여하는 것을 포함함)를 포함한다.Another object of the present invention is a method for treating a disease acting on FABP4, wherein the method provides a compound according to formula I, formula II or formula III to a subject (preferably a human) in need of such treatment. (optionally including co-administration of the other therapeutic agent as a single (or multiple) administration, either simultaneously or sequentially) in an effective amount.
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, FABP4를 저해하기 위한 방법으로, 이 방법은 이 같은 치료를 필요로 하는 개체(바람직하게는, 인간)에게 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 화합물을 유효량으로 투여하는 단계를 포함한다.Another object of the present invention is a method for inhibiting FABP4, wherein the method administers an effective amount of a compound according to Formula I, Formula II or Formula III to a subject (preferably, a human) in need of such treatment. It includes steps to
본 발명의 또 다른 목적은, 지방산 결합 단백질 FABP4에 작용하는 질병의 치료에 사용하기 위한 약제의 제조를 위한 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III에 따른 화합물의 용도이다. 이 같은 질병의 예로는 2형 당뇨병, 고혈당증, 대사 증후군, 비만, 죽상동맥경화증, 두개 내 죽상동맥경화성 질환, 비알코올성 지방간염, 천식, 혈관성 치매, 다발성 경화증, 알츠하이머병, 기타 만성 염증성 및 자가면역/염증성 질환, 만성 심장 질환, 다낭성 난소 증후군, 전자간증 및 암을 들 수 있다.Another object of the present invention is the use of a compound according to formula I, formula II or formula III for the manufacture of a medicament for use in the treatment of diseases which act on the fatty acid binding protein FABP4. Examples of such diseases include type 2 diabetes, hyperglycemia, metabolic syndrome, obesity, atherosclerosis, intracranial atherosclerotic disease, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, asthma, vascular dementia, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, and other chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. /Inflammatory diseases, chronic heart disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome, pre-eclampsia and cancer.
본 발명의 기타 특징 및 이점은 상세한 설명 및 청구범위로부터 명백하게 될 것이다.Other features and advantages of the present invention will become apparent from the detailed description and claims.
이제, 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 바람직한 실시형태를 기술한다. 다양한 도면에서 동일한 구성요소는 동일한 도면 부호로 식별된다.Now, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. Like elements in the various drawings are identified by like reference numerals.
이제, 본 발명의 각각의 실시형태를 상세하게 설명할 것이다. 이 같은 실시형태는 본 발명의 설명에 의해 제공되며, 본 발명은 이에 제한되는 것으로 의도되지 않는다. 사실상, 당업자라면 본 명세서를 읽고 본 도면을 볼 때 다양한 변형 및 변경이 이루어질 수 있음을 인식할 수 있다.Now, each embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail. Such embodiments are provided by way of explanation of the present invention, and the present invention is not intended to be limited thereto. In fact, those skilled in the art will recognize that various modifications and changes may be made upon reading this specification and viewing the drawings.
하나의 실시형태에서, 본 발명은 화학식 I의 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염 또는 입체 이성질체이다:In one embodiment, the invention is a compound of Formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof:
[화학식 I][Formula I]
(상기 식에서,(In the above formula,
W1-4 및 Z1 내지 Z5는 각각 독립적으로 -C, -CH, CH2, O, S 또는 N이고;W 1-4 and Z 1 to Z 5 are each independently -C, -CH, CH 2 , O, S or N;
X는 독립적으로 CH2, N 또는 CHR4이고;X is independently CH 2 , N or CHR 4 ;
Y는 독립적으로 CH2 또는 CHR5이고;Y is independently CH 2 or CHR 5 ;
n은 0 내지 3의 숫자이고;n is a number from 0 to 3;
고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되며, 이때 치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴은 수소, CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴, SO2NH2로 치환될 수 있고;At least one R 1 on ring Z is CN, OH, COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isomers, substituted amines, ethers and halogens, substituted or It is independently selected from the group consisting of unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted cyclic or heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl, wherein the substituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl is hydrogen, CN, OH , COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isomers, substituted amines, ethers and halogens, substituted or unsubstituted alkyls, substituted or unsubstituted cyclics or a heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl, SO 2 NH 2 ;
고리(W) 상의 하나 이상의 R2는 CN, OH, CHF2, CH2F, CF3, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 할로겐 및 이환형 헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되고;At least one R 2 on ring (W) is CN, OH, CHF 2 , CH 2 F, CF 3 , COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isostere, halogen and bicyclic independently selected from the group consisting of heteroaryl;
R7은 수소 또는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;R 7 is hydrogen or CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R은 알킬이고;R is alkyl;
R3, R4, R5 또는 R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은,R 3 , R 4 , R 5 or R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0,
(1) 수소;(1) hydrogen;
(2) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬 또는 에테르,(2) a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl or ether having 1 to 12 carbon atoms;
(3) 치환된 아민, 또는(3) a substituted amine, or
(4) --(CH2)mG로부터 각각 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,(4) --(CH 2 ) m G, wherein m is 1 to 12, and G is,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬,(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) 아릴 또는 헤테로아릴,(b) aryl or heteroaryl;
(c) CF3, CF2H 또는 CFH2, 또는(c) CF 3 , CF 2 H or CFH 2 , or
(d) 헤테로사이클로부터 독립적으로 선택되고,(d) independently selected from heterocycles;
단, R3, R4, R5, R8 또는 R6은 모두 수소가 아님).provided that none of R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 or R 6 are hydrogen.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R1 및 R2 둘 모두가 존재하는 경우, 각각 독립적으로 CN, COOH 또는 CONH2이다.Also, in the compounds of formula I, when both R 1 and R 2 are present, each independently is CN, COOH or CONH 2 .
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, 화학식 I은 다수의 R1 및 R2를 포함한다.Also, in the compound of formula (I), formula (I) includes a plurality of R 1 and R 2 .
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 4개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of formula (I), R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 are each independently an alkyl having 4 carbon atoms.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 5개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of formula (I), R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 are each independently an alkyl having 5 carbon atoms.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of formula (I), R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 are each independently an alkyl having 6 carbon atoms.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물의 고리 Z는 다양한 크기를 가질 수 있다(예를 들어, 5-원 고리, 6-원 고리 등일 수 있음).Also, ring Z of the compound of Formula I may have various sizes (eg, it may be a 5-membered ring, a 6-membered ring, etc.).
일부 실시예에서, 화학식 I의 화합물의 고리 Z는 Z1 내지 Z4를 함유한다.In some embodiments, ring Z of a compound of Formula I contains Z 1 to Z 4 .
기타 실시예에서, 화학식 I의 화합물의 고리 Z는 Z1 내지 Z5를 함유한다.In other embodiments, ring Z of the compound of Formula I contains Z 1 to Z 5 .
실시예에서, 고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 할로겐이다.In an embodiment, one or more R 1 on ring Z is halogen.
실시예에서, 고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN이다.In an embodiment, one or more R 1 on ring Z is CN.
실시예에서, 고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CF3다.In an embodiment, one or more R 1 on Ring Z is CF 3 .
실시예에서, 고리(W) 상의 하나 이상의 R2는 할로겐이다.In an embodiment, one or more R 2 on ring (W) is halogen.
실시예에서, 고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN 및/또는 할로겐을 포함한다.In an embodiment, one or more R 1 on ring Z comprises CN and/or halogen.
실시예에서, 고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN 및/또는 할로겐을 포함하고, 고리(W) 상의 하나 이상의 R2는 다른 할로겐을 포함한다. 일부 실시예에서, 할로겐은 다른 하나의 할로겐과 동일하다. 기타 실시예에서, 할로겐은 다른 하나의 할로겐과 상이하다.In an embodiment, one or more R 1 on ring Z includes CN and/or halogen and one or more R 2 on ring (W) includes another halogen. In some embodiments, a halogen is the same as another halogen. In other embodiments, the halogen is different from another halogen.
다른 실시형태에서, 본 발명은 화학식 II의 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염이다:In another embodiment, this invention is a compound of Formula II or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
[화학식 II][Formula II]
(상기 식에서,(In the above formula,
n은 0, 1 또는 2이고;n is 0, 1 or 2;
R1은 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체 및 할로겐으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되고;R 1 is selected from the group consisting of CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isosteres and halogens;
R2는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 할로겐 및 이환형 화합물로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되고;R 2 is selected from the group consisting of CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isosteres, halogens and bicyclic compounds;
R7은 수소 또는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;R 7 is hydrogen or CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R은 알킬이고;R is alkyl;
R3, R4, R5 또는 R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은,R 3 , R 4 , R 5 or R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0,
(1) 수소;(1) hydrogen;
(2) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬, 또는(2) alkyl having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, or
(3) --(CH2)mG로부터 각각 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,(3) --(CH 2 ) m G, wherein m is 1 to 12, and G is,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 사이클로알킬,(a) cycloalkyl having 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) 아릴 또는 헤테로아릴, 또는(b) aryl or heteroaryl, or
(c) CF3, CF2H 또는 CFH2로부터 독립적으로 선택되고;(c) independently selected from CF 3 , CF 2 H or CFH 2 ;
단, G는 질소-함유 또는 산소-함유 기가 아니고;provided that G is not a nitrogen-containing or oxygen-containing group;
단, R3, R4, R5, R8 또는 R6은 모두 수소가 아님).provided that none of R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 or R 6 are hydrogen.
또한, 화학식 II의 화합물에서, R1 및 R2가 둘 모두 존재하는 경우, 각각은 독립적으로 CN, COOH 또는 CONH2이다.Also, in the compound of Formula II, when both R 1 and R 2 are present, each is independently CN, COOH or CONH 2 .
또한, 화학식 II의 화합물은 다수의 R1 및 R2를 포함한다.Compounds of Formula II also include a plurality of R 1 and R 2 .
또한, 화학식 II의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 4개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of Formula II, R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 is each independently an alkyl having 4 carbon atoms.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 5개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of formula (I), R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 are each independently an alkyl having 5 carbon atoms.
또한, 화학식 I의 화합물에서, R3, R4, R5, R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은 각각 독립적으로 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬이다.Further, in the compound of formula (I), R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0 are each independently an alkyl having 6 carbon atoms.
또 다른 실시형태에서, 본 발명은 화학식 III의 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염이다:In another embodiment, the invention is a compound of Formula III or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
[화학식 III][Formula III]
(상기 식에서,(In the above formula,
n은 0, 1 또는 2이고;n is 0, 1 or 2;
R1 및 R2는 각각 독립적으로 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;R 1 and R 2 are each independently CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R은 알킬이고;R is alkyl;
R3은,R 3 is
(1) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬;(1) alkyl having 1 to 12 carbon atoms;
(2) --(CH2)mG로부터 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,(2) --(CH 2 ) m is independently selected from G, where m is 1 to 12, and G is
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬; 및(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms; and
(b) 페닐로부터 독립적으로 선택되고;(b) independently selected from phenyl;
단, G는 질소-함유 또는 산소-함유 기가 아님).provided that G is not a nitrogen-containing or oxygen-containing group).
화학식 III에 따른 화합물에서, n은 0이고, R3은 h-, i- 또는 j-위치에 부착되어 있다.In the compound according to formula III, n is 0 and R 3 is attached at the h-, i- or j-position.
화학식 III에 따른 화합물에서, n은 1이고, R3은 h-, i- 또는 j-위치에 부착되어 있다.In the compound according to formula III, n is 1 and R 3 is attached at the h-, i- or j-position.
화학식 III에 따른 화합물에서, n은 2이고, R3은 h-, i- 또는 j-위치에 부착되어 있다.In the compound according to formula III, n is 2 and R 3 is attached at the h-, i- or j-position.
화학식 III에 따른 화합물은 순수한 광학 이성질체이다.Compounds according to formula III are pure optical isomers.
화학식 III에 따른 화합물은 (+)-이성질체이다.Compounds according to formula III are (+)-isomers.
정의Justice
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "산 등배전자체"란 용어는 R이 알킬기인 하기 작용기를 포함하지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다:As used herein, the term "acid isomer" includes, but is not limited to, the following groups where R is an alkyl group:
"알킬"이란 용어는 1개 내지 10개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 포화된 직쇄 또는 분지쇄 탄화수소기를 지칭한다. 대표적인 알킬기로는 메틸, 에틸, n-프로필, 이소프로필, 2-메틸-1-프로필, 2-메틸-2-프로필, 2-메틸-1-부틸, 3-메틸-1-부틸, 2-메틸-3-부틸, 2,2-디메틸-1-프로필, 2-메틸-1-펜틸, 3-메틸-1-펜틸, 4-메틸-1-펜틸, 2-메틸-2-펜틸, 3-메틸-2-펜틸, 4-메틸-2-펜틸, 2,2-디메틸-1-부틸, 3,3-디메틸-1-부틸, 2-에틸-1-부틸, 부틸, 이소부틸, t-부틸, n-펜틸, 이소펜틸, 네오펜틸, n-헥실 등, 및 보다 긴 알킬기, 예를 들어 헵틸, 옥틸 등을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "저급 알킬"은 1개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬을 의미한다.The term "alkyl" refers to a saturated straight or branched chain hydrocarbon group having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms. Representative alkyl groups include methyl, ethyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, 2-methyl-1-propyl, 2-methyl-2-propyl, 2-methyl-1-butyl, 3-methyl-1-butyl, 2-methyl -3-butyl, 2,2-dimethyl-1-propyl, 2-methyl-1-pentyl, 3-methyl-1-pentyl, 4-methyl-1-pentyl, 2-methyl-2-pentyl, 3-methyl -2-pentyl, 4-methyl-2-pentyl, 2,2-dimethyl-1-butyl, 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyl, 2-ethyl-1-butyl, butyl, isobutyl, t-butyl, n-pentyl, isopentyl, neopentyl, n-hexyl, and the like, and longer alkyl groups such as heptyl, octyl, and the like, but are not limited thereto. As used herein, "lower alkyl" means an alkyl having from 1 to 6 carbon atoms.
"알킬렌일"이란 용어는 2가 알킬기를 지칭한다.The term "alkylenyl" refers to a divalent alkyl group.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "알콕시"란 용어는 -O-(알킬)을 포함하며, 여기서 알킬은 상기에 정의되어 있다.As used herein, the term "alkoxy" includes -O-(alkyl), where alkyl is defined above.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "아미노"란 용어는 -NH2 기를 지칭한다.As used herein, the term "amino" refers to the -NH 2 group.
"아릴"은 단일, 이환형 또는 삼환형의 방향족 기를 의미하고, 여기서 기의 모든 고리는 방향족이며, 모든 고리 원자는 탄소 원자이다. 이환형 또는 삼환형 시스템에 있어서, 개개의 방향족 고리는 서로 융합된다. 아릴기의 예로는 6-원 및 10-원 아릴이 있다. 아릴기의 추가의 예로는 페닐, 나프탈렌 및 안트라센을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다.“Aryl” means a mono, bicyclic or tricyclic aromatic group wherein all rings of the group are aromatic and all ring atoms are carbon atoms. In bicyclic or tricyclic systems, the individual aromatic rings are fused to each other. Examples of aryl groups include 6-membered and 10-membered aryl. Additional examples of aryl groups include, but are not limited to, phenyl, naphthalene, and anthracene.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "시아노"란 용어는 3중 결합에 의해 질소 원자에 결합된 탄소 원자를 갖는 치환기를 의미한다.As used herein, the term “cyano” refers to a substituent having a carbon atom bonded to a nitrogen atom by a triple bond.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "중수소"란 용어는 하나의 양성자 및 하나의 중성자를 갖는 수소의 안정한 동위 원소를 의미한다.As used herein, the term "deuterium" refers to a stable isotope of hydrogen having one proton and one neutron.
"할로"란 용어는 클로로, 플루오로, 브로모 또는 요오도를 나타낸다. 일부 실시형태에서, 할로는 클로로, 플루오로 또는 브로모이다. 본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "할로겐"란 용어는 불소, 염소, 브롬 또는 요오드를 지칭한다.The term "halo" denotes chloro, fluoro, bromo or iodo. In some embodiments, halo is chloro, fluoro or bromo. As used herein, the term “halogen” refers to fluorine, chlorine, bromine or iodine.
"하이드록시"란 용어는 -OH 기를 의미한다.The term "hydroxy" means an -OH group.
"옥소"란 용어는 =O 기를 의미하고, 탄소 원자 또는 황 원자에 부착될 수 있다.The term "oxo" refers to the group ═O and may be attached to either a carbon atom or a sulfur atom.
"N-산화물"이란 용어는 질소 원자의 산화된 형태를 지칭한다.The term "N-oxide" refers to the oxidized form of the nitrogen atom.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "사이클로알킬"이란 용어는 3개 내지 15개의 탄소 고리 원자를 갖는 포화 또는 부분 포화된 단일 환형, 융합된 다중 환형, 가교된 다중 환형 또는 스피로 다중 환형의 카르보사이클을 지칭한다. 사이클로알킬기의 비제한적인 카테고리는 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 포화 또는 부분 포화된 단일 환형의 카르보사이클이다. 사이클로알킬기의 예시적인 예로는 하기 모이어티(moiety)를 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다:As used herein, the term “cycloalkyl” refers to a saturated or partially saturated single-cyclic, fused-multicyclic, bridged-multicyclic, or spiro-multicyclic carbocycle having from 3 to 15 carbon ring atoms. refers to A non-limiting category of cycloalkyl groups is a saturated or partially saturated single cyclic carbocycle having 3 to 6 carbon atoms. Illustrative examples of cycloalkyl groups include, but are not limited to, the following moieties:
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "헤테로사이클로알킬"은 단일 환형 또는 융합 또는 가교되거나, 스피로 다중 환형 고리 구조를 지칭하는 것으로, 이는 포화 또는 부분 포화되고, 탄소 원자로부터 선택되는 3개 내지 12개의 고리 원자 및 질소, 산소 및 황으로부터 선택되는 최대 3개의 헤테로원자를 갖는다. 고리 구조는 선택적으로 탄소 또는 황 고리 멤버 또는 N-산화물 상의 최대 2개의 옥소기를 함유할 수 있다. 예시적인 헤테로사이클로알킬 엔티티(entity)로는 하기를 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다:As used herein, "heterocycloalkyl" refers to a single cyclic or fused or bridged, spiro multicyclic ring structure, which is saturated or partially saturated, and contains from 3 to 12 ring atoms selected from carbon atoms. and up to 3 heteroatoms selected from nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur. The ring structure may optionally contain up to two oxo groups on carbon or sulfur ring members or N-oxides. Exemplary heterocycloalkyl entities include, but are not limited to:
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "헤테로아릴"이란 용어는 탄소, 산소, 질소 및 황으로부터 선택되는 3개 내지 15개의 고리 원자를 갖는 단일 환형 또는 융합된 다중 환형의 방향족 헤테로사이클을 지칭한다. 적합한 헤테로아릴기는 방향족으로 하전되어야 하는 고리 시스템(예를 들어, 피릴륨)을 포함하지 않는다. 적합한 5-원 헤테로아릴 고리(단일 환형 헤테로아릴로서 또는 다중 환형 헤테로아릴의 일부로서)는 하나의 산소, 황 또는 질소 고리 원자를 갖거나, 하나의 질소 및 하나의 산소 또는 황, 또는 2개, 3개 또는 4개의 질소 고리 원자를 갖는다. 적합한 6-원 헤테로아릴 고리(단일 환형 헤테로아릴로서 또는 다중 환형 헤테로아릴의 일부로서)는 1개, 2개 또는 3개의 질소 고리 원자를 갖는다. 헤테로아릴기의 예로는 피리딘일, 이미다졸일, 이미다조피리딘일, 피리미딘일, 피라졸일, 트리아졸일, 피라진일, 테트라졸일, 푸릴, 티에닐, 이소옥사졸일, 티아졸일, 옥사졸일, 이소티아졸일, 피롤일, 퀴놀린일, 이소퀴놀린일, 인돌일, 벤즈이미다졸일, 벤조푸란일, 시놀린일, 인다졸일, 인돌리진일, 프탈라진일, 피리다진일, 트리아진일, 이소인돌일, 프테리딘일, 퓨린일, 옥사디아졸일, 트리아졸일, 티아디아졸일, 푸라잔일, 벤조푸라잔일, 벤조티오페닐, 벤조티아졸일, 벤즈옥사졸일, 퀴나졸린일, 퀴녹살린일, 나프티리딘일 및 푸로피리딘일을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다.As used herein, the term “heteroaryl” refers to a single cyclic or fused multicyclic aromatic heterocycle having 3 to 15 ring atoms selected from carbon, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur. Suitable heteroaryl groups do not contain a ring system that must be aromatically charged (eg, pyrylium). A suitable 5-membered heteroaryl ring (either as a single cyclic heteroaryl or as part of a multicyclic heteroaryl) has one oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen ring atom, or one nitrogen and one oxygen or sulfur, or two, It has 3 or 4 nitrogen ring atoms. A suitable 6-membered heteroaryl ring (either as a single cyclic heteroaryl or as part of a multicyclic heteroaryl) has 1, 2 or 3 nitrogen ring atoms. Examples of heteroaryl groups include pyridinyl, imidazolyl, imidazopyridinyl, pyrimidinyl, pyrazolyl, triazolyl, pyrazinyl, tetrazolyl, furyl, thienyl, isoxazolyl, thiazolyl, oxazolyl, iso Thiazolyl, pyrrolyl, quinolinyl, isoquinolinyl, indolyl, benzimidazolyl, benzofuranyl, cinolinyl, indazolyl, indolizinyl, phthalazinyl, pyridazinyl, triazinyl, isoindoleyl , pteridinyl, purinyl, oxadiazolyl, triazolyl, thiadiazolyl, furazanyl, benzofurazanyl, benzothiophenyl, benzothiazolyl, benzoxazolyl, quinazolinyl, quinoxalinyl, naphthyridinyl and furopyridinyl, but is not limited thereto.
"이환형 헤테로아릴"이란 용어는 2개의 구성용 방향족 고리를 갖는, 상기에서 정의된 바와 같은 헤테로아릴을 지칭하며, 여기서 2개의 고리는 서로 융합되어 있으며, 고리 중 적어도 하나는 상기에서 정의된 바와 같은 헤테로아릴이다. 이환형 헤테로아릴은 O, N 또는 S로부터 선택되는 1개, 2개, 3개 또는 4개의 헤테로원자 고리 원자를 포함하는 이환형 헤테로아릴기를 포함한다. 헤테로원자가 N인 특정 실시형태에서, 이는 N-산화물일 수 있다. 또한, 이환형 헤테로아릴은 8-원, 9-원 또는 10-원 이환형 헤테로아릴기를 포함한다. 이환형 헤테로아릴은 또한 O, N 또는 S로부터 선택되는 1개, 2개, 3개 또는 4개의 헤테로원자 고리 원자를 갖는 8-원, 9-원 또는 10-원 이환형 헤테로아릴기를 포함한다. 이환형 헤테로아릴의 예시적인 예로는 하기를 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다:The term "bicyclic heteroaryl" refers to a heteroaryl as defined above having two constituent aromatic rings, wherein the two rings are fused together and at least one of the rings is as defined above. It is the same heteroaryl. Bicyclic heteroaryl includes bicyclic heteroaryl groups containing 1, 2, 3 or 4 heteroatom ring atoms selected from O, N or S. In certain embodiments where the heteroatom is N, it may be an N-oxide. Bicyclic heteroaryl also includes 8-, 9- or 10-membered bicyclic heteroaryl groups. Bicyclic heteroaryl also includes 8-, 9- or 10-membered bicyclic heteroaryl groups having 1, 2, 3 or 4 heteroatom ring atoms selected from O, N or S. Illustrative examples of bicyclic heteroaryls include, but are not limited to:
당업자라면 상기에 나열되고 예시된 헤테로아릴, 사이클로알킬 및 헤테로사이클로알킬기의 종류가 총망라된 것은 아니며, 이들 정의된 용어의 범주 내에 있는 추가적인 종류가 또한 선택될 수 있다는 것을 인식할 것이다.Those skilled in the art will recognize that the types of heteroaryl, cycloalkyl and heterocycloalkyl groups listed and exemplified above are not exhaustive and that additional types within the scope of these defined terms may also be selected.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "치환된"이란 용어는 특정의 기 또는 모이어티가 하나 이상의 적합한 치환기를 보유한다는 것을 의미한다. 본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "비치환된"이란 용어는 특정의 기가 치환기를 보유하지 않는다는 것을 의미한다. 본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "선택적으로 치환된"이란 용어는 특정의 기가 치환되지 않거나 특정 개수의 치환기로 치환된다는 것을 의미한다. "치환된"이란 용어가 구조 시스템을 설명하기 위해 사용되는 경우, 치환은 시스템 상의 임의의 원자가 허용 위치에서 발생한다는 것을 의미한다.As used herein, the term “substituted” means that a particular group or moiety bears one or more suitable substituents. As used herein, the term “unsubstituted” means that a particular group does not have substituents. As used herein, the term "optionally substituted" means that a specified group is unsubstituted or substituted with a specified number of substituents. When the term “substituted” is used to describe a structural system, substitution means that any atom on the system occurs at a permissive position.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "하나 이상의 치환기"란 표현은 시스템 상의 임의의 원자가 허용 위치에서 발생할 수 있는 1개 내지 최대 가능한 개수의 치환(들)을 나타낸다. 특정 실시형태에서, 하나 이상의 치환기는 1개, 2개, 3개, 4개 또는 5개의 치환기를 의미한다. 다른 실시형태에서, 하나 이상의 치환기는 1개, 2개 또는 3개의 치환기를 의미한다.As used herein, the expression “one or more substituents” refers to from one to the maximum possible number of substitution(s) that can occur at any valence permissive position on the system. In certain embodiments, one or more substituents means 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 substituents. In another embodiment, one or more substituents means 1, 2 or 3 substituents.
본원에서 불충족 원자가가 있는 것으로 나타나 있는 임의의 원자는 원자의 원자가를 만족시키기에 충분한 개수의 수소 원자를 갖는 것으로 추정된다.Any atom shown herein to have an unsatisfied valence is presumed to have a sufficient number of hydrogen atoms to satisfy the valence of the atom.
임의의 변수(예를 들어, 알킬 또는 Ra)가 본원에서 제공된 임의의 화학식 또는 설명에서 1개 초과의 장소에서 나타나는 경우, 각각의 경우의 이 변수의 정의는 기타 모든 경우의 이의 정의와는 관계가 없다.When any variable (eg, alkyl or R a ) appears in more than one place in any formula or description provided herein, the definition of that variable in each instance does not concern its definition in all other instances. there is no
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, 수치 범위는 순차적인 모든 숫자를 포함하는 것으로 의도된다. 예를 들어, "0 내지 4" 또는 "0~4"로서 표현된 범위는 0, 1, 2, 3 및 4를 포함한다.As used herein, numerical ranges are intended to include all sequential numbers. For example, a range expressed as "0 to 4" or "0 to 4" includes 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4.
다기능성 모이어티가 나타나 있는 경우, 화학식의 나머지에 대한 부착점은 다기능성 모이어티 상의 임의의 점에 있을 수 있다. 일부 실시형태에서, 부착점은 라인 또는 하이픈으로 나타나 있다. 예를 들어, '아릴옥시-'는 산소 원자가 코어 분자에 대한 부착점인 반면, 아릴은 산소 원자에 부착되어 있는 모이어티를 지칭한다.When a multifunctional moiety is present, the point of attachment to the rest of the formula can be at any point on the multifunctional moiety. In some embodiments, attachment points are indicated by lines or hyphens. For example, 'aryloxy-' refers to the moiety where the oxygen atom is the point of attachment to the core molecule, whereas aryl is attached to the oxygen atom.
추가적인 정의additional definition
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "양성자 핵자기 공명" 또는 1H NMR은, 물질의 분자의 구조를 결정하기 위해 이의 분자 내의 수소-1 핵에 대해 NMR 분광법에서의 핵자기 공명을 적용하는 것이다.As used herein, “proton nuclear magnetic resonance” or 1H NMR is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy to the hydrogen -1 nuclei in a molecule of a substance to determine its structure.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "개체"란 용어는 포유동물 및 비포유동물을 포함한다. 포유동물의 예로는 포유동물 부류의 임의의 멤버, 즉 인간; 비인간 영장류(예를 들어, 침팬지 및 기타 유인원 및 원숭이 종); 농장 동물(예를 들어, 소, 말, 양, 염소, 돼지); 가내 동물(예를 들어, 토끼, 개 및 고양이); 및 실험 동물(래트, 마우스 및 기니피그와 같은 설치류를 포함함) 등을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 비포유동물의 예로는, 조류, 어류 등을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 본 발명의 하나의 실시형태에서, 포유동물은 인간이다.As used herein, the term "individual" includes mammals and non-mammals. Examples of mammals include any member of the mammalian class, namely humans; non-human primates (eg, chimpanzees and other apes and monkey species); farm animals (eg, cows, horses, sheep, goats, pigs); domestic animals (eg rabbits, dogs and cats); and laboratory animals (including rodents such as rats, mice, and guinea pigs); and the like, but are not limited thereto. Examples of non-mammals include, but are not limited to, birds and fish. In one embodiment of the invention, the mammal is a human.
"환자"는 인간 및 동물 둘 모두를 포함한다."Patient" includes both humans and animals.
"저해제"란 용어는 특정 생물학적 활성을 차단하거나, 그렇지 않으면 이를 방해하는 분자, 예를 들어 화합물, 약물, 효소 활성화제 또는 호르몬을 지칭한다.The term "inhibitor" refers to a molecule, such as a compound, drug, enzyme activator or hormone, which blocks or otherwise interferes with a particular biological activity.
"조정제"란 용어는 주어진 효소 또는 단백질의 활성을 증가 또는 감소시키거나, 그렇지 않으면 이에 영향을 미치는 본 발명의 화합물과 같은 분자를 지칭한다.The term “modulator” refers to a molecule, such as a compound of the invention, that increases or decreases or otherwise affects the activity of a given enzyme or protein.
"유효량" 또는 "치료적 유효량"이란 용어는 목적하는 생물학적 결과를 제공하기에 충분한 약제의 양을 지칭한다. 이 결과는 질환 또는 의료적 병태의 징후, 증상 또는 원인의 감소 및/또는 경감이거나, 생물학적 시스템의 임의의 기타 목적하는 변경일 수 있다. 예를 들어, 치료적 사용을 위한 "유효량"은 화합물, 또는 화합물을 포함하는 조성물의 양으로, 질환 상태, 증상 또는 의료적 병태에서의 임상적 관련 변화를 제공하도록 요구된다. 임의의 개별 경우에 적절한 "유효"량은 통상의 실험을 이용하여 당업자에 의해 결정될 수 있다. 따라서, "유효량"이란 표현은 일반적으로 활성 물질이 치료적으로 목적하는 효과를 갖는 양을 지칭한다.The terms "effective amount" or "therapeutically effective amount" refer to an amount of an agent sufficient to provide a desired biological result. This result may be reduction and/or alleviation of the signs, symptoms, or causes of a disease or medical condition, or any other desired alteration of a biological system. For example, an "effective amount" for therapeutic use is the amount of a compound, or composition comprising the compound, required to provide a clinically relevant change in a disease state, symptom, or medical condition. An "effective" amount appropriate for any individual case can be determined by one skilled in the art using routine experimentation. Accordingly, the expression “effective amount” generally refers to an amount of an active substance that has a therapeutically desired effect.
본원에서 사용된 바와 같이, "치료하다" 또는 "치료"란 용어는 "예방적" 및 "근치적(curative)" 치료 둘 모두를 포함한다. "예방적" 치료는 질환, 질환의 증상 또는 의료적 병태의 발생의 지연, 발생 가능한 증상의 억제, 질환 또는 증상이 발생할 위험성 또는 이의 재발 위험성의 감소를 나타낸다는 것을 의미한다. "근치적" 치료는 기존의 질환, 증상 또는 병태의 중증도를 감소시키거나, 이의 악화를 억제하는 것을 포함한다. 따라서, 치료는 기존의 질환 증상의 악화를 개선 또는 예방하거나, 추가적인 증상이 발생하는 것을 예방하거나, 증상의 기저의 대사성 원인을 개선 또는 예방하거나, 질병 또는 질환을 억제하거나, 예를 들어 질병 또는 질환의 발생을 저지하거나, 질병 또는 질환을 완화시키거나, 질병 또는 질환의 퇴행을 야기하거나, 질환 또는 질병에 의해 야기된 병태를 완화시키거나, 질환 또는 질병의 증상을 중단시키는 것을 포함한다.As used herein, the terms "treat" or "treatment" include both "prophylactic" and "curative" treatment. “Prophylactic” treatment means delaying the onset of a disease, symptom of a disease, or medical condition, suppressing possible symptoms, or reducing the risk of developing a disease or condition or the risk of its recurrence. A “curative” treatment includes reducing the severity of, or inhibiting the worsening of, an existing disease, symptom or condition. Thus, treatment can ameliorate or prevent a pre-existing disease symptom from worsening, prevent additional symptoms from occurring, ameliorate or prevent an underlying metabolic cause of a symptom, inhibit a disease or disorder, for example, a disease or disorder. stopping the occurrence of, alleviating a disease or condition, causing regression of a disease or condition, alleviating a condition or condition caused by a condition, or stopping the condition or symptoms of a condition.
추가적인 화학적 설명Additional chemical explanation
본원에 주어진 임의의 화학식은 구조식으로 도시된 구조를 갖는 화합물뿐만 아니라, 특정 변경 또는 형태를 나타내기 위한 것이다. 예를 들어, 본원에 주어진 임의의 화학식의 화합물은 비대칭 또는 키랄 중심을 가질 수 있으며, 따라서 상이한 입체 이성질체 형태로 존재할 수 있다. 일반 화학식의 화합물의 모든 입체 이성질체(광학 이성질체, 거울상 이성질체 및 부분 입체 이성질체를 포함함) 및 이들의 혼합물은 화학식의 범주 내에 있는 것으로 간주된다. 또한, 특정 구조는 기하학적 이성질체(즉, 시스 및 트란스 이성질체), 토토머 또는 회전 장애 이성질체로서 존재할 수 있다. 이 같은 모든 이성질체 형태 및 이들의 혼합물이 본원에서 본 발명의 일부로서 고려된다. 따라서, 본원에 주어진 임의의 화학식은 라세미 화합물, 하나 이상의 거울상 이성질체 형태, 하나 이상의 부분 입체 이성질체 형태, 하나 이상의 토토머 또는 회전 장애 이성질체 형태 및 이들의 혼합물을 나타내기 위한 것이다.Any formula given herein is intended to represent specific variations or forms, as well as compounds having structures depicted as structural formulas. For example, compounds of any of the formulas given herein may have asymmetric or chiral centers and, therefore, may exist in different stereoisomeric forms. All stereoisomers (including optical isomers, enantiomers and diastereomers) and mixtures thereof of the compounds of the general formula are considered to be within the scope of the formula. In addition, certain structures may exist as geometric isomers (ie, cis and trans isomers), tautomeric or atropisomers. All such isomeric forms and mixtures thereof are contemplated herein as part of the present invention. Thus, any formula given herein is intended to represent a racemic compound, one or more enantiomeric forms, one or more diastereomeric forms, one or more tautomeric or atropisomeric forms, and mixtures thereof.
부분 입체 이성질체성 혼합물은 당업자에게 잘 알려져 있는 방법에 의해, 예를 들어 크로마토그래피 및/또는 분별 결정화에 의해 이들의 물리적/화학적 차이 근거하여 이들의 개별 부분 입체 이성질체로 분리될 수 있다. 거울상 이성질체는, 적절한 광학적 활성 화합물(예를 들어, 키랄 알코올 또는 모셔(Mosher)의 산 클로라이드와 같은 키랄 보조제)과의 반응 또는 부분 입체 이성질체성 염의 혼합물의 형성에 의해 거울상 이성질체성 혼합물을 부분 입체 이성질체성 혼합물로 전환시키고, 부분 입체 이성질체를 분리하고, 개별 부분 입체 이성질체를 상응하는 순수한 거울상 이성질체로 전환(예를 들어, 가수분해 또는 탈염)시킴으로써 분리될 수 있다. 거울상 이성질체는 또한 키랄 HPLC 칼럼을 사용하여 분리될 수 있다. 본 발명의 화합물의 키랄 중심은 IUPAC 1974 권장 사항에 의해 정의된 바와 같이 "R" 또는 "S"로 지정될 수 있다.Diastereomeric mixtures can be separated into their individual diastereomers on the basis of their physical/chemical differences by methods well known to those skilled in the art, for example by chromatography and/or fractional crystallization. Enantiomers can be converted into diastereomeric mixtures by reaction with appropriate optically active compounds (eg chiral alcohols or chiral auxiliaries such as Mosher's acid chlorides) or by formation of mixtures of diastereomeric salts. It can be separated by conversion to a sex mixture, separation of the diastereomers, and conversion (eg, hydrolysis or desalting) of the individual diastereomers to the corresponding pure enantiomers. Enantiomers can also be separated using chiral HPLC columns. The chiral center of the compounds of the present invention may be designated as "R" or "S" as defined by the IUPAC 1974 recommendation.
본 발명의 화합물은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염을 형성할 수 있으며, 이는 또한 본 발명의 범주 내에 있다. "약학적으로 허용 가능한 염"은 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물의 유리산 또는 유리 염기의 염을 지칭하며, 이는 독성이 없고, 생리학적으로 용인 가능하고, 이것이 제형화되는 약학 조성물과 상용성이며, 그 외에도 제형화 및/또는 개체에 대한 투여에 적합하다. 본원의 화합물에 대한 언급은 달리 표시하지 않는 한 상기 화합물의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염에 대한 언급을 포함하는 것으로 이해된다.The compounds of the present invention may form pharmaceutically acceptable salts, which are also within the scope of the present invention. "Pharmaceutically acceptable salt" refers to a salt of a free acid or free base of a compound of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III, which is non-toxic, physiologically acceptable, and is compatible with the pharmaceutical composition in which it is formulated. compatible and otherwise suitable for formulation and/or administration to a subject. References to compounds herein are understood to include references to pharmaceutically acceptable salts of such compounds unless otherwise indicated.
화합물 염은 무기산 및/또는 유기산과 함께 형성되는 산성 염뿐만 아니라, 무기 염기 및/또는 유기 염기와 함께 형성되는 염기성 염을 포함한다. 또한, 주어진 화합물이 염기성 모이어티(피리딘 또는 이미다졸을 포함하지만, 이에 제한되지 않음) 및 산성 모이어티(카르복실산을 포함하지만, 이에 제한되지 않음) 둘 모두를 함유하는 경우, 당업자라면 화합물이 양쪽성 이온("내부 염")으로서 존재할 수 있다는 것을 인식할 것이고; 이 같은 염은 본원에서 사용된 바와 같이 "염"이란 용어 내에 포함된다. 본 발명의 화합물의 염은, 예를 들어 염이 침전하는 매질과 같은 매질에서, 또는 수성 매질에서 화합물을 소정량, 예를 들어 등가량의 적합한 산 또는 염기와 반응시킨 후, 동결 건조함으로써 제조될 수 있다.Compound salts include acidic salts formed with inorganic and/or organic acids, as well as basic salts formed with inorganic and/or organic bases. In addition, if a given compound contains both basic moieties (including but not limited to pyridine or imidazole) and acidic moieties (including but not limited to carboxylic acids), it will be appreciated by those skilled in the art that the compound It will be appreciated that it can exist as a zwitterion ("internal salt"); Such salts are included within the term "salts" as used herein. Salts of a compound of the present invention may be prepared, for example, by reacting the compound with an amount, eg an equivalent amount, of a suitable acid or base in the same medium in which the salt precipitates, or in an aqueous medium, followed by lyophilization. can
예시적인 염으로는 설페이트, 시트레이트, 아세테이트, 옥살레이트, 클로라이드, 브로마이드, 요오다이드, 니트레이트, 바이설페이트, 포스페이트, 산 포스페이트, 이소니코티네이트, 락테이트, 살리실레이트, 산 시트레이트, 타르트레이트, 올리에이트, 타네이트, 판토테네이트, 바이타르트레이트, 아스코르베이트, 숙시네이트, 말리에이트, 겐티시네이트, 푸마레이트, 글루코네이트, 글루쿠로네이트, 사카레이트, 포르메이트, 벤조에이트, 글루타메이트, 메탄설포네이트("메실레이트"), 에탄설포네이트, 벤젠설포네이트, p-톨루엔설포네이트 및 파모에이트(즉, 1,1'-메틸렌-비스(2-하이드록시-3-나프토에이트)) 염을 들 수 있지만, 이에 제한되지 않는다. 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염은 아세테이트 이온, 숙시네이트 이온 또는 기타 반대 이온과 같은 다른 분자의 포함을 수반할 수 있다. 반대 이온은 모 화합물 상의 전하를 안정화시키는 임의의 유기 또는 무기 모이어티일 수 있다. 또한, 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염은 이의 구조 내에 1개 초과의 하전된 원자를 가질 수 있다. 다중 하전된 원자가 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염의 일부인 사례는 다수의 반대 이온을 가질 수 있다. 이로 인해, 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염은 하나 이상의 하전된 원자 및/또는 하나 이상의 반대 이온을 가질 수 있다.Exemplary salts include sulfate, citrate, acetate, oxalate, chloride, bromide, iodide, nitrate, bisulfate, phosphate, acid phosphate, isonicotinate, lactate, salicylate, acid citrate, Tartrate, oleate, tannate, pantothenate, bitartrate, ascorbate, succinate, maleate, genticinate, fumarate, gluconate, glucuronate, saccharate, formate, benzoate , glutamate, methanesulfonate (“mesylate”), ethanesulfonate, benzenesulfonate, p-toluenesulfonate and pamoate (i.e., 1,1′-methylene-bis(2-hydroxy-3-naphtho 8)) salts, but are not limited thereto. Pharmaceutically acceptable salts may involve the inclusion of other molecules such as acetate ions, succinate ions or other counter ions. The counter ion can be any organic or inorganic moiety that stabilizes the charge on the parent compound. Also, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt may have more than one charged atom in its structure. Instances where multiple charged atoms are part of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt may have multiple counter ions. As such, a pharmaceutically acceptable salt may have one or more charged atoms and/or one or more counter ions.
예시적인 산 부가염으로는 아세테이트, 아스코르베이트, 벤조에이트, 벤젠설포네이트, 바이설페이트, 보레이트, 부티레이트, 시트레이트, 캄포레이트, 캄포설포네이트, 푸마레이트, 하이드로클로라이드, 하이드로브로마이드, 하이드로요오다이드, 락테이트, 말리에이트, 메탄설포네이트, 나프탈렌설포네이트, 니트레이트, 옥살레이트, 포스페이트, 프로피오네이트, 살리실레이트, 숙시네이트, 설페이트, 타르트레이트, 티오시아네이트, 톨루엔설포네이트(토실레이트로도 알려져 있음) 등을 들 수 있다.Exemplary acid addition salts include acetate, ascorbate, benzoate, benzenesulfonate, bisulfate, borate, butyrate, citrate, camphorate, camphorsulfonate, fumarate, hydrochloride, hydrobromide, hydroiodide. , lactate, maleate, methanesulfonate, naphthalenesulfonate, nitrate, oxalate, phosphate, propionate, salicylate, succinate, sulfate, tartrate, thiocyanate, toluenesulfonate (as tosylate) also known).
예시적인 염기성 염으로는 암모늄염, 알칼리 금속염(예를 들어, 나트륨염, 리튬염 및 칼륨염), 알칼리 토금속염(예를 들어, 칼슘염 및 마그네슘염), 유기 염기(예를 들어, 유기 아민)을 갖는 염(예를 들어, 디사이클로헥실아민), t-부틸 아민, 및 아미노산(예를 들어, 아르기닌, 리신 등)을 갖는 염을 들 수 있다. 염기성 질소-함유 기는 저급 알킬 할라이드(예를 들어, 메틸, 에틸 및 부틸 클로라이드, 브로마이드 및 요오다이드), 디알킬 설페이트(예를 들어, 디메틸, 디에틸 및 디부틸 설페이트), 장쇄 할라이드(예를 들어, 데실, 라우릴 및 스테아릴 클로라이드, 브로마이드 및 요오다이드), 아르알킬 할라이드(예를 들어, 벤질 및 페네틸 브로마이드) 등과 같은 약제로 4차화될 수 있다Exemplary basic salts include ammonium salts, alkali metal salts (eg sodium, lithium and potassium salts), alkaline earth metal salts (eg calcium and magnesium salts), organic bases (eg organic amines) (eg, dicyclohexylamine), t-butyl amine, and salts with amino acids (eg, arginine, lysine, etc.). Basic nitrogen-containing groups include lower alkyl halides (eg methyl, ethyl and butyl chloride, bromide and iodide), dialkyl sulfates (eg dimethyl, diethyl and dibutyl sulfate), long chain halides (eg For example, decyl, lauryl and stearyl chlorides, bromides and iodides), aralkyl halides (eg benzyl and phenethyl bromides), etc.
추가적으로, 일반적으로 약학적 화합물로부터 약학적으로 유용한 염을 형성하는 데 적합한 것으로 간주되는 산 및 염기는, 예를 들어 문헌[P. Stahl et al., Camille G. (eds.) Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection and Use. (2002) Zurich: Wiley-VCH]; 문헌[S. Berge et al., J. Pharm. Sci. (1977) 66(1) 1-19]; 문헌[P. Gould, Int. J. Pharm. (1986) 33 201-217]; 문헌[Anderson et al., The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry (1996), Academic Press, New York]; 및 문헌[The Orange Book (Food & Drug Administration, MD, FDA에서 입수 가능함]에 논의되어 있다. 이들 개시내용은 이를 참고하여 본원에 포함된다.Additionally, acids and bases generally considered suitable for forming pharmaceutically useful salts from pharmaceutical compounds are described, for example, in P. Stahl et al. , Camille G. (eds.) Handbook of Pharmaceutical Salts: Properties, Selection and Use. (2002) Zurich: Wiley-VCH]; Literature [S. Berge et al. , J. Pharm. Sci. (1977) 66(1) 1-19]; Literature [P. Gould, Int. J. Pharm. (1986) 33 201-217]; See Anderson et al. , The Practice of Medicinal Chemistry (1996), Academic Press, New York]; and The Orange Book, available from Food & Drug Administration, MD, FDA These disclosures are incorporated herein by reference.
추가적으로, 본원에 기술된 임의의 화합물은, 이 같은 형태가 명시적으로 나열되어 있지 않더라도, 임의의 비용매화된 형태, 또는 이 같은 화합물의 수화물, 용매화물 또는 다형체 및 이들의 혼합물을 또한 지칭하는 것으로 의도된다. "용매화물"은 하나 이상의 용매 분자와 본 발명의 화합물의 물리적 결합을 의미한다. 이러한 물리적 결합은 다양한 정도의 이온 결합 및 공유 결합(수소 결합을 포함함)을 포함한다. 특정 경우에서, 용매화물은, 예를 들어 하나 이상의 용매 분자가 결정성 고체의 결정 격자 내에 혼입될 때 단리 가능할 것이다. "용매화물"은 용액상 및 단리 가능한 용매화물 둘 모두를 포함한다. 적합한 용매화물은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 용매(예를 들어, 물, 에탄올 등)를 사용하여 형성된 것을 포함한다. 일부 실시형태에서, 용매는 물이고, 용매화물은 수화물이다.Additionally, any compound described herein may also refer to any unsolvated form, or hydrate, solvate or polymorph of such compound and mixtures thereof, even if such form is not explicitly recited. it is intended to "Solvate" means a physical association of a compound of the present invention with one or more solvent molecules. These physical bonds include varying degrees of ionic and covalent bonds (including hydrogen bonds). In certain cases, a solvate will be capable of isolation, for example when one or more solvent molecules are incorporated within the crystal lattice of a crystalline solid. "Solvate" includes both solution phase and isolateable solvates. Suitable solvates include those formed using pharmaceutically acceptable solvents (eg, water, ethanol, etc.). In some embodiments, the solvent is water and the solvate is a hydrate.
본 발명의 하나 이상의 화합물은 선택적으로 용매화물로 전환될 수 있다. 용매화물의 제조 방법은 일반적으로 알려져 있다. 따라서, 예를 들어 문헌[M. Caira et al., J. Pharm. Sci., 93(3), 601-611 (2004)]에는 에틸 아세테이트에서 뿐만 아니라 물로부터의 항진균성 플루코나졸의 용매화물의 제조가 기술되어 있다. 용매화물, 반용매화물, 수화물 등의 유사한 제조가 문헌[E. C. van Tonder et al., AAPS PharmSciTech., 5(1), article 12 (2004)]; 및 문헌[A. L. Bingham et al., Chem. Commun., 603-604 (2001)]에 기술되어 있다. 전형적이고 비제한적 과정은 본 발명의 화합물을 주위 온도보다 높은 온도에서 적합한 양의 용매(유기 용매, 물 또는 이들의 혼합물)에 용해시키고, 결정을 형성하기에 충분한 속도로 용액을 냉각시키고, 이어 이 결정을 표준 방법에 의해 단리하는 단계를 수반한다. 예를 들어, 적외선 분광법과 같은 분석 기법은 용매화물(또는 수화물)로서의 결정 내에 용매(또는 물)의 존재를 보여준다.One or more compounds of the present invention may optionally be converted to a solvate. Methods for preparing solvates are generally known. Thus, for example, literature [M. Caira et al. , J. Pharm. Sci. , 93(3), 601-611 (2004) describes the preparation of solvates of antifungal fluconazole from water as well as from ethyl acetate. Similar preparations of solvates, hemi-solvates, hydrates and the like are described by EC van Tonder et al. , AAPS PharmSciTech., 5(1), article 12 (2004)]; and AL Bingham et al. , Chem. Commun., 603-604 (2001). A typical, non-limiting procedure is to dissolve a compound of the present invention in a suitable amount of solvent (organic solvent, water, or mixtures thereof) at a temperature above ambient, cool the solution at a rate sufficient to form crystals, followed by isolating the crystals by standard methods. Analytical techniques such as, for example, infrared spectroscopy show the presence of solvent (or water) in the crystal as a solvate (or hydrate).
또한, 본 발명은 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 전구약물, 및 이 같은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 전구약물을 이용하는 치료 방법에 관한 것이다. "전구약물"이란 용어는 개체에 대한 투여 이후에 가용매분해(solvolysis) 또는 효소적 개열과 같은 화학적 또는 생리적 과정을 통해, 또는 생리적 조건(예를 들어, 생리적 pH에 도달할 때 전구약물은 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물로 전환됨) 하에 생체 내에서 화합물을 수득하는 지정 화합물의 전구체를 의미한다. "약학적으로 허용 가능한 전구약물"은 독성이 없고, 생물학적으로 용인 가능하며, 그 외에도 제형화 및/또는 개체에 대한 투여에 적합한 전구약물이다. 적합한 전구약물 유도체를 선택 및 제조하기 위한 예시적인 절차는, 예를 들어 문헌["Design of Prodrugs", ed. H. Bundgaard, Elsevier, 1985]에 기술되어 있다.The present invention also relates to pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs of compounds of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III, and methods of treatment using such pharmaceutically acceptable prodrugs. The term "prodrug" refers to a prodrug of Formula I, either through a chemical or physiological process such as solvolysis or enzymatic cleavage after administration to a subject, or when physiological conditions (e.g., physiological pH are reached). , converted to a compound of formula II or formula III) to obtain the compound in vivo. A “pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug” is a prodrug that is non-toxic, biologically acceptable, and otherwise suitable for formulation and/or administration to a subject. Exemplary procedures for selecting and preparing suitable prodrug derivatives are described, for example, in "Design of Prodrugs", ed. H. Bundgaard, Elsevier, 1985].
전구약물의 예로는 본 발명의 화합물의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 에스테르를 들 수 있으며, 이는 본 발명의 일부로서 또한 간주된다. 본 화합물의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 에스테르는 하기 기를 포함한다: (1) 에스테르기의 카르복실산 일부의 비-카르보닐 모이어티가 직쇄 또는 분지쇄 알킬(예를 들어, 아세틸, n-프로필, t-부틸 또는 n-부틸), 알콕시알킬(예를 들어, 메톡시메틸), 아르알킬(예를 들어, 벤질), 아릴옥시알킬(예를 들어, 페녹시메틸), 아릴(예를 들어, 할로겐, C1-4알킬, C1-4알콕시 또는 아미노로 예를 들어 선택적으로 치환된 페닐)로부터 선택되는, 하이드록시기의 에스테르화에 의해 수득되는 카르복실산 에스테르; (2) 알킬- 또는 아르알킬설포닐(예를 들어, 메탄설포닐)과 같은 설포네이트 에스테르; (3) 아미노산 에스테르(예를 들어, L-발릴 또는 L-이소류실); (4) 포스포네이트 에스테르; 및 (5) 모노-, 디- 또는 트리포스페이트 에스테르. 포스페이트 에스테르는, 예를 들어 C1-20 알코올 또는 이의 반응성 유도체 또는 2,3-디(C6-24)아실 글리세롤에 의해 추가로 에스테르화될 수 있다. 전구약물에 대한 추가적인 논의는 문헌[T. Higuchi and V. Stella, Pro-drugs as Novel Delivery Systems (1987) 14 of the A.C.S. Symposium Series] 및 문헌[Bioreversible Carriers in Drug Design, (1987) Edward B. Roche, ed., American Pharmaceutical Association and Pergamon Press]에서 제공된다.Examples of prodrugs include pharmaceutically acceptable esters of the compounds of this invention, which are also considered part of this invention. Pharmaceutically acceptable esters of this compound include the following groups: (1) the non-carbonyl moiety of the carboxylic acid portion of the ester group is a straight or branched chain alkyl (eg, acetyl, n-propyl, t -butyl or n-butyl), alkoxyalkyl (eg methoxymethyl), aralkyl (eg benzyl), aryloxyalkyl (eg phenoxymethyl), aryl (eg halogen , phenyl optionally substituted, for example with C 1-4 alkyl, C 1-4 alkoxy or amino), obtained by esterification of a hydroxy group; (2) sulfonate esters such as alkyl- or aralkylsulfonyl (eg methanesulfonyl); (3) amino acid esters (eg, L-valyl or L-isoleucyl); (4) phosphonate esters; and (5) mono-, di- or triphosphate esters. Phosphate esters may be further esterified, for example with C 1-20 alcohols or reactive derivatives thereof or 2,3-di(C 6-24 )acyl glycerols. Further discussion of prodrugs can be found in T. Higuchi and V. Stella, Pro-drugs as Novel Delivery Systems (1987) 14 of the ACS Symposium Series and Bioreversible Carriers in Drug Design, (1987) Edward B. Roche, ed., American Pharmaceutical Association and Pergamon Press. is provided in
예를 들어, 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물이 카르복실산 작용기를 함유하는 경우, 전구약물은, 예를 들어 (C1-C8)알킬, (C2-C12)알카노일옥시메틸, 4개 내지 9개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 1-(알카노일옥시)에틸, 5개 내지 10개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 1-메틸-1-(알카노일옥시)-에틸, 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알콕시카르보닐옥시메틸, 4개 내지 7개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 1-(알콕시카르보닐옥시)에틸, 5개 내지 8개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 1-메틸-1-(알콕시카르보닐옥시)에틸, 3개 내지 9개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 N-(알콕시카르보닐)아미노메틸, 4개 내지 10개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 1-(N-(알콕시카르보닐)아미노)에틸, 3-프탈리딜, 4-크로토노락토닐, 감마-부티로락톤-4-일, 디-N,N-(C1-C2)알킬아미노(C2-C3)알킬(예를 들어, β-디메틸아미노에틸), 카르바모일-(C1-C2)알킬, N,N-디(C1-C2)알킬카르바모일-(C1-C2)알킬 및 피페리디노-, 피롤리디노- 또는 모르폴린 (C2-C3)알킬 등과 같은 기로 산기(acid group)의 수소 원자를 교체함으로써 형성되는 에스테르를 포함할 수 있다.For example, when a compound of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III contains a carboxylic acid functional group, the prodrug may be, for example, (C 1 -C 8 )alkyl, (C 2 -C 12 )alkanoyloxy. Methyl, 1-(alkanoyloxy)ethyl with 4 to 9 carbon atoms, 1-methyl-1-(alkanoyloxy)-ethyl with 5 to 10 carbon atoms, 3 to 6 carbon atoms Alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl having , 1-(alkoxycarbonyloxy)ethyl having 4 to 7 carbon atoms, 1-methyl-1-(alkoxycarbonyloxy)ethyl having 5 to 8 carbon atoms, N-(alkoxycarbonyl)aminomethyl with 3 to 9 carbon atoms, 1-(N-(alkoxycarbonyl)amino)ethyl with 4 to 10 carbon atoms, 3-phthalidyl, 4- crotonolactonil, gamma-butyrolacton-4-yl, di-N,N-(C 1 -C 2 )alkylamino(C 2 -C 3 )alkyl (eg β-dimethylaminoethyl), Carbamoyl-(C 1 -C 2 )alkyl, N,N-di(C 1 -C 2 )alkylcarbamoyl-(C 1 -C 2 )alkyl and piperidino-, pyrrolidino- or esters formed by replacing a hydrogen atom of an acid group with a group such as a poline (C 2 -C 3 )alkyl or the like.
유사하게, 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물이 알코올 작용기를 함유하면, 전구약물은, 예를 들어 (C1-C6)알카노일옥시메틸, 1-((C1-C6)알카노일옥시)에틸, 1-메틸-1-((C1-C6)알카노일옥시)에틸, (C1-C6)알콕시카르보닐옥시메틸, N-(C1-C6)알콕시카르보닐아미노메틸, 숙시노일, (C1-C6)알카노일, α-아미노(C1-C4)알칸일, 아릴아실 및 α-아미노아실, 또는 α-아미노아실-α-아미노아실과 같은 기로 알코올기의 수소 원자를 교체함으로써 형성될 수 있으며, 여기서 각각의α-아미노아실기는 자연적으로 발생하는 L-아미노산, P(O)(OH)2, -P(O)(O(C1-C6)알킬)2 또는 글리코실(헤미아세탈 형태의 탄수화물의 하이드록실기의 제거로부터 얻어지는 라디칼) 등으로부터 독립적으로 선택된다.Similarly, if a compound of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III contains an alcohol functional group, the prodrug may be, for example, (C 1 -C 6 )alkanoyloxymethyl, 1-((C 1 -C 6 )alka Noyloxy)ethyl, 1-methyl-1-((C 1 -C 6 )alkanoyloxy)ethyl, (C 1 -C 6 )alkoxycarbonyloxymethyl, N-(C 1 -C 6 )alkoxycarbonyl groups such as aminomethyl, succinoyl, (C 1 -C 6 )alkanoyl, α-amino(C 1 -C 4 )alkanyl, arylacyl and α-aminoacyl, or α-aminoacyl-α-aminoacyl. It can be formed by replacing the hydrogen atom of an alcohol group, wherein each α-aminoacyl group is a naturally occurring L-amino acid, P(O)(OH) 2 , -P(O)(O(C 1 -C 6 ) alkyl) 2 or glycosyl (a radical resulting from the removal of a hydroxyl group of a carbohydrate in the hemiacetal form); and the like.
화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물이 아민 작용기를 포함하면, 전구약물은, 예를 들어 R"-카르보닐, R"O-카르보닐, NR"R'-카르보닐(여기서, R" 및 R'는 각각 독립적으로 (C1-C10)알킬, (C3-C7) 사이클로알킬, 벤질이거나, R"-카르보닐은 천연 α-아미노아실 또는 천연 α-아미노아실임), -C(OH)C(O)OY1(여기서, Y1은 H임), (C1-C6)알킬 또는 벤질, -C(OY2)Y3(여기서, Y2는 (C1-C4) 알킬이고, Y3은 (C1-C6)알킬, 카르복시(C1-C6)알킬, 아미노(C1-C4)알킬 또는 모노-N- 또는 디-N,N-(C1-C6)알킬아미노알킬임), -C(Y4)Y5(여기서, Y4는 H 또는 메틸이고, Y5는 모노-N- 또는 디-N,N-(C1-C6)알킬아미노 모르폴리노, 피페리딘-1-일 또는 피롤리딘-1-일임) 등과 같은 기로 아민기 내의 수소 원자를 교체함으로써 형성될 수 있다.When the compound of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III contains an amine functional group, the prodrug may be, for example, R"-carbonyl, R"O-carbonyl, NR"R'-carbonyl (wherein R" and Each R' is independently (C 1 -C 10 )alkyl, (C 3 -C 7 ) cycloalkyl, benzyl, or R"-carbonyl is natural α-aminoacyl or natural α-aminoacyl), -C (OH)C(O)OY 1 where Y 1 is H, (C 1 -C 6 )alkyl or benzyl, —C(OY 2 )Y 3 where Y 2 is (C 1 -C 4 ) alkyl, Y 3 is (C 1 -C 6 )alkyl, carboxy(C 1 -C 6 )alkyl, amino(C 1 -C 4 )alkyl or mono-N- or di-N,N-(C 1 -C 6 )alkylaminoalkyl), -C(Y 4 )Y 5 where Y 4 is H or methyl and Y 5 is mono-N- or di-N,N-(C 1 -C 6 ) alkylamino morpholino, piperidin-1-yl or pyrrolidin-1-yl) and the like) by replacing a hydrogen atom in the amine group.
또한, 본 발명은 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물의 약학적 활성 대사산물, 및 본 발명의 방법에서의 이 같은 대사산물의 용도에 관한 것이다. "약학적 활성 대사산물"은 인체 내에서의 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물 또는 이의 염의 물질대사의 약리학적 활성 생성물을 의미한다. 화합물의 전구약물 및 활성 대사산물은 당해 기술분야에 알려져 있거나 이용 가능한 통상의 기법을 사용하여 결정될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 문헌[Bertolini et al., J. Med. Chem. 1997, 40, 2011-2016]; 문헌[Shan et al., J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86 (7), 765-767]; 문헌[Bagshawe, Drug Dev. Res. 1995, 34, 220-230]; 문헌[Bodor, Adv. Drug Res. 1984, 13, 255-331]; 문헌[Bundgaard, Design of Prodrugs (Elsevier Press, 1985)]; 및 문헌[Larsen, Design and Application of Prodrugs, Drug Design and Development (Krogsgaard-Larsen et al., eds., Harwood Academic Publishers, 1991)]을 참고한다.The invention also relates to pharmaceutically active metabolites of compounds of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III, and the use of such metabolites in the methods of the invention. "Pharmaceutically active metabolite" means a pharmacologically active product of the metabolism of a compound of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III or a salt thereof in the human body. Prodrugs and active metabolites of a compound can be determined using conventional techniques known or available in the art. See, eg, Bertolini et al. , J. Med. Chem . 1997, 40 , 2011-2016]; See Shan et al. , J. Pharm. Sci . 1997, 86 (7) , 765-767]; See Bagshawe, Drug Dev. Res . 1995, 34 , 220-230]; See Bodor, Adv. Drug Res . 1984, 13 , 255-331]; Bundgaard, Design of Prodrugs (Elsevier Press, 1985); and Larsen, Design and Application of Prodrugs, Drug Design and Development (Krogsgaard-Larsen et al. , eds., Harwood Academic Publishers, 1991).
본원에 주어진 임의의 화학식은 또한 화합물의 표지되지 않은 형태 뿐만 아니라 동위 원소-표지 형태를 나타내기 위한 것이다. 동위 원소-표지 화합물은 하나 이상의 원자가 선택된 원자 질량 또는 질량수를 갖는 원자에 의해 교체된다는 것을 제외하고, 본원에 주어진 화학식에 의해 표시된 구조를 갖는다. 본 발명의 화합물 내로 혼입될 수 있는 동위 원소의 예로는 각각 2H, 3H, 11C, 13C, 14C, 15N, 18O, 17O, 31P, 32P, 35S, 18F, 36Cl 및 125I와 같은 수소, 탄소, 질소, 산소, 인, 불소, 염소 및 요오드의 동위 원소를 들 수 있다. 이 같은 동위 원소-표지 화합물은 (예를 들어, 14C를 이용한) 대사성 연구, (예를 들어 2H 또는 3H를 이용한) 반응 속도론 연구, 약물 또는 기질 조직 분포 검정을 포함하는 검출 또는 이미징 기법[예를 들어, 양전자 방출 단층 촬영(PET) 또는 단일 광자 방출 컴퓨터 단층 촬영(SPECT)]에 유용하거나, 환자를 방사성 치료하는 데 유용하다. 특히, 18F 또는 11C-표지 화합물은 PET 또는 SPECT 연구에 특히 적합할 수 있다. 더욱이, 중수소(즉, 2H)와 같은 보다 무거운 동위 원소에 의한 치환은 보다 높은 대사성 안정성으로부터 얻어지는 특정 치료적 이점, 예를 들어 생체 내 반감기의 증가 또는 투여량 요건의 감소를 제공할 수 있다. 본 발명의 동위 원소-표지 화합물 및 이의 전구약물은 일반적으로 반응식 또는 실시예에 개시된 절차, 및 비-동위 원소-표지 시약을 이용이 용이한 동위 원소-표지 시약으로 치환함으로써 하기에 기술된 제조에 의해 제조될 수 있다.Any formula given herein is also intended to represent unlabeled as well as isotopically-labeled forms of the compound. Isotopically-labeled compounds have structures represented by the formulas given herein except that one or more atoms are replaced by an atom having a selected atomic mass or mass number. Examples of isotopes that can be incorporated into the compounds of the present invention are 2 H, 3 H, 11 C, 13 C, 14 C, 15 N, 18 O, 17 O, 31 P, 32 P, 35 S, 18 F, respectively. , isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, fluorine, chlorine and iodine, such as 36 Cl and 125 I. Such isotopically-labeled compounds may be detected by detection or imaging techniques, including metabolic studies (eg, using 14 C), kinetic studies (eg, using 2 H or 3 H), drug or substrate tissue distribution assays. [eg, positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)], or for radiation therapy of patients. In particular, 18 F or 11 C-labeled compounds may be particularly suitable for PET or SPECT studies. Furthermore, substitution with heavier isotopes such as deuterium (ie 2 H) may provide certain therapeutic benefits resulting from higher metabolic stability, such as increased in vivo half-life or reduced dosage requirements. Isotopically-labeled compounds of the present invention and their prodrugs are generally prepared by the procedures disclosed in the Schemes or Examples, and by substituting readily available isotopically-labeled reagents for non-isotopically-labeled reagents, followed by the preparations described below. can be produced by
본원에 기술된 화합물에 대하여 "염", "용매화물", "다형체", "전구약물" 등의 용어의 사용은 본 발명의 화합물의 거울상 이성질체, 입체 이성질체, 회전 이성질체, 토토머, 회전 장애 이성질체 및 라세미 화합물의 염, 용매화물, 다형체 및 전구약물 형태에 동일하게 적용하기 위한 것이다.Use of the terms “salt,” “solvate,” “polymorph,” “prodrug,” and the like with respect to the compounds described herein refers to enantiomers, stereoisomers, rotational isomers, tautomers, and atropisomers of the compounds of the present invention. It is intended to apply equally to salts, solvates, polymorphs and prodrug forms of isomers and racemates.
또한, 본 발명은,In addition, the present invention,
5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-플루오로-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(6-시아노피리딘-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(6-카르바모일피리딘-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 6-({4-카르복시-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-5-일}메틸)피리딘-2-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노-2-플루오로페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(1,3-벤즈옥사졸-6-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(1,3-벤즈옥사졸-5-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(6-플루오로피리딘-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(2-플루오로피리딘-4-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-{[6-(트리플루오로메틸)피리딘-2-일]메틸}-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-{[2-(트리플루오로메틸)피리딘-4-일]메틸}-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(5-시아노피리딘-3-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(5-시아노티오펜-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(4-시아노티오펜-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(5-시아노푸란-2-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3,5-디메틸-1,2-옥사졸-4-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-(3-시아노벤조일)-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(1,3-벤즈옥사졸-7-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(5-시아노티오펜-3-일)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(1H-인돌-4-일)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-프로필-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(피리딘-3-일)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-메톡시페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-클로로페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-하이드록시페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(2-메톡시피리딘-4-일)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(4-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(2-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(4-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(2-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(2-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-부틸-5-[(2-플루오로페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-펜틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-펜틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-(2-페닐에틸)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-(2-페닐에틸)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-옥틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-옥틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-플루오로페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(피리딘-3-일)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(3-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(3-메톡시페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-클로로페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(2-메톡시피리딘-4-일)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(4-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(2-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(4-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(4-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(2-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 7-헥실-5-[(2-메틸페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(2-플루오로페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(4-플루오로페닐)메틸]-7-헥실-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-플루오로페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(피리딘-3-일)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(3-메틸페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(3-메톡시페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-클로로페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(3-하이드록시페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(2-메톡시피리딘-4-일)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(4-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(2-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(4-메틸페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(4-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(2-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-헥실-9-[(2-메틸페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(2-플루오로페닐)메틸]-2-헥실-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-(2-페닐에틸)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-(2-페닐에틸)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-4-(2-페닐에틸)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-4-(2-페닐에틸)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-프로필-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-프로필-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 2-부틸-9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 1-부틸-9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-1-(펜틸옥시)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-1-(펜틸옥시)-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 1-부틸-9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 6-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 6-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-1-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-1-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-1-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-1-프로폭시-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-4-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 4-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-3-에틸-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 4-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-3-에틸-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 3-부틸-4-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 3-부틸-4-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 2-부틸-4-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 2-부틸-4-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-10-에틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-10-에틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-10-프로필-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-10-프로필-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-4-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-3-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 10-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 10-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-10-펜틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-10-펜틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 4-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 4-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-2-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-7-에틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-7-에틸-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-3-에틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-4-프로필-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-3-프로필-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-3-프로필-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 4-부틸-9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 4-부틸-9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 3-부틸-9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 3-부틸-9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-4-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-4-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-3-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 9-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-3-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산, 4-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-3-프로필-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 4-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-3-프로필-1H,2H,3H,4H-사이클로펜타[b]인돌-5-카르복실산, 2-({7-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-일}포름아미도)아세트산, 2-({7-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-일}포름아미도)아세트산, 7-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-N-(2-하이드록시에틸)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복스아미드, 7-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-N-(2-하이드록시에틸)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복스아미드, 7-부틸-5-[(3-플루오로페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산 및 7-부틸-5-[(3-카르복시페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되는 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염 또는 입체 이성질체일 수 있다.5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-fluoro-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[ (6-cyanopyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(6-carboxylic acid Bamoylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 6-({4-carboxy-7- Hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indol-5-yl}methyl)pyridine-2-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyano-2-fluorophenyl) Methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(1,3-benzoxazol-6-yl)methyl] -7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(1,3-benzoxazol-5-yl)methyl]-7 -Hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(6-fluoropyridin-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H ,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(2-fluoropyridin-4-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H ,8H,9H,10H-Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-{[6-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]methyl}-5H,6H,7H ,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-{[2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-4-yl]methyl}-5H,6H,7H ,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(5-cyanopyridin-3-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H ,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(5-cyanothiophen-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclo Hepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(4-cyanothiophen-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b] Indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(5-cyanofuran-2-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[ b] indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3,5-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-4-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H- Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-(3-cyanobenzoyl)-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxyl Acid, 5-[(1,3-benzoxazol-7-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(5-cyanothiophen-3-yl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl- 5-[(1H-indol-4-yl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl )methyl]-7-propyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl] -5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H ,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[ b] indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[( 3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]- 5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)methyl]-5H,6H, 7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H -Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9 H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole -4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(2-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7 -Butyl-5-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(2-fluoro Lophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-5H ,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-pentyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H ,10H-Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H -Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-(2-phenylethyl)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta [b] indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4- Carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[( 3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-octyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl ]-7-octyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H, 6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H, 10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4 -carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H -Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4 -carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(2-methoxypyridin-4-yl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid , 5-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(4-carba Moylphenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7 -Hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H ,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[ b] indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(2-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxyl acid, 7-hexyl-5-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(2-fluoro Phenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-7-hexyl -5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4, 9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8 -carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-fluoro Rophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl-9-[(pyridin-3-yl)methyl]-2 ,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl-9-[(3-methylphenyl)methyl]-2,3 ,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl-9-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-car Bazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl- 9-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl-9-[(2-methoxypyridine-4 -yl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4, 9-Tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(4-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole- 8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(2-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl- 9-[(4-methylphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(4-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl- 2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(2-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro- 1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-hexyl-9-[(2-methylphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9- [(2-fluorophenyl)methyl]-2-hexyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl] -2-(2-phenylethyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-(2- Phenylethyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-4-(2-phenylethyl)-2 ,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-4-(2-phenylethyl)-2,3,4,9 -Tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-propyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8 -Carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophene Nyl)methyl]-2-propyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 2-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2 ,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro- 1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 1-Butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl )methyl]-1-(pentyloxy)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-1-(pentyl Oxy)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 1-butyl-9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9- Tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 6-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole -4-carboxylic acid, 6-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 9 -[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-1-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl ]-1-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-1-ethyl-2,3,4, 9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-1-propoxy-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole -8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-4-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 4-[ (3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-ethyl-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3 -Ethyl-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 3-butyl-4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-1H,2H,3H,4H- Cyclopenta[b]indole-5 -carboxylic acid, 3-butyl-4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 2-butyl-4-[ (3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 2-butyl-4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-1H ,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-ethyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H- Cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-ethyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4 -Carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-propyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5- [(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-propyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl ]-4-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-ethyl-2,3, 4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 10-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta [b] indole-4-carboxylic acid, 10-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carb Boxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-10-pentyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[( 3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-10-pentyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl ]-2-pentyl-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-1H,2H,3H, 4H-Cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8 -carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-2-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole -8-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-7-ethyl-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyano Phenyl)methyl]-3-ethyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-4-propyl-2 ,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro- 1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 4-Butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 4-butyl-9-[(3- Cyanophenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 3-butyl-9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2,3 ,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 3-butyl-9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-car Bazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-4-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9- [(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-4-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl] -3-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 9-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3-pentyl-2,3,4, 9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid, 4-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5 -carboxylic acid, 4-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-3-propyl-1H,2H,3H,4H-cyclopenta[b]indole-5-carboxylic acid, 2-({7-butyl -5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indol-4-yl}formamido)acetic acid, 2-({7- Butyl-5-[(3-cia nophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indol-4-yl}formamido)acetic acid, 7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl) Methyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxamide, 7-butyl-5-[(3-cyano Phenyl)methyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxamide, 7-butyl-5-[(3- Fluorophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid and 7-butyl-5-[(3-carboxyphenyl)methyl]-5H, It may be a compound selected from the group consisting of 6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof.
또 다른 실시형태는 화합물의 투여를 필요로 하는 개체(예를 들어, 인간)에게 본 발명의 약학적 제형을 투여함으로써 개체에게 본 발명의 화합물을 투여하기 위한 방법이다.Another embodiment is a method for administering a compound of the present invention to a subject in need thereof (eg, a human) by administering a pharmaceutical formulation of the present invention to the subject.
또 다른 실시형태는 본 발명의 적어도 하나의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 화합물 및 선택적으로 하나 이상의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 첨가제 또는 부형제를 혼합으로써 본 발명의 약학적 제형을 제조하는 방법이다.Another embodiment is a method for preparing a pharmaceutical formulation of the present invention by mixing at least one pharmaceutically acceptable compound of the present invention and optionally one or more pharmaceutically acceptable additives or excipients.
본 발명에서 기술된 화합물로부터 약학 조성물을 제조하기 위해, 비활성의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체는 고체 또는 액체일 수 있다. 고체형 제제는 분말, 정제, 분산성 과립, 캡슐, 카셰(cachet) 및 좌제를 포함한다. 분말 및 정제는 약 5% 내지 약 95%의 유효성분으로 구성될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 탄산마그네슘, 스테아르산마그네슘, 활석, 당 또는 락토오스와 같은 적합한 고체 담체가 당해 기술분야에 알려져 있다. 정제, 분말, 카셰 및 캡슐은 경구 투여용으로 적합한 고체 투여 형태로서 사용될 수 있다. 다양한 조성물을 위한 약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체 및 제조 방법의 예는 문헌[A. Gennaro (ed.), Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, 18th Edition, (1990), Mack Publishing Co., Easton, Pa]에서 찾아볼 수 있다.For preparing pharmaceutical compositions from the compounds described herein, inert, pharmaceutically acceptable carriers can be solid or liquid. Solid form preparations include powders, tablets, dispersible granules, capsules, cachets and suppositories. Powders and tablets may consist of about 5% to about 95% of the active ingredient. Suitable solid carriers are known in the art, such as, for example, magnesium carbonate, magnesium stearate, talc, sugar or lactose. Tablets, powders, cachets and capsules can be used as solid dosage forms suitable for oral administration. Examples of pharmaceutically acceptable carriers and methods of preparation for various compositions are described in A. Gennaro (ed.), Remington's Pharmaceutical Sciences, 18th Edition, (1990), Mack Publishing Co., Easton, Pa.].
본 발명의 조성물 및 제형은 멸균 조성물 및 멸균 제형으로서 투여될 수 있다. 멸균된 약학적 제형은 당업자에게 알려져 있는 의약품 등급의 멸균 표준(예를 들어, United States Pharmacopeia Chapters 797, 1072, and 1211; California Business & Professions Code 4127.7; 16 California Code of Regulations 1751, 21 Code of Federal Regulations 21, or ex-U.S. counterparts to such regulations)에 따라 혼합 또는 제조된다.Compositions and formulations of the present invention can be administered as sterile compositions and sterile formulations. Sterile pharmaceutical formulations may be prepared according to pharmaceutical grade sterilization standards known to those skilled in the art (e.g., United States Pharmacopeia Chapters 797, 1072, and 1211; California Business & Professions Code 4127.7; 16 California Code of Regulations 1751, 21 Code of Federal Regulations 21, or ex-U.S. counterparts to such regulations).
액체형 제제는 용액, 현탁액 및 유화액을 포함한다. 일례로서, 경구용 용액, 현탁액 및 유화액을 위한 감미제 및 유백제(opacifier)의 비경구 주사 또는 첨가를 위한 물 또는 물-프로필렌 글리콜 용액이 언급될 수 있다. 또한, 액체형 제제는 비강 내 투여를 위한 용액을 포함할 수 있다.Liquid form preparations include solutions, suspensions and emulsions. As an example, water or water-propylene glycol solutions for parenteral injection or addition of sweeteners and opacifiers for oral solutions, suspensions and emulsions may be mentioned. Also, liquid formulations may include solutions for intranasal administration.
흡입용으로 적합한 에어로졸 제제는 용액 및 분말 형태의 고체를 포함할 수 있으며, 이는 비활성 압축 기체, 예를 들어 질소와 같은 약학적으로 허용 가능한 담체와 조합될 수 있다.Aerosol preparations suitable for inhalation may include solutions and solids in powder form, which may be combined with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier such as an inert compressed gas such as nitrogen.
사용 직전에 경구 또는 비경구 투여를 위한 액체형 제제로 전환되도록 의도된 고체형 제제가 또한 포함된다. 이 같은 액체 형태는 용액, 현탁액 및 유화액을 포함한다.Solid form preparations intended to be converted immediately prior to use into liquid form preparations for oral or parenteral administration are also included. Such liquid forms include solutions, suspensions and emulsions.
또한, 본 발명의 화합물은 경피 전달 가능할 수 있다. 경피용 조성물은 크림, 로션, 에어로졸 및/또는 유화액의 형태를 취할 수 있으며, 이를 위해 당해 기술분야에서 통상적인 것과 같이 매트릭스 또는 저장소 유형의 경피 패치 내에 포함될 수 있다.In addition, the compounds of the present invention may be transdermally deliverable. Transdermal compositions may take the form of creams, lotions, aerosols and/or emulsions, and for this purpose may be incorporated into matrix or reservoir type transdermal patches as is conventional in the art.
본 발명의 화합물은 또한 피하 전달될 수 있다.Compounds of the present invention may also be delivered subcutaneously.
화합물은 경구 또는 정맥 내 투여될 수 있다.The compounds may be administered orally or intravenously.
약학적 제제는 단위 투여 형태일 수 있다. 이 같은 형태에서, 제제는 활성 성분을 목적하는 목적을 달성하기에 적절한 양, 예를 들어 유효량으로 함유하는 적절한 크기의 단위 용량으로 세분된다.The pharmaceutical formulation may be in unit dosage form. In this form, the preparation is subdivided into unit doses of appropriate size containing the active ingredient in an amount suitable, eg, an effective amount, to achieve the desired purpose.
제제의 단위 용량 내 활성 화합물의 양은 특정 적용에 따라 약 1 ㎎ 내지 약 1,000 ㎎, 예를 들어 약 1 ㎎ 내지 약 500 ㎎, 특히 약 1 ㎎ 내지 약 250 ㎎, 또는 약 1 ㎎ 내지 약 25 ㎎으로 변경 또는 조절될 수 있다.The amount of active compound in a unit dose of the formulation may be from about 1 mg to about 1,000 mg, for example from about 1 mg to about 500 mg, particularly from about 1 mg to about 250 mg, or from about 1 mg to about 25 mg, depending on the particular application. may be altered or adjusted.
사용된 실제 투여량은 환자의 요건 및 치료될 병태의 중증도에 따라 달라질 수 있다. The actual dosage employed may vary depending on the requirements of the patient and the severity of the condition being treated.
특정 상황에 적절한 투여 용법의 결정은 당해 기술분야 내에서 이루어진다. 편의상, 총 1일 투여량은 필요에 따라 하루 동안에 수회 나눠 투여될 수 있다.Determination of the appropriate dosage regimen for a particular situation is within the skill of the art. For convenience, the total daily dose may be administered in several divided doses during the day as needed.
본 발명의 화합물 및/또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염의 투여량 및 투여 빈도는 치료될 증상의 중증도뿐만 아니라 환자의 나이, 상태 및 크기와 같은 인자를 고려하여 주치의의 판단에 따라 조절될 것이다. 경구 투여를 위한 전형적인 권장 1일 투여 용법은 2회 내지 4회의 분할 투여량으로 약 1 ㎎/일 내지 약 500 ㎎/일, 바람직하게는 1 ㎎/일 내지 200 ㎎/일의 범위일 수 있다.The dosage and frequency of administration of the compound of the present invention and/or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt will be adjusted according to the judgment of the attending physician in consideration of factors such as the age, condition and size of the patient as well as the severity of the symptom to be treated. A typical recommended daily dosage regimen for oral administration may range from about 1 mg/day to about 500 mg/day, preferably from 1 mg/day to 200 mg/day in two to four divided doses.
반응식 및 실시예Schemes and Examples
이제, 본 발명의 화합물의 제조에 유용한 예시적이고 비제한적인 화학적 엔티티 및 방법은 후술한 이들의 일반적인 제조를 위한 예시적인 합성 반응식 및 하기의 특정 실시예를 참고하여 기술될 것이다. 당업자라면 본 발명에 따른 화합물을 합성하기 위해 기타 합성 경로를 사용할 수 있다는 것을 인식할 것이다. 본원에서 특정 출발 물질 및 시약을 나타내고 논의하였지만, 다양한 유도체 및/또는 반응 조건을 제공하기 위해 기타 출발 물질 및 시약으로 용이하게 교체할 수 있다. 또한, 상술한 방법에 의해 제조된 많은 예시적인 화합물은 당업자에게 잘 알려져 있는 통상적인 화학을 이용하여 본 개시내용을 고려하여 추가로 개질될 수 있다.Exemplary and non-limiting chemical entities and methods useful in the preparation of the compounds of this invention will now be described with reference to the illustrative synthetic reaction schemes for their general preparation described below and the specific examples below. Those skilled in the art will recognize that other synthetic routes may be used to synthesize the compounds according to the present invention. Although specific starting materials and reagents are shown and discussed herein, other starting materials and reagents may be readily substituted to provide a variety of derivatives and/or reaction conditions. In addition, many of the exemplary compounds prepared by the methods described above may be further modified in light of this disclosure using conventional chemistry well known to those skilled in the art.
당업자라면, 본원의 다양한 화합물을 수득하기 위해, 궁극적으로 목적하는 치환기가 목적하는 생성물을 수득하기에 적절한 보호 유무에 관계없이 반응식을 통해 전달될 수 있도록 출발 물질을 적절히 선택할 수 있다는 것을 인지할 것이다. 대안적으로, 궁극적으로 목적하는 치환기 대신에 반응식을 통해 전달될 수 있고 목적하는 치환기와 적절하게 교체될 수 있는 적합한 기를 이용하는 것이 필수적이거나 바람직할 수 있다. 반응식에서 나타낸 반응 각각은 바람직하게는 약 0℃에서 사용된 용매의 환류 온도까지의 온도에서 진행하였다. 달리 명시하지 않는 한, 하기 반응식에 나타나 있는 변수는 화학식 I을 참고하여 상기에서 정의된 바와 같다.One skilled in the art will appreciate that, to obtain the various compounds herein, starting materials may be suitably selected so that the ultimately desired substituents can be carried through the reaction scheme with or without appropriate protection to yield the desired products. Alternatively, it may be necessary or desirable to use a suitable group that can be carried through the reaction scheme in place of the ultimately desired substituent and is suitably interchangeable with the desired substituent. Each of the reactions shown in the scheme is preferably carried out at a temperature from about 0° C. up to the reflux temperature of the solvent used. Unless otherwise specified, the variables shown in the schemes below are as defined above with reference to Formula I.
본 발명에 따른 화합물은, 특히 본원에 포함된 설명을 고려하여 화학 분야에 잘 알려진 과정, 및 각각이 명확히 참고로 포함되는 문헌[Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II, Editors Katritzky and Rees, Elsevier, 1997, e.g. Volume 3; Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, (9): 1910-16, (1985)]; 문헌[Helvetica Chimica Acta, 41: 1052-60, (1958)]; 문헌[Arzneimittel-Forschung, 40(12): 1328-31, (1990)]에 기술된 기타 헤테로사이클을 위한 과정과 유사한 과정을 포함하는 합성 경로에 의해 합성될 수 있다. 출발 물질은 Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals(미국 위스콘신주 밀워키 소재)와 같은 상용 공급처로부터 일반적으로 이용 가능하거나, 당업자에게 잘 알려진 방법을 사용하여 용이하게 제조된다(예를 들어, 보충판을 포함하는 문헌[Louis F. Fieser and Mary Fieser, Reagents for Organic Synthesis, v. 1-23, Wiley, N.Y. (1967-2006 ed.)] 또는 문헌[Beilsteins Handbuch der organischen Chemie, 4, Aufl. ed. Springer-Verlag, Berlin]에 일반적으로 기술된 방법(Beilstein 온라인 데이터베이스를 통해 또한 이용 가능함)에 의해 제조됨).The compounds according to the present invention can be prepared according to procedures well known in the chemical arts, particularly in view of the description contained herein, and to Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II, Editors Katritzky and Rees, Elsevier, 1997, e.g. Volume 3; Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, (9): 1910-16, (1985)]; Helvetica Chimica Acta, 41: 1052-60, (1958); It can be synthesized by a synthetic route involving a procedure similar to that for other heterocycles described in Arzneimittel-Forschung, 40(12): 1328-31, (1990). Starting materials are generally available from commercial sources such as Sigma-Aldrich Chemicals (Milwaukee, Wis., USA) or are readily prepared using methods well known to those skilled in the art (see, e.g., Louis et al., including supplement). F. Fieser and Mary Fieser, Reagents for Organic Synthesis, v. 1-23, Wiley, N.Y. (1967-2006 ed.) or Beilsteins Handbuch der organischen Chemie, 4, Aufl. ed. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. (also available via the Beilstein online database).
본 발명에 따른 화합물, 필요한 시약 및 중간체의 합성에 유용한 합성 화학 변환 및 보호기 방법(보호 및 탈보호)은 당해 기술분야에 알려져 있으며, 예를 들어 문헌[R. Larock, Comprehensive Organic Transformations, VCH Publishers (1989)]; 문헌[T. W. Greene and P. G .M. Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 3rd Ed., John Wiley and Sons (1999)]; 및 문헌[L. Paquette, ed., Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley and Sons (1995)] 및 이들의 후판(subsequent edition)에 기술된 방법을 포함한다. 이 같은 보호의 필요성은 원위 작용기(remote functionality)의 특성 및 제조 방법의 조건에 따라 달라질 것이다. 적합한 아미노-보호기는 아세틸, 트리플루오로아세틸, t-부톡시카르보닐(BOC), 벤질옥시카르보닐(CBz) 및 9-플루오렌일메틸렌옥시카르보닐(Fmoc)를 포함한다. 이 같은 보호의 필요성은 당업자에 의해 용이하게 결정된다.Synthetic chemical transformations and protecting group methods (protection and deprotection) useful for the synthesis of the compounds, necessary reagents and intermediates according to the present invention are known in the art and are described, for example, in R. Larock, Comprehensive Organic Transformations, VCH Publishers (1989)]; Literature [T. W. Greene and P.G.M. Wuts, Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 3rd Ed., John Wiley and Sons (1999)]; and L. Paquette, ed., Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, John Wiley and Sons (1995)] and their subsequent editions. The need for such protection will depend on the nature of the remote functionality and the conditions of the manufacturing method. Suitable amino-protecting groups include acetyl, trifluoroacetyl, t-butoxycarbonyl (BOC), benzyloxycarbonyl (CBz) and 9-fluorenylmethyleneoxycarbonyl (Fmoc). The need for such protection is readily determined by one skilled in the art.
본 발명의 화합물의 제조에 특히 유용한 추가적인 반응은 알킬화, 환원성 아민화, 산화, 환원 및 가수분해 반응을 포함한다. 이 같은 변환은 충분히 당해 기술분야 내에 있다.Additional reactions that are particularly useful in the preparation of the compounds of this invention include alkylation, reductive amination, oxidation, reduction and hydrolysis reactions. Such transformations are well within the skill of the art.
본 발명에 따른 화합물은 단독으로 제조될 수 있거나, 예를 들어 적어도 2개 또는 5개 내지 1,000개의 화합물 또는 10개 내지 100개의 화합물을 포함하는 화합물 라이브러리로서 제조될 수 있다. 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 화합물 라이브러리는 조합적 "분리 및 혼합(split and mix)" 접근법에 의해 제조될 수 있거나, 용액상 또는 고체상 화학을 이용하는 다수의 병행 합성에 의해, 또는 당업자에게 알려져 있는 절차에 의해 제조될 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명의 추가의 양태에 따르면 화학식 I, 화학식 II 또는 화학식 III의 적어도 2개의 화합물 또는 이의 약학적으로 허용 가능한 염을 포함하는 화합물 라이브러리가 제공된다.The compounds according to the present invention may be prepared alone or as a compound library comprising, for example, at least 2 or 5 to 1,000 compounds or 10 to 100 compounds. Libraries of compounds of formula I, formula II or formula III can be prepared by a combinatorial "split and mix" approach, or by multiple parallel synthesis using solution phase or solid phase chemistry, or known to those skilled in the art. It can be manufactured by a procedure in which Accordingly, according to a further aspect of the present invention there is provided a compound library comprising at least two compounds of Formula I, Formula II or Formula III, or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
발명에 따른 화합물을 제조하는 방법에서, 반응 생성물을 서로 분리하고/하거나, 이들을 출발 물질로부터 분리하는 것이 유리할 수 있다. 각각의 단계 또는 일련의 단계의 목적하는 생성물은 당해 기술분야에서 흔히 쓰이는 기법에 의해 목적하는 균질도까지 분리 및/또는 정제된다. 전형적으로, 이 같은 분리는 다중상 추출, 용매 또는 용매 혼합물로부터의 결정화, 증류, 승화 또는 크로마토그래피를 수반한다. 크로마토그래피는, 예를 들어 역상 및 순상; 크기 배제; 이온 교환; 고압, 중간압 및 저압 액체 크로마토그래피 방법 및 장치; 소규모 분석; 모의 이동층(SMB) 및 제조용 박층 또는 후막층 크로마토그래피뿐만 아니라, 소규모 박층 및 플래시 크로마토그래피 기법을 비롯한 다수의 임의의 방법을 수반할 수 있다. In the process for preparing the compounds according to the invention, it may be advantageous to separate the reaction products from one another and/or to separate them from starting materials. The desired product of each step or series of steps is isolated and/or purified to the desired degree of homogeneity by techniques commonly used in the art. Typically, such separation involves multi-phase extraction, crystallization from a solvent or solvent mixture, distillation, sublimation or chromatography. Chromatography may include, for example, reverse phase and normal phase; size exclusion; ion exchange; high, medium and low pressure liquid chromatography methods and apparatus; small scale analysis; It may involve any of a number of methods, including simulated moving bed (SMB) and preparative thin or thick layer chromatography, as well as small scale thin layer and flash chromatography techniques.
다른 부류의 분리 방법은 목적하는 생성물, 미반응 출발 물질, 반응 부산물 등에 결합하거나 이들을 분리할 수 있도록 선택한 시약을 이용한 혼합물의 처리를 수반한다. 이 같은 시약은 활성탄, 분자체, 이온 교환 매질 등과 같은 흡착제 또는 흡수제를 포함한다. 대안적으로, 시약은 염기성 물질의 경우에는 산, 산성 물질의 경우에는 염기, 항체와 같은 결합 시약, 결합 단백질, 크라운 에테르와 같은 선택적 킬레이트제, 액체/액체 이온 추출 시약(LIX) 등일 수 있다. 적당한 분리 방법의 선택은 관련된 물질의 성질, 예를 들어 증류 및 승화 시의 비등점 및 분자량, 크로마토그래피에서의 극성 작용기의 존재 또는 부재, 다중상 추출 시의 산성 및 염기성 매질 중의 물질의 안정성 등에 따라 달라진다.Another class of separation methods involves treatment of the mixture with reagents selected to bind to or separate the desired product, unreacted starting materials, reaction by-products, and the like. Such reagents include adsorbents or absorbents such as activated carbon, molecular sieves, ion exchange media, and the like. Alternatively, the reagent may be an acid in the case of a basic substance, a base in the case of an acidic substance, a binding reagent such as an antibody, a binding protein, a selective chelating agent such as a crown ether, a liquid/liquid ion extraction reagent (LIX), and the like. The choice of an appropriate separation method depends on the nature of the substances involved, e.g. boiling point and molecular weight during distillation and sublimation, presence or absence of polar functional groups in chromatography, stability of the substance in acidic and basic media during multiphase extraction, etc. .
단일 입체 이성질체(예를 들어, 실질적으로 이의 입체 이성질체가 없는 거울상 이성질체)는 광학 활성 분할제를 이용한 부분 입체 이성질체의 형성과 같은 방법을 이용하여 라세미 혼합물을 분해함으로써 수득될 수 있다(문헌[Eliel, E. and Wilen, S. "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds," John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1994]; 문헌[Lochmuller, C. H., (1975) J. Chromatogr., 113(3): 283-302]). 본 발명의 키랄 화합물의 라세미 혼합물은 임의의 적합한 방법에 의해 분리 및 단리할 수 있으며, 이러한 방법으로 (1) 키랄 화합물을 이용한 이온성 부분 입체 이성질체성 염의 형성 및 분별 결정화 또는 기타 방법에 의한 분리, (2) 키랄 유도체화 시약을 이용한 부분 입체 이성질체성 화합물의 형성, 부분 입체 이성질체의 분리 및 순수한 입체 이성질체로의 변환, (3) 키랄 조건 하에 직접 실질적으로 순수하거나 농축된 입체 이성질체의 분리를 들 수 있다(문헌["Drug Stereochemistry, Analytical Methods and Pharmacology," Irving W. Wainer, Ed., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York (1993)] 참조).Single stereoisomers (e.g., enantiomers that are substantially free of their stereoisomers) can be obtained by resolving racemic mixtures using methods such as diastereomer formation with optically active resolving agents (see Eliel , E. and Wilen, S. "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds," John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1994;Lochmuller, C. H., (1975) J. Chromatogr., 113(3): 283- 302]). Racemic mixtures of the chiral compounds of the present invention can be separated and isolated by any suitable method, in which case (1) formation of ionic diastereomeric salts using the chiral compounds and separation by fractional crystallization or other methods. , (2) formation of diastereomeric compounds using chiral derivatization reagents, separation of diastereomers and conversion to pure stereoisomers, and (3) separation of substantially pure or enriched stereoisomers directly under chiral conditions. (See "Drug Stereochemistry, Analytical Methods and Pharmacology," Irving W. Wainer, Ed., Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York (1993)).
방법 (1) 하에, 부분 입체 이성질체성 염은 거울상 이성질적으로 순수한 키랄 염기, 예를 들어 브루신(brucine), 퀴닌(quinine), 에페드린(ephedrine), 스트리크닌(strychnine), α-메틸-β-페닐에틸아민(암페타민) 등을 카르복시산 및 설폰산과 같은 산성 작용기를 보유한 비대칭 화합물과 반응시킴으로써 형성될 수 있다. 부분 입체 이성질체성 염은 분별 결정화 또는 이온 크로마토그래피에 의해 분리되도록 유도될 수 있다. 아미노 화합물의 광학 이성질체의 분리를 위해, 키랄 카르복시산 또는 설폰산, 예를 들어 캄포설폰산, 타르타르산, 만델산 또는 락트산의 첨가는 부분 입체 이성질체성 염의 형성을 초래할 수 있다.Under method (1), diastereomeric salts are enantiomerically pure chiral bases such as brucine, quinine, ephedrine, strychnine, α-methyl-β- It can be formed by reacting phenylethylamine (amphetamine) and the like with asymmetric compounds having acidic functional groups such as carboxylic acids and sulfonic acids. Diastereomeric salts can be brought to separation by fractional crystallization or ion chromatography. For the separation of optical isomers of amino compounds, addition of chiral carboxylic or sulfonic acids, such as camphorsulfonic acid, tartaric acid, mandelic acid or lactic acid, can result in the formation of diastereomeric salts.
대안적으로, 방법 (2)에서는 분해될 기질을 키랄 화합물의 하나의 거울상 이성질체와 반응시켜 부분 입체 이성질체 쌍을 형성한다(문헌[E. and Wilen, S. "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds", John Wiley & Sons, Inc.,1994, p. 322]). 부분 입체 이성질체성 화합물은, 비대칭 화합물을 거울상 이성질적으로 순수한 키랄 유도체화 시약, 예를 들어 멘틸 유도체와 반응시킨 후, 부분 입체 이성질체를 분리하고 가수분해하여 순수하거나 농축된 거울상 이성질체를 수득함으로써 형성될 수 있다. 광학 순도를 측정하는 방법은 염기의 존재 하에 멘틸 에스테르, 예를 들어 (-) 멘틸 클로로포르메이트와 같은 키랄 에스테르를 제조하거나, 라세미 혼합물의 모셔 에스테르, 즉 α-메톡시-α-(트라이플루오로메틸)페닐 아세테이트를 제조하는 단계, 및 2개의 회전 장애 이성질체성 거울상 이성질체 또는 부분 입체 이성질체의 존재에 대해 1H NMR 스펙트럼을 분석하는 단계를 포함한다(문헌[Jacob III. J. Org. Chem. (1982)47: 4165]). 회전 장애 이성질체성 화합물의 안정한 부분 입체 이성질체는 회전 장애 이성질체성 나프틸-이소퀴놀린을 분리하기 위한 방법 이후에 순상 및 역상 크로마토그래피에 의해 분리 및 단리될 수 있다(WO 96/15111). 방법 (3)에 의하면, 2개의 거울상 이성질체의 라세미 혼합물은 키랄 정지상을 이용한 크로마토그래피에 의해 분리할 수 있다(문헌["Chiral Liquid Chromatography" (1989) W. J. Lough, Ed., Chapman and Hall, New York; Okamoto, J. Chromatogr., (1990) 513: 375-378]). 농축 또는 정제된 거울상 이성질체는 기타 키랄 분자를 비대칭 탄소원자와 구별하는데 사용되는 방법, 예를 들어 광학 회전 및 원편광 이색성에 의해 구별될 수 있다.Alternatively, in method (2), the substrate to be resolved is reacted with one enantiomer of a chiral compound to form a diastereomeric pair (E. and Wilen, S. "Stereochemistry of Organic Compounds", John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1994, p. 322]). Diastereomeric compounds can be formed by reacting an asymmetric compound with an enantiomerically pure chiral derivatizing reagent, such as a menthyl derivative, followed by separation of the diastereomers and hydrolysis to obtain the pure or enriched enantiomers. can Methods for measuring optical purity include preparation of chiral esters such as menthyl esters, for example (-) menthyl chloroformate, in the presence of a base, or Mosher esters of racemic mixtures, i.e., α-methoxy-α-(trifluoro). preparing romethyl)phenyl acetate, and analyzing the 1H NMR spectrum for the presence of two atropisomeric enantiomers or diastereomers (Jacob III. J. Org. Chem. 1982) 47: 4165]). Stable diastereomers of atropisomeric compounds can be separated and isolated by methods for separating atropisomeric naphthyl-isoquinolines followed by normal and reverse phase chromatography (WO 96/15111). By method (3), a racemic mixture of the two enantiomers can be separated by chromatography using a chiral stationary phase ("Chiral Liquid Chromatography" (1989) W. J. Lough, Ed., Chapman and Hall, New York; Okamoto, J. Chromatogr., (1990) 513: 375-378]). Enriched or purified enantiomers can be distinguished by methods used to distinguish other chiral molecules from asymmetric carbon atoms, such as optical rotation and circular dichroism.
실험의 상세한 설명Detailed description of the experiment
합성 방법 A: Synthesis method A :
베타-치환된 환형 케톤 및 2-카르복실레이트-페닐 히드라진을 이용한 피셔 인돌 합성(Fisher indole synthesis), 및 그 이후의 에스테르화에 의해 인돌 중간체를 얻었다. 필요한 알킬 브로마이드를 이용한 인돌 질소의 알킬화, 및 그 이후의 가수분해에 의해 정제 이후에 목적하는 생성물을 얻었다.Indole intermediates were obtained by Fisher indole synthesis with beta-substituted cyclic ketones and 2-carboxylate-phenyl hydrazine, followed by esterification. Alkylation of the indole nitrogen with the required alkyl bromide and subsequent hydrolysis gave the desired product after purification.
대표적인 실시예: 7-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산Representative Example: 7-Butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid
단계 1.1: 히드라진(1.12 g) 및 케톤(3 g)을 AcOH 중에서 혼합하고, 130℃에서 교반시켰으며, 3시간 후에 AcOH를 증류 제거하였다. 이어서, 반응액을 포화 중탄산나트륨으로 중화시키고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(30% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 1 g의 목적하는 인돌 생성물을 얻었다. Step 1.1 : Hydrazine (1.12 g) and ketone (3 g) were mixed in AcOH, stirred at 130° C., after 3 hours the AcOH was distilled off. The reaction was then neutralized with saturated sodium bicarbonate and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (30% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 1 g of the desired indole product.
단계 1.2: 1 g의 인돌을 15 ㎖의 MeOH에 용해하였다. 1 ㎖의 H2SO4를 첨가하고, 80℃에서 가열하였다. 16시간 후, MeOH를 반응 혼합물로부터 증류 제거하고, 포화 중탄산나트륨으로 중화시키고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(20% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 900 ㎎의 목적하는 인돌 에스테르 생성물을 얻었다. Step 1.2 : 1 g of indole was dissolved in 15 ml of MeOH. 1 mL of H 2 SO 4 was added and heated at 80 °C. After 16 hours, MeOH was distilled off from the reaction mixture, neutralized with saturated sodium bicarbonate and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (20% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 900 mg of the desired indole ester product.
단계 2.1: 인돌 에스테르(900 ㎎) 및 3-시아노-벤질 브로마이드(1.18 g)를 DMSO(10 ㎖)에 용해한 후, KOH(842 ㎎)를 실온에서 첨가하고 교반하였다. 2시간 후, 반응액을 물로 희석하고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(15% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 700 ㎎의 목적하는 인돌 에스테르 생성물을 얻었다. Step 2.1 : Indole ester (900 mg) and 3-cyano-benzyl bromide (1.18 g) were dissolved in DMSO (10 mL), then KOH (842 mg) was added at room temperature and stirred. After 2 hours, the reaction was diluted with water and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (15% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 700 mg of the desired indole ester product.
단계 2.2: 벤질 인돌을 EtOH:H2O(30:6 ㎖)에 용해한 후, KOH(473 ㎎)를 실온에서 첨가하고, 70℃까지 가열하였다. 15분 후, 반응액을 실온까지 냉각시키고, 1 N HCl 용액으로 중화시키고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였다. 이어서, 모은 유기 추출물을 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. MS 유도형 정제를 이용한 정제에 의해 110 ㎎의 7-부틸-5-[(3-시아노페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산 및 105 ㎎의 7-부틸-5-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-사이클로헵타[b]인돌-4-카르복실산을 얻었다. Step 2.2 : Benzyl indole was dissolved in EtOH:H 2 O (30:6 mL), then KOH (473 mg) was added at room temperature and heated to 70 °C. After 15 min, the reaction was cooled to room temperature, neutralized with 1 N HCl solution, and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3). The combined organic extracts were then dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using MS guided tablets yielded 110 mg of 7-butyl-5-[(3-cyanophenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4- carboxylic acid and 105 mg of 7-butyl-5-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-5H,6H,7H,8H,9H,10H-cyclohepta[b]indole-4-carboxylic acid got it
합성 방법 B: 비치환된 환형 케톤 및 2-카르복실레이트-페닐 히드라진을 이용한 피셔 인돌 합성, 및 그 이후의 에스테르화에 의해 인돌 중간체를 얻었다. 필요한 친핵체를 이용한 TFAA-DMSO 알킬화 프로토콜(문헌[Masanori Tayu et al., Org. Biomol. Chem. (2013) 11 496]), 및 그 이후의 에스테르 가수분해에 의해 정제 이후에 목적하는 생성물을 얻었다. Synthesis method B : Fischer indole synthesis using an unsubstituted cyclic ketone and 2-carboxylate-phenyl hydrazine, followed by esterification to obtain an indole intermediate. A TFAA-DMSO alkylation protocol with the required nucleophile (Masanori Tayu et al. , Org. Biomol. Chem. (2013) 11 496) followed by ester hydrolysis gave the desired product after purification.
대표적인 실시예: 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산Representative Example: 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8-carboxylic acid
단계 1.1: 히드라진(6.0 g) 및 케톤(6.2 g)을 AcOH(100 ㎖)에서 혼합하고, 130℃에서 교반시켰으며, 3시간 후에 AcOH를 증류 제거하였다. 이어서, 반응액을 포화 중탄산나트륨으로 중화시키고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(30% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 5 g의 목적하는 인돌 생성물을 얻었다. Step 1.1 : Hydrazine (6.0 g) and ketone (6.2 g) were mixed in AcOH (100 mL), stirred at 130° C., after 3 hours AcOH was distilled off. The reaction was then neutralized with saturated sodium bicarbonate and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (30% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 5 g of the desired indole product.
단계 1.2: 5 g의 인돌을 100 ㎖의 MeOH에 용해하였다. 7 ㎖의 진한 H2SO4를 첨가하고, 80℃에서 가열하였다. 16시간 후, MeOH를 반응 혼합물로부터 증류 제거하고, 포화 중탄산나트륨으로 중화시키고, EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(20% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 4.2 g의 목적하는 인돌 에스테르 생성물을 얻었다. Step 1.2 : 5 g of indole was dissolved in 100 ml of MeOH. 7 mL of conc. H 2 SO 4 was added and heated at 80 °C. After 16 hours, MeOH was distilled off from the reaction mixture, neutralized with saturated sodium bicarbonate and extracted with EtOAc (300 mL x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (20% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 4.2 g of the desired indole ester product.
단계 2: 인돌 에스테르(3 g)를 DMSO(50 ㎖)에 용해한 후, KOH(3.675 g)를 실온에서 첨가하였다. 이어서, 3-시아노-벤질 브로마이드(5.13 g)를 소분하여 첨가하고, 교반하였다. 2시간 후, 반응액을 빙수조가 구비된 플라스크 내 1 N HCl에 천천히 부은 후, 유기물을 EtOAc(300 ㎖ x 3)로 추출하였으며, 이를 건조하고, 회전 증발에 의해 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(20% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 3.5 g의 목적하는 인돌 에스테르 생성물을 얻었다. Step 2 : The indole ester (3 g) was dissolved in DMSO (50 mL), then KOH (3.675 g) was added at room temperature. 3-Cyano-benzyl bromide (5.13 g) was then added in portions and stirred. After 2 hours, the reaction solution was slowly poured into 1 N HCl in a flask equipped with an ice-water bath, and the organic matter was extracted with EtOAc (300 ml x 3), which was dried and concentrated by rotary evaporation. Purification using column chromatography (20% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 3.5 g of the desired indole ester product.
단계 3: -40℃에서 디클로로메탄(7 ㎖) 중의 인돌 에스테르(500 ㎎) 용액에 DMSO(0.315 ㎖)를 첨가하였다. 이러한 혼합물에 트리플루오로-아세트산 무수물(0.617 ㎖)을 적가하고, -40℃에서 교반하였다. 1시간 후, 에틸 마그네슘 브로마이드(17.647 ㎖, 1 M)를 이러한 혼합물에 적가하였다. 2시간 후, 반응액을 10 ㎖의 포화 NaHCO3 + 20 ㎖의 H2O + 30 ㎖의 EtOAc 용액에 천천히 부었다. 유기층을 분리하고, 건조하고, 진공 하에 농축하였다. 칼럼 크로마토그래피(20% EtOAc:석유 에테르)를 이용한 정제에 의해 300 ㎎의 목적하는 생성물을 얻었다. Step 3 : To a solution of the indole ester (500 mg) in dichloromethane (7 mL) at -40 °C was added DMSO (0.315 mL). Trifluoro-acetic anhydride (0.617 mL) was added dropwise to this mixture and stirred at -40 °C. After 1 hour, ethyl magnesium bromide (17.647 mL, 1 M) was added dropwise to this mixture. After 2 hours, the reaction solution was slowly poured into a solution of 10 ml of saturated NaHCO 3 + 20 ml of H 2 O + 30 ml of EtOAc. The organic layer was separated, dried and concentrated in vacuo. Purification using column chromatography (20% EtOAc:petroleum ether) gave 300 mg of the desired product.
단계 4: 벤질 인돌(150 ㎎)을 EtOH:H2O(5:2 ㎖)에 용해한 후, KOH(156 ㎎)을 실온에서 첨가하고, 교반하였다. 16시간 후, 반응액을 1 N HCl 용액으로 중화시키고, 9-[(3-카르바모일페닐)메틸]-2-펜틸-2,3,4,9-테트라하이드로-1H-카르바졸-8-카르복실산(30 ㎎)으로서 고체를 여과하였다. Step 4 : Benzyl indole (150 mg) was dissolved in EtOH:H 2 O (5:2 mL), then KOH (156 mg) was added at room temperature and stirred. After 16 hours, the reaction solution was neutralized with 1 N HCl solution, and 9-[(3-carbamoylphenyl)methyl]-2-pentyl-2,3,4,9-tetrahydro-1H-carbazole-8 - The solid was filtered as carboxylic acid (30 mg).
상기의 기술적 결과는 하기 표 1에 반영되어 있다:The above technical results are reflected in Table 1 below:
사용 가능한 대표적인 HPLC 방법은 하기를 포함한다:Representative HPLC methods that can be used include:
방법 AMethod A
칼럼: Kinetex EVO C18(50 ㎜ x 4.6 ㎜; 5 ㎛)Column: Kinetex EVO C18 (50 mm x 4.6 mm; 5 μm)
이동상: B1: 수중 0.1% FA, A1: 아세토니트릴 중의 0.1% FAMobile phase: B1: 0.1% FA in water, A1: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile
구배: 시간(분)/A1(%): 0/2, 0.4/2, 2.7/98, 3.40/98, 3.41/2, 3.5/2Gradient: Time (min)/A1 (%): 0/2, 0.4/2, 2.7/98, 3.40/98, 3.41/2, 3.5/2
칼럼 유량: 2.0 ㎖/분Column flow: 2.0 mL/min
칼럼 온도: 45℃Column temperature: 45°C
방법 BMethod B
칼럼: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(50 ㎜ x 2.1㎜; 1.7 ㎛)Column: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 (50 mm x 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm)
이동상: B1: 수중 0.1% FA, A1: 아세토니트릴 중의 0.1% FAMobile phase: B1: 0.1% FA in water, A1: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile
구배: 시간(분)/A1(%): 0/2, 0.4/2, 2.8/98, 3.4/98, 3.41/2, 3.5/2Gradient: Time (min)/A1 (%): 0/2, 0.4/2, 2.8/98, 3.4/98, 3.41/2, 3.5/2
칼럼 유량: 0.6 ㎖/분Column flow: 0.6 ml/min
칼럼 온도: 60℃Column temperature: 60°C
방법 CMethod C
칼럼: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(50 ㎜ x 2.1㎜; 1.7 ㎛)Column: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 (50 mm x 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm)
이동상: B1: 수중 0.1% FA, A1: 아세토니트릴 중의 0.1% FAMobile phase: B1: 0.1% FA in water, A1: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile
구배: 시간(분)/A1(%): 0/2, 0.3/2, 2.3/98, 2.8/98, 2.81/2, 3.0/2Gradient: Time (min)/A1 (%): 0/2, 0.3/2, 2.3/98, 2.8/98, 2.81/2, 3.0/2
칼럼 유량: 0.8 ㎖/분Column flow: 0.8 ml/min
칼럼 온도: 60℃Column temperature: 60°C
방법 DMethod D
칼럼: X-BRIDGE C18(4.6 ㎜ x 150 ㎜) 5 ㎛Column: X-BRIDGE C18 (4.6 mm x 150 mm) 5 μm
이동상: A: 10 mM 아세트산암모늄(aqs), B: 아세토니트릴Mobile phase: A: 10 mM ammonium acetate (aqs), B: acetonitrile
구배 시간: B(%):희석제 0/10, 1/10, 12/95, 15/98, 20/98, 20.01/10Gradient time: B (%): Diluent 0/10, 1/10, 12/95, 15/98, 20/98, 20.01/10
칼럼 온도: 주위 온도Column Temperature: Ambient Temperature
유량: 1 ㎖/분(ACN:물)Flow rate: 1 mL/min (ACN:water)
방법 EMethod E
칼럼: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(50 ㎜ x 2.1㎜; 1.7 ㎛)Column: ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 (50 mm x 2.1 mm; 1.7 μm)
이동상: B1: 수중 0.1% FA, A1: ACNACN 중의 0.1% FA:Mobile phase: B1: 0.1% FA in water, A1: 0.1% FA in ACNACN:
구배: 시간(분)/A1(%): 0/2, 0.2/2, 5.0/98, 5.8/98, 5.81/2.0, 6.00/2.0Gradient: Time (min)/A1 (%): 0/2, 0.2/2, 5.0/98, 5.8/98, 5.81/2.0, 6.00/2.0
칼럼 유량: 0.8 ㎖/분Column flow: 0.8 ml/min
칼럼 온도: 60℃Column temperature: 60°C
방법 FMethod F
이동상 A: 수중 0.1% FAMobile phase A: 0.1% FA in water
이동상 B: 아세토니트릴 중의 0.1% FAMobile phase B: 0.1% FA in acetonitrile
B의 구배(%): 0/5, 0.3/5, 1.5/60, 2/98, 4/98, 5/5Gradient (%) of B: 0/5, 0.3/5, 1.5/60, 2/98, 4/98, 5/5
흐름: 0.6 ㎖/분Flow: 0.6 ml/min
칼럼: BEH C18, 2.1 ㎜ x 50 ㎜, 1.7 ㎛.Column: BEH C18, 2.1 mm x 50 mm, 1.7 μm.
하기 표 2는 IUPAC 명칭 하에 사용된 HPLC 방법과의 상관관계를 보여준다:Table 2 below shows the correlation with the HPLC method used under the IUPAC nomenclature:
분화된 3T3-L1 마우스 지방세포에서 지방세포 글루코오스의 소비에 대한 화합물의 활성을 검사하였다. 3T3-L1 지방 전구세포(ATCC)를 DMEM 고글루코오스(Sigma), 10% FBS(Gibco), 10 U/㎖의 페니실린 및 10 ㎍/㎖의 스트렙토마이신(P/S; Gibco)으로 구성된 성장 배지에서 통상적으로 배양하였다. 지방 생성 분화를 유도하기 위해, 3T3-L1 세포의 밀집층(confluent layer)을 2 μM 로시글리타존(rosiglitazone), 1 μM 덱사메사손, 500 μM IBMX 및 1 ㎍/㎖의 인슐린(Sigma)을 함유하는 성장 배지로 인큐베이션하였다. 사십팔(48) 시간 후(2일째 날), 및 4일 및 6일째 날에, 세포의 배지를 1 ㎍/㎖의 인슐린을 함유하는 신선한 배지로 교체하였다. 8일 및 10일째 날에, 배지를 정상 성장 배지로 보충하고, 인슐린 첨가를 생략하였다. 11일 또는 12일째 날에, 세포의 배지를 표시된 화합물(10 μM)을 함유하거나, 화합물이 용해된 비히클(DMSO)을 함유하는 신선한 배지로 교체하였다. DMSO의 최종 농도는 0.1%(v/v)이었다. 0.1% DMSO를 함유하는 성장 배지를 세포를 함유하지 않은 배양 웰에서 인큐베이션하였으며, 이를 대조군으로 사용하였다. 22시간 내지 24시간 후, 배지를 수확하고, 5분 동안 10,000 g로 원심분리하였다. 상층액 중의 글루코오스 농도를 비색 검정(글루코오스 검정 키트 I, Eton Biosciences)을 사용하여 측정하였다. 화합물-처리 및 비히클-처리 세포에서의 글루코오스 소비를 배양 배지로부터의 글루코오스의 손실로서 측정하였으며, 이를 평균 배수 변화(화합물/DMSO) ± 표준 편차(SD)로서 나타냈다.The activity of the compounds on adipocyte glucose consumption was examined in differentiated 3T3-L1 mouse adipocytes. 3T3-L1 preadipocytes (ATCC) were cultured in a growth medium composed of DMEM high glucose (Sigma), 10% FBS (Gibco), 10 U/ml penicillin and 10 μg/ml streptomycin (P/S; Gibco). cultured normally. To induce adipogenic differentiation, a confluent layer of 3T3-L1 cells was grown containing 2 μM rosiglitazone, 1 μM dexamethasone, 500 μM IBMX and 1 μg/ml insulin (Sigma). medium was incubated. After forty-eight (48) hours (day 2), and on days 4 and 6, the medium of the cells was replaced with fresh medium containing 1 μg/ml insulin. On days 8 and 10, medium was supplemented with normal growth medium and insulin addition was omitted. On day 11 or 12, the medium of the cells was replaced with fresh medium containing the indicated compound (10 μM) or the vehicle in which the compound was dissolved (DMSO). The final concentration of DMSO was 0.1% (v/v). Growth medium containing 0.1% DMSO was incubated in culture wells that did not contain cells and was used as a control. After 22-24 hours, the medium was harvested and centrifuged at 10,000 g for 5 minutes. Glucose concentration in the supernatant was measured using a colorimetric assay (Glucose Assay Kit I, Eton Biosciences). Glucose consumption in compound-treated and vehicle-treated cells was measured as loss of glucose from culture medium and was expressed as mean fold change (compound/DMSO) ± standard deviation (SD).
테르븀(Tb) 기반 시간 분해 형광 에너지 전달(TR-FRET) 검정을 사용하여 FABP4를 이용한 화합물의 활성을 프로파일링하였다. 검정에서는 항-His6-태그 항체 상의 TB 공여체 분자로부터 수용체 BODIPY 모이어티로의 에너지 전달을 기록함으로써 His6-태깅된 인간 재조합 FABP4(His6-FABP4; Cayman Chemicals; 카탈로그 번호: 10009549)로부터의 형광 지방산 BODIPY FL C12(Thermo Fisher; 카탈로그 번호: D3822)의 화합물-매개 변위가 측정된다. 간단하게는, 화합물을 DMSO 중에서 0.362 mM 및 0.0362 mM의 농도로 제조하고, BODIPY FL C12를 4.2 μM로 제조하였다. 1.2 ㎕의 각각의 화합물 또는 DMSO(비히클 대조군) 및 1.2 ㎕의 BODIPY FL C12를 384-웰 흑색 폴리프로필렌 플레이트의 웰 내에 첨가하였다. His6-FABP4 및 Tb 항-His6 항체를 검정 완충액(25 mM 트리스/HCl, pH 7.4, 0.4 ㎎/㎖의 γ-글로블린, 0.010% NP-40, 1 mM DTT)에서 각각 83 nM 및 49.6 nM의 농도로 제조하였다. 이어서, 단백질 및 항체 용액을 34:7(v/v)의 비율로 혼합하고, 얼음 상에서 30분 동안 인큐베이션하였다. 41 ㎕의 얻어진 단백질/항체 용액을 화합물 및 BODIPY FL C12를 함유하는 웰에 첨가함으로써 검정을 개시하였다. 플레이트를 원심분리하고, 실온에서 10분 동안 인큐베이션하였다. EnVision Multilabel 플레이트 판독기(PerkinElmer; TB 여기: 320 ㎚, BODIPY FL C12 방출: 520 ㎚; TB 방출: 615 ㎚)를 사용하여 TR-FRET 신호를 기록하였다. FABP4에 대한 BODIPY C12 FL 지방산 결합의 화합물-매개 저해를 계산하기 위해 상대 형광 비율(520 ㎚ * 10,000/615 ㎚)을 사용하였다. 화합물을 3회 시험하였으며, 그 결과는 평균 저해 백분율(화합물 * 100/DMSO) ± 표준 편차(SD)로서 표시하였다. 글루코오스 소비 및 FABP4 저해는 하기 표 3에 나타나 있다.A terbium (Tb) based time resolved fluorescence energy transfer (TR-FRET) assay was used to profile the activity of compounds with FABP4. In the assay, fluorescent fatty acid BODIPY FL from His6-tagged human recombinant FABP4 (His6-FABP4; Cayman Chemicals; catalog number: 10009549) was recorded by recording the energy transfer from the TB donor molecule to the acceptor BODIPY moiety on an anti-His6-tag antibody. Compound-mediated displacement of C12 (Thermo Fisher; catalog number: D3822) is measured. Briefly, compounds were prepared at concentrations of 0.362 mM and 0.0362 mM in DMSO, and BODIPY FL C12 was prepared at 4.2 μM. 1.2 μl of each compound or DMSO (vehicle control) and 1.2 μl of BODIPY FL C12 were added into wells of a 384-well black polypropylene plate. His6-FABP4 and Tb anti-His6 antibodies were administered at concentrations of 83 nM and 49.6 nM, respectively, in assay buffer (25 mM Tris/HCl, pH 7.4, 0.4 mg/mL of γ-globulin, 0.010% NP-40, 1 mM DTT). was made with The protein and antibody solutions were then mixed in a ratio of 34:7 (v/v) and incubated on ice for 30 minutes. The assay was initiated by adding 41 μl of the resulting protein/antibody solution to wells containing compound and BODIPY FL C12. Plates were centrifuged and incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature. TR-FRET signals were recorded using an EnVision Multilabel plate reader (PerkinElmer; TB excitation: 320 nm, BODIPY FL C12 emission: 520 nm; TB emission: 615 nm). Relative fluorescence ratios (520 nm * 10,000/615 nm) were used to calculate compound-mediated inhibition of BODIPY C12 FL fatty acid binding to FABP4. Compounds were tested in triplicate and results were expressed as mean percent inhibition (compound * 100/DMSO) ± standard deviation (SD). Glucose consumption and FABP4 inhibition are shown in Table 3 below.
본 발명이 특히 상세한 정도로 기술되어 있을지라도, 예시를 목적으로만 본 발명이 개시되어 있고, 본 발명의 진의 및 범주에서 벗어나지 않는 한 부분의 구성 및 배열에 대한 세부사항에서의 다양한 변경이 이루어질 수 있는 것으로 이해되어야 한다.Although the invention has been described to a particular degree of detail, it is disclosed for purposes of illustration only, and various changes may be made in the details of construction and arrangement of parts without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention. should be understood as
Claims (46)
[화학식 I]
(상기 식에서,
W1-4 및 Z1-Z5는 각각 독립적으로 -C, -CH, CH2, O, S 또는 N이고;
X는 독립적으로 CH2, N 또는 CHR4이고;
Y는 독립적으로 CH2 또는 CHR5이고;
n은 0 내지 3의 숫자이고;
고리 Z 상의 하나 이상의 R1은 CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체(acid isostere), 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되며, 이때 상기 치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴은 수소, CN, OH, COOH, OCH3, CF3, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 치환된 아민, 에테르 및 할로겐, 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬, 치환 또는 비치환된 환형 또는 헤테로환형의 치환 또는 비치환된 사이클로아릴 또는 사이클로헤테로아릴 및 SO2NH2로 치환될 수 있고;
고리(W) 상의 하나 이상의 R2는 CN, OH, CHF2, CH2F, CF3, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 할로겐 및 이환형 헤테로아릴로 이루어진 군으로부터 독립적으로 선택되고;
R7은 수소 또는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;
R은 알킬이고;
R3, R4, R5 또는 R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은,
(1) 수소;
(2) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 치환 또는 비치환된 알킬 또는 에테르,
(3) 치환된 아민, 또는
(4) --(CH2)mG로부터 각각 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬,
(b) 아릴 또는 헤테로아릴,
(c) CF3, CF2H 또는 CFH2, 또는
(d) 헤테로사이클로부터 독립적으로 선택되고,
단, R3, R4, R5, R8 또는 R6은 모두 수소가 아님).A compound of formula I or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or stereoisomer thereof:
[Formula I]
(In the above formula,
W 1-4 and Z 1 -Z 5 are each independently -C, -CH, CH 2 , O, S or N;
X is independently CH 2 , N or CHR 4 ;
Y is independently CH 2 or CHR 5 ;
n is a number from 0 to 3;
At least one R 1 on ring Z is CN, OH, COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isostere, substituted amine, ether and It is independently selected from the group consisting of halogen, substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted cyclic or heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl, wherein the substituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl is Hydrogen, CN, OH, COOH, OCH 3 , CF 3 , CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isomers, substituted amines, ethers and halogens, substituted or unsubstituted alkyls, substituted or unsubstituted cyclic or heterocyclic substituted or unsubstituted cycloaryl or cycloheteroaryl and SO 2 NH 2 ;
At least one R 2 on ring (W) is CN, OH, CHF 2 , CH 2 F, CF 3 , COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isostere, halogen and bicyclic independently selected from the group consisting of heteroaryl;
R 7 is hydrogen or CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R is alkyl;
R 3 , R 4 , R 5 or R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0,
(1) hydrogen;
(2) a substituted or unsubstituted alkyl or ether having 1 to 12 carbon atoms;
(3) a substituted amine, or
(4) --(CH 2 ) m G, wherein m is 1 to 12, and G is,
(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) aryl or heteroaryl;
(c) CF 3 , CF 2 H or CFH 2 , or
(d) independently selected from heterocycles;
provided that none of R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 or R 6 are hydrogen.
[화학식 II]
(상기 식에서,
n은 0, 1 또는 2이고;
R1은 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체 및 할로겐으로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되고;
R2는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2, 산 등배전자체, 할로겐 및 이환형 화합물로 이루어진 군으로부터 선택되고;
R7은 수소 또는 CN, COOH, CONH2, B(OH)2, B(OR)2 또는 산 등배전자체이고;
R은 알킬이고;
R3, R4, R5 또는 R8, 또는 n이 0이 아닌 경우의 R6은,
(1) 수소;
(2) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬, 또는
(3) --(CH2)mG로부터 각각 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬,
(b) 아릴 또는 헤테로아릴, 또는
(c) CF3, CF2H 또는 CFH2로부터 독립적으로 선택되며;
단, G는 질소-함유 또는 산소-함유 기가 아니고;
단, R3, R4, R5, R8 또는 R6은 모두 수소가 아님).A compound of Formula II or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
[Formula II]
(In the above formula,
n is 0, 1 or 2;
R 1 is selected from the group consisting of CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isosteres and halogens;
R 2 is selected from the group consisting of CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 , acid isosteres, halogens and bicyclic compounds;
R 7 is hydrogen or CN, COOH, CONH 2 , B(OH) 2 , B(OR) 2 or an acid isostere;
R is alkyl;
R 3 , R 4 , R 5 or R 8 , or R 6 when n is not 0,
(1) hydrogen;
(2) alkyl having 1 to 12 carbon atoms, or
(3) --(CH 2 ) m G, wherein m is 1 to 12, and G is,
(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) aryl or heteroaryl, or
(c) independently selected from CF 3 , CF 2 H or CFH 2 ;
provided that G is not a nitrogen-containing or oxygen-containing group;
provided that none of R 3 , R 4 , R 5 , R 8 or R 6 are hydrogen.
[화학식 III]
(상기 식에서,
n은 0, 1 또는 2이고;
R1 및 R2는 각각 독립적으로 CN, COOH 또는 CONH2이고;
R3은,
(1) 1개 내지 12개의 탄소 원자를 갖는 알킬;
(2) --(CH2)mG로부터 독립적으로 선택되며, 여기서 m은 1 내지 12이고, G는,
(a) 3개 내지 6개의 탄소 원자를 함유하는 사이클로알킬;
(b) 페닐로부터 독립적으로 선택되며;
단, G는 질소-함유 또는 산소-함유 기가 아님).A compound of Formula III or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof:
[Formula III]
(In the above formula,
n is 0, 1 or 2;
R 1 and R 2 are each independently CN, COOH or CONH 2 ;
R 3 is
(1) alkyl having 1 to 12 carbon atoms;
(2) --(CH 2 ) m is independently selected from G, where m is 1 to 12, and G is
(a) cycloalkyl containing 3 to 6 carbon atoms;
(b) independently selected from phenyl;
provided that G is not a nitrogen-containing or oxygen-containing group).
포유동물에게 제1항, 제17항 및 제23항 중 어느 한 항에 따른 화합물을 유효량으로 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 것인, 포유동물에서 지방산 결합 단백질 FABP4를 저해하는 방법.A method of inhibiting fatty acid binding protein FABP4 in a mammal, comprising:
A method of inhibiting fatty acid binding protein FABP4 in a mammal, comprising administering to the mammal an effective amount of a compound according to any one of claims 1, 17 and 23.
이 같은 치료를 필요로 하는 개체에게 제1항, 제17항 및 제23항 중 어느 한 항에 따른 화합물을 유효량으로 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 것인, 지방산 결합 단백질 FABP4에 작용하는 질병의 예방 또는 치료를 위한 방법.As a method for preventing or treating a disease acting on the fatty acid binding protein FABP4,
Prevention of a disease affecting the fatty acid binding protein FABP4, comprising administering an effective amount of a compound according to any one of claims 1, 17 and 23 to a subject in need of such treatment; or method for treatment.
이 같은 치료를 필요로 하는 개체에게 제1항, 제17항 및 제23항 중 어느 한 항에 따른 화합물을 유효량으로 투여하는 단계를 포함하는 것인, FABP4를 저해하기 위한 방법.As a method for inhibiting FABP4,
A method for inhibiting FABP4 comprising administering to a subject in need of such treatment an effective amount of a compound according to any one of claims 1, 17 and 23.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US202063045079P | 2020-06-27 | 2020-06-27 | |
| US63/045,079 | 2020-06-27 | ||
| PCT/US2021/039470 WO2021263246A1 (en) | 2020-06-27 | 2021-06-28 | Novel cell metabolism modulating compounds and uses thereof |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20230031322A true KR20230031322A (en) | 2023-03-07 |
Family
ID=79166603
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020237003178A KR20230031322A (en) | 2020-06-27 | 2021-06-28 | Compositions of Compounds that Modulate Cellular Metabolism and Methods of Use |
Country Status (11)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US12084419B2 (en) |
| EP (1) | EP4171736A4 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP2023532888A (en) |
| KR (1) | KR20230031322A (en) |
| CN (1) | CN115803085A (en) |
| AU (1) | AU2021297465A1 (en) |
| BR (1) | BR112022026550A2 (en) |
| CA (1) | CA3184282A1 (en) |
| IL (1) | IL299002A (en) |
| MX (1) | MX2023000036A (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2021263246A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2021263246A1 (en) | 2020-06-27 | 2021-12-30 | Crescenta Biosciences | Novel cell metabolism modulating compounds and uses thereof |
| WO2022010951A1 (en) * | 2020-07-06 | 2022-01-13 | Crescenta Biosciences | Antiviral use of fabp4 modulating compounds |
| CN114456052B (en) * | 2022-01-25 | 2023-08-25 | 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳) | Asymmetric 1, 4-addition method of unsaturated carbonyl or unsaturated imine compound |
Family Cites Families (85)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3542785A (en) | 1967-05-15 | 1970-11-24 | Ciba Geigy Corp | 2-hydroxy-4-aryl-quinolines |
| US3555034A (en) | 1968-06-18 | 1971-01-12 | American Home Prod | Certain 5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1,6-naphthyridin-2-ol esters |
| US3668207A (en) | 1970-01-22 | 1972-06-06 | Ciba Geigy Corp | 2-amino-4-aryl-quinolines |
| US4009181A (en) | 1973-01-22 | 1977-02-22 | Hoffmann-La Roche Inc. | Cyclopenta[b]indole-2-carboxylic acids and derivatives thereof |
| DE2431292A1 (en) | 1974-06-27 | 1976-01-15 | Schering Ag | Anti-inflammatory carbazole derivs - specif. e.g. 1-ethoxycarbonyl-6-methoxy-carbazole and 8-methyl-carbazole-1-carboxylic acid |
| EP0307077A1 (en) * | 1987-07-21 | 1989-03-15 | Merck Frosst Canada Inc. | Tetrahydrocarbazoles for the improvement of cyclosporin therapy |
| US4775680A (en) * | 1987-07-21 | 1988-10-04 | Merck & Co., Inc. | Cyclohept[b]indolealkanoic acids, pharmaceutical compositions and use |
| AU6130594A (en) | 1991-03-05 | 1994-08-15 | Miris Medical Corporation | Method and device for correcting the drift offset of a pressure sensor of a flowmeter |
| US6540154B1 (en) | 1991-04-24 | 2003-04-01 | Aerogen, Inc. | Systems and methods for controlling fluid feed to an aerosol generator |
| US5938117A (en) | 1991-04-24 | 1999-08-17 | Aerogen, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for dispensing liquids as an atomized spray |
| EP1693080A3 (en) | 1991-07-02 | 2007-07-25 | Nektar Therapeutics | Method and device for delivering aeroslized medicaments |
| FR2682107B1 (en) | 1991-10-03 | 1995-04-21 | Orstom Inst Fs Rech Scient | 2-SUBSTITUTED QUINOLEINS FOR THE TREATMENT OF LEISHMANIOSIS. |
| US6509006B1 (en) | 1992-07-08 | 2003-01-21 | Inhale Therapeutic Systems, Inc. | Devices compositions and methods for the pulmonary delivery of aerosolized medicaments |
| US5819726A (en) | 1993-01-29 | 1998-10-13 | Aradigm Corporation | Method for the delivery of aerosolized drugs to the lung for the treatment of respiratory disease |
| US5743250A (en) | 1993-01-29 | 1998-04-28 | Aradigm Corporation | Insulin delivery enhanced by coached breathing |
| US6098620A (en) | 1993-01-29 | 2000-08-08 | Aradigm Corporation | Device for aerosolizing narcotics |
| US5888477A (en) | 1993-01-29 | 1999-03-30 | Aradigm Corporation | Use of monomeric insulin as a means for improving the bioavailability of inhaled insulin |
| US6024090A (en) | 1993-01-29 | 2000-02-15 | Aradigm Corporation | Method of treating a diabetic patient by aerosolized administration of insulin lispro |
| US5994314A (en) | 1993-04-07 | 1999-11-30 | Inhale Therapeutic Systems, Inc. | Compositions and methods for nucleic acid delivery to the lung |
| US6228383B1 (en) | 1994-03-03 | 2001-05-08 | Gs Development Ab | Use of fatty acid esters as bioadhesive substances |
| US6051256A (en) | 1994-03-07 | 2000-04-18 | Inhale Therapeutic Systems | Dispersible macromolecule compositions and methods for their preparation and use |
| NZ331353A (en) | 1994-09-21 | 1999-07-29 | Inhale Therapeutic Syst | Apparatus and methods for dispensing dry powder medicaments |
| US5522385A (en) | 1994-09-27 | 1996-06-04 | Aradigm Corporation | Dynamic particle size control for aerosolized drug delivery |
| US5543523A (en) | 1994-11-15 | 1996-08-06 | Regents Of The University Of Minnesota | Method and intermediates for the synthesis of korupensamines |
| US6085740A (en) | 1996-02-21 | 2000-07-11 | Aerogen, Inc. | Liquid dispensing apparatus and methods |
| US6427682B1 (en) | 1995-04-05 | 2002-08-06 | Aerogen, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for aerosolizing a substance |
| DK0885002T3 (en) | 1996-03-04 | 2011-08-22 | Penn State Res Found | Materials and methods for enhancing cellular internalization |
| US5985309A (en) | 1996-05-24 | 1999-11-16 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Preparation of particles for inhalation |
| US6254854B1 (en) | 1996-05-24 | 2001-07-03 | The Penn Research Foundation | Porous particles for deep lung delivery |
| US5855913A (en) | 1997-01-16 | 1999-01-05 | Massachusetts Instite Of Technology | Particles incorporating surfactants for pulmonary drug delivery |
| US6503480B1 (en) | 1997-05-23 | 2003-01-07 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Aerodynamically light particles for pulmonary drug delivery |
| SE9602496D0 (en) | 1996-06-20 | 1996-06-20 | Bengt Guss | Method and means for producing a fibrinogen binding protein and its use in biotechnology |
| US5906202A (en) | 1996-11-21 | 1999-05-25 | Aradigm Corporation | Device and method for directing aerosolized mist to a specific area of the respiratory tract |
| US6349719B2 (en) | 1997-02-24 | 2002-02-26 | Aradigm Corporation | Formulation and devices for monitoring the efficacy of the delivery of aerosols |
| US5855564A (en) | 1997-08-20 | 1999-01-05 | Aradigm Corporation | Aerosol extrusion mechanism |
| US6257233B1 (en) | 1998-06-04 | 2001-07-10 | Inhale Therapeutic Systems | Dry powder dispersing apparatus and methods for their use |
| WO2000015229A1 (en) | 1998-09-17 | 2000-03-23 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | METHOD FOR TREATING DIABETES EMPLOYING AN aP2 INHIBITOR AND COMBINATION |
| JP2002526397A (en) | 1998-10-05 | 2002-08-20 | ザ ペン ステイト リサーチ ファンデーション | Compositions and methods for enhancing receptor-mediated cell internalization |
| CA2361335A1 (en) | 1999-02-12 | 2000-08-17 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Inhibiting formation of atherosclerotic lesions |
| US6548529B1 (en) | 1999-04-05 | 2003-04-15 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Heterocyclic containing biphenyl aP2 inhibitors and method |
| AU3294701A (en) | 2000-01-28 | 2001-08-07 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Tetrahydropyrimidone inhibitors of fatty acid binding protein and method |
| US6543443B1 (en) | 2000-07-12 | 2003-04-08 | Aerogen, Inc. | Methods and devices for nebulizing fluids |
| ES2311563T3 (en) | 2000-10-16 | 2009-02-16 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | DERIVATIVES OF INDOLINA AND ITS USE AS 5-HT2 RECEIVER LIGANDS. |
| JP2004536023A (en) | 2000-11-20 | 2004-12-02 | ブリストル−マイヤーズ スクイブ カンパニー | Pyridone derivatives as aP2 inhibitors |
| US6546927B2 (en) | 2001-03-13 | 2003-04-15 | Aerogen, Inc. | Methods and apparatus for controlling piezoelectric vibration |
| US6550472B2 (en) | 2001-03-16 | 2003-04-22 | Aerogen, Inc. | Devices and methods for nebulizing fluids using flow directors |
| EP1423366A1 (en) * | 2001-08-09 | 2004-06-02 | Eli Lilly And Company | Cyclopenta b ! indole derivatives as spla2 inhibitors |
| WO2004063156A1 (en) * | 2003-01-08 | 2004-07-29 | Biovitrum Ab | Novel indole derivates as fabp-4 inhibitors |
| CA2524221A1 (en) | 2003-04-30 | 2004-11-18 | The Institutes For Pharmaceutical Discovery, Llc | Substituted heteroaryls as inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases |
| US9254293B2 (en) * | 2006-06-16 | 2016-02-09 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Methods and compositions for inhibiting or reducing hair loss, acne, rosacea, prostate cancer, and BPH |
| CN101588716B (en) | 2006-11-22 | 2014-03-05 | 住友化学株式会社 | Substance capable of inhibiting cytokinin signaling |
| ITMI20062254A1 (en) | 2006-11-24 | 2008-05-25 | Acraf | USE OF A METHOXY-ALCANOIC ACID OF THE INZOL TO PREPARE A PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION |
| US7722789B2 (en) | 2007-11-30 | 2010-05-25 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Defoaming method, defoaming device and manufacturing method of transfer mold |
| JP2012508692A (en) | 2008-11-12 | 2012-04-12 | シェーリング コーポレイション | Inhibitors of fatty acid binding protein (FABP) |
| EP2403605B1 (en) | 2009-03-05 | 2015-05-06 | President and Fellows of Harvard College | Compositions comprising an aP2-specific antibody or a fragment thereof for use in treating diabetes, glucose intolerance or obesity-induced insulin resistance |
| WO2010151799A2 (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-29 | University Of Massachusetts | Compounds for modulating rna binding proteins and uses therefor |
| US8470879B2 (en) | 2009-11-02 | 2013-06-25 | Life Technologies Corporation | Fatty acid inhibitors |
| US8889739B2 (en) | 2010-07-09 | 2014-11-18 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Use of trans-palmitoleate in identifying and treating metabolic disease |
| US20130116231A1 (en) | 2010-07-12 | 2013-05-09 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| US8889683B2 (en) | 2010-09-27 | 2014-11-18 | Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. | Substituted quinoxalines as inhibitors of fatty acid binding protein |
| WO2012139028A2 (en) | 2011-04-06 | 2012-10-11 | The Trustees Of Princeton University | Anti-viral combination therapy |
| US20140315889A1 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2014-10-23 | Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corp. | Hydroxamate derivatives for hdac inhibitor, and the pharmaceutical composition comprising thereof |
| PE20142282A1 (en) | 2011-11-04 | 2015-01-08 | Hoffmann La Roche | NEW ARYL-QUINOLINE DERIVATIVES |
| JP6653573B2 (en) * | 2012-05-22 | 2020-02-26 | トラスティーズ・オブ・ダートマウス・カレッジ | Methods, compounds and methods for synthesizing cycloalkanyl [b] indole, cycloalkanyl [b] benzofuran, cycloalkanyl [b] benzothiophene |
| BR112014030474A2 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2017-06-27 | Hoffmann La Roche | new bicyclic thiophenylamide compounds |
| EP2874987B1 (en) | 2012-07-20 | 2020-03-25 | The Research Foundation Of State University Of New York | alpha-AND gamma-TRUXILLIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITIONS THEREOF |
| RU2648247C2 (en) | 2012-08-24 | 2018-03-23 | Ф. Хоффманн-Ля Рош Аг | Bicyclic pyridine derivatives useful as fatty acid binding protein (fabp) 4 and / or 5 inhibitor |
| AU2013305591B2 (en) | 2012-08-24 | 2017-04-13 | Board Of Regents Of The University Of Texas System | Pro-neurogenic compounds |
| JP6383357B2 (en) | 2012-09-12 | 2018-08-29 | エフ.ホフマン−ラ ロシュ アーゲーF. Hoffmann−La Roche Aktiengesellschaft | Acyclic thiophenylamides as inhibitors of fatty acid binding protein (FABP) 4 and / or 5 |
| US20150330992A1 (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2015-11-19 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Rapid discovery and screening of enzyme activity using mass spectrometry |
| CA2897924A1 (en) | 2013-03-20 | 2014-09-25 | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ag | Urea derivatives and their use as fatty-acid binding protein (fabp) inhibitors |
| WO2014177593A1 (en) | 2013-04-29 | 2014-11-06 | MAX-PLANCK-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e.V. | Amorfrutin analogs as ppargamma-modulators |
| WO2014201326A1 (en) | 2013-06-13 | 2014-12-18 | Monsanto Technology Llc | Acetyl-coa carboxylase modulators |
| AR096613A1 (en) | 2013-06-13 | 2016-01-20 | Monsanto Technology Llc | MODULATORS OF OIL-COA CARBOXYLASE |
| EP3191454B1 (en) | 2014-09-09 | 2018-10-24 | Bristol-Myers Squibb Company | Cyclopropanecarboxylic acid gpr120 modulators |
| WO2016061642A1 (en) | 2014-10-22 | 2016-04-28 | Katholieke Universiteit Leuven Ku Leuven Research & Development | Modulating adipose tissue and adipogenesis |
| US9968616B2 (en) * | 2014-10-25 | 2018-05-15 | The Chinese University Of Hong Kong | Discovery of FDA-approved drugs as inhibitors of fatty acid binding protein 4 using molecular docking screening |
| KR102697810B1 (en) | 2015-08-03 | 2024-08-21 | 브리스톨-마이어스 스큅 컴퍼니 | Heterocyclic compounds useful as modulators of TNF alpha |
| US11130736B2 (en) | 2015-08-21 | 2021-09-28 | University Of Kansas | Human TLR8-selective agonists |
| CA3023032A1 (en) | 2016-05-04 | 2017-11-09 | Genoscience Pharma | Substituted 2,4-diamino-quinoline derivatives for use in the treatment of proliferative diseases |
| EP3246028A1 (en) | 2016-05-18 | 2017-11-22 | Max-Planck-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der Wissenschaften e.V. | Quinoline compounds for increasing insuline release |
| US11229624B2 (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2022-01-25 | Ticure Ltd. | FABP4 as a therapeutic target in skin diseases |
| US11367509B2 (en) | 2017-06-13 | 2022-06-21 | Bostongene Corporation | Systems and methods for generating, visualizing and classifying molecular functional profiles |
| WO2019018785A2 (en) | 2017-07-20 | 2019-01-24 | University Of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. | Compositions and methods for treatment of central nervous system tumors |
| WO2021263246A1 (en) | 2020-06-27 | 2021-12-30 | Crescenta Biosciences | Novel cell metabolism modulating compounds and uses thereof |
-
2021
- 2021-06-28 WO PCT/US2021/039470 patent/WO2021263246A1/en active Application Filing
- 2021-06-28 IL IL299002A patent/IL299002A/en unknown
- 2021-06-28 CN CN202180045833.8A patent/CN115803085A/en active Pending
- 2021-06-28 MX MX2023000036A patent/MX2023000036A/en unknown
- 2021-06-28 CA CA3184282A patent/CA3184282A1/en active Pending
- 2021-06-28 BR BR112022026550A patent/BR112022026550A2/en unknown
- 2021-06-28 JP JP2022580402A patent/JP2023532888A/en active Pending
- 2021-06-28 AU AU2021297465A patent/AU2021297465A1/en active Pending
- 2021-06-28 US US17/361,052 patent/US12084419B2/en active Active
- 2021-06-28 KR KR1020237003178A patent/KR20230031322A/en active Search and Examination
- 2021-06-28 US US18/012,985 patent/US20230331673A1/en active Pending
- 2021-06-28 EP EP21829660.6A patent/EP4171736A4/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| BR112022026550A2 (en) | 2023-01-17 |
| EP4171736A1 (en) | 2023-05-03 |
| JP2023532888A (en) | 2023-08-01 |
| US12084419B2 (en) | 2024-09-10 |
| CA3184282A1 (en) | 2021-12-30 |
| AU2021297465A1 (en) | 2023-03-02 |
| EP4171736A4 (en) | 2024-07-03 |
| US20230331673A1 (en) | 2023-10-19 |
| WO2021263246A1 (en) | 2021-12-30 |
| MX2023000036A (en) | 2023-02-01 |
| CN115803085A (en) | 2023-03-14 |
| IL299002A (en) | 2023-02-01 |
| US20220002243A1 (en) | 2022-01-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6923683B2 (en) | Opioid receptor ligands and their usage and manufacturing methods | |
| EP2271341B1 (en) | Specific inhibitors for vascular endothelial growth factor receptors | |
| CN103848785B (en) | One class deuterated 3-cyano quinoline compound, its Pharmaceutical composition, preparation method and its usage | |
| CN104540828B (en) | As the substituted pyrazoloquinazolone and pyrrolo- quinazolinone of the allosteric modulators of II group metabotropic glutamate receptors | |
| JP6991993B2 (en) | How to treat hyperalgesia | |
| KR20230031322A (en) | Compositions of Compounds that Modulate Cellular Metabolism and Methods of Use | |
| WO2020020189A1 (en) | Compounds as neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists and uses thereof | |
| KR20230129627A (en) | Phenyl-2-hydroxy-acetylamino-2-methyl-phenyl compounds | |
| BR112018075736B1 (en) | UNSATURATED ALPHA AND BETA AMIDE COMPOUND DERIVED FROM BENZOTRIAZOLE USED AS TGF-BETAR1 INHIBITOR | |
| TW200825079A (en) | Antidepressant, neuroprotectant, amyloid β deposition inhibitor or age retardant containing heterocyclic compound having specific structure | |
| JP2018138609A (en) | Naphthyridinedione derivatives | |
| WO2020063788A1 (en) | Fgfr4 inhibitor and use thereof | |
| EP2646427A1 (en) | Quinolin-4 (1h) -one derivatives as inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases | |
| CN108699030B (en) | Substituted amino six-membered nitrogen heterocyclic compound and preparation and application thereof | |
| WO2020233618A1 (en) | Inhibitors for programmed cell necrosis and preparation method therefor and use thereof | |
| EP3992195A1 (en) | Spiro (3,3'-isopropyl pyrrolidine oxindole) liver x receptor regulator, preparation method therefor, and use thereof | |
| JP2021519316A (en) | Compounds as regulators of TLR2 signaling | |
| WO2021150645A1 (en) | Novel cell metabolism modulating compounds and uses thereof | |
| CN115724844B (en) | Heterocyclic compound with antitumor activity and application thereof | |
| WO2017215600A1 (en) | Substituted tricyclic herteocyclic compounds and use thereof | |
| US20230255933A1 (en) | Antiviral use of fabp4 modulating compounds | |
| TWI548637B (en) | Phthalazinone derivatives, preparation process and pharmaceutical use thereof | |
| WO2007124355A2 (en) | Vascular endothelial receptor specific inhibitors | |
| BR112018016264B1 (en) | SIX-MEMBERS NITRIC HETEROCYCLIC RING COMPOUND REPLACED BY AMINO AND PREPARATION AND USE THEREOF |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination |