JP7232978B2 - Method for Cooling Infrared Sensors and Bolometer Infrared Receivers of Infrared Sensors - Google Patents
Method for Cooling Infrared Sensors and Bolometer Infrared Receivers of Infrared Sensors Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP7232978B2 JP7232978B2 JP2018201387A JP2018201387A JP7232978B2 JP 7232978 B2 JP7232978 B2 JP 7232978B2 JP 2018201387 A JP2018201387 A JP 2018201387A JP 2018201387 A JP2018201387 A JP 2018201387A JP 7232978 B2 JP7232978 B2 JP 7232978B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- period
- domain
- regularly arranged
- peltier
- holes
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 61
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 title claims description 33
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 223
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 96
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 63
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 62
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 57
- 230000000737 periodic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 52
- 230000000903 blocking effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 123
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 64
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 46
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 43
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 22
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 19
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 description 17
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 16
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000005679 Peltier effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 11
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 10
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 8
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 7
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 4
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052681 coesite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052906 cristobalite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000000609 electron-beam lithography Methods 0.000 description 3
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 3
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 229910052682 stishovite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052905 tridymite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012808 vapor phase Substances 0.000 description 3
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002772 conduction electron Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010292 electrical insulation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 2
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N AsGa Chemical compound [As]#[Ga] JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000673 Indium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- GPXJNWSHGFTCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Indium phosphide Chemical compound [In]#P GPXJNWSHGFTCBW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005678 Seebeck effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910004541 SiN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910002370 SrTiO3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XHCLAFWTIXFWPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[V+5].[V+5] Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[V+5].[V+5] XHCLAFWTIXFWPH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003574 free electron Substances 0.000 description 1
- WPYVAWXEWQSOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium antimonide Chemical compound [Sb]#[In] WPYVAWXEWQSOGY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RPQDHPTXJYYUPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium arsenide Chemical compound [In]#[As] RPQDHPTXJYYUPQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron(III) oxide Inorganic materials O=[Fe]O[Fe]=O JEIPFZHSYJVQDO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910003465 moissanite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002086 nanomaterial Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012552 review Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001935 vanadium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/0225—Shape of the cavity itself or of elements contained in or suspended over the cavity
- G01J5/023—Particular leg structure or construction or shape; Nanotubes
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/0225—Shape of the cavity itself or of elements contained in or suspended over the cavity
- G01J5/024—Special manufacturing steps or sacrificial layers or layer structures
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/06—Arrangements for eliminating effects of disturbing radiation; Arrangements for compensating changes in sensitivity
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/06—Arrangements for eliminating effects of disturbing radiation; Arrangements for compensating changes in sensitivity
- G01J5/061—Arrangements for eliminating effects of disturbing radiation; Arrangements for compensating changes in sensitivity by controlling the temperature of the apparatus or parts thereof, e.g. using cooling means or thermostats
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/08—Optical arrangements
- G01J5/0853—Optical arrangements having infrared absorbers other than the usual absorber layers deposited on infrared detectors like bolometers, wherein the heat propagation between the absorber and the detecting element occurs within a solid
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/10—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry using electric radiation detectors
- G01J5/20—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry using electric radiation detectors using resistors, thermistors or semiconductors sensitive to radiation, e.g. photoconductive devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N10/00—Thermoelectric devices comprising a junction of dissimilar materials, i.e. devices exhibiting Seebeck or Peltier effects
- H10N10/10—Thermoelectric devices comprising a junction of dissimilar materials, i.e. devices exhibiting Seebeck or Peltier effects operating with only the Peltier or Seebeck effects
- H10N10/17—Thermoelectric devices comprising a junction of dissimilar materials, i.e. devices exhibiting Seebeck or Peltier effects operating with only the Peltier or Seebeck effects characterised by the structure or configuration of the cell or thermocouple forming the device
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N15/00—Thermoelectric devices without a junction of dissimilar materials; Thermomagnetic devices, e.g. using the Nernst-Ettingshausen effect
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N15/00—Thermoelectric devices without a junction of dissimilar materials; Thermomagnetic devices, e.g. using the Nernst-Ettingshausen effect
- H10N15/10—Thermoelectric devices using thermal change of the dielectric constant, e.g. working above and below the Curie point
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01J—MEASUREMENT OF INTENSITY, VELOCITY, SPECTRAL CONTENT, POLARISATION, PHASE OR PULSE CHARACTERISTICS OF INFRARED, VISIBLE OR ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT; COLORIMETRY; RADIATION PYROMETRY
- G01J5/00—Radiation pyrometry, e.g. infrared or optical thermometry
- G01J5/02—Constructional details
- G01J5/06—Arrangements for eliminating effects of disturbing radiation; Arrangements for compensating changes in sensitivity
- G01J5/061—Arrangements for eliminating effects of disturbing radiation; Arrangements for compensating changes in sensitivity by controlling the temperature of the apparatus or parts thereof, e.g. using cooling means or thermostats
- G01J2005/062—Peltier
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Photometry And Measurement Of Optical Pulse Characteristics (AREA)
Description
本開示は、赤外線センサおよび赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法に関する。 The present disclosure relates to infrared sensors and methods of cooling bolometric infrared receivers of infrared sensors.
特許文献1は、梁を用いてベース基板から熱型赤外線受光部を離間させる構造を開示している。この構造は、赤外線受光部をベース基板から熱的に絶縁させることを目的としている。この構造を有する熱型赤外線センサでは、梁の断熱性能が高いほど赤外線の検出感度が向上する。
特許文献2および非特許文献1は、薄膜の熱伝導率を減少させる、複数の貫通孔により構成される周期構造を開示している。この周期構造では、平面視の薄膜において、ナノメートルのオーダー(1nmから1000nmの領域)内の周期で規則的に貫通孔が配列されている。この周期構造は、フォノニック結晶構造の一種である。このタイプのフォノニック結晶構造は、貫通孔の配列を構成する最小単位を単位格子とする周期構造である。
薄膜の熱伝導率は、例えば、特許文献1に開示されているように、多孔質化により低減できる。多孔質化により薄膜に導入された空隙が、薄膜の熱伝導率を減少させるためである。一方、フォノニック結晶構造によれば、薄膜を構成する母材自身の熱伝導率が低減可能である。このため、単なる多孔質化に比べて、熱伝導率のさらなる低減が期待される。 The thermal conductivity of thin films can be reduced by porosification, for example, as disclosed in US Pat. This is because the voids introduced into the thin film by porosity decrease the thermal conductivity of the thin film. On the other hand, according to the phononic crystal structure, the thermal conductivity of the base material itself that constitutes the thin film can be reduced. For this reason, a further reduction in thermal conductivity is expected as compared to mere porosity.
絶縁体および半導体において、熱は、主として、フォノンと呼ばれる格子振動によって運ばれる。絶縁体または半導体から構成される材料の熱伝導率は、材料が有するフォノンの分散関係により決定される。フォノンの分散関係とは、周波数と波数との関係、またはバンド構造を意味している。絶縁体および半導体において、熱を運ぶフォノンは、100GHzから10THzの幅広い周波数帯域に及ぶ。この周波数帯域は、熱の帯域である。材料の熱伝導率は、熱の帯域にあるフォノンの分散関係により定められる。 In insulators and semiconductors, heat is primarily carried by lattice vibrations called phonons. The thermal conductivity of a material composed of an insulator or a semiconductor is determined by the phonon dispersion relation of the material. The phonon dispersion relation means the relation between frequency and wave number, or band structure. In insulators and semiconductors, heat-carrying phonons span a wide frequency band from 100 GHz to 10 THz. This frequency band is the thermal band. The thermal conductivity of a material is determined by the dispersion relation of phonons in the thermal zone.
上述のフォノニック結晶構造によれば、貫通孔の周期構造によって、材料が有するフォノンの分散関係が制御可能である。即ち、フォノニック結晶構造によれば、材料、例えば薄膜の母材、の熱伝導率そのものが制御可能である。とりわけ、フォノニック結晶構造によるフォノニックバンドギャップ(PBG)の形成は、材料の熱伝導率を大きく低減させうる。PBG内にフォノンは存在できない。このため、熱の帯域に位置するPBGは、熱伝導のギャップとなりうる。また、PBG以外の周波数帯域においても、フォノンの分散曲線の傾きがPBGによって小さくなる。傾きの低減はフォノンの群速度を低下させ、熱伝導速度を低下させる。これらの点は、材料の熱伝導率の低減に大きく寄与する。 According to the above-described phononic crystal structure, the periodic structure of the through-holes can control the phonon dispersion relation of the material. That is, according to the phononic crystal structure, it is possible to control the thermal conductivity itself of the material, for example, the base material of the thin film. Among other things, the formation of a phononic bandgap (PBG) by the phononic crystal structure can greatly reduce the thermal conductivity of the material. Phonons cannot exist in the PBG. Therefore, the PBG located in the heat zone can become a heat conduction gap. Also in frequency bands other than PBG, the slope of the phonon dispersion curve is reduced by PBG. Reducing the tilt reduces the phonon group velocity and reduces the heat transfer velocity. These points greatly contribute to the reduction of the thermal conductivity of the material.
このようなフォノニック結晶構造を、赤外線受光部を支持する梁に導入することにより、赤外線センサの検出感度を向上させることが出来る。 The detection sensitivity of the infrared sensor can be improved by introducing such a phononic crystal structure into the beam supporting the infrared light receiving section.
梁の断熱性能を高めることで、赤外線センサの検出感度を向上させることができる。しかし、それと同時に赤外線受光部の温度変化が遅くなり、赤外線センサの応答速度が低下するという課題がある。 By increasing the heat insulation performance of the beam, the detection sensitivity of the infrared sensor can be improved. However, at the same time, there is a problem that the temperature change of the infrared light receiving section is slowed down, and the response speed of the infrared sensor is lowered.
そこで、赤外線センサの応答速度を向上させる手段として、例えば、特許文献1に開示されている赤外線センサにおいて、ベース基板に接続された梁の形状を有するペルチェ素子を赤外線受光部に接するように配置することが考えられる。ペルチェ素子を用いて赤外線受光部から局所的に熱を吸い出すことで、赤外線の入射によって上昇した赤外線受光部の温度を低下させる。しかし、ペルチェ素子を導入することで、赤外線受光部およびベース基板の間における熱コンダクタンスが増加するため、赤外線の検出感度の低下を招く。
Therefore, as means for improving the response speed of the infrared sensor, for example, in the infrared sensor disclosed in
また、半導体基板上にモノリシックに梁の形状を有するペルチェ素子を作製する場合、シリコンプロセスで使用されている半導体材料を使用する必要がある。この場合、通常使用される半導体材料(例えば、SiやSiGe)はペルチェ効果が低いため、十分な吸熱機能を得ることが困難である。 Moreover, when a Peltier element having a beam shape is monolithically produced on a semiconductor substrate, it is necessary to use a semiconductor material used in the silicon process. In this case, it is difficult to obtain a sufficient endothermic function because the normally used semiconductor materials (eg, Si and SiGe) have a low Peltier effect.
本開示の目的は、優れた検出感度および優れた応答速度を両立することができる赤外線センサおよび当該赤外線センサの赤外線受光部を冷却する方法を提供することである。 An object of the present disclosure is to provide an infrared sensor capable of achieving both excellent detection sensitivity and excellent response speed, and a method for cooling the infrared light receiving section of the infrared sensor.
本開示の赤外線センサは、
凹部を有するベース基板、
ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第1梁、および
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部および前記凹部の間に挟まれており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁およびn型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端は、前記ベース基板に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ペルチェ素子、前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備する。
The infrared sensor of the present disclosure is
a base substrate having a recess;
bolometer infrared receiver and Peltier element,
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a first bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer; and a second bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer;
is equipped with
The Peltier element is sandwiched between the bolometer infrared light receiving portion and the recess,
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
said Peltier element comprising a first Peltier beam made of a p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam made of an n-type semiconductor material;
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
one end of the first bolometer beam, one end of the second bolometer beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are connected to the base substrate;
The bolometer infrared light receiving unit, the Peltier element, the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate,
The first bolometer beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second bolometer beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The Peltier first beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second Peltier beam has a fourth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes.
本開示による赤外線センサにおいて、抵抗変化層およびベース基板を離間させているボロメータ第1梁、ボロメータ第2梁、ペルチェ第1梁、およびペルチェ第2梁の各々は、フォノニック結晶構造を備える。これにより、抵抗変化層およびベース基板の間における熱コンダクタンスが大幅に抑制される。この結果、赤外線の優れた検出感度を実現できる。 In the infrared sensor according to the present disclosure, each of the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam separating the variable resistance layer and the base substrate comprises a phononic crystal structure. As a result, thermal conductance between the variable resistance layer and the base substrate is significantly suppressed. As a result, excellent infrared detection sensitivity can be realized.
さらに、ペルチェ素子として機能するペルチェ第1梁およびペルチェ第2梁の各々は、フォノニック結晶を備えるため、シリコンプロセスで用いられるペルチェ効果が低い半導体材料(例えば、SiまたはSiGe)をペルチェ第1梁およびペルチェ第2梁の材料として用いた場合でも、赤外線の吸収に伴って上昇したボロメータ赤外線受光部の温度を十分に低下させることができる。本開示の構成によってペルチェ効果を高められる理由は、フォノニック結晶構造をペルチェ第1梁およびペルチェ第2梁の各々に導入することで、ペルチェ第1梁およびペルチェ第2梁を構成する材料の電気伝導率は変化しないまま、熱伝導率だけを低減することが出来るためである。すなわち、フォノニック結晶構造では、電子輸送に依存する電気伝導率は変化せず、フォノン輸送に依存する熱伝導率だけが変化するためである。優れたペルチェ効果によって、ボロメータ赤外線受光部を短時間で冷却することができる。これにより、赤外線センサの応答速度を向上することができる。 Furthermore, since each of the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam functioning as a Peltier element includes a phononic crystal, a semiconductor material with a low Peltier effect (eg, Si or SiGe) used in the silicon process is used as the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam. Even when it is used as the material for the second Peltier beam, it is possible to sufficiently lower the temperature of the bolometer infrared light receiving portion, which rises due to the absorption of infrared rays. The reason why the Peltier effect can be enhanced by the configuration of the present disclosure is that by introducing a phononic crystal structure into each of the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam, the electrical conductivity of the material constituting the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam is reduced. This is because only the thermal conductivity can be reduced while the modulus remains unchanged. That is, in the phononic crystal structure, the electrical conductivity, which depends on electron transport, does not change, but only the thermal conductivity, which depends on phonon transport. Due to the excellent Peltier effect, the bolometer infrared receiver can be cooled in a short period of time. Thereby, the response speed of the infrared sensor can be improved.
本開示は、優れた検出感度および優れた応答速度を両立することができる赤外線センサおよび当該赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法を提供する。 The present disclosure provides an infrared sensor capable of achieving both excellent detection sensitivity and excellent response speed, and a method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor.
以下本開示の実施の形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。特開2017-223644号公報、特開2017-223644号公報に対応する米国特許出願2015/497353、および中国出願201710274259.9は本願に参照として援用される。 Embodiments of the present disclosure will be described below with reference to the drawings. JP 2017-223644, US Patent Application 2015/497353 corresponding to JP 2017-223644, and Chinese Application 201710274259.9 are incorporated herein by reference.
(実施形態1)
実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aが図1A~図1Cに示される。図1Bには、図1Aの赤外線センサ1Aの断面1B-1Bが示される。図1Cには、図1Aの赤外線センサ1Aの断面1C-1Cが示される。赤外線センサ1Aは、ボロメータ赤外線センサである。
(Embodiment 1)
An
赤外線センサ1Aは、凹部32を有するベース基板11、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12A、ペルチェ素子12Pを備える。また、赤外線センサ1Aは、電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dを備える。電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dは、ベース基板11上に設けられている。
The
ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aは、赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層201、抵抗変化層201に電気的に接続されている梁101a、および抵抗変化層201に電気的に接続されている梁101bを備える。なお、梁101aおよび梁101bは、それぞれ、ボロメータ第1梁およびボロメータ第2梁とも称される。また、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aは、抵抗変化層201の上に形成された絶縁膜202、および絶縁膜202の上に形成された赤外線吸収層203を備える。ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aは膜の形状を有する。ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aが設けられた面は、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aの表側の面と称される。また、抵抗変化層201が設けられた面は、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aの裏側の面と称される。
The bolometer
ペルチェ素子12Pは、p型半導体材料から形成されている梁102aおよびn型半導体材料から形成されている梁102bを備える。なお、梁102aおよび梁102bは、それぞれ、ペルチェ第1梁およびペルチェ第2梁とも称される。また、ペルチェ素子12Pは、第1配線16および絶縁膜17を備える。
図1Aおよび図1Bに示されるように、梁101aの一端および梁101bの一端は、ベース基板11に接続されている。また、梁101aの他端および梁101bの他端は、抵抗変化層201に接続されている。また、梁101a、101bは、それぞれ、第2配線14a、14bと電気的に接続されている。第2配線14a、14bは、それぞれ、電極パッド13a、13bに電気的に接続されている。
As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B, one end of
図1Aおよび図1Cに示されるように、梁102aの一端および梁102bの一端は、ベース基板11に接続されている。また、梁102aの他端は梁102bの他端に接続され、界面103が形成されている。界面103を跨ぐように、梁102a、102bを電気的に接続する第1配線16が梁102a、102bの上に形成されている。さらに、第1配線16を覆うように、絶縁膜17は、第1配線16、梁102a、および梁102bの上に形成されている。また、梁102a、102bは、それぞれ、第2配線14c、14dと電気的に接続されている。第2配線14c、14dは、それぞれ、電極パッド15a、15bに電気的に接続されている。
As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1C, one end of
図1A~図1Cに示されるように、ベース基板11は、赤外線受光部12Aが設けられた上面31に凹部32を有する。
As shown in FIGS. 1A to 1C, the
平面視において、赤外線受光部12Aの面積に比べて凹部32の面積は大きい。また、平面視において、赤外線受光部12Aは、凹部32の外縁に囲まれている。なお、本明細書において、「平面視」とは、対象物の主面に垂直な方向から対象物を視ることを意味する。また、「主面」とは、最も広い面積を有する面を意味する。本実施形態では、主面は上面31である。
In plan view, the area of the
ベース基板11が凹部32を有する理由は、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203に蓄積される熱を逃げにくくするためである。当該技術分野においてよく知られているように、このように熱を逃げにくくすることで赤外線センサの検出感度が向上する。
The reason why the
図1Bに示されるように、凹部32は、赤外線受光部12Aおよび梁101a、101bと、ベース基板11との間に位置している。図1Cに示されるように、ペルチェ素子12Pは、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aおよび凹部32の間に挟まれている。また、ペルチェ素子12Pは、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aを冷却するために、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aの裏側の面に接している。具体的には、絶縁膜17は、抵抗変化層201に接している。界面103は、抵抗変化層201および凹部32の間に挟まれている。絶縁膜17は、抵抗変化層201、ならびに梁102aおよび梁102bの間に挟まれている。ボロメータ赤外線受光部12A、ペルチェ素子12P、梁101a、101b、102a、102bは、ベース基板11の上部で懸架されている。当該技術分野においてよく知られているように、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12Aをこのように懸架することで赤外線センサの検出感度が向上する。
As shown in FIG. 1B,
梁101a、101bは、赤外線吸収層203に入射した赤外線の検出信号を読み出すために用いられる。
The
梁101a、101bは、導電性を有する材料からなる。導電性を有する材料は、例えば、金属および半導体である。より好ましくは、導電性を有する材料は、半導体である。これは、金属において熱を運ぶ媒体は、フォノンではなく、主として自由電子であるためである。半導体は、例えば、SiまたはGeといった単一元素の半導体、SiN、SiC、SiGe、GaAs、InAs、InSb、InP、GaN、またはAlNといった化合物半導体、並びにFe2O3、VO2、TiO2、またはSrTiO3といった酸化物半導体である。
The
梁101aおよび梁101bの各々は、ベース基板11に対する抵抗変化層201の断熱性能を高めるために、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成されたフォノニック結晶構造を有している。フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の梁101aにおけるベース基板11に接続された梁101aの一端および抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間111a、ならびに平面視の梁101bにおけるベース基板11に接続された梁101bの一端および抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間111bに設けられていることが望ましい。フォノニック結晶構造の詳細は後述される。
Each of
梁102a、102bは、熱電対を構成し、ペルチェ素子12Pとして機能する。すなわち、梁102a、102bは、赤外線受光部12Aで発生した熱を吸熱するために用いられる。界面103がペルチェ素子12Pの冷接点に対応する。梁102a、102bの一方は、p型半導体材料からなる。梁102a、102bの他方は、n型半導体材料からなる。p型半導体材料およびn型半導体材料は、例えば、シリコンプロセスで使用されるシリコン系半導体材料(例えば、SiまたはSiGe)であることが望ましい。
The
界面103の上に第1配線16が設けられている理由は、梁102a、102bの間に電流を流しやすくするためである。第1配線16がなくても、ペルチェ素子12Pは機能するが、ペルチェ素子12Pは第1配線16を有することが望ましい。
The reason why the
なお、図1Dに示されるように、界面103を有さないペルチェ素子12Pが用いられる場合、梁102aを梁102bに電気的に接続する第1配線16は必須である。この場合、第1配線16が、ペルチェ素子12Pの冷接点に対応する。図1Dに示されるように、第1配線16は、抵抗変化層201および凹部32の間に挟まれている。
Note that, as shown in FIG. 1D, when a
赤外線センサ1Aは、複数の界面103を有することが望ましい。複数の界面103は、抵抗変化層201の面内に分散して配置されていることが望ましい。これは、ペルチェ効果によって吸熱される領域は、界面103近傍の局所領域に限られるからである。したがって、複数の界面103が抵抗変化層201の上に分散して配置された構成では、より均一に抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を冷却することができる。図4Aおよび図4Bに示されるように、この構成として、抵抗変化層201の平面が4つの均等な領域に分割されたときに、少なくとも2つの領域に複数の界面103が存在することが好ましい。なお、図4Aおよび図4Bでは、第1配線16、絶縁膜17、絶縁膜202および赤外線吸収層203は省略されている。
As for
また、図5Aおよび図5Bに示されるように、赤外線受光部12Aの平面が複数の領域に均等に分割されたときに、少なくとも2つの領域に渡って一つの界面103が配置されてもよい。この構成により、効率的に赤外線受光部12Aからの吸熱が可能になる。なお、図5Aおよび図5Bでは、第1配線16、絶縁膜17、絶縁膜202および赤外線吸収層203は省略されている。
Also, as shown in FIGS. 5A and 5B, when the plane of the infrared
梁102aおよび梁102bの各々は、ベース基板11に対する抵抗変化層201の断熱性能を高めるために、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成されたフォノニック結晶構造を有している。フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の梁102aにおけるベース基板11に接続された梁102aの一端および抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間112a、ならびに平面視の梁102bにおけるベース基板11に接続された梁102bの一端および抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間112bに設けられていることが望ましい。
Each of
ベース基板11は、典型的には、半導体から構成される。半導体は、例えば、Siである。Siから構成されるベース基板11の上面31には、酸化膜が形成されていてもよい。酸化膜は、例えば、SiO2膜である。
抵抗変化層201は、抵抗温度係数の大きい材料、例えば、アモルファスSiや酸化バナジウム、またはプラチナから構成される。絶縁膜202は、例えば、SiNから構成される。赤外線吸収層203の材料は、金属(例えば、Ti、Cr、Au、Al、Cu、またはNi)または窒化物(例えば、TiNまたはSiN)であることが望ましい。これら以外にも、赤外線吸収層203の材料として、酸化物(例えば、SiO)を用いてもよい。
The
第1配線16は、例えば、ドープされた半導体、または金属から構成される。金属は、例えば、Alである。
The
第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dは、例えば、ドープされた半導体、または金属から構成される。金属は、例えば、Alである。
The
絶縁膜17は、抵抗変化層201をペルチェ素子12Pから電気的に絶縁するために設けられている。絶縁膜17は、例えば、SiNから構成される。
The insulating
電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15bは、例えば、Alから構成される。
The
電極パッド13a、13bは、梁101a、101bに電流を印加する信号処理回路(不図示)に電気的に接続される。なお、当該信号処理回路はベース基板11の上に設けられていてもよいし、ベース基板11の外部に設けられていてもよい。
The
電極パッド15a、15bは、ペルチェ素子12Pに電流を印加する信号処理回路(不図示)に電気的に接続される。なお、当該信号処理回路はベース基板11の上に設けられていてもよいし、ベース基板11の外部に設けられていてもよい。
The
以下の説明は、梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々が有するフォノニック結晶構造に関する。梁101bが有するフォノニック結晶構造を例にとり、その詳細が以下に説明される。なお、この説明は、梁101a、102a、102bにも共通する。
The following description relates to the phononic crystal structure possessed by each of the
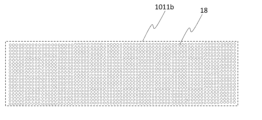
フォノニック結晶構造の一例が図7Aおよび図7Bに示される。図7Aは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、赤外線吸収層203、および梁101bの付近の模式的な拡大図の一例を示す。図7Bは、図7Aのフォノニック結晶構造の領域7Bの拡大図である。梁101bは、例えば、10nm以上500nm以下の厚さを有する薄膜である。梁101bは、平面視において、長方形である。梁101bの長辺の方向は、抵抗変化層201および第2配線14bを結ぶ方向、即ち、赤外線センサ1Aにおけるマクロな熱の伝達方向、と一致している。梁101bには、梁101bの厚さ方向に延びる複数の貫通孔18が設けられている。梁101bが有するフォノニック結晶構造は、複数の貫通孔18が面内方向に規則的に配列された二次元フォノニック結晶構造である。このように、フォノニック結晶構造は、複数の貫通孔18により構成される周期構造を備える。
An example of a phononic crystal structure is shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B. FIG. 7A shows an example of a schematic enlarged view of the vicinity of the
フォノニック結晶領域であるドメインは、複数の貫通孔18の配列の周期をPとして、平面視において、例えば、25P2以上の面積を有する領域である。ここで、図7Bに示されるように、周期Pは、平面視において隣接する貫通孔18間の中心間距離により定められる。
A domain, which is a phononic crystal region, is a region having an area of, for example, 25P 2 or more in plan view, where P is the period of the arrangement of the plurality of through
フォノニック結晶構造によってフォノンの分散関係を制御するには、ドメインは、少なくとも25P2以上の面積を有していてもよい。平面視において正方形のドメインでは、5×P以上の周期とすることで、25P2以上の面積が確保可能である。 Domains may have areas of at least 25P 2 or more to control the phonon dispersion relation through the phononic crystal structure. In a square domain in plan view, an area of 25P 2 or more can be secured by setting the period to 5×P or more.
貫通孔18の配列の周期Pは、例えば、1nm以上300nm以下である。これは、熱を運ぶフォノンの波長が、主として、1nmから300nmの範囲に及ぶためである。梁101a、101b、102a、102bに配列された各貫通孔18の周期は、互いに異ならせてもよいし、同一でもよい。
The period P of the arrangement of the through-
図7Bに示される貫通孔18の開口の形状は円である。複数の貫通孔18の直径Dは、周期Pに対する比D/Pにより表して、例えば、D/P≧0.5である。比D/P<0.5である場合、梁101bにおける空隙率が過度に低下して、熱伝導率が十分に低下しないことがある。ここで、比D/Pの上限は、隣接する貫通孔18同士が接しないために、例えば、0.9未満である。貫通孔18の開口の形状は平面視において円でなくてもよい。この場合、直径Dは、開口の面積と同じ面積を有する仮想の円の直径により定められる。
The shape of the opening of the through-
規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔18により構成される単位格子19の種類は、例えば、正方格子(図6A)、六方格子(図6B)、長方格子(図6C)、及び面心長方格子(図6D)である。ただし、単位格子19の種類は、これらの例に限定されない。フォノニック結晶構造を構成する単位格子19の種類は梁101bの全域に渡って一種類であっても良く、数種類であっても良い。
Types of the
以下、フォノニック結晶構造の例が示される。梁101bが有するフォノニック結晶構造を例にとり、その詳細が以下に説明される。なお、この説明は、梁101a、102a、102bにも共通する。
Examples of phononic crystal structures are given below. Taking the phononic crystal structure of the
図8Aは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、赤外線吸収層203、および梁101bの付近の模式的な拡大図の別の一例を示す。この例では、梁101bは3つのフォノニックドメイン21a、21b、21cを含む。
FIG. 8A shows another example of a schematic enlarged view of the vicinity of the
図8B、図8C、および、図8Dは、それぞれ、フォノニックドメイン21aの一部91、フォノニックドメイン21bの一部92、およびフォノニックドメイン21cの一部93の拡大図を示す。図8Bに示されるように、フォノニックドメイン21aは、径D1および周期P1を有する。図8Cに示されるように、フォノニックドメイン21bは、径D2および周期P2を有する。図8Dに示されるように、フォノニックドメイン21cは、径D3および周期P3を有する。この例では、D1<D2<D3、およびP1<P2<P3が満たされる。すなわち、図8Aに示されるように、赤外線受光部12A側からベース基板11側に向かう方向に沿って、貫通孔18の直径が増大し、かつ、複数の貫通孔18の配列の周期が増大するように配置される。
Figures 8B, 8C, and 8D show enlarged views of a
一例として、周期P1は50nm以下であり、周期P2は50nmより大きく、150nm以下であり、かつ周期P3は150nmより大きく、300nm以下であってもよい。 As an example, the period P1 may be 50 nm or less, the period P2 may be greater than 50 nm and 150 nm or less, and the period P3 may be greater than 150 nm and 300 nm or less.
他の例として、周期P1は50nm以下であり、周期P2は100nm以上150nm以下であり、かつ周期P3は200nm以上300nm以下であってもよい。 As another example, the period P1 may be 50 nm or less, the period P2 may be 100 nm or more and 150 nm or less, and the period P3 may be 200 nm or more and 300 nm or less.
赤外線センサ1Aでは、赤外線を受光した際、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202および赤外線吸収層203の温度が上昇し、梁101bにおいて温度勾配が発生する。このとき、抵抗変化層201側が高温、ベース基板11側が低温となる。このため、梁101bにおいて、抵抗変化層201側における熱の帯域の周波数が、ベース基板11側における熱の帯域の周波数よりも高くなる。したがって、抵抗変化層201側のPBGを高周波に、ベース基板11側のPBGを低周波にするように、すなわち、抵抗変化層201からベース基板11に向かって貫通孔18の周期が増大するように構成することで、より優れた断熱性能が得られる。
In the
なお、フォノニックドメインの数は多ければ多いほど断熱効果は高まる。これは、複数のフォノニックドメインの間において複数の貫通孔18の周期構造が異なれば、梁101bは異なる複数のフォノン分散を持ち、隣り合うフォノニックドメインの間では、フォノン群速度のミスマッチによって界面熱抵抗が発生するためである。隣り合うフォノニックドメインを配列する間隔は周期的でも良いし、ランダムでも良い。
Note that the greater the number of phononic domains, the higher the heat insulating effect. This is because if the periodic structures of the plurality of through-
図9Aは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、赤外線吸収層203、および梁101bの付近の模式的な拡大図のまた別の一例を示す。この例では、梁101bは、フォノニックドメイン21a、21bによって構成されている。フォノニックドメイン21a、21bの各々は、一つの周期構造を構成する複数の貫通孔18同士の間隙に、この周期構造とは異なる周期構造を含む。
FIG. 9A shows yet another example of a schematic enlarged view of the vicinity of the
具体的には、フォノニックドメイン21aは、直径D1の複数の貫通孔18が周期P1で配列された第1周期構造25aの間隙の中に、直径D2の複数の貫通孔18が周期P2(図9B参照)で配列されたもう一つの第2周期構造26aが存在する階層構造からなるマルチ周期構造を含む。フォノニックドメイン21bは、直径D3の複数の貫通孔18が周期P3で配列された第1周期構造25bの間隙の中に、直径D4の複数の貫通孔18が周期P4(図9C参照)で配列されたもう一つの第2周期構造26bが存在する階層構造からなるマルチ周期構造を含む。このように複数の周期構造を一つのフォノニックドメイン内に形成することで、複数のPBGを一度に形成することができる。さらに、複数のPBGで熱の帯域を挟み込むように周期構造を形成すれば、バンド端効果によって熱の帯域のフォノンの群速度を低下させることができる。これにより、さらなる熱伝導率の低減効果が得られる。
Specifically, the
図9Aに示される例でも、図8Aに示される例と同様に、隣り合うフォノニックドメイン間では異なる周期構造を有する。具体的には、梁101bでは、抵抗変化層201側からベース基板11側に向かう方向に沿って、第1周期構造25a、25bおよび第2周期構造26a、26bの周期が増大するように配置される。すなわち、P1<P3、かつP2<P4が満たされる。なお、少なくともP1<P3またはP2<P4のいずれかが満たされれば、上述の図8Aに示される例と同様な効果を得ることができる。
Similar to the example shown in FIG. 8A, the example shown in FIG. 9A also has different periodic structures between adjacent phononic domains. Specifically, in the
例えば、周期P1は150nm以下であり、かつ周期P3は200nm以上300nm以下であってもよい。例えば、周期P2は150nm以下であり、かつ周期P4は200nm以上300nm以下であってもよい。 For example, the period P1 may be 150 nm or less, and the period P3 may be 200 nm or more and 300 nm or less. For example, the period P2 may be 150 nm or less, and the period P4 may be 200 nm or more and 300 nm or less.
なお、図9Aでは、一つのフォノニックドメイン内に2種類の周期構造が形成されているが、一つのフォノニックドメインを構成する周期構造は3種類以上あってもよい。例えば、直径D1の複数の貫通孔が周期P1で配列された第1周期構造25aの間隙の中に、直径D2の貫通孔が周期P2で配列された第2周期構造26aが存在し、さらに第2周期構造26aの間隙に、もう一つの第3周期構造が存在する構造でもよい。
Although two types of periodic structures are formed in one phononic domain in FIG. 9A, one phononic domain may have three or more types of periodic structures. For example, a second
図10Aは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、赤外線吸収層203、および梁101bの付近の模式的な拡大図のさらにまた別の一例を示す。この例では、梁101bは、フォノニックドメイン21a、21bによって構成されている。フォノニックドメイン21aは、直径D1の複数の貫通孔18が周期Ps1(図10B参照)で配列することで形成される複数のミクロ周期構造27aを含む。フォノニックドメイン21bは、直径D2の複数の貫通孔18が周期Ps2(図10C参照)で配列することで形成される複数のミクロ周期構造27bを含む。この例では、D1=D2、かつPs1=Ps2が満たされる。ミクロ周期構造27a、27bはそれぞれ、サブフォノニックドメイン28a、28bと称される。
FIG. 10A shows yet another example of a schematic enlarged view of the vicinity of the
フォノニックドメイン21aを構成するサブフォノニックドメイン28aは、一様な形状からなり、周期Pm1の間隔で配列され、マクロ周期構造29aを形成している。同様に、フォノニックドメイン21bを構成するサブフォノニックドメイン28bは、一様な形状からなり、周期Pm2の間隔で配列され、マクロ周期構造29bを形成している。なお、サブフォノニックドメイン28a、28bの形状は、一様であれば円形でも良く、三角形や四角形、六角形などの多角形でも良い。
The
サブフォノニックドメイン28aの一辺の長さLs(図10A参照)が、フォノニックドメイン21aの全体の形状に対して十分に小さい場合、例えば、本実施形態において、Ls/梁101bの幅W(図10A参照)<0.2の場合、波長の長いフォノンに対して、一つのサブフォノニックドメイン28aは、図11の模式的に示されるように一つの大きな貫通孔として機能する。このため、サブフォノニックドメイン28aは、波長の長いフォノンに対してフォノニック結晶構造として断熱性能を発揮する。サブフォノニックドメイン28bもサブフォノニックドメイン28aと同様の効果を有する。
If the length L s (see FIG. 10A) of one side of the
一方、波長の短いフォノンに対しては、サブフォノニックドメイン28a内のミクロ周期構造27aが断熱性能を発揮する。ミクロ周期構造27bもミクロ周期構造27aと同様の効果を有する。
On the other hand, for phonons with short wavelengths, the
ミクロ周期構造27aを構成する複数の貫通孔18の周期Ps1は、Ps1/Ls≦0.1を満たす必要がある。これは、Ps1/Ls>0.1の場合、長い波長のフォノンはミクロ周期構造27aによって散乱され、フォノニック結晶構造として機能しないためである。
The period P s1 of the plurality of through
このように複数の周期構造を一つのフォノニックドメイン内に形成することで、複数のPBGを一度に形成することができる。複数のPBGで熱の帯域を挟み込むように周期構造を形成することで、バンド端効果によって熱の帯域のフォノンの群速度を低下させることができる。これにより、さらなる熱伝導率の低減効果が得られる。 By forming a plurality of periodic structures in one phononic domain in this way, a plurality of PBGs can be formed at once. By forming a periodic structure so as to sandwich the thermal zone with a plurality of PBGs, the group velocity of phonons in the thermal zone can be reduced by the band edge effect. As a result, a further effect of reducing thermal conductivity is obtained.
図10Aに示される例でも、図8Aに示される例と同様に、隣り合うフォノニックドメイン間では異なる周期構造を有する。具体的には、梁101bでは、図10Aに示すように、抵抗変化層201側からベース基板11側に向かう方向に沿って、マクロ周期構造29a、29bの周期が増大するように配置される。すなわち、Pm1<Pm2が満たされる。この条件が満たされなくても、Ps1<Ps2が満たされれば、上述の図8Aに示される例と同様な効果を得ることができる。
Similar to the example shown in FIG. 8A, the example shown in FIG. 10A also has different periodic structures between adjacent phononic domains. Specifically, in the
ミクロ周期構造27a、27bのそれぞれの周期Ps1、Ps2は、1nmから30nmの範囲内であることが好ましい。一方、マクロ周期構造29a、29bのそれぞれの周期Pm1、Pm2は、ミクロ周期構造27a、27bのそれぞれの周期Ps1、Ps2に応じて、10nmから300nmであることが好ましい。
The respective periods P s1 and P s2 of the
サブフォノニックドメイン28a、28bのそれぞれを構成するミクロ周期構造27a、27bでは、5周期分以上の複数の貫通孔が整列している必要がある。すなわち、5つ以上の貫通孔18を設ける必要がある。この条件はサブフォノニックドメイン28a、28bのそれぞれによって形成されるマクロ周期構造29a、29bにも当てはまる。
In the
フォノニックドメイン21a、21bの形状は円形でも多角形でも良い。
The shape of the
実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの製造方法の一例が以下に説明される。
An example of a method for manufacturing the
まず、Silicon On Insulator(SOI)ウエハ111が用意される。図12Aおよび図12Bに示されるように、SOIウエハ111は、下部のSi層501、中間のSiO2層502、および上部のSi層503からなる積層構造を有する。
First, a Silicon On Insulator (SOI)
SOIウエハ111の代わりに、半導体基板(例えばSi基板)の上に、ポリイミドまたはSiO2からなる犠牲層が形成され、犠牲層の上に厚みが10~500nmのSi薄膜またはSiGe薄膜が形成された積層構造を用いてもよい。
Instead of the
次に、図13A~図13Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびイオン注入により、梁101aとなる領域1011a、梁101bとなる領域1011b、梁102aとなる形成する領域1021a、および梁102bとなる領域1021bにイオンがドープされる。このとき、領域1021a、1021bには互いに異なるドーピング処理が行われる。なお、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bは、四角の外形を有する領域Rに含まれている。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 13A to 13C, photolithography and ion implantation are performed to form a
次に、SOIウエハ111は、熱処理に供される。これにより、ドーピング処理において注入されたイオンが活性化される。
The
次に、複数の貫通孔18が、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bにおいて、周期的に形成される。一例として、複数の貫通孔18が形成された領域1011bの拡大図が図13Dに示される。なお、図13A~図13Cにおいては、貫通孔18の図示は省略されている。100nmから300nmの周期構造を有する貫通孔の作製には電子線リソグラフィーが用いられる。1nmから100nmの周期構造を有する貫通孔の作製にはブロック共重合体リソグラフィーが用いられる。このようにして、フォノニック結晶構造が形成される。
Next, a plurality of through
次に、図14A~図14Eに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびエッチングにより、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bを除いた領域R(図13A)のSi層503が除去され、梁101a、101b、102a、102bを形成する。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 14A to 14E, photolithography and etching are used to remove the
次に、図15A~図15Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィー、エッチング、および公知の薄膜形成方法(例えば、スパッタリング、蒸着、または化学気相成長法(CVD))を用いて、第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dおよび電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15bが形成される。これと並行して、同様の手法を用いて、梁102a、102bを電気的に接続する第1配線16が形成される。そして、フォトリソグラフィーおよび公知の薄膜形成方法により、第1配線16を覆うようにSiNからなる絶縁膜17が形成される。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 15A to 15C, photolithography, etching, and known thin film formation methods (eg, sputtering, vapor deposition, or chemical vapor deposition (CVD)) are used to form the
次に、図16A~図16Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよび公知の薄膜形成方法により抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203が積層され、赤外線受光部12Aを形成する。Ti、TiN、またはSiNからなる赤外線吸収層203が用いられる場合、さらに赤外線吸収層203の上にSiの保護膜を形成してもよい。これは、次の工程において、気相フッ酸エッチングから赤外線吸収層203を保護するためである。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 16A to 16C, a
最後に、図17A~図17Cに示されるように、気相フッ酸エッチングによってSOIウエハ111の中間のSiO2層502が部分的に除去される。
Finally, as shown in FIGS. 17A-17C, the middle SiO 2 layer 502 of the
以上のようにして、実施形態1による赤外線センサ1Aが作製される。
As described above, the
実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの動作が以下に説明される。動作は2段階に分かれる。
The operation of the
第1段階では、梁101a、101bを介して、赤外線吸収層203に入射した赤外線の強度が測定される。具体的には、まず、信号処理回路によって、電極パッド13a、13bおよび第2配線14a、14bを介して定電圧が梁101a、101bに印加され、抵抗変化層201に流れる電流量が信号処理回路によって監視される。次に、赤外線吸収層203に赤外線が入射すると、赤外線吸収層203によって赤外線が吸収される。これにより、赤外線吸収層203、赤外線吸収層203と熱的に接触している絶縁膜202、および抵抗変化層201の温度が上昇する。その結果、抵抗変化層201の温度変化に対応して抵抗変化層201の電気抵抗が変化する。この時の抵抗変化層201の電気抵抗の変化に伴う電流量の変化が信号処理回路において測定され、赤外線の強度が算出される。
At the first stage, the intensity of infrared rays incident on the
後述されるように、実施例1による赤外線センサの梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々はフォノニック結晶構造を有し、実施例1による赤外線センサは優れた検出感度を有する(図32A参照)。一方、比較例1による赤外線センサの梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々はフォノニック結晶構造を有さず、その検出感度は実施例1による赤外線センサのそれよりも劣っている(図32E参照)。なお、図32Aに示されるグラフの縦軸は、信号処理回路において測定された電流値を示す。電流値が大きいほど、検出感度は高い。このように、梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々にフォノニック結晶構造を設けてその断熱性能を高めることで、赤外線センサ1Aの検出感度を高めることができる。
As will be described later, each of the
次に、第2段階に移行する。 Next, the process moves to the second stage.
第2段階では、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203がペルチェ素子12Pを用いて冷却され、赤外線の入射に伴って上昇した抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203の温度が環境温度まで戻される。抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を冷却するために、信号処理回路によって、電極パッド15a、15bおよび第2配線14c、14dを介して梁102a、102bにパルス状の電流が印加される。その結果、ペルチェ効果によって、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203が冷却される。これにより、赤外線受光部12Aの温度を環境温度まで瞬時に冷却することが可能になる。後述されるように、赤外線を遮断後に実施例1による赤外線センサのペルチェ素子12Pに電流を印加することで、立下り時間、すなわち、冷却時間が大幅に短縮される(図32Bおよび図32D参照)。従って、ペルチェ素子12Pによる冷却により、赤外線センサ1Aの応答速度を大幅に高めることができる。
In the second stage, the
なお、フォノニック結晶構造を有する梁102a、102bが優れた断熱性能を有するものの、上述のペルチェ効果が得られる理由は以下の通りである。
Although the
熱は、フォノンと呼ばれる格子振動、または伝導電子によって運ばれる。梁102a、102bにおいてフォノニック結晶構造が設けられているため、格子振動による熱の伝導は抑制されている。一方で、フォノニック結晶構造は、単純に空隙が増えることにより、伝導電子による熱の伝導をごくわずかに抑制するに過ぎない。このため、梁102a、102bに電流を印加することで上述のペルチェ効果が得られる。
Heat is carried by lattice vibrations, called phonons, or conduction electrons. Since the
以上のようにして、赤外線センサ1Aは動作する。
The
赤外線センサ1Aの変形例である赤外線センサ1Bは、図2に示されるように、梁101aおよび梁102aを物理的に接続する絶縁部401a、ならびに梁101bおよび梁102bを物理的に接続する絶縁部401bをさらに備える。これにより、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を中空に維持するための機械強度を高めることができる。なお、絶縁部401a、401bは、絶縁材料から構成されている。このため、梁101aおよび梁102aの間、ならびに梁101bおよび梁102bの間の電気的な絶縁が確保される。
An
赤外線センサ1Aの別の変形例である赤外線センサ1Cは、図3に示されるように、梁101a、101b、102a、102b以外にも梁104a、104bをさらに備える。これにより、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を中空に維持するための機械強度を高めることができる。
An
(実施形態2)
実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dが図18A~図18Cに示される。図18Bには、図18Aの赤外線センサ1Dの断面18B-18Bが示される。図18Cには、図18Aの赤外線センサ1Dの断面18C-18Cが示される。赤外線センサ1Dは、ボロメータ赤外線センサである。
(Embodiment 2)
An
赤外線センサ1Dは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aとは異なり、ベース基板11の上面31に配置された支柱34a、34b、34c、34dをさらに備える。ベース基板11は、凹部32を有していない。支柱34a、34b、34c、34dは、ベース基板11の上面31から離れる方向に延びている。梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々の一端部は、それぞれ、支柱34a、34b、34c、34dに電気的に接続されている。
Unlike the
抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、赤外線吸収層203は、梁101a、101b、102a、102bによって、ベース基板11とは離間した状態で支持されている。図18Bに示されるように、ボロメータ赤外線受光部12A、梁101a、および梁101bは、支柱34a、34bによってベース基板11の上部で懸架されている。また、図18Cに示されるように、ペルチェ素子12P、梁102a、および梁102bは、支柱34cおよび支柱34dによってベース基板11の上部で懸架されている。当該技術分野においてよく知られているように、これらをこのように懸架することで赤外線センサの検出感度が向上する。
The
梁101aは、支柱34aを介して第2配線14aと電気的に接続されている。梁101bは、支柱34bを介して第2配線14bと電気的に接続されている。梁102aは、支柱34cを介して第2配線14cと電気的に接続されている。梁101dは、支柱34dを介して第2配線14dと電気的に接続されている。
The
界面103は、第1配線16および絶縁膜17を介して抵抗変化層201と熱的に接続されている。
The
支柱34a、34b、34c、34dは、導電性材料から構成される。導電性材料は、例えば、金属である。支柱34a、34b、34c、34dの各々を構成する金属は、例えば、Cu、およびAlである。
The
赤外線センサ1Dは、ベース基板11の上面31に赤外線反射膜をさらに有していてもよい。この形態では、赤外線センサ1Dの検出感度をさらに高めることができる。赤外線反射膜を構成する材料は、例えば、Al、およびAuである。
The
フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の梁101aにおける支柱34aおよび抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間111a、平面視の梁101bにおける支柱34bおよび抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間111b、平面視の梁102aにおける支柱34cおよび抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間112a、ならびに平面視の梁102bにおける支柱34dおよび抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間112bに設けられていることが望ましい。
The phononic crystal structure includes a
実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dにおけるその他の構成は、好ましい態様を含め、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける対応する構成と同様である。また、実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dの動作は、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの動作と同じである。
Other configurations of the
実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dの製造方法の一例が以下に説明される。
An example of a method for manufacturing the
まず、ベース基板11として、半導体基板が用意される。半導体基板は、例えば、Siから構成される。
First, a semiconductor substrate is prepared as the
次に、図20に示されるように、電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dがベース基板11の上面31に形成される。電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dの形成には、スパッタリング法、または蒸着法といった薄膜形成手法、およびフォトリソグラフィー法といったパターン形成手法を含む公知の方法が利用可能である。電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dと共に、赤外線反射膜がベース基板11の上面31に形成されてもよい。
Next,
次に、図21A~図21Cに示されるように、ベース基板11の上面31に犠牲層504および梁層505a、505bが順に形成される。犠牲層504は、電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15b、および第2配線14a、14b、14c、14dを覆うように形成される。犠牲層504は、典型的には、樹脂から構成される。犠牲層504の厚さとして、製造する赤外線センサ1Dにおける梁101a、101b、102a、102bおよびベース基板11の離間距離が選択可能である。樹脂は、例えば、ポリイミドである。犠牲層504は、例えば、CVD法、スパッタリング法、またはスピンコーティング法といった公知の薄膜形成手法により形成できる。梁層505aを構成する材料は、例えば、n型Siである。梁層505bを構成する材料は、例えば、p型Siである。梁層505a、505bは、CVD法およびフォトリソグラフィーにより形成できる。梁層505a、505bの各々の厚さは、例えば、10nm以上500nm以下である。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 21A to 21C, a
次に、図22A~図22Cに示されるように、複数の貫通孔18が、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bにおいて、周期的に形成される。なお、図22A~図22Cにおいては、複数の貫通孔18の図示は省略されている。複数の貫通孔18の形成方法は上述の通りである。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 22A-22C, a plurality of through
次に、図23A~図23Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびエッチングにより、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bを除いた領域の梁層505a、505bが除去され、梁101a、101b、102a、102bを形成する。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 23A-23C, photolithography and etching are used to remove the
次に、図24Aおよび図24Bに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびエッチングにより、梁102a、102bを電気的に接続する第1配線16が形成される。そして、フォトリソグラフィーおよび公知の薄膜形成方法により、第1配線16を覆うようにSiNからなる絶縁膜17が形成される。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 24A and 24B, photolithography and etching are used to form the
次に、図25A~図25Cに示されるように、支柱34a、34b、34c、34dが形成される。支柱34a、34b、34c、34dの形成には、支柱34a、34b、34c、34dを形成する空間を確保するための選択的エッチング、および確保した空間に支柱34a、34b、34c、34dを形成するためのスパッタリング法、または蒸着法といった薄膜形成手法が利用可能である。
Next, struts 34a, 34b, 34c, 34d are formed as shown in FIGS. 25A-25C. The formation of the
次に、図26A~図26Cに示されるように、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203が形成される。抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203の各々の構成および形成方法は上記の通りである。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 26A to 26C,
最後に、選択的エッチングによって犠牲層504が除去される。
Finally,
以上のようにして、図18A~図18Cに示される実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dが得られる。
As described above, the
上述のペルチェ素子12Pの代わりに、図18Dに示されるように、界面103を有さないペルチェ素子12Pを用いることができる。この場合、第1配線16が、ペルチェ素子12Pの冷接点に対応する。第1配線16は、絶縁膜17を介して、抵抗変化層201と熱的に接続されている。
Instead of the
赤外線センサ1Dの変形例である赤外線センサ1Eは、図19に示されるように、梁104a、104bをさらに備える。これにより、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を中空に維持するための機械強度を高めることができる。
An
(実施形態3)
実施形態3の赤外線センサ1Fが図27A~図27Cに示される。図27Bには、図27Aの赤外線センサ1Fの断面27B-27Bが示される。図27Cには、図27Aの赤外線センサ1Fの断面27C-27Cが示される。赤外線センサ1Fは、ボロメータ赤外線センサである。
(Embodiment 3)
An
赤外線センサ1Fの赤外線受光部12Bは、実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dの赤外線受光部12Aとは異なり、梁101aの上に形成された薄膜301a、および梁101bの上に形成された薄膜301bをさらに備える。なお、薄膜301aおよび薄膜301bは、それぞれ、ボロメータ第1薄膜およびボロメータ第2薄膜とも称される。
Unlike the infrared
赤外線センサ1Fのペルチェ素子21Pは、実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dのペルチェ素子12Pとは異なり、梁102aの上に形成された薄膜302a、および梁102bの上に形成された薄膜302bをさらに備える。なお、薄膜302aおよび薄膜302bは、それぞれ、ペルチェ第1薄膜およびペルチェ第2薄膜とも称される。
Unlike the
薄膜301a、301b、302a、302bの各々の一端部は、それぞれ、支柱34a、34b、34c、34dに電気的に接続されている。
One end of each of
薄膜301aの他端および301bの他端は、抵抗変化層201に接続されている。
The other ends of the
薄膜302aの他端は薄膜302bの他端に接続され、界面104が形成されている。界面104を跨ぐように、薄膜302a、302bを電気的に接続する第1配線16が薄膜302a、302bの上に形成されている。さらに、第1配線16を覆うように、絶縁膜17が第1配線16、および薄膜302a、302bの上に形成されている。
The other end of the
抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203は、梁101a、101b、102a、102bおよび薄膜301a、301b、302a、302bによって、ベース基板11とは離間した状態で支持されている。図27Bおよび図27Cに示されるように、断面視において、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203および梁101a、101b、102a、102bが、支柱34a、34b、34c、34dによってベース基板11の上部で懸架されている。
The
梁101a、101b、102a、102bの各々は絶縁材料からなる。
Each of the
薄膜301a、301bは、赤外線受光部12Bに入射した赤外線の検出信号を読み出すために用いられる。
The
薄膜301a、301bは、導電性を有する材料からなる。導電性を有する材料は、例えば、熱伝導率の低い金属(例えば、TiまたはTiN)および半導体である。より好ましくは、導電性を有する材料は、不純物が添加されたSiまたはSiGeといった半導体である。
The
薄膜301a、301bの各々は、フォノニック結晶構造を有している。フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の薄膜301aにおける、支柱34aおよび抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間311a、ならびに平面視の薄膜301bにおける、支柱34bおよび抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間311bに設けられていることが望ましい。
Each of
薄膜301a、301bの各々の材料として金属が用いられる場合は、フォノニック結晶構造による断熱効果が現れにくい。この場合、断熱効果を得るために、厚さを10nm以下にすることが望ましい。
When metal is used as the material for each of the
薄膜302a、302bは、熱電対を構成し、ペルチェ素子として機能する。すなわち、薄膜302a、302bは、赤外線受光部12Bで発生した熱を吸熱するために用いられる。界面104がペルチェ素子の冷接点に対応する。界面104は、第1配線16および絶縁膜17を介して抵抗変化層201と熱的に接続されている。薄膜302a、302bの一方は、p型半導体材料からなる。薄膜302a、302bの他方は、n型半導体材料からなる。p型半導体材料およびn型半導体材料の各々は、シリコンプロセスで使用されるシリコン系半導体材料(例えば、SiまたはSiGe)であることが望ましい。
The
薄膜302a、302bの各々は、フォノニック結晶構造を有している。フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の薄膜302aにおける、支柱34cおよび抵抗変化層201の一端の間の区間312a、ならびに平面視の薄膜302bにおける、支柱34dおよび抵抗変化層201の他端の間の区間312bに設けられていることが望ましい。
Each of the
実施形態3の赤外線センサ1Fにおけるその他の構成は、好ましい態様を含め、実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dにおける対応する構成と同様である。また、実施形態3の赤外線センサ1Fの動作は、梁101a、101bの代わりに薄膜301a、薄膜301bが赤外線の検出信号を読み出すこと、梁102a、102bの代わりに薄膜302a、薄膜302bがペルチェ素子として機能することを除いて、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの動作と同じである。
Other configurations of the
当業者は、実施形態2の赤外線センサ1Dの製造方法の記載を参照することにより、実施形態3による赤外線センサ1Fを容易に製造することができる。
A person skilled in the art can easily manufacture the
上述のペルチェ素子21Pの代わりに、図27Dに示されるように、界面104を有さないペルチェ素子を用いることができる。この場合、第1配線16が、ペルチェ素子の冷接点に対応する。第1配線16は、絶縁膜17を介して、抵抗変化層201と熱的に接続されている。
Instead of the
赤外線センサ1Fの変形例である赤外線センサ1Gは、図28に示されるように、梁101aおよび梁102aを物理的に接続する絶縁部401a、および梁101bおよび梁102bを物理的に接続する絶縁部401bをさらに備える。これにより、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を中空に維持するための機械強度を高めることができる。なお、絶縁部401a、401bは、絶縁材料から構成されている。このため、梁101aおよび梁102aの間、並びに梁101bおよび梁102bの間の電気的な絶縁が確保される。
As shown in FIG. 28, an
赤外線センサ1Fの別の変形例である赤外線センサ1Hは、図29に示されるように、梁104a、104bをさらに備える。これにより、抵抗変化層201、絶縁膜202、および赤外線吸収層203を中空に維持するための機械強度を高めることができる。
An
(実施形態4)
実施形態4の赤外線センサ1Iが図30A~図30Cに示される。図30Bには、図30Aの赤外線センサ1Iの断面30B-30Bが示される。図30Cには、図30Aの赤外線センサ1Iの断面30C-30Cが示される。赤外線センサ1Iは、サーモパイル赤外線センサである。
(Embodiment 4)
An infrared sensor 1I of
赤外線センサ1Iの赤外線受光部12Cは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの赤外線受光部12Aとは異なり、梁101a、101b、赤外線吸収層203、第1配線16a、絶縁膜17aを備える。
Unlike the infrared
梁101aの一端および梁101bの一端は、ベース基板11に接続されている。梁101aの他端は梁101bの他端に接続され、界面103aが形成されている。赤外線センサ1Iは、第1配線16aおよび絶縁膜17aをさらに備える。第1配線16aは、界面103aを跨ぐように梁101a、101bの上に形成されている。第1配線16aは、梁101a、101bを電気的に接続している。絶縁膜17aは、第1配線16a、梁101a、および梁101bの上に形成されている。
One end of the
梁101a、101bは、赤外線吸収層203に入射した赤外線の検出信号を読み出すために用いられる。梁101a、101bの一方は、p型半導体材料からなる。梁101a、101bの他方は、n型半導体材料からなる。なお、梁101aおよび梁101bは、それぞれ、サーモパイル第1梁およびサーモパイル第2梁とも称される。
The
赤外線センサ1Iのペルチェ素子12Pは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aのペルチェ素子12Pと同じ構成を有する。
The
実施形態4の赤外線センサ1Iにおけるその他の構成は、好ましい態様を含め、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aにおける対応する構成と同様である。
Other configurations of the infrared sensor 1I of the fourth embodiment are the same as corresponding configurations of the
実施形態4の赤外線センサ1Iの動作が以下に説明される。
The operation of the infrared sensor 1I of
赤外線吸収層203に赤外線が入射すると、赤外線吸収層203によって赤外線が吸収される。これにより、赤外線受光部12B、および絶縁膜17aを介して赤外線吸収層203と熱的に接触している梁101a、101bの温度が上昇する。その結果、梁101a、101bでは、赤外線吸収層203からベース基板11に向かう方向に温度差が生じる。これにより、梁101a、101bでは、ゼーベック効果による起電力が生じる。生じた起電力が、電極パッド13a、13bに接続された信号処理回路で測定され、赤外線の検出強度が算出される。
When infrared rays are incident on the
この後、ペルチェ素子によって赤外線吸収層203が冷却される。この冷却方法は、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの冷却方法と同じである。
After that, the
以上のようにして、赤外線センサ1Iは動作する。 The infrared sensor 1I operates as described above.
当業者は、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aの製造方法の記載を参照することにより、実施形態4による赤外線センサ1Iを容易に製造することができる。
A person skilled in the art can easily manufacture the infrared sensor 1I according to the fourth embodiment by referring to the description of the manufacturing method of the
上述のペルチェ素子12Pの代わりに、図30Dに示されるように、界面103bを有さないペルチェ素子12Pを用いることができる。この場合、第1配線16bが、ペルチェ素子の冷接点に対応する。第1配線16bは、絶縁膜17bを介して、抵抗変化層201と熱的に接続されている。
Instead of the
赤外線センサ1Iの変形例である赤外線センサ1Jは、図31Aおよび図31Bに示されるように、絶縁層222、梁101c、101d、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102l、および第1配線16c、16d、16e、16f、16g、16h、16i、16j、16k、16l、16m、16nをさらに備える。
An
絶縁層222は、例えば、Siからなる。
The insulating
第1配線16a、16c、16d、16f、16h、16j、16l、16nは、絶縁層222の上に形成されている。
The
赤外線吸収層203は絶縁層222の上に形成されている。
The infrared
梁101a、101b、101c、101d、102a、102b、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102lの各々の一端は絶縁層222に接続されている。
One end of each of
梁101a、101b、101c、101d、102a、102b、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102lの各々の他端はベース基板11に接続されている。
The other ends of the
梁101a、101b、101c、101dは、第1配線16a、16b、16cによって電気的に直列に接続されている。梁101a、101cおよび梁101b、101dの各々の一方は、p型半導体材料からなる。梁101a、101cおよび梁101b、101dの各々の他方は、n型半導体材料からなる。
The
梁101a、101b、101c、101d、102a、102b、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102lの各々は、フォノニック結晶構造を有している。
Each of the
梁102a、102b、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102lは、第1配線16d、16e、16f、16g、16h、16i、16j、16k、16l、16m、16nによって電気的に直列に接続されている。梁102a、102c、102e、102g、102i、102kおよび梁102b、102d、102f、102h、102j、102lの各々の一方は、p型半導体材料からなる。梁102a、102c、102e、102g、102i、102kおよび梁102b、102d、102f、102h、102j、102lの各々の他方は、n型半導体材料からなる。第1配線16d、16f、16h、16j、16l、16nは、ペルチェ素子の冷接点に対応する。赤外線吸収層203は、絶縁層222を介して間接的に冷却される。赤外線センサ1Jは複数の冷接点を有するため、より優れた冷却効果を有する。
The
(実施例1)
実施例1による赤外線センサは、実施形態1の赤外線センサ1Aと同様の構成を有して
いた。
(Example 1)
The infrared sensor according to Example 1 had the same configuration as the
半導体プロセスを用いて、実施例1による赤外線センサが以下のようにして作製された。
まず、SOIウエハ111(信越化学工業株式会社製)が購入された。図12Aおよび図12Bに示されるように、SOIウエハ111は、厚みが625μmの下部のSi層501、厚みが2μmの中間のSiO2層502および厚みが150nmの上部のSi層503からなる積層構造を有していた。
Using a semiconductor process, an infrared sensor according to Example 1 was produced as follows.
First, an SOI wafer 111 (manufactured by Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.) was purchased. As shown in FIGS. 12A and 12B, the
次に、図13A~図13Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびイオン注入により、梁101aとなる領域1011a、梁101bとなる領域1011b、梁102aとなる領域1021a、および梁102bとなる領域1021bの各々に後述されるイオンがドープされた。なお、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bは四角の外形を有する領域Rに含まれている。領域1011a、1011bの各々は、20keVの加速電圧、9.3×1014原子/cm2のドーズ量でホウ素(B)によりドープされた。一方で、領域1021aは、20keVの加速電圧、9.3×1014原子/cm2のドーズ量でホウ素によりドープされた。領域1021bは、55keVの加速電圧、9.0×1014原子/cm2のドーズ量でリンによりドープされた。そして、SOIウエハ111は、1000℃の窒素雰囲気下で5分間、熱処理に供された。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 13A to 13C, photolithography and ion implantation are performed to form a
次に、直径が80nmの複数の貫通孔18が、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bにおいて、電子線リソグラフィーおよびエッチングにより、100nm毎に周期的に形成された。図13Dは、複数の貫通孔18が形成された領域1011bの拡大図を示す。このようにして、フォノニック結晶構造が形成された。周期100nmに対する貫通孔18の直径80nmの比は0.8であった。
A plurality of through-
次に、図14A~図14Eに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびエッチングにより、領域1011a、1011b、1021a、1021bを除いた領域R(図13A)のSi層503が除去され、梁101a、101b、102a、102bを形成した。梁101a、101bの各々は、1μmの幅W1および14μmの長さL1を有していた。ペルチェ素子として機能する梁102a、102bの各々は、1μmの幅W2および16μmの長さL2を有していた。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 14A to 14E, photolithography and etching are used to remove the
次に、図15A~図15Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびスパッタリングにより100nmの厚みを有するAlからなる第2配線14a、14b、14c、14d、および100nmの厚みを有するAlからなる電極パッド13a、13b、15a、15bが形成された。これと並行して、フォトリソグラフィーおよびスパッタリングにより梁102a、102bを電気的に接続する厚み100nmのAlからなる第1配線16が形成された。そして、フォトリソグラフィーおよびスパッタリングにより、第1配線16を覆うように厚み30nmのSiNからなる絶縁膜17が形成された。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 15A to 15C,
次に、図16A~図16Cに示されるように、フォトリソグラフィーおよびスパッタリングにより、アモルファスSiからなる抵抗変化層201、SiNからなる絶縁膜202、およびCrからなる赤外線吸収層203が積層され、赤外線受光部12Aを形成した。赤外線受光部12Aは、12μm×12μmの大きさを有していた。抵抗変化層201は200nmの厚みを有していた。絶縁膜202は30nmの厚みを有していた。赤外線吸収層203は5nmの厚みを有していた。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 16A to 16C, a
最後に、図17A~図17Cに示されるように、気相フッ酸エッチングによってSiO2層502が部分的に除去された。このようにして、実施例1による赤外線センサが作製された。 Finally, the SiO 2 layer 502 was partially removed by vapor-phase hydrofluoric acid etching, as shown in FIGS. 17A-17C. Thus, an infrared sensor according to Example 1 was produced.
(実施例2)
電子線リソグラフィーの代わりにブロック共重合体リソグラフィーを用いて、直径が27.2nmの貫通孔18が34nm毎に周期的に形成されたことを除いては、実施例1と同様に、赤外線センサが作製された。周期34nmに対する貫通孔18の直径27.2nmの比は、実施例1と同様に0.8であった。従って、実施例1および実施例2において、空隙率は等しい。ここで、空隙率とは、平面視における複数の貫通孔18の面積の総和が領域1011a、1011b、1021aまたは1021bの面積に占める割合を意味する。例えば、領域1011aの面積をS1(図13A)、領域1011aに形成された貫通孔18の個数をn1、および各貫通孔18の面積をs1(図7B)とすると、空隙率は、n1×s1/S1によって算出される。
(Example 2)
In the same manner as in Example 1, except that block copolymer lithography was used instead of electron beam lithography, and through-
(比較例1)
貫通孔18が形成されなかったことを除いては、実施例1と同様のプロセスを用いて赤外線センサが作製された。
(Comparative example 1)
An infrared sensor was fabricated using the same process as in Example 1, except that the through
(ペルチェ素子の性能)
実施例1、2および比較例1による赤外線センサのペルチェ効果の性能が検証された。3mAの定常電流を梁102a、102bに流すことにより赤外線受光部12Aを冷却しながら、2Vの定常電圧が梁101a、101bに印加された。このときの抵抗変化層201を流れる電流が測定され、その抵抗変化から赤外線受光部12Aの温度が算出された。冷却前の赤外線受光部12Aの温度は25.0℃であった。
(Performance of Peltier device)
The Peltier effect performance of the infrared sensors according to Examples 1 and 2 and Comparative Example 1 was verified. A steady voltage of 2V was applied to the
表1は実施例1、2および比較例1の結果を示す。 Table 1 shows the results of Examples 1, 2 and Comparative Example 1.
表1から明らかなように、実施例1および2による赤外線センサのペルチェ効果は、比較例1による赤外線センサのペルチェ効果よりも優れている。また、ペルチェ素子として機能する梁102a、102bの各々がフォノニック結晶を有する場合、フォノニック結晶の周期が小さくなるにつれて、ペルチェ素子の冷却性能を高められることがわかる。
As is clear from Table 1, the Peltier effects of the infrared sensors according to Examples 1 and 2 are superior to the Peltier effect of the infrared sensor according to Comparative Example 1. Moreover, when each of the
(時間応答試験)
実施例1および比較例1による赤外線センサが時間応答試験に供された。時間応答試験において、まず、信号処理回路によって、電極パッド13a、13bおよび第2配線14a、14bを介して定電圧が梁101a、101bに印加され、抵抗変化層201に流れる電流量が信号処理回路によって監視された。次に、赤外線が赤外線受光部12Aに5ms間照射された。この後、赤外線が遮断された。これと同時に25μAのパルス電流が梁102a、102bに印加され始めた直後に、25μAのパルス電流が梁102a、102bに0.010ms間印加された。
(Time response test)
The infrared sensors according to Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 were subjected to a time response test. In the time response test, first, the signal processing circuit applies a constant voltage to the
図32Aは、実施例1による赤外線センサの梁102に電流が印加されたときの時間応答試験の結果を示すグラフである。図32Bは、図32Aの点線で囲まれた部分Bの拡大図である。図32Cは、実施例1による赤外線センサの梁102に電流が印加されなかったときの時間応答試験の結果を示すグラフである。図32Dは、図32Cの点線で囲まれた部分Dの拡大図である。図32Eは、比較例1による赤外線センサの梁102に電流が印加されなかったときの時間応答試験の結果を示すグラフである。 32A is a graph showing the results of a time response test when current is applied to beam 102 of the infrared sensor according to Example 1. FIG. FIG. 32B is an enlarged view of portion B enclosed by a dotted line in FIG. 32A. 32C is a graph showing the results of a time response test when no current was applied to beam 102 of the infrared sensor according to Example 1. FIG. FIG. 32D is an enlarged view of portion D enclosed by a dotted line in FIG. 32C. 32E is a graph showing the results of a time response test when no current was applied to beam 102 of the infrared sensor according to Comparative Example 1. FIG.
図32Aおよび図32Eから明らかなように、実施例1による赤外線センサの抵抗変化層201の電流値は、比較例1による赤外線センサの抵抗変化層201の電流値よりも大きい。すなわち、フォノニック結晶を有する実施例1による赤外線センサは、フォノニック結晶を有さない比較例1による赤外線センサよりも優れた検出感度を有する。
32A and 32E, the current value of
また、図32Bおよび図32Dから明らかなように、梁102a、102bを流れるパルス電流によって、立下り時間が0.4msから0.015msまで大幅に減少する。ここで、赤外線の遮断時の時刻をt0、時刻t0における電流値をI0、赤外線の遮断後、電流値がI0×exp(-1)になる時刻をt1とする。立下り時間は、t1-t0で定義される。第1の赤外線の遮断後に立下り時間が短ければ、次に赤外線受光部12Aに入射する第2の赤外線を、第1の赤外線の遮断後から短時間で正確に検出し始めることができる。このため、例えば、離れた対象物の温度を測定する場合には、対象物の温度の低下をすばやく検出することができる。
Also, as can be seen from Figures 32B and 32D, the pulsed current through
以上から、ペルチェ素子を用いて赤外線受光部12Aを冷却することにより、赤外線センサの応答速度(すなわち、第1の赤外線の遮断後から第2の赤外線を正確に検出し始めるまでの時間の短さ)を向上することができる。
From the above, by cooling the infrared
本開示の構成において、優れた検出感度および優れた応答速度を両立することができる赤外線センサを提供することができる。 In the configuration of the present disclosure, it is possible to provide an infrared sensor capable of achieving both excellent detection sensitivity and excellent response speed.
上記の開示内容から導出される発明は以下の通りである。 Inventions derived from the above disclosure are as follows.
(項目A1)
赤外線センサであって、
ベース基板、
ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第1支柱
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第2支柱、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第3支柱、および
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第4支柱、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第1梁、および
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁およびn型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端部、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端部、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端部、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端部は、それぞれ、前記第1支柱、前記第2支柱、前記第3支柱、および前記第4支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ボロメータ第1梁、および前記ボロメータ第2梁は、前記第1支柱および前記第2支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ペルチェ素子、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記第3支柱および前記第4支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備する、
赤外線センサ。
(Item A1)
an infrared sensor,
base board,
bolometer infrared receiver and Peltier element,
a first post extending away from the base substrate; a second post extending away from the base substrate;
a third pillar extending away from the base substrate; and a fourth pillar extending away from the base substrate;
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a first bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer; and a second bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer;
is equipped with
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
The Peltier element comprises a first Peltier beam made of p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam made of n-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
One end of the first bolometer beam, one end of the second bolometer beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are, respectively, the first support, the second support, connected to the third strut and the fourth strut,
The bolometer infrared light receiving unit, the first bolometer beam, and the second bolometer beam are suspended above the base substrate by the first support and the second support,
The Peltier element, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate by the third support and the fourth support,
The first bolometer beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second bolometer beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes comprising a fourth phononic crystal structure
Infrared sensor.
(項目A2)
項目A1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1梁における、前記第1支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2梁における、前記第2支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記第3支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記第4支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。
(Item A2)
The infrared sensor according to item A1,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between the first support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between the second support and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second bolometer beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between the third support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between the fourth support and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view.
(項目A3)
項目A1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。
(Item A3)
The infrared sensor according to item A1,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
(項目A4)
項目A3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item A4)
The infrared sensor according to item A3,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目A5)
項目A1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層に熱的に接続されている。
(Item A5)
The infrared sensor according to item A1,
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is thermally connected to the variable resistance layer.
(項目A6)
項目A1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端は、前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されておらず、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、前記ペルチェ第2梁に第1配線によって電気的に接続されており、
前記第1配線は、前記抵抗変化層と熱的に接続されている。
(Item A6)
The infrared sensor according to item A1,
The other end of the first Peltier beam is not connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam,
The first Peltier beam is electrically connected to the second Peltier beam by a first wiring,
The first wiring is thermally connected to the variable resistance layer.
(項目A7)
項目A5に記載の赤外線センサであって、
平面視において、前記抵抗変化層は面積が等しい4つの領域を有し、
前記界面は、少なくとも2つの前記領域に接する。
(Item A7)
The infrared sensor according to item A5,
In a plan view, the variable resistance layer has four regions of equal area,
The interface borders at least two of the regions.
(項目A8)
項目A3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、および前記第4ドメインは、それぞれ、前記第1フォノニック結晶構造、前記第2フォノニック結晶構造、前記第3フォノニック結晶構造、および前記第4フォノニック結晶構造を含み、
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第5ドメイン、第6ドメイン、第7ドメイン、および第8ドメインを含み、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第5フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第6フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第7フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第8ドメインにおいて、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第8フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第5周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第6周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第7周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ
前記第8周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item A8)
The infrared sensor according to item A3,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
The first domain, the second domain, the third domain, and the fourth domain are the first phononic crystal structure, the second phononic crystal structure, the third phononic crystal structure, and the fourth phononic crystal structure, respectively. contains a crystal structure,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a fifth domain, a sixth domain, a seventh domain, and an eighth domain;
A fifth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period is formed in the fifth domain,
A sixth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period is formed in the sixth domain,
A seventh phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period is formed in the seventh domain,
an eighth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in an eighth period is formed in the eighth domain,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
the value of the fifth period is greater than the value of the first period;
the value of the sixth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the seventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and the value of the eighth period is greater than the value of the fourth period.
(項目A9)
項目A8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメインにおいて、前記第1ドメインに前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第1周期とは異なる第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第2ドメインにおいて、前記第2ドメインに前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第2周期とは異なる第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第3ドメインにおいて、前記第3ドメインに前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第3周期とは異なる第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第4ドメインにおいて、前記第4ドメインに前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第4周期とは異なる第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、前記第5ドメインに前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第5周期とは異なる第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、前記第6ドメインに前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第6周期とは異なる第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、前記第7ドメインに前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第7周期とは異なる第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、かつ
前記第8ドメインにおいて、前記第8ドメインに前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第8周期とは異なる第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されている。
(Item A9)
The infrared sensor according to item A8,
In the first domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period in the first domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a ninth period different from the first period through holes are formed,
In the second domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period in the second domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a tenth period different from the second period through holes are formed,
In the third domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period in the third domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in an eleventh period different from the third period through holes are formed,
In the fourth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period in the fourth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 12th period different from the fourth period through holes are formed,
In the fifth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period in the fifth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a thirteenth period different from the fifth period through holes are formed,
In the sixth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the sixth domain in the sixth period, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 14th period different from the sixth period through holes are formed,
In the seventh domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the seventh period in the seventh domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a fifteenth period different from the seventh period and in the eighth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth domain in the eighth period, a period different from the eighth period is formed. A plurality of through holes arranged regularly in 16 cycles are formed.
(項目A10)
項目A8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数の各々は、5つ以上である。
(Item A10)
The infrared sensor according to item A8,
The number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period number of the plurality of through holes, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period, in the sixth period the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged, the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the seventh period, and the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the eighth period is 5 or more.
(項目A11)
項目A8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、前記第4ドメイン、前記第5ドメイン、前記第6ドメイン、前記第7ドメイン、および前記第8ドメインの各々を構成する周期構造の単位格子は、正方格子、六方格子、長方格子、または面心長方格子のいずれかである。
(Item A11)
The infrared sensor according to item A8,
A unit cell having a periodic structure that constitutes each of the first domain, the second domain, the third domain, the fourth domain, the fifth domain, the sixth domain, the seventh domain, and the eighth domain is either a square lattice, a hexagonal lattice, a rectangular lattice, or a face-centered rectangular lattice.
(項目A12)
項目A8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、前記第4周期、前記第5周期、前記第6周期、前記第7周期、および前記第8周期の各々の値は、1nm以上かつ300nm以下である。
(Item A12)
The infrared sensor according to item A8,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, the fourth period, the fifth period, the sixth period, the seventh period, and the eighth period is 1 nm or more and 300 nm. It is below.
(項目A13)
項目A8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第1周期の値で除した値、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第2周期の値で除した値、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第3周期の値で除した値、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第4周期の値で除した値、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第5周期の値で除した値、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第6周期の値で除した値、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第7周期の値で除した値、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第8周期の値で除した値の各々は、0.5以上かつ0.9以下である。
(Item A13)
The infrared sensor according to item A8,
The value obtained by dividing the diameter value of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period by the value in the first period, the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter by the value of the second period, a value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period by the value of the third period , A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fourth period by the value of the fourth period, the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fifth period The value obtained by dividing the value of the fifth period by the value of the fifth period, the value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the sixth period by the value of the sixth period, the A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in seven periods by the value of the seventh period, and the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth period is divided by the value of the eighth period is 0.5 or more and 0.9 or less.
(項目A14)
項目A1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメインは、第1周期で規則的に配列された複数の第1サブドメインを具備し、
前記第2ドメインは、第2周期で規則的に配列された複数の第2サブドメインを具備し、
前記第3ドメインは、第3周期で規則的に配列された複数の第3サブドメインを具備し、
前記第4ドメインは、第4周期で規則的に配列された複数の第4サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第1サブドメインの各々は、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第2サブドメインの各々は、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第3サブドメインの各々は、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、かつ
前記複数の第4サブドメインの各々は、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されている。
(Item A14)
The infrared sensor according to item A1,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
the first domain comprises a plurality of first subdomains regularly arranged in a first period;
the second domain comprises a plurality of second subdomains regularly arranged in a second period;
the third domain comprises a plurality of third subdomains regularly arranged in a third period;
the fourth domain comprises a plurality of fourth subdomains regularly arranged in a fourth period;
Each of the plurality of first subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period,
Each of the plurality of second subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period,
Each of the plurality of third subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period, and each of the plurality of fourth subdomains is formed of a It is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged at intervals.
(項目A15)
項目A14に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、第5ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、第6ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、第7ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、第8ドメインをさらに含み、
前記第5ドメインは、第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の第5サブドメインを具備し、
前記第6ドメインは、第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の第6サブドメインを具備し、
前記第7ドメインは、第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の第7サブドメインを具備し、
前記第8ドメインは、第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の第8サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第5サブドメインの各々は、第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第6サブドメインの各々は、第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第7サブドメインの各々は、第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第8サブドメインの各々は、第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第9周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第10周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第11周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ、
前記第12周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item A15)
The infrared sensor according to item A14,
the bolometer first beam further includes a fifth domain;
the second bolometer beam further includes a sixth domain;
The Peltier first beam further includes a seventh domain,
The Peltier second beam further includes an eighth domain,
The fifth domain comprises a plurality of fifth subdomains regularly arranged in a ninth period,
The sixth domain comprises a plurality of sixth subdomains regularly arranged in a tenth period,
The seventh domain comprises a plurality of seventh subdomains regularly arranged in an 11th period,
The eighth domain comprises a plurality of eighth subdomains regularly arranged in a 12th period,
Each of the plurality of fifth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 13th period,
Each of the plurality of sixth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 14th period,
Each of the plurality of seventh subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 15th period,
Each of the plurality of eighth subdomains is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 16th period,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
The value of the ninth period is greater than the value of the first period,
the value of the tenth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the eleventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and
The value of the 12th period is greater than the value of the 4th period.
(項目A16)
赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、以下を具備する:
(a)以下を具備する前記赤外線センサを用意する工程、
凹部を有するベース基板、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第1支柱
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第2支柱、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第3支柱、および
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第4支柱、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第1梁、および
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁およびn型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端部、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端部、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端部、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端部は、それぞれ、前記第1支柱、前記第2支柱、前記3支柱、および前記第4支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ボロメータ第1梁、および前記ボロメータ第2梁は、前記第1支柱および前記第2支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ペルチェ素子、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記第3支柱および前記第4支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
(b)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に前記赤外線を入射させる工程、
(c)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に入射していた前記赤外線を遮断する工程、および
(d)前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁に電流を印加し、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する工程。
(Item A16)
A method of cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor comprising:
(a) providing the infrared sensor comprising:
a base substrate having a recess;
the bolometer infrared receiver, and a Peltier element,
a first post extending away from the base substrate; a second post extending away from the base substrate;
a third pillar extending away from the base substrate; and a fourth pillar extending away from the base substrate;
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a first bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer; and a second bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer;
is equipped with
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
The Peltier element comprises a first Peltier beam made of p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam made of n-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
One end of the first bolometer beam, one end of the second bolometer beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are, respectively, the first support, the second support, connected to the three struts and the fourth strut,
The bolometer infrared light receiving unit, the first bolometer beam, and the second bolometer beam are suspended above the base substrate by the first support and the second support,
The Peltier element, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate by the third support and the fourth support,
The first bolometer beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second bolometer beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes comprising a fourth phononic crystal structure,
(b) making the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver;
(c) blocking the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver; and ( d ) applying a current to the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam to cool the bolometer infrared receiver. .
(項目A17)
項目A16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1梁における、前記ボロメータ第1梁の他端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2梁における、前記ボロメータ第2梁の他端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。
(Item A17)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item A16,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between the other end of the first bolometer beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between the other end of the second bolometer beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second bolometer beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between the other end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between the other end of the second Peltier beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view.
(項目A18)
項目A16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。
(Item A18)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item A16,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
(項目A19)
項目A18に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item A19)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor according to item A18,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目A20)
項目A16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。
(Item A20)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item A16,
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is sandwiched between the variable resistance layer and the recess.
(項目B1)
赤外線センサであって、
ベース基板、
ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第1支柱
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第2支柱、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第3支柱、および
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第4支柱、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
第1絶縁材料から形成されているボロメータ第1梁、
第2絶縁材料から形成されているボロメータ第2梁、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の上に形成されたボロメータ第1薄膜、および
前記ボロメータ第2梁の上に形成されたボロメータ第2薄膜、
を具備しており、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜は、前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、
第3絶縁材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁、
第4絶縁材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の上に形成されたペルチェ第1薄膜、および
前記ペルチェ第2梁の上に形成されたペルチェ第2薄膜、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、p型半導体材料から形成されており、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、n型半導体材料から形成されており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端部および前記ボロメータ第1薄膜の一端部は、前記第1支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端部および前記ボロメータ第2薄膜の一端部は、前記第2支柱に接続されており、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端部および前記ペルチェ第1薄膜の一端部は、前記第3支柱に接続されており、
前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端部および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の一端部は、前記第4支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第1薄膜、前記ボロメータ第2梁、および前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、前記第1支柱および前記第2支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ペルチェ素子、前記ペルチェ第1梁、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜、前記ペルチェ第2梁、および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、前記第3支柱および前記第4支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備する、
赤外線センサ。
(Item B1)
an infrared sensor,
base board,
bolometer infrared receiver and Peltier element,
a first post extending away from the base substrate; a second post extending away from the base substrate;
a third pillar extending away from the base substrate; and a fourth pillar extending away from the base substrate;
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a bolometer first beam formed from a first insulating material;
a second bolometer beam formed from a second insulating material;
a bolometer first thin film formed on the bolometer first beam; and a bolometer second thin film formed on the bolometer second beam;
is equipped with
The bolometer first thin film is electrically connected to the variable resistance layer,
The bolometer second thin film is electrically connected to the variable resistance layer,
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
The Peltier element is
a Peltier first beam formed from a third insulating material;
a Peltier second beam formed from a fourth insulating material;
a Peltier first thin film formed on the Peltier first beam; and a Peltier second thin film formed on the Peltier second beam;
is equipped with
The Peltier first thin film is made of a p-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier first thin film is made of an n-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
One end of the first bolometer beam and one end of the first bolometer thin film are connected to the first support,
One end of the second bolometer beam and one end of the second bolometer thin film are connected to the second support,
one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the first Peltier thin film are connected to the third support,
one end of the second Peltier beam and one end of the second Peltier thin film are connected to the fourth support,
The bolometer infrared receiver, the first bolometer beam, the first bolometer thin film, the second bolometer beam, and the second bolometer thin film are suspended above the base substrate by the first support and the second support. and
The Peltier element, the first Peltier beam, the first Peltier thin film, the second Peltier beam, and the second Peltier thin film are suspended above the base substrate by the third support and the fourth support. ,
The bolometer first thin film has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The bolometer second thin film has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier thin film has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier thin film is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes. comprising a fourth phononic crystal structure
Infrared sensor.
(項目B2)
項目B1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1薄膜における、前記第1支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2薄膜における、前記第2支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1薄膜における、前
記第3支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2薄膜における、前記第4支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。
(Item B2)
The infrared sensor according to item B1,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between the first support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer thin film in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between the second support and the other end of the resistance change layer in the planar view of the second bolometer thin film,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between the third support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the Peltier first thin film in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between the fourth support and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier thin film in plan view.
(項目B3)
項目B1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。
(Item B3)
The infrared sensor according to item B1,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
(項目B4)
項目B3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item B4)
The infrared sensor according to item B3,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目B5)
項目B1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜の他端が前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層と熱的に接続されている。
(Item B5)
The infrared sensor according to item B1,
the other end of the first Peltier thin film is connected to the other end of the second Peltier thin film to form an interface between the first Peltier thin film and the second Peltier thin film;
The interface is thermally connected to the variable resistance layer.
(項目B6)
項目B1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜の他端は、前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の他端に接続されておらず、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、前記ペルチェ第2薄膜に第1配線によって電気的に接続されており、
前記第1配線は、前記抵抗変化層と熱的に接続されている。
(Item B6)
The infrared sensor according to item B1,
The other end of the first Peltier thin film is not connected to the other end of the second Peltier thin film,
The Peltier first thin film is electrically connected to the Peltier second thin film by a first wiring,
The first wiring is thermally connected to the variable resistance layer.
(項目B7)
項目B5に記載の赤外線センサであって、
平面視において、前記抵抗変化層は面積が等しい4つの領域を有し、
前記界面は、少なくとも2つの前記領域に接する。
(Item B7)
The infrared sensor according to item B5,
In plan view, the variable resistance layer has four regions of equal area,
The interface borders at least two of the regions.
(項目B8)
項目B3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜、前記ボロメータ第2薄膜、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜、および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、および前記第4ドメインは、それぞれ、前記第1フォノニック結晶構造、前記第2フォノニック結晶構造、前記第3フォノニック結晶構造、および前記第4フォノニック結晶構造を含み、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜、前記ボロメータ第2薄膜、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜、および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、それぞれ、第5ドメイン、第6ドメイン、第7ドメイン、および第8ドメインを含み、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第5フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第6フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第7フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第8ドメインにおいて、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第8フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第5周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第6周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第7周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ
前記第8周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item B8)
The infrared sensor according to item B3,
the bolometer first thin film, the bolometer second thin film, the Peltier first thin film, and the Peltier second thin film respectively include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
The first domain, the second domain, the third domain, and the fourth domain are the first phononic crystal structure, the second phononic crystal structure, the third phononic crystal structure, and the fourth phononic crystal structure, respectively. contains a crystal structure,
the bolometer first thin film, the bolometer second thin film, the Peltier first thin film, and the Peltier second thin film each include a fifth domain, a sixth domain, a seventh domain, and an eighth domain;
A fifth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period is formed in the fifth domain,
A sixth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period is formed in the sixth domain,
A seventh phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period is formed in the seventh domain,
an eighth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in an eighth period is formed in the eighth domain,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
the value of the fifth period is greater than the value of the first period;
the value of the sixth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the seventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and the value of the eighth period is greater than the value of the fourth period.
(項目B9)
項目B8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメインにおいて、前記第1ドメインに前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第1周期とは異なる第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第2ドメインにおいて、前記第2ドメインに前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第2周期とは異なる第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第3ドメインにおいて、前記第3ドメインに前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第3周期とは異なる第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第4ドメインにおいて、前記第4ドメインに前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第4周期とは異なる第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、前記第5ドメインに前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第5周期とは異なる第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、前記第6ドメインに前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第6周期とは異なる第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、前記第7ドメインに前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第7周期とは異なる第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、かつ
前記第8ドメインにおいて、前記第8ドメインに前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第8周期とは異なる第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されている。
(Item B9)
The infrared sensor according to item B8,
In the first domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period in the first domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a ninth period different from the first period through holes are formed,
In the second domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period in the second domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a tenth period different from the second period through holes are formed,
In the third domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period in the third domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in an eleventh period different from the third period through holes are formed,
In the fourth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period in the fourth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 12th period different from the fourth period through holes are formed,
In the fifth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period in the fifth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a thirteenth period different from the fifth period through holes are formed,
In the sixth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the sixth domain in the sixth period, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 14th period different from the sixth period through holes are formed,
In the seventh domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the seventh period in the seventh domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a fifteenth period different from the seventh period and in the eighth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth domain in the eighth period, a period different from the eighth period is formed. A plurality of through holes are formed which are regularly arranged in 16 cycles.
(項目B10)
項目B8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数の各々は、5つ以上である。
(Item B10)
The infrared sensor according to item B8,
The number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period number of the plurality of through holes, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period, in the sixth period the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged, the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the seventh period, and the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the eighth period is 5 or more.
(項目B11)
項目B8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、前記第4ドメイン、前記第5ドメイン、前記第6ドメイン、前記第7ドメイン、および前記第8ドメインの各々を構成する周期構造の単位格子は、正方格子、六方格子、長方格子、または面心長方格子のいずれかである。
(Item B11)
The infrared sensor according to item B8,
A unit cell having a periodic structure that constitutes each of the first domain, the second domain, the third domain, the fourth domain, the fifth domain, the sixth domain, the seventh domain, and the eighth domain is either a square lattice, a hexagonal lattice, a rectangular lattice, or a face-centered rectangular lattice.
(項目B12)
項目B8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、前記第4周期、前記第5周期、前記第6周期、前記第7周期、および前記第8周期の各々の値は、1nm以上かつ300nm以下である。
(Item B12)
The infrared sensor according to item B8,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, the fourth period, the fifth period, the sixth period, the seventh period, and the eighth period is 1 nm or more and 300 nm. It is below.
(項目B13)
項目B8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第1周期の値で除した値、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第2周期の値で除した値、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第3周期の値で除した値、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第4周期の値で除した値、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第5周期の値で除した値、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第6周期の値で除した値、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第7周期の値で除した値、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第8周期の値で除した値の各々は、0.5以上かつ0.9以下である。
(Item B13)
The infrared sensor according to item B8,
The value obtained by dividing the diameter value of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period by the value in the first period, the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter by the value of the second period, a value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period by the value of the third period , A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fourth period by the value of the fourth period, the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fifth period The value obtained by dividing the value of the fifth period by the value of the fifth period, the value obtained by dividing the diameter value of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the sixth period by the value of the sixth period, the A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in seven periods by the value of the seventh period, and the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth period is divided by the value of the eighth period is 0.5 or more and 0.9 or less.
(項目B14)
項目B1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメインは、第1周期で規則的に配列された複数の第1サブドメインを具備し、
前記第2ドメインは、第2周期で規則的に配列された複数の第2サブドメインを具備し、
前記第3ドメインは、第3周期で規則的に配列された複数の第3サブドメインを具備し、
前記第4ドメインは、第4周期で規則的に配列された複数の第4サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第1サブドメインの各々は、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第2サブドメインの各々は、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第3サブドメインの各々は、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、かつ
前記複数の第4サブドメインの各々は、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されている。
(Item B14)
The infrared sensor according to item B1,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
the first domain comprises a plurality of first subdomains regularly arranged in a first period;
the second domain comprises a plurality of second subdomains regularly arranged in a second period;
the third domain comprises a plurality of third subdomains regularly arranged in a third period;
the fourth domain comprises a plurality of fourth subdomains regularly arranged in a fourth period;
Each of the plurality of first subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period,
Each of the plurality of second subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period,
Each of the plurality of third subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period, and each of the plurality of fourth subdomains is formed of a It is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged at intervals.
(項目B15)
項目B14に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、第5ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、第6ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、第7ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、第8ドメインをさらに含み、
前記第5ドメインは、第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の第5サブドメインを具備し、
前記第6ドメインは、第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の第6サブドメインを具備し、
前記第7ドメインは、第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の第7サブドメインを具備し、
前記第8ドメインは、第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の第8サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第5サブドメインの各々は、第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第6サブドメインの各々は、第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第7サブドメインの各々は、第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第8サブドメインの各々は、第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第9周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第10周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第11周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ、
前記第12周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item B15)
The infrared sensor according to item B14,
the bolometer first beam further includes a fifth domain;
the second bolometer beam further includes a sixth domain;
The Peltier first beam further includes a seventh domain,
The Peltier second beam further includes an eighth domain,
The fifth domain comprises a plurality of fifth subdomains regularly arranged in a ninth period,
The sixth domain comprises a plurality of sixth subdomains regularly arranged in a tenth period,
The seventh domain comprises a plurality of seventh subdomains regularly arranged in an 11th period,
The eighth domain comprises a plurality of eighth subdomains regularly arranged in a 12th period,
Each of the plurality of fifth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 13th period,
Each of the plurality of sixth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 14th period,
Each of the plurality of seventh subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 15th period,
Each of the plurality of eighth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 16th period,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
The value of the ninth period is greater than the value of the first period,
the value of the tenth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the eleventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and
The value of the 12th period is greater than the value of the 4th period.
(項目B16)
赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、以下を具備する:
(a)以下を具備する前記赤外線センサを用意する工程、
赤外線センサであって、
ベース基板、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第1支柱
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第2支柱、
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第3支柱、および
前記ベース基板から離れる方向に延びている第4支柱、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
第1絶縁材料から形成されているボロメータ第1梁、
第2絶縁材料から形成されているボロメータ第2梁、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の上に形成されたボロメータ第1薄膜、および
前記ボロメータ第2梁の上に形成されたボロメータ第2薄膜、
を具備しており、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜は、前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、
第3絶縁材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁、
第4絶縁材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の上に形成されたペルチェ第1薄膜、および
前記ペルチェ第2梁の上に形成されたペルチェ第2薄膜、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、p型半導体材料から形成されており、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、n型半導体材料から形成されており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端部および前記ボロメータ第1薄膜の一端部は、前記第1支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端部および前記ボロメータ第2薄膜の一端部は、前記第2支柱に接続されており、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端部および前記ペルチェ第1薄膜の一端部は、前記第3支柱に接続されており、
前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端部および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の一端部は、前記第4支柱に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第1薄膜、前記ボロメータ第2梁、および前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、前記第1支柱および前記第2支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ペルチェ素子、前記ペルチェ第1梁、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜、前記ペルチェ第2梁、および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、前記第3支柱および前記第4支柱によって前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2薄膜は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
(b)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に前記赤外線を入射させる工程、
(c)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に入射していた前記赤外線を遮断する工程、および
(d)前記ペルチェ第1薄膜および前記ペルチェ第1薄膜に電流を印加し、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する工程。
(Item B16)
A method of cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor comprising:
(a) providing the infrared sensor comprising:
an infrared sensor,
base board,
the bolometer infrared receiver, and a Peltier element,
a first post extending away from the base substrate; a second post extending away from the base substrate;
a third pillar extending away from the base substrate; and a fourth pillar extending away from the base substrate;
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a bolometer first beam formed from a first insulating material;
a second bolometer beam formed from a second insulating material;
a bolometer first thin film formed on the bolometer first beam; and a bolometer second thin film formed on the bolometer second beam;
is equipped with
The bolometer first thin film is electrically connected to the variable resistance layer,
The bolometer second thin film is electrically connected to the variable resistance layer,
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
The Peltier element is
a Peltier first beam formed from a third insulating material;
a Peltier second beam formed from a fourth insulating material;
a Peltier first thin film formed on the Peltier first beam; and a Peltier second thin film formed on the Peltier second beam;
is equipped with
The Peltier first thin film is made of a p-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier first thin film is made of an n-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
One end of the first bolometer beam and one end of the first bolometer thin film are connected to the first support,
One end of the second bolometer beam and one end of the second bolometer thin film are connected to the second support,
one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the first Peltier thin film are connected to the third support,
one end of the second Peltier beam and one end of the second Peltier thin film are connected to the fourth support,
The bolometer infrared receiver, the first bolometer beam, the first bolometer thin film, the second bolometer beam, and the second bolometer thin film are suspended above the base substrate by the first support and the second support. and
The Peltier element, the first Peltier beam, the first Peltier thin film, the second Peltier beam, and the second Peltier thin film are suspended above the base substrate by the third support and the fourth support. ,
The bolometer first thin film has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The bolometer second thin film has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier thin film has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier thin film is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes a fourth phononic crystal structure,
(b) making the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver;
(c) blocking the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver; and ( d ) applying a current to the Peltier first thin film and the Peltier first thin film to cool the bolometer infrared receiver. .
(項目B17)
項目B16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1薄膜における、前記第1支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2薄膜における、前記第2支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1薄膜における、前記第3支柱および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2薄膜における、前記第4支柱および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。
(Item B17)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor according to item B16,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between the first support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer thin film in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between the second support and the other end of the resistance change layer in the planar view of the second bolometer thin film,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between the third support and one end of the variable resistance layer in the Peltier first thin film in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between the fourth support and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier thin film in plan view.
(項目B18)
項目B16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。
(Item B18)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor according to item B16,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
(項目B19)
項目B18に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item B19)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor according to item B18,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目B20)
項目B16に記載の赤外線センサのボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記ペルチェ第1薄膜の他端が前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1薄膜および前記ペルチェ第2薄膜の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層と熱的に接続されている。
(Item B20)
A method for cooling the bolometer infrared receiver of the infrared sensor according to item B16,
the other end of the first Peltier thin film is connected to the other end of the second Peltier thin film to form an interface between the first Peltier thin film and the second Peltier thin film;
The interface is thermally connected to the variable resistance layer.
(項目C1)
赤外線センサであって、
凹部を有するベース基板、
サーモパイル赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部は、
赤外線吸収層、
前記赤外線吸収層に熱的に接続されており、かつ第1p型半導体材料から形成されているサーモパイル第1梁、および
前記赤外線吸収層に熱的に接続されており、かつ第1n型半導体材料から形成されているサーモパイル第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部および前記凹部の間に挟まれており、
前記赤外線は前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、第2p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁および第2n型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記サーモパイル第1梁の一端、前記サーモパイル第2梁の一端、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端は、前記ベース基板に接続されており、
前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部、前記ペルチェ素子、前記サーモパイル第1梁、前記サーモパイル第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記サーモパイル第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記サーモパイル第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備する。
(Item C1)
an infrared sensor,
a base substrate having a recess;
thermopile infrared receiver and Peltier element,
and
here,
The thermopile infrared receiver is
infrared absorbing layer,
a thermopile first beam thermally connected to the infrared absorbing layer and formed from a first p-type semiconductor material; and thermally connected to the infrared absorbing layer and from a first n-type semiconductor material. thermopile second beam being formed;
is equipped with
The Peltier element is sandwiched between the thermopile infrared light receiving portion and the recess,
The infrared rays are applied to the surface on the front side of the thermopile infrared light receiving unit,
said Peltier element comprising a first Peltier beam formed from a second p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam formed from a second n-type semiconductor material;
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the thermopile infrared light receiving unit,
one end of the first thermopile beam, one end of the second thermopile beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are connected to the base substrate;
The thermopile infrared light receiving portion, the Peltier element, the first thermopile beam, the second thermopile beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate,
The thermopile first beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The thermopile second beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes and a fourth phononic crystal structure.
(項目C2)
項目C1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記サーモパイル第1梁における、前記サーモパイル第1梁の一端および前記赤外線吸収層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記サーモパイル第2梁における、前記サーモパイル第2梁の一端および前記赤外線吸収層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端および前記赤外線吸収層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端および前記赤外線吸収層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている、
赤外線センサ。
(Item C2)
The infrared sensor according to item C1,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between one end of the first thermopile beam and one end of the infrared absorbing layer in the first thermopile beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between one end of the second thermopile beam and the other end of the infrared absorption layer in the second thermopile beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the infrared absorbing layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between one end of the second Peltier beam and the other end of the infrared absorbing layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view,
Infrared sensor.
(項目C3)
項目C1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている、
赤外線センサ。
(Item C3)
The infrared sensor according to item C1,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period,
Infrared sensor.
(項目C4)
項目C3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item C4)
The infrared sensor according to item C3,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目C5)
項目C1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記赤外線吸収層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。
(Item C5)
The infrared sensor according to item C1,
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is sandwiched between the infrared absorbing layer and the recess.
(項目C6)
項目C1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端は、前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されておらず、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、前記ペルチェ第2梁に第1配線によって電気的に接続されており、
前記第1配線は、前記赤外線吸収層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。
(Item C6)
The infrared sensor according to item C1,
The other end of the first Peltier beam is not connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam,
The first Peltier beam is electrically connected to the second Peltier beam by a first wiring,
The first wiring is sandwiched between the infrared absorption layer and the recess.
(項目C7)
項目C5に記載の赤外線センサであって、
平面視において、前記赤外線吸収層は面積が等しい4つの領域を有し、
前記界面は、少なくとも2つの前記領域に接する。
(Item C7)
The infrared sensor according to item C5,
In a plan view, the infrared absorbing layer has four regions of equal area,
The interface borders at least two of the regions.
(項目C8)
項目C3に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記サーモパイル第1梁、前記サーモパイル第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、および前記第4ドメインは、それぞれ、前記第1フォノニック結晶構造、前記第2フォノニック結晶構造、前記第3フォノニック結晶構造、および前記第4フォノニック結晶構造を含み、
前記サーモパイル第1梁、前記サーモパイル第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第5ドメイン、第6ドメイン、第7ドメイン、および第8ドメインを含み、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第5フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第6フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第7フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第8ドメインにおいて、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第8フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記第5周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第6周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第7周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ
前記第8周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item C8)
The infrared sensor according to item C3,
the first thermopile beam, the second thermopile beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
The first domain, the second domain, the third domain, and the fourth domain are the first phononic crystal structure, the second phononic crystal structure, the third phononic crystal structure, and the fourth phononic crystal structure, respectively. contains a crystal structure,
the first thermopile beam, the second thermopile beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a fifth domain, a sixth domain, a seventh domain, and an eighth domain;
A fifth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period is formed in the fifth domain,
A sixth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period is formed in the sixth domain,
A seventh phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period is formed in the seventh domain,
an eighth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in an eighth period is formed in the eighth domain,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
the value of the fifth period is greater than the value of the first period;
the value of the sixth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the seventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and the value of the eighth period is greater than the value of the fourth period.
(項目C9)
項目C8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメインにおいて、前記第1ドメインに前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第1周期とは異なる第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第2ドメインにおいて、前記第2ドメインに前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第2周期とは異なる第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第3ドメインにおいて、前記第3ドメインに前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第3周期とは異なる第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第4ドメインにおいて、前記第4ドメインに前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第4周期とは異なる第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、前記第5ドメインに前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第5周期とは異なる第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、前記第6ドメインに前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第6周期とは異なる第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、前記第7ドメインに前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第7周期とは異なる第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、かつ
前記第8ドメインにおいて、前記第8ドメインに前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第8周期とは異なる第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されている。
(Item C9)
The infrared sensor according to item C8,
In the first domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period in the first domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a ninth period different from the first period through holes are formed,
In the second domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period in the second domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a tenth period different from the second period through holes are formed,
In the third domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period in the third domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in an eleventh period different from the third period through holes are formed,
In the fourth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period in the fourth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 12th period different from the fourth period through holes are formed,
In the fifth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period in the fifth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a thirteenth period different from the fifth period through holes are formed,
In the sixth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the sixth domain in the sixth period, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 14th period different from the sixth period through holes are formed,
In the seventh domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the seventh period in the seventh domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a fifteenth period different from the seventh period and in the eighth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth domain in the eighth period, a period different from the eighth period is formed. A plurality of through holes are formed which are regularly arranged in 16 cycles.
(項目C10)
項目C8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数の各々は、5つ以上である。
(Item C10)
The infrared sensor according to item C8,
The number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period number of the plurality of through holes, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period, in the sixth period the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged, the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the seventh period, and the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the eighth period is 5 or more.
(項目C11)
項目C8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、前記第4ドメイン、前記第5ドメイン、前記第6ドメイン、前記第7ドメイン、および前記第8ドメインの各々を構成する周期構造の単位格子は、正方格子、六方格子、長方格子、または面心長方格子のいずれかである。
(Item C11)
The infrared sensor according to item C8,
A unit cell having a periodic structure that constitutes each of the first domain, the second domain, the third domain, the fourth domain, the fifth domain, the sixth domain, the seventh domain, and the eighth domain is either a square lattice, a hexagonal lattice, a rectangular lattice, or a face-centered rectangular lattice.
(項目C12)
項目C8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、前記第4周期、前記第5周期、前記第6周期、前記第7周期、および前記第8周期の各々の値は、1nm以上かつ300nm以下である。
(Item C12)
The infrared sensor according to item C8,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, the fourth period, the fifth period, the sixth period, the seventh period, and the eighth period is 1 nm or more and 300 nm. It is below.
(項目C13)
項目C8に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第1周期の値で除した値、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第2周期の値で除した値、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第3周期の値で除した値、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第4周期の値で除した値、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第5周期の値で除した値、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第6周期の値で除した値、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第7周期の値で除した値、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第8周期の値で除した値の各々は、0.5以上かつ0.9以下である。
(Item C13)
The infrared sensor according to item C8,
The value obtained by dividing the diameter value of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period by the value in the first period, the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter by the value of the second period, a value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period by the value of the third period , A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fourth period by the value of the fourth period, the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fifth period The value obtained by dividing the value of the fifth period by the value of the fifth period, the value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the sixth period by the value of the sixth period, the A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in seven periods by the value of the seventh period, and the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth period is divided by the value of the eighth period is 0.5 or more and 0.9 or less.
(項目C14)
項目C1に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記サーモパイル第1梁、前記サーモパイル第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメインは、第1周期で規則的に配列された複数の第1サブドメインを具備し、
前記第2ドメインは、第2周期で規則的に配列された複数の第2サブドメインを具備し、
前記第3ドメインは、第3周期で規則的に配列された複数の第3サブドメインを具備し、
前記第4ドメインは、第4周期で規則的に配列された複数の第4サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第1サブドメインの各々は、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第2サブドメインの各々は、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第3サブドメインの各々は、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、かつ
前記複数の第4サブドメインの各々は、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されている。
(Item C14)
The infrared sensor according to item C1,
the first thermopile beam, the second thermopile beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
the first domain comprises a plurality of first subdomains regularly arranged in a first period;
the second domain comprises a plurality of second subdomains regularly arranged in a second period;
the third domain comprises a plurality of third subdomains regularly arranged in a third period;
the fourth domain comprises a plurality of fourth subdomains regularly arranged in a fourth period;
Each of the plurality of first subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period,
Each of the plurality of second subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period,
Each of the plurality of third subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period, and each of the plurality of fourth subdomains is formed of a It is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged at intervals.
(項目C15)
項目C14に記載の赤外線センサであって、
前記サーモパイル第1梁は、第5ドメインをさらに含み、
前記サーモパイル第2梁は、第6ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、第7ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、第8ドメインをさらに含み、
前記第5ドメインは、第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の第5サブドメインを具備し、
前記第6ドメインは、第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の第6サブドメインを具備し、
前記第7ドメインは、第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の第7サブドメインを具備し、
前記第8ドメインは、第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の第8サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第5サブドメインの各々は、第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第6サブドメインの各々は、第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第7サブドメインの各々は、第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第8サブドメインの各々は、第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記赤外線吸収層の間に挟まれており、
前記第9周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第10周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第11周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ、
前記第12周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。
(Item C15)
The infrared sensor according to item C14,
The thermopile first beam further includes a fifth domain,
the thermopile second beam further includes a sixth domain;
The Peltier first beam further includes a seventh domain,
The Peltier second beam further includes an eighth domain,
The fifth domain comprises a plurality of fifth subdomains regularly arranged in a ninth period,
The sixth domain comprises a plurality of sixth subdomains regularly arranged in a tenth period,
The seventh domain comprises a plurality of seventh subdomains regularly arranged in an 11th period,
The eighth domain comprises a plurality of eighth subdomains regularly arranged in a 12th period,
Each of the plurality of fifth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 13th period,
Each of the plurality of sixth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 14th period,
Each of the plurality of seventh subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 15th period,
Each of the plurality of eighth subdomains is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 16th period,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
In the plan view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the infrared absorbing layer,
The value of the ninth period is greater than the value of the first period,
the value of the tenth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the eleventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and
The value of the 12th period is greater than the value of the 4th period.
(項目C16)
赤外線センサのサーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、以下を具備する:
(a)以下を具備する前記赤外線センサを用意する工程、
凹部を有するベース基板、
前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部は、
赤外線吸収層、
前記赤外線吸収層に熱的に接続されており、かつ第1p型半導体材料から形成されているサーモパイル第1梁、および
前記赤外線吸収層に熱的に接続されており、かつ第1n型半導体材料から形成されているサーモパイル第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部および前記凹部の間に挟まれており、
赤外線は前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、第2p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁および第2n型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記サーモパイル第1梁の一端、前記サーモパイル第2梁の一端、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端は、前記ベース基板に接続されており、
前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部、前記ペルチェ素子、前記サーモパイル第1梁、前記サーモパイル第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記サーモパイル第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記サーモパイル第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備し。
(b)前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部に前記赤外線を入射させる工程、
(c)前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部に入射していた前記赤外線を遮断する工程、および
(d)前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁に電流を印加し、前記サーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する工程。
(Item C16)
A method of cooling a thermopile infrared receiver of an infrared sensor comprising:
(a) providing the infrared sensor comprising:
a base substrate having a recess;
the thermopile infrared receiver, and a Peltier element,
and
here,
The thermopile infrared receiver is
infrared absorbing layer,
a thermopile first beam thermally connected to the infrared absorbing layer and formed from a first p-type semiconductor material; and thermally connected to the infrared absorbing layer and from a first n-type semiconductor material. thermopile second beam being formed;
is equipped with
The Peltier element is sandwiched between the thermopile infrared light receiving portion and the recess,
Infrared rays are applied to the surface on the front side of the thermopile infrared light receiving part,
said Peltier element comprising a first Peltier beam formed from a second p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam formed from a second n-type semiconductor material;
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the thermopile infrared light receiving unit,
one end of the first thermopile beam, one end of the second thermopile beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are connected to the base substrate;
The thermopile infrared light receiving portion, the Peltier element, the first thermopile beam, the second thermopile beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate,
The thermopile first beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The thermopile second beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes and a quaternary phononic crystal structure.
(b) making the infrared rays incident on the thermopile infrared receiver;
(c) blocking the infrared rays incident on the thermopile infrared receiver; and ( d ) applying a current to the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam to cool the thermopile infrared receiver. .
(項目C17)
項目C16に記載の赤外線センサのサーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記サーモパイル第1梁における、前記サーモパイル第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記サーモパイル第2梁における、前記サーモパイル第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。
(Item C17)
A method for cooling the thermopile infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item C16,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between one end of the first thermopile beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first thermopile beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between one end of the second thermopile beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second thermopile beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between one end of the second Peltier beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view.
(項目C18)
項目C16に記載の赤外線センサのサーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。
(Item C18)
A method for cooling the thermopile infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item C16,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
(項目C19)
項目C18に記載の赤外線センサのサーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。
(Item C19)
A method for cooling the thermopile infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item C18,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
(項目C20)
項目C16に記載の赤外線センサのサーモパイル赤外線受光部を冷却する方法であって、
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。
(Item C20)
A method for cooling the thermopile infrared receiving part of the infrared sensor according to item C16,
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is sandwiched between the variable resistance layer and the recess.
1A、1B、1C、1D、1E、1F、1G、1H、1I、1J 赤外線センサ
11 ベース基板
12A、12B (ボロメータ)赤外線受光部
12C (サーモパイル)赤外線受光部
12P ペルチェ素子
13a、13b 電極パッド
14a、14b、14c、14d 第2配線
15a、15b 電極パッド
16、16a、16b、16c、16d、16e、16f、16g、16h、16i、16j、16k、16l、16m、16n 第1配線
17、17a、17b 絶縁膜
18 貫通孔
19 単位格子
21a、21b、21c フォノニックドメイン
21P ペルチェ素子
25a、25b 第1周期構造
26a、26b 第2周期構造
27a、27b ミクロ周期構造
28a、28b サブフォノニックドメイン
29a、29b マクロ周期構造
31 上面
32 凹部
34a、34b、34c、34d 支柱
91、92、93 フォノニックドメイン
101a、101b、101c、101d 梁
102a、102b、102c、102d、102e、102f、102g、102h、102i、102j、102k、102l 梁
103 界面
104a、104b 梁
111 ウエハ
111a、111b、112a、112b 区間
201 抵抗変化層
202 絶縁膜
203 赤外線吸収層
222 絶縁層
301a、301b、302a、302b 薄膜
311a、311b、312a、312b 区間
401a、401b 絶縁部
404 犠牲層
501 Si層
502 SiO2層
503 Si層
504 犠牲層
505a、505b 梁層
1011a、1011b、1021a、1021b 領域
1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1G, 1H, 1I, 1J
3 11a, 311b, 312a,
Claims (20)
凹部を有するベース基板、
ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第1梁、および
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部および前記凹部の間に挟まれており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁およびn型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端は、前記ベース基板に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ペルチェ素子、前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備する、
赤外線センサ。 an infrared sensor,
a base substrate having a recess;
bolometer infrared receiver and Peltier element,
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a first bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer; and a second bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer;
is equipped with
The Peltier element is sandwiched between the bolometer infrared light receiving portion and the recess,
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
said Peltier element comprising a first Peltier beam made of a p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam made of an n-type semiconductor material;
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
one end of the first bolometer beam, one end of the second bolometer beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are connected to the base substrate;
The bolometer infrared light receiving unit, the Peltier element, the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate,
The first bolometer beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second bolometer beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes comprising a fourth phononic crystal structure
Infrared sensor.
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1梁における、前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2梁における、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。 The infrared sensor according to claim 1,
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between one end of the first bolometer beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between one end of the second bolometer beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second bolometer beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between one end of the second Peltier beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view.
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。 The infrared sensor according to claim 1,
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。 An infrared sensor according to claim 3,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。 The infrared sensor according to claim 1,
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is sandwiched between the variable resistance layer and the recess.
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端は、前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されておらず、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、前記ペルチェ第2梁に第1配線によって電気的に接続されており、
前記第1配線は、前記抵抗変化層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。 The infrared sensor according to claim 1,
The other end of the first Peltier beam is not connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam,
The first Peltier beam is electrically connected to the second Peltier beam by a first wiring,
The first wiring is sandwiched between the variable resistance layer and the recess.
平面視において、前記抵抗変化層は面積が等しい4つの領域を有し、
前記界面は、少なくとも2つの前記領域に接する。 An infrared sensor according to claim 5,
In plan view, the variable resistance layer has four regions of equal area,
The interface borders at least two of the regions.
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、および前記第4ドメインは、それぞれ、前記第1フォノニック結晶構造、前記第2フォノニック結晶構造、前記第3フォノニック結晶構造、および前記第4フォノニック結晶構造を含み、
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第5ドメイン、第6ドメイン、第7ドメイン、および第8ドメインを含み、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第5フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第6フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第7フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
前記第8ドメインにおいて、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第8フォノニック結晶構造が形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第5周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第6周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第7周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ
前記第8周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。 The infrared sensor according to claim 3,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
The first domain, the second domain, the third domain, and the fourth domain are the first phononic crystal structure, the second phononic crystal structure, the third phononic crystal structure, and the fourth phononic crystal structure, respectively. contains a crystal structure,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a fifth domain, a sixth domain, a seventh domain, and an eighth domain;
A fifth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period is formed in the fifth domain,
A sixth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period is formed in the sixth domain,
A seventh phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period is formed in the seventh domain,
an eighth phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in an eighth period is formed in the eighth domain,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
the value of the fifth period is greater than the value of the first period;
the value of the sixth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the seventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and the value of the eighth period is greater than the value of the fourth period.
前記第1ドメインにおいて、前記第1ドメインに前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第1周期とは異なる第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第2ドメインにおいて、前記第2ドメインに前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第2周期とは異なる第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第3ドメインにおいて、前記第3ドメインに前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第3周期とは異なる第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第4ドメインにおいて、前記第4ドメインに前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第4周期とは異なる第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第5ドメインにおいて、前記第5ドメインに前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第5周期とは異なる第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第6ドメインにおいて、前記第6ドメインに前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第6周期とは異なる第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、
前記第7ドメインにおいて、前記第7ドメインに前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第7周期とは異なる第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されており、かつ
前記第8ドメインにおいて、前記第8ドメインに前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔同士の間に、前記第8周期とは異なる第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔が形成されている。 An infrared sensor according to claim 8,
In the first domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period in the first domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a ninth period different from the first period through holes are formed,
In the second domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period in the second domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a tenth period different from the second period through holes are formed,
In the third domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period in the third domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in an eleventh period different from the third period through holes are formed,
In the fourth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period in the fourth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 12th period different from the fourth period through holes are formed,
In the fifth domain, between the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period in the fifth domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a thirteenth period different from the fifth period through holes are formed,
In the sixth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the sixth domain in the sixth period, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a 14th period different from the sixth period through holes are formed,
In the seventh domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the seventh period in the seventh domain, a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a fifteenth period different from the seventh period and in the eighth domain, between the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth domain in the eighth period, a period different from the eighth period is formed. A plurality of through holes arranged regularly in 16 cycles are formed.
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の数の各々は、5つ以上である。 The infrared sensor according to claim 8,
The number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period, the number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period number of the plurality of through holes, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fourth period, number of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the fifth period, in the sixth period the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged, the number of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the seventh period, and the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged with the eighth period is 5 or more.
前記第1ドメイン、前記第2ドメイン、前記第3ドメイン、前記第4ドメイン、前記第5ドメイン、前記第6ドメイン、前記第7ドメイン、および前記第8ドメインの各々を構成する周期構造の単位格子は、正方格子、六方格子、長方格子、または面心長方格子のいずれかである。 An infrared sensor according to claim 8,
A unit cell having a periodic structure that constitutes each of the first domain, the second domain, the third domain, the fourth domain, the fifth domain, the sixth domain, the seventh domain, and the eighth domain is either a square lattice, a hexagonal lattice, a rectangular lattice, or a face-centered rectangular lattice.
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、前記第4周期、前記第5周期、前記第6周期、前記第7周期、および前記第8周期の各々の値は、1nm以上かつ300nm以下である。 An infrared sensor according to claim 8,
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, the fourth period, the fifth period, the sixth period, the seventh period, and the eighth period is 1 nm or more and 300 nm. It is below.
前記第1周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第1周期の値で除した値、前記第2周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第2周期の値で除した値、前記第3周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第3周期の値で除した値、前記第4周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第4周期の値で除した値、前記第5周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第5周期の値で除した値、前記第6周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第6周期の値で除した値、前記第7周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第7周期の値で除した値、および前記第8周期で規則的に配列された前記複数の貫通孔の直径の値を前記第8周期の値で除した値の各々は、0.5以上かつ0.9以下である。 An infrared sensor according to claim 8,
The value obtained by dividing the diameter value of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the first period by the value in the first period, the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the second period A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter by the value of the second period, a value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the third period by the value of the third period , A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fourth period by the value of the fourth period, the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the fifth period The value obtained by dividing the value of the fifth period by the value of the fifth period, the value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through holes regularly arranged in the sixth period by the value of the sixth period, the A value obtained by dividing the value of the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in seven periods by the value of the seventh period, and the diameter of the plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in the eighth period is divided by the value of the eighth period is 0.5 or more and 0.9 or less.
前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、それぞれ、第1ドメイン、第2ドメイン、第3ドメイン、および第4ドメインを含み、
前記第1ドメインは、第1周期で規則的に配列された複数の第1サブドメインを具備し、
前記第2ドメインは、第2周期で規則的に配列された複数の第2サブドメインを具備し、
前記第3ドメインは、第3周期で規則的に配列された複数の第3サブドメインを具備し、
前記第4ドメインは、第4周期で規則的に配列された複数の第4サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第1サブドメインの各々は、第5周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第2サブドメインの各々は、第6周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第3サブドメインの各々は、第7周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、かつ
前記複数の第4サブドメインの各々は、第8周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されている。 The infrared sensor according to claim 1,
the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam each include a first domain, a second domain, a third domain, and a fourth domain;
the first domain comprises a plurality of first subdomains regularly arranged in a first period;
the second domain comprises a plurality of second subdomains regularly arranged in a second period;
the third domain comprises a plurality of third subdomains regularly arranged in a third period;
the fourth domain comprises a plurality of fourth subdomains regularly arranged in a fourth period;
Each of the plurality of first subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a fifth period,
Each of the plurality of second subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a sixth period,
Each of the plurality of third subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through holes regularly arranged in a seventh period, and each of the plurality of fourth subdomains is formed of a It is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged at intervals.
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、第5ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、第6ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、第7ドメインをさらに含み、
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、第8ドメインをさらに含み、
前記第5ドメインは、第9周期で規則的に配列された複数の第5サブドメインを具備し、
前記第6ドメインは、第10周期で規則的に配列された複数の第6サブドメインを具備し、
前記第7ドメインは、第11周期で規則的に配列された複数の第7サブドメインを具備し、
前記第8ドメインは、第12周期で規則的に配列された複数の第8サブドメインを具備し、
前記複数の第5サブドメインの各々は、第13周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第6サブドメインの各々は、第14周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第7サブドメインの各々は、第15周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
前記複数の第8サブドメインの各々は、第16周期で規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔を具備するフォノニック結晶から形成されており、
平面視において、前記第1ドメインは、前記第5ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第2ドメインは、前記第6ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第3ドメインは、前記第7ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記平面視において、前記第4ドメインは、前記第8ドメインおよび前記抵抗変化層の間に挟まれており、
前記第9周期の値は、前記第1周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第10周期の値は、前記第2周期の値よりも大きく、
前記第11周期の値は、前記第3周期の値よりも大きく、かつ、
前記第12周期の値は、前記第4周期の値よりも大きい。 An infrared sensor according to claim 14,
the bolometer first beam further includes a fifth domain;
the second bolometer beam further includes a sixth domain;
The Peltier first beam further includes a seventh domain,
The Peltier second beam further includes an eighth domain,
The fifth domain comprises a plurality of fifth subdomains regularly arranged in a ninth period,
The sixth domain comprises a plurality of sixth subdomains regularly arranged in a tenth period,
The seventh domain comprises a plurality of seventh subdomains regularly arranged in an 11th period,
The eighth domain comprises a plurality of eighth subdomains regularly arranged in a 12th period,
Each of the plurality of fifth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 13th period,
Each of the plurality of sixth subdomains is formed from a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 14th period,
Each of the plurality of seventh subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 15th period,
Each of the plurality of eighth subdomains is formed of a phononic crystal having a plurality of through-holes regularly arranged in a 16th period,
In plan view, the first domain is sandwiched between the fifth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the second domain is sandwiched between the sixth domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the plan view, the third domain is sandwiched between the seventh domain and the variable resistance layer,
In the planar view, the fourth domain is sandwiched between the eighth domain and the variable resistance layer,
The value of the ninth period is greater than the value of the first period,
the value of the tenth period is greater than the value of the second period;
The value of the eleventh period is greater than the value of the third period, and
The value of the 12th period is greater than the value of the 4th period.
(a)以下を具備する前記赤外線センサを用意する工程、
凹部を有するベース基板、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、および
ペルチェ素子、
を具備し、
ここで、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部は、
赤外線の吸収により抵抗が変化する抵抗変化層、
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第1梁、および
前記抵抗変化層に電気的に接続されているボロメータ第2梁、
を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部および前記凹部の間に挟まれており、
前記赤外線は前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の表側の面に照射され、
前記ペルチェ素子は、p型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第1梁およびn型半導体材料から形成されているペルチェ第2梁を具備しており、
前記ペルチェ素子は、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部の裏側の面に接しており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端、および前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端は、前記ベース基板に接続されており、
前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部、前記ペルチェ素子、前記ボロメータ第1梁、前記ボロメータ第2梁、前記ペルチェ第1梁、および前記ペルチェ第2梁は、前記ベース基板の上部で懸架されており、
前記ボロメータ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第1フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ボロメータ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第2フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
前記ペルチェ第1梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第3フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、かつ
前記ペルチェ第2梁は、規則的に配列された複数の貫通孔から構成された第4フォノニック結晶構造を具備し、
(b)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に前記赤外線を入射させる工程、
(c)前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部に入射していた前記赤外線を遮断する工程、および
(d)前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁に電流を印加し、前記ボロメータ赤外線受光部を冷却する工程。 A method of cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor comprising:
(a) providing the infrared sensor comprising:
a base substrate having a recess;
the bolometer infrared receiver, and a Peltier element,
and
here,
The bolometer infrared receiver is
resistance change layer whose resistance changes by absorbing infrared rays;
a first bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer; and a second bolometer beam electrically connected to the variable resistance layer;
is equipped with
The Peltier element is sandwiched between the bolometer infrared light receiving portion and the recess,
The infrared rays are irradiated onto the surface on the front side of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
The Peltier element comprises a first Peltier beam made of p-type semiconductor material and a second Peltier beam made of n-type semiconductor material,
The Peltier element is in contact with the back surface of the bolometer infrared light receiving unit,
one end of the first bolometer beam, one end of the second bolometer beam, one end of the first Peltier beam, and one end of the second Peltier beam are connected to the base substrate;
The bolometer infrared light receiving unit, the Peltier element, the first bolometer beam, the second bolometer beam, the first Peltier beam, and the second Peltier beam are suspended above the base substrate,
The first bolometer beam has a first phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The second bolometer beam has a second phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes,
The first Peltier beam has a third phononic crystal structure composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes, and the second Peltier beam is composed of a plurality of regularly arranged through holes comprising a fourth phononic crystal structure,
(b) making the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver;
(c) blocking the infrared rays incident on the bolometer infrared receiver; and ( d ) applying a current to the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam to cool the bolometer infrared receiver. .
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造は、平面視の前記ボロメータ第1梁における、前記ボロメータ第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第1区間に設けられており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ボロメータ第2梁における、前記ボロメータ第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第2区間に設けられており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第1梁における、前記ペルチェ第1梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の一端の間の第3区間に設けられており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造は、前記平面視の前記ペルチェ第2梁における、前記ペルチェ第2梁の一端および前記抵抗変化層の他端の間の第4区間に設けられている。 17. A method for cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor according to claim 16, comprising:
The first phononic crystal structure is provided in a first section between one end of the first bolometer beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first bolometer beam in plan view,
The second phononic crystal structure is provided in a second section between one end of the second bolometer beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second bolometer beam in plan view,
The third phononic crystal structure is provided in a third section between one end of the first Peltier beam and one end of the variable resistance layer in the first Peltier beam in plan view,
The fourth phononic crystal structure is provided in a fourth section between one end of the second Peltier beam and the other end of the variable resistance layer in the second Peltier beam in plan view.
前記第1フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第1周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第2フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第2周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第3フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第3周期で規則的に配列されており、
前記第4フォノニック結晶構造の前記複数の貫通孔は、第4周期で規則的に配列されている。 17. A method for cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor according to claim 16, comprising:
The plurality of through-holes of the first phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a first period,
The plurality of through-holes of the second phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a second period,
The plurality of through-holes of the third phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a third period,
The plurality of through-holes of the fourth phononic crystal structure are regularly arranged in a fourth period.
前記第1周期、前記第2周期、前記第3周期、および前記第4周期の各々の値は等しい。 A method for cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor according to claim 18, comprising:
Each value of the first period, the second period, the third period, and the fourth period is equal.
前記ペルチェ第1梁の他端が前記ペルチェ第2梁の他端に接続されて、前記ペルチェ第1梁および前記ペルチェ第2梁の間に界面が形成されており、
前記界面は、前記抵抗変化層および前記凹部の間に挟まれている。 A method for cooling a bolometric infrared receiver of an infrared sensor according to claim 16, comprising:
the other end of the first Peltier beam is connected to the other end of the second Peltier beam to form an interface between the first Peltier beam and the second Peltier beam;
The interface is sandwiched between the variable resistance layer and the recess.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017236574 | 2017-12-11 | ||
| JP2017236574 | 2017-12-11 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019105624A JP2019105624A (en) | 2019-06-27 |
| JP7232978B2 true JP7232978B2 (en) | 2023-03-06 |
Family
ID=66735335
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018201387A Active JP7232978B2 (en) | 2017-12-11 | 2018-10-26 | Method for Cooling Infrared Sensors and Bolometer Infrared Receivers of Infrared Sensors |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US10605667B2 (en) |
| JP (1) | JP7232978B2 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN110006536B (en) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110770548B (en) * | 2018-05-22 | 2024-08-13 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Infrared sensor and phonon crystal |
| KR20210141978A (en) | 2019-03-11 | 2021-11-23 | 플리어 커머셜 시스템즈, 인코포레이티드 | Microbolometer system and method |
| WO2021079733A1 (en) * | 2019-10-25 | 2021-04-29 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Thermoelectric conversion device, method for controlling thermoelectric conversion device, method for cooling and/or heating object by using thermoelectric conversion device, and electronic device |
| EP4137789A4 (en) * | 2020-04-13 | 2023-10-11 | Kyoto University | Infrared sensing device and resistance-variable film using same |
| WO2022239611A1 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2022-11-17 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor, and method for manufacturing infrared sensor |
| JPWO2022239610A1 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2022-11-17 | ||
| WO2023013354A1 (en) * | 2021-08-03 | 2023-02-09 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Conductive thermal insulating material and infrared sensor |
| CN113506996B (en) * | 2021-09-13 | 2022-01-07 | 中国科学院光电技术研究所 | Microwave low-reflection temperature control unit, superstructure and design method |
| CN118235023A (en) | 2021-11-17 | 2024-06-21 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Infrared sensor, sensing system and infrared sensing method |
| JP2023114908A (en) * | 2022-02-07 | 2023-08-18 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | Detection element and electronic apparatus |
| WO2024090197A1 (en) * | 2022-10-25 | 2024-05-02 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
| WO2024090199A1 (en) * | 2022-10-25 | 2024-05-02 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
| WO2024090198A1 (en) * | 2022-10-25 | 2024-05-02 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012054777A2 (en) | 2010-10-22 | 2012-04-26 | California Institute Of Technology | Nanomesh phononic structures for low thermal conductivity and thermoelectric energy conversion materials |
| US20170069818A1 (en) | 2011-10-20 | 2017-03-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Fabrication methods for thermoelectric phononic structures |
| JP2017223644A (en) | 2016-06-13 | 2017-12-21 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
Family Cites Families (50)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5006505A (en) * | 1988-08-08 | 1991-04-09 | Hughes Aircraft Company | Peltier cooling stage utilizing a superconductor-semiconductor junction |
| JP2725494B2 (en) | 1991-09-19 | 1998-03-11 | 日本電気株式会社 | Infrared detector |
| JP3560414B2 (en) * | 1996-05-07 | 2004-09-02 | 北川工業株式会社 | Peltier element |
| US6100463A (en) * | 1997-11-18 | 2000-08-08 | The Boeing Company | Method for making advanced thermoelectric devices |
| EP1137918B1 (en) * | 1998-11-30 | 2006-05-31 | Daewoo Electronics Corporation | Infrared bolometer |
| JP2000230857A (en) * | 1999-02-12 | 2000-08-22 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | Thermal type infrared sensor and thermal type infrared array element |
| JP3228267B2 (en) * | 1999-04-27 | 2001-11-12 | 日本電気株式会社 | Electronic device |
| JP2005506693A (en) * | 2001-10-05 | 2005-03-03 | リサーチ・トライアングル・インスティチュート | Phonon blocking electron transfer low dimensional structure |
| WO2005054119A2 (en) * | 2003-12-01 | 2005-06-16 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Illinois | Methods and devices for fabricating three-dimensional nanoscale structures |
| US8217381B2 (en) * | 2004-06-04 | 2012-07-10 | The Board Of Trustees Of The University Of Illinois | Controlled buckling structures in semiconductor interconnects and nanomembranes for stretchable electronics |
| JP4385255B2 (en) * | 2004-06-10 | 2009-12-16 | 日本電気株式会社 | Bolometer type infrared detector and method for reducing afterimage |
| US7309830B2 (en) * | 2005-05-03 | 2007-12-18 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Nanostructured bulk thermoelectric material |
| US9865790B2 (en) * | 2004-12-07 | 2018-01-09 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Nanostructured bulk thermoelectric material |
| US7709795B2 (en) * | 2005-08-17 | 2010-05-04 | Panasonic Electric Works Co., Ltd. | Infrared sensor unit and process of fabricating the same |
| JP2007115812A (en) * | 2005-10-19 | 2007-05-10 | Seiko Epson Corp | Peltier module and electronic device |
| US7825324B2 (en) * | 2006-12-29 | 2010-11-02 | Alcatel-Lucent Usa Inc. | Spreading thermoelectric coolers |
| US7733198B1 (en) * | 2007-05-15 | 2010-06-08 | Sandia Corporation | Microfabricated bulk wave acoustic bandgap device |
| US8094023B1 (en) * | 2008-03-10 | 2012-01-10 | Sandia Corporation | Phononic crystal devices |
| US8054145B2 (en) * | 2008-04-30 | 2011-11-08 | Georgia Tech Research Corporation | Phononic crystal wave structures |
| CN102197290A (en) * | 2008-09-25 | 2011-09-21 | 松下电工株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
| US8508370B1 (en) * | 2009-02-27 | 2013-08-13 | Sandia Corporation | Synthetic thermoelectric materials comprising phononic crystals |
| BRPI1008160A2 (en) * | 2009-05-28 | 2016-03-08 | Gmz Energy Inc | apparatus, solar electric generator and method |
| TWI424687B (en) * | 2009-12-02 | 2014-01-21 | Ind Tech Res Inst | Resonator and periodic structure |
| US8927934B2 (en) * | 2010-09-13 | 2015-01-06 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Thermal infrared sensor and manufacturing method thereof |
| US9679779B2 (en) * | 2011-03-30 | 2017-06-13 | The Aerospace Corporation | Systems and methods for depositing materials on either side of a freestanding film using selective thermally-assisted chemical vapor deposition (STA-CVD), and structures formed using same |
| US8969850B2 (en) * | 2011-09-23 | 2015-03-03 | Rockwell Collins, Inc. | Nano-structure arrays for EMR imaging |
| SG192390A1 (en) * | 2012-02-01 | 2013-08-30 | Agency Science Tech & Res | Radiation sensor |
| US9059388B2 (en) * | 2012-03-21 | 2015-06-16 | University Of Maryland College Park | Phoniton systems, devices, and methods |
| US9236552B2 (en) * | 2013-04-04 | 2016-01-12 | William N. Carr | Thermoelectric micro-platform for cooling and temperature sensing |
| US9006857B1 (en) * | 2013-04-04 | 2015-04-14 | William N. Carr | Platform comprising an infrared sensor |
| US9722165B2 (en) * | 2016-03-29 | 2017-08-01 | William N. Carr | Thermoelectric pixel for temperature sensing, temperature control and thermal energy harvesting |
| US9817130B1 (en) * | 2016-06-24 | 2017-11-14 | William N. Carr | Radiation dosimeter with thermal reset and readout |
| US20180374981A1 (en) * | 2017-06-26 | 2018-12-27 | William N. Carr | Metamaterial Thermal Pixel for Limited Bandwidth Electromagnetic Sourcing and Detection |
| US20180364153A1 (en) * | 2017-06-15 | 2018-12-20 | William N Carr | Absorptive Spectrometer with Integrated Photonic and Phononic Structures |
| WO2014168894A2 (en) * | 2013-04-07 | 2014-10-16 | The Regents Of The University Of Colorado, A Body Corporate | Nanophononic metamaterials |
| WO2015012914A2 (en) * | 2013-04-22 | 2015-01-29 | Northeastern University | Nano- and micro-electromechanical resonators |
| JP2014235064A (en) | 2013-05-31 | 2014-12-15 | シャープ株式会社 | Infrared sensor and infrared sensor device |
| WO2014199583A1 (en) * | 2013-06-10 | 2014-12-18 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
| KR102273850B1 (en) * | 2013-10-31 | 2021-07-05 | 하마마츠 포토닉스 가부시키가이샤 | Light-detecting device |
| WO2016049446A1 (en) * | 2014-09-26 | 2016-03-31 | Urzhumov Yaroslav A | Artificially-structured superconducting materials |
| US10444431B2 (en) * | 2015-01-15 | 2019-10-15 | National Institute Of Standards And Technology | Reticulated resonator, process for making and use of same |
| US9978926B2 (en) * | 2015-05-14 | 2018-05-22 | The Hong Kong University Of Science And Technology | Thermal radiation microsensor comprising thermoelectric micro pillars |
| US9696492B1 (en) * | 2016-03-03 | 2017-07-04 | National Technology & Engineering Solutions Of Sandia, Llc | On-chip photonic-phononic emitter-receiver apparatus |
| DE102016207551B4 (en) * | 2016-05-02 | 2023-07-27 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Integrated thermoelectric structure, method for producing an integrated thermoelectric structure, method for operating the same as a detector, thermoelectric generator and thermoelectric Peltier element |
| US11231382B2 (en) * | 2016-06-15 | 2022-01-25 | William N. Carr | Integrated thermal sensor comprising a photonic crystal |
| CN110770548B (en) * | 2018-05-22 | 2024-08-13 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Infrared sensor and phonon crystal |
| CN113015890B (en) * | 2019-02-28 | 2024-04-02 | 松下知识产权经营株式会社 | Infrared sensor and infrared sensor array |
| US11381761B2 (en) * | 2020-11-30 | 2022-07-05 | William N. Carr | Phononically-enhanced imager (PEI) pixel |
| JPWO2022239610A1 (en) * | 2021-05-11 | 2022-11-17 | ||
| WO2023013354A1 (en) * | 2021-08-03 | 2023-02-09 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Conductive thermal insulating material and infrared sensor |
-
2018
- 2018-10-26 JP JP2018201387A patent/JP7232978B2/en active Active
- 2018-11-16 US US16/193,152 patent/US10605667B2/en active Active
- 2018-12-06 CN CN201811486361.6A patent/CN110006536B/en active Active
-
2020
- 2020-02-20 US US16/796,115 patent/US11320313B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2012054777A2 (en) | 2010-10-22 | 2012-04-26 | California Institute Of Technology | Nanomesh phononic structures for low thermal conductivity and thermoelectric energy conversion materials |
| US20170069818A1 (en) | 2011-10-20 | 2017-03-09 | California Institute Of Technology | Fabrication methods for thermoelectric phononic structures |
| JP2017223644A (en) | 2016-06-13 | 2017-12-21 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Infrared sensor |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20200191658A1 (en) | 2020-06-18 |
| US10605667B2 (en) | 2020-03-31 |
| CN110006536A (en) | 2019-07-12 |
| JP2019105624A (en) | 2019-06-27 |
| US20190178718A1 (en) | 2019-06-13 |
| US11320313B2 (en) | 2022-05-03 |
| CN110006536B (en) | 2024-06-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP7232978B2 (en) | Method for Cooling Infrared Sensors and Bolometer Infrared Receivers of Infrared Sensors | |
| JP6311133B2 (en) | Infrared sensor | |
| US9698281B2 (en) | CMOS bolometer | |
| JP7352884B2 (en) | Infrared sensors and phononic crystals | |
| CN113015890B (en) | Infrared sensor and infrared sensor array | |
| US7544942B2 (en) | Thermal detector for electromagnetic radiation and infrared detection device using such detectors | |
| JP2009122104A (en) | Electromagnetic radiation detector having nanowire connection, and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US20140091217A1 (en) | Microbolometer detector with centrally-located support structure | |
| JP2013539053A (en) | Superlattice quantum well infrared detector | |
| US10483416B2 (en) | Medium wave infrared (MWIR) and long wavelength infrared (LWIR) operating microbolometer with raised strut design | |
| US6953931B2 (en) | Bolometer type infrared detector | |
| CN114364954A (en) | Heat detector | |
| US20160111460A1 (en) | Back-lit photodetector | |
| US20230088920A1 (en) | Infrared sensor and method of controlling infrared sensor | |
| US6201244B1 (en) | Bolometer including an absorber made of a material having a low deposition-temperature and a low heat-conductivity | |
| CA2791933C (en) | Microbolometer detector with centrally-located support structure | |
| EP1131612A1 (en) | Bolometer including an absorber made of a material having a low deposition-temperature and a low heat-conductivity |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20181214 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20190124 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20211007 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20220622 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20220802 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20221020 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20230110 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20230123 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 7232978 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |