KR20110104918A - Novel epoxy resin and epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulant - Google Patents
Novel epoxy resin and epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulant Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20110104918A KR20110104918A KR1020110023975A KR20110023975A KR20110104918A KR 20110104918 A KR20110104918 A KR 20110104918A KR 1020110023975 A KR1020110023975 A KR 1020110023975A KR 20110023975 A KR20110023975 A KR 20110023975A KR 20110104918 A KR20110104918 A KR 20110104918A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- epoxy resin
- resin composite
- formula
- semiconductor encapsulation
- composite
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 147
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 title claims abstract description 147
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 69
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 62
- 239000008393 encapsulating agent Substances 0.000 title description 2
- 238000005538 encapsulation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 41
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 239000011256 inorganic filler Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 229910003475 inorganic filler Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 32
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical group O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910021536 Zeolite Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- OJMOMXZKOWKUTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminum;borate Chemical compound [Al+3].[O-]B([O-])[O-] OJMOMXZKOWKUTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N dioxosilane;oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Si]=O.O=[Al]O[Al]=O HNPSIPDUKPIQMN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- NJLLQSBAHIKGKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N dipotassium dioxido(oxo)titanium Chemical compound [K+].[K+].[O-][Ti]([O-])=O NJLLQSBAHIKGKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010445 mica Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052618 mica group Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910003455 mixed metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010457 zeolite Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 125000001624 naphthyl group Chemical group 0.000 abstract description 13
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 abstract description 6
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 48
- UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Naphthalene Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C21 UFWIBTONFRDIAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 40
- ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N diphenyl Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 24
- NXPPAOGUKPJVDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene-1,2-diol Chemical compound C1=CC=CC2=C(O)C(O)=CC=C21 NXPPAOGUKPJVDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 15
- -1 dihydroxy naphthalene compound Chemical class 0.000 description 14
- 235000010290 biphenyl Nutrition 0.000 description 13
- 239000004305 biphenyl Substances 0.000 description 13
- ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Butanone Chemical compound CCC(C)=O ZWEHNKRNPOVVGH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 150000001412 amines Chemical class 0.000 description 12
- BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Epichlorohydrin Chemical compound ClCC1CO1 BRLQWZUYTZBJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 11
- 150000001335 aliphatic alkanes Chemical class 0.000 description 11
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 10
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000000376 reactant Substances 0.000 description 10
- LNEPOXFFQSENCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N haloperidol Chemical compound C1CC(O)(C=2C=CC(Cl)=CC=2)CCN1CCCC(=O)C1=CC=C(F)C=C1 LNEPOXFFQSENCJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 125000003700 epoxy group Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000000805 composite resin Substances 0.000 description 7
- WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acetonitrile Chemical compound CC#N WEVYAHXRMPXWCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dichloromethane Chemical compound ClCCl YMWUJEATGCHHMB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Methanol Chemical compound OC OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Dimethylformamide Chemical compound CN(C)C=O ZMXDDKWLCZADIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M Sodium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+] HEMHJVSKTPXQMS-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 6
- ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Triethylamine Chemical compound CCN(CC)CC ZMANZCXQSJIPKH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 6
- RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N triphenylphosphine Chemical compound C1=CC=CC=C1P(C=1C=CC=CC=1)C1=CC=CC=C1 RIOQSEWOXXDEQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1 ISWSIDIOOBJBQZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 238000011049 filling Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 4
- JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N N,N-Diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA) Chemical compound CCN(C(C)C)C(C)C JGFZNNIVVJXRND-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 4
- 150000008064 anhydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 230000001588 bifunctional effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000006356 dehydrogenation reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 4
- 150000002790 naphthalenes Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 229920003986 novolac Polymers 0.000 description 4
- QWVGKYWNOKOFNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N o-cresol Chemical compound CC1=CC=CC=C1O QWVGKYWNOKOFNN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000035882 stress Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000001993 wax Substances 0.000 description 4
- AHDSRXYHVZECER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,4,6-tris[(dimethylamino)methyl]phenol Chemical compound CN(C)CC1=CC(CN(C)C)=C(O)C(CN(C)C)=C1 AHDSRXYHVZECER-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LXBGSDVWAMZHDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methyl-1h-imidazole Chemical compound CC1=NC=CN1 LXBGSDVWAMZHDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 125000003277 amino group Chemical group 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 3
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 125000002887 hydroxy group Chemical group [H]O* 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000003786 synthesis reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- SRPWOOOHEPICQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimellitic anhydride Chemical compound OC(=O)C1=CC=C2C(=O)OC(=O)C2=C1 SRPWOOOHEPICQU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Chemical compound O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- LTVUCOSIZFEASK-MPXCPUAZSA-N (3ar,4s,7r,7as)-3a-methyl-3a,4,7,7a-tetrahydro-4,7-methano-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione Chemical compound C([C@H]1C=C2)[C@H]2[C@H]2[C@]1(C)C(=O)OC2=O LTVUCOSIZFEASK-MPXCPUAZSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,2-tetramine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCN VILCJCGEZXAXTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2,2,4,4,6,6-hexaphenoxy-1,3,5-triaza-2$l^{5},4$l^{5},6$l^{5}-triphosphacyclohexa-1,3,5-triene Chemical compound N=1P(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)(OC=2C=CC=CC=2)=NP=1(OC=1C=CC=CC=1)OC1=CC=CC=C1 RNFJDJUURJAICM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- YTWBFUCJVWKCCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-heptadecyl-1h-imidazole Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC1=NC=CN1 YTWBFUCJVWKCCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RNLHGQLZWXBQNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(aminomethyl)-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohexan-1-amine Chemical compound CC1(C)CC(N)CC(C)(CN)C1 RNLHGQLZWXBQNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WADSJYLPJPTMLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-(cycloundecen-1-yl)-1,2-diazacycloundec-2-ene Chemical compound C1CCCCCCCCC=C1C1=NNCCCCCCCC1 WADSJYLPJPTMLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WVRNUXJQQFPNMN-VAWYXSNFSA-N 3-[(e)-dodec-1-enyl]oxolane-2,5-dione Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCC\C=C\C1CC(=O)OC1=O WVRNUXJQQFPNMN-VAWYXSNFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- VQVIHDPBMFABCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5-(1,3-dioxo-2-benzofuran-5-carbonyl)-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1=C2C(=O)OC(=O)C2=CC(C(C=2C=C3C(=O)OC(=O)C3=CC=2)=O)=C1 VQVIHDPBMFABCQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MWSKJDNQKGCKPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-methyl-3a,4,5,7a-tetrahydro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1CC(C)=CC2C(=O)OC(=O)C12 MWSKJDNQKGCKPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- MQJKPEGWNLWLTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dapsone Chemical compound C1=CC(N)=CC=C1S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1 MQJKPEGWNLWLTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Diethylenetriamine Chemical compound NCCNCCN RPNUMPOLZDHAAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000006087 Silane Coupling Agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- QHWKHLYUUZGSCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrabromophthalic anhydride Chemical compound BrC1=C(Br)C(Br)=C2C(=O)OC(=O)C2=C1Br QHWKHLYUUZGSCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FDLQZKYLHJJBHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-(aminomethyl)phenyl]methanamine Chemical compound NCC1=CC=CC(CN)=C1 FDLQZKYLHJJBHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- IMUDHTPIFIBORV-UHFFFAOYSA-N aminoethylpiperazine Chemical compound NCCN1CCNCC1 IMUDHTPIFIBORV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 150000004982 aromatic amines Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229910052794 bromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003054 catalyst Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 2
- QGBSISYHAICWAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N dicyandiamide Chemical compound NC(N)=NC#N QGBSISYHAICWAH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000000113 differential scanning calorimetry Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 2
- ANSXAPJVJOKRDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N furo[3,4-f][2]benzofuran-1,3,5,7-tetrone Chemical compound C1=C2C(=O)OC(=O)C2=CC2=C1C(=O)OC2=O ANSXAPJVJOKRDJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NAQMVNRVTILPCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexane-1,6-diamine Chemical compound NCCCCCCN NAQMVNRVTILPCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004898 kneading Methods 0.000 description 2
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- RTWNYYOXLSILQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N methanediamine Chemical compound NCN RTWNYYOXLSILQN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000003960 organic solvent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000005011 phenolic resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035484 reaction time Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 2
- FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetraethylenepentamine Chemical compound NCCNCCNCCNCCN FAGUFWYHJQFNRV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DJKGDNKYTKCJKD-BPOCMEKLSA-N (1s,4r,5s,6r)-1,2,3,4,7,7-hexachlorobicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-ene-5,6-dicarboxylic acid Chemical compound ClC1=C(Cl)[C@]2(Cl)[C@H](C(=O)O)[C@H](C(O)=O)[C@@]1(Cl)C2(Cl)Cl DJKGDNKYTKCJKD-BPOCMEKLSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WYTZZXDRDKSJID-UHFFFAOYSA-N (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane Chemical compound CCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)CCCN WYTZZXDRDKSJID-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MUTGBJKUEZFXGO-OLQVQODUSA-N (3as,7ar)-3a,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-2-benzofuran-1,3-dione Chemical compound C1CCC[C@@H]2C(=O)OC(=O)[C@@H]21 MUTGBJKUEZFXGO-OLQVQODUSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JRQJLSWAMYZFGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1'-biphenyl;phenol Chemical compound OC1=CC=CC=C1.C1=CC=CC=C1C1=CC=CC=C1 JRQJLSWAMYZFGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATWLRNODAYAMQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,1-dibromopropane Chemical compound CCC(Br)Br ATWLRNODAYAMQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WZCQRUWWHSTZEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1,3-phenylenediamine Chemical compound NC1=CC=CC(N)=C1 WZCQRUWWHSTZEM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MCTWTZJPVLRJOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-methyl-1H-imidazole Chemical compound CN1C=CN=C1 MCTWTZJPVLRJOU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylphenol;3-methylphenol;4-methylphenol Chemical compound CC1=CC=C(O)C=C1.CC1=CC=CC(O)=C1.CC1=CC=CC=C1O QTWJRLJHJPIABL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UUEWCQRISZBELL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 3-trimethoxysilylpropane-1-thiol Chemical compound CO[Si](OC)(OC)CCCS UUEWCQRISZBELL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- IGSBHTZEJMPDSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 4-[(4-amino-3-methylcyclohexyl)methyl]-2-methylcyclohexan-1-amine Chemical compound C1CC(N)C(C)CC1CC1CC(C)C(N)CC1 IGSBHTZEJMPDSZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ULKLGIFJWFIQFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 5K8XI641G3 Chemical compound CCC1=NC=C(C)N1 ULKLGIFJWFIQFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BVNYUDLTUUORJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N C1(=CC=CC=C1)O.CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C Chemical group C1(=CC=CC=C1)O.CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C BVNYUDLTUUORJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002841 Lewis acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241001136616 Methone Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002732 Polyanhydride Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000021355 Stearic acid Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- DPRMFUAMSRXGDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N ac1o530g Chemical compound NCCN.NCCN DPRMFUAMSRXGDE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K aluminium hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[OH-].[Al+3] WNROFYMDJYEPJX-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- SESFRYSPDFLNCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N benzyl benzoate Chemical compound C=1C=CC=CC=1C(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 SESFRYSPDFLNCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006267 biphenyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000006229 carbon black Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007810 chemical reaction solvent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229930003836 cresol Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229910002026 crystalline silica Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XOSYHSRXLVMOBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclopenta-1,3-diene;phenol Chemical compound C1C=CC=C1.C1C=CC=C1.OC1=CC=CC=C1 XOSYHSRXLVMOBA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 235000014113 dietary fatty acids Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N diethanolamine Chemical compound OCCNCCO ZBCBWPMODOFKDW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 125000006182 dimethyl benzyl group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- XXBDWLFCJWSEKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N dimethylbenzylamine Chemical compound CN(C)CC1=CC=CC=C1 XXBDWLFCJWSEKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002118 epoxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- FWDBOZPQNFPOLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethenyl(triethoxy)silane Chemical compound CCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)C=C FWDBOZPQNFPOLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002360 explosive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000194 fatty acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229930195729 fatty acid Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000004665 fatty acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000005350 fused silica glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001879 gelation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 125000005843 halogen group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- FLBJFXNAEMSXGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N het anhydride Chemical compound O=C1OC(=O)C2C1C1(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)C2(Cl)C1(Cl)Cl FLBJFXNAEMSXGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MUTGBJKUEZFXGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexahydrophthalic anhydride Chemical compound C1CCCC2C(=O)OC(=O)C21 MUTGBJKUEZFXGO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001771 impaired effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052740 iodine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007517 lewis acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229940018564 m-phenylenediamine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 1
- VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L magnesium dihydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[OH-].[Mg+2] VTHJTEIRLNZDEV-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 239000000347 magnesium hydroxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001862 magnesium hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910000000 metal hydroxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004692 metal hydroxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- GKTNLYAAZKKMTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N n-[bis(dimethylamino)phosphinimyl]-n-methylmethanamine Chemical compound CN(C)P(=N)(N(C)C)N(C)C GKTNLYAAZKKMTQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZCIJAGHWGVCOHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N naphthalene phenol Chemical compound C1(=CC=CC=C1)O.C1(=CC=CC=C1)O.C1=CC=CC2=CC=CC=C12.C1(=CC=CC=C1)O ZCIJAGHWGVCOHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BDJRBEYXGGNYIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N nonanedioic acid Chemical compound OC(=O)CCCCCCCC(O)=O BDJRBEYXGGNYIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(O)=O QIQXTHQIDYTFRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N octadecanoic acid Natural products CCCCCCCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(O)=O OQCDKBAXFALNLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005580 one pot reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012188 paraffin wax Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005191 phase separation Methods 0.000 description 1
- GQDSSPVCELQEFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N phenol;1,4-xylene Chemical group OC1=CC=CC=C1.CC1=CC=C(C)C=C1 GQDSSPVCELQEFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000768 polyamine Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 150000003141 primary amines Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 238000010298 pulverizing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011342 resin composition Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920002545 silicone oil Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002379 silicone rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004945 silicone rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005476 soldering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000008117 stearic acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001424 substituent group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- AGGKEGLBGGJEBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetramethylenedisulfotetramine Chemical compound C1N(S2(=O)=O)CN3S(=O)(=O)N1CN2C3 AGGKEGLBGGJEBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000930 thermomechanical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- BPSIOYPQMFLKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N trimethoxy-[3-(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)propyl]silane Chemical compound CO[Si](OC)(OC)CCCOCC1CO1 BPSIOYPQMFLKFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- BIKXLKXABVUSMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N trizinc;diborate Chemical compound [Zn+2].[Zn+2].[Zn+2].[O-]B([O-])[O-].[O-]B([O-])[O-] BIKXLKXABVUSMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007039 two-step reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc stearate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- XAEWLETZEZXLHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc;dioxido(dioxo)molybdenum Chemical compound [Zn+2].[O-][Mo]([O-])(=O)=O XAEWLETZEZXLHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G59/00—Polycondensates containing more than one epoxy group per molecule; Macromolecules obtained by polymerising compounds containing more than one epoxy group per molecule using curing agents or catalysts which react with the epoxy groups
- C08G59/02—Polycondensates containing more than one epoxy group per molecule
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/18—Oxygen-containing compounds, e.g. metal carbonyls
- C08K3/20—Oxides; Hydroxides
- C08K3/22—Oxides; Hydroxides of metals
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/00—Use of inorganic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K3/34—Silicon-containing compounds
- C08K3/36—Silica
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/54—Silicon-containing compounds
- C08K5/549—Silicon-containing compounds containing silicon in a ring
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L63/00—Compositions of epoxy resins; Compositions of derivatives of epoxy resins
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/48—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor body packages
- H01L33/52—Encapsulations
- H01L33/56—Materials, e.g. epoxy or silicone resin
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Epoxy Resins (AREA)
- Structures Or Materials For Encapsulating Or Coating Semiconductor Devices Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 두 개의 대칭적인 나프탈렌 구조가 알칸디일 구조로 연결된 내흡습성 및 결정성이 우수하며 용융점도가 낮은 새로운 에폭시 수지 및 이를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 관한 것이다. 본 발명에 의하면, 하기 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지; 및 상기 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지, 무기 필러, 및 경화제를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체가 제공된다.
[화학식 3]
(상기 식에서 A는
[화학식 4-1]
혹은
[화학식 4-2]
(단, 상기 화학식 4-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다.)이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수이다.) 상기 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 우수한 내흡습성, 낮은 용융점도 및 상온 결정성을 갖는 것으로, 반도체 장치 봉지시 공정성 및 제품의 신뢰성이 개선된다. The present invention relates to a novel epoxy resin having excellent hygroscopicity and crystallinity and low melt viscosity in which two symmetric naphthalene structures are connected to an alkanediyl structure, and an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the same. According to the present invention, the epoxy resin of the formula (3); And an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, comprising an epoxy resin of Formula 3, an inorganic filler, and a curing agent.
(3)
Where A is
[Formula 4-1]
or
[Formula 4-2]
(Wherein R is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group), and n is an integer of 1 to 10. The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation has excellent hygroscopicity and low melting point. Having a degree of crystallinity and room temperature, processability and reliability of a product are improved when encapsulating a semiconductor device.
Description
본 발명은 내흡습성 및 결정성이 우수하고 용융점도가 낮은 새로운 에폭시 수지 및 이를 포함하는 에폭시 수지 복합체에 관한 것이다. 보다 상세하게 본 발명은 우수한 내흡습성 및 결정성 그리고 낮은 용융점도를 갖는 두 개의 대칭적인 나프탈렌 구조가 알칸디일 구조로 연결된 새로운 에폭시 수지 및 이를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to a new epoxy resin having excellent hygroscopicity and crystallinity and low melt viscosity and an epoxy resin composite comprising the same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a novel epoxy resin in which two symmetric naphthalene structures having excellent hygroscopicity and crystallinity and low melt viscosity are connected to an alkanediyl structure and an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the same.
종래 다이오드, 트랜지스터, 집적회로, 반도체 소자 등의 전자부품은 일반적으로 에폭시 수지 복합체로 봉지된다. 더욱이, 근래 전자기기의 소형화, 경량화, 고성능화에 따라, 고도의 반도체 소자의 고집적화 및 반도체 장치의 표면 실장화가 요구된다.
BACKGROUND ART Electronic components such as diodes, transistors, integrated circuits, and semiconductor devices are generally encapsulated with an epoxy resin composite. Moreover, with the recent miniaturization, weight reduction and high performance of electronic devices, high integration of semiconductor devices and surface mounting of semiconductor devices are required.
반도체 장치의 소형화 및 박형화에 따라 반도체 장치의 표면실장 등에 사용되는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체의 보다 높은 유동성, 즉 낮은 용융점도, 내흡습성 및 상온 결정성이 요구된다.
With the miniaturization and thinning of semiconductor devices, higher fluidity, ie, low melt viscosity, hygroscopicity and room temperature crystallinity, are required for semiconductor encapsulation epoxy resin composites used for surface mounting of semiconductor devices.
즉, 에폭시 수지 복합체와 반도체 구성요소(예를들어, 무기물인 실리콘 웨이퍼)의 현저한 열팽창계수의 차이(CTE-mismatch)로 인하여 열응력이 발생하며 이로 인한 무기층 및 봉지제 계면에서의 크랙 생성, 기판의 휨 발생, 코팅층의 박리(peeling-off), 기판 깨짐 등 제품불량이 발생하고 따라서, 제품의 신뢰성 확보가 문제시된다. 이를 방지하기 위해, 반도체 봉지용 수지 복합체의 열팽창계수를 감소시킬 필요가 있으며, 따라서, 에폭시 수지에 열팽창계수가 낮은 무기 필러가 다량 배합된다. 구체적으로, 현재 반도체 봉지용 수지 복합체에서는 에폭시 수지 약 10wt% 내지 30wt%와 무기 필러 약 60wt% 내지 90wt%가 배합된다. 그러나, 이와 같은 다량의 무기필러의 배합으로 인하여, 반도체 봉지용 수지 복합체의 유동성이 저하되며, 이로 인하여 반도체 봉지시 미충진 및 골드 와이어(gold wire) 움직임 등이 문제시된다.
That is, the thermal stress is generated due to the significant difference in the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE-mismatch) between the epoxy resin composite and the semiconductor component (for example, an inorganic silicon wafer), resulting in crack generation at the interface between the inorganic layer and the encapsulant, Product defects such as warpage of the substrate, peeling-off of the coating layer, and cracking of the substrate occur, thus ensuring the reliability of the product. In order to prevent this, it is necessary to reduce the thermal expansion coefficient of the resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation. Therefore, a large amount of inorganic filler having a low thermal expansion coefficient is incorporated into the epoxy resin. Specifically, in the resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, about 10 wt% to 30 wt% of epoxy resin and about 60 wt% to 90 wt% of inorganic filler are blended. However, due to the blending of such a large amount of inorganic filler, the fluidity of the resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation is lowered, thereby causing problems such as unfilled and gold wire (gold wire) movement during semiconductor encapsulation.
따라서, 다량의 무기 필러가 에폭시수지와 고르게 잘 섞일 수 있고, 에폭시 수지 복합체가 미세한 반도체 칩 및 배선회로 기판간의 미세한 간극 및 공극에 고도로 충진될 수 있도록 하기 위해서는 공정온도에서의 에폭시 수지의 용융점도가 가능한 한 낮은 것이 바람직하다.
Therefore, in order to allow a large amount of inorganic filler to be evenly mixed with the epoxy resin and to allow the epoxy resin composite to be highly filled in minute gaps and voids between the fine semiconductor chip and the wiring circuit board, the melt viscosity of the epoxy resin at the process temperature is high. It is desirable to be as low as possible.
한편, 흡습한 반도체 장치는 땜납 처리시 고온에 노출되면 기화된 수증기로 인하여 폭발적인 응력이 발생하며, 이로 인하여 반도체 장치에 크랙이 발생하거나, 소자나 리드 프레임과 반도체 봉지용 수지 조성물의 경화물의 경계면에 박리가 발생하여 얻어지는 반도체 장치의 전기적 신뢰성이 손상된다. 따라서, 내리플로우성을 향상시키기 위해 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 우수한 내흡습성이 요구된다.
On the other hand, when the moisture absorbed semiconductor device is exposed to high temperatures during soldering, an explosive stress is generated due to vaporized water vapor, which causes cracks in the semiconductor device, The electrical reliability of the semiconductor device obtained by peeling off is impaired. Therefore, in order to improve reflow resistance, the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation requires excellent moisture resistance.
이와 같이, 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 상온에서는 고형이어서 봉지공정에 적용하기 용이할 뿐만 아니라, 100℃ 내지 200℃의 고온에서는 용융되어 효과적으로 충진될 수 있도록 매우 높은 유동성이 요구된다. 즉, 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 낮은 용융점도와 상온 결정성이 요구된다. 그러나, 종래, 비결정성 에폭시 수지의 경우, 복합체의 용융점도를 낮추기 위해 에폭시 수지의 분자량을 감소시키면, 물성이 저하될 뿐만 아니라, 상온 결정성이 충족되지 않아 사용이 불가능한 문제가 있었다.
As such, the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation is not only easy to apply to the encapsulation process because it is solid at room temperature, and very high fluidity is required to be melted and effectively filled at high temperatures of 100 ° C to 200 ° C. That is, the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation requires low melt viscosity and room temperature crystallinity. However, conventionally, in the case of the amorphous epoxy resin, when the molecular weight of the epoxy resin is reduced in order to lower the melt viscosity of the composite, not only the physical properties are lowered but also the room temperature crystallinity is not satisfied, and thus there is a problem that cannot be used.
현재 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 에폭시 수지로는 오르소-크레졸 노볼락형 에폭시 수지 및 비페닐 에폭시 수지 등이 사용된다. 오르소-크레졸 노볼락형 에폭시 수지는 상온에서 비결정질 고체이다. 따라서, 공정조건에서 저용융점도가 되도록 하기 위해서는 분자량을 감소시켜야 한다. 그러나, 분자량이 감소되면, 연화점이 낮아져서 상온 결정성이 확보되지 않으므로 취급이 곤란해 진다. 즉, 작업성이 문제시된다.
Currently, ortho-cresol novolac type epoxy resins and biphenyl epoxy resins are used as epoxy resins in epoxy resin composites for semiconductor encapsulation. Ortho-cresol novolac-type epoxy resins are amorphous solids at room temperature. Therefore, in order to achieve low melt viscosity under process conditions, the molecular weight must be reduced. However, when the molecular weight is reduced, the softening point is lowered, so that room temperature crystallinity is not secured, and handling becomes difficult. That is, workability is a problem.
한편, 하기 화학식 1 및 2의 비페닐 에폭시 수지는 저분자량 에폭시 수지로서 용융점도가 낮고 대칭구조로 인하여 우수한 상온 결정성을 나타낸다. 따라서, 상온에서 고형으로의 취급 및 공정성이 우수하고, 융점이상의 온도(구체적으로는 약 105℃ 이상)에서는 매우 낮은 점도를 나타내므로, 무기 필러를 다량 배합할 수 있다. 그러나, 대칭성이 좀더 우수한 비페닐 구조에 치환체를 갖지 않는 하기 화학식 1의 비페닐 에폭시 수지는 고융점(150℃)이며 경화제 등과의 상용성이 좋지 않다. 즉, 화학식 1의 비페닐 에폭시 수지는 경화제와 혼합한 다음에 온도를 내리면 상분리되므로 가공성 측면에서 바람직하지 않다. 이로 인하여, 화학식 1의 비페닐 에폭시 수지는 겔화속도 및 경도 유지를 위하여 하기 화학식 2의 치환된 비페닐 에폭시 수지와 함께 배합하여 사용하거나, 화학식 2를 단독으로 사용한다.
On the other hand, the biphenyl epoxy resins of the formulas (1) and (2) are low molecular weight epoxy resins with low melt viscosity and exhibit excellent room temperature crystallinity due to a symmetrical structure. Therefore, since it is excellent in handling and processability from normal temperature to solid, and exhibits very low viscosity at the temperature above melting | fusing point (specifically about 105 degreeC or more), an inorganic filler can be mix | blended abundantly. However, the biphenyl epoxy resin of the following general formula (1) having no substituent in a biphenyl structure having better symmetry has a high melting point (150 ° C.) and is not compatible with a curing agent. That is, the biphenyl epoxy resin of the general formula (1) is not preferable in view of workability because the phase separation when the temperature is lowered after mixing with a curing agent. For this reason, the biphenyl epoxy resin of the formula (1) is used in combination with the substituted biphenyl epoxy resin of the following formula (2) or the formula (2) alone to maintain the gelation rate and hardness.
[화학식 1][Formula 1]
[화학식 2][Formula 2]
따라서, 낮은 용융점도, 우수한 결정성 및 내흡습성을 가지며, 복합체 제조시 경화제와 상분리되지 않는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 및 이를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체가 요구된다. Therefore, there is a need for an epoxy resin for semiconductor encapsulation having a low melt viscosity, excellent crystallinity and hygroscopicity, and not being separated from a curing agent in the manufacture of a composite, and an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the same.
본 발명의 일 구현에 의하면, 낮은 용융점도, 상온 결정성 및 우수한 내흡습성을 갖는 새로운 에폭시 수지가 제공된다.
According to one embodiment of the present invention, a new epoxy resin having low melt viscosity, room temperature crystallinity and excellent hygroscopicity is provided.
본 발명의 다른 구현에 의하면, 낮은 용융점도, 상온 결정성 및 우수한 내흡습성을 갖는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체가 제공된다. According to another embodiment of the present invention, an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation having low melt viscosity, room temperature crystallinity and excellent hygroscopicity is provided.
본 발명의 일 견지에 의하면,According to one aspect of the invention,
하기 화학식 3으로 나타내어지는 에폭시 수지가 제공된다.
An epoxy resin represented by the following formula (3) is provided.
[화학식 3](3)
상기 식에서 A는 Where A is
[화학식 4-1] [Formula 4-1]
혹은 or
[화학식 4-2][Formula 4-2]
(단, 상기 화학식 4-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다.)(However, in Formula 4-2, R is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group.)
이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수이다.
And n is an integer of 1 to 10.
본 발명의 다른 견지에 의하면, According to another aspect of the present invention,
상기 화학식 3으로 나타내어지는 에폭시 수지; An epoxy resin represented by Chemical Formula 3;
무기 필러; 및 Inorganic fillers; And
경화제를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체가 제공된다. An epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising a curing agent is provided.
본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지의 유연한 알칸디일 연결구조(moiety)로 인하여 우수한 배향성 및 낮은 용융점도를 그리고 단단한 결정성 코어 나프탈렌의 대칭구조로 인하여 상온 결정성 및 우수한 내열성을 나타낸다. 낮은 용융점도로 인하여 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체 제조시, 공정성이 개선될 뿐만 아니라, 이로 봉지된 반도체 장치의 신뢰성, 구체적으로 미세한 간극 사이의 충진성이 개선된다. 또한, 새로운 에폭시 수지는 강한 소수성의 나프탈렌 구조와 알칸디일 연결 구조로 인하여 우수한 내흡습성을 나타내며, 상기 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 우수한 내리플로우성을 나타낸다.
The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the new epoxy resin according to the present invention has excellent orientation and low melt viscosity due to the flexible alkanediyl moiety of the new epoxy resin according to the present invention. Due to the symmetrical structure, it exhibits room temperature crystallinity and excellent heat resistance. Due to the low melt viscosity, not only the processability is improved when manufacturing the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, but also the reliability of the encapsulated semiconductor device, in particular, the filling between fine gaps. In addition, the new epoxy resin exhibits excellent hygroscopicity due to the strong hydrophobic naphthalene structure and the alkanediyl linking structure, and the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation including the epoxy resin exhibits excellent reflowability.
반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 또한, 나프탈렌 구조의 강직성 및 필러의 고충진으로 인하여 낮은 열팽창계수, 즉, 개선된 열팽창특성을 나타내며, 이로 인하여, 반도체 장치의 크랙 생성, 기판의 휨 발생, 코팅층의 박리(peeling-off), 기판 깨짐 등 제품불량이 감소되고 제품의 신뢰성이 개선된다. The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation also exhibits a low coefficient of thermal expansion, i.e. improved thermal expansion, due to the stiffness of the naphthalene structure and the high filling of the filler, resulting in cracking of the semiconductor device, occurrence of warpage of the substrate, peeling of the coating layer. Product defects such as peeling-off and substrate breakage are reduced and product reliability is improved.
도 1은 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지 구조의 개략도이며,
도 2는 물성평가 1에서 얻어진 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지의 용융온도를 나타내는 그래프이며,
도 3은 물성평가 2에서 얻어진 본 발명에 의한 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 대한 DSC 시험결과를 나타내는 그래프이다. 1 is a schematic diagram of a novel epoxy resin structure according to the present invention,
2 is a graph showing the melting temperature of the new epoxy resin according to the present invention obtained in physical property evaluation 1,
3 is a graph showing the DSC test results for the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation according to the present invention obtained in physical property evaluation 2.
이하, 본 발명에 대하여 보다 상세히 설명한다. 본 발명은 상기한 바와 같은 낮은 용융점도, 우수한 결정성 및 내흡습성을 갖는 에폭시 수지 및 이를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체를 제공하기 위해 제안된 것으로, 본 발명에 의하면, 두 개의 대칭되는 나프탈렌 구조가 알칸디일 그룹으로 연결된 새로운 에폭시 수지가 제공된다.
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail. The present invention has been proposed to provide an epoxy resin having a low melt viscosity, excellent crystallinity and hygroscopicity as described above, and an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the same, and according to the present invention, two symmetric naphthalene structures New epoxy resins are provided in which alkanediyl groups are linked.
본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지는 하기 화학식 3로 나타내어진다.
The new epoxy resin according to the present invention is represented by the following formula (3).
[화학식 3](3)
상기 식에서 A는 하기 화학식 4-1 또는 4-2의 나프탈렌 구조이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수, 바람직하게는 1 내지 3의 정수이다.
In the formula, A is a naphthalene structure of the formula 4-1 or 4-2, n is an integer of 1 to 10, preferably an integer of 1 to 3.
[화학식 4-1] [Formula 4-1]
혹은 or
[화학식 4-2][Formula 4-2]
(단, 상기 화학식 4-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다.) (However, in Formula 4-2, R is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group.)
상기 화학식 4-1 및 4-2에서 연결부위는 특정되지 않았으며, 어떠한 연결부위에서 연결될 수 있다.
In Formulas 4-1 and 4-2, the linking site is not specified, and may be linked at any linking site.
본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지(에폭시 화합물)는, 도 1에 나타낸 새로운 에폭시 수지 구조의 개략도 및 상기 화학식 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 대칭인(symmetric) 2개의 나프탈렌 유니트가 유연한(flexible)한 알칸디일 구조로 연결된 것으로, 상온 결정성일 뿐만 아니라, 낮은 용융점도를 나타내므로, 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 사용하기에 적합하다. 한편, 알칸디일 연결 구조에서 n값은 1 내지 10의 정수일 수 있다.
The novel epoxy resin (epoxy compound) according to the present invention is a schematic diagram of the new epoxy resin structure shown in FIG. 1 and alkanediyl in which two naphthalene units are symmetrically flexible, as shown in Formula 3 above. It is connected to the structure, and not only normal temperature crystallinity, but also shows a low melt viscosity, and thus is suitable for use in an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation. Meanwhile, in the alkanediyl linking structure, the n value may be an integer of 1 to 10.
본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지는 유연한 알칸디일 연결구조(moiety)에 의해 우수한 배향성 및 낮은 용융점도를 나타낸다. 또한, 단단한 결정성 코어 나프탈렌의 대칭구조로 인하여 상온에서 결정성을 나타낼 뿐만 아니라 우수한 내열성을 나타낸다. 따라서, 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지는 상온에서는 결정성(고체)을 나타내지만, 100℃ 이상의 온도에서 용융되는 경우에, 유연한 알칸디일 구조로 인하여 낮은 점도, 즉, 큰 유동성을 나타내며, 이러한 낮은 용융점도로 인하여 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체 제조시, 다량의 무기 필러와 배합될 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 무기 필러와의 배합이 용이하고 충진제가 고르게 섞일 수 있으므로 우수한 공정성을 나타낸다.
The novel epoxy resins according to the present invention exhibit excellent orientation and low melt viscosity due to the flexible alkanediyl moiety. In addition, due to the symmetrical structure of the hard crystalline core naphthalene, not only shows crystallinity at room temperature but also excellent heat resistance. Therefore, the new epoxy resin according to the present invention shows crystallinity (solid) at room temperature, but when melted at a temperature of 100 ° C. or higher, due to the flexible alkanediyl structure, it exhibits low viscosity, that is, high fluidity. Due to the melt viscosity, not only can be blended with a large amount of inorganic filler when preparing an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, but also easy to mix with the inorganic filler and evenly mixed with the filler, it shows excellent processability.
또한, 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지는 강한 소수성의 나프탈렌 구조와 알칸디일 연결 구조로 인하여 내흡습성이 우수하며, 따라서, 이러한 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 우수한 내리플로우성을 나타낸다.
In addition, the new epoxy resin according to the present invention has excellent hygroscopicity due to the strong hydrophobic naphthalene structure and the alkanediyl linking structure, and therefore, the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation including such epoxy resin exhibits excellent reflowability. .
나아가, 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 충진제를 다량 포함하는 고충진의 경우에도, 낮은 용융점도로 인하여 박형 패키지 및 소형 패키지의 미세한 간극 사이에도 효율적으로 고충진될 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 골드 와이어(gold wire)의 움직임이 방지된다.
Furthermore, the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation including the epoxy resin according to the present invention can be efficiently filled even in a high gap between the thin package and the small package due to the low melt viscosity even in the case of high filling containing a large amount of filler. Rather, the movement of the gold wire is prevented.
상기 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지는 먼저, 이관능성 알칸과 디히드록시 나프탈렌의 반응으로 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌을 형성한 후 (제 1단계), 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌과 에피클로로히드린의 반응으로 나프탈렌의 히드록시 그룹을 에폭시화하여 제조할 수 있다 (제 2단계).
The epoxy resin according to the present invention first forms naphthalene connected by alkanediyl chain by reaction of difunctional alkanes with dihydroxy naphthalene (first step), followed by naphthalene and epichlorohydrin connected by alkanediyl chain. It can be prepared by epoxidizing the hydroxy group of naphthalene by the reaction of (second step).
즉, 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지는 이관능성 알칸 1당량에 대하여 디히드록시 나프탈렌이 3당량 내지 10당량이 되도록 용매 및 염기 존재하에서 상온 내지 200℃로 10분 내지 24시간 동안 반응시켜서 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌을 형성하는 제 1 단계; 및 상기 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌 1 당량에 대하여 에피클로로히드린이 4 당량 내지 15 당량이 되도록 염기 및 임의의 용매 존재하에서 0℃ 내지 200 ℃로 1시간 내지 24시간 동안 반응시키는 제 2단계에 의해 제조된다.
That is, the epoxy resin according to the present invention is reacted for 10 minutes to 24 hours at room temperature to 200 ° C in the presence of a solvent and a base such that dihydroxy naphthalene is 3 equivalents to 10 equivalents to 1 equivalent of difunctional alkane, and thus an alkanediyl chain. Forming a naphthalene connected with; And a second step of reacting epichlorohydrin at 4 to 15 equivalents with respect to 1 equivalent of naphthalene linked by the alkanediyl chain at 0 ° C. to 200 ° C. for 1 hour to 24 hours in the presence of a base and an optional solvent. Is manufactured by.
상기 제 1단계 반응에 대하여 설명한다. 상기 이관능성 알칸으로는 하기 화학식 5의 이관능성 알칸이 사용될 수 있다.
The first step reaction will be described. As the bifunctional alkanes, bifunctional alkanes represented by the following Formula 5 may be used.
[화학식 5][Chemical Formula 5]
(상기 식 중, X는 Cl, Br, I와 같은 할라이드, 또는 -O-SO2-CH3이며, X는 1 내지 10의 정수, 바람직하게는 1 내지 3의 정수이다.)
(Wherein, X is a halide such as Cl, Br, I, or -O-SO 2 -CH 3 , X is an integer of 1 to 10, preferably an integer of 1 to 3.)
상기 디히드록시 나프탈렌으로는 하기 화학식 6-1 또는 6-2의 디히드록시 나프탈렌이 사용될 수 있다.
As the dihydroxy naphthalene, dihydroxy naphthalene of the following Chemical Formula 6-1 or 6-2 may be used.
[화학식 6-1][Formula 6-1]
[화학식 6-2][Formula 6-2]
(단, 상기 식 중 6-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다)Wherein R in 6-2 is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group
상기 화학식 6-1 및 6-2에서 -OH 및 -R의 연결부위는 특정되지 않으며, 어떠한 연결부위에서 연결될 수 있다.
In Formulas 6-1 and 6-2, the linking site of —OH and —R is not specified, and may be connected at any linking site.
상기 제 1단계 반응에서는 이관능성 알칸과 디히드록시 나프탈렌을 이관능성 알칸 1 당량에 대하여 디히드록시 나프탈렌이 3 당량 내지 10 당량이 되도록 용매 및 염기 존재하에서 상온 (구체적으로는 약 20℃ 내지 25℃) 내지 200 ℃로 10분 내지 24시간 동안 반응시킨다. 상기 제 1 단계 반응에서는 염기에 의해 디히드록시 나프탈렌이 탈수소화되고 탈수소화된 디히드록시 나프탈렌과 이관능성 알칸의 반응으로 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌이 형성된다. 상기 1단계 반응은 용매 및 염기 존재하에서 디히드록시 나프탈렌과 이관능성 알칸을 반응시키므로써 행하여지는 것으로 기재하였으나, 구체적인 공정에서, 디히드록시 나프탈렌, 염기 및 이관능성 알칸은 순차적으로 첨가되거나, 혹은 모든 반응물을 첨가하고 반응을 진행시킬 수도 있으며, 혹은 시간 간격을 두고 디히드록시 나프탈렌의 탈수소화 후에 이관능성 알칸이 첨가될 수도 있다. 탈수소화는 화학물질의 합성에 있어서 일반적으로 알려져 있는 공정으로서 이 기술분야의 기술자는 상기 기재된 제 1 단계 공정에 따라, 디히드록시 나프탈렌이 탈수소화되고 탈수소화된 디히드록시 나프탈렌과 이관능성 알칸의 반응으로 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌이 형성되도록 반응물을 적합하게 첨가하여 반응시킬 수 있다.
In the first stage reaction, difunctional alkanes and dihydroxy naphthalenes are converted to 3 equivalents to 10 equivalents of dihydroxy naphthalene with respect to 1 equivalent of difunctional alkanes at room temperature (specifically, about 20 ° C. to 25 ° C.). To 200 ° C. for 10 minutes to 24 hours. In the first step reaction, dihydroxy naphthalene is dehydrogenated by a base, and naphthalene is connected to an alkanediyl chain by reaction of dehydrogenated dihydroxy naphthalene with a bifunctional alkan. The one-step reaction is described as being carried out by reacting dihydroxy naphthalene with difunctional alkanes in the presence of a solvent and a base, but in a specific process, dihydroxy naphthalene, base and difunctional alkanes are added sequentially, or all The reactants may be added and the reaction proceeded, or bifunctional alkanes may be added after dehydrogenation of the dihydroxy naphthalene over time intervals. Dehydrogenation is a commonly known process for the synthesis of chemicals, and the skilled person is skilled in the art, according to the first step process described above, of dihydroxy naphthalene and difunctional alkanes of dehydrogenated and dehydrogenated dihydroxy naphthalene. The reactants may be reacted by the addition of the reactants as appropriate to form naphthalenes linked by alkanediyl chains.
제 1단계 반응의 반응온도 및 반응시간은 사용되는 디히드록시 나프탈렌 화합물의 나프탈렌 구조에 의존하므로 사용되는 디히드록시 나프탈렌 화합물에 따라 달라질 수 있으나, 구체적으로는 상온(약 20℃ 내지 25℃) 내지 200℃에서 10분 내지 24 시간 동안 반응시키므로써 이관능성 알칸의 이탈기(leaving group)와 탈수소화된 디히드록시 나프탈렌의 반응으로 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌이 얻어진다.
The reaction temperature and reaction time of the first stage reaction may vary depending on the dihydroxy naphthalene compound used because it depends on the naphthalene structure of the dihydroxy naphthalene compound used, and specifically, room temperature (about 20 ° C. to 25 ° C.) to By reacting at 200 ° C. for 10 minutes to 24 hours, the reaction of the leaving group of difunctional alkanes with dehydrogenated dihydroxy naphthalene yields naphthalenes linked by alkanediyl chains.
제 1 단계 반응에서 용매로는 반응물을 잘 용해할 수 있으며, 반응에 어떠한 악영향을 미치지 않고 반응 후에 쉽게 제거될 수 있는 한 어떠한 유기용매가 사용될 수 있으며, 이로써 특히 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 아세토니트릴, THF(tetrahydrofuran), MEK(methyl ethyl ketone), DMF(dimethyl formamide), DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), 메틸렌 클로라이드 등이 사용될 수 있다. 이들 용매는 단독으로 혹은 2가지 이상이 함께 사용될 수 있다. 용매의 사용양은 특히 한정하는 것은 아니며, 반응물이 충분히 용해되고 반응에 바람직하지 않은 영향을 미치지 않는 범위에서 적합한 양으로 사용될 수 있으며, 이 기술분야의 기술자는 이를 고려하여 적합하게 선택할 수 있다.
As the solvent in the first stage reaction, any organic solvent can be used as long as it can dissolve the reactants well and can be easily removed after the reaction without adversely affecting the reaction. Thus, although not particularly limited, for example, Acetonitrile, THF (tetrahydrofuran), MEK (methyl ethyl ketone), DMF (dimethyl formamide), DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), methylene chloride and the like can be used. These solvents may be used alone or in combination of two or more. The amount of the solvent to be used is not particularly limited, and may be used in a suitable amount within a range in which the reactants are sufficiently dissolved and do not adversely affect the reaction, and those skilled in the art may select appropriately in consideration of this.
제 1 단계 반응에서 염기로는 이로서 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, KOH, NaOH, K2CO3, KHCO3, NaH, 트리에틸아민, 디이소프로필에틸 아민이 사용될 수 있다. 이들 염기는 단독으로 혹은 2가지 이상의 함께 사용될 수 있으며, 염기는 디하이드록시 나프탈렌 1당량 대비 2 ~5 당량을 사용하는 것이 반응효율 측면에서 좋다.
As the base in the first stage reaction, but not limited thereto, for example, KOH, NaOH, K 2 CO 3 , KHCO 3 , NaH, triethylamine, diisopropylethyl amine can be used. These bases may be used alone or in combination of two or more, and the base may be used in an amount of 2 to 5 equivalents based on 1 equivalent of dihydroxy naphthalene in terms of reaction efficiency.
그 후, 제 2 단계 반응에서, 상기와 같은 제 1단계 반응에서 얻어진 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌을 과량의 에피클로로히드린과 반응시켜서 디히드록시 그룹을 에폭시화하므로써 본 발명에 의한 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지가 얻어진다.
Then, in the second stage reaction, the naphthalene linked by the alkanediyl chain obtained in the first stage reaction as described above is reacted with an excess epichlorohydrin to epoxidize the dihydroxy group so that An epoxy resin is obtained.
제 2 단계 반응에서는, 상기 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌과 에피클로로히드린을 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌 1당량에 대하여 에피클로로히드린 4 당량 내지 15 당량이 되도록 염기 및 임의의 용매 존재하에서 0℃ 내지 200℃로 1시간 내지 24시간 동안 반응시킨다.
In the second stage reaction, the naphthalene and epichlorohydrin linked by the alkanediyl chain are 4 to 15 equivalents of epichlorohydrin with respect to 1 equivalent of naphthalene linked by the alkanediyl chain in the presence of a base and any solvent. The reaction is carried out at 1 ° C. to 200 ° C. for 1 hour to 24 hours.
상기 제 2 단계 반응에서는 염기에 의해 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌중의 히드록시기에서 탈수소화되고 탈수소화된 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌과 에피클로로히드린의 반응으로 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지가 얻어진다. 상기 2단계 반응은 염기 및 임의의 용매 존재하에서 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌과 에피클로로히드린을 반응시키므로써 행하여지는 것으로 기재하였으나, 구체적인 공정에서, 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌, 염기 및 에피클로로히드린은 순차적으로 첨가되거나, 혹은 모든 반응물을 첨가하고 반응을 진행시킬 수도 있으며, 혹은 시간 간격을 두고 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌의 탈수소화 후에 에피클로로히드린이 첨가될 수도 있다. 탈수소화는 화학물질의 합성에 있어서 일반적으로 알려져 있는 공정으로서 이 기술분야의 기술자는 상기 기재된 제 2 단계 공정에 따라, 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌이 탈수소화되고 탈수소화된 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌과 에피클로로히드린의 반응으로 상기 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지(에폭시 화합물)가 형성되도록 반응물을 적합하게 첨가하여 반응시킬 수 있다.
In the second step reaction, an epoxy resin of formula (3) is obtained by reaction of epichlorohydrin with naphthalene connected with dehydrogenated and dehydrogenated alkanediyl chain in a hydroxyl group in naphthalene linked by an alkanediyl chain by a base. The two-step reaction was described by reacting epichlorohydrin with naphthalene linked by alkanediyl chain in the presence of a base and any solvent, but in a specific process, naphthalene, base and epichloro linked by alkanediyl chain Hydrin may be added sequentially, or all reactants may be added and the reaction proceeded, or epichlorohydrin may be added after dehydrogenation of the naphthalenes linked by alkanediyl chains at timed intervals. Dehydrogenation is a commonly known process for the synthesis of chemicals and the skilled person is skilled in the art according to the second step process described above, wherein the alkanediyl chained naphthalene is linked with the dehydrogenated and dehydrogenated alkanediyl chain. By reacting naphthalene and epichlorohydrin, a reactant may be appropriately added to form an epoxy resin (epoxy compound) of Formula 3 above.
제 2 단계 반응의 반응온도 및 반응시간은 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌의 나프탈렌 구조에 의존하므로 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌의 종류에 따라 달라지지만, 구체적으로는 0℃ 내지 200℃에서 1시간 내지 24시간 반응시키므로써 본 발명에 의한 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지가 얻어진다.
The reaction temperature and reaction time of the second stage reaction depend on the naphthalene structure of the naphthalene linked by the alkanediyl chain, and thus, depending on the type of the naphthalene linked by the alkanediyl chain, specifically, the reaction temperature is from 1 hour at 0 ° C to 200 ° C. By reacting for 24 hours, the epoxy resin of the formula (3) according to the present invention is obtained.
제 2 반응 단계에서는 용매는 필요에 따라 임의로 사용될 수 있다. 예를들어, 제 2 반응단계에서는 에피클로로히드린의 양이 별도의 용매없이 반응물을 충분히 용해시키는 양이면 별도의 용매를 사용하지 않을 수도 있다. 용매를 사용할 경우, 가능한 용매로는 반응물을 잘 용해할 수 있으며, 반응에 어떠한 악영향을 미치지 않고 반응 후에 쉽게 제거될 수 있는 한 어떠한 유기용매가 사용될 수 있으며, 이로써 특히 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 아세토니트릴, THF(tetra hydro furan), MEK(methyl ethyl ketone), DMF(dimethyl formamide), DMSO(dimethyl sulfoxide), 메틸렌 클로라이드 등이 사용될 수 있다. 이들 용매는 단독으로 혹은 2가지 이상이 함께 사용될 수 있다. 용매의 사용양은 특히 한정하는 것은 아니며, 반응물이 충분히 용해되고 반응에 바람직하지 않은 영향을 미치지 않는 범위에서 적합한 양으로 사용될 수 있으며, 이 기술분야의 기술자는 이를 고려하여 적합하게 선택할 수 있다.
In the second reaction step, a solvent may optionally be used as necessary. For example, in the second reaction step, if the amount of epichlorohydrin is an amount sufficient to dissolve the reactants without a separate solvent, a separate solvent may not be used. In the case of using a solvent, a possible solvent may dissolve the reactant well, and any organic solvent may be used as long as it can be easily removed after the reaction without adversely affecting the reaction, and this is not particularly limited, for example. , Acetonitrile, THF (tetra hydrofuran), MEK (methyl ethyl ketone), DMF (dimethyl formamide), DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), methylene chloride and the like can be used. These solvents may be used alone or in combination of two or more. The amount of the solvent to be used is not particularly limited, and may be used in a suitable amount within a range in which the reactants are sufficiently dissolved and do not adversely affect the reaction, and those skilled in the art may select appropriately in consideration of this.
상기 제 2 반응 단계에서 염기로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, KOH, NaOH, K2CO3, KHCO3, NaH, 트리에틸아민, 디이소프로필에틸 아민이 사용될 수 있다. 이들 염기는 단독으로 혹은 2가지 이상의 함께 사용될 수 있으며, 염기는 알칸디일 사슬로 연결된 나프탈렌 1 당량에 대하여 2 당량 내지 5 당량으로 사용하는 것이 반응효율 측면에서 좋다.
The base in the second reaction step is not limited thereto, and for example, KOH, NaOH, K 2 CO 3 , KHCO 3 , NaH, triethylamine, diisopropylethyl amine can be used. These bases may be used alone or in combination of two or more thereof. It is preferable to use the bases in an amount of 2 to 5 equivalents based on 1 equivalent of naphthalene linked by an alkanediyl chain.
상기 제 1 단계 반응 및 제 2 단계 반응의 반응스킴의 예는 하기 반응식 1과 같다. Examples of the reaction scheme of the first step reaction and the second step reaction are shown in Scheme 1 below.
[반응식 1]Scheme 1
(1) 제 1 단계
(1) first step
(X는 Cl, Br, 또는 I의 할로겐원자 혹은 -O-SO2-CH3의 좋은 이탈기이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수, 바람직하게는 1 내지 3의 정수임.)
(X is a halogen atom of Cl, Br, or I or a good leaving group of -O-SO 2 -CH 3 , n is an integer of 1 to 10, preferably an integer of 1 to 3.)
(2) 제 2 단계 (2) second stage
(n은 1 내지 10의 정수, 바람직하게는 1 내지 3의 정수임.)
(n is an integer from 1 to 10, preferably an integer from 1 to 3.)
본 발명의 다른 구현에 의하면, 본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지; 무기 필러; 및 경화제를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체가 제공된다. 즉, 본 발명의 구현에 의하면, 에폭시 수지, 무기필러 및 경화제를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 있어서, 에폭시 수지로서 본 발명에 의한 상기 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 에폭시 수지 복합체가 제공된다. 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지 복합체는 본 발명에 의한 화학식 3의 에폭시 수지가 사용됨을 기술적 특징으로 하는 것으로 무기필러, 경화제 및 기타 첨가제로는 종래 이 기술분야에 알려져 있는 물질이 이 기술분야에 일반적으로 사용되는 함량으로 배합될 수 있으며, 이들의 종류 및 함량이 한정되는 것은 아니다.
According to another embodiment of the present invention, a novel epoxy resin according to the present invention; Inorganic fillers; And an epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising a curing agent is provided. That is, according to the embodiment of the present invention, in the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising an epoxy resin, an inorganic filler and a curing agent, an epoxy resin composite comprising the epoxy resin of the formula (3) according to the present invention as an epoxy resin is provided. . The epoxy resin composite according to the present invention is characterized in that the epoxy resin of the general formula (3) according to the present invention is used. As the inorganic filler, the curing agent, and other additives, materials known in the art are generally used in the art. It may be formulated in an amount that is, and the kind and content thereof are not limited.
본 발명에 의한 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 상기 새로운 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 것으로, 새로운 에폭시 수지의 낮은 용융점도로 인하여 보다 많은 양의 무기 필러와 배합될 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 무기 필러가 엉기지 않고 고르게 분산 및 혼합되는 우수한 공정가공성을 나타낸다.
The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation according to the present invention includes the new epoxy resin, which can be blended with a larger amount of inorganic filler due to the low melt viscosity of the new epoxy resin, and the inorganic filler is dispersed evenly without tangling. And excellent processability to be mixed.
또한, 본 명세서에서 사용된 용어 "에폭시 수지 복합체"는 에폭시 수지, 무기 필러 및 경화제 뿐만 아니라, 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체에 필요에 따라 일반적으로 배합될 수 있는 성분으로 알려져 있는 어떠한 임의의 첨가제 등을 포함하는 경화반응 전 및 후의 조성물을 모두 포함하는 광범위한 의미로 사용된다.
In addition, the term "epoxy resin composite" as used herein refers to epoxy resins, inorganic fillers, and curing agents, as well as any optional additives known as components that can be generally formulated into epoxy resin composites for semiconductor encapsulation. It is used in a broad sense including both before and after curing reactions.
상기 무기 필러로는 반도체 봉지용 수지 복합체에 일반적으로 사용되는 것으로 알려져 있는 어떠한 무기 필러가 사용될 수 있다. 무기 필러로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 실리카 (결정성 실리카 및 용융 실리카 포함), 지르코니아, 티타니아, 알루미나, 질화규소, 질화알루미나, 중질탄산칼슘, 연질탄산칼슘, Ba2SO4, Al(OH)3, Mg(OH)2, 탈크(talc), 마이카(mica), 제올라이트, 티탄산 칼륨, 붕산알루미늄, 또는 이들을 포함하는 혼합된 금속산화물(예를들어, 실리카-Zr 산화물) 및 실세스퀴녹산 등이 단독으로 또는 2종 이상의 혼합물로 사용될 수 있다. 상기 실세스퀴녹산(silsesquioxane)은 케이지(cage)형, T-10형, 래더(ladder)형이 있으며, 이들은 본 발명에서 모두 사용될 수 있다.
As the inorganic filler, any inorganic filler known to be generally used in a resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation may be used. Inorganic fillers include, but are not limited to, for example, silica (including crystalline silica and fused silica), zirconia, titania, alumina, silicon nitride, alumina nitride, heavy calcium carbonate, soft calcium carbonate, Ba 2 SO 4 , Al (OH) 3 , Mg (OH) 2 , talc, mica, zeolite, potassium titanate, aluminum borate, or mixed metal oxides (eg, silica-Zr oxides) and silses comprising them Quinoxane or the like may be used alone or in a mixture of two or more thereof. The silsesquioxane (silsesquioxane) is a cage (cage), T-10 type, ladder (ladder) type, these can all be used in the present invention.
상기 무기 필러로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 복합체의 사용용도, 구체적으로는 무기 필러의 분산성 등을 고려하여, 입자크기가 0.5㎚ 내지 수십 ㎛인 무기 필러가 사용될 수 있다. 무기 필러는 에폭시 수지에 분산되므로 입자크기에 따른 분산성의 차이로 인하여 상기한 크기의 무기 필러가 사용되는 것이 바람직하다.
The inorganic filler is not limited thereto, but an inorganic filler having a particle size of 0.5 nm to several tens of micrometers may be used in consideration of the use of the composite, specifically, the dispersibility of the inorganic filler. Since the inorganic filler is dispersed in the epoxy resin, it is preferable to use the inorganic filler of the above size due to the difference in dispersibility according to the particle size.
본 발명에 의한 에폭시 조성물 중 에폭시 수지와 무기필러의 혼합 중량을 기준으로 성형성, 저응력성, 고온강도 등의 물성에 따라 다르지만, 에폭시 수지 5중량% 내지 70중량%, 바람직하게는 5중량% 내지 50중량% 및 무기필러 30중량% 내지 95중량%, 바람직하게는 50중량% 내지 95중량%로 배합될 수 있다. 무기 필러의 배합량이 30중량% 미만이면 복합체의 유리전이온도 상승 및 내열성 개선이 불충분하다는 점에서 바람직하지 않고, 95중량%을 초과하면 복합체의 점도가 상승하여 가공성이 크게 감소한다는 점에서 바람직하지 않다.
Depending on the physical properties such as moldability, low stress, high temperature strength, etc., based on the mixed weight of the epoxy resin and the inorganic filler in the epoxy composition according to the present invention, 5 wt% to 70 wt% of the epoxy resin, preferably 5 wt% To 50% by weight and inorganic filler 30% to 95% by weight, preferably 50% to 95% by weight. If the amount of the inorganic filler is less than 30% by weight, it is not preferable in that the glass transition temperature and the heat resistance improvement of the composite are insufficient, and in the case of more than 95% by weight, the viscosity of the composite is increased and the workability is greatly reduced. .
경화제로는 에폭시 수지 경화제로 일반적으로 알려져 있는 어떠한 경화제가 사용될 수 있다. 이로써 특히 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 아민계 경화제, 페놀계 경화제, 무수산화물계 경화제 등이 사용될 수 있다. 보다 구체적으로, 아민계 경화제로는 지방족 아민, 지환족 아민, 방향족 아민, 기타 아민 및 변성폴리아민을 사용할 수 있으며, 2개 이상의 일차 아민기를 포함하는 아민 화합물을 사용할 수 있다. 상기 아민 경화제의 구체적인 예로는 4,4'-디메틸아닐린(디아미노 디페닐 메톤) (4,4'-Dimethylaniline(diamino diphenyl methone, DAM 또는 DDM), 디아미노 디페닐설폰(diamino diphenyl sulfone, DDS), m-페닐렌 디아민(m-phenylene diamine)로 구성되는 그룹으로부터 선택된 1종 이상의 방향족 아민, 디에틸렌트리아민(diethylene triamine, DETA), 디에틸렌테트라아민(diethylene tetramine), 트리에틸렌테트라아민(triethylene tetramine, TETA), m-자일렌 디아민(m-xylene diamine, MXDA), 메탄 디아민(methane diamine, MDA), N,N'-디에틸에틸렌디아민(N,N'-diethylenediamine, N,N'-DEDA), 테트라에틸렌펜타아민(tetraethylenepentamine, TEPA), 및 헥사메틸렌디아민(hexamethylenediamine)로 구성되는 그룹으로부터 선택된 최소 1종 이상의 지방족 아민, 이소포론 디아민(isophorone diamine, IPDI), N-아미노에틸 피페라진(N-aminoethyl piperazine, AEP), 비스 (4-아미노 3-메틸시클로헬실)메탄(bis(4-amino 3-methylcyclohexyl)methane, Larominc 260)로 구성되는 그룹으로부터 선택된 1종 이상의 지환족아민, 디시안디아미드(DICY) 등과 같은 기타 아민, 폴리아미드계, 에폭사이드계등의 변성아민을 들 수 있다.
As the curing agent, any curing agent generally known as an epoxy resin curing agent may be used. Although it does not specifically limit by this, For example, an amine hardening | curing agent, a phenol type hardening | curing agent, an anhydride type hardening | curing agent, etc. can be used. More specifically, as the amine curing agent, aliphatic amines, cycloaliphatic amines, aromatic amines, other amines and modified polyamines may be used, and amine compounds including two or more primary amine groups may be used. Specific examples of the amine curing agent include 4,4'-dimethylaniline (diamino diphenyl metone) (4,4'-Dimethylaniline (diamino diphenyl methone, DAM or DDM), diamino diphenyl sulfone (DDS) , at least one aromatic amine selected from the group consisting of m-phenylene diamine, diethylene triamine (DETA), diethylene tetramine, triethylene tetraamine tetramine, TETA), m-xylene diamine (MXDA), methane diamine (MDA), N, N'-diethylenediamine (N, N'- DEDA), tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA), and at least one aliphatic amine selected from the group consisting of hexamethylenediamine, isophorone diamine (IPDI), N-aminoethyl piperazine ( N-aminoethyl piperazine, AEP), bis (4-ami One or more alicyclic amines selected from the group consisting of 3-methylcyclohexyl) methane (bis (4-amino 3-methylcyclohexyl) methane, Larominc 260), dicyandiamide (DICY), and other amines, polyamides, And modified amines such as epoxides.
상기 아민 경화제는 에폭시기와의 반응으로 복합체의 경화도를 조절할 수 있으며, 목적하는 경화도 범위에 따라 에폭시 수지의 에폭시기의 농도를 기준으로 하여 아민 경화제의 함량을 조절할 수 있다. 특히, 상기 아민 경화제와 에폭시 그룹의 당량(equivalent) 반응에서는 에폭시기 2개당 1개의 아민기가 정량 농도로서, 당량 반응에서는 아민 경화제는 에폭시기[epoxy group]/아민기[NH2]의 몰비가 2/1이 되는 농도비로 사용할 수 있다. 따라서, 본 발명에서 상기 아민 경화제의 함량은 상기 에폭시 수지의 에폭시기를 기준으로 에폭시기[epoxy group]/아민기[NH2]의 몰비가 0.5 내지 3.0이 될 수 있도록, 바람직하게는 1.0 내지 2.5이 될 수 있도록 조절하여 사용하는 것이 바람직하다.
The amine curing agent may adjust the degree of curing of the composite by reaction with an epoxy group, and may adjust the content of the amine curing agent based on the concentration of the epoxy group of the epoxy resin according to the desired degree of curing. In particular, in the equivalent reaction of the amine curing agent and the epoxy group, one amine group per two epoxy groups is a quantitative concentration, and in the equivalent reaction, the amine curing agent has a molar ratio of epoxy group / amine group [NH 2 ] of 2/1. It can be used in the concentration ratio which becomes. Therefore, the content of the amine curing agent in the present invention is preferably 1.0 to 2.5 so that the molar ratio of the epoxy group [epoxy group] / amine group [NH 2 ] to 0.5 to 3.0 based on the epoxy group of the epoxy resin. It is preferable to use it so that it can be adjusted.
이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 페놀계 경화제의 예로는 페놀노볼락, 디시클로펜타디엔-페놀 노볼락(DCPD-페놀), 크레졸 노볼락, 페놀 p-자일렌 수지, 페놀 4,4'-디메틸비페닐렌 수지, 페놀 디시클로펜타디엔 수지, 자일록(xylok), 비페닐계 페놀수지, 나프탈렌계 페놀 수지 등을 들 수 있다.
Examples of the phenol-based curing agent include, but are not limited to, phenol novolac, dicyclopentadiene-phenol novolac (DCPD-phenol), cresol novolac, phenol p- xylene resin, phenol 4,4'-dimethylbiphenyl Lene resins, phenol dicyclopentadiene resins, xylok, biphenyl phenol resins, naphthalene phenol resins, and the like.
이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 무수산화물계 경화제의 예로는 도데세닐 숙신산 무수물(dodecenyl succinic anhydride, DDSA), 폴리 아젤라익 폴리 안하이드리드(poly azelaic poly anhydride)등과 같은 지방족 무수산화물, 헥사하이드로프탈릭 안하이드리드(hexahydrophthalic anhydride, HHPA), 메틸 테트라하이드로프탈릭 안하이드리드(methyl tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, MeTHPA), 메틸나딕 안하이드리드(methylnadic anhydride, MNA) 등과 같은 지환족 무수산화물, 트리멜리트 안하이드리드(trimellitic anhydride, TMA), 피로멜리트산 디안하이드리드(pyromellitic acid dianhydride, PMDA), 벤조페논테트라카르복시산 디안하이드리드(benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride, BTDA) 등과 같은 방향족 무수산화물, 테트라브로모프탈릭 안하이드리드(tetrabromophthalic anhydride, TBPA), 클로렌딕 안하이드리드(chlorendic anhydride, HET)등과 같은 할로겐계 무수화합물 등을 들 수 있다.
Although not limited thereto, examples of the anhydride-based curing agent include aliphatic anhydrides such as dodecenyl succinic anhydride (DDSA), poly azelaic poly anhydride, and hexahydrophthalic. Hexahydrophthalic anhydride, Cycloaliphatic anhydrides such as HHPA), methyl tetrahydrophthalic anhydride (MeTHPA), methylnadic anhydride (MNA), trimellitic anhydride (TMA), Aromatic anhydrides such as pyromellitic acid dianhydride (PMDA), benzophenonetetracarboxylic dianhydride (BTDA), tetrabromophthalic anhydride (TBPA), chlorendic acid And halogen-based anhydrides such as chlorendic anhydride (HET).
나아가, 상기 본 발명의 에폭시 수지 복합체는 필요로 하는 물성을 개선하기 위해, 실란커플링제, 촉매, 이형제, 착색제, 저응력 첨가제, 난연제 등 반도체 봉지용 수지 복합체에 일반적으로 배합되는 것으로 알려져 있는 어떠한 첨가제가 필요에 따라 물성을 개선하기 위해 사용될 수 있다. 이러한 임의의 첨가제의 배합비는 특히 한정하는 것은 아니며, 이 기술분야에서 일반적으로 배합가능한 양으로 알려져 있는 범위에서 복합체의 물성 개선에 적합한 양으로 배합될 수 있다. 구체적으로 예를들면, 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 상기 첨가제는 다른 성분과의 상용성 및 작용,효과를 고려하여 에폭시 수지에 대하여 20phr(parts per hundred, 에폭시 수지 100중량부당의 중량부)이하로 필요에 따라 배합될 수 있다. 이러한 첨가제는 필요에 따라 임의로 배합될 수 있는 성분으로 하한값은 한정되지 않는다.
In addition, the epoxy resin composite of the present invention, in order to improve the required physical properties, any additives generally known to be compounded in a semiconductor encapsulating resin composite such as a silane coupling agent, a catalyst, a release agent, a colorant, a low stress additive, a flame retardant May be used to improve physical properties as necessary. The blending ratio of such optional additives is not particularly limited, and may be blended in an amount suitable for improving physical properties of the composite in the range known in the art as general blendable amount. Specifically, for example, but not limited thereto, the additive is required to be 20 phr (parts per hundred) per 100 parts by weight of epoxy resin in consideration of compatibility, function, and effect with other components. It can be combined according to. These additives are components which can be optionally blended as necessary, and the lower limit thereof is not limited.
실란커플링제는 무기필러와 고분자간의 계면결합력을 향상시키기 위해 사용되는 것으로, 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 비닐트리에톡시실란, 아미노프로필트리에톡시실란, 글리시독시프로필트리메톡시실란, 메르캅토프로필트리메톡시실란 등이 사용될 수 있다.
The silane coupling agent is used to improve the interfacial bonding force between the inorganic filler and the polymer, but is not limited thereto. For example, vinyltriethoxysilane, aminopropyltriethoxysilane, glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane , Mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane and the like can be used.
촉매로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 트리페닐포스핀, 디메틸 벤질 아르닌(dimethyl benzyl arnine, BDMA), 2,4,6-트리스(디메틸아미노메틸)페놀(2,4,6-tris(dimethylaminomethyl)phenol, DMP-30)등과 같은 3급 아민, 1-메틸이미다졸, 2-메틸이미다졸(2MZ), 2-에틸-4-메틸-이미다졸(2E4M), 1-부틸-2-메틸 이미다졸, 2-헵타데실이미다졸(heptadecylimidazole, 2HDI) 등과 같은 이미다졸, 디아자비시클로운데센(diazabicycloundecene, DBU) 등과 같은 3급아민류, BF3-모노에틸 아민(BF3-MEA) 등과 같은 루이스산을 들 수 있다. 이형제로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 카르나바 왁스 등의 천연 왁스, 폴리에틸렌 왁스 등의 합성 왁스, 스테아린산이나 스테아린산아연 등의 고급 지방산 혹은 그 금속염, 또는 파라핀 등이 사용될 수 있다. 착색제로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 카본 블랙, 벵갈라 등이 사용될 수 있다. 저응력 첨가제로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 실리콘 오일, 실리콘 고무 등이 사용될 수 있다. 난연제로는 이로써 한정하는 것은 아니지만, 예를들어, 수산화알루미늄, 수산화마그네슘 등의 금속 수산화물, 붕산아연, 몰리브덴산 아연, 포스파젠 등이 사용될 수 있다.
Examples of the catalyst include, but are not limited to, triphenylphosphine, dimethyl benzyl arnine (BDMA), 2,4,6-tris (dimethylaminomethyl) phenol (2,4,6- tertiary amines such as tris (dimethylaminomethyl) phenol, DMP-30), 1-methylimidazole, 2-methylimidazole (2MZ), 2-ethyl-4-methyl-imidazole (2E4M), 1-butyl Tertiary amines such as 2-methyl imidazole, 2-heptadecylimidazole (2HDI), diazabicycloundecene (DBU), and the like, BF3-monoethyl amine (BF3-MEA) Lewis acids, such as these, etc. are mentioned. Examples of the release agent include, but are not limited to, natural waxes such as carnava wax, synthetic waxes such as polyethylene wax, higher fatty acids such as stearic acid and zinc stearate, metal salts thereof, and paraffin. Examples of the colorant include, but are not limited to, carbon black, bengal and the like. The low stress additives include, but are not limited to, silicone oil, silicone rubber, and the like, for example. Examples of the flame retardant include, but are not limited to, metal hydroxides such as aluminum hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide, zinc borate, zinc molybdate, phosphazene and the like.
본 발명의 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 에폭시 수지, 무기 필러, 경화제 및 기타 첨가제 등을 예를들어 믹서 등을 이용하여 상온에서 균일하게 혼합하고, 그 후 필요에 따라 가열 롤, 니더 또는 압출기 등의 혼련기를 이용하여 용융 혼련하고, 계속해서 냉각, 분쇄함으로써 얻을 수 있다. 이 수지 조성물의 분산도나 유동성 등은 필요에 따라 조정할 수 있다.
The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation of the present invention is uniformly mixed with an epoxy resin, an inorganic filler, a curing agent and other additives at room temperature using a mixer, for example, and then, if necessary, such as a heating roll, a kneader or an extruder It can obtain by melt-kneading using a kneading machine, and then cooling and pulverizing. Dispersion degree, fluidity | liquidity, etc. of this resin composition can be adjusted as needed.
본 발명에 의한 새로운 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 상기 에폭시 수지의 유연한 알칸디일 연결구조(moiety)에 의해 우수한 배향성 및 낮은 용융점도를 그리고 단단한 결정성 코어 나프탈렌의 대칭구조로 인한 상온 결정성 및 우수한 내열성을 나타낸다. 낮은 용융점도로 인하여 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체 제조시 공정성이 개선될 뿐만 아니라, 이로 봉지된 반도체 장치의 신뢰성, 구체적으로는 미세한 간극 사이의 충진성이 개선된다.
The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising the new epoxy resin according to the present invention has excellent orientation and low melt viscosity due to the flexible alkanediyl moiety of the epoxy resin and due to the symmetrical structure of the hard crystalline core naphthalene. It exhibits room temperature crystallinity and excellent heat resistance. The low melt viscosity not only improves the processability in manufacturing the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, but also improves the reliability of the encapsulated semiconductor device, specifically the filling between fine gaps.
반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체는 새로운 에폭시 수지의 강한 소수성 나프탈렌 구조와 알칸디일 연결 구조로 인하여 우수한 내흡습성을 나타내며, 따라서, 우수한 내리플로우성을 나타낸다.
The epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation shows excellent hygroscopicity due to the strong hydrophobic naphthalene structure and the alkanediyl linking structure of the new epoxy resin, and thus shows excellent reflow resistance.
또한, 나프탈렌 구조의 강직성 및 필러의 고충진으로 인하여 낮은 열팽창계수, 즉, 개선된 열팽창특성을 나타내며, 이로 인하여, 반도체 장치의 크랙 생성기판의 휨 발생, 코팅층의 박리(peeling-off), 기판 깨짐 등 제품불량이 감소되고 제품의 신뢰성이 개선된다.
In addition, due to the stiffness of the naphthalene structure and the high filling of the filler, it exhibits a low coefficient of thermal expansion, i.e., improved thermal expansion characteristics, and as a result, warpage of the crack generating substrate of the semiconductor device, peeling-off of the coating layer, and cracking of the substrate Product defects are reduced and product reliability is improved.
본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지 복합체를 사용하여 봉지할 수 있는 반도체 소자로는 특별히 한정되지 않으나, 예를 들어 집적회로, 대규모 집적회로, 트랜지스터, 사이리스터, 다이오드, 고체 촬상 소자 등을 들 수 있다. 본 발명의 반도체 장치의 형태로는 특별히 한정되지 않지만, 예를 들어 듀얼·인라인·패키지(DIP), 플라스틱·리드부착 칩·캐리어(PLCC), 쿼드·플랫·패키지(QFP), 스몰·아웃라인·패키지(S0P), 스몰·아웃라인-J리드·패키지(S0J), 박형 스몰·아웃라인·패키지(TS0P), 박형 쿼드·플랫·패키지(TQFP), 테이프·캐리어·패키지(TCP), 볼·그리드·어레이(BGA), 칩·사이즈·패키지(CSP) 등을 들 수 있다.
Although it does not specifically limit as a semiconductor element which can be sealed using the epoxy resin composite by this invention, For example, an integrated circuit, a large scale integrated circuit, a transistor, a thyristor, a diode, a solid-state image sensor, etc. are mentioned. Although it does not specifically limit as the form of the semiconductor device of this invention, For example, a dual inline package (DIP), the plastic lead chip carrier (PLCC), the quad flat package (QFP), the small outline Package (S0P), Small Outline-J Lead Package (S0J), Thin Small Outline Package (TS0P), Thin Quad Flat Package (TQFP), Tape Carrier Package (TCP), Ball A grid array (BGA), a chip size package (CSP), etc. are mentioned.
이하, 실시예를 통하여 본 발명을 보다 상세히 설명한다. 다만, 하기 실시예는 본 발명의 예시하는 것으로 이로써 본 발명을 한정하는 것은 아니다.
Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in more detail by way of examples. However, the following examples are intended to illustrate the present invention, which does not limit the present invention.
실시예 1: 새로운 에폭시 수지의 합성 Example 1 Synthesis of New Epoxy Resin
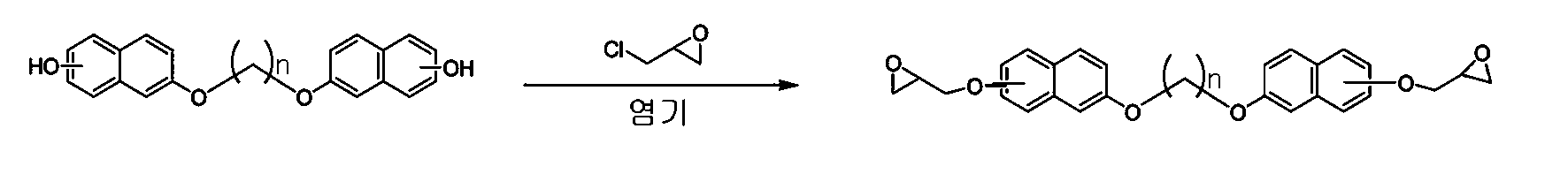
플라스크에 디히드록시 나프탈렌 48g, K2CO3 10g, 및 DMF (dimethyl formamide) 300㎖을 넣고 균일한 용액이 되도록 상온에서 5분간 교반하였다. 그 후, 상기 용액에 디브로모프로판 20g을 첨가하고, 23시간동안 상온에서 반응시켰다. 반응 완료 후, 반응용매를 휘발시킨 다음에 얻어지는 고형분을 메탄올을 이용하여 재결정하여 디히드록시 나프탈렌 이합체를 얻었다.
48 g of dihydroxy naphthalene, 10 g of K 2 CO 3 , and 300 ml of DMF (dimethyl formamide) were added to the flask and stirred for 5 minutes at room temperature to obtain a uniform solution. Thereafter, 20 g of dibromopropane was added to the solution, and the mixture was reacted at room temperature for 23 hours. After completion of the reaction, the reaction solvent was volatilized, and the obtained solid was recrystallized from methanol to obtain a dihydroxy naphthalene dimer.
얻어진 디히드록시 나프탈렌 이합체 36g을 다시 DMF 500㎖에 녹인 다음에, 아이스 배스(ice bath)에서 NaH 10g을 천천히 추가하였다. NaH 첨가가 완료 후, 반응기의 온도를 상온으로 올린 후 에피클로로히드린 100g을 넣고 상온에서 23시간 반응시켰다. 반응 완료 후, 고형분을 메탄올에 재침전시켜서 새로운 나프탈렌계 이합체 에폭시 수지를 얻었다. 반응 스킴을 하기 반응식 2에 나타내었다.
36 g of the obtained dihydroxy naphthalene dimer was dissolved in 500 ml of DMF again, and then 10 g of NaH was slowly added in an ice bath. After the NaH addition was completed, the temperature of the reactor was raised to room temperature, 100 g of epichlorohydrin was added thereto, and the reaction was performed at room temperature for 23 hours. After completion of the reaction, the solid content was reprecipitated in methanol to obtain a new naphthalene dimer epoxy resin. The reaction scheme is shown in Scheme 2 below.
1H NMR (500MHz, CDCl3): δ2.39 (t, 2H), 2.51 (m, 2H), 2.94 (m, 2H), 3.43 (m, 2H), 4.05 (m, 2H), 4.33 (m, 6H), 7.03-7.11 (m, 8H), 7.65-7.68 (d, 4H)
1 H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ 2.39 (t, 2H), 2.51 (m, 2H), 2.94 (m, 2H), 3.43 (m, 2H), 4.05 (m, 2H), 4.33 (m , 6H), 7.03-7.11 (m, 8H), 7.65-7.68 (d, 4H)
[반응식 2] Scheme 2
실시예 2: 새로운 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 복합체의 제조 Example 2 Preparation of Composites Comprising New Epoxy Resin
실시예 1에서 제조된 에폭시 수지 1g, 페놀계 경화제 (HF-1M, 상품명, Meiwa Kasei Co) 0.36g, 및 트리페닐포스핀 0.02g을 120℃에서 용융혼합(melt mixing)으로 균일하게 혼합하였다. 제조된 혼합물을 120℃로 예열된 진공 오븐에서 넣고 버블을 제거 한 후, 120℃로 예열된 몰드에 부었다. 그 후, 150℃에서 2시간, 200℃에서 2시간 동안 반응시킨 다음에 온도를 올려서 230℃에서 2시간 동안 추가 경화 반응을 시켜서, 경화된 에폭시 수지 복합체를 얻었다.
1 g of the epoxy resin prepared in Example 1, 0.36 g of a phenolic curing agent (HF-1M, trade name, Meiwa Kasei Co), and 0.02 g of triphenylphosphine were uniformly mixed at 120 ° C. by melt mixing. The prepared mixture was placed in a vacuum oven preheated to 120 ° C., bubbles were removed, and then poured into a mold preheated to 120 ° C. Thereafter, the reaction was carried out at 150 ° C. for 2 hours and at 200 ° C. for 2 hours, and then the temperature was increased to undergo an additional curing reaction at 230 ° C. for 2 hours to obtain a cured epoxy resin composite.
비교예 1 : 비페닐 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 복합체 제조 Comparative Example 1 : Preparation of a Composite Comprising Biphenyl Epoxy Resin
상기 화학식 2의 비페닐 에폭시 수지 1g, 페놀계 경화제 (HF-1M, 상품명, Meiwa Kasei Co) 0.58g, 및 트리페닐포스핀 0.02g을 120℃에서 용융혼합(melt mixing)으로 균일하게 혼합하였다. 제조된 혼합물을 120℃로 예열된 진공 오븐에서 넣고 버블을 제거 한 후, 120℃로 예열된 몰드에 부었다. 그 후, 150℃에서 2시간, 200℃에서 2시간 동안 반응시킨 다음에 온도를 올려서 230℃에서 2시간 동안 추가 경화 반응을 시켜서, 경화된 에폭시 수지 복합체를 얻었다.
1 g of the biphenyl epoxy resin of Formula 2, 0.58 g of a phenol-based curing agent (HF-1M, trade name, Meiwa Kasei Co), and 0.02 g of triphenylphosphine were uniformly mixed at 120 ° C. by melt mixing. The prepared mixture was placed in a vacuum oven preheated to 120 ° C., bubbles were removed, and then poured into a mold preheated to 120 ° C. Thereafter, the reaction was carried out at 150 ° C. for 2 hours and at 200 ° C. for 2 hours, and then the temperature was increased to undergo an additional curing reaction at 230 ° C. for 2 hours to obtain a cured epoxy resin composite.
물성평가 1: 에폭시 수지의 결정성 평가 Physical property evaluation 1 : crystallinity evaluation of epoxy resin
실시예 1에서 합성된 에폭시 수지의 상온 결정성 여부 및 용융온도는 차등주사열량계(Differential Scanninig Calorimetry, DSC)를 이용한 히트 플로우(heat flow)로 측정으로 평가하였다. 0℃ 내지 200℃의 측정구간에서 10℃/min의 속도로 측정하였으며, 결과를 도 2에 나타내었다. 도 2에서 알 수 있듯이, 에폭시 수지는 약 110℃ 부근에서 열을 흡수하여 용융됨을 나타내었다. 즉, 에폭시 수지의 용융 온도는 약 110℃ 이었다. 이로부터 실시예 1에서 합성된 에폭시 수지는 상온에서 결정성이며, 반도체 공정온도에서 용융되어 낮은 점도를 나타냄을 알 수 있다.
The crystallinity and melting temperature of the epoxy resin synthesized in Example 1 were evaluated by heat flow measurement using a differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). In the measurement interval of 0 ℃ to 200 ℃ was measured at a rate of 10 ℃ / min, the results are shown in FIG. As can be seen in FIG. 2, the epoxy resin absorbed heat at about 110 ° C. and melted. That is, the melting temperature of the epoxy resin was about 110 degreeC. It can be seen that the epoxy resin synthesized in Example 1 is crystalline at room temperature, and melts at a semiconductor process temperature to exhibit low viscosity.
물성평가 2: 경화특성 평가 Physical property evaluation 2 : evaluation of hardening properties
차등주사열량계를 이용한 히트 플로우(heat flow)로 측정으로 실시예 2의 에폭시 수지 복합체에서 에폭시 수지와 경화제의 상용성 및 경화조건을 평가하였다. 0℃ 내지 300℃의 측정구간에서 10℃/min의 속도로 측정하였으며, 결과를 도 3에 나타내었다. 도 3에 나타낸 바와 같이, 약 150℃ 부근에서 발열이 측정되었으며 이로부터 에폭시 수지의 다른 첨가제가 함께 반응하여 복합체(경화물)를 형성함을 알 수 있다. 또한, 경화제와 에폭시 수지의 상용성 부재시 나타나는 도 2에 나타낸 바와 같은 에폭시 수지의 결정성 피크(에폭시 수지의 용융피크)가 관찰되지 않았다. 이로부터 150℃ 부근에서 경화반응이 잘 진행됨을 알 수 있다.
The compatibility and curing conditions of the epoxy resin and the curing agent in the epoxy resin composite of Example 2 were evaluated by heat flow measurement using a differential scanning calorimeter. In the measurement interval of 0 ℃ to 300 ℃ was measured at a rate of 10 ℃ / min, the results are shown in FIG. As shown in FIG. 3, the exotherm was measured around 150 ° C. from which it can be seen that other additives of the epoxy resin react together to form a composite (cured product). In addition, no crystalline peak of the epoxy resin (melt peak of the epoxy resin) as shown in Fig. 2 appeared in the absence of compatibility between the curing agent and the epoxy resin. From this it can be seen that the curing reaction proceeds well around 150 ℃.
물성평가 3: 흡습특성 평가 Physical property evaluation 3 : moisture absorption evaluation
실시예 2 및 비교예 1에서 제조된 에폭시 수지 복합체에 물방울을 떨어뜨린 후, 수지복합체와 물방울 사이의 접촉각(Drop shape Analysis system)을 측정하여 에폭시 수지 복합체의 흡습성을 평가하였다. 실시예 2의 에폭시 수지 복합체의 접촉각(contact angle) 은 88°였으며, 비교예 1의 에폭시 수지 복합체의 접촉각은 81 °였다. 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 실시예 2의 수지 복합체가 기존의 바이페닐계 에폭시 수지 복합체인 비교예 1 보다 큰 접촉각을 나타내었으며 이로부터 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 실시예 2의 복합체가 우수한 내흡습성을 나타냄을 알 수 있다. 이러한 실시예 2의 에폭시 수지 복합체의 우수한 내흡습성은 내흡습성이 우수한 나프탈렌 코아가 OH기가 없는 스페이서를 통하여 연결된 구조에 기인된 것으로 판단된다.
After dropping water droplets on the epoxy resin composites prepared in Example 2 and Comparative Example 1, the hygroscopicity of the epoxy resin composite was evaluated by measuring a drop shape analysis system between the resin composite and the droplets. The contact angle of the epoxy resin composite of Example 2 was 88 ° and the contact angle of the epoxy resin composite of Comparative Example 1 was 81 °. The resin composite of Example 2 containing the epoxy resin according to the present invention exhibited a larger contact angle than that of Comparative Example 1, which is a conventional biphenyl epoxy resin composite, from which the composite of Example 2 containing the epoxy resin according to the present invention. It can be seen that exhibits excellent hygroscopicity. The excellent hygroscopicity of the epoxy resin composite of Example 2 is believed to be due to the structure in which naphthalene cores having excellent hygroscopicity are connected through a spacer free of OH groups.
물성평가 4: 열팽창특성 평가 Physical property evaluation 4 : evaluation of thermal expansion characteristics
실시예 2 및 비교예 1에서 제조된 에폭시 수지 복합체의 열팽창 특성을 TMA(Thermo-mechanical Aanlysizer, Expansion mode, Force 0.03N)에 의한 에폭시 수지 복합체의 치수변화(dimensional change)로 평가하였으며, 측정된 열팽창계수(CTE)(Tg이하에서의 열팽창계수 α1)를 하기 표 1에 나타내었다. 샘플은 너비×길이×두께를 5×5×3(㎣)의 크기로 제조하였다.
The thermal expansion characteristics of the epoxy resin composites prepared in Example 2 and Comparative Example 1 were evaluated by dimensional change of the epoxy resin composite by TMA (Thermo-mechanical Aanlysizer, Expansion mode, Force 0.03N), and measured thermal expansion. The coefficient (CTE) (coefficient of thermal expansion α 1 below Tg) is shown in Table 1 below. Samples were prepared in a size of width x length x thickness of 5 x 5 x 3 (mm 3).
상기 표 1에서 알 수 있듯이, 본 발명에 의한 에폭시 수지를 포함하는 실시예 2의 복합체(경화물)은 비교예 1의 바이페닐계 에폭시 수지 복합체에 비하여 낮은 CTE를 나타내며, 이로부터 내열특성 및 치수안정성이 개선됨을 알 수 있다. As can be seen in Table 1, the composite (cured) of Example 2 containing the epoxy resin according to the present invention shows a lower CTE than the biphenyl-based epoxy resin composite of Comparative Example 1, from which the heat resistance and dimensions It can be seen that the stability is improved.
Claims (5)
[화학식 3]
(상기 식에서 A는
[화학식 4-1]
혹은
[화학식 4-2]
(단, 상기 화학식 4-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다.)이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수이다.)
An epoxy resin represented by the following formula (3).
(3)
Where A is
[Formula 4-1]
or
[Formula 4-2]
(Wherein R is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group), and n is an integer of 1 to 10.
(상기 식에서 A는
[화학식 4-1]
혹은
[화학식 4-2]
(단, 상기 화학식 4-2에서 R은 단일결합 또는 C1 내지 C5 알칸디일 그룹이다.)이며, n은 1 내지 10의 정수이다.)
무기 필러; 및
경화제를 포함하는 반도체 봉지용 에폭시 수지 복합체.
Epoxy resin represented by the following formula (3);
Where A is
[Formula 4-1]
or
[Formula 4-2]
(Wherein R is a single bond or a C1 to C5 alkanediyl group), and n is an integer of 1 to 10.
Inorganic fillers; And
An epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprising a curing agent.
The method of claim 2, wherein the inorganic filler is silica, zirconia, titania, alumina, silicon nitride, alumina nitride, heavy calcium carbonate, soft calcium carbonate, Ba 2 SO 4 , Al (OH) 3 , Mg (OH) 2 , talc ( talc), mica, zeolite, potassium titanate, aluminum borate, or mixed metal oxides and cage-type, T-10 and ladder-type silsesquinoxanes alone or in combination thereof Epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation, characterized in that used as a mixture of paper.
The method of claim 2, wherein the epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation comprises 5% to 70% by weight of epoxy resin, and 30% to 95% by weight inorganic filler based on the mixed weight of the epoxy resin and the inorganic filler. An epoxy resin composite for semiconductor encapsulation.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020100023962 | 2010-03-17 | ||
| KR20100023962 | 2010-03-17 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20110104918A true KR20110104918A (en) | 2011-09-23 |
| KR101202028B1 KR101202028B1 (en) | 2012-11-16 |
Family
ID=44955471
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110023975A KR101202028B1 (en) | 2010-03-17 | 2011-03-17 | Novel Epoxy Resin and Epoxy Resin Composite for Semiconductor Encapsulant |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101202028B1 (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013180375A1 (en) * | 2012-06-01 | 2013-12-05 | 한국생산기술연구원 | Composition and cured article comprising inorganic particles and epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group, use for same, and production method for epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group |
| US9150686B2 (en) | 2011-08-25 | 2015-10-06 | Korea Institute Of Industrial Technology | Epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group, method of preparing the same, composition and cured product comprising the same, and uses thereof |
| US11827741B2 (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2023-11-28 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Epoxy compound, composition prepared therefrom, semiconductor device prepared therefrom, electronic device prepared therefrom, article prepared therefrom, and method of preparing epoxy compound |
| US11840601B2 (en) | 2019-11-15 | 2023-12-12 | Korea Institute Of Industrial Technology | Composition of alkoxysilyl-functionalized epoxy resin and composite thereof |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5135702B2 (en) | 2006-03-31 | 2013-02-06 | Dic株式会社 | Epoxy resin composition, cured product thereof, semiconductor sealing material, and semiconductor device |
| JP2007308601A (en) | 2006-05-18 | 2007-11-29 | Sakamoto Yakuhin Kogyo Co Ltd | Thermosetting epoxy resin composition |
| JP5228404B2 (en) | 2007-08-27 | 2013-07-03 | Dic株式会社 | Epoxy resin composition, cured product thereof, resin composition for buildup film, novel epoxy resin, and production method thereof |
-
2011
- 2011-03-17 KR KR1020110023975A patent/KR101202028B1/en active IP Right Grant
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9150686B2 (en) | 2011-08-25 | 2015-10-06 | Korea Institute Of Industrial Technology | Epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group, method of preparing the same, composition and cured product comprising the same, and uses thereof |
| US9896535B2 (en) | 2011-08-25 | 2018-02-20 | Korea Institute Of Industrial Technology | Epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group, method of preparing the same, composition and cured product comprising the same, and uses thereof |
| WO2013180375A1 (en) * | 2012-06-01 | 2013-12-05 | 한국생산기술연구원 | Composition and cured article comprising inorganic particles and epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group, use for same, and production method for epoxy compound having alkoxysilyl group |
| US11840601B2 (en) | 2019-11-15 | 2023-12-12 | Korea Institute Of Industrial Technology | Composition of alkoxysilyl-functionalized epoxy resin and composite thereof |
| US11827741B2 (en) | 2020-12-15 | 2023-11-28 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Epoxy compound, composition prepared therefrom, semiconductor device prepared therefrom, electronic device prepared therefrom, article prepared therefrom, and method of preparing epoxy compound |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR101202028B1 (en) | 2012-11-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101202028B1 (en) | Novel Epoxy Resin and Epoxy Resin Composite for Semiconductor Encapsulant | |
| JPH0450223A (en) | Epoxy resin composition and semiconductor device | |
| JPWO2016104136A1 (en) | Epoxy resin composition for electronic material, cured product thereof and electronic member | |
| JP5397578B2 (en) | Heat-resistant liquid phenol novolac resin, production method thereof and cured product thereof | |
| JP5246760B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and semiconductor device | |
| WO2008020594A1 (en) | Modified liquid epoxy resin, epoxy resin composition using the same, and cured product thereof | |
| TWI414536B (en) | Epoxy resin, fabricating method thereof, epoxy resin composition by using the epoxy resin and cured product thereof | |
| WO2018164042A1 (en) | Curable resin composition, cured product thereof, and method for producing curable resin composition | |
| JP7155502B2 (en) | SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICE, MANUFACTURING METHOD THEREOF, AND ENCLOSURE RESIN COMPOSITION | |
| JPH09165433A (en) | Production of epoxy resin, epoxy resin composition and semiconductor sealing material | |
| KR101157566B1 (en) | Epoxy Resin Having Side Functional Group and Thermosetting Polymer Composite Comprising the Same | |
| KR102665491B1 (en) | Epoxy resin composition for encapsulating semiconductor device and semiconductor device encapsulated using the same | |
| JP4435342B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and epoxy resin composition for semiconductor encapsulation | |
| JP4568945B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and semiconductor device | |
| JP3582552B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and semiconductor device | |
| JP3852540B2 (en) | Phosphonium borate compound, method for producing the same, curing catalyst for epoxy resin composition, and epoxy resin composition | |
| JP3267636B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and electronic component sealing material | |
| US6232411B1 (en) | Hydrogenated diglycidyl ethers of bipheny-4,4′-diol | |
| JP5040404B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition for sealing material, cured product thereof and semiconductor device | |
| JPH04337316A (en) | Epoxy resin composition | |
| JPH06256364A (en) | Organic silicon compound, its production and resin composition containing the same | |
| JP3731585B2 (en) | Production method of epoxy resin | |
| JP4334446B2 (en) | Semiconductor sealing material | |
| JP7160512B1 (en) | Phenolic resin mixture, curable resin composition and cured product thereof | |
| JP3118763B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and semiconductor encapsulating material |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20151113 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20161107 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20161118 Year of fee payment: 19 |