KR102339677B1 - optical inspection device - Google Patents
optical inspection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR102339677B1 KR102339677B1 KR1020197009783A KR20197009783A KR102339677B1 KR 102339677 B1 KR102339677 B1 KR 102339677B1 KR 1020197009783 A KR1020197009783 A KR 1020197009783A KR 20197009783 A KR20197009783 A KR 20197009783A KR 102339677 B1 KR102339677 B1 KR 102339677B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- unit
- light emitting
- light
- imaging means
- coaxial illumination
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/88—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination
- G01N21/8851—Scan or image signal processing specially adapted therefor, e.g. for scan signal adjustment, for detecting different kinds of defects, for compensating for structures, markings, edges
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01B—MEASURING LENGTH, THICKNESS OR SIMILAR LINEAR DIMENSIONS; MEASURING ANGLES; MEASURING AREAS; MEASURING IRREGULARITIES OF SURFACES OR CONTOURS
- G01B11/00—Measuring arrangements characterised by the use of optical techniques
- G01B11/30—Measuring arrangements characterised by the use of optical techniques for measuring roughness or irregularity of surfaces
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/17—Systems in which incident light is modified in accordance with the properties of the material investigated
- G01N21/21—Polarisation-affecting properties
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/86—Investigating moving sheets
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/88—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination
- G01N21/8806—Specially adapted optical and illumination features
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/88—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination
- G01N21/95—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination characterised by the material or shape of the object to be examined
- G01N21/958—Inspecting transparent materials or objects, e.g. windscreens
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01N—INVESTIGATING OR ANALYSING MATERIALS BY DETERMINING THEIR CHEMICAL OR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
- G01N21/00—Investigating or analysing materials by the use of optical means, i.e. using sub-millimetre waves, infrared, visible or ultraviolet light
- G01N21/84—Systems specially adapted for particular applications
- G01N21/88—Investigating the presence of flaws or contamination
- G01N21/8851—Scan or image signal processing specially adapted therefor, e.g. for scan signal adjustment, for detecting different kinds of defects, for compensating for structures, markings, edges
- G01N2021/8887—Scan or image signal processing specially adapted therefor, e.g. for scan signal adjustment, for detecting different kinds of defects, for compensating for structures, markings, edges based on image processing techniques
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Immunology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Investigating Materials By The Use Of Optical Means Adapted For Particular Applications (AREA)
- Length Measuring Devices By Optical Means (AREA)
Abstract
결함이 피검사물의 단면의 어느 위치에 있었다고 해도, 1개의 장치 또한 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있는 광학 검사 장치를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다. 본 발명의 광학 검사 장치는, 1차원 촬상 수단(13)을 이용하여 피검사물(G)을 대략 연직 상향으로부터 쵤상할 때에, 1차원 촬상 수단(13)을 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 면인 중심면(S1) 상에 중심축(ax)이 위치하는 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역(31)과, 제1 영역(31)의 양단에 형성된 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역(32) 및 제 3영역(33)에 설치된 복수의 발광부(30)로부터 피검사물(G)에 광을 조사한다. 제1 영역에 있어서는, 중심면(S1)의 근방 이외의 영역에, 피검사물(G)의 반송 방향(F)과 대략 직교하는 방향을 따라 발광부(30a)가 늘어놓여져 있다. 또 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)에 있어서는, 중심면(S1) 상의 위치에 발광부(30a)가 늘어놓여져 있다. It aims at providing the optical inspection apparatus which can test|inspect a defect with one apparatus and one test|inspection even if a defect exists in any position of the cross section of a to-be-inspected object. In the optical inspection apparatus of the present invention, when the inspected object G is viewed from a substantially vertical upward direction using the one-dimensional imaging means 13, the central plane ( A first region 31 having a substantially semi-cylindrical surface on which the central axis ax is located on S1), and a second region 32 having a substantially semi-spherical or semi-elliptical surface formed at both ends of the first region 31 And the light is irradiated to the inspection target object (G) from the plurality of light emitting units (30) provided in the third region (33). In a 1st area|region, the light emitting part 30a is arrange|positioned along the direction substantially orthogonal to the conveyance direction F of the to-be-inspected object G in areas other than the vicinity of the center plane S1. Moreover, in the 2nd area|region 32 and the 3rd area|region 33, the light emitting part 30a is arranged in the position on the center plane S1.
Description
본 발명은 광학 검사 장치에 관한 것이다. The present invention relates to an optical inspection apparatus.
특허 문헌 1에는, 피검사물에 조사되어 1차원 촬상 수단에 입사되는 광이 각각 정반사광, 확산반사광, 투과광으로 되도록 복수의 조명 장치가 배치되어 있고, 이들의 점등 타이밍을 1차원 촬상 수단의 전송회(回)마다 변경하고, 1차원 촬상 수단으로부터 전송된 화상 데이터를 같은 조명 장치가 점등 한 화상 데이터마다 집적하여 집적 화상 데이터를 작성하는 촬상 광학 검사 장치가 개시되어 있다. In
특허 문헌 1에 기재의 발명은, 투명한 판형상의 피검사물을 검사하는 것이다. 투명한 판형상의 피검사물로서는, 예를 들면 휴대단말 등에 이용되는 커버 유리를 들 수 있다. 커버 유리는, 대략 직사각형 형상이며, 단면이 연마 가공되어 있다. 이러한 커버 유리 등의 단면 가공에 있어서의 결함(예를 들면, 단면의 이지러짐)을 검사하기 위해서는 모든 단면에 똑같이 광을 비추고, 그 반사광을 촬상 수단에 입사시킬 필요가 있다. The invention described in
특허 문헌 1에 기재의 발명에서는, 1차원 촬상 수단의 광축이 피검사물의 법선에 대해서 45°정도 기울어져 있다. 따라서, 특허 문헌 1에 기재의 발명에서는, 일부의 단면(단면 I로 함)에서 반사한 광은 촬상 수단에 입사하지만, 단면 I 이외의 단면(단면 II로 함)에서 반사한 광은 촬상 수단에 입사하지 않을 우려가 있다. 그리고, 단면 II에 있어서는, 결함을 촬상할 수가 없는, 즉 결함을 검출할 수가 없다고 하는 문제가 있다. In the invention described in
본 발명은 이러한 사정을 감안하여 이루어진 것으로, 결함이 피검사물의 단면의 어느 위치에 있었다고 해도, 1개의 장치 또한 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있는 광학 검사 장치를 제공하는 것을 목적으로 한다. The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide an optical inspection apparatus capable of inspecting a defect with one device and one inspection even if the defect is located at any position in the cross section of the object to be inspected.
상기 과제를 해결하기 위해서, 본 발명과 관련되는 광학 검사 장치는, 예를 들면, 수평 방향으로 피검사물을 재치하는 재치부와, 상기 재치부에 재치된 피검사물을 반송 방향을 따라 이동시키는 반송부와, 상기 피검사물을 대략 연직 상향으로부터 촬상하는 1차원 촬상 수단으로서, 길이 방향이 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하도록 배치된 1차원 촬상 수단과, 상기 피검사물에 광을 조사하는 발광부를 복수 가지는 광조사부를 구비하고, 상기 광조사부는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 면인 중심면의 상에 중심축이 위치하는 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역과, 상기 제1 영역의 양단에 형성된 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역 및 제3 영역을 가지고, 상기 제1 영역에 있어서는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향을 따라 상기 발광부가 늘어놓여진 띠모양 발광부를 복수 가지고, 상기 띠모양 발광부는, 상기 제1 영역에 있어서의 상기 중심면의 근방 이외의 영역에 설치되고, 상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 중심면의 상에 상기 발광부가 늘어놓여지는 것을 특징으로 한다. In order to solve the above problems, the optical inspection apparatus according to the present invention includes, for example, a mounting unit that mounts an inspection target in a horizontal direction, and a transport unit that moves the inspection target placed on the mounting unit along a conveying direction. and a one-dimensional imaging means for imaging the object to be inspected from substantially vertically upward, the one-dimensional imaging means arranged so that a longitudinal direction is substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction, and a light emitting unit having a plurality of light emitting units for irradiating light to the object The light irradiation unit includes a first region of a substantially semi-cylindrical surface in which a central axis is positioned on a central plane that is a plane in a substantially vertical direction including the one-dimensional imaging means, and formed at both ends of the first region. It has a second region and a third region of a substantially hemispherical surface or a substantially semi-elliptical surface, and in the first region, a plurality of band-shaped light emitting units in which the light emitting units are arranged along a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction; The pattern light emitting part is provided in a region other than the vicinity of the central plane in the first region, and in the second region and the third region, the light emitting part is arranged on the central plane, do.
본 발명과 관련되는 광학 검사 장치에 의하면, 1차원 촬상 수단을 이용하여 피검사물을 대략 연직 상향으로부터 촬상할 때에, 1차원 촬상 수단을 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 면인 중심면의 상에 중심축이 위치하는 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역과, 제1 영역의 양단에 형성된 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역 및 제3 영역에 설치된 복수의 광조사부로부터 피검사물에 광을 조사한다. 제1 영역에 있어서는, 중심면 근방 이외의 영역에, 피검사물의 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향을 따라 발광부가 늘어놓여진다. 이에 의해 피검사물의 선단면 및 후단면에서 반사한 광을 1차원 촬상 수단에 입사시킬 수가 있다. 또, 제2 영역 및 제3 영역에 있어서는, 중심면의 상의 위치에 발광부가 늘어놓여진다. 이에 의해 피검사물의 좌우 단면에서 반사한 광을 1차원 촬상 수단에 입사시킬 수가 있다. 따라서, 결함이 피검사물의 단면의 어느 위치에 있었다고 해도, 1개의 장치 또한 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. According to the optical inspection apparatus according to the present invention, when an object to be inspected is imaged from substantially vertically upward using the one-dimensional imaging means, the central axis is positioned on the central plane, which is a plane in the substantially vertical direction including the one-dimensional imaging means. Light is irradiated to the object to be inspected from a plurality of light irradiating units provided in a first region having a substantially semi-cylindrical surface, and a second region and a third region having a substantially hemispherical or substantially semi-elliptical surface formed at both ends of the first region. In a 1st area|region, the light emitting part is arranged in the area|region other than the center plane vicinity along the direction substantially orthogonal to the conveyance direction of a to-be-inspected object. Accordingly, the light reflected from the front end surface and the rear end surface of the object to be inspected can be made incident on the one-dimensional imaging means. Moreover, in the 2nd area|region and 3rd area|region, the light emitting part is arranged in the position on the image of a center plane. Thereby, the light reflected from the left and right end surfaces of the object to be inspected can be made incident on the one-dimensional imaging means. Therefore, even if a defect exists in any position of the cross section of a to-be-inspected object, a defect can be test|inspected by one apparatus and one test|inspection.
여기서, 상기 띠모양 발광부는, 광축과, 상기 중심면과 상기 재치부의 상면의 교선이 교차하도록 설치되고, 상기 띠모양 발광부는, 광축과 상기 중심면과의 이루는 각도가 대략 8°또는 대략 17°인 제1 띠모양 발광부를 가져도 좋다. 이에 의해 펄 안료(pearl pigment)를 이용한 경우 또는 펄 안료를 이용하지 않는 경우에 대해, 인쇄부의 색얼룩 등을 검출 가능한 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. Here, the band-shaped light emitting unit is provided such that an intersection line between the optical axis and the central plane and the upper surface of the mounting unit intersects, and the band-shaped light emitting unit has an angle between the optical axis and the central plane of about 8° or about 17° You may have a 1st strip|belt-shaped light emitting part which is phosphorus. Thereby, in the case where a pearl pigment is used, or when a pearl pigment is not used, the image which can detect the color unevenness of a printing part etc. can be imaged.
여기서, 일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 일정한 간격으로 화상을 촬상하도록 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 구동하고, 또한 상기 1차원 촬상 수단에 의한 촬상에 동기하여, 상기 제1 영역의 상기 중심면에서 구분된 반의 영역인 제1 발광 영역, 상기 제1 영역 중의 상기 제1 발광 영역 이외의 제2 발광 영역, 상기 제2 영역 중의 상기 중심면의 상의 제3 발광 영역, 상기 제3 영역 중의 상기 중심면의 상의 제4 발광 영역, 상기 제1 띠모양 발광부를 제각기 조사시키는 제어부를 구비하여도 좋다. 이에 의해 선단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 후단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 좌우단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 인쇄부의 결함이 다른 인쇄부보다 어두운 화상을, 피검사물을 1회 반송하는 동안에 제각기의 타이밍으로 촬영할 수가 있다. Here, the conveying unit is controlled to convey the object to be inspected at a constant speed, the one-dimensional imaging means is driven to capture images at regular intervals, and in synchronization with the imaging by the one-dimensional imaging means, the first area a first light emitting area that is a half area separated from the center plane of a second light emitting area other than the first light emitting area in the first area, a third light emitting area on the central plane of the second area, the third A control unit may be provided for irradiating the fourth light emitting region and the first band-shaped light emitting portion on the central plane of the region, respectively. As a result, an image in which the defect in the front end P surface shines, an image in which the defect in the rear end P surface shines, an image in which the defect in the left and right ends P surface shines, and an image in which the defect in the printed part is darker than in other print parts, are obtained as the inspected object. You can take pictures at different timings during one transfer.
여기서, 상기 광조사부는, 상기 띠모양 발광부와, 상기 중심면과 상기 재치부의 상면과의 교선과의 사이에 배치된 원통 렌즈(cylindrical lens)를 가져도 좋다. 이에 의해 띠모양 발광부로부터 조사된 광을 집광하고, 1차원 촬상 수단의 촬상 주파수를 높게(촬상 시간을 짧게) 할 수가 있다. Here, the light irradiation unit may include a cylindrical lens disposed between the band-shaped light emitting unit and an intersection between the central plane and the upper surface of the mounting unit. Thereby, the light irradiated from the strip|belt-shaped light emitting part can be condensed, and the imaging frequency of a one-dimensional imaging means can be made high (imaging time shortened).
여기서, 상기 재치부의 상측 또는 하측에 설치되는 제1 촬상 수단과, 광축이 상기 제1 촬상 수단의 광축과 일치하도록, 상기 제1 촬상 수단과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 촬상 수단과, 상기 피검사물에 법선 방향으로부터 평행광을 조사하는 제1 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제1 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제1 동축 조명과, 상기 제1 동축 조명과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제2 동축 조명을 구비하고, 상기 제1 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고, 상기 제2 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제2 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광, 및 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 투과한 광이 입사해도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물의 불투명한 부분의 결함(예를 들면 인쇄 부분의 흠집, 인쇄 가장자리(edge)의 이지러짐 등)을 검출 가능한 투과 화상, 피검사물의 표면이나 이면의 흠집이나 이물질 등을 검출 가능한 정반사 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. Here, a first imaging unit provided above or below the mounting unit, and a second imaging unit provided on the opposite side with the first imaging unit and the mounting unit interposed therebetween so that the optical axis coincides with the optical axis of the first imaging unit; , a first coaxial illumination for irradiating parallel light from a normal direction to the object to be inspected, a first coaxial illumination that is a coaxial illumination of the first imaging means, and a first coaxial illumination provided on the opposite side with the first coaxial illumination and the mounting unit interposed
여기서, 일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제1 형태, 상기 제2 동축 조명을 상기 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제2 형태, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제2의 강도로 조사하는 제3 형태의 3개의 조사 패턴으로 상기 제1 동축 조명 또는 상기 제2 동축 조명을 조사시키고, 또한 상기 제1 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제1 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제2 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제3 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하도록, 상기 제1 촬상 수단 및 상기 제2 촬상 수단을 구동하는 제2 제어부를 구비하여도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물을 1회 반송하는 동안에 제각기의 타이밍으로 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬영할 수가 있다. Here, a first mode in which the transport unit is controlled to transport the object to be inspected at a constant speed, and irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a first intensity, and a second mode for irradiating the second coaxial illumination with the first intensity form, irradiating the first coaxial illumination or the second coaxial illumination with three irradiation patterns of a third type for irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a second intensity, and further, according to the irradiation of the
여기서, 광축이 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 광축과 일치하도록, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 촬상 수단과, 상기 피검사물에 법선 방향으로부터 평행광을 조사하는 제1 동축 조명으로서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제1 동축 조명과, 상기 제1 동축 조명과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제2 동축 조명을 구비하고, 상기 광조사부는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 반송부의 사이에 설치되고, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단에는, 상기 광조사부 또는 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고, 상기 제2 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제2 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광, 및 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 투과한 광이 입사해도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물의 불투명한 부분의 결함을 검출 가능한 투과 화상, 피검사물의 표면이나 이면의 흠집이나 이물질 등을 검출 가능한 정반사 화상을 보다 적은 촬상 수단으로 촬상할 수가 있다. Here, the second imaging means provided on the opposite side with the one-dimensional imaging means and the mounting unit interposed therebetween so that the optical axis coincides with the optical axis of the one-dimensional imaging means; A first coaxial illumination that is coaxial illumination of the one-dimensional imaging means and a second coaxial illumination provided on the opposite side with the first coaxial illumination and the mounting unit interposed therebetween, the first coaxial illumination being coaxial illumination of the
여기서, 일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제1 형태, 상기 제2 동축 조명을 상기 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제2 형태, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제2의 강도로 조사하는 제3 형태의 3개의 조사 패턴으로 상기 제1 동축 조명 또는 상기 제2 동축 조명을 조사시키고, 또한 상기 제1 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 1차원 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제2 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제3 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하도록, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단 및 상기 제2 촬상 수단을 구동하는 제3 제어부를 구비하여도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물을 1회 반송하는 동안에 제각기의 타이밍으로 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬영할 수가 있다. Here, a first mode in which the transport unit is controlled to transport the object to be inspected at a constant speed, and irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a first intensity, and a second mode for irradiating the second coaxial illumination with the first intensity form, irradiating the first coaxial illumination or the second coaxial illumination with three irradiation patterns of a third type of irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a second intensity, and also irradiating the 1 the one-dimensional image is acquired by a dimensional imaging means, an image is acquired by the second imaging means in accordance with the irradiation of the second form, and an image is acquired by the second imaging means in accordance with the irradiation of the third mode; An imaging unit and a third control unit for driving the second imaging unit may be provided. Thereby, a transmission image and a specular reflection image can be image|photographed at respective timings while the to-be-inspected object is conveyed once.
여기서, 상기 광조사부는, 상기 발광부에 인접하여 설치되고, 상기 발광부로부터 조사된 광을 확산하는 광확산판을 가져도 좋다. 이에 의해 복수의 발광부로부터 조사된 광을 광확산판으로 가늘고 긴 면광원으로 하고, 피검사물에 발광부의 점형상의 광이 비쳐 버리는 부적합함을 방지할 수가 있다. Here, the light irradiation part may have a light diffusion plate which is provided adjacent to the light emitting part and diffuses the light irradiated from the light emitting part. Thereby, the light irradiated from the plurality of light emitting units is used as an elongated surface light source by the light diffusion plate, and it is possible to prevent inappropriateness in which the dotted light of the light emitting unit is reflected on the object to be inspected.
여기서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 초점거리를 조정하는 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자와, 상기 재치부에 인접하여 설치된 반사경을 구비하고, 상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자 및 상기 반사경은, 상기 중심면의 상에 설치되고, 평면시(平面視)에 있어서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 연직 방향 하측에, 상기 피검사물이 재치되는 상기 재치부 상의 영역인 재치 영역이 위치하고, 평면시에 있어서, 상기 반사경은, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향에 있어서, 상기 재치 영역의 외측 또한 상기 재치 영역에 인접하는 위치에 설치되고, 상기 반사경의 반사면은 대략 평면이며, 상기 반사면은, 상기 중심면과 교차하는 선이 수평면에 대해서 경사지도록, 상기 반송 방향으로 대략 따라 연설(延設)되고, 상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 반사경을 묶는 선과 겹치도록 배치되어도 좋다. 이에 의해 측면에 부분적인 원통 형상 또는 타원통 형상을 가지는 커버 유리라도, 1회의 검사로 측면의 결함에 대해서도 검사할 수가 있다. 즉, 피검사물의 측면의 상을 반사경에서 반사하여 1차원 촬상 수단에 유도하고, 요컨데 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자로 1차원 촬상 수단의 초점거리를 늘임으로써, 피검사물의 평면보다 하측에 있는 측면에 초점을 맞출 수가 있다. Here, an optical element for adjusting a focal length for adjusting the focal length of the one-dimensional imaging means and a reflecting mirror provided adjacent to the mounting unit are provided, wherein the optical element for adjusting the focal length and the reflecting mirror are installed on the central plane In a plan view, a placement area, which is an area on the placement unit on which the inspection object is placed, is located below the one-dimensional imaging means in the vertical direction, and in a plan view, the reflector is In a direction substantially orthogonal to the direction, it is provided outside the mounting area and at a position adjacent to the mounting area, the reflecting surface of the reflecting mirror is substantially flat, and the reflecting surface is a horizontal plane where a line intersecting the central plane is a horizontal plane. The optical element for focal length adjustment may be arranged so as to overlap a line joining the one-dimensional imaging means and the reflecting mirror, while extending substantially along the conveying direction so as to be inclined with respect to the . Thereby, even if it is a cover glass which has a partial cylindrical shape or an elliptical-cylindrical shape on a side surface, it can test|inspect also about a defect on a side surface by one test|inspection. That is, by reflecting the image of the side of the object to be inspected by the reflector and guiding it to the one-dimensional imaging means, in other words, by increasing the focal length of the one-dimensional imaging means with the optical element for focal length adjustment, focus on the side below the plane of the object to be inspected can match
여기서, 상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자는, 유리판이고, 판두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 양단면이 수평으로 되도록 설치되어도 좋다. 이에 의해 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자에 입사하는 과정, 및 광이 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자로부터 출사하는 과정에서 광이 굴절하고, 1차원 촬상 수단의 초점 위치를 늘일 수가 있다. Here, the said optical element for focal length adjustment is a glass plate, and you may provide so that both end surfaces substantially orthogonal to a plate|board thickness direction may become horizontal. Thereby, light is refracted in the process of entering the optical element for focal length adjustment and the process of light exiting from the optical element for focal length adjustment, and the focal position of the one-dimensional imaging means can be extended.
여기서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동부와, 상기 피검사물의 높이를 취득하는 높이 취득부와, 상기 높이 취득부가 취득한 정보에 기초하여 상기 이동부를 제어하여, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 하를 통과하는 상기 피검사물의 높이 변화에 맞추어 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동 제어부를 구비하여도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물의 높이가 변화하는 경우라도, 초점이 맞은 뚜렷한 상을 1차원 촬상 수단으로 촬상할 수가 있다. Here, a moving unit for moving the one-dimensional imaging means in an up-down direction, a height acquiring unit for acquiring the height of the object to be inspected, and controlling the moving part based on the information acquired by the height acquiring unit, the one-dimensional imaging means A movement control unit may be provided for moving the one-dimensional imaging means in an up-down direction in accordance with a change in height of the object to be inspected passing through. Accordingly, even when the height of the object to be inspected changes, a clear image in focus can be captured by the one-dimensional imaging means.
여기서, 상기 높이 취득부는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향으로 광을 조사하는 면광원과, 상기 면광원으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 통과한 광이 입사하는 측면 촬상 수단을 가져도 좋다. 이에 의해 피검사물에 의해 광이 차단된 부분은 어둡고, 그 외의 부분은 밝은 그림자 그림과 같은 화상을 측면 촬상 수단으로 촬상함으로써, 피검사물의 높이를 정확하게 취득할 수가 있다. Here, the said height acquisition part may have a surface light source which irradiates light in the direction substantially orthogonal to the said conveyance direction, and the side image pickup means which irradiates from the said surface light source, and which the light which passed through the said object is incident. Accordingly, the height of the inspected object can be accurately acquired by capturing an image such as a dark shadow picture in the portion blocked by the inspected object and light in the other portions by the side imaging means.
여기서, 상기 광조사부는, 상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서, 상기 발광부가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록과, 상기 발광부로부터 조사된 광이 통과하는 제2 원통 렌즈를 가지고, 상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 발광 블록의 연설(延設) 방향은 수평 방향에 대해서 기울어져 있고, 상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 발광 블록의 연설 방향에 대해서, 상기 제2 원통 렌즈의 연설 방향이 기울어져 있어도 좋다. 이에 의해 제2 영역 및 제3 영역으로부터 조사된 광의 초점을 피검사물에 맞출 수가 있다. 또, 제2 영역, 제3 영역이 제1 영역을 보충하도록 하여, 제1 영역의 띠모양 발광부가 가지는 발광부의 수를 줄일 수가 있다. Here, the light irradiation unit includes, in the second region and the third region, a light emitting block in which the light emitting units are arranged in a line, and a second cylindrical lens through which the light irradiated from the light emitting unit passes, In the region and the third region, the extension direction of the light emitting block is inclined with respect to the horizontal direction, and in the second region and the third region, with respect to the extension direction of the light emitting block, the The extension direction of the second cylindrical lens may be inclined. Thereby, the focus of the light irradiated from the 2nd area|region and the 3rd area|region can be adjusted to the object to be inspected. In addition, since the second region and the third region supplement the first region, the number of light emitting units included in the band-shaped light emitting unit of the first region can be reduced.
여기서, 상기 광조사부는, 열전도성이 높은 재료로 형성된 방열 부재를 가지고, 상기 발광부는, 상기 방열 부재에 설치되어도 좋다. 이에 의해 발광부로부터 발생한 열을 효율적으로 방열할 수가 있다. Here, the light irradiation part may have a heat dissipation member formed of a material with high thermal conductivity, and the light emitting part may be provided in the heat dissipation member. Thereby, the heat generated from the light emitting part can be efficiently dissipated.
여기서, 상기 방열 부재에 송풍하는 송풍부를 구비하고, 상기 방열 부재는, 상기 발광부가 설치된 플레이트를 복수 가지고, 상기 플레이트는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향으로 연설되어 있고, 상기 송풍부는, 상기 플레이트의 연설 방향을 따른 방향의 바람을 보내어도 좋다. 이에 의해 방열 부재에 의한 냉각 효과를 향상시킬 수가 있다. Here, the heat dissipating member is provided with a blower for blowing air, the heat dissipating member has a plurality of plates provided with the light emitting section, the plates extending in a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction, and the blowing section includes the plate You may send the wind in a direction along the direction of the speech. Thereby, the cooling effect by a heat radiating member can be improved.
여기서, 상기 제2 촬상 수단은, 상기 재치부의 하측에 설치되고, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 상측에는, 원편광 필터가 설치되고, 상기 원편광 필터는, 두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향의 평면이, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 광축과 대략 직교하는 방향에 대해서 조금 경사하지록 설치되어 있어도 좋다. 이에 의해 재치부의 하측에 설치된 제2 촬상 수단의 촬상 렌즈 표면에서 반사한 광이, 재치부의 상측에 설치된 카메라에 입사하고, 이 카메라로 촬상된 화상에 밝은 광의 선이 포함되지 않게 할 수가 있다. Here, the second imaging means is provided below the mounting unit, and above the second imaging means, a circularly polarizing filter is provided, the circularly polarizing filter having a plane in a direction substantially perpendicular to the thickness direction, It may be provided so that it may incline slightly with respect to the direction substantially orthogonal to the optical axis of the said 2nd imaging means. Thereby, the light reflected by the imaging lens surface of the 2nd imaging means provided below the mounting part enters the camera provided above the mounting part, and it can prevent the bright light line from being included in the image picked up by this camera.
본 발명에 의하면, 결함이 피검사물의 단면의 어느 위치에 있었다고 해도, 1개의 장치 또한 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, even if a defect exists in any position of the cross section of a to-be-inspected object, a defect can be test|inspected by one apparatus and one test|inspection.
도 1은 제1의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(1)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다.
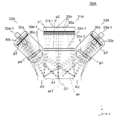
도 2는 입체 조명부(30)의 상세를 나타내는 도이다.
도 3은 띠모양 발광부(31a)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다.
도 4는 제1 영역(31)을 포함하도록 광학 검사 장치(1)를 xz평면과 평행한 면으로 절단했을 때에 있어서의 광학 검사 장치(1)의 단면을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이다.
도 5는 입체 조명부(30)의 평면 모식도이다.
도 6은 띠모양 발광부(32a)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다.
도 7은 광학 검사 장치(1)의 전기적인 구성을 나타내는 블록도이다.
도 8은 출력부(73)와 광학 검사 장치(1)의 각 구성과의 전기적인 접속을 설명하는 블록도이다.
도 9는 출력부(73)로부터 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 동축 조명부(20)로 출력되는 신호에 대해 설명하는 도이다.
도 10은 도 9에 나타내는 처리에 있어서의 타이밍 차트(timing chart)이다.
도 11은 출력부(73)로부터 제3 카메라(13) 및 입체 조명부(30)로 출력되는 신호에 대해 설명하는 도이다.
도 12는 도 11에 나타내는 신호 출력과 입체 조명부(30)에서 촬상되는 화상에 포함되는 결함과의 대응을 나타내는 도이다.
도 13은 커버 유리 G의 단면에 있어서의 광의 모습을 나타내는 도이고 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다.
도 14는 도 11에 나타내는 처리에 있어서의 타이밍 차트이다.
도 15는 커버 유리 G의 투과 화상의 일례이다.
도 16은 커버 유리 G의 정반사 화상의 일례이다.
도 17은 커버 유리 G의 선단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상(부분 확대도)의 일례이다.
도 18은 커버 유리 G의 인쇄부의 결함이 다른 인쇄부보다 어두운 화상(부분 확대도)의 일례이다.
도 19는 변형예와 관련되는 발광 블록(30b-1)을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이고, (A)는 측면도이며, (B)는 (A)에 나타내는 상태를 도에 있어서의 하방향으로부터 본 도이다.
도 20은 제2의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(2)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다.
도 21은 촬상 처리의 차례와 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)에서 촬상되는 화상과의 대응을 나타내는 도이다.
도 22는 제3의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(3)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다.
도 23은 광학 검사 장치(3)의 일부를 확대 표시한 사시도이다.
도 24는 광학 검사 장치(3)를 중심면 S1로 절단한 상태에 있어서의 개략 구성을 나타내는 도이다.
도 25는 커버 유리 G1의 위치와 제3 카메라(13)에서 촬상되는 화상과의 관계를 나타내는 도이고, (A)는 커버 유리 G1의 측면 부분의 확대도이며, (B)는 제3 카메라(13)에서 촬상되는 화상의 일부를 나타낸다.
도 26은 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 측정하는 모습을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이고, 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하는 방향으로부터 본 도이다.
도 27은 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 측정하는 모습을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이고, 반송 방향 F를 따라 본 도이다.
도 28은 제3의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치가 구비하는 입체 조명부(30A)의 개략을 나타내는 사시도이다.
도 29는 띠모양 발광부(31a-1)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다.
도 30은 띠모양 발광부(32a-1)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다.
도 31은 입체 조명부(30A)로부터 조사되는 광의 경로에 대해 설명하는 도이다.
도 32는 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다. 1 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
2 is a diagram showing the details of the three-
3 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the band-shaped
4 : is a figure which shows typically the cross section of the
5 is a schematic plan view of the three-
6 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the strip-shaped
7 is a block diagram showing an electrical configuration of the
8 is a block diagram for explaining the electrical connection between the
9 is a diagram for explaining signals output from the
Fig. 10 is a timing chart in the process shown in Fig. 9;
11 is a diagram for explaining signals output from the
12 is a diagram showing correspondence between the signal output shown in FIG. 11 and a defect included in an image captured by the
13 : is a figure which shows the mode of the light in the cross section of cover glass G, and shows the path|route of light by the dashed-dotted line.
Fig. 14 is a timing chart in the process shown in Fig. 11;
15 : is an example of the transmission image of the cover glass G. FIG.
16 : is an example of the specular reflection image of the cover glass G. FIG.
17 : is an example of the image (partially enlarged view) in which the defect in P inner surface of the front-end|tip of cover glass G shined.
18 : is an example of the image (partially enlarged view) in which the defect of the printing part of cover glass G is darker than other printing parts.
Fig. 19 is a view schematically showing a
20 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
21 : is a figure which shows the correspondence between the order of imaging processing, and the image imaged by the
22 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
23 is an enlarged perspective view of a part of the
24 : is a figure which shows schematic structure in the state which cut|disconnected the
25 : is a figure which shows the relationship between the position of cover glass G1, and the image imaged by the
It is a figure which shows typically a mode that measures the height of cover glass G1, and is the figure seen from the direction substantially orthogonal to conveyance direction F.
It is a figure which shows typically a mode that measures the height of cover glass G1, and is the figure which looked along the conveyance direction F.
Fig. 28 is a perspective view schematically showing a
29 is a schematic diagram showing details of the strip-shaped
30 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the strip-shaped
Fig. 31 is a diagram for explaining the path of light emitted from the three-
32 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
이하, 본 발명의 실시 형태를 도면을 참조하여 상세하게 설명한다. 각 도면에 있어, 동일한 요소에는 동일한 부호가 붙어져 있고 중복된 부분에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. EMBODIMENT OF THE INVENTION Hereinafter, embodiment of this invention is described in detail with reference to drawings. In each drawing, the same reference numerals are attached to the same elements, and descriptions of overlapping parts are omitted.
본 발명은, 피검사물인 휴대단말 등의 커버 유리 G를 검사하는 광학 검사 장치이다. 광학 검사 장치로 촬상된 화상에 기초하여, 커버 유리 G의 단면이나 표면, 이면에 있어서의 흠집, 연마 얼룩짐 등의 결함이나, 커버 유리 G에 인쇄된 부분의 인쇄 얼룩짐, 이지러짐 등의 결함이 검사 가능하다. 또한, 본 실시의 형태에 있어서는, 광학 검사 장치가 휴대단말 등의 커버 유리 G를 검사하는 형태를 예시하지만, 광학 검사 장치가 검사하는 피검사물은 커버 유리에 한정되지 않는다. This invention is an optical inspection apparatus which test|inspects cover glass G, such as a portable terminal which is a to-be-inspected object. Defects such as scratches and polishing irregularities on the end face, surface, and back surface of the cover glass G, and defects such as print irregularities and cracks in the portion printed on the cover glass G are inspected based on the image captured by the optical inspection device It is possible. In addition, in this embodiment, although the form which an optical inspection apparatus test|inspects cover glass G, such as a portable terminal, is illustrated, the to-be-inspected object which an optical inspection apparatus test|inspects is not limited to a cover glass.
커버 유리 G는, 사방이 곡면으로 되도록 연마되어 있다. 또, 커버 유리 G의 이면에는, 부분적으로 인쇄가 되어 있다. 이하, 둘레면의 원호 형상의 연마면을 폴리쉬(polish)면(이하, P면)이라고 한다. 또, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄 부분에는, 단색의 유기 도료를 도포하는 단색 인쇄나, 베이스 칼라(base color)로 되는 단색 안료를 도포하고, 반투명의 입자를 투명한 이산화 티타늄 등으로 덮은 펄 안료(pearl pigment)를 포함하는 투명층을 겹쳐서 도포하는 펄(pearl) 도장이 행해지고 있다. The cover glass G is grind|polished so that all sides may become a curved surface. Moreover, on the back surface of the cover glass G, printing is carried out partially. Hereinafter, the circular arc-shaped polished surface of the circumferential surface is referred to as a polish surface (hereinafter, P surface). In addition, to the printed part of the cover glass G, monochromatic printing in which a monochromatic organic paint is applied, or a monochromatic pigment serving as a base color is applied, and translucent particles are covered with transparent titanium dioxide or the like, pearl pigment ), a transparent layer containing a layered coating of pearl (pearl) coating is performed.
<제1의 실시의 형태> <First embodiment>
도 1은 제1의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(1)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다. 광학 검사 장치(1)는, 주로 촬상부(10)와, 동축 조명부(20)와, 입체 조명부(30)와, 재치부(40)와, 반송부(50)(도 8 참조)를 가진다. 1 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
재치부(40)는, 복수의 롤러(roller)(40a)를 가지고, 상측에는 커버 유리 G가 재치된다. 반송부(50)는, 재치부(40)에 설치된 커버 유리 G를 반송 방향 F(여기에서는, x방향)로 이동시키는 것이고, 예를 들면 롤러(40a)를 회전시키는 액츄에이터(actuator)(도시하지 않음) 등을 가진다. 재치부(40) 및 반송부(50)는 이미 공지이기 때문에 설명을 생략한다. The mounting
촬상부(10)는, 주로 제1 카메라(11)와, 제2 카메라(12)와, 제3 카메라(13)(본 실시의 형태에 있어서는, 각각 본 발명의 제1 촬상 수단과, 제2 촬상 수단과, 1차원 촬상 수단에 상당)를 가진다. 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12), 제3 카메라(13)는, 주로 촬상 렌즈(11a, 12a, 13a)와, 라인 CCD, CMOS 등의 라인 센서(11b, 12b, 13b)를 가진다. 라인 센서(11b, 12b, 13b)는, 길이 방향이 커버 유리 G의 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하도록(즉, y방향을 따라) 배치된다. 촬상부(10)는 이미 공지이기 때문에 설명을 생략한다. The
제1 카메라(11)는, 재치부(40)의 상측(+z측)에 설치되고, 커버 유리 G를 대략 연직 상향(+z방향)으로부터 촬상한다. 제2 카메라(12)는, 제1 카메라(11)와 재치부(40)를 사이에 두고 반대측(재치부(40)의 하측(-z측))에 설치되고, 커버 유리 G를 대략 연직 하향(-z방향)으로부터 촬상한다. 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)는, 광축 oax가 일치하도록 설치된다. The
제3 카메라(13)는, 재치부(40)의 상측(+z측)에 설치되고, 커버 유리 G를 대략 연직 상향으로부터 촬상한다. 또, 제3 카메라(13)는, 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)와 수평 방향에 있어서의 위치(xy평면과 평행한 면에 있어서의 위치)가 다르도록 배치된다. The
동축 조명부(20)는, 제1 카메라(11)의 동축 조명인 상측 동축 조명(21)과, 제2 카메라(12)의 동축 조명인 하측 동축 조명(22)을 가진다. 상측 동축 조명(21) 및 하측 동축 조명(22)은, 이른바 쾰러 조명(Kohler illumination)이며, 커버 유리 G에 법선 방향(z방향)으로부터 평행광을 조사한다. 상측 동축 조명(21) 및 하측 동축 조명(22)은, 광축 oax가 일치하도록, 재치부(40)를 사이에 두고 반대측(상측 동축 조명(21)은 재치부(40)의 +z측, 하측 동축 조명(22)은 재치부(40)의 -z측)에 설치된다. The
상측 동축 조명(21) 및 하측 동축 조명(22)의 구성에 대해 설명한다. 상측 동축 조명(21) 및 하측 동축 조명(22)은, 각각 광원(21a, 22a)과, 조도 분포를 균일화하는 유리제의 인테그레이터(integrator)(21b, 22b)와, 집광 렌즈(21c, 22c)와, 집광 렌즈(21c, 22c)의 초점과 대략 일치하는 위치에 설치되는 조리개(21d, 22d)와, 광을 평행광으로 변환하는 콜리메이터 렌즈(collimator lens)(21e, 22e)와, 광로를 구부리는 미러(mirror)(21f, 22f)와, 평행 직선 모양의 홈(groove)을 가지고, 광을 직선 상에 집광시키는 프레스넬 렌즈(Fresnel lens)(21g, 22g)와, 광로를 구부리는 하프미러(half mirror)(21h, 22h)를 가진다. The configuration of the upper
광원(21a, 22a)은, 알루미늄 등의 금속판에 발광 부재가 면실장되어 있다. 금속판의 배면에는, 방열판(히트 싱크(heat sink))이 설치되어 있다. 발광 부재는, 백색(예를 들면, 색온도가 5700K)의 LED이며, 그 조사각은 120°정도이다. As for the
광원(21a, 22a)과 인테그레이터(21b, 22b)는 인접하여 설치된다. LED로부터는 비교적 광역으로 광이 조사되기 때문에, 일부의 광은 인테그레이터(21b, 22b)에 입사되지 않고 누출되어 버리지만, 대부분의 광은 인테그레이터(21b, 22b)에 입사되어 커버 유리 G에 조사된다. The
하프미러(half mirror)(21h)는, 제1 카메라(11)의 광축 상에 설치된다. 따라서, 하프미러(21h)에서 반사된 광은, 커버 유리 G에 대해 수직으로 조사되고, 커버 유리 G에서 정반사한 광은 제1 카메라(11)에 입사한다. 또, 하프미러(21h)에서 반사된 광은, 커버 유리 G를 투과하고, 제2 카메라(12)에 입사한다. A
하프미러(22h)는, 제2 카메라(12)의 광축 상에 설치된다. 따라서, 하프미러(22h)에서 반사된 광은, 커버 유리 G에 대해 수직으로 조사되고, 커버 유리 G에서 정반사한 광은 제2 카메라(12)에 입사한다. The
입체 조명부(30)는, 복수의 방향으로부터 커버 유리 G에 광을 조사한다. 입체 조명부(30)로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G에서 반사한 광은, 제3 카메라(13)에 입사한다. 도 2는 입체 조명부(30)의 상세를 나타내는 도이다. 도 2에 있어서는, 제3 카메라(13)(촬상 렌즈(13a), 라인 센서(13b))를 점선으로 나타내고, 제3 카메라(13)의 시야 위치(13c) 및 제3 카메라(13)로의 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다. The three-
입체 조명부(30)는, 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역(31)과, 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)을 가진다. 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)은, 같은 형상이며, 제1 영역(31)의 양단에 배치된다. The
제1 영역(31)에 있어서는, 대략 반원통면의 상에 발광부(30a)가 설치된다. 발광부(30a)는, 광원(21a, 22a)과 마찬가지이고, 백색의 LED와 방열 부재를 가진다. 제1 영역(31)의 중심축 ax는, 제3 카메라(13)를 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 면인 중심면 S1 상에 위치한다. In the
제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)에 있어서는, 대략 반구면의 상(上) 또는 대략 반타원구면의 상에 발광부(30a)가 설치된다. 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)의 중심점은 중심면 S1 상에 위치한다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)은 대략 반구면이지만, 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)의 형상은 이에 한정되지 않는다. In the
제1 영역(31)에 있어서는, 제3 카메라(13)와 재치부(40)의 사이, 즉 중심면 S1의 근방 이외의 영역에, 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하는 방향(즉, y방향)을 따라 발광부(30a)가 늘어놓여져 있다. y방향을 따라 늘어놓여진 발광부(30a)를, 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31b, 31c, 32d, 31e, 31f, 31g···)(후에 상술)로 한다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 10개의 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)(도 4 참조)를 가지지만, 띠모양 발광부의 수는 이에 한정되지 않는다. In the 1st area|
도 3은 띠모양 발광부(31a)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다. 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)는 같은 구성이기 때문에, 띠모양 발광부(31a)에 대해서만 설명하고, 띠모양 발광부(31b~31j)에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. 3 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a)는, 전체의 길이가 3L이며, 길이 방향의 길이가 L로 되도록 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30b)을 3개 가진다. The strip-shaped light-emitting
발광부(30a)는, 가로폭 w가 3.4㎜ 정도, 길이 h가 3.4㎜ 정도이며, 인접하는 발광부(30a) 사이의 거리는 대략 0.2㎜이다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 발광 블록(30b)의 길이 L이 대략 50㎜이기 때문에, 1개의 발광 블록(30b)에 발광부(30a)가 13개 정도 늘어놓여진다. 이에 의해 띠모양 발광부(31a)로부터는, 띠모양(선 형상)의 광이 조사된다. The
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 발광부(30a)로서 백색 LED를 이용하지만, 발광부(30a)에 이용되는 것은 백색 LED에 한정되지 않는다. 발광부(30a)에는, 예를 들면, 청색 또는 자외 LED와 황색 형광체를 조합한 것, 적녹청의 3색 칩(chip)을 조합한 것, 청색 LED와 적색 및 녹색 형광제를 조합한 것의 어느 것을 이용하도록 해도 좋다. In addition, although a white LED is used as the
다음에, 입체 조명부(30)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)의 배치에 대해 설명한다. 도 4는 제1 영역(31)을 포함하도록 광학 검사 장치(1)를 xz평면과 평행한 면으로 절단했을 때에 있어서의 광학 검사 장치(1)의 단면을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이다. 도 4에 있어서 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)로부터 조사되는 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다. Next, the arrangement of the band-shaped
제1 영역(31)의 중심축 ax는, 커버 유리 G의 상면 근방에 위치하고, 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)는, 중심축 ax를 중심으로 한 반경 R의 원주(도 4에 있어서의 점선 참조) 상에 설치된다. 또한, 커버 유리 G의 두께는 미소하기 때문에, 커버 유리 G의 상면의 위치는, 중심면 S1과 재치부(40)(도 4에서는 도시 생략)의 상면과의 교선과 대략 일치한다. 반경 R은, 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)의 길이 3L과 대략 같다. The central axis ax of the
띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)는, 광축(도 4에 있어서의 일점 쇄선 참조)이 중심면 S1과 재치부(40)와의 교선(중심면 S1과 커버 유리 G와의 교선), 즉 중심축 ax와 교차하도록 설치된다. As for the strip|belt-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a~31e)는, 중심면 S1보다 +x측에 위치하고, 띠모양 발광부(31f~31j)는, 중심면 S1보다 -x측에 위치한다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)는, 중심면 S1에 가장 가까운 위치에 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ1은 대략 8°이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)는, 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)의 외측에, 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)에 인접하여 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ2는 대략 17°이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31c, 31h)는, 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)의 외측에, 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)에 인접하여 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31c, 31h)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ3은 대략 26°이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31d, 31i)는, 띠모양 발광부(31c, 31h)의 외측에, 띠모양 발광부(31c, 31h)에 인접하여 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31d, 31i)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ4는 대략 35°이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31e, 31j)는, 띠모양 발광부(31d, 31i)의 외측에, 띠모양 발광부(31d, 31i)에 인접하여 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31e, 31j)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ5는 대략 44°이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)는, 광축 상에 설치된 원통 렌즈(30c)를 가진다. 원통 렌즈(30c)는, 예를 들면 아크릴제의 봉재(棒材)를 중심 축을 따라 절단하고, 절단면을 연마함으로써 형성된다. 원통 렌즈(30c)는, 발광부(30a)와 중심축 ax와의 사이에 설치되고, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광을 중심축 ax 근방에 집광한다. The band-shaped
도 5는 입체 조명부(30)의 평면 모식도이다. 도 5에 있어서는, 제3 카메라(13)의 시야 위치(13c)를 점선으로 나타낸다. 또, 도 5에 있어서는, 발광 블록(30d)(후에 상술)을 파선으로 나타낸다. 5 is a schematic plan view of the three-
제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)은, 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)를 가진다. 또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 각 9개의 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)를 가지지만, 띠모양 발광부의 수는 이에 한정되지 않는다. The
띠모양 발광부(32a, 33a)는, 중심면 S1 상에 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(32b~32e, 33b~33e)는, 각각 띠모양 발광부(31a~31d)의 연장선의 상에 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(32f~32i, 33f~33i)는, 각각 띠모양 발광부(31f~31i)의 연장선의 상에 설치된다. The band-shaped
도 6은 띠모양 발광부(32a)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다. 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)는 대략 마찬가지의 구성이기 때문에, 띠모양 발광부(32a)에 대해서만 설명하고, 띠모양 발광부(32b~32i, 33a~33i)에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. 6 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the strip-shaped
띠모양 발광부(32a)는, 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30d)을 복수 가진다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 발광 블록(30d)의 길이 l이 대략 18.5㎜이며, 인접하는 발광부(30a) 사이의 거리는 대략 0.2㎜이기 때문에, 1개의 발광 블록(30d)에 발광부(30a)가 5개 정도 늘어놓여진다. 발광 블록(30d)은, 발광부(30a)가 반경 R의 대략 원통면의 상(도 6 점선 참조)에 위치하도록 인접하여 늘어놓여진다. The strip-shaped
도 5의 설명으로 되돌아온다. 띠모양 발광부(32a~32c, 32f, 32g, 33a~33c, 33f, 33g)에 있어서의 발광 블록(30d)의 수는 5개이며, 띠모양 발광부(32d, 32h, 33d, 33h)에 있어서의 발광 블록(30d)의 수는 4개이며, 띠모양 발광부(32d, 32h, 33d, 33h)에 있어서의 발광 블록(30d)의 수는 2개이지만, 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)에 있어서의 발광 블록(30d)의 수는 이에 한정되지 않는다. Returning to the description of FIG. 5 . The number of light-emitting
띠모양 발광부(32a, 33a)에 있어서의 각 발광 블록(30d)의 광축은, 제2 영역(32), 제3 영역(33)의 중심점 O2, O3을 향하고 있다. 띠모양 발광부(32b~32i, 33a~33i)에 있어서의 각 발광 블록(30d)의 광축은, 제1 영역(31)의 중심점 O1을 향하고 있다. 다만, 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)에 있어서의 각 발광 블록(30d)의 광축의 방향은, 도 5에 나타내는 형태에 한정되지 않는다. The optical axis of each
도 7은 광학 검사 장치(1)의 전기적인 구성을 나타내는 블록도이다. 광학 검사 장치(1)는, 집적회로(71)와, 입력부(72)와, 출력부(73)와, 전원부(74)와, 통신 인터페이스(I/F)(75)를 가진다. 7 is a block diagram showing an electrical configuration of the
집적회로(71)는, 예를 들면 FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)이고, 프로그램에 기초하여 동작하고, 각부의 제어를 행한다. 집적회로(71)는, 광학 검사 장치(1)의 각부를 제어하는 제어부(본 발명의 제어부, 제2 제어부를 포함)의 기능을 가진다. 구체적으로는, 집적회로(71)는, 입력부(72), 출력부(73) 등으로부터 신호를 취득하고, 취득한 신호에 기초하여 출력부(73)로부터 출력하는 신호를 생성한다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 집적회로(71)인 FPGA에 각 기능을 실현하는 프로그램이 격납되어 있지만, 집적회로(71)는 FPGA에 한정되지 않고, 프로그램의 실행 방법도 이에 한정되지 않는다. The
입력부(72)에는, 위치 검출 센서(81, 82) 등의 각종 센서로부터 신호가 입력된다. 입력부(72)는, 출력부(73)의 각 채널의 출력 모드 설정, 촬상부(10)의 촬상 주파수의 설정 등을 행하는 스위치를 가진다. Signals are input to the
출력부(73)는, 복수의 채널을 가지고, 촬상부(10), 동축 조명부(20), 입체 조명부(30) 등에 다른 채널로부터 출력을 행한다. 예를 들면, 출력부(73)는, 구동 모터 펄스를 반송부(50)로 출력하고, 수평 동기 신호 및 수직 동기 신호 등을 촬상부(10)로 출력한다. 또, 출력부(73)는, 통신 에러(error), 타임 아웃(time out) 등의 에러 표시, 커버 유리 G의 주행중, 촬상부(10)의 캡처(capture) 대기중, 동축 조명부(20)나 입체 조명부(30)의 조명중 등을 나타내는 LED, 7세그먼트 디스플레이(7 segment display) 등의 표시 소자를 가진다. The
도 8은 출력부(73)와 광학 검사 장치(1)의 각 구성과의 전기적인 접속을 설명하는 블록도이다. 출력부(73)는, 촬상부(10)(제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 제3 카메라(13))와, 동축 조명부(20)(상측 동축 조명(21) 및 하측 동축 조명(22))과, 입체 조명부(30)(띠모양 발광부(31a~31j, 32a~32i, 33a~33i)와, 반송부(50)에 신호를 출력한다. 8 is a block diagram for explaining the electrical connection between the
출력부(73)로부터 출력되는 신호는, 통신 I/F(75)를 통해 퍼스널 컴퓨터(PC)(100)로부터 입력되는 수평 동기 신호 등에 기초하여 집적회로(71)에서 생성된다. The signal output from the
도 7의 설명으로 되돌아온다. 전원부(74)는, 예를 들면 AC 100V의 전압이 입력되는 것이고, 필요한 전압으로 변환하는 스위칭(switching) 전원을 내부에 포함한다. 전원부(74)는, 동축 조명부(20)나 입체 조명부(30)에 전력을 공급한다. Returning to the description of FIG. 7 . The
통신 I/F(75)는, 외부 기기로부터 데이터를 수신하여 집적회로(71)에 송신함과 아울러, 집적회로(71)가 생성한 데이터를 다른 기기에 송신한다. 또, 통신 I/F(75)는, 집적회로(71)의 프로그래밍, 디버그(debug)를 행하기 위한 커넥터를 가진다. 통신 I/F(75)는, PC(personal computer)(100)로부터, 수평 동기 신호 및 수직 동기 신호, 구동 모터 스타트(start) 신호 등을 취득하고, 집적회로(71)로 출력한다. 또, 통신 I/F(75)는, PC(100) 등에 촬상부(10)가 촬상한 화상 데이터를 출력한다. The communication I/
위치 검출 센서(81, 82)는, 커버 유리 G의 위치를 검출한다. 위치 검출 센서(81)는, 커버 유리 G가 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12) 하로 반송된 것 및 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)의 하를 다 통과한 것을 검출한다. 위치 검출 센서(82)는, 커버 유리 G가 제3 카메라(13) 하로 반송된 것 및 제3 카메라(13)의 하를 다 통과한 것을 검출한다. The
PC(100)는, CPU(Central Processing Unit)(101)와, RAM(Random Access Memory)(102)과, ROM(Read Only Memory)(103)과, 입출력 인터페이스(I/F)(104)와, 통신 인터페이스(I/F)(105)와, 미디어 인터페이스(I/F)(106)를 가진다.
CPU(101)는, RAM(102), ROM(103)에 격납된 프로그램에 기초하여 동작하고, 각부의 제어를 행한다. CPU(101)로부터 출력된 신호는, 통신 I/F(105)를 통해 광학 검사 장치(1)로 출력된다. The
RAM(102)은, 휘발성 메모리이다. RAM(102)은, CPU(101)가 실행하는 프로그램 및 CPU(101)가 사용하는 데이터 등을 격납한다. ROM(103)은, 각종 제어 프로그램 등이 기억되어 있는 불휘발성 메모리이다. CPU(101)는, RAM(102), ROM(103)에 격납된 프로그램에 기초하여 동작하고, 각부의 제어를 행한다. ROM(103)은, PC(100)의 기동시에 CPU(101)가 행하는 부트(boot) 프로그램이나, PC(100)의 하드웨어에 의존하는 프로그램 등을 격납한다.
CPU(101)는, 입출력 I/F(104)를 통해, 키보드나 마우스 등의 입력 장치(111)나, 표시 장치 등의 출력 장치(112)를 제어한다. CPU(101)는, 통신 I/F(105)를 통해, 네트워크 등을 통해 광학 검사 장치(1)나 다른 기기로부터 데이터를 취득함과 아울러, 생성한 데이터를 광학 검사 장치(1)로 출력한다. The
CPU(101)는, 입력 장치(111)로부터의 입력에 기초하여, 출력부(73)의 채널의 출력 설정, 집적회로(71)에 있어서의 점등 신호 출력의 차례, 처리의 루프(loop) 설정, 커버 유리 G의 가장자리 검출로부터 촬상 개시까지의 커버 유리 G의 이동 거리(공주행(空走行) 거리)의 설정 등, 각종 설정을 행하고, 이들의 설정 데이터를 생성한다. 통신 I/F(105)는, CPU(101)가 생성한 설정 데이터를 광학 검사 장치(1)로 출력한다. 또, CPU(101)는, 촬상부(10)에서 촬상된 화상을 광학 검사 장치(1)로부터 취득하고, 검사용의 화상을 생성한다. 화상 생성 처리의 자세한 것은 후에 상술한다. Based on the input from the
미디어 I/F(106)는, 기억 매체(113)에 격납된 프로그램 또는 데이터를 읽어내고, RAM(102)에 격납한다. 또한, 기억 매체(113)는, 예를 들면, IC카드, SD카드, DVD 등이다. The media I/
또한, 각 기능을 실현하는 프로그램은, 예를 들면, 기억 매체(113)로부터 읽어내져, RAM(102)를 통해 광학 검사 장치(1)에 인스톨(install)되고, CPU(101)에 의해 실행된다. Further, a program for realizing each function is read from, for example, the
도 7에 나타내는 광학 검사 장치(1) 및 PC(100)의 구성은, 본 실시 형태의 특징을 설명하는데 즈음하여 주요 구성을 설명한 것으로서, 예를 들면 일반적인 정보처리 장치가 구비하는 구성을 배제하는 것은 아니다. 광학 검사 장치(1)의 구성 요소는, 처리 내용에 따라 더 많은 구성 요소로 분류되어도 좋고, 1개의 구성 요소가 복수의 구성 요소의 처리를 실행해도 좋다. 또, 도 7에 있어서는, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 PC(100)를 다른 장치로 하였지만, PC(100)의 구성 요소가 광학 검사 장치(1)에 포함되어 있어도 좋다. The configuration of the
이와 같이 구성된 광학 검사 장치(1)로 행하는 처리에 대해 설명한다. 이하의 처리는, 주로 집적회로(71)로 행해진다. The processing performed by the
집적회로(71)는 재치부(40)의 롤러(40a)를 구동하는 구동 모터 펄스를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 반송부(50)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G가 재치부(40) 상을 반송 방향 F를 따라 일정한 속도로 이동한다. The
위치 검출 센서(81)로부터 커버 유리 G가 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 하로 반송된 것이 검출되면, 검출 신호가 위치 검출 센서(81)로부터 입력부(72)를 통해 집적회로(71)에 입력된다. 이 검출 신호가 입력되면, 집적회로(71)는, 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상하는 처리를 개시한다. 이하, 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리에 있어서, 도 9, 10을 이용하여 설명한다. When it is detected that the cover glass G has been conveyed from the
<투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리> <Processing of capturing a transmitted image and a specular reflection image>
도 9는 출력부(73)로부터 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 동축 조명부(20)로 출력되는 신호에 대해 설명하는 도이다. 채널(이하, ch라고 함)은, 출력부(73)가 가지는 채널의 일부이며, ch1~3은 상측 동축 조명(21)으로의 출력이며, ch4~6은 하측 동축 조명(22)으로의 출력이다. ROOP는, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호이며, 집적회로(71)로 출력된다. 또한, 도 9의 ch1~6에 기재된 수치는, 상측 동축 조명(21), 하측 동축 조명(22)을 조사하는 시간이며, 단위는 ㎲(마이크로초(micro second))이다. 9 is a diagram for explaining signals output from the
도 10은 도 9에 나타내는 처리에 있어서의 타이밍 차트이다. 촬상 신호는, 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)를 구동하는 신호이며, 일정한 주기로 입력되는 수평 동기 신호에 기초하여 집적회로(71)에 있어서 생성된다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 촬상 신호의 주파수가 3㎑이며, 촬상 신호의 간격 T는 대략 330㎲이다. 촬상 신호는, 촬상 기간 T1은 하이(High), 블랭킹(blanking) 기간 T2가 로우(Low)로 되는 신호이며, 촬상 기간 T1을 조정함으로써 제1 카메라(11)나 제2 카메라(12)의 광량(촬상되는 화상의 밝음)을 조정한다. 동축 조명용 신호는, 촬상 신호에 동기하여 생성된다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 촬상 기간 T1을 300㎲로 하지만, 촬상 기간 T1은 이에 한정되지 않는다. Fig. 10 is a timing chart in the process shown in Fig. 9; The imaging signal is a signal for driving the
이하, 도 9, 10에 나타내는 차례 1~3의 처리에 대해 자세하게 설명한다. Hereinafter, the processes of
(차례 1) (Top 1)
집적회로(71)는, 상측 동축 조명(21)을 5㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이 신호를 상측 동축 조명(21)으로 출력한다. 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제2 카메라(12)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제2 카메라(12)에는 커버 유리 G를 투과한 광이 입사하고, 제2 카메라(12)로 투과 화상이 촬상된다. 투과 화상에서는, 불투명한 부분의 결함, 예를 들면 인쇄 부분의 흠집, 인쇄 가장자리의 이지러짐 등을 검출할 수가 있다. The
차례 1에 있어서, 상측 동축 조명(21)을 조사시키는 신호는, 촬상 신호가 하이(High)로 됨과 동시에 하이(High)로 되고, 5㎲ 경과후에 로우(Low)로 된다. 상측 동축 조명(21)을 조사하는 5㎲라고 하는 시간은, 촬상 기간 300㎲에 비해 매우 짧다. 유리에 있어서는, 4% 정도의 광이 반사하고, 나머지의 96% 정도의 광이 투과한다. 따라서, 상측 동축 조명(21)을 조사하는 시간을 짧게 함으로써, 적절한 명도의 투과 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. In
또한, 차례 1에 있어서는, 상측 동축 조명(21)을 5㎲로 조사하고, 제2 카메라(12)로 투과 화상을 촬상하였지만, 하측 동축 조명(22)을 5㎲로 조사하고, 제1 카메라(11)로 투과 화상을 촬상해도 좋다. Further, in
(차례 2) (Top 2)
집적회로(71)는, 상측 동축 조명(21)을 100㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이 신호를 상측 동축 조명(21)으로 출력한다. 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제1 카메라(11)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제1 카메라(11)에는 커버 유리 G의 표면에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고, 제1 카메라(11)로 정반사 화상이 촬상된다. The
상측 동축 조명(21)으로부터는 커버 유리 G에 수직 방향으로부터 광을 조사한다. 따라서, 커버 유리 G의 표면의 흠집, 이물질 등이 없는 부분은, 광이 정반사하여 제1 카메라(11)에 입사하기 때문에, 촬상된 화상에 있어서 밝게 비친다. 이에 반해 커버 유리 G의 표면에 흠집이나 이물질 등이 있는 부분은, 광이 난반사하여 제1 카메라(11)에 입사하지 않기 때문에, 촬상된 화상에 있어서 어둡게 비친다. 이와 같이 하여 커버 유리 G의 표면의 흠집이나 이물질 등을 검출할 수가 있다. 또한, 정반사광으로 표면의 흠집이나 이물질 등을 검출하는 것은, 경면 등 반사율이 높은 것에만 유효하다. Light is irradiated from the upper side
(차례 3) (Top 3)
집적회로(71)는, 하측 동축 조명(22)을 100㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이 신호를 하측 동축 조명(22)으로 출력한다. 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제2 카메라(12)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제2 카메라(12)에는 커버 유리 G의 이면에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고, 제2 카메라(12)로 반사 화상이 촬상된다. 이와 같이 하여 커버 유리 G의 이면의 흠집이나 이물질 등을 검출할 수가 있다. The
또, 집적회로(71)는, 차례 3의 출력을 행함과 동시에 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 생성한다. 출력부(73)는, 하측 동축 조명(22)에 신호를 출력함과 동시에, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 집적회로(71)로 출력한다. 집적회로(71)는, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 받아, 처리를 최초로 되돌리고, 차례 1~3에 나타내는 신호를 차례로 출력하는 처리를 반복한다. In addition, the
차례 2, 3에 있어서, 상측 동축 조명(21)이나 하측 동축 조명(22)을 조사시키는 신호는, 촬상 신호가 하이(High)로 됨과 동시에 하이(High)로 되고, 100㎲ 경과후에 로우(Low)로 된다. 차례 2에서 상측 동축 조명(21), 차례 3에서 하측 동축 조명(22)을 조사하는 100㎲라고 하는 시간은, 촬상 기간 T1(300㎲)의 1/3 정도이며, 차례 1에 있어서의 조사 시간(5㎲)에 비해 대폭 길다. 이와 같이, 정반사 화상을 촬상할 때는 상측 동축 조명(21)이나 하측 동축 조명(22)을 조사하는 시간을 길게 함으로써, 적절한 명도의 반사 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. In Steps 2 and 3, the signal for irradiating the upper
집적회로(71)는, 상기 차례 1~3의 조사 패턴의 신호 출력과 동시에, 출력부(73)를 통해 반송부(50)에 구동 모터 펄스를 출력한다. 이에 의해 재치부(40) 상에서 커버 유리 G를 일정한 속도로 반송하여 커버 유리 G와 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)와의 위치를 상대적으로 변화시키면서, 제1 카메라(11) 또는 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상이 행해진다. The
이에 의해 피검사물을 1회 반송하는 동안에, 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 다른 타이밍으로 촬영할 수가 있다. 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)로 커버 유리 G의 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리는, 커버 유리 G가 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)를 다 통과할 때까지 계속한다. 커버 유리 G가 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)를 다 통과하면, 위치 검출 센서(81)에 의한 검출 신호가 집적회로(71)에 입력된다. 이 검출 신호가 입력되면, 집적회로(71)는, 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 동축 조명부(20)로의 신호 출력을 종료한다. Thereby, the transmission image and the specular reflection image can be image|photographed at different timings while the to-be-inspected object is conveyed once. In the process of imaging the transmission image and the specular reflection image of the cover glass G with the
집적회로(71)는, 출력부(73)를 통해 반송부(50)로 구동 모터 펄스를 계속하여 출력한다. 위치 검출 센서(82)에 의해 커버 유리 G가 제3 카메라(13) 하로 반송된 것이 검출되면, 검출 신호가 위치 검출 센서(82)로부터 입력부(72)를 통해 집적회로(71)에 입력된다. 이 검출 신호가 입력되면, 집적회로(71)는, 반사 화상을 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상하는 처리를 개시한다. 이하, 반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리에 대해 도 11~도 14를 이용하여 설명한다. The
<반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리> <Process of capturing a reflected image>
도 11은 출력부(73)로부터 제3 카메라(13) 및 입체 조명부(30)로 출력되는 신호에 대해 설명하는 도이다. ch11~46은, 출력부(73)가 가지는 채널의 일부이다. ch11~46에 기재된 수치는, 입체 조명부(30)를 조사하는 시간이며, 단위는 ㎲이다. 도 11에 있어서는, 일부의 ch에 대한 도시를 생략한다. 또, 도 12는 도 11에 나타내는 신호 출력과 제3 카메라(13)에서 촬상되는 화상에 포함되는 결함과의 대응을 나타내는 도이다. 도 13은 커버 유리 G의 단면에 있어서의 광의 모습을 나타내는 도이고 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다. 도 14는 도 11에 나타내는 처리에 있어서의 타이밍 차트이다. 11 is a diagram for explaining signals output from the
도 11에 있어서, ch11~40은 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)로의 출력이다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 발광 블록(30b)마다 1개의 채널이 할당되어 있다. 예를 들면, ch11~13은 띠모양 발광부(31a)(이를 구성하는 3개의 발광 블록(30d), 이하 같음)으로의 출력이며, ch14~16은 띠모양 발광부(31b)로의 출력이며, ch17~19는 띠모양 발광부(31c)로의 출력이며, ch20~22는 띠모양 발광부(31d)로의 출력이며, ch23~25는 띠모양 발광부(31e)로의 출력이며, ch26~28은 띠모양 발광부(31f)로의 출력이며, ch29~31은 띠모양 발광부(31g)로의 출력이며, ch32~34는 띠모양 발광부(31h)로의 출력이며, ch35~37은 띠모양 발광부(31i)로의 출력이며, ch38~40은 띠모양 발광부(31j)로의 출력이다. In Fig. 11, ch11 to 40 are outputs to the band-shaped
또, ch41은 띠모양 발광부(32a)로의 출력이며, ch42는 띠모양 발광부(32b~32e)로의 출력이며, ch43는 띠모양 발광부(32f~32i)로의 출력이다. 또한, ch44는 띠모양 발광부(33a)로의 출력이며, ch45는 띠모양 발광부(33b~33e)로의 출력이며, ch46는 띠모양 발광부(33f~33i)로의 출력이다. Note that ch41 is an output to the band-shaped light-emitting
이하, 도 11, 13에 나타내는 차례 1~9의 처리에 대해 자세하게 설명한다. Hereinafter, the processes of
(차례 1) (Top 1)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(31f)를 100㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31g)를 120㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31h)를 150㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31i)를 180㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31j)를 210㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(31f~31j)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 -x방향으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 선단(+x측의 끝)의 P면의 내측의 면(이하, P내면이라고 함)에서 반사한 광이 입사한다(도 13 참조). 차례 1에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 선단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함(인쇄 얼룩짐, 연마 얼룩짐, 흠집 등)이 빛난 화상이다(도 12 참조). In the
(차례 2) (Top 2)
커버 유리 G의 인쇄 부분에 펄(pearl) 도장이 되어 있는 경우에는, 집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(31b)를 300㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31g)를 300㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는, +x방향 17°및 -x방향 17°로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄부에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. When the printed portion of the cover glass G is coated with pearl, the
또, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄 부분에 펄(pearl) 도장 이외의 인쇄(단색 인쇄 등)가 되어 있는 경우에는, 집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(31a)를 300㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31f)를 300㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)로 출력한다. 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는, +x방향 8°및 -x방향 8°로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄부에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. In addition, when printing other than pearl coating (monochromatic printing, etc.) is performed on the printed part of the cover glass G, the
차례 2에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄부의 결함(얼룩 등)이 다른 인쇄부와 다른 콘트라스트(contrast)의 화상(예를 들면, 인쇄부의 결함이 다른 인쇄부보다 어둡거나 밝거나 하는 화상)이다(도 12 참조). The image captured by the
(차례 3) (Top 3)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(31a)를 100㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31b)를 120㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31c)를 150㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31d)를 180㎲, 띠모양 발광부(31e)를 210㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(31a~31e)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 +x방향으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 후단(-x측의 끝)의 P내면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다(도 13 참조). 차례 3에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 후단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상이다(도 12 참조). In the
(차례 4) (Top 4)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(32a)를 200㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(32a)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 -y방향으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 좌단(+y측의 끝)의 P내면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. 차례 4에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 좌단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상이다(도 12 참조). The
(차례 5) (Top 5)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(33a, 33f~33i, 31f~31j)를 3㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(33a, 33f~33i, 31f~31j)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 +y방향 및 +y방향과 -x방향과의 사이로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 좌단 또한 좌후단측의 P면의 표측(表側)(이하 P표면이라고 함)에서 반사한 광이 입사한다(도 13 참조). 차례 5에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 좌단 또한 좌후단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 화상이다(도 12 참조). 이 화상에서는, P표면에 있어서의 흠집, 이물질 등의 결함의 대부분이 어둡게 비친다. The
(차례 6) (Top 6)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(33b~33e)를 3㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(33b~33e)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 +y방향과 +x방향과의 사이로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 좌단으로부터 선단측의 P표면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. 차례 6에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 좌단으로부터 선단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 화상이다(도 12 참조). The
(차례 7) (Top 7)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(33a)를 200㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(33a)로 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 +y방향으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 우단(-y측의 끝)의 P내면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. 차례 7에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 우단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상이다(도 12 참조). The
(차례 8) (Top 8)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(32f~32i)를 3㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(32f~32i)에 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 -y방향과 -x방향과의 사이로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 우단으로부터 후단측의 P표면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. 차례 8에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 우단으로부터 후단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 화상이다(도 12 참조). The
(차례 9) (Top 9)
집적회로(71)는, 띠모양 발광부(32a~32e, 31a~31e)를 3㎲로 조사시키는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 이 신호를 띠모양 발광부(32a~32e, 31a~31e)에 출력한다(도 11 참조). 이와 동시에 집적회로(71)는 촬상 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 제3 카메라(13)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)에는 -y방향 및 -y방향과 +x방향과의 사이로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G의 우단으로부터 우선단측의 P표면에서 반사한 광이 입사한다. 차례 9에서 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상되는 것은, 커버 유리 G의 우단 또한 우선단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 화상이다(도 12 참조). The
또, 집적회로(71)는, 차례 9의 출력을 행함과 동시에 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 집적회로(71)로 출력한다. 집적회로(71)는, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 받아, 처리를 최초로 되돌리고, 차례 1~9에 나타내는 신호를 차례로 출력하는 처리를 반복한다. In addition, the
여기서, 차례 4, 7에 있어서 각각 좌단, 우단의 P내면을 검사할 때는, 차례 5, 6, 8, 9에 있어서 P표면을 검사할 때보다 훨씬 긴 시간, 띠모양 발광부(32a, 33a)를 조사한다. 따라서, 차례 4, 7에 있어서 제3 카메라(13)에서는, 각각 커버 유리 G의 P면이 새하얗게 빛난, 포화한 화상이 촬상된다. Here, when inspecting the inner surface of the P at the left end and the right end in
또한, 도 11, 12 등에 나타내는 차례 1~9는 일례이며, 검사 부위나 검사 내용의 차례는 임의로 정할 수가 있다. 또, 차례 1에서 나타내는 커버 유리 G의 선단의 P내면의 검사, 및 차례 6에서 나타내는 커버 유리 G의 좌단으로부터 선단측의 P표면의 검사는, 커버 유리 G의 중앙부, 후단부에서는 불필요하고, 차례 3에서 나타내는 커버 유리 G의 후단의 P내면의 검사, 및 차례 8에서 나타내는 커버 유리 G의 우단으로부터 후단측의 P표면의 검사는, 커버 유리 G의 선단부, 중앙부에서는 불필요하다. 집적회로(71)는, 커버 유리 G의 길이를 나타내는 정보로부터 구동 모터 펄스(pulse) 수를 산출하고, 출력한 구동 모터 펄스 수에 기초하여 커버 유리 G의 위치를 구하고, 커버 유리 G의 위치에 따라 차례 1, 3, 6, 8을 생략하도록 해도 좋다. In addition, the order 1-9 shown to FIG. 11, 12 etc. are an example, and the order of an examination site|part and examination content can be set arbitrarily. In addition, the test|inspection of the P inner surface of the front-end|tip of the cover glass G shown in
도 14는 도 11에 나타내는 처리에 있어서의 타이밍 차트이다. 또한, 차례 1에 있어서는, 100㎲로 조사시키는 신호만을 표시한다. 촬상 신호는 도 10에 나타내는 것과 마찬가지이다. 입체 조명부(30)를 조사시키는 신호는, 촬상 신호가 하이(High)로 됨과 동시에 하이(High)로 되고, 각각 조사 시간 경과후에 로우(Low)로 된다. Fig. 14 is a timing chart in the process shown in Fig. 11; In addition, in
또한, P표면에서 반사한 광을 제3 카메라(13)에 입사시키는 경우와 인쇄부에서 반사한 광을 제3 카메라(13)에 입사시키는 경우에는, 필요한 광량은 1:100 정도이다. 따라서, P면에서 반사한 광을 제3 카메라(13)에 입사시키는 경우와 인쇄부에서 반사한 광을 제3 카메라(13)에 입사시키는 경우에 입체 조명부(30)의 조사 시간을 다르게 한다. In addition, when the light reflected from the P surface is made to enter the
집적회로(71)는, 상기 차례 1~9의 신호 출력과 동시에, 출력부(73)를 통해 반송부(50)에 구동 모터 펄스를 출력한다. 이에 의해 재치부(40) 상에서 커버 유리 G를 일정한 속도로 반송하여 커버 유리 G와 제3 카메라(13)와의 위치를 상대적으로 변화시키면서, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상이 행해진다. The
이에 의해 선단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 후단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 좌우단 P면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 화상, 인쇄부의 결함이 다른 인쇄부보다 어두운 화상을, 커버 유리 G를 1회 반송하는 동안에 제각기의 타이밍으로 촬영할 수가 있다. 제3 카메라(13)로 커버 유리 G의 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리는, 커버 유리 G가 제3 카메라(13)를 다 통과할 때까지 계속한다. 커버 유리 G가 제3 카메라(13)를 다 통과하면, 위치 검출 센서(82)에 의한 검출 신호가 집적회로(71)에 입력된다. 이 검출 신호가 입력되면, 집적회로(71)는, 제3 카메라(13) 및 입체 조명부(30)로의 신호 출력을 종료한다. Thereby, the image in which the defect in the front end P surface shines, the image in which the defect in the rear end P surface shines, the image in which the defect in the left and right ends P surface shines, and the image in which the defect in a printed part is darker than other printed parts are obtained by the cover glass During one transfer of G, it is possible to take pictures at different timings. The process of imaging the transmission image of the cover glass G and the specular reflection image with the
그 후, 집적회로(71)는, 소정의 펄스 수만큼 반송부(50)에 구동 모터 펄스 출력하고, 커버 유리 G를 처리 종료 위치까지 이동시킨다. 그리고, 집적회로(71)는, 일련의 처리를 종료한다. Then, the
일련의 처리가 종료하면, 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상은, 출력부(73)를 통해 PC(100)로 출력된다. CPU(101)는, 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상으로부터 검사용의 화상을 생성한다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, CPU(101)는, 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 및 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상 중에서, 같은 조명 패턴으로 촬상된 화상을 추출하고, 이들을 연결하여 평면 화상을 생성한다. 이하, 화상 생성 처리에 대해 설명한다. When the series of processing is finished, the images captured by the
CPU(101)는, 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상된 화상으로부터 투과 화상 및 정반사 화상을 생성한다. 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리에서는, 도 9, 10에 나타내듯이, 차례 1~3의 조사 패턴의 조사를 반복해 가고 있다. 따라서, CPU(101)는, 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상된 화상중 1프레임째를 기준으로 하여 3프레임 띄움(1프레임째, 4프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 투과 화상(평면 화상)이 생성된다. 투과 화상은, 도 15에 나타내듯이, 불투명한 인쇄 부분이 어둡게 비친 화상이며, 인쇄의 결함부(도 15에 있어서의 점선의 둥근 표시부)가 확인 가능하다. The
또, CPU(101)는, 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상된 화상중 2프레임째를 기준으로 하여 3프레임 띄움(2프레임째, 5프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 상측의 정반사 화상, 즉 커버 유리 G의 표면에 있어서의 정반사 화상(평면 화상)이 생성된다. 정반사 화상은, 도 16에 나타내듯이, 결함(도 16에서는 흠집을 예시하고 있음)이 없는 부분은 밝고, 흠집이 어둡게 비친 화상이다. 또한, 흠집이 인쇄 부분과 겹쳐있다고 해도, 인쇄 부분보다 유리 표면에서의 반사율이 높기 때문에, 흠집은 다른 부분보다 어둡게 비친다. Further, the
또한, CPU(101)는, 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상된 화상중 3프레임째를 기준으로 하여 3프레임 띄움(3프레임째, 6프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 하측의 정반사 화상, 즉 커버 유리 G의 이면에 있어서의 정반사 화상(평면 화상)이 생성된다. Further, the
또, CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상으로부터 반사 화상을 생성한다. 반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리에서는, 도 11~13에 나타내듯이, 차례 1~9의 조사 패턴의 조사를 반복해 가고 있다. 따라서, CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 1프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(1프레임째, 10프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 도 17에 나타내듯이, 커버 유리 G의 선단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. Further, the
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 2프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(2프레임째, 11프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 도 18에 나타내듯이, 커버 유리 G의 인쇄부의 결함이 다른 인쇄부보다 어둡게 비친 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다.
또한, 설명을 위해 도 17, 도 18은 평면 화상의 일부를 확대하고 있고, 결함의 주위에 흑선을 표시하고 있다. In addition, for explanation, a part of the planar image is enlarged in FIGS. 17 and 18, and black lines are displayed around the defect.
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 3프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(3프레임째, 12프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 후단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다.
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 4프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(4프레임째, 13프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 좌단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 5프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(5프레임째, 14프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 좌단 또한 후단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 6프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(6프레임째, 15프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 좌단으로부터 선단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 7프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(7프레임째, 16프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 우단의 P내면에 있어서의 결함이 빛난 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 8프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(8프레임째, 17프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 우단으로부터 후단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
CPU(101)는, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중 9프레임째를 기준으로 하여 9프레임 띄움(9프레임째, 18프레임째···)의 프레임을 추출하고, 이들 화상을 연결하여 2차원의 화상을 생성한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G의 우단 또한 선단측의 P표면에 있어서의 결함이 비친 커버 유리 G의 평면 화상이 생성된다. The
본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 입체 조명부(30)를 이용하여 여러 가지 방향으로부터 광을 커버 유리 G에 조사하여 화상을 촬상하기 때문에, 결함이 커버 유리 G의 단면의 어느 위치에 있었다고 해도, 1개의 광학 검사 장치(1)를 이용하여, 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. According to this embodiment, since the cover glass G is irradiated with light from various directions using the
특히, 제1 영역(31)에 있어서는, 중심면 S1의 근방 이외의 영역에, y방향을 따라 발광부(30a)가 늘어놓여져 있다. 따라서, 띠모양의 광을 커버 유리 G에 조사하고, y방향의 위치에 의하지 않고 중심축 ax 근방의 영역을 마찬가지로 검사할 수가 있다. In particular, in the
또, 복수의 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)를 구비하기 때문에, 여러 가지 각도로부터 중심축 ax 근방의 영역에 광을 조사할 수가 있다. P면에 있어서의 결함의 전체상을 촬상하기 위해서는, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도가 8°근방인 광원으로부터 44°근방인 광원까지 동시에 광을 조사하는 것이 중요하다. 따라서, 선단이나 후단의 P면에 있어서의 결함의 전체상을 촬상하기 위해서는, 복수의 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)를 구비하는 것이 중요하다. 또, 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)에 있어서는, 중심면 S1 상의 위치에 띠모양 발광부(32a, 33a)가 설치되어 있기 때문에, 좌우 양측의 P면에 대해 결함의 전체상을 촬상할 수가 있다. Further, since the plurality of band-shaped
또, 본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ2가 대략 17°로 되도록 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)가 배치되어 있고, 펄 인쇄에서 광이 반사했을 때의 산란광을 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상함으로써, 펄재(pearl material)의 광택에 비해 결함의 콘트라스트(contrast)가 커진 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. In addition, according to this embodiment, the band-shaped
예를 들면, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ1이 대략 8°인 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)로 촬상한 경우에는, 펄재의 광택이 강하게 비쳐들어가 버린다. 또, 예를 들면, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ3이 대략 26°인 띠모양 발광부(31c, 31h)로 촬상한 경우나, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ4가 대략 35°인 띠모양 발광부(31d, 31i)로 촬상한 경우에는, 펄(pearl) 도장의 결함 부분의 콘트라스트가 작아져 버린다. For example, when an image is captured by the band-shaped
이에 반해 본 실시의 형태와 같이, 법선 방향에 대해서 17°의 각도로부터 커버 유리 G에 광을 조사함으로써, 펄(pearl) 도장의 결함 부분의 콘트라스트가 다른 부분에 대해서 낮게 되고 또는 높게 된 화상을 촬상할 수가 있고, 또한 펄재의 광택이 결함 검출의 문턱값에 걸리기 어렵다. 따라서, 이 촬상 화상에 기초하여 펄(pearl) 도장의 결함을 용이하게 검출할 수가 있다. On the other hand, as in the present embodiment, by irradiating the cover glass G with light from an angle of 17° with respect to the normal direction, an image in which the contrast of the defective portion of the pearl coating becomes low or high with respect to other portions is captured. It can be done, and the luster of the pearl material does not easily hit the threshold value of defect detection. Accordingly, a defect in the pearl coating can be easily detected based on this captured image.
또, 본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ1이 대략 8°로 되도록 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)가 배치되어 있고, 법선 방향에 대해서 8°의 각도로부터 커버 유리 G에 광을 조사함으로써 단색 인쇄의 결함 부분의 콘트라스트가 다른 부분에 대해서 낮게 되고 또는 높게 된 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. Moreover, according to this embodiment, the strip|belt-shaped
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 촬상부(10)의 촬상 시간을 변경하지 않고, 동축 조명부(20), 입체 조명부(30)로부터의 광의 조사 시간을 변경함으로써, 촬상 내용에 따라 광량을 다르게 할 수가 있다. In addition, in this embodiment, without changing the imaging time of the
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 제3 카메라(13)에 대응하여 입체 조명부(30)를 설치하고, 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상된 화상중에서 같은 조사 패턴으로 촬상된 화상을 뽑아내고, 조사 패턴마다 다른 평면 화상을 생성함으로써, 복수의 카메라를 사용한 촬상과 동등의 화상을 최소의 카메라 수로 실현할 수가 있다. Moreover, in this embodiment, the three-
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 광학 검사 장치(1)는 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)와 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)를 양쪽 모두 구비하고 있기 때문에, 같은 장치로, 펄 안료를 이용한 경우, 펄 안료를 이용하지 않는 경우의 어느 것에 대해서도, 인쇄부의 색얼룩 등을 검출 가능한 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. Moreover, in this embodiment, since the
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ1이 대략 8°이지만, 각도 θ1은 대략 8~10°이면 좋다. 또, 각도 θ2~θ5도 도시한 각도에 한정되지 않는다. In the present embodiment, the angle θ1 between the optical axis of the band-shaped
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, PC(100)로 결함 검출용의 화상을 생성하였지만, PC(100)에 있어서, 생성한 화상에 기초하여 커버 유리 G의 결함을 검출하도록 해도 좋다. 예를 들면, 도 14에 나타내는 화상에 있어서는, 화소치와 문턱값을 비교함으로써 결함을 검출할 수가 있다. 또, 예를 들면, 도 15에 나타내는 화상에 있어서는, 복수 화소의 평균치를 산출하고, 그 평균치와 문턱값(threshold)을 비교함으로써 결함을 검출할 수가 있다. Moreover, in this embodiment, although the image for defect detection was produced|generated with PC100, you may make it detect the defect of the cover glass G based on the created image in PC100. For example, in the image shown in FIG. 14, a defect can be detected by comparing a pixel value and a threshold value. Moreover, in the image shown in FIG. 15, for example, a defect can be detected by calculating the average value of a plurality of pixels, and comparing the average value with a threshold value.
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)의 광축 상에 원통 렌즈(cylindrical lens)(30c)를 설치하였지만, 원통 렌즈(30c)는 필수는 아니다. 다만, 원통 렌즈(30c)를 가지는 경우에는, 원통 렌즈(30c)에 의해 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광을 중심축 ax 근방에 집광할 수가 있고, 이에 의해 제3 카메라(13)를 향하는 광량을 증가시킬 수가 있다. 따라서, 촬상부(10)의 촬상 주파수를 높게(촬상 시간을 짧게) 할 수가 있다. Moreover, in this embodiment, although a
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 도 11에 나타내듯이, 띠모양 발광부(32a, 32b~32e, 32f~32i)를 각각 다른 채널에 접속하고, 띠모양 발광부(33a, 33b~33e, 33f~33i)를 각각 다른 채널에 접속하였지만, 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)와 채널과의 관계는 이에 한정되지 않는다. 예를 들면, 띠모양 발광부(32b~32i, 33b~33i)를 1개의 채널에 접속해도 좋고, 띠모양 발광부(32a~32i, 33a~33i)를 각각 다른 채널에 접속해도 좋다. Moreover, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 11, the strip|belt-shaped light-emitting
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 도 9, 10, 11, 13에 나타내는 각 조사 패턴에 있어서의 조사 시간을 나타냈지만, 조사 시간은 예시이며, 조사 시간은 이들에 기재된 값에 한정되는 것은 아니다. 또, 도 9, 10, 11, 13에 나타내는 각 조사 패턴에 있어서는, 조사 시간을 ㎲로 규정하였지만, 조사 시간은, 촬상 시간에 대한 비율로 규정해도 좋다. In addition, in this embodiment, although the irradiation time in each irradiation pattern shown in FIGS. 9, 10, 11, and 13 was shown, irradiation time is an illustration, and irradiation time is not limited to the value described in these. Moreover, in each irradiation pattern shown in FIGS. 9, 10, 11, and 13, although irradiation time was prescribed|regulated to microsecond, you may prescribe|regulate irradiation time as a ratio with respect to imaging time.
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30b, 30d)을 가지지만, 발광 블록(30b, 30d)이 광확산판을 가지고 있어도 좋다. 도 19는 변형예와 관련되는 발광 블록(30b-1)을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이고, 도 19(A)는 측면도이며, 도 19(B)는 도 19(A)에 나타내는 상태를 도 19(A)에 있어서의 하방향으로부터 본 도이다. Moreover, in this embodiment, although the
발광 블록(30b-1)은, 발광부(30a)에 인접하여 광확산판인 렌티큘러 렌즈(Lenti cular lens)(30e)가 설치된다. 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)는, 복수의 발광부(30a)를 덮도록 설치된다. 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)는, 단면이 가운데 볼록한 가늘고 긴 볼록 렌즈를 균등한 피치(pitch)로 다수 늘어놓은 것이고, 볼록 렌즈의 배열 방향(볼록 렌즈의 길이 방향과 직교하는 방향)과 동방향의 광의 성분을 확산한다. 발광 블록(30b-1)에서는, 볼록 렌즈의 배열 방향과 발광부(30a)는 같다. 따라서, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광이 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)에서 확산되고, 복수의 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광을 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)에서 가늘고 긴 1개의 면광원으로 할 수가 있다. In the
예를 들면, 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)가 없는 경우에는, 커버 유리 G의 선단 P면이나 후단 P면에서 정반사한 광에 기초하여 검사를 행할 때, 선단 P면이나 후단 P면에 발광부(30a)의 점형상의 광이 비쳐 버릴 가능성이 있지만, 발광부(30a)를 덮도록 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)를 설치함으로써, 이러한 부적합함의 발생을 방지할 수가 있다. For example, when there is no
또한, 선단 P면이나 후단 P면의 검사로서, 띠모양 발광부(31b)나 띠모양 발광부(31g)를 약하게 빛나게 하여, 선단 P면이나 후단 P면에 띠모양 발광부(31b)나 띠모양 발광부(31g)의 광을 비쳐 넣는 방법을 생각할 수 있다. 이 때, 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)에 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)가 없는 경우에는, 선단 P면이나 후단 P면에 점형상의 광이 비쳐 버려, 잘 검사할 수 없다. 이에 반해 띠모양 발광부(31b, 31g)에 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)가 설치되어 있는 경우에는, 선단 P면이나 후단 P면에 점형상의 광이 비치기 때문에, 이 광이 구부러져 있는지 아닌지로 선단 P면이나 후단 P면의 연마에 관한 부적합함을 검사할 수가 있다. In addition, as an inspection of the front-end P-surface or the rear-end P-surface, the band-shaped light-emitting
또한, 도 19에서는, 1개의 발광 블록(30b-1)에 1매의 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)가 설치되었지만, 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)의 매수는 이에 한정되지 않는다. 복수의 렌티큘러 렌즈를 늘어놓은 것을 복수의 발광부(30a)를 덮도록 설치해도 좋다. 또, 광확산판은 렌티큘러 렌즈에 한정되지 않는다. In addition, although one
<제2의 실시의 형태> <Second embodiment>
본 발명의 제1의 실시의 형태에서는, 동축 조명을 이용한 화상과 입체 조명을 이용한 화상을 다른 카메라로 촬상하였지만, 동축 조명을 이용한 화상과 입체 조명을 이용한 화상을 같은 카메라로 촬상해도 좋다. In the first embodiment of the present invention, an image using coaxial illumination and an image using stereoscopic illumination are captured by different cameras. However, an image using coaxial illumination and an image using stereoscopic illumination may be captured by the same camera.
본 발명의 제2의 실시의 형태는, 2개의 카메라로 촬상을 행하는 형태이다. 이하, 제2의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(2)에 대해 설명한다. 또한, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 동일한 부분에 대해서는 동일한 부호를 붙이고 설명을 생략한다. A second embodiment of the present invention is a form of imaging with two cameras. Hereinafter, the
도 20은 제2의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(2)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다. 광학 검사 장치(2)는, 주로 촬상부(10A)와, 동축 조명부(20)와, 입체 조명부(30)와 ,재치부(40)와, 반송부(50)(도시 생략)를 가진다. 20 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
촬상부(10A)는, 제1 카메라(11)(본 실시의 형태에 있어서는, 본 발명의 1차원 촬상 수단에 상당)와, 제2 카메라(12)(본 발명의 제2 촬상 수단에 상당)를 가진다. 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)의 배치는, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 마찬가지이다. The
입체 조명부(30)는, 제1 카메라(11)와 재치부(40)의 사이에 설치된다. 또, 입체 조명부(30)는, 중심축 ax가 제1 카메라(11)의 광축과 교차하는 위치에 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31a, 31f)의 광축과 중심면 S1이 이루는 각도 θ1(도 4 참조)이 대략 8°이기 때문에, 상측 동축 조명(21)으로부터의 광은 입체 조명부(30)에 의해 차단되지 않는다. The
이와 같이 구성된 광학 검사 장치(2)로 행하는 처리에 대해 설명한다. 집적회로(71)(본 발명의 제3 제어부를 포함)는 재치부(40)의 롤러(40a)를 구동하는 구동 모터 펄스를 생성하고, 출력부(73)는 이를 반송부(50)로 출력한다. 이에 의해 커버 유리 G가 재치부(40) 상을 반송 방향 F를 따라 일정한 속도로 이동한다. The processing performed by the
위치 검출 센서(81)로부터 커버 유리 G가 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12) 하로 반송된 것이 검출되면, 검출 신호가 위치 검출 센서(81)로부터 입력부(72)를 통해 집적회로(71)에 입력된다. 이 검출 신호가 입력되면, 집적회로(71)는, 반사 화상을 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상하는 처리, 및 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 제1 카메라(11) 및 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상하는 처리를 개시한다. When it is detected that the cover glass G has been conveyed from the
도 21은 촬상 처리의 차례와 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)에서 촬상되는 화상과의 대응을 나타내는 도이다. 21 : is a figure which shows the correspondence between the order of imaging processing, and the image imaged by the
반사 화상을 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상하는 처리(도 21에 있어서의 차례 1~9의 처리)는, 집적회로(71)가 생성한 촬상 신호를 제1 카메라(11)로 출력하는 점 이외는, 광학 검사 장치(1)에 있어서 행해진 처리(도 11, 도 12 및 도 14)와 마찬가지이기 때문에 상세한 설명을 생략한다. The processing of capturing the reflected image with the first camera 11 (processes in
집적회로(71)는, 차례 1~9의 처리가 끝나면, 차례 10~12에 나타내는 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상하는 처리를 개시한다. 차례 10~12에 나타내는 처리는, 도 9, 10에 나타내는 처리(차례 1~3의 처리)와 마찬가지이기 때문에 상세한 설명을 생략한다. The
집적회로(71)는 차례 12의 출력을 행함과 동시에 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 생성하고, 출력부(73)를 통해 집적회로(71)로 출력한다. 집적회로(71)는, 반복 처리를 나타내는 신호를 받아, 처리를 최초로 되돌리고, 차례 1~12에 나타내는 신호를 차례로 출력하는 처리를 반복한다. The
본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 1개의 광학 검사 장치(2)를 이용하여, 1회의 검사로 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. 또, 최소한(2개)의 카메라 수로 반사 화상, 투과 화상, 정반사 화상을 촬상할 수가 있다. According to this embodiment, a defect can be test|inspected by one test|inspection using one
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 제1 카메라(11)의 광축 상에 하프미러(21h)가 설치되어 있기 때문에, 입체 조명부(30)로부터 조사되고, 제1 카메라(11)에 입사하는 광량은, 광학 검사 장치(1)에 있어서 입체 조명부(30)로부터 조사되고, 제3 카메라(13)에 입사하는 광량의 대략 반으로 된다. 따라서, 입체 조명부(30)로부터 조사되는 광을 밝게 하는 것이 바람직하다. 또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상하는 화상 수가 제1의 실시의 형태와 비교하여 많기 때문에, 입체 조명부(30)로부터 조사되는 광을 밝게 하고, 촬상 주파수를 높게 하는 것이 바람직하다. In addition, in this embodiment, since the
<제3의 실시의 형태> <Third embodiment>
본 발명의 제1의 실시의 형태에서는, 주위에 원호 형상의 P면이 형성된 커버 유리 G의 검사를 행하는 것이지만, 커버 유리의 형태는 이에 한정되지 않는다. 최근에는, 커버 유리의 주위의 곡면이 깊어져, 이 곡면 부분이 부분적인 원통 형상 또는 타원통 형상으로 된 커버 유리가 이용되게 되어 있다. In 1st Embodiment of this invention, although it test|inspects the cover glass G in which the circular arc-shaped P surface was formed in the periphery, the form of a cover glass is not limited to this. In recent years, the curved surface around a cover glass deepens, and the cover glass in which this curved-surface part became a partial cylindrical shape or an elliptical-cylindrical shape is used.
본 발명의 제3의 실시의 형태는, 주위에 부분적인 원통 형상 또는 타원통 형상을 가지는 커버 유리를 검사하는 형태이다. 이하, 제3의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(3)에 대해 설명한다. 또한, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 동일한 부분에 대해서는 동일한 부호를 붙이고 설명을 생략한다. 3rd Embodiment of this invention is an aspect which test|inspects the cover glass which has a partial cylindrical shape or an elliptical-cylindrical shape around. Hereinafter, the
도 22는 제3의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(3)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다. 광학 검사 장치(3)는, 주로 촬상부(10)와, 동축 조명부(20)와, 입체 조명부(30)와, 재치부(40)와, 반송부(50)(도시 생략)와, 측면 검사부(60)와, 높이 취득부(90)를 가진다. 22 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
도 23은 광학 검사 장치(3)의 일부를 확대 표시한 사시도이다. 측면 검사부(60)는, 주로 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)와 반사경(63, 64)을 가진다. 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62) 및 반사경(63, 64)은, 제3 카메라(13)를 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 중심면 S1 상에 위치한다. 23 is an enlarged perspective view of a part of the
초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)는, 제3 카메라(13)의 초점거리를 조정하는 광학 소자이다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)로서 후판형상의 유리판을 이용한다. 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)는, 판두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 양단면이 수평으로 되도록 설치된다. The optical elements for
초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61)와 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(62)는, x방향 및 z방향의 위치는 대략 같고, 제3 카메라(13)의 중심을 통과하는 z방향으로 뻗는 선 ax1을 사이에 두고 대향하도록 설치된다. 또, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)는, 입체 조명부(30)보다 상측(+z측)에 설치된다. The
반사경(63, 64)은, 커버 유리 G1의 측면의 상을 반사하고, 제3 카메라(13)에로 유도하는 부재이다. 반사경(63, 64)은, 대략 판형상이며, 재치부(40)에 인접하여 설치된다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 인접하는 롤러(40a)와 롤러(40a)의 사이에 설치된다. The reflecting mirrors 63 and 64 are members which reflect the image of the side surface of the cover glass G1, and guide|guide it to the
반사경(63)과 반사경(64)은, x방향 및 z방향의 위치는 대략 같고, 제3 카메라(13)의 중심을 통과하는 z방향으로 뻗는 선 ax1을 사이에 두고 대향하도록 설치된다. 또 평면시에 있어서, 반사경(63)과 반사경(64)은, 각각 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하는 방향에 있어서, 재치 영역의 외측 또한 재치 영역에 인접하는 위치에 설치된다. 여기서, 재치 영역이란, 커버 유리 G1이 재치되는 재치부(40) 상의 영역이며, 제3 카메라(13)의 연직 방향 하측의 영역을 포함한다. 도 23에서는, 재치 영역에 커버 유리 G1이 재치된 상태를 도시하고 있다. The reflecting
도 24는 광학 검사 장치(3)를 중심면 S1로 절단한 상태에 있어서의 개략 구성을 나타내는 도이다. 도 24는 반송 방향 F 하류측(+x방향)으로부터 본 모습을 나타낸다. 도 24에 있어서의 2점 쇄선은, 제3 카메라(13)에 입사하는 광의 경로를 모식적으로 나타낸다. 24 : is a figure which shows schematic structure in the state which cut|disconnected the
반사경(63, 64)의 반사면(63a, 64a)은, 대략 평면이며, 중심면 S1과 교차하는 선(도 24에 있어서 반사면(63a, 64a)을 나타내는 선)이 수평면에 대해서 경사지도록, 반송 방향 F를 대략 따라 연설(延設)된다. The
중심면 S1 상에서는, 반사경(63)과 반사경(64)은, 각각 커버 유리 G1의 양측에 위치한다. 커버 유리 G1은, 재치부(40)에 재치된 상태에 있어서, 수평 방향과 평행한 평면 Ga와 수평 방향에 대해서 기울어져 있는 측면 Gb를 가진다. 측면 Gb는, 부분적인 원통 형상 또는 타원통 형상이며, 측면 Gb의 수평 방향에 대한 기울기는 대략 30~45°이다. 또, 양측의 측면 Gb의 끝 Ge가 롤러(40a)에 재치된다. On central plane S1, the reflecting
평면 Ga의 상은, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하지 않고 촬상 렌즈(13a)에 유도된다. 바꾸어 말하면, 촬상 렌즈(13a)와 평면 Ga를 묶는 선의 상에는, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)가 존재하지 않는다. The plane Ga image is guided to the
이에 반해 측면 Gb의 상은, 반사면(63a, 64a)에서 반사하고, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하고, 촬상 렌즈(13a)에 유도된다. 바꾸어 말하면, 촬상 렌즈(13a)와 반사면(63a, 64a)을 묶는 선과 겹치도록, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)가 배치된다. On the other hand, the image of the side surface Gb is reflected by the
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 촬상 렌즈(13a)와 평면 Ga를 묶는 선의 상에 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)가 위치하지 않게, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)는, 내측이 일부 노치(notch)되어 있다. In addition, in this embodiment, the optical elements for
초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하지 않는 경우의 초점 위치 F1은, 커버 유리 G1의 평면 Ga의 위치이다. 커버 유리 G1의 판두께는 대략 0.5㎜이며, 초점 위치 F1은 평면 Ga에 있어서의 판두께 방향의 중심 근방에 위치하는 것이 바람직하다. The focal position F1 in the case of not passing the
초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하는 경우에는, 광이 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)에 입사하는 과정, 및 광이 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)로부터 출사하는 과정에서 광이 굴절하기 때문에, 초점 위치 F2는 초점 위치 F1보다 먼 위치에 있다. 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하는 것에 의한 초점 위치의 늘어남(도 24에 있어서의 검은 화살표 참조)은, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)의 판압(板壓)을 T로 하고, 유리의 굴절률을 n으로 하면, T-T/n로 나타낼 수 있다. 예를 들면 T가 12㎜이며, n이 1.5이라고 하면, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과함으로써 초점 위치가 4㎜ 늘어난다. 즉, 초점 위치 F2는, 초점 위치 F1보다 4㎜만큼 -z측에 위치한다. When passing through the optical elements for
도 25는 커버 유리 G1의 위치와 제3 카메라(13)에서 촬상되는 화상과의 관계를 나타내는 도이고, (A)는 커버 유리 G1의 측면 부분의 확대도이며, (B)는 제3 카메라(13)에서 촬상되는 화상의 일부를 나타낸다. 도 25(A)에서는, 반사면(63a)을 점선으로 나타내고, 반사면(63a)에서 반사되어 제3 카메라(13)에 입사하는 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다. 25 : is a figure which shows the relationship between the position of cover glass G1, and the image imaged by the
커버 유리 G1의 평면 Ga 및 커버 유리 G1의 측면 Gb의 평면 Ga 가까이의 일부의 영역(영역 I)에 있어서는, 그 상은, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하지 않고 촬상 렌즈(13a)에 유도된다. 초점 위치 F1은 평면 Ga의 위치에 있기 때문에, 영역 I의 상은 뚜렷한 상으로 된다. 측면 Gb의 상은, 조금 초점이 맞지 않은 흐릿한 상으로 된다(도 25 그물망을 친 부분 참조). In a part of the area (region I) near the plane Ga of the cover glass G1 and the plane Ga of the side surface Gb of the cover glass G1, the image does not pass through the
측면 Gb 및 평면 Ga의 측면 Gb 가까이의 일부의 영역(영역 II)의 상은, 반사면(63a)(반사면 64a에 대해서도 마찬가지임)에서 반사하여 촬상 렌즈(13a)에 유도된다. 따라서, 영역 II의 상은 좌우 반전하고, 측면 Gb의 끝 Ge의 상이 내측으로 되고, 측면 Gb의 평면 Ga측의 상이 외측으로 된다. The images of the side surface Gb and a part of the region (region II) near the side surface Gb of the plane Ga are reflected by the
또, 영역 II의 상은, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과하여 촬상 렌즈(13a)에 유도된다. 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과함으로써 초점 위치 F2는 초점 위치 F1보다 하측에 위치하기 때문에, 측면 Gb의 대부분에 대해서는 초점이 맞는 뚜렷한 상으로 된다. 본 실시의 형태에서는, 제3 카메라(13)의 초점 심도와 측면 Gb의 높이를 대략 일치시킴으로써, 측면 Gb의 전체에 대해 초점이 맞는 뚜렷한 상을 얻을 수 있다. 또, 평면 Ga와 측면 Gb의 경계 부분에 있어서는, 조금 초점이 맞지 않은 흐릿한 상으로 된다(도 25 그물망 친 부분 참조). 또한, 영역 II의 상의 가장 중심측은, 커버 유리 G1이 없는 부분이며, 제3 카메라(13)에서는 검은 상이 촬상된다. In addition, the image of the region II is guided to the
영역 I와 영역 II는, 일부 겹치도록 설정하는 것이 바람직하다. 이에 의해 평면 Ga와 측면 Gb의 경계 부분에 대해서는, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 통과한 화상과 통과하지 않는 화상과의 2개의 화상을 얻을 수 있기 때문에, 일방의 화상의 초점이 맞지 않은 경우에도 평면 Ga와 측면 Gb의 경계 부분에 대한 결함을 검출할 수가 있다. It is preferable to set the area|region I and area|region II so that it may partially overlap. As a result, for the boundary portion between the plane Ga and the side surface Gb, two images, an image passing through the
도 23의 설명으로 되돌아온다. 광학 검사 장치(3)는, 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 취득하는 높이 취득부(90)를 가진다. 높이 취득부(90)는, 측면 검사부(60)보다 반송 방향 F의 상류측(-x측)에 설치되고, 주로 면광원(91)과, 카메라(92)와, 반사경(93)을 가진다. Returning to the description of FIG. 23 . The
도 26, 도 27은 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 측정하는 모습을 모식적으로 나타내는 도이고, 도 26은 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하는 방향(여기에서는, -y방향)으로부터 본 도이며, 도 27은 반송 방향 F를 따라(여기에서는, +x방향) 본 도이다. 도 27의 2점 쇄선은, 면광원(91)으로부터 조사된 광의 경로를 나타낸다. 26 and 27 are diagrams schematically illustrating a state of measuring the height of the cover glass G1, and FIG. 26 is a diagram viewed from a direction (here, -y direction) substantially orthogonal to the conveyance direction F, FIG. It is the figure seen along the conveyance direction F (here, +x direction). The dashed-dotted line in FIG. 27 shows the path of the light irradiated from the
면광원(91)과, 카메라(92) 및 반사경(93)은, 재치부(40)를 사이에 두고 설치된다. 면광원(91)은, 반송 방향 F와 대략 직교하는 방향(여기에서는, +y방향)으로 광을 조사한다. 카메라(92)는, 면광원(91)으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G1을 통과하고, 반사경(93)에서 반사된 광이 입사한다. 이에 의해 카메라(92)에서는, 커버 유리 G1에 의해 광이 차단된 부분은 어둡고, 그 외의 부분은 밝은 그림자 그림과 같은 화상이 얻어진다. 따라서, 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 정확하게 취득할 수가 있다. 또한, 반사경(93)은 필수는 아니고, 면광원(91)으로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G1을 통과한 광이 카메라(92)에 입사하도록 해도 좋다. The
커버 유리 G1의 선단 Gc와 후단 Gd는, 평면 Ga보다 높이가 낮다. 따라서, 재치부(40)에 의해 커버 유리 G1을 반송 방향 F로 이동시키면서 면광원(91)으로부터 y방향으로 광을 조사하고, 커버 유리 G1을 통과한 광을 카메라(92)로 촬상함으로써, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd의 높이 변화를 취득할 수가 있다. The front-end|tip Gc and rear-end|tip Gd of cover glass G1 are lower in height than plane Ga. Therefore, the front-end|tip by irradiating light from the
도 23의 설명으로 되돌아온다. 제3 카메라(13)에는, 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동부(95)가 설치된다. 이동부(95)는, 구동원인 액츄에이터(도시 생략)와, 액츄에이터의 구동을 전달하여 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동 기구(도시 생략)를 가진다. 이동 기구에는, 피드 스크루(feed screw) 등의 여러 가지 공지의 기술을 이용할 수가 있다. Returning to the description of FIG. 23 . The
CPU(101)(도 7 참조)는, 카메라(92)로 촬상된 화상에 기초하여 이동부(95)를 제어하고, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd의 높이 변화에 맞추어 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시킨다. ROM(103)(도 7 참조)에는, 카메라(92)로 촬상된 후, 커버 유리 G1이 제3 카메라(13)의 바로 아래에 위치하기까지, 커버 유리 G1을 반송 방향 F로 보내는 펄스 수가 격납되어 있다. 또, ROM(103)에는, 액츄에이터의 구동량과 제3 카메라(13)의 이동량과의 관계가 격납되어 있다. CPU(101)는, ROM(103)에 격납된 정보에 기초하여 이동부(95)의 액츄에이터를 구동함으로써, 제3 카메라(13)의 하를 통과하는 커버 유리 G1의 높이 변화에 맞추어 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시킨다. The CPU 101 (refer to Fig. 7) controls the moving
본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)를 이용하여 제3 카메라(13)의 초점거리를 늘이고, 반사경(63, 64)을 이용하여 제3 카메라(13)에 입사하는 광을 반사시킴으로써, 측면 Gb를 가지는 커버 유리 G1이라도, 1회의 검사로 측면 Gb의 결함에 대해서도 검사할 수가 있다. According to the present embodiment, the focal length of the
또, 본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 커버 유리의 형상에 따라 반사경(63, 64)의 위치나 기울기를 변경함으로써 여러 가지 종류의 커버 유리에 대응할 수가 있다. 예를 들면, 측면 Gb의 수평 방향에 대한 기울기에 따라 반사면(63a, 64a)의 수평 방향에 대한 기울기를 설정함으로써, 측면 Gb의 수평 방향에 대한 기울기에 의하지 않고 측면 Gb의 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. 또 예를 들면, 커버 유리의 폭에 따라 반사경(63, 64)의 y방향의 위치를 변경함으로써, 커버 유리의 폭에 의하지 않고 측면 Gb의 결함을 검사할 수가 있다. Moreover, according to this embodiment, it can respond to various types of cover glass by changing the position and inclination of the reflecting mirrors 63 and 64 according to the shape of a cover glass. For example, by setting the inclination with respect to the horizontal direction of the
또, 본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 제3 카메라(13)의 하를 통과하는 커버 유리 G1의 높이 변화에 맞추어 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시킴으로써, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd의 높이가 변화하는 경우라도, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd에 대해서도 초점이 맞은 뚜렷한 상을 제3 카메라(13)로 촬상할 수가 있다. 따라서, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd에 대해서도, 결함을 확실하게 검사할 수가 있다. Moreover, according to this embodiment, the height of front-end|tip Gc and rear-end Gd changes by moving the
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)로서 후판형상의 유리판을 이용하였지만, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)의 형태는 이에 한정되지 않는다. 예를 들면, 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)로서로서 오목 렌즈를 이용해도 좋다. 또한, 유리판의 두께나 오목 렌즈의 형상은 커버 유리의 형상에 따라 설정되지만, 오목 렌즈를 이용하면 초점거리가 용이하게 늘어나므로, 측면 Gb의 높이가 낮은 경우에는 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자(61, 62)로서 유리판을 이용하는 것이 바람직하다. In addition, in this embodiment, although the thick plate-shaped glass plate was used as the
또, 본 실시의 형태에서는, CPU(101)가 카메라(92)로 촬상된 화상에 기초하여 이동부(95)를 제어함으로써, 제3 카메라(13)의 하를 통과하는 커버 유리 G1의 높이 변화에 맞추어 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시켰지만, 제3 카메라(13)의 하를 통과하는 커버 유리 G1의 높이 변화에 맞추어 제3 카메라(13)를 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 방법은 이에 한정되지 않는다. 예를 들면, 선단 Gc 및 후단 Gd의 높이 변화에 관한 정보를 미리 ROM(103)에 격납해 두고, 이 정보에 기초하여 CPU(101)가 이동부(95)를 제어해도 좋다. 또 예를 들면, 레이저 변위계로 커버 유리 G1의 높이를 측정하고, 이 측정 결과에 기초하여 CPU(101)가 이동부(95)를 제어해도 좋다. Moreover, in this embodiment, the height change of cover glass G1 which passes under the
<제4의 실시의 형태> <Fourth embodiment>
본 발명의 제1의 실시의 형태에서는, 입체 조명부(30)가 제1 영역(31), 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)을 가지고, 제2 영역(32), 제3 영역(33)에서는 발광부(30a)가 대략 원통면의 상에 배치되었지만, 입체 조명부의 형태는 이에 한정되지 않는다. In the first embodiment of the present invention, the
본 발명의 제4의 실시의 형태는, 입체 조명부를 구성하는 모든 띠모양 발광부가, 발광부(30a)를 직선 모양으로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록을 가지는 형태이다. 이하, 제4의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(4)에 대해 설명한다. 또한, 제4의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(4)와 광학 검사 장치(1)의 차이는 입체 조명부뿐이기 때문에, 제4의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(4)가 구비하는 입체 조명부(30A)에 대해 설명하고, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 동일한 부분에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. A fourth embodiment of the present invention is an embodiment in which all the band-shaped light-emitting units constituting the three-dimensional lighting unit have light-emitting blocks in which the light-emitting
도 28은 광학 검사 장치(4)가 구비하는 입체 조명부(30A)의 개략을 나타내는 사시도이다. 입체 조명부(30A)는, 복수의 방향으로부터 커버 유리 G에 광을 조사한다. 입체 조명부(30A)로부터 조사되고, 커버 유리 G에서 반사한 광은, 제3 카메라(13)(도 1 참조)에 입사한다. 28 : is a perspective view which shows the outline of the
입체 조명부(30A)는, 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역(31A)과, 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역(32A) 및 제3 영역(33A)을 가진다. 입체 조명부(30A)에 있어서의 제1 영역(31a), 제2 영역(32A) 및 제3 영역(33A)은, 각각 입체 조명부(30)에 있어서의 제1 영역(31), 제2 영역(32) 및 제3 영역(33)에 상당한다. The
제1 영역(31A)은, 띠모양 발광부(31a-1, 31b-1, 31c-1, 32d-1, 31e-1, 31f-1, 31g-1, 31h-1, 31i-1, 31j-1)를 가진다. 입체 조명부(30A)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)는, 입체 조명부(30)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(31a~31j)에 상당한다. The
제2 영역(32A)은, 띠모양 발광부(32a-1, 32b-1, 32c-1, 32d-1, 32f-1, 32g-1, 32h-1)를 가지고, 제3 영역(33A)은, 띠모양 발광부(33a-1, 33b-1, 33c-1, 33d-1, 33f-1, 33g-1, 33h-1)를 가진다. 입체 조명부(30A)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(32a-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1)는, 입체 조명부(30)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(32a~32d, 32f~32h)에 상당한다. 입체 조명부(30A)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1)는, 입체 조명부(30)에 있어서의 띠모양 발광부(33a~33d, 33f~33h)에 상당한다. The
또 입체 조명부(30A)는, 제1 영역(31a), 제2 영역(32A) 및 제3 영역(33A)을 일체화하는 프레임(34)을 가진다. 프레임(34)은, 알루미늄 등의 열전도성이 뛰어난 금속으로 형성된다. 프레임(34)은 2매의 플레이트(34a)를 가지고, 이 2매의 플레이트(34a)의 사이에 제1 영역(31A)이 설치된다. 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)은, 플레이트(34a)의 외측에 설치된다. Moreover, the
도 29는 띠모양 발광부(31a-1)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다. 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)는 같은 구성이기 때문에, 띠모양 발광부(31a-1)에 대해서만 설명하고, 띠모양 발광부(31b-1~31j-1)에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. 29 is a schematic diagram showing details of the strip-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a-1)는, 길이 방향의 길이가 L로 되도록 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30b)과, 원통 렌즈(30c-1)와, 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e-1)를 가지는 발광 유닛이다. 원통 렌즈(30c)와 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 차이는 길이 방향의 길이뿐이다. 또, 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e)와 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e-1)의 차이는, 길이 방향의 길이뿐이다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a-1)는, 직선 모양으로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30b)을 2개 가진다. 2개의 발광 블록(30b)은, 부착 부재(34b)를 통해 플레이트(34a)에 직접 장착된다. 원통 렌즈(30c-1)는, 부착 부재(34c)를 통해 플레이트(34a)에 직접 장착된다. The band-shaped
발광 블록(30b)과 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 사이에는, 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e-1)가 설치된다. 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e-1)는, 지지부재(30f)를 통해 발광 블록(30b)에 장착된다. A
발광 블록(30b) 및 원통 렌즈(30c-1)는, 발광 블록(30b)의 발광부(30a)가 설치된 선단면 p1과 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 상면 p2가 대략 평행하게 되도록, 플레이트(34a)에 설치된다. 바꾸어 말하면, 발광 블록(30b)의 연설(延設) 방향과 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 연설 방향은 대략 평행이다. The
도 30은 띠모양 발광부(32a-1)의 상세를 나타내는 모식도이다. 띠모양 발광부(32a-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1, 33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1)는 같은 구성이기 때문에, 띠모양 발광부(32a-1)에 대해서만 설명하고, 띠모양 발광부(32b-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1, 33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1)에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. 30 is a schematic diagram showing the details of the strip-shaped
띠모양 발광부(32a-1)는, 길이 방향의 길이가 L로 되도록 발광부(30a)가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록(30b)과, 원통 렌즈(30c-2)와, 플레이트(30g)를 가지는 발광 유닛이다. 원통 렌즈(30c)와 원통 렌즈(30c-2)의 차이는 길이 방향의 길이뿐이다. The band-shaped
플레이트(30g)에는, 발광 블록(30b) 및 원통 렌즈(30c-2)가 장착된다. 플레이트(30g)는, 알루미늄 등의 열전도성이 뛰어난 금속으로 형성된다. 플레이트(30g)에는, 플레이트(30g)를 플레이트(34a)에 부착하기 위한 절곡부(30h)가 형성된다. A
발광 블록(30b) 및 원통 렌즈(30c-2)는, 발광 블록(30b)의 발광부(30a)가 설치된 선단면 p3에 대해서, 원통 렌즈(30c-2)의 상면 p4가 기울어지도록 플레이트(30g)에 설치된다. 바꾸어 말하면, 발광 블록(30b)의 연설 방향에 대해서, 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 연설 방향이 기울어져 있다. The
또한, 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)는 렌티큘러 렌즈(30e-1)를 가지지만, 띠모양 발광부(32a-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1, 33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1)는 렌티큘러 렌즈를 가지지 않는다. 이것은 커버 유리 G의 좌단 및 우단에 형성된 P면에 발광부(30a)의 점형상의 광이 늘어놓여서 비치는 것이 없기 때문이다. In addition, the band-shaped
도 28의 설명으로 되돌아온다. 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31e-1)는, 중심면 S1보다 +x측에 위치하고, 띠모양 발광부(31f-1~31j-1)는, 중심면 S1보다 -x측에 위치한다. 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)는, 중심면 S1 상에 배치되지 않는다. It returns to the description of FIG. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)는, 광축이 중심면 S1과 재치부(40)(도 28에서는 도시 생략)의 교선, 즉 중심축 ax(도 31 참조)와 교차하도록 설치된다(후에 상술). The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(32a-1, 33a-1)는, 중심면 S1 상에 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(32b-1~32d-1, 33b-1~33d-1)는, 중심면 S1보다 +x측에 위치하고, 띠모양 발광부(32f-1~32h-1, 33f-1~33h-1)는, 중심면 S1보다 -x측에 위치한다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(32a-1, 33a-1)는, 중심축이 입체 조명부(30A)의 중심축 ax1과 재치부(40)의 교점(중심점 O1, 도 31 참조)을 향하고 있다. 띠모양 발광부(32b-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1, 33b-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1)는, 띠모양 발광부(32a-1, 33a-1)와 대략 평행하게 설치된다. The band-shaped
도 31은 입체 조명부(30A)로부터 조사되는 광의 경로에 대해 설명하는 도이다. 도 31에 있어서는, 입체 조명부(30A)를 중심면 S1로 절단했을 때의 개략 구성을 나타냄과 아울러, 광의 경로를 2점 쇄선으로 나타낸다. Fig. 31 is a diagram for explaining the path of light emitted from the three-
띠모양 발광부(31f-1)는, 광축이 중심축 ax와 교차하도록 설치된다. 띠모양 발광부(31f-1)에 있어서, 원통 렌즈(30c-1)는, 발광 블록(30b)과 중심축 ax와의 사이에 설치되고, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광을 중심축 ax 근방에 집광한다. 제1 영역(31A)에 있어서는, 발광부(30a)가 대략 수평으로 늘어놓여 있고, 발광 블록(30b)의 선단면 p1과 원통 렌즈(30c-1)의 상면 p2가 대략 평행이기 때문에, 발광 블록(30b)으로부터 조사되는 광은, 원통 렌즈(30c-1)를 통과하여 중심축 ax에 초점을 맺는다. The band-shaped
띠모양 발광부(32a-1, 33a-1)는, 중심축이 중심점 O1을 향하고 있다. 원통 렌즈(30c-2)는, 발광 블록(30b)과 중심점 O1(중심축 ax)의 사이에 설치되고, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광을 중심축 ax 근방에 집광한다. The central axis of the band-shaped
제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)에 있어서는, 발광부(30a)가 대략 수평으로 늘어놓여 있지 않고, 발광 블록(30b)의 연설 방향이 수평 방향에 대해서 기울어져 있다. 만일 발광 블록(30b)의 선단면 p3와 원통 렌즈(30c-2)의 상면 p4가 대략 평행이라고 하면, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사되는 광은 선단면 p3와 대략 평행한 선의 상에 초점을 맺고, 중심축 ax에 초점을 맺지 않는다. 따라서, 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)에 있어서는, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사되는 광이 중심축 ax에 초점을 맺도록 선단면 p3에 대해서 상면 p4를 기울인다. In the
이에 의해 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)에 있어서, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광은, 원통 렌즈(30c-2)를 통과하고, 커버 유리 G의 좌단 및 우단에 형성된 P면에 광을 조사하고, 또한 그 광의 초점을 P면에 맺을 수가 있다. 또, 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)은, 제1 영역(31A)이 광을 조사 가능한 범위 A1의 외측의 영역 A2에 광을 조사한다. 이와 같이, 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)이 제1 영역(31A)를 보충하는 기능을 가진다. Thereby, in the 2nd area|
본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 입체 조명부(30A)를 이용하여 여러 가지 방향으로부터 광을 커버 유리 G에 조사할 수가 있다. 특히, 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)에 있어서 선단면 p3에 대해서 상면 p4를 기울임으로써, 발광부(30a)로부터 조사된 광의 초점을 커버 유리 G의 좌단 및 우단에 형성된 P면에 맞출 수가 있다. 또, 선단면 p3에 대해서 상면 p4를 기울임으로써, 제2 영역(32a), 제3 영역(33A)가 제1 영역(31A)를 보충할 수가 있다. 그 결과, 띠모양 발광부(31a-1~31j-1)가 가지는 발광 블록(30b)의 수를 줄일 수가 있다. According to this embodiment, light can be irradiated to the cover glass G from various directions using 30 A of stereoscopic illumination parts. In particular, in the
또, 본 실시의 형태에 의하면, 열전도성이 높은 재료로 형성된 프레임(34)및 플레이트(30g)가 일체화되어 방열 부재를 구성하고 있기 때문에, 발광부(30a) 등으로부터 발생한 열을 효율적으로 방열할 수가 있다. Further, according to this embodiment, since the
또한, 도 28에 나타내듯이, 입체 조명부(30A)의 근방에 송풍부(35)를 설치하는 것이 바람직하다. 송풍부(35)로부터 입체 조명부(30A)에 바람을 보냄으로써, 방열 부재(프레임(34)및 플레이트(30g))에 의한 냉각 효과를 향상시킬 수가 있다. 또한, 플레이트(30g)가 y방향으로 연설되어 있기 때문에, 송풍부(35)는, 측면(+y방향 및 -y방향의 적어도 일방)으로부터, 플레이트(30g)의 연설 방향을 따른 방향(도 28의 굵은 화살표 참조)의 바람을 입체 조명부(30A)에 보내는 것이 바람직하다. 또한, 도 28에서는, 입체 조명부(30A)의 -y방향으로 송풍부(35)를 설치하고 있지만, 송풍부(35)의 위치는 이에 한정되지 않는다. 또, 도 28에서는 송풍부(35)를 1개 설치하고 있지만, 송풍부(35)의 수도 이에 한정되지 않는다. Moreover, as shown in FIG. 28, it is preferable to provide the
<제5의 실시의 형태> <Fifth embodiment>
본 발명의 제1의 실시의 형태에서는, 동축 조명부(20)는, 제1 카메라(11)의 동축 조명인 상측 동축 조명(21)과, 제2 카메라(12)의 동축 조명인 하측 동축 조명(22)을 가졌지만, 동축 조명부의 형태는 이에 한정되지 않는다. In the first embodiment of the present invention, the
본 발명의 제5의 실시의 형태는, 동축 조명부가 C-PL 필터를 가지는 형태이다. 이하, 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)에 대해 설명한다. 또한, 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)와 광학 검사 장치(1)의 차이는 동축 조명부뿐이기 때문에, 제4의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)가 구비하는 동축 조명부(20A)에 대해 설명하고, 광학 검사 장치(1)와 동일한 부분에 대해서는 설명을 생략한다. A fifth embodiment of the present invention is an aspect in which the coaxial illumination unit has a C-PL filter. Hereinafter, the
도 32는 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)의 개략을 나타내는 정면도이다. 동축 조명부(20A)는, 제1 카메라(11)의 동축 조명인 상측 동축 조명(21)과, 제2 카메라(12)의 동축 조명인 하측 동축 조명(22)과, C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)를 가진다. C-PL 필터(23a)는, 제1 카메라(11)의 하측에 설치되고, C-PL 필터(23b)는, 제2 카메라(12)의 상측에 설치된다. 32 : is a front view which shows the outline of the
C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)는, 각각 편광판과 편광판을 투과한 투과광에 1/4λ의 위상차를 주는 1/4λ 위상차 판을 가지는 원편광 필터이다. 1/4λ 위상차 판은, 직선 편광을 원편광으로 변환한다. C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)는, 각각 하프미러(half mirror)(21h, 22h)측에 편광판이 위치하고, 하프미러(21h, 22h)로부터 먼 측에 1/4λ 위상차 판이 위치하도록 설치된다. C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)는 이미 공지이기 때문에 상세한 설명을 생략한다. The C-
C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)는, 각각 제1 카메라(11), 제2 카메라(12)에 인접하여 설치된다. 또, C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)는, 각각 두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향의 평면이, 광축 oax와 대략 직교하는 방향에 대해서 조금 경사지도록 설치된다. The C-
광원(21a)으로부터 조사되고, 하프미러(21h)에서 하향으로 반사된 광 중의 일부가 커버 유리 G를 투과하여 촬상 렌즈(12a) 표면에서 반사하는 경우가 있다. 이 반사광이 제1 카메라(11)에 입사하면, 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상된 화상의 중앙에 밝은 광의 선이 포함되어 버릴 우려가 있다. C-PL 필터(23b)는, 커버 유리 G를 투과하여 촬상 렌즈(12a) 표면에서 반사한 광이 제1 카메라(11)에 입사하지 않게 한다. 이에 의해 제1 카메라(11)로 촬상된 화상의 중앙에 밝은 광의 선이 포함되지 않게 할 수가 있다. A part of the light irradiated from the
마찬가지로 C-PL 필터(23a)는, 광원(22a)으로부터 조사되고, 하프미러(22h)에서 상향으로 반사되어 커버 유리 G를 투과하여 촬상 렌즈(11a) 표면에서 반사한 광이 제2 카메라(12)에 입사하지 않게 한다. 이에 의해 제2 카메라(12)로 촬상된 화상의 중앙에 밝은 광의 선이 포함되지 않게 할 수가 있다. Similarly, the C-PL filter 23a is irradiated from the
또한, 본 실시의 형태에서는, C-PL 필터(23a, 23b)를 가졌지만, C-PL 필터(23a)는 필수는 아니다. In addition, in this embodiment, although the C-
이상, 이 발명의 실시 형태를 도면을 참조하여 상술해 왔지만, 구체적인 구성은 이 실시 형태에 한정되는 것은 아니고, 이 발명의 요지를 일탈하지 않는 범위의 설계 변경 등도 포함된다. 당업자라면, 실시 형태의 각 요소를 적당하게 변경, 추가, 변환 등을 하는 것이 가능하다. 예를 들면, 제4, 5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(4, 5)에 대해서, 측면 검사부(60)와 높이 취득부(90)를 적용해도 좋다. 또 예를 들면, 제2의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(2)와 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)를 조합해도 좋고, 제4의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(4)와 제5의 실시의 형태와 관련되는 광학 검사 장치(5)를 조합해도 좋다. As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described above with reference to drawings, a specific structure is not limited to this embodiment, The design change etc. of the range which do not deviate from the summary of this invention are included. It is possible for those skilled in the art to appropriately change, add, or convert each element of the embodiment. For example, you may apply the
또, 상기 실시의 형태에서는, 광학 검사 장치(1~5)의 피검사물(검사 대상)이 커버 유리 G, G1이었지만, 광학 검사 장치(1~5)의 검사 대상은 커버 유리에 한정되지 않는다. 예를 들면, 광학 검사 장치(1~5)의 검사 대상이, 랩탑형(laptop type) 퍼스널 컴퓨터의 터치 패드에 이용되는 유리라도 좋다. Moreover, in the said embodiment, although the to-be-inspected object (inspection object) of the optical inspection apparatuses 1-5 was cover glass G and G1, the inspection object of the optical inspection apparatuses 1-5 is not limited to a cover glass. For example, the inspection object of the optical inspection apparatuses 1-5 may be glass used for the touchpad of a laptop-type personal computer.
또, 본 발명에 있어서, 「대략」이란 엄밀하게 동일한 경우뿐만 아니라, 동일성을 잃지 않는 정도의 오차나 변형을 포함한 개념이다. 예를 들면, 대략 수평이란, 엄밀하게 수평의 경우에 한정되지 않고, 예를 들면 몇도 정도의 오차를 포함한 개념이다. 또, 예를 들면, 단지 평행, 직교 등으로 표현하는 경우에 있어서도, 엄밀하게 평행, 직교 등의 경우뿐만 아니라, 대략 평행, 대략 직교 등의 경우를 포함하는 것으로 한다. 또, 본 발명에 있어서 「근방」이란, 기준으로 되는 위치의 가까이의 어느 범위(임의로 정할 수가 있음)의 영역을 포함하는 것을 의미한다. In addition, in the present invention, "approximately" is a concept including not only the strictly identical case, but also errors and deformations to the extent that the identity is not lost. For example, substantially horizontal is not limited to the case of being strictly horizontal, For example, it is a concept including the error of about several degrees. Also, for example, in the case of expressing only parallel, orthogonal, etc., not only strictly parallel, orthogonal cases, but also substantially parallel, substantially orthogonal, etc. cases are included. In the present invention, "near" means including a region in a certain range (which can be arbitrarily determined) near the reference position.
1, 2 : 광학 검사 장치
10, 10A : 촬상부
11 : 제1 카메라 12 : 제2 카메라
13 : 제3 카메라
11a, 12a, 13a : 촬상 렌즈
11b, 12b, 13b : 라인 센서
13c : 제3 카메라의 시야 위치
20, 20A : 동축 조명부
21, 21A : 상측 동축 조명 22, 22A : 하측 동축 조명
21a, 22a : 광원
21b, 22b : 인테그레이터(integrator)
21c, 22c : 집광 렌즈 21d, 22d : 조리개
21e, 22e : 콜리메이터 렌즈(collimator lens)
21f, 22f : 미러(mirror)
21g, 22g : 프레스넬 렌즈(Fresnel lens)
21h, 22h : 하프미러(half mirror) 23a, 23b : C-PL 필터
30, 30A : 입체 조명부
30a : 발광부 30b : 발광 블록
30c, 30c-1, 30c-2 : 원통 렌즈 30d : 발광 블록
30e, 30e-1 : 렌티큘러 렌즈
30g : 플레이트(plate) 30h : 절곡부
31, 31A : 제1 영역
31a~31j, 31a-1~31j-1 : 띠모양 발광부
32, 32A : 제2 영역
32a~32i, 32a-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1 : 띠모양 발광부
33, 33A : 제3 영역
33a~33i, 33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1 : 띠모양 발광부
34 : 프레임(frame)
34a : 플레이트 34b, 34c : 부착부재
35 : 송풍부
40 : 재치부 40a : 롤러(roller)
50 : 반송부 60 : 측면 검사부
61, 62 : 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자
63, 64 : 반사경 63a, 64a : 반사면
71 : 집적회로
72 : 입력부 73 : 출력부
74 : 전원부
75 : 통신 I/F(interface)
81 : 위치 검출 센서 82 : 위치 검출 센서
90 : 높이 취득부
91 : 면광원 92 : 카메라
93 : 반사경 95 : 이동부
100 : 퍼스널 컴퓨터(PC : prersonal computer)
101 : CPU(Central Processing Unit)
102 : RAM(Random Access Memory) 103 : ROM(Read Only Memory)
104 : 입출력 인터페이스
105 : 통신 I/F(interface) 106 : 미디어 I/F(interface)
111 : 입력 장치 112 : 출력 장치
113 : 기억 매체1, 2: Optical inspection device
10, 10A: imaging unit
11: first camera 12: second camera
13: third camera
11a, 12a, 13a: imaging lens
11b, 12b, 13b: line sensor
13c: the viewing position of the third camera
20, 20A: coaxial lighting unit
21, 21A: upper
21a, 22a: light source
21b, 22b: integrator
21c, 22c: condensing
21e, 22e: collimator lens
21f, 22f : mirror
21g, 22g : Fresnel lens
21h, 22h:
30, 30A: three-dimensional lighting unit
30a:
30c, 30c-1, 30c-2:
30e, 30e-1 : Lenticular Lens
30g:
31, 31A: first area
31a~31j, 31a-1~31j-1: band-shaped light emitting part
32, 32A: second area
32a~32i, 32a-1~32d-1, 32f-1~32h-1: band-shaped light emitting part
33, 33A: third area
33a~33i, 33a-1~33d-1, 33f-1~33h-1: band-shaped light emitting part
34: frame
34a:
35: blower
40: mounting
50: conveyance unit 60: side inspection unit
61, 62: optical element for focal length adjustment
63, 64: reflection mirrors 63a, 64a: reflection surface
71: integrated circuit
72: input unit 73: output unit
74: power supply
75: communication I/F (interface)
81: position detection sensor 82: position detection sensor
90: height acquisition part
91: surface light source 92: camera
93: reflector 95: moving part
100: personal computer (PC: personal computer)
101: CPU (Central Processing Unit)
102: RAM (Random Access Memory) 103: ROM (Read Only Memory)
104: input/output interface
105: Communication I/F (interface) 106: Media I/F (interface)
111: input device 112: output device
113: storage medium
Claims (17)
상기 재치부에 재치된 상기 피검사물을 반송 방향을 따라 이동시키는 반송부와,
상기 피검사물을 대략 연직 상향으로부터 촬상하는 1차원 촬상 수단으로서, 길이 방향이 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하도록 배치된 1차원 촬상 수단과,
상기 피검사물에 광을 조사하는 발광부를 복수 가지는 광조사부를 구비하고,
상기 광조사부는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 포함하는 대략 연직 방향의 면인 중심면의 상에 중심축이 위치하는 대략 반원통면의 제1 영역과, 상기 제1 영역의 양단에 형성된 대략 반구면 또는 대략 반타원구면의 제2 영역 및 제3 영역을 가지고,
상기 제1 영역에 있어서는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향을 따라 상기 발광부가 늘어놓여진 띠모양 발광부를 복수 가지고,
상기 띠모양 발광부는, 상기 제1 영역에 있어서의 상기 중심면의 근방 이외의 영역에 설치되고,
상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 중심면의 상에 상기 발광부가 늘어놓여진 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. A mounting unit for placing the object to be inspected in the horizontal direction;
a conveying unit for moving the inspected object placed on the mounting unit along a conveying direction;
One-dimensional imaging means for imaging the object to be inspected from substantially vertically upward, the one-dimensional imaging means arranged so that a longitudinal direction is substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction;
and a light irradiation unit having a plurality of light emitting units for irradiating light to the object to be inspected,
The light irradiation unit includes a first area of a substantially semi-cylindrical surface in which a central axis is located on a center surface, which is a surface in a substantially vertical direction including the one-dimensional imaging means, and a substantially hemispherical surface formed at both ends of the first area; or having a second area and a third area of a substantially semi-elliptical surface,
in the first region, a plurality of band-shaped light-emitting units in which the light-emitting units are arranged along a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction;
the strip-shaped light emitting part is provided in a region other than the vicinity of the central plane in the first region;
In the second region and the third region, the light emitting units are arranged on the central plane.
상기 띠모양 발광부는, 광축과, 상기 중심면과 상기 재치부의 상면의 교선이 교차하도록 설치되고,
상기 띠모양 발광부는, 광축과 상기 중심면과의 이루는 각도가 대략 8°또는 대략 17°인 제1 띠모양 발광부를 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. The method of claim 1,
The band-shaped light emitting unit is installed so that the optical axis and the intersection line of the central plane and the upper surface of the mounting part intersect,
The optical inspection apparatus according to claim 1, wherein the band-shaped light emitting unit has a first band-shaped light emitting unit whose angle between the optical axis and the central plane is approximately 8° or approximately 17°.
일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 일정한 간격으로 화상을 촬상하도록 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 구동하고, 또한 상기 1차원 촬상 수단에 의한 촬상에 동기하여, 상기 제1 영역의 상기 중심면에서 구분된 반의 영역인 제1 발광 영역, 상기 제1 영역 중의 상기 제1 발광 영역 이외의 제2 발광 영역, 상기 제2 영역 중의 상기 중심면의 상의 제3 발광 영역, 상기 제3 영역 중의 상기 중심면의 상의 제4 발광 영역, 상기 제1 띠모양 발광부를 제각기 조사시키는 제어부를 구비하는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 3. The method of claim 2,
The conveying unit is controlled to convey the object to be inspected at a constant speed, the one-dimensional imaging means is driven to capture images at regular intervals, and in synchronization with the imaging by the one-dimensional imaging means, the first area is A first light emitting area that is a half area separated from the center plane, a second light emitting area other than the first light emitting area in the first area, a third light emitting area on the central plane in the second area, and among the third areas and a control unit for irradiating a fourth light emitting region on the central plane and the first band-shaped light emitting unit, respectively.
상기 광조사부는, 상기 띠모양 발광부와, 상기 중심면과 상기 재치부의 상면과의 교선과의 사이에 배치된 원통 렌즈를 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The light irradiation unit includes the strip-shaped light emitting unit and a cylindrical lens disposed between an intersection between the central plane and the upper surface of the mounting unit.
상기 재치부의 상측 또는 하측에 설치되는 제1 촬상 수단과,
광축이 상기 제1 촬상 수단의 광축과 일치하도록, 상기 제1 촬상 수단과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 촬상 수단과,
상기 피검사물에 법선 방향으로부터 평행광을 조사하는 제1 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제1 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제1 동축 조명과,
상기 제1 동축 조명과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제2 동축 조명을 구비하고,
상기 제1 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고,
상기 제2 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제2 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광, 및 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 투과한 광이 입사하는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
a first imaging means installed on the upper side or the lower side of the mounting unit;
second imaging means provided on the opposite side with the first imaging means and the mounting unit interposed therebetween so that the optical axis coincides with the optical axis of the first imaging means;
first coaxial illumination for irradiating parallel light from a normal direction to the object to be inspected, the first coaxial illumination being coaxial illumination of the first imaging means;
A second coaxial illumination provided on the opposite side with the first coaxial illumination and the mounting unit interposed therebetween, comprising a second coaxial illumination that is a coaxial illumination of the second imaging means;
Light irradiated from the first coaxial illumination and specularly reflected from the inspection object is incident on the first imaging means,
Optical inspection characterized in that the light irradiated from the second coaxial illumination and specularly reflected from the inspection object, and the light irradiated from the first coaxial illumination and transmitted through the inspection object enter the second imaging means Device.
일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제1 형태, 상기 제2 동축 조명을 상기 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제2 형태, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제2의 강도로 조사하는 제3 형태의 3개의 조사 패턴으로 상기 제1 동축 조명 또는 상기 제2 동축 조명을 조사시키고, 또한 상기 제1 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제1 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제2 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제3 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하도록, 상기 제1 촬상 수단 및 상기 제2 촬상 수단을 구동하는 제2 제어부를 구비하는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 6. The method of claim 5,
A first aspect in which the conveying unit is controlled to convey the object to be inspected at a constant speed and irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a first intensity, a second mode of irradiating the second coaxial illumination with the first intensity, The first coaxial illumination or the second coaxial illumination is irradiated with three irradiation patterns of a third type for irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a second intensity, and further, the first imaging according to the irradiation of the first type means for acquiring an image, acquiring an image by the second imaging means in accordance with irradiation of the second form, and acquiring an image by the second imaging means in accordance with irradiation of the third mode; and a second control unit for driving the second imaging unit.
광축이 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 광축과 일치하도록, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 촬상 수단과,
상기 피검사물에 법선 방향으로부터 평행광을 조사하는 제1 동축 조명으로서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제1 동축 조명과,
상기 제1 동축 조명과 상기 재치부를 사이에 두고 반대측에 설치된 제2 동축 조명으로서, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 동축 조명인 제2 동축 조명을 구비하고,
상기 광조사부는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 반송부와의 사이에 설치되고,
상기 1차원 촬상 수단에는, 상기 광조사부 또는 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광이 입사하고,
상기 제2 촬상 수단에는, 상기 제2 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물에서 정반사한 광, 및 상기 제1 동축 조명으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 투과한 광이 입사하는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
second imaging means provided on the opposite side with the one-dimensional imaging means and the mounting unit interposed therebetween so that the optical axis coincides with the optical axis of the one-dimensional imaging means;
first coaxial illumination for irradiating parallel light from a normal direction to the object to be inspected, the first coaxial illumination being coaxial illumination of the one-dimensional imaging means;
A second coaxial illumination provided on the opposite side with the first coaxial illumination and the mounting unit interposed therebetween, comprising a second coaxial illumination that is a coaxial illumination of the second imaging means;
The light irradiation unit is provided between the one-dimensional imaging means and the transport unit,
Light irradiated from the light irradiator or the first coaxial illumination and specularly reflected from the inspection object is incident on the one-dimensional imaging means,
Optical inspection characterized in that the light irradiated from the second coaxial illumination and specularly reflected from the inspection object, and the light irradiated from the first coaxial illumination and transmitted through the inspection object enter the second imaging means Device.
일정한 속도로 상기 피검사물을 반송하도록 상기 반송부를 제어하고, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제1 형태, 상기 제2 동축 조명을 상기 제1의 강도로 조사하는 제2 형태, 상기 제1 동축 조명을 제2의 강도로 조사하는 제3 형태의 3개의 조사 패턴으로 상기 제1 동축 조명 또는 상기 제2 동축 조명을 조사시키고, 또한 상기 제1 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 1차원 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제2 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하고, 상기 제3 형태의 조사에 맞추어 상기 제2 촬상 수단으로 화상을 취득하도록, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단 및 상기 제2 촬상 수단을 구동하는 제3 제어부를 구비하는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 8. The method of claim 7,
A first aspect in which the conveying unit is controlled to convey the object to be inspected at a constant speed and irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a first intensity, a second mode of irradiating the second coaxial illumination with the first intensity, The first coaxial illumination or the second coaxial illumination is irradiated with three irradiation patterns of a third form for irradiating the first coaxial illumination with a second intensity, and the one-dimensional imaging according to the irradiation of the first type means for acquiring an image by means of a second imaging means, acquiring an image by the second imaging means in accordance with the irradiation of the second mode, and acquiring an image by the second imaging means in accordance with the irradiation of the third mode; and a third control unit for driving the second imaging unit.
상기 광조사부는, 상기 발광부에 인접하여 설치되고, 상기 발광부로부터 조사된 광을 확산하는 광확산판을 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The light emitting unit is provided adjacent to the light emitting unit, the optical inspection apparatus characterized in that it has a light diffusion plate for diffusing the light irradiated from the light emitting unit.
상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 초점거리를 조정하는 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자와,
상기 재치부에 인접하여 설치된 반사경을 구비하고,
상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자 및 상기 반사경은, 상기 중심면의 상에 설치되고,
평면시에 있어서, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 연직 방향 하측에, 상기 피검사물이 재치되는 상기 재치부 상의 영역인 재치 영역이 위치하고,
평면시에 있어서, 상기 반사경은, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향에 있어서, 상기 재치 영역의 외측 또한 상기 재치 영역에 인접하는 위치에 설치되고,
상기 반사경의 반사면은 대략 평면이며,
상기 반사면은, 상기 중심면과 교차하는 선이 수평면에 대해서 경사지도록, 상기 반송 방향으로 대략 따라 연설되고,
상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자는, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단과 상기 반사경을 묶는 선과 겹치도록 배치되는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
an optical element for adjusting a focal length for adjusting the focal length of the one-dimensional imaging means;
and a reflector installed adjacent to the mounting unit,
The optical element for adjusting the focal length and the reflecting mirror are installed on the central plane,
In a plan view, a placement area, which is an area on the placement unit on which the object to be inspected is placed, is located below the one-dimensional imaging means in the vertical direction,
In a plan view, the reflecting mirror is provided at a position outside the mounting area and adjacent to the mounting area in a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction;
The reflective surface of the reflector is approximately planar,
the reflective surface extends substantially along the conveying direction such that a line intersecting the central plane is inclined with respect to the horizontal plane;
The optical inspection device according to claim 1, wherein the optical element for adjusting the focal length is disposed so as to overlap a line joining the one-dimensional imaging means and the reflecting mirror.
상기 초점거리 조정용 광학 소자는, 유리판이고, 판두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 양단면이 수평으로 되도록 설치되는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 11. The method of claim 10,
The optical element for adjusting the focal length is a glass plate and is provided so that both end surfaces substantially orthogonal to the plate thickness direction are horizontal.
상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동부와,
상기 피검사물의 높이를 취득하는 높이 취득부와,
상기 높이 취득부가 취득한 정보에 기초하여 상기 이동부를 제어하여, 상기 1차원 촬상 수단의 하를 통과하는 상기 피검사물의 높이 변화에 맞추어 상기 1차원 촬상 수단을 상하 방향으로 이동시키는 이동 제어부를 구비하는것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
a moving unit for moving the one-dimensional imaging means in an up-down direction;
a height acquisition unit for acquiring the height of the object to be inspected;
A movement control unit for controlling the moving unit based on the information obtained by the height obtaining unit to move the one-dimensional imaging unit in an up-down direction in accordance with a change in the height of the object to be inspected passing under the one-dimensional imaging unit; Optical inspection device characterized.
상기 높이 취득부는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향으로 광을 조사하는 면광원과, 상기 면광원으로부터 조사되고, 상기 피검사물을 통과한 광이 입사하는 측면 촬상 수단을 가지는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 13. The method of claim 12,
The height acquisition unit includes a surface light source for irradiating light in a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction, and a side imaging means through which the light irradiated from the surface light source and passed through the inspection object is incident. Optical inspection, characterized in that Device.
상기 광조사부는, 상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서, 상기 발광부가 일렬로 늘어놓여진 발광 블록과, 상기 발광부로부터 조사된 광이 통과하는 제2 원통 렌즈를 가지고,
상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 발광 블록의 연설 방향은 수평 방향에 대해서 기울어져 있고,
상기 제2 영역 및 상기 제3 영역에 있어서는, 상기 발광 블록의 연설 방향에 대해서, 상기 제2 원통 렌즈의 연설 방향이 기울어져 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The light irradiation unit includes, in the second region and the third region, a light emitting block in which the light emitting units are arranged in a line, and a second cylindrical lens through which the light irradiated from the light emitting unit passes,
In the second region and the third region, the extension direction of the light emitting block is inclined with respect to the horizontal direction,
The optical inspection apparatus according to claim 1, wherein in the second region and the third region, the extension direction of the second cylindrical lens is inclined with respect to the extension direction of the light emitting block.
상기 광조사부는, 열전도성이 높은 재료로 형성된 방열 부재를 가지고,
상기 발광부는, 상기 방열 부재에 설치되는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 4. The method according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The light irradiation unit has a heat dissipation member formed of a material with high thermal conductivity,
The light emitting unit is an optical inspection device, characterized in that provided in the heat dissipation member.
상기 방열 부재에 송풍하는 송풍부를 구비하고,
상기 방열 부재는, 상기 발광부가 설치된 플레이트를 복수 가지고,
상기 플레이트는, 상기 반송 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향으로 연설되어 있고,
상기 송풍부는, 상기 플레이트의 연설 방향을 따른 방향의 바람을 보내는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 16. The method of claim 15,
and a blower for blowing air to the heat dissipation member;
The heat dissipation member has a plurality of plates provided with the light emitting part,
The plate extends in a direction substantially orthogonal to the conveying direction,
The blower unit, optical inspection device, characterized in that the wind in a direction along the extension direction of the plate.
상기 제2 촬상 수단은, 상기 재치부의 하측에 설치되고,
상기 제2 촬상 수단의 상측에는, 원편광 필터가 설치되고,
상기 원편광 필터는, 두께 방향과 대략 직교하는 방향의 평면이, 상기 제2 촬상 수단의 광축과 대략 직교하는 방향에 대해서 조금 경사지도록 설치되어 있는 것을 특징으로 하는 광학 검사 장치. 6. The method of claim 5,
The second imaging means is provided below the mounting unit,
A circularly polarizing filter is installed above the second imaging means,
The circularly polarizing filter is provided so that a plane in a direction substantially orthogonal to the thickness direction is slightly inclined with respect to a direction substantially orthogonal to the optical axis of the second imaging means.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016218616 | 2016-11-09 | ||
| JPJP-P-2016-218616 | 2016-11-09 | ||
| PCT/JP2017/040231 WO2018088423A1 (en) | 2016-11-09 | 2017-11-08 | Optical inspection device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20190082198A KR20190082198A (en) | 2019-07-09 |
| KR102339677B1 true KR102339677B1 (en) | 2021-12-14 |
Family
ID=62110631
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020197009783A KR102339677B1 (en) | 2016-11-09 | 2017-11-08 | optical inspection device |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6912824B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR102339677B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN109804238B (en) |
| WO (1) | WO2018088423A1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108535265A (en) * | 2018-04-10 | 2018-09-14 | 深圳市纳研科技有限公司 | A kind of multi-angle polisher and acquisition system |
| JP7167641B2 (en) * | 2018-11-08 | 2022-11-09 | 日本電気硝子株式会社 | Work manufacturing method and work inspection method |
| CN110208290A (en) * | 2019-06-19 | 2019-09-06 | 海南梯易易智能科技有限公司 | A kind of 3D bend glass defect detecting device based on line scan camera |
| US11340284B2 (en) * | 2019-07-23 | 2022-05-24 | Kla Corporation | Combined transmitted and reflected light imaging of internal cracks in semiconductor devices |
| JPWO2021090827A1 (en) * | 2019-11-05 | 2021-05-14 | ||
| JP2021096112A (en) * | 2019-12-16 | 2021-06-24 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | Inspection device for transparent body |
| KR102216999B1 (en) * | 2020-09-28 | 2021-02-18 | 주식회사 하이브비젼 | Non-Lambertian Surface Inspecting System For Line Scan |
| KR102535869B1 (en) * | 2021-03-02 | 2023-05-26 | 주식회사 디쌤 | Visual inspection assembly |
| CN116745577A (en) * | 2021-05-18 | 2023-09-12 | Lg电子株式会社 | Thickness measuring device |
| TWI782695B (en) * | 2021-09-06 | 2022-11-01 | 致茂電子股份有限公司 | Dual sided optical detection system with fluorescence detection function |
| KR102368707B1 (en) * | 2021-09-07 | 2022-02-28 | 주식회사 하이브비젼 | Non-Lambertian Surface Inspecting System For Line Scan |
| TWI781840B (en) * | 2021-12-02 | 2022-10-21 | 友達光電股份有限公司 | A light control device, testing system and method for dark field photography |
| CN218726727U (en) * | 2022-12-12 | 2023-03-24 | 宁德时代新能源科技股份有限公司 | Appearance detection device and battery cell manufacturing equipment |
| WO2024190081A1 (en) * | 2023-03-15 | 2024-09-19 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Image recognition method and device |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002196338A (en) | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Liquid crystal display element |
| JP2003224353A (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2003-08-08 | Hitachi Ltd | Method for mounting substrate of electronic component |
| JP2005265741A (en) | 2004-03-22 | 2005-09-29 | Mega Trade:Kk | Lighting system |
| JP2010122047A (en) | 2008-11-19 | 2010-06-03 | Mega Trade:Kk | Lighting system |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH1075051A (en) * | 1996-07-05 | 1998-03-17 | Toyota Motor Corp | Visual inspection device |
| JP3316501B2 (en) * | 2000-03-28 | 2002-08-19 | 科学技術振興事業団 | Sensor head, luminance distribution measuring device including the same, and display unevenness evaluation device |
| US7113313B2 (en) * | 2001-06-04 | 2006-09-26 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Dome-shaped apparatus for inspecting a component or a printed circuit board device |
| CN2867100Y (en) * | 2005-07-13 | 2007-02-07 | 王锦峰 | On-line light supply generation device |
| DE102008047085B4 (en) * | 2008-09-12 | 2016-02-18 | Gp Inspect Gmbh | lighting device |
| JP5806808B2 (en) | 2010-08-18 | 2015-11-10 | 倉敷紡績株式会社 | Imaging optical inspection device |
| FI125320B (en) * | 2012-01-05 | 2015-08-31 | Helmee Imaging Oy | EVENTS AND SIMILAR OPTICAL MEASUREMENT PROCEDURES |
| CN103293162B (en) * | 2013-06-17 | 2015-03-11 | 浙江大学 | Lighting system and method used for dark field detection of defect in spherical optical element surface |
| JP6287360B2 (en) * | 2014-03-06 | 2018-03-07 | オムロン株式会社 | Inspection device |
| US9885671B2 (en) * | 2014-06-09 | 2018-02-06 | Kla-Tencor Corporation | Miniaturized imaging apparatus for wafer edge |
-
2017
- 2017-11-08 KR KR1020197009783A patent/KR102339677B1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2017-11-08 CN CN201780062143.7A patent/CN109804238B/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2017-11-08 WO PCT/JP2017/040231 patent/WO2018088423A1/en active Application Filing
- 2017-11-08 JP JP2018550225A patent/JP6912824B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002196338A (en) | 2000-12-22 | 2002-07-12 | Toshiba Corp | Liquid crystal display element |
| JP2003224353A (en) | 2002-01-30 | 2003-08-08 | Hitachi Ltd | Method for mounting substrate of electronic component |
| JP2005265741A (en) | 2004-03-22 | 2005-09-29 | Mega Trade:Kk | Lighting system |
| JP2010122047A (en) | 2008-11-19 | 2010-06-03 | Mega Trade:Kk | Lighting system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2018088423A1 (en) | 2019-10-03 |
| WO2018088423A1 (en) | 2018-05-17 |
| CN109804238A (en) | 2019-05-24 |
| KR20190082198A (en) | 2019-07-09 |
| CN109804238B (en) | 2021-12-28 |
| JP6912824B2 (en) | 2021-08-04 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR102339677B1 (en) | optical inspection device | |
| JP5806808B2 (en) | Imaging optical inspection device | |
| US9110035B2 (en) | Method and system for detecting defects of transparent substrate | |
| WO2016121878A1 (en) | Optical appearance inspection device and optical appearance inspection system using same | |
| US20110310244A1 (en) | System and method for detecting a defect of a substrate | |
| US8681211B2 (en) | High speed optical inspection system with adaptive focusing | |
| TWI557434B (en) | Lighting system | |
| US10887500B2 (en) | Optical inspection system | |
| KR101588937B1 (en) | Pattern inspection apparatus and pattern inspection method | |
| US20120044346A1 (en) | Apparatus and method for inspecting internal defect of substrate | |
| JP5720134B2 (en) | Image inspection apparatus and image forming apparatus | |
| KR101577119B1 (en) | Pattern inspection apparatus and pattern inspection method | |
| JP2015227793A (en) | Inspection device of optical components and inspection method thereof | |
| KR20180116154A (en) | Inspection apparatus for cover glass | |
| KR101245622B1 (en) | Vision inspection apparatus using stereo vision grid pattern | |
| CN109540899B (en) | Inspection apparatus and inspection method | |
| JP2007078404A (en) | Inspection device of solar cell panel | |
| EP3428626B1 (en) | Inspecting method, inspection system and manufacturing method | |
| KR100671766B1 (en) | Inspection device for substrate | |
| KR101245623B1 (en) | Vision inspection apparatus using grid pattern of visible ray and ultraviolet ray or infrared light | |
| KR101124567B1 (en) | Wafer inspecting apparatus having hybrid illumination | |
| JP2022501580A (en) | Multi-modality multiplexed lighting for optical inspection systems | |
| KR101485425B1 (en) | Cover-glass Analysis Apparatus | |
| JP6175819B2 (en) | Image inspection apparatus and image inspection method | |
| KR20120086333A (en) | High speed optical inspection system with adaptive focusing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant |