KR100552849B1 - Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer - Google Patents
Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR100552849B1 KR100552849B1 KR1020030098368A KR20030098368A KR100552849B1 KR 100552849 B1 KR100552849 B1 KR 100552849B1 KR 1020030098368 A KR1020030098368 A KR 1020030098368A KR 20030098368 A KR20030098368 A KR 20030098368A KR 100552849 B1 KR100552849 B1 KR 100552849B1
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- ion implantation
- trench
- oxide film
- device isolation
- semiconductor substrate
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 35
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 19
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 33
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 23
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 claims description 10
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000007943 implant Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052743 krypton Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N krypton atom Chemical compound [Kr] DNNSSWSSYDEUBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- FHNFHKCVQCLJFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N xenon atom Chemical compound [Xe] FHNFHKCVQCLJFQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052724 xenon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 abstract description 7
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000014759 maintenance of location Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910019142 PO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021480 group 4 element Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910021472 group 8 element Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K phosphate Chemical compound [O-]P([O-])([O-])=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-K 0.000 description 1
- 239000010452 phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
- H01L21/762—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers
- H01L21/76224—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers using trench refilling with dielectric materials
- H01L21/76237—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers using trench refilling with dielectric materials introducing impurities in trench side or bottom walls, e.g. for forming channel stoppers or alter isolation behavior
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/265—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation
- H01L21/26586—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation characterised by the angle between the ion beam and the crystal planes or the main crystal surface
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Element Separation (AREA)
Abstract
소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 제시한다. 본 발명의 일 관점에 따르면, 반도체 기판에 패드 산화막 및 하드 마스크를 형성하고, 반도체 기판을 선택적으로 식각하여 트렌치(trench)를 형성한 후, 트렌치의 입구 부위에 국부적 비정질화를 위해 선택적으로 이온 주입을 수행한다. 트렌치를 메우는 소자 분리막을 형성하고 하드 마스크 및 패드 산화막을 제거한 후, 소자 분리막에 의해 설정되는 반도체 기판 상에 산화막을 성장시킨다. A method of device isolation and oxide film formation is provided. According to an aspect of the present invention, after forming a pad oxide film and a hard mask on the semiconductor substrate, selectively etching the semiconductor substrate to form a trench, and selectively ion implantation in the inlet portion of the trench for localized amorphous Do this. After forming a device isolation film that fills the trench and removing the hard mask and pad oxide film, an oxide film is grown on the semiconductor substrate set by the device isolation film.
터널 산화막, 박화 현상, 이온 주입, 비정질화, STITunnel oxide, thinning, ion implantation, amorphous, STI
Description
도 1a 및 도 1b는 종래의 소자 분리 형성 방법을 설명하기 위해서 개략적으로 도시한 단면도들이다. 1A and 1B are cross-sectional views schematically illustrating a conventional method of forming device isolation.
도 2 내지 도 5는 본 발명의 실시예에 의한 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 설명하기 위해서 개략적으로 도시한 단면도들이다. 2 to 5 are cross-sectional views schematically illustrating a device isolation and oxide film formation method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
본 발명은 반도체 소자에 관한 것으로, 특히, 반도체 소자의 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법에 관한 것이다. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention The present invention relates to semiconductor devices, and in particular, to device isolation and oxide film formation methods of semiconductor devices.
비활성 메모리(non volatile memory) 소자인 플래시(flash) 메모리 셀(cell)은 데이터 보유(data retention) 특성이 매우 중요하게 평가된다. 데이터 보유 특성은 플로팅 게이트(floating gate)에 있는 전자들이 ONO(Oxide Nitride Oxide) 및 터널 산화막(tunnel oxide)을 통해 빠져나가는 것을 평가하는 것인데, 특히, 반도체 기판의 활성 영역(active region)의 에지(edge)쪽을 통해 리키지(leakage)가 발생한다. 그 이유는 에지 쪽의 터널 산화막의 두께가 정상적인 산화막의 두께보다 얇기 때문이다.In flash memory cells, which are non-volatile memory devices, data retention characteristics are very important. The data retention characteristic evaluates the escape of electrons in the floating gate through Oxide Nitride Oxide (ONO) and tunnel oxide (ONO), in particular the edge of the active region of the semiconductor substrate ( Leakage occurs through the edges. The reason is that the thickness of the tunnel oxide film on the edge side is smaller than the thickness of the normal oxide film.
이와 같이 터널 산화막의 두께가 활성 영역의 에지 쪽에서 얇아지는 박화 현상은, 소자 분리막을 형성할 때, 소자 분리막에 의해 설정되는 활성 영역의 에지 부위가 노출되기 때문이다. 이러한 활성 영역의 에지 부위의 노출에 의해서 활성 영역 상에 터널 산화막이 형성될 때, 에지 부위에서 산화막의 성장 속도(oxide growth rate)가 상대적으로 낮아져, 이러한 터널 산화막의 에지쪽 박화 현상이 발생한다. The thinning phenomenon in which the thickness of the tunnel oxide film becomes thinner at the edge side of the active region is because the edge portion of the active region set by the element isolation film is exposed when the device isolation film is formed. When the tunnel oxide film is formed on the active region by the exposure of the edge portion of the active region, the oxide growth rate of the oxide layer is relatively low at the edge portion, such that the edge-side thinning phenomenon of the tunnel oxide film occurs.
도 1a 및 도 1b는 종래의 소자 분리 형성 방법을 설명하기 위해서 개략적으로 도시한 단면도들이다. 1A and 1B are cross-sectional views schematically illustrating a conventional method of forming device isolation.
도 1a 및 도 1b를 참조하면, 종래의 소자 분리 형성 방법은, 반도체 기판(10)에 트렌치(trench)를 형성하고, 트렌치를 메우는 소자 분리막(15)을 형성하는 방법, 예컨대, 얕은 트렌치 소자 분리(STI)로 수행된다. Referring to FIGS. 1A and 1B, a conventional device isolation forming method includes forming a trench in a
이때, 도 1a에 제시된 바와 같이 소자 분리막(15)에 의해 설정되는 활성 영역의 반도체 기판(10) 상에 형성되는 플로팅 게이트(30) 아래의 터널 산화막(20)은 활성 영역의 에지 쪽이 상대적으로 얇아지는 현상이 발생된다. 이는 도 1b에 제시된 바와 같이 소자 분리막(15)을 화학 기계적 연마(CMP) 등으로 평탄화한 후 연마 종료점 등으로 이용된 하드 마스크(hard mask) 등을 제거할 때, 소자 분리막(15)과 반도체 기판(10)의 계면 부위가 취약하여 덴트(dent:11) 등이 발생되기 때문이다.At this time, as shown in FIG. 1A, the
이에 따라, 활성 영역의 반도체 기판(10) 상에 터널 산화막을 성장시킬 때, 활성 영역의 에지 부위가 노출되므로, 이러한 부위에서의 터널 산화막의 성장 속도 가 결정 구조의 차이에 의해서 상대적으로 느려진다. 따라서, 터널 산화막(20)의 얇아지는 현상(25)이 발생된다. Accordingly, when the tunnel oxide film is grown on the
본 발명이 이루고자 하는 기술적 과제는, 터널 산화막과 같은 활성 영역의 반도체 기판 상에 형성되는 산화막이 활성 영역의 에지 부위에서 상대적으로 얇아지는 것을 방지할 수 있는 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 제공하는 데 있다. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION An object of the present invention is to provide a device isolation and oxide film formation method which can prevent the oxide film formed on the semiconductor substrate in the active region such as the tunnel oxide film from being relatively thin at the edge portion of the active region. .
상기의 기술적 과제들을 달성하기 위한 본 발명의 일 관점은, 반도체 기판에 패드 산화막 및 하드 마스크를 형성하는 단계, 상기 반도체 기판을 선택적으로 식각하여 트렌치(trench)를 형성하는 단계, 상기 트렌치의 입구 부위에 국부적 비정질화를 위해 선택적으로 이온 주입을 수행하는 단계, 상기 트렌치를 메우는 소자 분리막을 형성하고 상기 하드 마스크 및 패드 산화막을 제거하는 단계, 및 상기 소자 분리막에 의해 설정되는 상기 반도체 기판 상에 산화막을 성장시키는 단계를 포함하는 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 제시한다. One aspect of the present invention for achieving the above technical problem, the step of forming a pad oxide film and a hard mask on the semiconductor substrate, selectively etching the semiconductor substrate to form a trench (trench), the inlet portion of the trench Selectively performing ion implantation for local amorphous to, forming a device isolation film filling the trench, removing the hard mask and pad oxide film, and depositing an oxide film on the semiconductor substrate set by the device isolation film. A device isolation and oxide film formation method comprising the step of growing is provided.
상기 이온 주입은 상기 하드 마스크에 의해서 선택적으로 주입될 이온이 차단되어 상기 트렌치 입구 부위에 선택적으로 이온 주입되도록 하기 위해 경사 이온 주입으로 수행될 수 있다. The ion implantation may be performed by gradient ion implantation in order to selectively block the ions to be selectively implanted by the hard mask to selectively implant ions into the trench inlet.
상기 경사(tilt) 이온 주입은 상기 반도체 기판 면에 대해 수직한 방향에 대해 20° 내지 70° 기울어지게 수행되는 것일 수 있다. The tilt ion implantation may be performed at an angle of 20 ° to 70 ° with respect to a direction perpendicular to the surface of the semiconductor substrate.
상기 이온 주입은 실리콘(Si) 또는 게르마늄(Ge) 이온을 주입하는 것일 수 있다. The ion implantation may be to implant silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge) ions.
상기 이온 주입은 아르곤(Ar), 크세논(Xe) 또는 크립톤(Kr) 이온을 주입하는 것일 수 있다. The ion implantation may be to inject argon (Ar), xenon (Xe) or krypton (Kr) ions.
상기 이온 주입은 1E12 내지 1E15 도즈/㎠의 도즈량으로 수행되는 것일 수 있다. The ion implantation may be performed at a dose of 1E12 to 1E15 doses / cm 2.
상기 이온 주입은 4KeV 내지 50KeV의 가속 에너지로 수행되는 것일 수 있다. The ion implantation may be performed at an acceleration energy of 4KeV to 50KeV.
상기 이온 주입을 수행하기 이전에 상기 트렌치 내벽을 산화하는 산화 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다. The method may further include an oxidation step of oxidizing the inner wall of the trench before performing the ion implantation.
상기 이온 주입을 수행하기 이후에 상기 소자 분리막을 형성하기 이전에 상기 트렌치 내벽을 산화하는 산화 단계를 더 포함할 수 있다. The method may further include an oxidation step of oxidizing the inner wall of the trench after the ion implantation and before forming the device isolation layer.
본 발명에 따르면, 터널 산화막과 같은 활성 영역의 반도체 기판 상에 형성되는 산화막이 활성 영역의 에지 부위에서 상대적으로 얇아지는 것을 방지할 수 있는 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 제공할 수 있다. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide a device isolation and oxide film formation method capable of preventing an oxide film formed on a semiconductor substrate in an active region such as a tunnel oxide film from becoming relatively thin at the edge portion of the active region.
이하, 첨부 도면을 참조하여 본 발명의 실시예를 상세히 설명한다. 그러나, 본 발명의 실시예들은 여러 가지 다른 형태로 변형될 수 있으며, 본 발명의 범위가 아래에서 상술하는 실시예들로 인해 한정되어지는 것으로 해석되어져서는 안되며, 당업계에서 평균적인 지식을 가진 자에게 본 발명을 보다 완전하게 설명하기 위해서 제공되어지는 것으로 해석되는 것이 바람직하다. Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. However, the embodiments of the present invention may be modified in many different forms, and the scope of the present invention should not be construed as being limited by the embodiments described below, and should be understood by those skilled in the art. It is preferred that the present invention be interpreted as being provided to more fully explain the present invention.
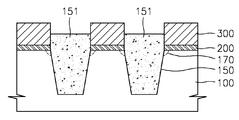
도 2 내지 도 5는 본 발명의 실시예에 의한 소자 분리 및 산화막 형성 방법을 설명하기 위해서 개략적으로 도시한 단면도들이다. 2 to 5 are cross-sectional views schematically illustrating a device isolation and oxide film formation method according to an embodiment of the present invention.
도 2를 참조하면, 본 발명의 실시예에 따른 소자 분리 형성 방법은, 반도체 기판(100) 상에 대략 100Å 두께의 패드 산화막(pad oxide:200)을 형성하고, 패드 산화막(200) 상에 하드 마스크(300)로 사용될 실리콘 질화물층을 바람직하게 형성한다. 이후에, 하드 마스크(300) 상에 식각 마스크(400)로서의 포토레지스트 패턴을 형성하고, 이에 노출되는 부분을 순차적으로 식각하여 반도체 기판(100)에 트렌치(150)를 형성한다. Referring to FIG. 2, in the device isolation forming method according to the exemplary embodiment of the present invention, a
도 3을 참조하면, 포토레지스트 패턴(400)을 제거한 후, 트렌치(150)의 입구 부위에 이온 주입을 실시한다. 이러한 이온 주입에 의해서 트렌치(150) 입구 부위의 반도체 기판(100)의 실리콘을 비정질화(amorphization)한다. Referring to FIG. 3, after the
이러한 이온 주입은 원소 주기율표 상의 4족 원소인 실리콘(Si) 또는 게르마늄(Ge)을 주입되는 이온 원소, 즉, 도펀트(dopant)로 이용할 수 있고, 또는 주기율표 상의 8족 원소인 아르곤(ar), 크세논(Xe) 또는 크립톤(Kr) 등을 도펀트로 이용할 수 있다. Such ion implantation may use silicon (Si) or germanium (Ge), a Group 4 element on the periodic table, as a dopant, or an argon (ar) or xenon group 8 element on the periodic table. (Xe) or krypton (Kr) may be used as the dopant.
이때, 이온 주입의 도즈(dose)량은 1E12 내지 1E15도즈/㎠ 일 수 있다. 또한, 이때 이온 가속 에너지(energy)는 대략 4KeV 내지 50KeV일 수 있다. 그리고, 이러한 이온 주입은 반도체 기판(100) 면에 수직한 방향, 즉 면 방향을 기준으로 대략 20° 내지 70° 기울어진 경사 이온 주입으로 수행되는 것이 바람직하다. 이와 같이 경사 이온 주입을 실시하면, 대부분의 이온은 하드 마스크(300)에 의해서 차단(blocking)되고 트렌치(150)의 내부 깊은 부분은 손상(damage)을 주지 않고, 필요한 부위, 즉, 트렌치(150) 입구 부위에 선택적으로 이온 주입을 실시할 수 있 다. 이러한 이온 주입에 의해서 트렌치(150) 입구 부위(170)는 비정질화 되게 된다. In this case, the dose of the ion implantation may be 1E12 to 1E15 dose / cm 2. In addition, the ion acceleration energy (energy) may be approximately 4KeV to 50KeV. In addition, the ion implantation may be performed by inclined ion implantation inclined by about 20 ° to 70 ° based on the direction perpendicular to the surface of the
도 4를 참조하면, 트렌치(150)를 채우는 소자 분리막(155)을 형성한다. 이때, 소자 분리막(155)은 화학 기상 증착(CVD)으로 증착되는 실리콘 산화물 또는 고밀도 플라즈마 증착(HDP)에 의해서 증착되는 실리콘 산화물로 형성될 수 있다. 이와 같이 소자 분리막(155)을 증착한 후, 하드 마스크(300)를 연마 종료로 이용하여 소자 분리막(155)을 CMP한다. Referring to FIG. 4, the isolation layer 155 filling the
이때, 소자 분리막(155)을 형성하기 이전에 트렌치(150) 내벽을 산화시켜 주는 산화 과정을 더 수행할 수 있다. 이러한 산화 과정을 수행할 때, 상기한 이온 주입 과정은 상기 산화 과정 전 또는 후에 수행될 수 있다. In this case, before the device isolation layer 155 is formed, an oxidation process for oxidizing the inner wall of the
도 5를 참조하면, 하드 마스크(300)를 인산 습식 식각 등으로 제거한 후, 패드 산화막(200)을 제거하고, 터널 산화막(250)을 반도체 기판(100) 상에 성장시킨다. Referring to FIG. 5, after removing the
이때, 상기한 바와 같은 이온 주입에 의해서 비정질화된 부분(170)에서의 산화물 성장 속도는 비정질화된 특성 때문에 상대적으로 향상되게 된다. 따라서, 목표 산화막 대비 상대적으로 두꺼운 산화막을 얻을 수 있다. 따라서, 종래와 같은 터널 산화막의 에지 부위에서의 두께 얇아짐 현상을 보상할 수 있다. At this time, the oxide growth rate in the
한편, 이러한 터널 산화막(250) 플래시 메모리 소자에 산화막이 이용될 경우에 해당되는 명칭으로 설명하였으나, 논리 트랜지스터(logic transistor) 등의 게이트 산화막을 형성하는 데에도 응용될 수 있다. On the other hand, the tunnel oxide film 250 has been described as a name when an oxide film is used in the flash memory device, but may be applied to forming a gate oxide film such as a logic transistor.
이상, 본 발명을 구체적인 실시예를 통하여 상세히 설명하였으나, 본 발명은 이에 한정되지 않고, 본 발명의 기술적 사상 내에서 당 분야의 통상의 지식을 가진 자에 의해 그 변형이나 개량이 가능함이 명백하다. As mentioned above, although this invention was demonstrated in detail through the specific Example, this invention is not limited to this, It is clear that the deformation | transformation and improvement are possible by the person of ordinary skill in the art within the technical idea of this invention.
상술한 본 발명에 따르면, 소자 분리에 의해 설정되는 활성 영역의 에지 부위에서 산화막이 얇아지는 것을 효과적으로 방지할 수 있다. According to the present invention described above, it is possible to effectively prevent the oxide film from thinning at the edge portion of the active region set by device isolation.
Claims (9)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030098368A KR100552849B1 (en) | 2003-12-27 | 2003-12-27 | Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030098368A KR100552849B1 (en) | 2003-12-27 | 2003-12-27 | Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20050066884A KR20050066884A (en) | 2005-06-30 |
| KR100552849B1 true KR100552849B1 (en) | 2006-02-22 |
Family
ID=37257892
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020030098368A KR100552849B1 (en) | 2003-12-27 | 2003-12-27 | Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| KR (1) | KR100552849B1 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR100694471B1 (en) * | 2005-08-24 | 2007-03-12 | 매그나칩 반도체 유한회사 | Method for fabrication of image sensor for improving optical property |
-
2003
- 2003-12-27 KR KR1020030098368A patent/KR100552849B1/en not_active IP Right Cessation
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20050066884A (en) | 2005-06-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4813055B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing flash memory device | |
| TWI242265B (en) | Method of manufacturing a flash memory cell | |
| KR100564989B1 (en) | Oxynitride shallow trench isolation and method of formation | |
| US20090017597A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing shallow trench isolation | |
| JPH088297B2 (en) | Element isolation method for semiconductor device | |
| US6946337B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing semiconductor devices | |
| CN109524346B (en) | Shallow trench isolation structure and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR100525915B1 (en) | Method for forming an isolation layer in a semiconductor device | |
| JP5020469B2 (en) | Method for forming element isolation film of semiconductor memory element | |
| KR100552849B1 (en) | Method for fabricating isolation and oxide layer | |
| KR101033359B1 (en) | method for fabricating semiconductor device | |
| KR100639194B1 (en) | Method for forming isolation layer in semiconductor device | |
| KR100449318B1 (en) | Method for forming isolation layer in semiconductor device | |
| KR100427538B1 (en) | Method of forming a isolation layer in a semiconductor device | |
| US6281093B1 (en) | Method to reduce trench cone formation in the fabrication of shallow trench isolations | |
| KR100967673B1 (en) | Method for forming isolation layer of semiconductor device | |
| US20050014344A1 (en) | Method of forming well in semiconductor device | |
| KR100731502B1 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| KR20020096136A (en) | Method for manufacturing isolation of semiconductor device | |
| KR100917106B1 (en) | Method for forming an isolation layer in semiconductor device | |
| KR100345521B1 (en) | Method for forming gate of transistor | |
| CN112382606A (en) | STI (shallow trench isolation) structure manufacturing method, STI structure and semiconductor device | |
| TW459340B (en) | Method for forming trench isolation structure | |
| KR20030086853A (en) | Method for forming isolation layer of semiconductor device | |
| CN112349586A (en) | Method for forming semiconductor structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| N231 | Notification of change of applicant | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E701 | Decision to grant or registration of patent right | ||
| GRNT | Written decision to grant | ||
| FPAY | Annual fee payment |
Payment date: 20120119 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| LAPS | Lapse due to unpaid annual fee |