KR101238232B1 - Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd - Google Patents
Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR101238232B1 KR101238232B1 KR1020110092319A KR20110092319A KR101238232B1 KR 101238232 B1 KR101238232 B1 KR 101238232B1 KR 1020110092319 A KR1020110092319 A KR 1020110092319A KR 20110092319 A KR20110092319 A KR 20110092319A KR 101238232 B1 KR101238232 B1 KR 101238232B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- ion implantation
- junction
- thin film
- frd
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 17
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 14
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 49
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 239000000872 buffer Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 26
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 22
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 21
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 16
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000038 ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 7
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910001385 heavy metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 230000001976 improved effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 3
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000012356 Product development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910001423 beryllium ion Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011065 in-situ storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007774 longterm Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004886 process control Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/872—Schottky diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Abstract
Description
본 발명은 고속으로 스위칭하는 고성능 FRD(Fast Recovery Diode) 소자 구조 및 그 제조 방법에 관한 것으로서, 더욱 상세하게는 고농도로 도핑된 p+-MHJ(Multiple Hetero-Junction) 구조로 저저항 오믹접합을 위한 p+ 애노드 층을 형성하여 쇼트키 접합을 위한 p- 층과 함께 사용하는 FRD 구조와 이를 제작하는 방법에 관한 것이다.The present invention relates to a high performance fast recovery diode (FRD) device structure and a method for manufacturing the same, and more particularly to a low resistance ohmic junction with a highly doped p + -MHJ (Multiple Hetero-Junction) structure. FRD structure for forming a p + anode layer for use with a p − layer for Schottky junctions and a method of fabricating the same.
FRD 소자는 고속으로 동작하는 스위칭 회로에서 회생 다이오드(free wheeling diode), 완충기(snubber), 클램프 다이오드(clamp diode) 등으로 사용되어 왔다. 그런데 최근 전력제어 주요 반도체 소자인 IGBT(Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor), GTO(Gate Turn-Off Thyristor), Power MOSFET의 동작속도가 더욱 빨라지면서 스위칭하는 전류제어 기울기(dI/dt)가 ~100 A/us급으로 급속하게 통제되게 되었고, 이에 따라 전력제어 스위칭시 과전압(over-voltage)과 전력손실과 같은 문제가 심각해졌다. 따라서 요즘의 FRD는 회복 동작에 있어서 더욱 작은 역회복전류(Irr)와 작은 전력손실에 대한 대책이 필요하게 되었다. 따라서 최근 FRD 기술은 과전압과 발진(oscillation)이 적은 연성 회복(soft recovery)동작특성을 개선하는데 중점을 두고 있다.FRD devices have been used as free wheeling diodes, buffers, clamp diodes, and the like in switching circuits operating at high speeds. However, the current control slope (dI / dt) of switching to the faster operation speed of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT), Gate Turn-Off Thyristor (GTO), and Power MOSFET, which are major power control semiconductor devices, is ~ 100 A / us. It has been rapidly controlled, and problems such as over-voltage and power loss in switching power control have become serious. As a result, the FRD needs to deal with a smaller reverse recovery current (Irr) and a smaller power loss in the recovery operation. Therefore, the recent FRD technology is focused on improving the soft recovery operation characteristics with less overvoltage and oscillation.
종래에는 전력제어의 정류기(rectifier)로서 일반적인 PIN 다이오드가 주로 사용되었으나 과전압의 문제로 인하여 스너버(snubber) 회로가 함께 사용되어야 했다. 그런데 스너버는 회로가 복잡하고 고가이므로 스너버 없이 이용할 수 있는 PIN 다이오드 소자를 개발하게 되었으며, 이의 성능을 높이기 위한 여러 가지 반도체 기술이 적용되어 왔다.Conventionally, a general PIN diode is mainly used as a rectifier for power control, but a snubber circuit has to be used together due to an overvoltage problem. However, snubber has developed a PIN diode device that can be used without a snubber because the circuit is complicated and expensive, and various semiconductor technologies have been applied to increase its performance.
최근의 반도체 기술이 발전하여 실리콘반도체가 가지는 고속동작과 내전압 특성의 한계를 동시에 확대하는 방법이 매우 매력적이라 하겠다. 근래에 FRD 소자에 대한 제품개발이 용이해졌음에도 불구하고 동작속도, 소비전력, 과전압, 신뢰성, 전력구동 측면에서 FRD 소자의 성능은 아직도 많은 발전이 요구된다. 한편으로 고내열 고내전압 특성을 갖는 SiC나 GaN과 같은 넓은 띠간격(wide bandgap) 반도체를 이용한 고전력 고전압 소자에 대한 기술이 주목되고 있다. 그러나 아직도 소자의 장기적 신뢰성 측면에서 실리콘을 위주로 하는 전력반도체 소자가 상당히 오랜 기간 핵심부품을 공급할 것으로 예상된다.Recent advances in semiconductor technology have made it very attractive to simultaneously extend the limits of high-speed operation and withstand voltage characteristics of silicon semiconductors. Despite the ease of product development for FRD devices in recent years, the performance of FRD devices still needs to be improved in terms of operation speed, power consumption, overvoltage, reliability, and power driving. Meanwhile, a technique for high power high voltage devices using wide bandgap semiconductors, such as SiC or GaN, having high heat resistance and high withstand voltage characteristics, has been attracting attention. However, in terms of device long-term reliability, silicon-based power semiconductor devices are expected to supply key components for a very long time.
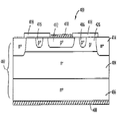
도 1a 내지 도 1f는 종래의 실리콘 반도체를 이용한 FRD에 대한 특허와 논문으로 주요 관련 기술의 현황을 보여준다. 1A to 1F show the status of major related technologies with patents and papers on FRDs using conventional silicon semiconductors.
도 1a는 특허문헌 1에서 제시한 FRD 구조로서, Pt를 확산하여 이용하는 경우 표면에 Pt가 고농도로 축적되어 n-type이 p-type으로 변형되어 누설전류가 Pt의 농도와 n-type의 농도에 의존하면서 발생하는 문제를 해결하기 위하여 격리를 강화한 구조이다. 그러나 p-와 n-(n+)의 계면이 증가하여 회복정전용량(Qr)과 역방향 회복시간(trr)의 성능저하가 우려된다.FIG. 1A is a FRD structure proposed in
도 1b는 특허문헌 2에서 제시한 반도체소자의 다이오드로서, 물결모양의 p+n- 접합이 형성되어 양극으로 주입되는 전자의 양을 증가시키고 역전류의 감소를 느리게 조절하여 내압특성을 향상시킨다. 그러나 기본적으로 n-p-n 접합구조로 부성 저항을 유발시키는 동작과 p- 금속접합의 고저항성 특성이 발생할 수 있다. FIG. 1B is a diode of the semiconductor device disclosed in
도 1c는 특허문헌 3에서 제시한 MPS(Merged-PIN-Schottky) 구조의 FRD로서, PIN과 쇼트키(Schottky) 접합의 장점을 조합하여 순방향 전압강하(Vf)과 역방향 회복시간(trr)을 감소시킨다. 그러나 쇼트키 접합에 의해 누설전류가 증가하고, 감소된 오믹접합으로 인하여 전류밀도가 높아지면 Vf가 오히려 증가하는 문제를 보인다.FIG. 1C is a FRD of MPS (Merged-PIN-Schottky) structure proposed in Patent Document 3, and combines the advantages of PIN and Schottky junctions to reduce forward voltage drop (Vf) and reverse recovery time (trr). Let's do it. However, when the leakage current increases due to the Schottky junction and the current density increases due to the reduced ohmic junction, Vf increases.
도 1d는 비특허문헌 1에서 제시한 MPS 소자구조의 FRD로서, 순방향 전류-전압 특성을 보여준다. 저전류 구역에서 쇼트키 접합에 의해 Vf가 작지만, 고전류 구역에서는 오믹저항이 커서 오히려 Vf가 커지는 특징을 보이며, 마찬가지로 쇼트키 접합 면적이 증가하면 이러한 현상은 더욱 심각해진다. 따라서 MPS 소자구조에 있어서 소자특성들을 트레이드-오프(trade-off)하는 기술적 중요성과 반도체 기판의 물리적 특성에 따른 한계가 아직도 남아 있음을 알 수 있다.FIG. 1D is a FRD of the MPS device structure shown in
도 1e는 비특허문헌 2에서 제시한 FRD로서, 순방향 전압강하(Vf)와 역방향 회복 손실에너지(Err)의 상충관계를 개선시키기 위해서 양극의 두께와 농도를 조절하고, 음극에 다결정 실리콘박막을 적용한 구조에 대한 연구결과를 제시하였다. 또한 LLP(Local Life Time control with Poly-Si), TWP(Thin Wafer Processing), BBDS(Broad p- buffer, Broad n- buffer)의 기술로 중금속 주입이나 전자선 조사가 필요 없는 FRD 소자구조 및 공정을 제시하였다. 그러나, TWP을 하는 소자의 구조는 공정이 복밥하며 수율이 낮아 생산비가 많이 드는 고가의 공정이다.FIG. 1E is a FRD proposed in
도 1f는 비특허문헌 3에서 제시한 FRD로서, p- 금속접합, p- 쇼트키 접합을 사용한 소자의 구조를 보인다. Vf와 역방향 회복특성 사이에 상충하는 관계를 개선하기 위하여 가드링과 HiRC 영역을 최적화하여 6.5 kV 초연성 고속 FRD 소자를 제시하였다. 즉 고전압으로 증가하면서 가드링에 대한 최적화된 설계로 연성 회복특성을 개선할 수 있음을 제시하고 있다.FIG. 1F shows the structure of a device using a p - metal junction and a p - Schottky junction as the FRD presented in Non-Patent Document 3. FIG. In order to improve the conflicting relationship between Vf and reverse recovery characteristics, a 6.5 kV super-ductile high-speed FRD device was proposed by optimizing the guard ring and HiRC region. In other words, it is suggested that the ductile recovery characteristics can be improved by the optimized design of the guard ring while increasing to high voltage.
한편, 종래에 널리 사용하던 단순구조의 정류기 소자는 역방향 회복시간(trr)이 0.1~1 us로 크고, EMI(ElectroMagnetic Interference)에 의한 잡음의 발생이 심각하다. 따라서 대체로 200V 이하의 비교적 저전압에는 역방향 회복시간(trr)<0.1us로 동작하는 SBD(Schottky Barrier Diode)를 주로 사용하였다. 또한 고전압인 150~ 수 kV에는 저력제어 성능이 우수한 FRD를 사용하여 전력손실과 EMI 측면을 강화하여 활용하고 있다. 특히 기존의 PIN이나 MPS 소자구조에 중금속(Pt, Au) 확산이나 전자선 조사와 같은 기술로 FRD 소자의 연성 회복 특성을 개선하였다. 그러나 최근 전력소자의 동작주파수가 1 KHz ~ 100 MHz로 높아지고, 구동전압도 수 kV대에 대한 요구가 증대하고 있어서 종래의 기술과 비교하여 더욱 고성능의 RFD에 대한 기술개발이 필요하게 되었다.Meanwhile, the rectifier element having a simple structure widely used in the related art has a large reverse recovery time (trr) of 0.1 to 1 us and seriously generates noise due to electromagnetic interference (EMI). Therefore, SBD (Schottky Barrier Diode) which operates with reverse recovery time (trr) <0.1us is mainly used for relatively low voltage below 200V. In addition, power loss and EMI are strengthened by using FRD with high power control performance at high voltage of 150 ~ several kV. In particular, the ductility recovery characteristics of FRD devices have been improved by technologies such as diffusion of heavy metals (Pt, Au) and electron beam irradiation into existing PIN or MPS device structures. However, in recent years, the operating frequency of power devices is increased from 1 KHz to 100 MHz, and the driving voltage is also increasing in demand for several kV bands, and thus, technology development for a higher performance RFD is required compared to the conventional technology.
반도체 소자는 성능지수 중 항복전압x동작속도가 대체로 일정한 값을 유지한다는 한계성을 가지고 동작한다. 즉, 구동전압을 높이기 위하여 항복전압을 높이면 동작속도가 감소하여 구동전압과 동작속도를 트레이드-오프(trade-off)하면서 사용하게 된다. 이러한 물리적 한계를 극복하기 위해서는 소자의 구조를 변경하거나 특성이 상이한 물질을 소재로 도입하여 사용하는 방법을 강구해야 한다. The semiconductor device operates with a limitation that the breakdown voltage x operating speed of the figure of merit remains substantially constant. In other words, when the breakdown voltage is increased to increase the driving voltage, the operating speed decreases, and the driving voltage and the operating speed are used while trade-off. In order to overcome these physical limitations, it is necessary to find a method of changing the structure of the device or introducing and using materials having different properties as materials.
위에서 살펴본 바와 같이 종래의 기술들은 대부분의 접합계면이 불순물 도판트(dopant)의 주입과 확산 공정을 이용하여 제조되며, 이온 주입 및 확산 공정을 통해 형성된 접합의 위치와 농도에 대한 재현성과 균일성이 불량하다. 대부분 실리콘 반도체 기판의 물리적 특성과 연계된 Vf와 trr의 상충 한계 내에서 소자를 제작할 수 있다. 따라서 종래의 방법으로는 FRD 소자의 연성 회복 특성을 월등하게 개선하는데 한계가 있다.As described above, the conventional techniques are that most of the junction interface is manufactured by the implantation and diffusion process of impurity dopant, and the reproducibility and uniformity of the position and concentration of the junction formed through the ion implantation and diffusion process Poor The device can be fabricated within the tradeoffs of Vf and trr, which are mostly associated with the physical properties of silicon semiconductor substrates. Therefore, the conventional method has a limit to significantly improve the ductility recovery characteristics of the FRD device.
상기와 같은 문제점을 해결하고자 본 발명은 FRD의 항복전압과 동작속도의 곱이 일정하게 유지된다는 물리적 한계를 극복하기 위하여 고유한 소자구조와 불순물 도핑층을 이용하는 FRD 구조와 제조방법을 제공하고자 한다.In order to solve the above problems, the present invention is to provide a FRD structure and a manufacturing method using a unique device structure and an impurity doped layer in order to overcome the physical limitation that the product of the breakdown voltage and the operating speed of the FRD is kept constant.
상기의 해결하고자 하는 과제를 위한 본 발명에 따른 MHJ(Multiple Hetero-Junction)-FRD 소자 구조는, 제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층보다 고농도의 반도체 기판; 상기 반도체 기판의 상부에 제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층; 상기 완충층의 상부에 형성된 진성의 베이스층; 상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 소정의 배치간격으로 형성한 제1이온주입층; 상기 제1이온주입층을 깊이 방향으로 일부 식각하고, 식각된 부분에 충진되는 제2도전형의 상기 제1이온주입층보다 고농도의 다이종 접합(Multiple Hetero-Junction) 박막층; 상기 다이종 접합 박막층 사이는 제2도전형의 불순물로 이온주입하여 확산시킨 제2이온주입층; 및 상기 다이종 접합 박막층 및 제2이온주입층 상부에 형성되는 금속층을 포함한 구조로 형성되어,According to an aspect of the present invention, there is provided a MHJ (Multiple Hetero-Junction) -FRD device structure including a semiconductor substrate having a higher concentration than a buffer layer doped with a first conductive impurity; A buffer layer doped with a first conductivity type impurity on the semiconductor substrate; An intrinsic base layer formed on the buffer layer; A first ion implantation layer formed by implanting and diffusing a second conductive impurity into the base layer at a predetermined batch interval; A portion of the first ion implantation layer partially etched in the depth direction, and having a higher concentration of a hetero-junction thin film layer than the first ion implantation layer of the second conductivity type filled in the etched portion; A second ion implantation layer between the die-type junction thin film layer and ion implanted and diffused with impurities of a second conductivity type; And a metal layer formed on the die-type junction thin film layer and the second ion implantation layer.
상기 상기 반도체 기판과 완충층은 제1접합부를 형성하고, 상기 완충층과 베이스층은 제2접합부를 형성하고, 상기 베이스층과 제2이온주입층은 제3접합부를 형성하고, 상기 베이스층과 제1이온주입층은 제4접합부를 형성하고, 상기 금속층은 상기 다이종 접합 박막층과는 저항성 접촉을 형성하고 상기 제2이온주입층과는 쇼트키(Schottky) 접합을 형성하는 것을 특징으로 한다.The semiconductor substrate and the buffer layer form a first junction, the buffer layer and the base layer form a second junction, the base layer and the second ion implantation layer form a third junction, and the base layer and the first The ion implantation layer forms a fourth junction, and the metal layer forms an ohmic contact with the die-type junction thin film layer and forms a Schottky junction with the second ion implantation layer.
본 발명의 일시 예로서, 완충층은 상기 제1접합부로부터 고농도에서 저농도로 경사 기울기 도핑(gradient slope doping)하고, 다이종 접합 박막층은 Si1-xGex(0<x<1)층으로 형성된 것을 특징으로 한다.As a temporary example of the present invention, the buffer layer is gradient slope doping from high concentration to low concentration from the first junction, and the die-type bonded thin film layer is formed of a Si 1-x Ge x (0 <x <1) layer. It features.
본 발명의 다른 일시 예로서, FRD(Fast Recovery Diode) 소자의 제조방법은,As another example of the present invention, a manufacturing method of a fast recovery diode (FRD) device,
제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층보다 고농도의 반도체 기판을 준비하는 단계;
상기 반도체 기판의 상부에 제1도전형 불순물로 상기 반도체 기판의 상부로부터 고농도에서 저농도로 경사 기울기를 도핑(gradient doping)된 완충층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 완충층의 상부에 진성의 베이스층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 베이스층 상부에 산화막을 증착하고 포토리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 소정의 배치간격으로 이온주입할 영역을 형성한 다음, 상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 제1이온주입층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 제1이온주입층을 깊이 방향으로 일부 식각하고, 식각된 부분에 제2도전형의 상기 제1이온주입층보다 고농도의 다이종 접합(Muti-Hetero Junction) 박막층을 충진하는 단계;
상기 산화막을 제거하고 다시 산화막을 전면에 증착하고 제2이온주입층을 형성할 영역을 포토리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 형성하고,상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 상기 제2이온주입층을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 다이종 접합 박막층 및 제2이온주입층 상부에 금속층을 형성하는 단계를 포함한다. Preparing a semiconductor substrate having a higher concentration than a buffer layer doped with a first conductive impurity;
Forming a buffer layer doped with a gradient from a high concentration to a low concentration from an upper portion of the semiconductor substrate with a first conductivity type impurity on the semiconductor substrate;
Forming an intrinsic base layer on top of the buffer layer;
After depositing an oxide film on the base layer and forming an ion implantation region at a predetermined interval by photolithography and etching, ion implantation and diffusion of the second conductive impurity into the base layer is performed to form a first ion implantation layer. Forming a;
Partially etching the first ion implantation layer in a depth direction, and filling the etched portion with a higher concentration of a Muti-Hetero Junction thin film layer than the first ion implantation layer of the second conductivity type;
The oxide layer is removed, the oxide layer is deposited on the entire surface, and a region for forming the second ion implantation layer is formed through photolithography and etching, and ion implanted and diffused into the base layer with a second conductive impurity to form the second ion implantation layer. Forming an ion implantation layer; And
Forming a metal layer on the die-type junction thin film layer and the second ion implantation layer.
본 발명의 일 실시 예로서, 다이종 접합 박막층은 Si1-xGex(0<x<1) 박막층을 RPCVD(Reduced Pressure CVD)나 UHVCVD(Utra-High Vacuum CVD)의 방법으로 800 oC 이하의 저온에서 선택적으로 에피택셜(epitaixl) 증착하는 것을 특징으로 한다.In one embodiment of the present invention, the die-bonded thin film layer is a Si 1-x Ge x (0 <x <1) thin film layer of less than 800 ° C by the method of Reduced Pressure CVD (RPCVD) or Ultra-High Vacuum CVD (UHVCVD) Selective epitaxial deposition (epitaixl) at a low temperature of.
본 발명에 따른 고농도로 도핑된 MHJ 접합을 이용한 FRD는 종래의 PIN이나 MPS의 소자구조와 비교하여 더욱 순방향 전압강하(Vf)와 역방향 회복시간(trr)을 감소시킬 수 있는 구조를 제공한다. 즉, MHJ의 특징을 이용하여 n- 층에 소수운반자에 의한 전하의 축적을 감소시키고, 스위치 오프(switch-off)시 소수운반자가 빠르게 소멸되도록 한다. 이로 인하여 연성 회복이 일어나 발진, EMI 유발, 전력손실을 격감시킨다. FRD using a heavily doped MHJ junction according to the present invention provides a structure that can further reduce the forward voltage drop (Vf) and reverse recovery time (trr) compared to the conventional PIN or MPS device structure. In other words, by using the characteristics of the MHJ to reduce the accumulation of charge by the minority carriers in the n - layer, and to allow the minority carriers to quickly disappear when switched off (switch-off). This results in ductility recovery, drastically reducing oscillations, EMI induction, and power losses.
본 발명에 따른 FRD는 필터나 SMPS와 같은 회로에 사용되는 경우에 스너버 회로를 사용할 필요가 없고, 소형화 및 저가격화를 이룰 수 있다. 근래에 활용이 증대하고 있는 전기자동차, 태양전지, LED 조명회로의 전력구동장치에서 전력소모와 EMI를 감소시킬 수 있음은 물론이고 친환경 및 고효율화에 대한 효과를 높일 수 있다.FRD according to the present invention does not need to use a snubber circuit when used in a circuit such as a filter or an SMPS, and can achieve miniaturization and low cost. It is possible to reduce power consumption and EMI, as well as increase the effect on environment-friendliness and efficiency in electric vehicle, solar cell, and LED driving circuits.
통상의 FRD 소자의 경우 짧고 분명한(snappy) 동작으로 인하여 50~100 kHz의 주파수 구간에서 EMI 강도가 70 dB V/m 정도로 높지만, 본 발명에 따라 연성 회복 특성을 개선함으로써 < 60 dB V/m 이하로 감소시켜 표준화 규격을 만족시킬 수 있다.In the case of conventional FRD devices, the EMI intensity is high as 70 dB V / m in the frequency range of 50 to 100 kHz due to the short and snappy operation, but it is <60 dB V / m or less by improving the ductility recovery characteristics according to the present invention. It can be reduced to meet the standard specification.
도 1a 내지 도 1f는 종래기술에 의한 FRD 소자의 단면도 및 특성 그래프이다.
도 2a 내지 도 2j는 본 발명의 소자구조와 제조공정에 따른 FRD의 제조공정 단면도이다.
도 3a와 도 3b는 종래기술과 본 발명의 전기적 특성을 비교한 특성 그래프이다.1A to 1F are cross-sectional views and characteristic graphs of a conventional FRD device.
2A to 2J are cross-sectional views of a manufacturing process of the FRD according to the device structure and manufacturing process of the present invention.
3a and 3b is a characteristic graph comparing the electrical characteristics of the prior art and the present invention.
이하 첨부된 도면을 참조하여 본 발명이 속하는 기술분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 자가 본 발명을 용이하게 실시할 수 있는 바람직한 실시 예를 상세히 설명한다. 다만, 본 발명의 바람직한 실시 예에 대한 동작 원리를 상세하게 설명함에 있어 관련된 공지 기능 또는 구성에 대한 구체적인 설명이 본 발명의 요지를 불필요하게 흐릴 수 있다고 판단되는 경우에는 그 상세한 설명을 생략한다.DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. However, in describing in detail the operating principle of the preferred embodiment of the present invention, if it is determined that the detailed description of the related known function or configuration may unnecessarily obscure the subject matter of the present invention, the detailed description thereof will be omitted.
또한, 도면 전체에 걸쳐 유사한 기능 및 작용을 하는 부분에 대해서는 동일한 도면 부호를 사용한다.The same reference numerals are used for portions having similar functions and functions throughout the drawings.
도 2a 내지 도 2j는 본 발명의 실시 예에 따른 MHJ(Multiple Hetero-Junction)-FRD(Fast Recovery Diode)의 제조 방법을 나타낸 공정 단면도이다.2A to 2J are cross-sectional views illustrating a method of manufacturing a multiple hetero-junction (MHJ) -fast recovery diode (FRD) according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2a에서 n+ 반도체 기판(201)에 n형 완충층(202)을 에피성장하고, 이어서 진성(intrinsic) 수준의 n- 베이스층(203)을 에피성장한다. 상기 n형 완충층(202)은 ~1020 cm-3의 고농도에서 ~1014 cm-3의 저농도로 변화하면서 원위치(in-situ) 도핑으로 제어한다. 상기 n형 완충층(202)에서 불순물 농도의 프로화일은 양극에서 주입되는 소수운반자(정공) 농도분포를 제어하는데 중요하다. 그리고 스위치-오프(switch-off)시 빠르게 소수운반자를 상부의 p+측으로 이동시켜 소멸되도록 한다. 상기에서 n+ 반도체 기판(201)과 n형 완충층(202) 사이에 제1접합부(301)가 형성되며, 이어서 n형 완충층(202)과 n- 베이스층(203) 사이에 제2접합부(302)가 형성된다.In FIG. 2A, the n-
도 2b에서는 n- 베이스층(203) 상부에 산화막(205)을 증착하고, 포토리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 이온주입할 영역(206)을 형성한 다음 p층을 위한 이온주입을 한다. 이온주입시 물리적 손상을 줄이고 열처리를 위하여 산화막(205)을 증착하기 전에 질화막과 같은 보호막(205-1)을 먼저 증착할 수 있다. p형 이온주입층(204)은 보론(B)을 30~200 keV의 에너지로 주입한다. 그림에서 FRD가 형성될 부분은 활성(active) 영역이고 필드(field) 영역은 가드 링(guard ring)이 형성된다.In FIG. 2B, an
도 2c에서는 이온주입된 p형 이온주입층(204)의 불순물을 확산하여 확산층(205)을 형성하면 p-n- 접합(304)을 형성된다. 기판의 온도를 800~1100 oC에서 열처리하면 불순물의 활성화 및 확산이 발생하고, 이후에 농도가 1018 cm- 3이상으로 접합이 형성되도록 제어한다. 상기 n- 베이스층(203)과 p 형의 이온주입(204)층 사이에 제4접합부(304)가 형성된다.In FIG. 2C, when the impurity of the ion implanted p-type
도 2d에서는 리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 p+층를 형성할 부분의 질화막(205-1)을 제거한다.In FIG. 2D, the nitride layer 205-1 of the portion where the p + layer is to be formed is removed by lithography and etching.
도 2e에서는 오픈된 질화막(208)을 통하여 p형 확산층(207)을 깊이 방향으로 일부 식각한다. 실리콘 기판의 식각은 건식식각을 이용하는 비등방형으로 하지만, 아래의 믿바닥 부분의 식각면(209)은 등방성으로 제어하여 고전압에서 전계가 균일하게 분포되도록 한다. 국부적으로 전계가 집속되지 않도록 식각계면의 프로화일을 제어하는 것은 불순물의 농도분포에도 직접적으로 영향을 미치게 된다.In FIG. 2E, the p-
도 2f에서는 아주 고농도의 p+형 다이종 접합(MHJ) 박막(210)을 증착한다. 상기 다이종 접합 박막층(210)은 다결정 또는 단결정으로 증착되며, p형 이온주입층과의 사이에 고농도로 도핑된 p+ MHJ(305)을 형성한다. p+ MHJ 접합의 예로서 실리콘 반도체 기판을 이용하는 경우 Si1-xGex(0<x<1)를 이용한다. SiGe층은 보론(B)을 고농도로 일부 구간에 집중시켜 p+층을 국부적으로 형성하는데 매우 유용하다. 그리고 SiGe 층의 선택적 에피성장은 패턴의 형태와 밀도에 따라 영향을 받게 되므로 그 배치가 MHJ 소자구조의 형태에 적합하게 반영되도록 한다. MHJ의 폭은 활성(active) 영역의 중앙은 1~3um이며, 가장자리 영역에는 3~5um으로 조절한다. MHJ의 배치 개수는 활성영역의 면적에 의해 비례하며 순방향 전압강하(Vf)와 역방향 누설전류(Ir)를 트레이드-오프(trade-off)하는 수준으로 결정된다. 반도체 기판의 온도가 800 oC 이하의 비교적 저온에서 MHJ 접합이 선택적으로 증착되므로, 제1접합계면(301)과 제2접합계면(302), 제3접합계면(303)에서 불순물의 확산이 제한되므로 MHJ-FRD 소자특성의 균일성과 재현성이 높게 유지된다. In FIG. 2F a very high concentration of p + type die species junction (MHJ)
SiGe 박막은 RPCVD(Reduced Pressure CVD)나 UHVCVD(Utra-High Vacuum CVD)의 방식으로 증착할 수 있다. 이용하는 반응가스로는 SiH4, HCl, SiCH6, DCS, GeH4가 있으며 p형 선택적 박막의 증착에는 B2H6 가스를 도핑하여 1018~1019 cm-3의 고농도로 B를 주입한다.The SiGe thin film may be deposited by reduced pressure CVD (RPCVD) or ultra-high vacuum CVD (UHVCVD). Reaction gases used are SiH 4 , HCl, SiCH 6 , DCS, GeH 4 , and the deposition of p-type selective thin film is doped with B 2 H 6 gas to inject B at a high concentration of 10 18 to 10 19 cm -3 .
도 2g에서는 p- 이온주입을 위해 기존에 형성된 질화막(205-1)과 산화막(205)을 제거하고 다시 질화막(225-1)과 산화막(225)을 증착하고 포토리소그래피 및 산화막의 식각으로 이온주입창(220)을 형성한다. In FIG. 2G, the nitride film 205-1 and the
이온주입창(220)을 통하여 B과 같은 p형 불순물의 이온주입을 30~100 keV의 에너지로 실행하여 p- 형의 이온주입층(211)을 형성한다. 상기 p- 형 이온주입층의 두께와 불순물 농도는 n- 캐소드 측으로 주입되는 소수운반자(정공)의 농도를 조절할 뿐만 아니라 상부의 금속과의 Schottky 접합 특성을 결정하게 되므로 매우 중요하여 정밀하게 조절되어야 한다. P - type
도 2h에서는 p- 형 이온주입층(211)을 열처리 확산을 통해 확산층(212)을 형성하면 n- 형의 베이스층과 제3접합계면(303)이 형성된다. 소수운반자의 수명을 제어하기 위해 통상적으로 알려진 방식으로 중금속 확산, He 이온주입, 전자선 조사를 추가적으로 할 수 있다. 중금속(Au, Pt)의 경우 약 1 nm 두께의 박막을 웨이퍼 뒷면에 증착하고 열처리하여 확산시켜 사용한다. He은 국부적인 영역에 집중적으로 소수운반자의 수명을 줄이는 유용하다. 전자선조사는 1.5~12 MeV로 주입하며, 웨이퍼의 전체에 균일하게 조사된다. 이렇게 소수운반자의 재결합센터를 인위적으로 주입함으로써 역방향 회복시간(trr)을 격감시키게 된다.In FIG. 2H, when the
도 2i에서는 산화막(225)과 질화막(225-1)을 제거하고 다시 산화막(235)을 전면에 형성시키고 활성영역을 식각하여 개방(213)한다.In FIG. 2I, the
도 2j에서는 개방된 금속접촉창(213)에 금속박막(214)을 증착하여 양극을 형성하여 금속-반도체 접합을 형성한다. p- 층 위에는 쇼트키접합이 형성되고, p+-MHJ층 위에는 저항이 작은 오믹접합이 형성된다. 또한 잡음과 누설전류에 의한 파괴를 방지하기 위해 기판 내부 및 산화막 위에 가드 링(guard ring)을 형성한다. 기판 내부는 p이온주입층에 형성된 전도층으로 형성하고, 산화막 위는 금속 박막에의 한 가드 링(215)을 설치한다.In FIG. 2J, a metal
도 3a에서 여러 종류의 FRD 소자에 대한 순방향 전기적 특성을 비교하여 소자구조에 의한 효과를 확인할 수 있다. A(PIN), B(MPS), C(MHJ)의 세 종류에 대한 특성을 비교하면, A는 일반적인 PIN 구조의 다이오드로서 저전류 영역에서 전압이 높다. B는 MPS 구조에서 Schottky접합으로 인하여 고전류 영역에서 온전압(Von)이 매우 높아진다. C는 MHJ 구조로서 MPS의 단점을 보완하여 저전류와 고전류 동작에 있어서 Von을 최소화하는 저저항 오믹접합의 효과를 보여준다.In FIG. 3A, the effect of the device structure may be confirmed by comparing forward electrical characteristics of various types of FRD devices. Comparing the characteristics of the three types A (PIN), B (MPS) and C (MHJ), A is a general PIN structure diode and has a high voltage in the low current region. B has very high on voltage (Von) in high current region due to Schottky junction in MPS structure. C is an MHJ structure that compensates for the shortcomings of MPS and shows the effect of a low resistance ohmic junction that minimizes Von in low current and high current operation.
도 3b는 turn-off시 시간에 대한 전류흐름의 상태를 확인할 수 있다. A(PIN), B(MPS), C(MHJ)의 세 종류에 대한 특성을 비교하면, A는 일반적인 PIN 구조의 다이오드로서 강성 회복과 링(ringing) 발생의 원인이 되는 발진을 볼 수 있다. B는 MPS 구조에서 연성 회복을 보인다. C는 MHJ 구조로서 MPS의 단점을 보완하여 소수운반자의 수명을 더욱 감소시키는 개선된 효과를 보여준다.Figure 3b can confirm the state of the current flow with time at turn-off. Comparing the characteristics of three types, A (PIN), B (MPS), and C (MHJ), A is a general PIN structure diode, and it can be seen that oscillation causes stiffness recovery and ringing. B shows a soft recovery in the MPS structure. C is an MHJ structure that compensates for the shortcomings of MPS and shows an improved effect of further reducing the life of minority carriers.
상술된 바와 같이 제1접합계면, 제2접합계면, 제3접합계면, 제4접합계면과 더불어 MHJ 접합에 금속접합을 연결하여 본 발명의 고성능 FRD소자가 완성된다. 도 2a에서 도 2j의 공정과정을 통하여 본 발명에 대한 FRD를 제조하는 공정단계는 매우 간단하다. 공정단계가 명료하고 마스크의 숫자도 적으므로 공정제어가 간편하고 정확하여 제품의 양산성과 신뢰성이 우수하다.As described above, the high-performance FRD device of the present invention is completed by connecting a metal junction to the MHJ junction together with the first junction interface, the second junction interface, the third junction interface, and the fourth junction interface. The process step of manufacturing the FRD for the present invention through the process of Fig. 2j in Figure 2a is very simple. Because the process steps are clear and the number of masks is small, the process control is easy and accurate, which is excellent in mass production and reliability.
본 발명은 상술한 다수의 반도체 접합층인 HMJ를 이용한 구조를 기본으로 하여 단순화 및 응용을 통해 여러 가지 변형된 형태로 소자를 제작하여 제품화 할 수 있다. 주지하는 바와 같이 통상적으로 제품의 양산에는 수율, 신뢰성, 생산성, 생산단가와 같은 점들을 제품의 성능과 비교하여 최적화하는 것이 일반적이다.The present invention can be manufactured and manufactured in a device in a variety of modified forms through the simplification and application on the basis of the structure using a plurality of semiconductor bonding layers described above HMJ. As is well known, it is common for the mass production of products to optimize points such as yield, reliability, productivity, and production cost in comparison with the performance of the product.
이상에서 설명한 본 발명은 전술한 실시 예 및 첨부된 도면에 의해 한정되는 것이 아니고, 본 발명의 기술적 사상을 벗어나지 않는 범위 내에서 여러 가지 치환, 변형 및 변경할 수 있다는 것은 본 발명이 속하는 기술 분야에서 통상의 지식을 가진 당업자에게 있어 명백할 것이다. The present invention described above is not limited to the above-described embodiments and the accompanying drawings, and it is common in the art that various substitutions, modifications, and changes can be made without departing from the technical spirit of the present invention. It will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
201: n+ 반도체 기판 202: n 완충층
203: n- 베이스층 204: p 이온주입층
205: 산화막 206: p 이온주입을 위한 윈도우
207: p 확산층 208: p+를 위한 윈도우
209: 식각면 210: p+ 증착층
211: p- 이온주입층 212: p- 확산층
213: 금속접촉 윈도우 214: 금속접합 양극
215: 금속 가드링 301: 제1접합부
302: 제2접합부 303: 제3접합부
304: 제4접합부 305: MHJ 접합부201: n + semiconductor substrate 202: n buffer layer
203: n - base layer 204: p ion implantation layer
205: oxide film 206: window for p ion implantation
207: p diffusion layer 208: window for p +
209: etching surface 210: p + deposition layer
211: p - ion implantation layer 212: p - diffusion layer
213: metal contact window 214: metal bonded anode
215: metal guard ring 301: first joint
302: second junction 303: third junction
304: fourth junction 305: MHJ junction
Claims (5)
제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층보다 고농도의 반도체 기판;
상기 반도체 기판의 상부에 제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층;
상기 완충층의 상부에 형성된 진성의 베이스층;
상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 소정의 배치간격으로 형성한 제1이온주입층;
상기 제1이온주입층을 깊이 방향으로 일부 식각하고, 식각된 부분에 충진되는 제2도전형의 상기 제1이온주입층보다 고농도의 다이종 접합(Multiple Hetero-Junction) 박막층;
상기 다이종 접합 박막층 사이는 제2도전형의 불순물로 이온주입하여 확산시킨 제2이온주입층; 및
상기 다이종 접합 박막층 및 제2이온주입층 상부에 형성되는 금속층을 포함한 구조로 형성되어,
상기 반도체 기판과 완충층은 제1접합부를 형성하고, 상기 완충층과 베이스층은 제2접합부를 형성하고, 상기 베이스층과 제2이온주입층은 제3접합부를 형성하고, 상기 베이스층과 제1이온주입층은 제4접합부를 형성하고, 상기 금속층은 상기 다이종 접합 박막층과는 저항성 접촉을 형성하고 상기 제2이온주입층과는 쇼트키(Schottky) 접합을 형성하는 것을 특징으로 하는 MHJ-FRD 소자 구조In the Fast Recovery Diode (FRD) structure,
A semiconductor substrate having a higher concentration than the buffer layer doped with the first conductive type impurity;
A buffer layer doped with a first conductivity type impurity on the semiconductor substrate;
An intrinsic base layer formed on the buffer layer;
A first ion implantation layer formed by implanting and diffusing a second conductive impurity into the base layer at a predetermined batch interval;
A portion of the first ion implantation layer partially etched in the depth direction, and having a higher concentration of a hetero-junction thin film layer than the first ion implantation layer of the second conductivity type filled in the etched portion;
A second ion implantation layer between the die-type junction thin film layer and ion implanted and diffused with impurities of a second conductivity type; And
Is formed in a structure including a metal layer formed on the die-type junction thin film layer and the second ion implantation layer,
The semiconductor substrate and the buffer layer form a first junction, the buffer layer and the base layer form a second junction, the base layer and the second ion implantation layer form a third junction, and the base layer and the first ion MHJ-FRD device, characterized in that the injection layer forms a fourth junction, the metal layer forms a resistive contact with the die-type junction thin film layer and a Schottky junction with the second ion implantation layer. rescue
상기 완충층은 상기 제1접합부로부터 고농도에서 저농도로 경사 기울기 도핑(gradient slope doping)된 것을 특징으로 하는 MHJ-FRD 소자 구조The method of claim 1,
MHJ-FRD device structure characterized in that the buffer layer is gradient slope doping from high concentration to low concentration from the first junction portion (gradient slope doping)
상기 다이종 접합 박막층은 Si1-xGex(0<x<1)층으로 형성된 것을 특징으로 하는 MHJ-FRD 소자 구조The method of claim 1,
MHJ-FRD device structure, characterized in that the die-bonded thin film layer is formed of a Si 1-x Ge x (0 <x <1) layer
제1도전형 불순물로 도핑된 완충층보다 고농도의 반도체 기판을 준비하는 단계;
상기 반도체 기판의 상부에 제1도전형 불순물로 상기 반도체 기판의 상부로부터 고농도에서 저농도로 경사 기울기를 도핑(gradient doping)된 완충층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 완충층의 상부에 진성의 베이스층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 베이스층 상부에 산화막을 증착하고 포토리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 소정의 배치간격으로 이온주입할 영역을 형성한 다음, 상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 제1이온주입층을 형성하는 단계;
상기 제1이온주입층을 깊이 방향으로 일부 식각하고, 식각된 부분에 제2도전형의 상기 제1이온주입층보다 고농도의 다이종 접합(Muti-Hetero Junction) 박막층을 충진하는 단계;
상기 산화막을 제거하고 다시 산화막을 전면에 증착하고 제2이온주입층을 형성할 영역을 포토리소그래피 및 식각공정을 통하여 형성하고,상기 베이스층에 제2도전형 불순물로 이온주입하고 확산시켜 상기 제2이온주입층을 형성하는 단계; 및
상기 다이종 접합 박막층 및 제2이온주입층 상부에 금속층을 형성하는 단계를 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 MHJ-FRD 소자 구조 제조 방법In the manufacturing method of the fast recovery diode (FRD) device,
Preparing a semiconductor substrate having a higher concentration than a buffer layer doped with a first conductive impurity;
Forming a buffer layer doped with a gradient from a high concentration to a low concentration from an upper portion of the semiconductor substrate with a first conductivity type impurity on the semiconductor substrate;
Forming an intrinsic base layer on top of the buffer layer;
After depositing an oxide film on the base layer and forming an ion implantation region at a predetermined interval by photolithography and etching, ion implantation and diffusion of the second conductive impurity into the base layer is performed to form a first ion implantation layer. Forming a;
Partially etching the first ion implantation layer in a depth direction, and filling the etched portion with a higher concentration of a Muti-Hetero Junction thin film layer than the first ion implantation layer of the second conductivity type;
The oxide layer is removed, the oxide layer is deposited on the entire surface, and a region for forming the second ion implantation layer is formed through photolithography and etching, and ion implanted and diffused into the base layer with a second conductive impurity to form the second ion implantation layer. Forming an ion implantation layer; And
MHJ-FRD device structure manufacturing method comprising the step of forming a metal layer on the die-bonded thin film layer and the second ion implantation layer
상기 다이종 접합 박막층은 Si1-xGex(0<x<1) 박막층을 RPCVD(Reduced Pressure CVD)나 UHVCVD(Utra-High Vacuum CVD)의 방법으로 800 oC 이하의 저온에서 선택적으로 에피택셜(epitaixl) 증착하는 것을 특징으로 하는 MHJ-FRD 소자 구조 제조 방법
5. The method of claim 4,
The die-bonded thin film layer is selectively epitaxially formed at a low temperature of 800 ° C. or less by Si 1-x Ge x (0 <x <1) thin film layer by reduced pressure CVD (RPCVD) or ultra-high vacuum CVD (UHVCVD). (epitaixl) MHJ-FRD device structure manufacturing method characterized in that the deposition
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110092319A KR101238232B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2011-09-14 | Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110092319A KR101238232B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2011-09-14 | Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR101238232B1 true KR101238232B1 (en) | 2013-03-04 |
Family
ID=48180945
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020110092319A KR101238232B1 (en) | 2011-09-14 | 2011-09-14 | Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR101238232B1 (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101398125B1 (en) | 2013-06-19 | 2014-05-27 | 주식회사 시지트로닉스 | Self aligned fast recovery diode and fabrication method thereof |
| CN107359117A (en) * | 2017-07-13 | 2017-11-17 | 深圳市金誉半导体有限公司 | High pressure recovers PIN diode and its manufacture method soon |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004503933A (en) | 2000-06-14 | 2004-02-05 | インターナショナル・レクチファイヤー・コーポレーション | Fast recovery diode and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2010073857A (en) | 2008-09-18 | 2010-04-02 | Toshiba Corp | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| WO2011024214A1 (en) | 2009-08-25 | 2011-03-03 | パナソニック株式会社 | Fast recovery diode |
-
2011
- 2011-09-14 KR KR1020110092319A patent/KR101238232B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004503933A (en) | 2000-06-14 | 2004-02-05 | インターナショナル・レクチファイヤー・コーポレーション | Fast recovery diode and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP2010073857A (en) | 2008-09-18 | 2010-04-02 | Toshiba Corp | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| WO2011024214A1 (en) | 2009-08-25 | 2011-03-03 | パナソニック株式会社 | Fast recovery diode |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| GAO YONG et al. CHIN. PHYS. LETT. Vol.21, No.2, pages 414-417(2004). * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101398125B1 (en) | 2013-06-19 | 2014-05-27 | 주식회사 시지트로닉스 | Self aligned fast recovery diode and fabrication method thereof |
| CN107359117A (en) * | 2017-07-13 | 2017-11-17 | 深圳市金誉半导体有限公司 | High pressure recovers PIN diode and its manufacture method soon |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10243066B2 (en) | Producing a semiconductor device by epitaxial growth | |
| JP5859319B2 (en) | Semiconductor elements and reverse conducting IGBTs. | |
| KR101398125B1 (en) | Self aligned fast recovery diode and fabrication method thereof | |
| US8154026B2 (en) | Silicon carbide bipolar semiconductor device | |
| JP5554042B2 (en) | Junction barrier Schottky diode method, diode and method of use | |
| CA2285067C (en) | Silicon carbide field controlled bipolar switch | |
| US7569431B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR101875287B1 (en) | A method for forming a semiconductor device | |
| KR101448158B1 (en) | Structure and Fabrication Method of High-Performance FRD for low voltage and high current | |
| KR101238232B1 (en) | Structure and fabrication method of mhj-frd | |
| KR101415878B1 (en) | Structure and Fabrication Method of High-Voltage UFRED | |
| TW202025249A (en) | Semiconductor structure and manufacturing method therefor | |
| KR101405511B1 (en) | Structure and Fabrication Method of High-Voltage FRD with strong avalanche capability | |
| CN108735823A (en) | A kind of diode and preparation method thereof | |
| CN116093152A (en) | Semiconductor device with a semiconductor layer having a plurality of semiconductor layers | |
| CN210325811U (en) | Silicon carbide heterojunction diode power device | |
| KR101355520B1 (en) | Structure and Fabrication Method of High Voltage Semiconductor Device | |
| CN206584933U (en) | One kind has high performance semiconductor devices | |
| EP3935671B1 (en) | Semiconductor device with gradual injection of charge carriers for softer reverse recovery | |
| KR101724464B1 (en) | Schottky barrier diode and method for manufacturing the same | |
| CN216871974U (en) | Multi-channel super-junction IGBT device | |
| CN118335773A (en) | Method for manufacturing P-doped grid in N-doped SIC layer | |
| CN108550630A (en) | A kind of diode and preparation method thereof | |
| CN114639599B (en) | Local service life control method for semiconductor device | |
| CN103219371B (en) | A kind of trench gate IGBT with Double side diffusion residual layer and manufacture method thereof |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |