KR101392160B1 - Liquid crystal display device - Google Patents
Liquid crystal display device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101392160B1 KR101392160B1 KR1020060124754A KR20060124754A KR101392160B1 KR 101392160 B1 KR101392160 B1 KR 101392160B1 KR 1020060124754 A KR1020060124754 A KR 1020060124754A KR 20060124754 A KR20060124754 A KR 20060124754A KR 101392160 B1 KR101392160 B1 KR 101392160B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- gate
- main line
- substrate
- pixel electrode
- gate main
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 58
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 64
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims description 44
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000000565 sealant Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N zinc indium(3+) oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O--].[Zn++].[In+3] YVTHLONGBIQYBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims 16
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 40
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 12
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 4
- 101100489584 Solanum lycopersicum TFT1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101100214488 Solanum lycopersicum TFT2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002834 transmittance Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000013256 coordination polymer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910004205 SiNX Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000007792 addition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006229 carbon black Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002224 dissection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/1333—Constructional arrangements; Manufacturing methods
- G02F1/1345—Conductors connecting electrodes to cell terminals
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/136—Liquid crystal cells structurally associated with a semi-conducting layer or substrate, e.g. cells forming part of an integrated circuit
- G02F1/1362—Active matrix addressed cells
- G02F1/136286—Wiring, e.g. gate line, drain line
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/786—Thin film transistors, i.e. transistors with a channel being at least partly a thin film
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F1/00—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics
- G02F1/01—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour
- G02F1/13—Devices or arrangements for the control of the intensity, colour, phase, polarisation or direction of light arriving from an independent light source, e.g. switching, gating or modulating; Non-linear optics for the control of the intensity, phase, polarisation or colour based on liquid crystals, e.g. single liquid crystal display cells
- G02F1/133—Constructional arrangements; Operation of liquid crystal cells; Circuit arrangements
- G02F1/136—Liquid crystal cells structurally associated with a semi-conducting layer or substrate, e.g. cells forming part of an integrated circuit
- G02F1/1362—Active matrix addressed cells
- G02F1/136286—Wiring, e.g. gate line, drain line
- G02F1/136295—Materials; Compositions; Manufacture processes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G02—OPTICS
- G02F—OPTICAL DEVICES OR ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE CONTROL OF LIGHT BY MODIFICATION OF THE OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE MEDIA OF THE ELEMENTS INVOLVED THEREIN; NON-LINEAR OPTICS; FREQUENCY-CHANGING OF LIGHT; OPTICAL LOGIC ELEMENTS; OPTICAL ANALOGUE/DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- G02F2201/00—Constructional arrangements not provided for in groups G02F1/00 - G02F7/00
- G02F2201/12—Constructional arrangements not provided for in groups G02F1/00 - G02F7/00 electrode
- G02F2201/123—Constructional arrangements not provided for in groups G02F1/00 - G02F7/00 electrode pixel
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Nonlinear Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mathematical Physics (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Liquid Crystal (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
Abstract
본 발명은 액정표시장치에 관한 것이다. 본 발명에 따른 액정표시장치는 표시영역을 가지는 제1기판과, 상기 제1기판과 대면하는 제2기판과, 상기 제1기판과 상기 제2기판 사이에 위치하는 액정층을 포함하며, 상기 제1기판은, 상기 표시영역 내에 위치하는 게이트 본선과; 상기 표시영역 외부에 위치하는 게이트 패드와; 상기 게이트 본선과 상기 게이트 패드를 전기적으로 연결하며 상기 게이트 본선보다 저항이 높은 물질로 이루어진 저항부를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 한다. 이에 의해 게이트 신호 지연 차이로 인한 휘도불균일이 감소된 액정표시장치가 제공된다.The present invention relates to a liquid crystal display device. A liquid crystal display device according to the present invention includes a first substrate having a display region, a second substrate facing the first substrate, and a liquid crystal layer disposed between the first substrate and the second substrate, 1 substrate includes: a gate main line positioned within the display area; A gate pad located outside the display region; And a resistance portion electrically connected to the gate main line and the gate pad and made of a material having a higher resistance than the gate main line. Thereby, a luminance unevenness due to a difference in gate signal delay is reduced, is provided.
Description
도 1은 본 발명의 제1실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 제1기판의 배치도이고,1 is a layout diagram of a first substrate in a liquid crystal display device according to a first embodiment of the present invention,
도 2는 도 1의 A부분의 확대도이고,Fig. 2 is an enlarged view of a portion A in Fig. 1,
도 3은 도 2의 Ⅲ-Ⅲ을 따른 단면도이고,3 is a cross-sectional view taken along the line III-III in Fig. 2,
도 4는 본 발명의 제1실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 화소전압에 따른 투과율을 나타낸 도면이고,4 is a graph showing the transmittance according to the pixel voltage in the liquid crystal display according to the first embodiment of the present invention,
도 5는 본 발명의 제1실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 화소의 등가회로도이고,5 is an equivalent circuit diagram of a pixel in the liquid crystal display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention,
도 6a 내지 도 6c는 게이트 신호 지연에 따른 휘도불균일을 설명하기 위한 도면이고,6A to 6C are diagrams for explaining luminance unevenness due to gate signal delay,
도 7은 도 1의 B부분의 확대도이고,7 is an enlarged view of a portion B in Fig. 1,
도 8은 도 7의 Ⅷ-Ⅷ을 따른 단면도이고,8 is a cross-sectional view taken along line VIII-VIII of FIG. 7,
도 9는 본 발명의 제1실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 휘도불균일 개선을 설명하기 위한 도면이고,FIG. 9 is a view for explaining improvement in luminance unevenness in the liquid crystal display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention,
도 10은 게이트 신호 지연과 휘도와의 관계를 나타낸 도면이고,10 is a diagram showing the relationship between the gate signal delay and the luminance,
도 11은 기생용량과 휘도와의 변화를 나타낸 도면이고,11 is a diagram showing a change in parasitic capacitance and luminance,
도 12는 저항부의 저항값에 따른 게이트 신호 지연을 나타낸 도면이고,12 is a view showing a gate signal delay according to the resistance value of the resistance portion,
도 13은 저항부의 저항값에 따른 화소전압을 나타낸 도면이고,13 is a diagram showing a pixel voltage according to a resistance value of a resistance portion,
도 14는 본 발명의 제2실시예에 따른 액정표시장치를 설명하기 위한 도면이고,FIG. 14 is a view for explaining a liquid crystal display according to a second embodiment of the present invention, and FIG.
도 15은 도 14의 ⅩⅤ-ⅩⅤ를 따른 단면도이고,Fig. 15 is a sectional view taken along the line XV-XV in Fig. 14,
도 16은 본 발명의 제3실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 화소의 등가회로도이고,16 is an equivalent circuit diagram of a pixel in a liquid crystal display device according to the third embodiment of the present invention,
도 17은 본 발명의 제3실시예에 따른 액정표시장치에서 시인성 개선 원리를 나타낸 것이고17 shows the principle of improving the visibility in the liquid crystal display device according to the third embodiment of the present invention
도 18은 본 발명의 제3실시예에 따른 액정표시장치의 배치도이고,18 is a layout diagram of a liquid crystal display device according to the third embodiment of the present invention,
도 19는 본 발명의 제4실시예에 따른 액정표시장치의 배치도이다.19 is a layout diagram of a liquid crystal display device according to a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
* 도면의 주요부분의 부호에 대한 설명 *Description of Reference Numerals of Major Parts of the Drawings [
121 : 게이트선 122 : 게이트 전극121: gate line 122: gate electrode
123 : 팬-아웃부 124 : 게이트 패드123: fan-out portion 124: gate pad
131 : 게이트 절연막 151 : 보호막131: gate insulating film 151: protective film
161 : 화소전극 166 : 화소전극 절개패턴161: pixel electrode 166: pixel electrode cut-out pattern
163 : 저항부 200 : 제2기판163: Resistor part 200: Second substrate
251 : 공통전극 252 : 공통전극 절개패턴 251: common electrode 252: common electrode incision pattern
300 : 실런트300: Sealant
본 발명은 액정표시장치에 관한 것으로, 더 상세하게는 게이트 신호 지연차이를 감소시켜 휘도균일성을 향상시킨 액정표시장치에 관한 것이다. BACKGROUND OF THE
액정표시장치는 박막트랜지스터가 형성되어 있는 제1기판과, 제1기판에 대향 배치되어 있는 제2기판, 그리고 이들 사이에 위치하는 액정층을 포함한다. A liquid crystal display device includes a first substrate on which a thin film transistor is formed, a second substrate opposed to the first substrate, and a liquid crystal layer interposed between the first substrate and the second substrate.
박막트랜지스터 기판에 마련된 게이트선과 데이터선은 서로 교차하면서 화소를 형성하며 각 화소는 박막트랜지스터에 연결되어 있다. 게이트선에 게이트 신호(게이트 온전압(Von))가 인가되어 박막트랜지스터가 턴온되면 데이터선을 통해 인가된 데이터 전압(Vd)이 화소에 충전된다. A gate line and a data line provided on a thin film transistor substrate intersect each other to form pixels, and each pixel is connected to a thin film transistor. When a gate signal (gate on voltage Von) is applied to the gate line and the thin film transistor is turned on, the data voltage Vd applied through the data line is charged in the pixel.
화소에 충전된 화소 전압(Vp)과 제2기판의 공통전극에 형성된 공통전압(Vcom) 사이에 형성된 전계에 따라 액정층의 배열상태가 결정된다. 데이터 전압(Vd)은 프레임 별로 극성을 달리하여 인가된다.The alignment state of the liquid crystal layer is determined according to the electric field formed between the pixel voltage Vp charged in the pixel and the common voltage Vcom formed at the common electrode of the second substrate. The data voltage Vd is applied with a different polarity for each frame.
화소에 인가된 데이터 전압(Vd)은 게이트 전극과 소스 전극(드레인 전극) 간의 기생 용량 (Cp)에 의해 강하되어 화소 전압(Vp)을 형성한다. 데이터 전압(Vd)과 화소 전압(Vp) 간의 전압 차이를 킥백 전압(Vkb)이라 한다.The data voltage Vd applied to the pixel is lowered by the parasitic capacitance Cp between the gate electrode and the source electrode (drain electrode) to form the pixel voltage Vp. The voltage difference between the data voltage Vd and the pixel voltage Vp is referred to as a kickback voltage Vkb.
게이트선은 단부에 연결되어 있는 게이트 패드를 통해 게이트 신호를 인가 받는다. 게이트 패드에 인접한 화소에는 지연이 적은 게이트 신호가 인가되고, 게이트 패드에서 먼 화소에는 게이트선의 저항에 의해 지연이 많이 된 게이트 신호가 인가된다.The gate line receives a gate signal through a gate pad connected to the end. A gate signal having a small delay is applied to the pixel adjacent to the gate pad and a gate signal having a large delay due to the resistance of the gate line is applied to the pixel distant from the gate pad.
그런데 게이트 신호의 지연 정도에 따라 킥백전압의 크기가 달라지고, 킥백전압의 변화에 의해 화소전압이 달라져 화면의 휘도가 불균일해지는 문제가 발생한다.However, the size of the kickback voltage varies depending on the degree of delay of the gate signal, and the pixel voltage varies due to the change of the kickback voltage, resulting in a problem that the brightness of the screen becomes uneven.
따라서 본 발명의 목적은 게이트 신호 지연 차이로 인한 휘도불균일이 감소된 액정표시장치를 제공하는 것이다.SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION Accordingly, it is an object of the present invention to provide a liquid crystal display device in which luminance unevenness due to gate signal delay difference is reduced.
상기 본 발명의 목적은 표시영역을 가지는 제1기판과, 상기 제1기판과 대면하는 제2기판과, 상기 제1기판과 상기 제2기판 사이에 위치하는 액정층을 포함하는 액정표시장치에 있어서, 상기 제1기판은, 상기 표시영역 내에 위치하는 게이트 본선과; 상기 표시영역 외부에 위치하는 게이트 패드와; 상기 게이트 본선과 상기 게이트 패드를 전기적으로 연결하며 상기 게이트 본선보다 저항이 높은 물질로 이루어진 저항부를 포함하는 것에 의하여 달성된다.It is an object of the present invention to provide a liquid crystal display device including a first substrate having a display region, a second substrate facing the first substrate, and a liquid crystal layer positioned between the first substrate and the second substrate The first substrate includes: a gate main line positioned in the display area; A gate pad located outside the display region; And a resistance portion electrically connected to the gate main line and the gate pad and made of a material having a higher resistance than the gate main line.
상기 제1기판은, 상기 게이트 본선에 연결되어 있는 박막트랜지스터와; 상기 박막트랜지스터에 전기적으로 연결되어 있는 화소전극을 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.The first substrate includes a thin film transistor connected to the gate main line; And a pixel electrode electrically connected to the thin film transistor.
상기 저항부는 상기 화소전극과 동일한 재질로 마련되어 있는 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that the resistance portion is formed of the same material as the pixel electrode.
상기 저항부는 ITO(indium tin oxide) 또는 IZO(indium zinc oxide)를 포함 하는 것이 바람직하다.The resistor may include indium tin oxide (ITO) or indium zinc oxide (IZO).
상기 저항부는 연결하는 상기 게이트 본선과 상기 게이트 패드와의 거리가 길수록 저항값이 작게 마련되는 것이 바람직하다.The resistive part preferably has a smaller resistance value as the distance between the gate main line and the gate pad is larger.
상기 게이트 패드와 상기 저항부 사이에 위치하는 팬-아웃부를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And a fan-out unit positioned between the gate pad and the resistor unit.
상기 게이트 본선, 상기 게이트 패드 및 상기 팬-아웃부는 동일한 층으로 형성되어 있는 것이 바람직하다.The gate main line, the gate pad, and the fan-out portion are preferably formed in the same layer.
상기 팬-아웃부 상에 형성되어 있으며, 상기 제1기판과 상기 제2기판을 결합시키는 실런트를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And a sealant that is formed on the fan-out portion and couples the first substrate and the second substrate.
상기 게이트 패드와 상기 저항부 사이에 위치하는 팬-아웃부를 더 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.And a fan-out unit positioned between the gate pad and the resistor unit.
상기 게이트 패드, 상기 팬-아웃부 및 상기 저항부는 같은 층으로 이루어진 것이 바람직하다.The gate pad, the fan-out portion, and the resistor portion may be formed of the same layer.
상기 저항부의 적어도 일부는 지그재그로 형성되어 있는 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that at least a part of the resistance portion is formed in a zigzag shape.
상기 액정층은 VA(vertical alignment) 모드인 것이 바람직하다.Preferably, the liquid crystal layer is in a vertical alignment (VA) mode.
화소전극은 화소전극 절개패턴이 형성되어 있으며, 상기 제2기판은 공통전극 절개패턴이 형성되어 있는 공통전극을 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that the pixel electrode includes a pixel electrode cut-out pattern, and the second substrate includes a common electrode on which a common electrode cut-out pattern is formed.
상기 화소전극은 서로 분리되어 있는 제1화소전극 및 제2화소전극을 포함하며, 상기 제1화소전극과 상기 제2화소전극에는 서로 다른 화소 전압이 인가되는 것이 바람직하다.The pixel electrode may include a first pixel electrode and a second pixel electrode that are separated from each other, and a different pixel voltage may be applied to the first pixel electrode and the second pixel electrode.
상기 박막트랜지스터는 드레인 전극을 포함하며, 상기 드레인 전극은 상기 제1화소전극에 직접 데이터 전압을 인가하는 제1드레인 전극과 상기 제2화소전극과 결합용량을 형성하는 제2드레인 전극을 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.The thin film transistor includes a drain electrode, and the drain electrode includes a first drain electrode for applying a data voltage directly to the first pixel electrode, and a second drain electrode for forming a coupling capacitance with the second pixel electrode desirable.
상기 박막트랜지스터는 상기 제1화소전극에 연결되어 있는 제1박막트랜지스터와 상기 제2화소전극에 연결되어 있는 제2박막트랜지스터를 포함하는 것이 바람직하다.The thin film transistor may include a first thin film transistor connected to the first pixel electrode and a second thin film transistor connected to the second pixel electrode.
상기 저항부의 총 저항은 상기 게이트 본선의 총 저항의 10% 내지 50%인 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that the total resistance of the resistance portion is 10% to 50% of the total resistance of the gate main line.
상기 게이트 본선의 게이트 신호 지연의 변화는 100%내에서 이루어지는 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that the change of the gate signal delay of the gate main line is made within 100%.
상기 본 발명의 목적은 표시영역을 가지는 제1기판과, 상기 제1기판과 대면하는 제2기판과, 상기 제1기 판과 상기 제2기판 사이에 위치하는 액정층을 포함하는 액정표시장치에 있어서, 상기 제1기판은, 상기 표시영역 내에 위치하는 게이트 본선과; 상기 표시영역 외부에 위치하는 게이트 패드와; 상기 게이트 본선과 상기 게이트 패드를 전기적으로 연결하며 상기 게이트 본선보다 저항이 높은 물질로 이루어진 저항부와; 상기 게이트 본선에 연결되어 있는 박막트랜지스터와; 상기 박막트랜지스터에 전기적으로 연결되어 있으며 상기 저항부와 동일한 재질로 이루어진 화소전극을 포함하며, 상기 액정층은 VA모드인 것이 의해서도 달성된다.It is an object of the present invention to provide a liquid crystal display device including a first substrate having a display region, a second substrate facing the first substrate, and a liquid crystal layer positioned between the first substrate and the second substrate Wherein the first substrate includes: a gate main line positioned within the display area; A gate pad located outside the display region; A resistor part electrically connected to the gate main line and the gate pad and made of a material having a higher resistance than the gate main line; A thin film transistor connected to the gate main line; And a pixel electrode electrically connected to the thin film transistor and made of the same material as the resistance portion, wherein the liquid crystal layer is in a VA mode.
상기 본 발명의 목적은 표시영역과 비표시영역을 갖는 기판, 상기 표시영역 내에 위치하는 게이트 본선과; 상기 표시영역 외부에 위치하는 게이트 패드와; 상 기 게이트 본선과 상기 게이트 패드를 전기적으로 연결하며 상기 게이트 본선보다 저항이 높은 물질로 이루어진 저항부와; 상기 게이트 본선에 연결되어 있는 박막트랜지스터와; 상기 박막트랜지스터에 전기적으로 연결되어 있으며 상기 저항부와 동일한 재질로 이루어진 화소전극을 포함하는 박막트랜지스터 어레이 기판을 포함하는 액정표시장이에 의해서도 달성된다.The above object of the present invention can be achieved by a display device comprising a substrate having a display area and a non-display area, a gate main line positioned in the display area, A gate pad located outside the display region; A resistor part electrically connected to the gate line and the gate pad and made of a material having a higher resistance than the gate line; A thin film transistor connected to the gate main line; And a thin film transistor array substrate including a pixel electrode electrically connected to the thin film transistor and made of the same material as the resistance portion.
이하 첨부된 도면을 참조로 하여 본 발명을 더욱 상세히 설명하겠다. 이하에서 어떤 막(층)이 다른 막(층)의 '상부에' 형성되어(위치하고) 있다는 것은, 두 막(층)이 접해 있는 경우 뿐 아니라 두 막(층) 사이에 다른 막(층)이 존재하는 경우도 포함한다.BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS The invention will now be described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which: FIG. Hereinafter, the fact that a certain film (layer) is formed (positioned) on another film (layer) means that not only when both films (layer) are in contact but also when another film And the case where it exists.
도 1 내지 도 3을 참조하여 본 발명에 따른 액정표시장치를 설명한다.A liquid crystal display according to the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS. 1 to 3. FIG.
액정표시장치(1)는 박막트랜지스터(T)가 형성되어 있는 제1기판(100), 제1기판(100)과 대향하는 제2기판(200), 양 기판(100, 200) 사이에 위치하는 액정층(300) 및 양 기판(100, 200)을 접합시키는 실런트(400)를 포함한다.The liquid
제1기판(100)은 표시영역과, 표시영역을 둘러싸는 비표시영역으로 나누어진다. 표시영역의 게이트선(121)은 비표시영역의 팬-아웃부(123)를 통해 게이트 패드(124)와 연결된다.The
먼저 제1 기판(100)에 대하여 설명한다.First, the
제1절연기판(111) 상에 게이트 배선이 형성되어 있다. 게이트 배선은 금속 단일층 또는 다중층일 수 있다. 게이트 배선은 표시영역 내에 위치하며 가로 방향으로 뻗어 있는 게이트 본선(121), 게이트 본선(121)에서 연결되어 있는 게이트 전극(122), 게이트 본선(121)에서 비표시영역으로 연장되어 있는 팬-아웃부(123) 및 팬-아웃부(123)의 단부에 연결되어 있는 게이트 패드(124) 그리고 게이트선(121)과 평행하게 연장되어 있는 유지전극선(125)을 포함한다. Gate wirings are formed on the first insulating
게이트 패드(124)는 게이트 구동부(도시하지 않음)에 연결되어, 게이트 신호를 인가받는다. 게이트 패드(124)는 게이트 본선(121)에 비해 폭이 크게 마련되어 있다.The
제1절연기판(111)위에는 실리콘 질화물(SiNx) 등으로 이루어진 게이트 절연막(131)이 게이트 배선을 덮고 있다.On the first insulating
게이트 전극(122)의 게이트 절연막(131) 상부에는 비정질 실리콘 등의 반도체로 이루어진 반도체층(132)이 형성되어 있으며, 반도체층(132)의 상부에는 실리사이드 또는 n형 불순물이 고농도로 도핑되어 있는 n+ 수소화 비정질 실리콘 등의 물질로 만들어진 저항 접촉층(133)이 형성되어 있다. 소스 전극(142)과 드레인 전극(143) 사이의 채널부에서는 저항 접촉층(133)이 제거되어 있다.A
저항 접촉층(133) 및 게이트 절연막(131) 위에는 데이터 배선이 형성되어 있다. 데이터 배선 역시 금속층으로 이루어진 단일층 또는 다중층일 수 있다. 데이터 배선은 세로방향으로 형성되어 게이트선(121)과 교차하여 화소를 형성하는 데이터선(141), 데이터선(141)의 분지이며 저항 접촉층(133)의 상부까지 연장되어 있는 소스 전극(142), 소스전극(142)과 분리되어 있으며 소스전극(142)의 반대쪽 저항 접촉층(133) 상부에 형성되어 있는 드레인 전극(143), 데이터선(141)에서 비표시영역으로 연장된 팬-아웃부(144) 및 팬-아웃부(144)의 단부에 연결되어 있는 데이터 패드(145)를 포함한다. Data wirings are formed on the
데이터 패드(145)는 데이터 구동부(도시하지 않음)에 연결되어, 데이터 구동 신호를 인가받는다. 데이터 패드(145)는 데이터 본선(141)에 비해 폭이 크게 마련되어 있다.The
데이터 배선 및 이들이 가리지 않는 반도체층(132)의 상부에는 보호막(151)이 형성되어 있다. 보호막(151)에는 드레인 전극(143)을 드러내는 접촉구(152)가 형성되어 있다. 도 7 및 도 8을 보면 보호막(151)에는 접촉구(153, 154, 155)가 더 형성되어 있으며, 이 부분에는 게이트 절연막(131)도 같이 제거되어 있다.A
보호막(151)의 상부에는 화소전극(161)이 형성되어 있다. 화소전극(161)은 통상 ITO(indium tin oxide) 또는 IZO(indium zinc oxide)등의 투명한 도전물질로 이루어진다. 화소전극(161)은 접촉구(152)를 통해 드레인 전극(143)과 연결되어 있다. 화소전극(161)에는 화소전극 절개패턴(166)가 형성되어 있다. A
화소전극(161)의 화소전극 절개패턴(166)은 후술하는 공통전극 절개패턴(252)과 함께 액정층(300)을 다수의 영역으로 분할한다.The pixel
이어 제2 기판(200)에 대하여 설명하겠다.Next, the
제2절연기판(211) 위에 블랙매트릭스(221)가 형성되어 있다. 블랙매트릭 스(221)는 일반적으로 적색, 녹색 및 청색 필터 사이를 구분하며, 제1기판(100)에 위치하는 박막트랜지스터로의 직접적인 광조사를 차단하는 역할을 한다. 블랙매트릭스(221)는 통상 검은색 안료가 첨가된 감광성 유기물질로 이루어져 있다. 상기 검은색 안료로는 카본블랙이나 티타늄 옥사이드 등을 사용한다.A
컬러필터(231)는 블랙매트릭스(221)를 경계로 하여 적색, 녹색 및 청색 필터가 반복되어 형성된다. 컬러필터(231)는 백라이트 유닛(도시하지 않음)으로부터 조사되어 액정층(300)을 통과한 빛에 색상을 부여하는 역할을 한다. 컬러필터(231)는 통상 감광성 유기물질로 이루어져 있다.The
컬러필터(231)와 컬러필터(231)가 덮고 있지 않은 블랙매트릭스(221)의 상부에는 오버코트층(241)이 형성되어 있다. 오버코트층(241)은 컬러필터(231)를 평탄화하면서, 컬러필터(231)를 보호하는 역할을 한다. 오버코트층(241)은 감광성 아크릴계 수지일 수 있다.An
오버코트층(241)의 상부에는 공통전극(251)이 형성되어 있다. 공통전극(251)은 ITO(indium tin oxide) 또는 IZO(indium zinc oxide)등의 투명한 도전물질로 이루어진다. 공통전극(251)은 박막트랜지스터 기판의 화소전극(161)과 함께 액정층(300)에 직접 전압을 인가한다. A
공통전극(251)에는 공통전극 절개패턴(252)이 형성되어 있다. 공통전극 절개패턴(252)은 화소전극(161)의 화소전극 절개패턴(166)과 함께 액정층(300)을 다수의 영역으로 나누는 역할을 한다. 화소전극 절개패턴(166)과 공통전극 절개패턴(252)은 실시예에 한정되지 않고 다양한 형상으로 형성될 수 있다. 다른 실시예 서는 절개패턴(166, 252) 대신 돌기부가 마련되어 액정층(300)을 다수의 영역으로 나눌 수 있다.A common
제1기판(100)과 제2기판(200)의 사이에는 액정층(300)이 위치한다. 액정층(300)은 VA(vertically aligned)모드로서, 액정분자는 전압이 가해지지 않은 상태에서는 길이방향이 수직을 이루고 있다. 전압이 가해지면 액정분자는 유전율 이방성이 음이기 때문에 전기장에 대하여 수직방향으로 눕는다. A
그런데 절개패턴(166, 252)이 형성되어 있지 않으면, 액정분자는 눕는 방위각이 결정되지 않아서 여러 방향으로 무질서하게 배열하게 되고, 배향 방향이 다른 경계면에서 전경선(disclination line)이 생긴다. 절개 패턴(166, 252)은 액정층(300)에 전압이 걸릴 때 프린지 필드를 만들어 액정 배향의 방위각을 결정해 준다. 또한 액정층(300)은 절개 패턴(166, 252)의 배치에 따라 다중영역으로 나누어진다.If the cutting
제1실시예에 따른 액정표시장치(1)은 노말리 블랙(normally black) 모드로서, 화소전압에 따른 투과율은 도 4와 같다. 도 4의 C부분에 도시한 저 계조에서의 투과율 변화는 TN(twisted nematic) 액정과 비교하여 약 3배 정도 급격하다.The liquid
이상 설명한 액정표시장치(1)에서 게이트본선(121)은 단부에 연결되어 있는 게이트 패드(124)를 통해 게이트 신호를 인가 받는다. 게이트본선(121)의 저항에 의해 게이트 패드(124)에 인접한 박막트랜지스터(T), 즉 좌측의 박막트랜지스터(T) 에는 지연이 적은 게이트 신호가 인가된다. 반면 게이트 패드(123)에서 먼 박막트랜지스터(T), 즉 우측의 박막트랜지스터(T)에는 지연이 많이 된 게이트 신호가 인가된다. In the
게이트 신호 지연의 차이에 따른 화면 휘도의 변화를 도 5 내지 도 6c를 참조하여 설명한다.The change of the screen brightness according to the difference of the gate signal delay will be described with reference to Figs. 5 to 6C.
킥백 전압(Vkb)은 다음과 같이 식 1로 표현된다.The kickback voltage Vkb is expressed by
식 1
Vkb = (Von-Voff)*Cp/(Clc+Cst+Cp)Vkb = (Von-Voff) * Cp / (Clc + Cst + Cp)
여기서 도 3 및 도5에서와 같이 Cp는 게이트 전극과 소스 전극간의 기생용량(Cgs) + 게이트 전극과 드레인 전극간의 기생용량(Cgd), Clc는 액정용량, Cst는 저장용량, Von은 게이트 온 전압, Voff는 게이트 오프 전압을 나타낸다.3 and 5, Cp denotes parasitic capacitance (Cgs) between the gate electrode and the source electrode, parasitic capacitance (Cgd) between the gate electrode and the drain electrode, Clc denotes the liquid crystal capacitance, Cst denotes the storage capacitance, , And Voff represents a gate-off voltage.
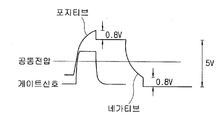
게이트 신호의 지연이 크면 게이트 온 전압 인가가 불량해져 킥백전압은 작아지며, 포지티브 화소전압이 인가될 때보다 네가티브 화소전압이 인가될 때 킥백전압은 더 커진다.If the delay of the gate signal is large, the gate-on voltage is poor and the kickback voltage becomes small. The kickback voltage becomes larger when the negative pixel voltage is applied than when the positive pixel voltage is applied.
도 6a 및 도 6b는 각각 게이트 신호의 지연이 작은 표시영역 좌측의 화소와 게이트 신호의 지연이 큰 표시영역 우측의 화소를 대상으로 킥백전압을 나타낸 것이다. 6A and 6B show a kickback voltage for a pixel on the left side of the display area with a small delay of the gate signal and a pixel on the right side of the display area where the delay of the gate signal is large.
도 6a에 나타낸 좌측 화소의 경우, 포지티브 화소전압 인가 시 킥백전압은 1V이고 네가티브 화소전압 인가 시 킥백전압은 1.2V이다. 도 8b에 나타낸 우측 화소의 경우, 포지티브 화소전압 인가 시와 네가티브 화소전압 인가 시 모두 킥백전압은 0.8V이다.In the case of the left pixel shown in FIG. 6A, the kickback voltage is 1 V when the positive pixel voltage is applied, and the kickback voltage is 1.2 V when the negative pixel voltage is applied. In the case of the right pixel shown in Fig. 8B, the kickback voltage is 0.8 V both when the positive pixel voltage is applied and when the negative pixel voltage is applied.
따라서 좌측 화소의 경우가 최종적으로 화소에 남게 되는 평균(root mean square) 화소 전압이 더 커지고, 화면은 좌측 화소에 해당하는 부분이 더 밝게 인식된다.Accordingly, the root mean square pixel voltage at which the left pixel finally remains in the pixel is larger, and the portion corresponding to the left pixel is recognized as brighter at the screen.
도 6c를 보면 게이트 패드(124)에 가까이 갈수록 게이트 신호 지연이 작고 킥백전압(Vkb)은 커진다. 반면, 게이트 패드(124)에서 멀어질수록 게이트 신호지연은 커지고 킥백전압(Vkb)은 작아진다. 따라서 좌측 화소가 우측 화소에 비해 평균(root mean square) 화소 전압이 더 커져 밝게 된다.Referring to FIG. 6C, the gate signal delay is smaller and the kickback voltage Vkb becomes larger toward the
이상과 같이 화면 좌우의 휘도가 달라지고, 이에 따라 가로줄이 인식되는 문제가 발생한다. 이와 같은 문제는 게이트 본선(121)이 길어 게이트 신호지연이 크게 발생하는 대형 액정표시장치에서 더욱 심각해진다.As described above, there is a problem that the luminance of the left and right sides of the screen is changed and the horizontal line is recognized accordingly. Such a problem becomes more serious in a large-sized liquid crystal display device in which the gate
본 발명의 제1실시예에서는 이와 같이 게이트 지연 차이에 의한 문제를 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124) 사이에 저항부(163)를 형성시켜 해결한다.In the first embodiment of the present invention, the problem caused by the gate delay difference is solved by forming the
도 7 내지 도 9를 참조하여 저항부(163)에 대하여 설명한다.The
저항부(163)는 비표시영역에서 팬-아웃부(123)와 게이트 본선(121) 사이에 위치한다. 저항부(163)는 화소전극(161)과 동일한 층으로 이루어져 있으며, 팬-아웃부(123)와 연결되는 제1부분(163a), 게이트 본선(121)과 연결되는 제2부분(163b) 및 제1부분(163a)과 제2부분(163b) 사이에 위치하는 제3부분(163c)을 포함한다The
제1부분(163a)은 접촉구(154)를 통해 팬-아웃부(123)과 접촉하며, 제2부분(163b)는 접촉구(155)를 통해 게이트 본선(21)과 접촉한다. The
접촉구(153)에 의해 노출된 게이트 패드(124)는 화소전극(161)과 동일한 층으로 이루어진 접촉부재(162)가 덮고 있다.The
저항부(163)는 ITO, IZO 등으로 이루어지는데, 이들 물질은 게이트 본선(121)을 이루는 금속물질에 비하여 저항이 크다. 저항이 큰 저항부(163)에 의해 게이트 신호는 표시영역에 들어가기 전에 도 9와 같이 이미 지연이 발생된다. The
따라서 게이트 신호의 지연 변화 폭과 킥백전압(Vkb) 변화 폭이 감소한다. 또한 표시영역 좌우에서의 휘도 차이도 감소한다.Therefore, the delay variation width of the gate signal and the variation width of the kickback voltage (Vkb) decrease. The luminance difference between the right and left of the display area also decreases.
게이트 본선(121)의 총 저항은 통상 4000Ω 내지 7000Ω인데, 저항부(163)의 총저항은 게이트 본선(121)의 총 저항의 10% 내지 50%일 수 있다. 저항부(163)의 저항값은 저항부(163)의 두께, 폭 및 길이를 조절하여 변화시킬 수 있다. The total resistance of the gate
저항부(163)의 저항값은 게이트 지연 변화가 100% 내에서 변화하도록, 즉 표시영역 최우측 화소의 게이트 지연값이 표시영역 최좌측 화소의 게이트 지연값의 2배 이내가 되도록 정해지는 것이 바람직하다.It is preferable that the resistance value of the
한편 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124)의 거리는 다양한데, 이로 인해 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124) 사이의 저항이 달라져 휘도가 달라지는 문제가 있다.On the other hand, the distance between the gate
저항부(163)의 제3부분(163c)의 길이는 해당하는 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124)의 거리에 반비례하도록 마련되어 있다. 이에 의해 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124)의 거리 차이로 인한 휘도의 불균일이 감소된다.The length of the
실런트(400)는 팬-아웃부(123) 상에 위치하여, 저항부(163)는 실런트(400) 내에 위치한다. 저항부(163)가 외부에 노출되어 있지 않기 때문에 저항부(163)가 부식되는 문제가 발생하지 않는다.The
제조과정에서는 외부로부터 유입되는 정전기가 박막트랜지스터(T) 등을 손상하는 문제가 발생할 수 있다. 제1실시예에 따르면 게이트 패드(124)를 통해 유입된 정전기는 저항이 큰 저항부(163)에서 어느 정도 소멸되어, 정전기로 인한 문제가 감소한다.In the manufacturing process, a static electricity introduced from the outside may damage the thin film transistor T or the like. According to the first embodiment, the static electricity introduced through the
다른 실시예에서 저항부(163)는 화소전극(161)과 별도로, 게이트 본선(121)보다 저항이 높은 다른 물질로 이루어질 수 있다. 또 다른 실시예에서, 저항부(163)의 형태는 모두 동일하며, 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(124) 간의 거리 차이는 팬-아웃부(123)의 형태를 변경하여 해결할 수 있다. In another embodiment, the
이하에서는 휘도불균일을 조절하기 위하여 게이트 신호 지연을 조절한 이유에 대하여 설명한다.Hereinafter, the reason why the gate signal delay is adjusted to control the luminance unevenness will be described.
도 10은 표시영역에서의 게이트 신호 지연값에 따른 휘도 편차율을 나타내었다. 휘도편차율은 (표시영역 좌측의 휘도-표시영역 중앙부분의 휘도)/표시영역 중앙부분의 휘도*100으로서, 수치가 크면 휘도 차이가 큰 것을 나타낸다. 10 shows the luminance deviation rate according to the gate signal delay value in the display area. The luminance deviation rate (luminance at the left side of the display area - luminance at the center part of the display area) / luminance at the center part of the display area * 100.
도 10을 보면 게이트 신호 지연값이 약 43%증가(2.55㎲에서 3.67㎲)할 경우, 휘도편차율은 약 64%증가(30.6%에서 50.3%)한다. Referring to FIG. 10, when the gate signal delay value increases by about 43% (3.67 μs at 2.55 μs), the luminance deviation rate increases by about 64% (30.6% to 50.3%).
도 11은 킥백전압에 비례하는 Cp/(Clc+Cst+Cp)에 따른 휘도 편차율을 나타내었다. 도 11을 보면 Cp/(Clc+Cst+Cp)이 24%증가(0.037에서 0.046)할 경우, 휘도편차율은 약 26.4%(35.6%에서 45%)증가한다.FIG. 11 shows the luminance deviation rate according to Cp / (Clc + Cst + Cp) proportional to the kickback voltage. 11, when the Cp / (Clc + Cst + Cp) is increased by 24% (0.037 to 0.046), the luminance deviation rate increases by about 26.4% (35.6% to 45%).
이상 도 10 및 도 11로부터 휘도불균일을 개선하기 위해서는 게이트 신호 지연값을 조절하는 것이 효과적임을 알 수 있다.It can be seen from FIG. 10 and FIG. 11 that it is effective to adjust the gate signal delay value in order to improve the luminance unevenness.
게이트 신호 지연과 화소전압은 비표시영역에서의 저항, 즉 게이트 패드에서 게이트 본선까지의 저항에 의해 변화되는데 이를 도 12 및 도 13을 참조하여 설명한다. The gate signal delay and the pixel voltage are changed by the resistance in the non-display area, that is, the resistance from the gate pad to the gate main line, which will be described with reference to FIGS. 12 and 13. FIG.
도 12 및 도 13에서 비표시영역에서의 저항은 1/6kΩ, 1/3kΩ, 1/2kΩ, 2/3kΩ의 4가지 값을 가진다. 0kΩ으로 표시된 데이터는 저항부가 존재하지 않고, 게이트 본선과 게이트 패드가 일체로 형성된 경우이다.In FIGS. 12 and 13, the resistance in the non-display region has four values of 1/6 k ?, 1/3 k ?, 1/2 k ?, and 2/3 k ?. The data indicated by 0 k? Is the case where there is no resistance portion and the gate main line and the gate pad are formed integrally.
도 12를 보면 비표시영역의 저항이 커질수록, 게이트 신호 지연 값은 전체적으로 커짐을 알 수 있다. 한편 비표시영역 저항이 커질수록, 우측 게이트 신호 지연값/좌측 게이트 신호 지연값이 감소한다.12, it can be seen that the gate signal delay value increases as the resistance of the non-display region increases. On the other hand, as the non-display area resistance increases, the right gate signal delay value / left gate signal delay value decreases.
즉 0kΩ의 경우 우측 게이트 신호 지연값/좌측 게이트 신호 지연값은 6.53(4.18/0.64)인데 반해, 2/3kΩ의 경우 우측 게이트 신호 지연값/좌측 게이트 신호 지연값은 1.77(8.12/4.57)이다.That is, in the case of 0 kΩ, the right gate signal delay value / left gate signal delay value is 6.53 (4.18 / 0.64), whereas in case of 2/3 kΩ, the right gate signal delay value / left gate signal delay value is 1.77 (8.12 / 4.57).
도 13을 보면 비표시영역 저항이 커질수록, 화소전압은 전체적으로 작아짐을 알 수 있다. 한편 저항부 저항이 커질수록, 좌측 화소전압/우측 화소전압이 감소한다. 즉 0kΩ의 경우 좌측 화소전압/우측 화소전압은 1.028(3.3/3.21)인데 반해, 2/3kΩ의 경우 좌측 화소전압/우측 화소전압은 1.012(3.19/3.15)이다.As shown in FIG. 13, as the non-display area resistance increases, the pixel voltage decreases as a whole. On the other hand, the larger the resistance of the resistor, the lower the left pixel voltage / the right pixel voltage. That is, in the case of 0 kΩ, the left pixel voltage / the right pixel voltage is 1.028 (3.3 / 3.21), whereas in the case of 2/3 kΩ, the left pixel voltage / right pixel voltage is 1.012 (3.19 / 3.15).
도 12와 도 13으로부터 비표시영역 저항을 증가시키면 게이트 신호 지연과 화소전압의 좌측 표시 영역과 우측 표시 영역에서의 차이를 감소시킬 수 있음을 알 수 있다. 다만, 비표시영역 저항이 커지면 게이트 신호 전달이 어려워지므로, 비표시영역 저항은 게이트 본선(121)의 총 저항 등을 감안하여 결정되어야 한다.It can be seen from FIG. 12 and FIG. 13 that by increasing the non-display area resistance, the difference between the gate signal delay and the pixel display voltage in the left display area and the right display area can be reduced. However, when the non-display area resistance becomes large, the gate signal transfer becomes difficult. Therefore, the non-display area resistance should be determined in consideration of the total resistance of the gate
이하 도 14 및 도 15를 참조하여 제2실시예에 대하여 설명한다.The second embodiment will be described below with reference to Figs. 14 and 15. Fig.
제2실시예에 따르면 게이트 패드(164)와 팬-아웃부(165)는 저항부(163)와 일체로 형성되어 있으며, ITO 또는 IZO로 이루어진다. 저항부(163)는 게이트 본선(121)과 접촉구(156)를 통해 연결된다. 제2실시예에서는 게이트 패드(164)와 팬-아웃부(165)도 제1실시예의 저항부(163)와 같은 역할을 한다.According to the second embodiment, the
제1실시예와 같이 저항부(163)는 해당하는 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(164)의 거리에 반비례하도록 마련되어 있다. 이에 의해 게이트 본선(121)과 게이트 패드(164)의 거리 차이로 인한 휘도의 불균일이 감소된다The
다른 실시예에서는 저항부(163) 없이, 팬-아웃부(165) 만을 ITO 또는 IZO로 만들어 게이트 신호를 지연시킬 수 있다.In another embodiment, without the
도 16 내지 도 18을 참조하여 제3실시예를 설명한다.The third embodiment will be described with reference to Figs. 16 to 18. Fig.
도 16을 보면 박막트랜지스터(T)에 2개의 액정용량(CLC1, CLC2)이 연결되어 있다. 제1액정용량(CLC1)은 제1화소전극(PE1)과 공통전극(CE) 사이에 형성되며, 제1화소전극(PE1)은 박막트랜지스터(T)에 직접 연결되어 있다. 제2액정용량(CLC2)은 제2화소전극(PE2)와 공통전극(CE) 사이에 형성되며, 제2화소전극(PE2)는 결합 용량(CCP)을 거쳐서 간접적으로 박막트랜지스터(T)와 연결되어 있다. 16, two liquid crystal capacitors C LC1 and C LC2 are connected to the thin film transistor T. In FIG. The first liquid crystal capacitance C LC1 is formed between the first pixel electrode PE1 and the common electrode CE and the first pixel electrode PE1 is directly connected to the thin film transistor T. The second liquid crystal capacitance C LC2 is formed between the second pixel electrode PE2 and the common electrode CE and the second pixel electrode PE2 is indirectly connected to the thin film transistor T through the coupling capacitance C CP . .
여기서 제1화소전극(PE1)과 제2화소전극(PE2)은 서로 분리되어 있다. Here, the first pixel electrode PE1 and the second pixel electrode PE2 are separated from each other.
제3실시예에 따르면 시인성이 향상되는데 이를 도 17을 참조하여 설명한다.According to the third embodiment, visibility is improved, which will be described with reference to FIG.
제1화소 전극(PE1)에는 박막트랜지스터(T)를 통해 데이터 신호가 정상적으로 인가된다. 반면 제2화소 전극(PE2)은 박막트랜지스터(T)로부터 직접적으로 데이터 신호를 받지 못하고, 제2화소전극(PE2)과 박막트랜지스터(T) 사이의 절연막에 의해 발생하는 결합용량(CCP)으로 인하여 유도되는 전압에 의해 신호를 인가 받는다. The data signal is normally applied to the first pixel electrode PE1 through the thin film transistor T. [ On the other hand, the second pixel electrode PE2 does not receive a data signal directly from the thin film transistor T, and the coupling capacitance C CP generated by the insulating film between the second pixel electrode PE2 and the thin film transistor T The signal is applied by the induced voltage.
따라서 제2화소 전극(PE2)에는 제1화소 전극(PE1)에 비하여 약한 신호가 인 가되어, 제1화소전극(PE1)에 해당하는 화소영역의 휘도와 제2화소전극(PE2)에 해당하는 화소영역의 휘도가 다르게 된다. 제2화소전극(PE2)에 인가되는 전압은 제1화소전극(PE1)에 인가되는 전압의 50% 내지 90%이다.Therefore, a weaker signal is applied to the second pixel electrode PE2 than the first pixel electrode PE1, and the brightness of the pixel region corresponding to the first pixel electrode PE1 and the brightness of the pixel electrode PE2 corresponding to the second pixel electrode PE2 The luminance of the pixel region becomes different. The voltage applied to the second pixel electrode PE2 is 50% to 90% of the voltage applied to the first pixel electrode PE1.
이와 같이 한 화소 내에 감마 커브가 다른 복수의 영역이 존재하는 것이다.이에 의해 정면과 측면의 휘도 및 칼러가 서로 보상되어 측면시인성이 향상되는 것이다. In this manner, a plurality of regions having different gamma curves exist in one pixel. This improves the lateral visibility by compensating the luminance and the color of the front and the side.
도 18을 보면 화소전극(161)은 화소전극 분리패턴(167)에 의해 서로 분리된 제1화소전극(161a)과 제2화소전극(161b)을 포함한다. 제2화소전극(161b)은 사다리꼴이며, 3면이 제1화소전극(161a)으로 둘러싸여 있다. 제1화소전극(161a)과 제2화소전극(161b)에는 각각 화소전극 분리패턴(167)과 나란한 화소전극 절개패턴(166)이 형성되어 있다.Referring to FIG. 18, the
드레인 전극(143)은 제1화소전극(161a)과 연결되어 제1화소전극(161a)에 직접 전기신호를 인가하는 제1드레인 전극(143a)과 제2화소전극(161b) 하부로 연장되어 잇는 제2드레인 전극(143b)을 포함한다. 제2드레인 전극(143b)은 제2화소전극(161b)과 함께 결합용량(Ccp)을 형성한다. The
화소전극 분리패턴(167)과 화소전극 절개패턴(166)은 공통전극 절개패턴(252)과 함께 액정층(300)을 다수의 영역으로 분할한다.The pixel
한편, 유지전극선(125)은 화소전극(161)의 둘레를 따라 형성되어 있으며, 상하부의 유지전극선(125)은 접촉구(157)와 브릿지 전극(168)을 통해 서로 연결되어 있다.The sustain
도 19를 참조하여 본 발명의 제4실시예를 설명한다.A fourth embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to Fig.
화소전극(161)은 전체적으로 사각형 형상이며 데이터선(141)의 연장방향으로 길게 형성되어 있다. 화소전극(161)은 상하로 대칭형상을 가지고 있다.The
화소전극(161)은 화소전극 분리패턴(167)에 의해 서로 분리되어 있는 제1화소전극(161a)과 제2화소전극(161b)을 포함한다. 제1화소전극(161a)은 화소의 중앙부에 위치하며 꺽쇠형상을 하고 있다. 제2화소전극(161b)은 제1화소전극(161a)의 내부, 상부, 하부를 감싸고 있다. 제2화소전극(161b)은 제1화소전극(161a)에 비해 넓게 형성되어 있다.The
박막트랜지스터(T)는 제1화소전극(161a)에 연결되어 있는 제1박막트랜지스터(TFT1)과 제2화소전극(161b)에 연결되어 있는 제2박막트랜지스터(TFT2)를 포함한다.The thin film transistor T includes a first thin film transistor TFT1 connected to the
각 박막트랜지스터(TFT1, TFT2)의 드레인 전극(143)은 화소전극(161)과 중첩되어 저장용량(Cst)을 형성하는 역할을 하며, 저장용량은 드레인 전극(143)과 화소전극(161)의 중첩 면적에 비례한다. The
제4실시예에서는 독립된 박막트랜지스터(TFT1, TFT2)를 이용하여 각 화소전극(161a, 161b)에 서로 다른 화소전압을 인가할 수 있다. 제4실시예에서의 시인성 개선 원리는 제3실시예와 동일하며 반복 설명은 생략한다.In the fourth embodiment, different pixel voltages can be applied to the
이상 설명한 제3실시예와 제4실시예에서 비표시영역의 구성은 제1실시예 또는 제2실시예를 따른다.In the third and fourth embodiments described above, the structure of the non-display region follows the first embodiment or the second embodiment.
한편 제3실시예와 제4실시예에서는 화소전극(161)이 나누어져 있어서 액정용량(Clc)과 저장용량(Cst)이 작다. 이로 인해 킥백전압(Vkb)이 커져(식 1 참조) 휘도 차이가 더욱 문제된다. 따라서 제3실시예와 제4실시예의 경우에는 저항부를 이용한 게이트 신호 지연의 균일화가 더욱 필요하다.In the third and fourth embodiments, the
비록 본발명의 실시예가 도시되고 설명되었지만, 본발명이 속하는 기술분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 당업자라면 본발명의 원칙이나 정신에서 벗어나지 않으면서 본 실시예를 변형할 수 있음을 알 수 있을 것이다. 본발명의 범위는 첨부된 청구항과 그 균등물에 의해 정해질 것이다.Although the embodiments of the present invention have been shown and described, those skilled in the art will appreciate that various modifications, additions and substitutions are possible, without departing from the scope or spirit of this invention. The scope of the present invention shall be determined by the appended claims and their equivalents.
이상 설명한 바와 같이, 본 발명에 따르면, 게이트 신호 지연 차이로 인한 휘도불균일이 감소된 액정표시장치가 제공된다.INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY As described above, according to the present invention, a liquid crystal display device in which luminance unevenness due to a gate signal delay difference is reduced is provided.
Claims (20)
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007179002A JP5727120B2 (en) | 2006-08-25 | 2007-07-06 | Liquid crystal display |
| US11/843,980 US8089598B2 (en) | 2006-08-25 | 2007-08-23 | Liquid crystal display device having delay compensation |
| EP07016646A EP1892697B1 (en) | 2006-08-25 | 2007-08-24 | Liquid crystal display device having delay compensation |
| CN2007101475633A CN101131491B (en) | 2006-08-25 | 2007-08-27 | Liquid crystal display device having delay compensation |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060081056 | 2006-08-25 | ||
| KR20060081056 | 2006-08-25 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20080018773A KR20080018773A (en) | 2008-02-28 |
| KR101392160B1 true KR101392160B1 (en) | 2014-05-08 |
Family
ID=39128815
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020060124754A KR101392160B1 (en) | 2006-08-25 | 2006-12-08 | Liquid crystal display device |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101392160B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN101131491B (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11430826B2 (en) | 2019-12-20 | 2022-08-30 | Lg Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film transistor array substrate for digital x-ray detector device and digital x-ray detector device including the same |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN102213848B (en) * | 2010-04-09 | 2013-03-13 | 北京京东方光电科技有限公司 | Method and system for measuring transmissivity of liquid crystal display panel |
| JP6022805B2 (en) * | 2012-04-23 | 2016-11-09 | 株式会社ジャパンディスプレイ | Display device |
| CN106773381B (en) * | 2012-09-20 | 2020-06-09 | 上海中航光电子有限公司 | Anti-static display panel |
| CN103745707B (en) * | 2013-12-31 | 2015-11-11 | 深圳市华星光电技术有限公司 | Compensate the method for gate driver circuit signal wire resistance and the display panels of application the method |
| CN104166284B (en) * | 2014-08-27 | 2018-01-09 | 深圳市华星光电技术有限公司 | Liquid crystal display panel and its sector region |
| CN105388647B (en) * | 2015-12-15 | 2019-09-24 | 武汉华星光电技术有限公司 | Liquid crystal display panel is fanned out to Wiring structure and liquid crystal display panel |
| CN105789184B (en) * | 2016-04-14 | 2018-06-01 | 北京京东方显示技术有限公司 | Substrate and preparation method thereof, display device |
| CN105867041B (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2019-05-07 | 武汉华星光电技术有限公司 | A kind of array substrate and liquid crystal display |
| CN107610636B (en) | 2017-10-30 | 2021-02-02 | 武汉天马微电子有限公司 | Display panel and display device |
| CN108039142B (en) * | 2017-11-30 | 2021-11-30 | 武汉天马微电子有限公司 | Display panel, display screen and display device |
| CN109872669A (en) * | 2019-04-19 | 2019-06-11 | 京东方科技集团股份有限公司 | Array substrate, display master blank, array substrate preparation method and test method |
| CN111445831B (en) | 2020-04-24 | 2021-08-03 | 深圳市华星光电半导体显示技术有限公司 | Display panel |
| CN114333697B (en) * | 2021-12-30 | 2023-04-07 | 深圳市华星光电半导体显示技术有限公司 | Display device |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2947299B2 (en) | 1991-03-22 | 1999-09-13 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Matrix display device |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR980003731A (en) * | 1996-06-11 | 1998-03-30 | 김광호 | Electrostatic destruction protection device for display panel and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP4313733B2 (en) * | 2004-07-12 | 2009-08-12 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Engine cylinder determination device |
| TWI399598B (en) * | 2004-12-27 | 2013-06-21 | Samsung Display Co Ltd | Liquid crystal display |
-
2006
- 2006-12-08 KR KR1020060124754A patent/KR101392160B1/en active IP Right Grant
-
2007
- 2007-08-27 CN CN2007101475633A patent/CN101131491B/en active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2947299B2 (en) | 1991-03-22 | 1999-09-13 | 三菱電機株式会社 | Matrix display device |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11430826B2 (en) | 2019-12-20 | 2022-08-30 | Lg Display Co., Ltd. | Thin film transistor array substrate for digital x-ray detector device and digital x-ray detector device including the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN101131491A (en) | 2008-02-27 |
| CN101131491B (en) | 2012-06-20 |
| KR20080018773A (en) | 2008-02-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR101392160B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| JP5727120B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR101359915B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| US10453869B2 (en) | Display apparatus | |
| KR101820796B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR101348754B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR101833498B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR101991371B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR20080054228A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| US7903220B2 (en) | Liquid crystal display device and electronic apparatus | |
| KR20140100126A (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| JP5429776B2 (en) | LCD panel | |
| KR20090038685A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| JP5681269B2 (en) | LCD panel | |
| KR101282403B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR20080000458A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| US10564502B1 (en) | Display device | |
| KR101282402B1 (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| KR20130042242A (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR20060114921A (en) | Liquid crystal display | |
| KR20080022355A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| KR20060062908A (en) | Liquid crystal display panel | |
| KR20080011598A (en) | Liquid crystal display and manufacturing method of the same | |
| KR20080030877A (en) | Liquid crystal display device | |
| KR20080076196A (en) | Liquid crystal display device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| N231 | Notification of change of applicant | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20180403 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20190401 Year of fee payment: 6 |