JP6962006B2 - Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method - Google Patents
Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6962006B2 JP6962006B2 JP2017109634A JP2017109634A JP6962006B2 JP 6962006 B2 JP6962006 B2 JP 6962006B2 JP 2017109634 A JP2017109634 A JP 2017109634A JP 2017109634 A JP2017109634 A JP 2017109634A JP 6962006 B2 JP6962006 B2 JP 6962006B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- battery
- voltage
- electric load
- automatic operation
- automatic driving
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
Description
本発明は、自動運転制御装置に関する。 The present invention relates to an automatic driving control device.
従来、二次電池やキャパシタといった充放電可能な蓄電装置(バッテリ)を搭載した車両が知られている。特許文献1には、補機に電力を供給し、また、オルタネータや回生制動力により生じた電気エネルギーを蓄電可能なバッテリを備えると共に、車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置を備える車両が開示されている。
Conventionally, vehicles equipped with a chargeable / discharging power storage device (battery) such as a secondary battery or a capacitor are known.
しかしながら、高出力アンプおよびヒーター等の消費電力の大きな負荷がバッテリに接続されると、バッテリの過放電や短時間での急激な電圧低下(以下、「瞬低」と呼ぶ)が発生するおそれがある。例えば、バッテリの充電・放電量を監視する電流センサよりも上流側(バッテリ側)に消費電力の大きな負荷を接続した場合、かかる負荷による放電量の増加分を検知できないために接続が維持され、バッテリの過放電や瞬低が突然生じるおそれがある。他方、電流センサよりも下流側に消費電力の大きな負荷を接続した場合であっても、車両設計時に想定された電流量よりも多くの電流量が消費されるため、バッテリの過放電や瞬低が突然生じるおそれがある。バッテリの過放電や瞬低が発生すると自動運転に悪影響を及ぼすおそれがある。そこで、バッテリに電気負荷が追加接続された場合におけるバッテリの過放電や瞬低の発生を抑制可能な技術が望まれている。 However, if a large power consumption load such as a high-power amplifier or heater is connected to the battery, there is a risk that the battery will be over-discharged or a sudden voltage drop (hereinafter referred to as "instantaneous low") will occur in a short period of time. be. For example, when a load with a large power consumption is connected to the upstream side (battery side) of the current sensor that monitors the charge / discharge amount of the battery, the connection is maintained because the increase in the discharge amount due to the load cannot be detected. The battery may suddenly over-discharge or drop. On the other hand, even if a load with a large power consumption is connected to the downstream side of the current sensor, a larger amount of current is consumed than the amount of current assumed at the time of vehicle design, resulting in over-discharging or instantaneous decrease of the battery. May occur suddenly. If the battery is over-discharged or momentarily lowered, it may adversely affect the automatic operation. Therefore, there is a demand for a technique capable of suppressing the occurrence of over-discharging and instantaneous drop of the battery when an electric load is additionally connected to the battery.
本発明は、上述の課題の少なくとも一部を解決するためになされたものであり、以下の形態として実現することが可能である。
[形態1]バッテリ(140)を搭載した車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置(10)であって、前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、を備え、前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路(Cp1)において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する電流検出部(152)と、前記バッテリの開放端電圧を推定する開放端電圧推定部(11)と、推定された前記開放端電圧を利用して前記バッテリの充電量を推定する充電量推定部(12)と、を、さらに備え、前記負荷接続検出部は、予め定められた時間における推定された前記充電量の変化量と、検出された前記電流の前記予め定められた時間における積算値と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、自動運転制御装置。
[形態2]バッテリ(140)を搭載した車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置(10)であって、前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、を備え、前記車両に搭載され、前記バッテリの電圧を測定する電圧センサ(151)と、測定された前記バッテリの電圧を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する第1電圧変化量特定部(13)と、を、さらに備え、前記負荷接続検出部は、前記車両に搭載された予め定められた装置が起動する前と、前記予め定められた装置が起動した後と、における特定された前記バッテリの電圧の変化量が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、自動運転制御装置。
[形態3]バッテリ(140)を搭載した車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置(10)であって、前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、を備え、前記車両に搭載され、前記バッテリの電圧を測定する電圧センサと、前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する電流検出部と、検出された前記電流を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する第2電圧変化量特定部(14)と、少なくとも前記電気負荷を含む前記車両に搭載された装置に対して前記バッテリの給電の実行と停止とを切り替えるリレー(41)と、を備え、前記負荷接続検出部は、前記リレーがオフからオンに切り替わる際の、前記電圧センサにより検出される前記バッテリの電圧の変化量と、前記第2電圧変化量特定部により特定された前記変化量と、の差である電圧変化量差分が、予め定められた量よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、自動運転制御装置。
[形態4]バッテリ(140)を搭載した車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置(10)であって、前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、を備え、前記バッテリは、前記バッテリの温度を検出する温度センサ(153)を有し、外気温度および前記車両の運転状態に基づいて前記バッテリの温度を推定する温度推定部(16)を、さらに備え、前記負荷接続検出部は、前記車両の走行開始時から予め定められた時間経過後における推定された前記バッテリの温度と、検出された前記バッテリの温度と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、自動運転制御装置。
The present invention has been made to solve at least a part of the above-mentioned problems, and can be realized as the following forms.
[Form 1] An automatic operation control device (10) for controlling the automatic operation of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140), which is a load connection for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery. The detection unit (17) and an automatic operation unit having an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation by supplying power from the battery when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. Among the automatic operation functions realized by (10c), an automatic operation control unit (10b) for limiting and executing at least a part of the functions is provided, and a power path between the battery and the automatic operation unit. In (Cp1), a current detection unit (152) that detects a current at a position closer to the automatic operation unit than a connection point with the electric load, and an open end voltage estimation unit (11) that estimates the open end voltage of the battery. ), And a charge amount estimation unit (12) that estimates the charge amount of the battery using the estimated open-end voltage, and the load connection detection unit estimates at a predetermined time. When the difference between the amount of change in the amount of charge and the integrated value of the detected current at the predetermined time is larger than the predetermined threshold, the electric load on the battery is electrical. An automatic operation control device that detects that it is connected to.
[Form 2] An automatic operation control device (10) for controlling the automatic operation of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140), which is a load connection for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery. The detection unit (17) and an automatic operation unit having an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation by supplying power from the battery when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. Among the automatic driving functions realized by (10c), an automatic driving control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the functions is provided, mounted on the vehicle, and measures the voltage of the battery. The load connection detection is further provided with a voltage sensor (151) and a first voltage change amount specifying unit (13) that specifies a change amount of the voltage of the battery by using the measured voltage of the battery. The unit is such that the amount of change in the voltage of the specified battery before the activation of the predetermined device mounted on the vehicle and after the activation of the predetermined device is from a predetermined threshold value. An automatic operation control device that detects that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery when the voltage is also large.
[Form 3] An automatic operation control device (10) for controlling the automatic operation of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140), which is a load connection for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery. The detection unit (17) and an automatic operation unit having an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation by supplying power from the battery when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. Among the automatic driving functions realized by (10c), an automatic driving control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the functions is provided, mounted on the vehicle, and measures the voltage of the battery. In the power path between the voltage sensor and the battery and the automatic operation unit, a current detection unit that detects a current at a position closer to the automatic operation unit than the connection point with the electric load, and the detected current. The second voltage change amount specifying unit (14) for specifying the change amount of the voltage of the battery, and the execution of the power supply of the battery to the device mounted on the vehicle including at least the electric load. The load connection detection unit includes a relay (41) for switching between stop and stop, and the load connection detection unit includes the amount of change in the voltage of the battery detected by the voltage sensor when the relay is switched from off to on, and the second. When the difference in the amount of voltage change, which is the difference between the amount of change specified by the voltage change amount specifying unit, is larger than a predetermined amount, the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. Automatic operation control device to detect.
[Form 4] An automatic operation control device (10) for controlling the automatic operation of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140), which is a load connection for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery. The detection unit (17) and an automatic operation unit having an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation by supplying power from the battery when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. The battery includes an automatic operation control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions realized by (10c), and the battery is a temperature sensor that detects the temperature of the battery. (153), further including a temperature estimation unit (16) for estimating the temperature of the battery based on the outside air temperature and the operating state of the vehicle, and the load connection detection unit from the start of traveling of the vehicle. When the difference between the estimated temperature of the battery after a lapse of a predetermined time and the detected temperature of the battery is larger than a predetermined threshold, the electric load on the battery is electrically applied to the battery. An automatic operation control device that detects the connection.
本発明の一実施形態によれば、自動運転制御装置が提供される。この自動運転制御装置(10)は、バッテリ(140)を搭載した車両の自動運転を制御する自動運転制御装置であって、前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と;前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と;を備える。 According to one embodiment of the present invention, an automatic driving control device is provided. The automatic driving control device (10) is an automatic driving control device that controls the automatic driving of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140), and detects that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery. With the load connection detection unit (17); when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery, power is supplied from the battery to have an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation. Among the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit (10c), at least a part of the automatic driving functions is restricted and executed, and the automatic driving control unit (10b) is provided.
この形態の自動運転制御装置によれば、バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、自動運転部により実現される自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させるので、バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に自動運転機能を制限しないで自動運転を実行させる構成に比べて、バッテリの消費電力を低下させることができる。このため、バッテリの過放電や瞬低の発生を抑制できる。 According to this form of automatic driving control device, when it is detected that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, at least some of the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit are restricted. When it is detected that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, the power consumption of the battery can be reduced as compared with the configuration in which the automatic operation is executed without limiting the automatic operation function. can. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the occurrence of over-discharge and instantaneous drop of the battery.
本発明は、種々の形態で実現することも可能である。例えば、自動運転制御方法、自動運転制御装置を搭載した車両、また、これらの装置や方法を実現するためのコンピュータプログラム等の形態で実現できる。 The present invention can also be realized in various forms. For example, it can be realized in the form of an automatic driving control method, a vehicle equipped with an automatic driving control device, a computer program for realizing these devices and methods, and the like.
A.第1実施形態:
A1.自動運転制御装置の装置構成:
図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図示しない車両に搭載され、後述の自動運転制御処理を実行することにより、車両の走行を制御して車両の自動運転を実現させる。自動運転制御処理では、バッテリ(後述のバッテリ140)に接続が予定されていない電気負荷(後述の電気負荷200)が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、バッテリの過放電および瞬間的に電圧が低下する現象(以下、「瞬低」と呼ぶ)の発生を抑制するために、自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して自動運転を実行する。
A. First Embodiment:
A1. Device configuration of automatic operation control device:
The automatic
自動運転制御装置10は、電源制御装置10aと、自動運転制御部10bとにより構成されている。電源制御装置10aは、バッテリ140の電力や、オルタネータ131による発電を制御する。電源制御装置10aは、アクセサリ系統電源ACCと、第1イグニッション系統電源IG1と、第2イグニッション系統電源IG2とを備える。アクセサリ系統電源ACCは、アクセサリ系統に接続された装置への給電のオンオフスイッチとして機能する。アクセサリ系統電源ACCには、図示しないリレー(後述のリレー41)を介して電気負荷200が接続されている。第1イグニッション系統電源IG1および第2イグニッション系統電源IG2は、エンジンスターター系統に接続された装置への給電のオンオフスイッチとして機能する。第1イグニッション系統電源IG1には、図示しないリレー(後述のリレー42)を介してエンジン130の補機類が接続されている。第2イグニッション系統電源IG2には、図示しないリレー(後述のリレー43)および自動運転制御部10bを介して自動運転部10cが接続されている。電源制御装置10aは、各電源系統ACC、IG1およびIG2に接続された図示しないリレーのオンとオフとを切り替えることにより、各電源系統に接続された装置への給電を制御する。リレーについての詳細は、第4実施形態において説明する。なお、図1では、電源線を太線で、信号線を細線で、それぞれ示している。
The automatic
電源制御装置10aは、電圧センサ151を備える。電圧センサ151は、電源線Cp1を介してバッテリ140と接続されており、バッテリ140の端子電圧を測定する。
The power control device 10a includes a voltage sensor 151. The voltage sensor 151 is connected to the
バッテリ140は、充放電可能な蓄電装置である。バッテリ140は、自動運転部10cおよび車両に搭載される補機等に電力を供給する。本実施形態において、バッテリ140は、二次電池により構成されている。二次電池としては、鉛蓄電池およびリチウムイオン電池等を利用してもよい。なお、バッテリ140は、二次電池に代えて、キャパシタにより構成されてもよい。バッテリ140は、温度センサ153を備える。温度センサ153は、バッテリ140の温度を検出する。
The
電気負荷200は、消費電力の比較的大きな電気負荷である。電気負荷200は、ユーザにより後付けされており、車両および自動運転制御装置10の設計時点では見込まれていない負荷である。本実施形態において、電気負荷200は、高出力アンプにより構成されている。なお、電気負荷200は、高出力アンプに代えて、ヒーター等の消費電力の比較的大きな電気負荷であってもよい。図1に示すように、電気負荷200は、電源制御装置10aのアクセサリ系統電源ACCに電気的に接続されている。また、電気負荷200は、バッテリ140と電流センサ152との間において電源線Cp1に接続されている。換言すると、電気負荷200は、電源線Cp1において、電流センサ152よりもバッテリ140に近い位置に配置されている。本実施形態において、電源線Cp1は、請求項における電力経路の下位概念に相当する。
The
電流センサ152は、電源線Cp1に流れる電流(実測値)を検出する。具体的には、電源線Cp1において、電気負荷200との接続点よりも下流側(電源制御装置10a側)であって、自動運転部10cとの接続点よりも上流側(バッテリ140側)における位置での電流を検出する。本実施形態において、電流センサ152は、請求項における電流検出部の下位概念に相当する。
The
エンジン130は、ガソリンや軽油などの燃料を燃焼させることによって動力を発生させる内燃機関である。エンジン130の動力は、図示しない駆動機構を介してオルタネータ131に伝達される。
The
オルタネータ131は、エンジン130の動力の一部を用いて発電を行う。オルタネータ131によって発電された電力は、バッテリ140に蓄電される。
The
自動運転制御部10bは、自動運転部10cを制御して自動運転を実現する。自動運転部10cは、バッテリ140からの給電を受け付ける。自動運転部10cは、EPS110と、ECB120と、図示しないアクセルと、を備える。EPS110は、電動パワーステアリングシステム(Elelctric Power Steering System)であり、車両の車輪の舵角を制御する。ECB120は、電子制御ブレーキシステム(Elelctronically Controlled Brake System)である。ECB120は、車両の室内外に搭載された各種センサの検出結果を利用して車両の制動力を算出し、得られた制動力に基づきブレーキ油圧を制御することにより車速を制御する。
The automatic
本実施形態において、自動運転制御装置10は、ECU(Electronic Control Unit)により構成されている。自動運転制御装置10は、図示しないCPU、ROMおよびRAMを有する。かかるCPUは、ROMに予め記憶されている制御プログラムをRAMに展開して実行することにより、開放端電圧推定部11と、充電量推定部12と、第1電圧変化量特定部13と、第2電圧変化量特定部14と、消費電流量推定部15と、温度推定部16と、負荷接続検出部17と、自動運転制御部10bとして機能する。
In the present embodiment, the automatic
開放端電圧推定部11は、バッテリ140の開放端電圧(OCV:Open Circuit Voltage)(以下、単に「OCV」と呼ぶ場合がある)を推定する。充電量推定部12は、推定された開放端電圧を利用して、バッテリ140の充電量(SOC:State Of Chage)(以下、単に「SOC」と呼ぶ場合がある)を推定する。第1電圧変化量特定部13は、電圧センサ151により検出されるバッテリ140の電圧を利用して電圧変化量を特定する。第2電圧変化量特定部14は、電流センサ152により検出される消費電流を利用してバッテリ140の電圧を算出して電圧変化量を特定する。
The open end
消費電流量推定部15は、第2電圧変化量特定部14により特定された電圧変化量と、バッテリ140の内部抵抗値とを利用して、電気負荷200の消費電流量を推定する。
The current consumption estimation unit 15 estimates the current consumption of the
温度推定部16は、外気温度および運転状態に基づいてバッテリ140の温度を推定する。例えば、車両が低速走行中である場合には、バッテリ140の充放電が行われやすいため、バッテリ140の温度は高温を維持していると推定する。また、例えば、車両が高速走行中である場合には、エンジンコンパートメント内に多量の風が入ってくることによりバッテリ140が冷却されるため、バッテリ140の温度は低下すると推定する。
The temperature estimation unit 16 estimates the temperature of the
負荷接続検出部17は、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出する。具体的には、負荷接続検出部17は、バッテリ140に流れる電流、バッテリ140の開放端電圧およびバッテリ140の充電量等を利用して、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出する。なお、具体的な検出方法については、後述する。
The load
自動運転制御部10bは、上述の自動運転部10cを制御して、車両の自動運転を実現させる。「自動運転」とは、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵を行って車両の走行や停止を自動的に実行することを意味する。「自動駆動」とは、車両の加速度を制御することにより、車速を制御して車両を自動走行させることを意味する。「自動制動」とは、目標減速度と車速とに応じてECB120を制御することにより、前方車両との間の距離を所定距離に保ちつつ、車両を自動走行させることを意味する。「自動操舵」とは、EPS110を制御することにより車両の向き(舵角)を制御することを意味する。
The automatic
車両に電気負荷200が後付けされると、車両および自動運転制御装置10の設計時点に想定された電流量よりも多くの電流量が消費されるため、バッテリ140の過放電や瞬低が突然生じて自動運転に悪影響を及ぼすおそれがある。しかし、後述の自動運転制御処理を実行することにより、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して自動運転を実行させるので、バッテリ140の過放電や瞬低の発生を抑制できる。
When the
A2.自動運転制御処理:
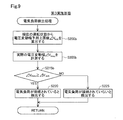
図2に示す自動運転制御処理は、車両の運転者が車両のエンジン130を始動させると、開始される。負荷接続検出部17は、追加された電気負荷を検出する処理(以下、「電気負荷検出処理」と呼ぶ)を実行する(ステップS100)。電気負荷検出処理とは、負荷接続検出部17は、電流センサ152よりもバッテリ140に近い位置に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたか否かを検出する処理である。電気負荷検出処理についての詳細な説明は後述する。
A2. Automatic operation control processing:
The automatic driving control process shown in FIG. 2 is started when the driver of the vehicle starts the
ステップS100の実行後、自動運転制御部10bは、自動運転要求があるか否かを判定する(ステップS105)。かかる自動運転要求は、車両の乗員が車両に搭載された自動運転開始を指示するボタンを押下することにより要求できる。なお、かかるボタンは、車両のインストルメントパネルや、シフトノブ近傍や、ハンドルなどの運転席近傍の場所に設けられた物理的なボタンの他、ディスプレイに表示されたメニュー画面上のソフトウエアボタンであってもよい。ディスプレイとしては、インストルメントパネルに限らず、車両に搭載されたナビゲーション装置の表示画面や、スマートフォンの表示画面であってもよい。また、車両の鍵等の車両の操作機器を利用してもよい。
After the execution of step S100, the automatic
自動運転要求があると判定された場合(ステップS105:YES)、負荷接続検出部17は、ステップS100の結果、電気負荷を検出したか否かを判定する(ステップS110)。電気負荷200を検出したと判定された場合(ステップS110:YES)、自動運転制御部10bは、自動運転機能を制限して自動運転を行う(ステップS115)。「自動運転機能を制限する」とは、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵の各機能が所定の制約を受けながら自動運転を実行することや、各機能を実行しないことを意味する。本実施形態では、自動運転制御部10bは、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵のすべての機能を実行しない。すなわち、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されていることが検出された場合、自動運転制御部10bは、自動運転を実行しない。ステップS115の実行後、自動運転制御処理は終了する。
When it is determined that there is an automatic operation request (step S105: YES), the load
上述のステップS110において、電気負荷200を検出していないと判定された場合(ステップS110:NO)、自動運転制御部10bは、自動運転機能を制限しないで自動運転を行う(ステップS120)。ステップS120の実行後、自動運転制御処理は終了する。
If it is determined in step S110 described above that the
上述のステップS105において、自動運転要求がないと判定された場合(ステップS105:NO)、上述のステップS115およびステップS120の実行後と同様に、自動運転制御処理は終了する。 If it is determined in step S105 above that there is no automatic operation request (step S105: NO), the automatic operation control process ends as in the execution of steps S115 and S120 described above.
A3.電気負荷検出処理の詳細:
先ず、図3に示す電気負荷検出処理の基本的な考え方を説明する。時間をおいて開放端電圧OCVから充電量SOCを2回推定した場合、その2回の推定値から求められる充電量SOCの変化量と、同じ時間における電流センサ152の示す電流値の積算値から求められる充電量SOCの変化量とは、通常であれば一致する。しかし、電気負荷200が接続されている場合には、2回の推定値から求められる充電量SOCの変化量は、電流センサ152の示す電流値の積算値から求められる充電量SOCの変化量よりも大きくなる。そこで、本実施形態では、これら2種類の変化量の差が所定の閾値(後述のK)よりも小さい場合に、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出する。以下、詳細に説明する。
A3. Details of electrical load detection processing:
First, the basic concept of the electric load detection process shown in FIG. 3 will be described. When the charge amount SOC is estimated twice from the open-end voltage OCV after a while, the change amount of the charge amount SOC obtained from the two estimated values and the integrated value of the current value indicated by the
図3に示すように、電気負荷検出処理が開始されると、充電量推定部12は、バッテリ140の開放端電圧OCVからバッテリ140の充電量SOCを推定する(ステップS200)。ステップS200において充電量SOCの推定に用いられる開放端電圧OCVは、バッテリ電圧を測定することにより推定される。ステップS200で推定するOCVを説明の便宜上、OCV1と呼ぶ。同様に、ステップS200で推定するSOCを説明の便宜上、SOC1と呼ぶ。開放端電圧OCVから充電量SOCを推定する方法は、公知の方法により実行され、例えば、特開2005−14637号公報に記載の方法により実行されてもよい。かかる推定方法について、以下、簡潔に説明する。
As shown in FIG. 3, when the electric load detection process is started, the charge
図4において、横軸は、時間を示している。図4において、最上段は電圧を調整する際の目標電圧である調整電圧[V]を、上から2段目はバッテリ電圧[V]を、上から3段目はバッテリ電流[A]を、それぞれ示している。バッテリ電流は、電流センサ152の示す電流値を二点鎖線で、実際の電流値を実線で、それぞれ示している。なお、「実際の電流値」とは、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されている場合におけるバッテリ140に流入・流出する電流値を意味する。
In FIG. 4, the horizontal axis represents time. In FIG. 4, the uppermost stage is the adjustment voltage [V] which is the target voltage for adjusting the voltage, the second stage from the top is the battery voltage [V], and the third stage from the top is the battery current [A]. Each is shown. As for the battery current, the current value indicated by the
図4に示すように、時間T0においてエンジン130が始動されると、オルタネータ131での発電が開始され、バッテリ電圧が増加するとともに、バッテリ電流が放電から充電へと遷移して充電電流が増加する。時間T1でオルタネータ131での発電が安定した後、時間T1から時間T2までの間において、バッテリ140が充電されるに伴いバッテリ電流は徐々に減少している。時間T2において、調整電圧が所定の電圧(例えば、11.8V)に調整されると、バッテリ電圧は略一定となり、バッテリ140が放電状態に遷移した後の時間T2と時間T3との間でバッテリ140の内部状態が安定する。バッテリ140の内部状態が安定した後の時間T3において、調整電圧を所定の電圧(11.8V)から徐々に増加させる。なお、調整電圧を徐々に増加させるのは、バッテリ140の充放電量を急激に変化させないためである。時間T4において、バッテリ電流は、二点鎖線に示すように、電流センサ152の示す電流値がゼロAとなり、バッテリ140の充放電量は微少になる。したがって、時間T4におけるバッテリ電圧は、バッテリ140の開放端子を物理的に開放した状態に近似する状態であるといえる。そこで、上述のステップS200では、時間T4におけるバッテリ電圧を測定し、測定されたバッテリ電圧をバッテリ140の開放端電圧OCV1と推定する。
As shown in FIG. 4, when the
時間T5において、バッテリ電流(実際の値)は、実線で示すようにゼロAとなる。ここで、電気負荷200が電流センサ152の上流側(バッテリ140側)に接続されている場合、電流センサ152は電気負荷200による放電量の増加分を検出できない。このため、開放端電圧OCV自体を求める場合、電流センサ152の示す電流値がゼロAとなる時間T4ではなく、実際の電流値がゼロAとなる時間T5において開放端電圧OCVを推定することが好ましい。例えば、図4に示すように、時間T4におけるバッテリ電圧と時間T5におけるバッテリ電圧とは、差分ΔVが存在するからである。しかし、時間をおいて推定した2回分の開放端電圧OCVから充電量SOCの変化量を算出する場合、かかる差分ΔVはキャンセルされることとなる。そこで、本実施形態では、電流センサ152の示す電流値がゼロAとなる時間T4において、開放端電圧OCV1を推定する。
At time T 5, the battery current (actual value) becomes zero A as shown by the solid line. Here, when the
図5において、横軸は開放端電圧OCVの推定値を示し、縦軸は充電量SOCの実測値を示している。図5に示す特性は、予め自動運転制御装置10に設定されている。図5に示すように、開放端電圧OCVが11.82Vのときに充電量SOCは0%であり、開放端電圧OCVが12.76Vのときに充電量SOCは100%である。このような開放端電圧OCVと充電量SOCとの相対的な関係を利用することにより、上述の方法により推定されたバッテリ140の開放端電圧OCVからバッテリ140の充電量SOCを推定できる。
In FIG. 5, the horizontal axis shows the estimated value of the open end voltage OCV, and the vertical axis shows the measured value of the charge amount SOC. The characteristics shown in FIG. 5 are set in advance in the automatic
図3に示すように、ステップS200の実行後、充電量推定部12は、電流積算値からSOCの変化量であるΔSOCを算出する(ステップS205)。具体的には、まず、充電量推定部12は、ステップS200の実行後から所定時間を経過するまでの電流センサ152の示す電流値を時間積分することにより電流積算値を算出する。次に、下記式(1)を用いてΔSOCを算出する。
ΔSOC[%]=電流積算値[Ah]/バッテリ140の容量[Ah]・・・(1)
As shown in FIG. 3, after the execution of step S200, the charge
ΔSOC [%] = integrated current value [Ah] /
ステップS205の実行後、充電量推定部12は、再びバッテリ140の開放端電圧OCVからSOCを推定する(ステップS210)。説明の便宜上、ステップS210で推定するOCVをステップS200で推定するOCV1と区別するために、OCV2と呼ぶ。同様に、ステップS210で推定するSOCをステップS200で推定するSOC1と区別するために、SOC2と呼ぶ。ステップS210では、上述のステップS200と同様の手順により、ステップS200の実行後から所定時間経過後におけるOCV2を推定し、推定されたOCV2からSOC2を推定する。なお、ステップS210が実行される際、電流センサ152の示す電流値がゼロAである。また、ステップS205およびステップS210における所定時間は、同じ時間である。したがって、ステップS205とステップS210とは、略同時に実行される。
After the execution of step S205, the charge
ステップS210の実行後、負荷接続検出部17は、下記式(2)を満たすか否かを判定する。
SOC2<SOC1+ΔSOC−K・・・(2)
上記式(2)において、Kは、予め定められた閾値である。かかる閾値は、実験により算出できる。上記式(2)を満たす場合、実際のSOC(SOC2)が、電気負荷200の消費電流を含んでいない場合に想定されるSOC(SOC1+ΔSOC)から閾値(K)を差し引いた値よりも小さいことを意味する。これは、電気負荷200によりバッテリ140の電流が消費されている場合に起こり得る。他方、上記式(2)を満たさない場合、実際のSOC(SOC2)が、想定されるSOC(SOC1+ΔSOC)から閾値(K)を差し引いた値以上であることを意味し、電気負荷200により電流が消費されていない場合に起こり得る。
After executing step S210, the load
SOC 2 <SOC 1 + ΔSOC-K ... (2)
In the above equation (2), K is a predetermined threshold value. Such a threshold can be calculated experimentally. When the above equation (2) is satisfied, the actual SOC (SOC 2 ) is larger than the value obtained by subtracting the threshold value (K) from the SOC (SOC 1 + ΔSOC) assumed when the current consumption of the
上記式(2)を満たすと判定された場合(ステップS215:YES)、負荷接続検出部17は、電気負荷200が接続されていると検出する(ステップS220)。他方、上記式(2)を満たさない場合(ステップS215:NO)、負荷接続検出部17は、電気負荷200が接続されていないと検出する(ステップS225)。ステップS220またはステップS225の実行後、電気負荷検出処理は終了し、図2に示す自動運転制御処理に戻って、上述のステップS105が実行される。
When it is determined that the above equation (2) is satisfied (step S215: YES), the load
上述の電気負荷検出処理の実行例を図6を用いて説明する。図6において、横軸は、時間を示している。図6において、最上段は調整電圧[V]を破線で示している。上から2段目は、バッテリ電圧[V]を実線で示している。上から3段目は、バッテリ電流[A]を示している。バッテリ電流のうち、電流センサ152の示す電流値を二点鎖線で、実際の電流値を実線で、それぞれ示している。上から4段目は、SOC[%]を示している。SOCのうち、電流積算値から算出されるSOCを実線で、実際のバッテリ140のSOCを一点鎖線で、それぞれ示している。
An execution example of the above-mentioned electric load detection process will be described with reference to FIG. In FIG. 6, the horizontal axis represents time. In FIG. 6, the uppermost stage shows the adjustment voltage [V] with a broken line. The second row from the top shows the battery voltage [V] with a solid line. The third row from the top shows the battery current [A]. Of the battery current, the current value indicated by the
図6に示す時間T0から時間T5は、図4を用いて説明した内容と同様であるので、その詳細な説明を省略する。時間T4において、上述のステップS200が実行されて、バッテリ140の開放端電圧OCV1が推定されるとともに、推定されたOCV1からSOC1が推定される。
Since the time T 0 to the time T 5 shown in FIG. 6 are the same as those described with reference to FIG. 4, detailed description thereof will be omitted. At time T 4, is executed step S200 described above, together with the open circuit voltage OCV 1 of the
時間T4から所定時間経過後である時間T6において、上述のステップS205およびステップS210が実行され、ステップS205では、電流積算値が算出されてΔSOCが算出される。図6に示すSOC2estは、時間T4におけるSOC1にΔSOCを加えた値である。かかるSOC2estは、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されていない場合において、時間T6で想定されるSOCである。また、ステップS210では、バッテリ電圧の開放端電圧OCV2が推定されるとともに、推定されたOCV2からSOC2が推定される。
At time T 6 is after a predetermined time has elapsed from the time T 4, step S205 and step S210 described above is executed. In step S205, the current integrated value ΔSOC is calculated is calculated. SOC 2Est shown in FIG. 6 is a value obtained by adding the ΔSOC to SOC 1 at time T 4. Such SOC 2est is the SOC assumed at time T 6 when the
次にステップS215が実行されて、上記式(2)が満たされるか否かが判定される。図6に示す例では、SOC2<SOC2est−Kを満たすか否かが判定される。左記式を満たす場合、すなわち、時間T4から所定時間経過後である時間T6における開放端電圧OCV2から推定されたSOC2が、当初想定したSOC2est(基準となるSOC1に電流積算値ΔSOCを加えた値)に比べて、所定の閾値Kよりも小さい場合には、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されていると判定される。
Next, step S215 is executed to determine whether or not the above equation (2) is satisfied. In the example shown in FIG. 6, it is determined whether or not SOC 2 <SOC 2est −K is satisfied. When the formula on the left is satisfied, that is, the SOC 2 estimated from the open-end voltage OCV 2 at the time T 6 after the lapse of a predetermined time from the time T 4 is the initially assumed SOC 2 est (current integrated value with the reference SOC 1). When it is smaller than the predetermined threshold value K as compared with the value obtained by adding ΔSOC), it is determined that the
以上の構成を有する第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、自動運転部10cにより実現される自動運転機能のすべてを制限して自動運転を実行しないので、バッテリ140の過放電や瞬低の発生を抑制できる。その結果、自動運転実行中における操舵不能、誤操舵および制動不能等の不具合の発生を防止できる。
According to the automatic
また、負荷接続検出部17は、バッテリ140の開放端電圧OCVから推定される充電量SOCの変化量と、電流センサ152により検出された電流の積算値により算出されるバッテリ140の充電量SOCと、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出するので、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されていることを容易に検出できる。
Further, the load
B.第2実施形態:
第2実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10と同様であるため、その詳細な説明は省略する。第2実施形態における自動運転制御処理は、電気負荷検出処理の手順において第1実施形態における電気負荷検出処理と異なり、他の処理手順は第1実施形態と同じである。
B. Second embodiment:
Since the automatic
図7に示す第2実施形態における電気負荷検出処理は、ステップS200に代えてステップS200aを実行する点と、ステップS205およびステップS210を省略する点と、ステップS215に代えてステップS215aを実行する点とにおいて、図3に示す第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と異なる。第2実施形態の電気負荷検出処理におけるその他の手順は、第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と同じであるので、同一の手順には同一の符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 In the electric load detection process according to the second embodiment shown in FIG. 7, a point where step S200a is executed instead of step S200, a point where step S205 and step S210 are omitted, and a point where step S215a is executed instead of step S215. Is different from the electric load detection process of the first embodiment shown in FIG. Since the other procedures in the electric load detection process of the second embodiment are the same as those of the electric load detection process of the first embodiment, the same procedures are designated by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
第2実施形態の電気負荷検出処理では、車両に搭載された予め定められた装置の起動する前と起動した後とにおけるバッテリ140の電圧の変化量が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出する。以下、詳細に説明する。
In the electric load detection process of the second embodiment, when the amount of change in the voltage of the
図7に示すように、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、消費電流の変化量が閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS200a)。具体的には、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、電流センサ152の示す電流値を利用して、バッテリ140の消費電流を所定時間の間繰り返し検出して消費電流の変化量を算出し、かかる変化量が予め実験により求めた閾値以上であるか否かを判定する。これは、バッテリ140の電圧変化量を特定する際に、消費電流の変化量が小さな場合と比べて、消費電流の変化量が大きな場合には、バッテリ140の電圧変化量を精度よく特定できるからである。例えば、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータのような消費電流の比較的大きな装置の起動前および起動後における消費電流を検出した場合には、消費電流の変化量が閾値以上となる。
As shown in FIG. 7, the first voltage change
消費電流の変化量が閾値以上であると判定された場合(ステップS200a:YES)、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、電圧変化量−予測値が閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS215a)。具体的には、まず、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、消費電流の変化量が閾値以上となる前後におけるバッテリ140の電圧変化量を特定する。かかる電圧変化量は、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータが起動する前における電圧センサ151の示す電圧値と、かかるアクチュエータが起動した後における電圧センサ151の示す電圧値との差から算出できる。次に、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、算出した電圧変化量と予測値とを比較する。かかる予測値は、例えば、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されていない場合におけるアクチュエータの起動する前と起動した後におけるバッテリ140の電圧変化量として設定される。
When it is determined that the amount of change in current consumption is equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S200a: YES), the first voltage change
電圧変化量−予測値が閾値以上であると判定された場合(ステップS215a:YES)、上述のステップS220が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていると検出される。他方、電圧変化量−予測値が閾値以上でないと判定された場合(ステップS215a:NO)、上述のステップS225が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていないと検出される。
When it is determined that the voltage change amount-predicted value is equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S215a: YES), the above-mentioned step S220 is executed, and it is detected that the
上述のステップS200aにおいて、消費電流の変化量が閾値以上でないと判定された場合(ステップS200a:NO)、電気負荷検出処理は終了する。 If it is determined in step S200a described above that the amount of change in current consumption is not equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S200a: NO), the electrical load detection process ends.
図8において、上段は負荷電流[A]とオルタネータ出力電流[A]との特性を、下段は負荷電流[A]とバッテリ電圧[V]との特性を、それぞれ示している。なお、「負荷電流」とは、バッテリ140に接続される全ての負荷で消費される電流の合計値を意味する。
In FIG. 8, the upper row shows the characteristics of the load current [A] and the alternator output current [A], and the lower row shows the characteristics of the load current [A] and the battery voltage [V]. The "load current" means the total value of the currents consumed by all the loads connected to the
図8上段に示すように、負荷電流が0からオルタネータ最大出力のI1までの範囲では、オルタネータ出力電流と負荷電流との差分がバッテリ140に充電される。また、負荷電流がI1を超えると、オルタネータ131では電力をまかないきれなくなり、バッテリ140が放電を行い、不足分の電流が負荷に供給される。
As shown in the upper part of FIG. 8, in the range from 0 to I 1 of the maximum output of the alternator, the difference between the alternator output current and the load current is charged to the
ここで、負荷電流が比較的小さなIB1であるときに、消費電流がILである電気負荷200がバッテリ140に接続されると、負荷電流はIL1となる。この場合、図8下段に示すように、電気負荷200が接続される前と接続された後とのバッテリ電圧の差分は、比較的小さなΔVである。他方、負荷電流が比較的大きなIB2であるときに、電気負荷200がバッテリ140に接続されると、負荷電流は比較的大きなIL2となる。この場合、図8下段に示すように、電気負荷200が接続される前と接続された後とのバッテリ電圧の差分は、比較的大きなΔV2である。かかる差分ΔV2は、ΔVよりも大きい。このように、負荷電流の相違に起因してバッテリ電圧の変化量の検出精度が異なる。したがって、負荷電流の変化量の差が閾値以上である場合にもともと予定している負荷電流よりも多くの負荷電流が流れていること、つまり、電気負荷200が接続されていることを精度よく検出できる。特に、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータのように消費電流が比較的大きな装置の起動前後のバッテリ電圧を検出することにより、バッテリ電圧の変化量を精度よく算出できる。
Here, when the load current is relatively small I B1, the current consumption
以上の構成を有する第2実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、負荷接続検出部17は、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータの起動する前と、起動した後とにおけるバッテリ140の電圧変化量が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出するので、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータの起動前および起動後を特定することにより、電気負荷200を容易に検出できる。
According to the automatic
C.第3実施形態:
第3実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10と同様であるため、その詳細な説明は省略する。第3実施形態における自動運転制御処理は、電気負荷検出処理の手順において第1実施形態における電気負荷検出処理と異なり、他の処理手順は第1実施形態と同じである。
C. Third Embodiment:
Since the automatic
図9に示す第3実施形態における電気負荷検出処理は、ステップS200に代えてステップS200bを実行する点と、ステップS205に代えてステップS205bを実行する点と、ステップS210を省略する点と、ステップS215に代えてステップS215bを実行する点とにおいて、図3に示す第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と異なる。第3実施形態の電気負荷検出処理におけるその他の手順は、第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と同じであるので、同一の手順には同一の符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 The electrical load detection process according to the third embodiment shown in FIG. 9 includes a point where step S200b is executed instead of step S200, a point where step S205b is executed instead of step S205, a point where step S210 is omitted, and a step. It differs from the electrical load detection process of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 3 in that step S215b is executed instead of S215. Since the other procedures in the electric load detection process of the third embodiment are the same as those of the electric load detection process of the first embodiment, the same procedures are designated by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
第3実施形態の電気負荷検出処理では、車両の運転状態からバッテリ140の電圧変動幅の上限値を予測し、予測した上限値と実際の電圧変動幅とを比較することにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出する。以下、詳細に説明する。
In the electric load detection process of the third embodiment, the
図9に示すように、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、現在の運転状態から電圧変動幅の予測上限値ΔVestを算出する(ステップS200b)。具体的には、まず、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、周期的に作動する負荷、例えば、イグナイタ等の点火装置の作動に伴い生じる電流の変化によるバッテリ電圧の最大値と最小値との差ΔV1を求める。ΔV1は、エンジン回転数や出力等のエンジンの運転状態に応じて変化するため、実験により求めることができる。ΔV1に対して所定の閾値を加算した値を予測上限値ΔVestとして算出する。ΔV1に対して所定の閾値を加算するのは、誤判定を抑制するためである。
As shown in FIG. 9, the first voltage change
ステップS200bの実行後、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、実際の電圧変動幅ΔVmesを計測する(ステップS205b)。具体的には、第1電圧変化量特定部13は、電圧センサ151の検出結果を利用して、バッテリ140の実際の電圧の最大値および最小値を検出して、その差分を電圧変動幅ΔVmesとする。
After the execution of step S200b, the first voltage change amount specifying unit 13 measures the actual voltage fluctuation width ΔV mes (step S205b). Specifically, the first voltage change
ステップS205bの実行後、負荷接続検出部17は、実際の電圧変動幅ΔVmesが電圧変動幅の予測上限値ΔVest以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS215b)。実際の電圧変動幅ΔVmesが電圧変動幅の予測上限値ΔVest以上であると判定された場合(ステップS215b:YES)、上述のステップS220が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていると検出される。他方、実際の電圧変動幅ΔVmesが電圧変動幅の予測上限値ΔVest以上でないと判定された場合(ステップS215b:NO)、上述のステップS225が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていないと検出される。
After executing step S205b, the load
図10において、横軸は、時間を示している。図10において、最上段は電気負荷200が接続されていない場合におけるバッテリ電圧[V]を実線で、上から2段目は電気負荷200が接続されている場合におけるバッテリ電圧[V]を破線で、最下段はバッテリ電流[A]を、それぞれ示している。図10に示すように、バッテリ電流は、例えば、イグナイタの作動に合わせて周期的に変化している。また、バッテリ電圧は、実線および破線で示すように、バッテリ140に電流が流れる場合に電圧が下がり、バッテリ140に電流が流れない場合に電圧が上がっている。ここで、バッテリ電圧は、破線で示すように電気負荷200が接続されている場合には、実線に示す電気負荷200が接続されていない場合の電圧の変動幅と比べて、大きい。
In FIG. 10, the horizontal axis represents time. In FIG. 10, the uppermost row shows the battery voltage [V] when the
図10に示すように、時間T1から所定時間Tmon経過後の時間T2までの間の時間において、電気負荷200が接続されていない場合におけるバッテリ電圧の変動幅は、ΔV1となる。また、電気負荷200が接続されている場合におけるバッテリ電圧の変動幅は、ΔVmesとなる。したがって、電圧変動幅の予測値ΔV1と実際の電圧変動幅ΔVmesとを比較することにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出できる。なお、電圧変動幅は、所定時間Tmonにおけるバッテリ電圧の最大値と最小値との差を使用してもよいし、所定時間Tmonにおけるバッテリ電圧の各変動幅の平均値を使用してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 10, in the time between the time T 1 to time T 2 of the predetermined time after T mon elapsed, the variation width of the battery voltage when the
以上の構成を有する第3実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、イグナイタの周期的な作動に応じて変化する電圧の変動幅が所定の閾値よりも大きい場合に、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出するので、電圧の変動が小さな安定した運転状態においても、電気負荷200が接続されていることを容易に検出できる。
According to the automatic
D.第4実施形態:
第4実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10と同様である。
D. Fourth Embodiment:
The automatic
図11では、図1で省略されていたリレー(後述のリレー41)を明示している。また、電気負荷200の内部構造の詳細を明示している。図11に示すように、電気負荷200は、電源制御装置10aのアクセサリ系統電源ACCにリレー41および第2電源経路を介して電気的に接続されている。また、電気負荷200は、第1電源経路を介して電源制御装置10aと接続されている。第1電源経路は、電流センサ152の上流側(バッテリ140に近い側)において電源線Cp1に接続されている。
In FIG. 11, the relay (
リレー41は、アクセサリ系統電源ACCを制御するための電気回路である。リレー41は、コイルc41と、スイッチsw41とを備える。コイルc41は、リレー41のコイルであり、コイルc41に電流を流すことで発生する磁力によりスイッチw41を切り替える。スイッチsw41は、電気負荷200の給電を切り替えるためのスイッチである。第1イグニッション系統電源IG1にはリレー42が、第2イグニッション系統電源IG2にはリレー43が、それぞれ接続されている。リレー42およびリレー43は、リレー41と同様な構成を有するので、その詳細な説明は省略する。なお、図11では、リレー42およびリレー43のそれぞれの下流側の装置の図示を省略している。
The
図11に示すように、電気負荷200は、リレー241と、内部回路250と、を備える。リレー241は、コイルc241と、スイッチsw241とを備える。コイルc241は、上述のコイルc41と同様な構成を有する。スイッチsw241は、上述のスイッチsw41と同様な構成を有する。内部回路250は、リレー241と電気的に接続されており、電気負荷200(高出力アンプ)の有する機能を実現する。内部回路250は、電気負荷200における電気的負荷として働く。
As shown in FIG. 11, the
アクセサリ系統電源ACCがオンしてコイルc41に電力が供給されると、スイッチsw41がオンし、リレー41はオフからオンに切り替わる。第2電源経路を介して電気負荷200のコイルc241に電力が供給されると、スイッチsw241がオンし、リレー241はオフからオンに切り替わる。そして、第1電源経路を介してバッテリ140から電気負荷200の内部回路250に電力が供給される。また、アクセサリ系統電源ACCがオフしてコイルc41に電力が供給されなくなると、スイッチsw41がオフし、リレー41はオンからオフに切り替わる。第2電源経路を介して電気負荷200のコイルc241に電力が供給されなくなると、スイッチsw241がオフし、リレー241はオンからオフに切り替わる。そして、第1電源経路を介してバッテリ140から電気負荷200の内部回路250への電力の供給が停止される。
When the accessory system power supply ACC is turned on and power is supplied to the coil c41, the switch sw41 is turned on and the
上述のように、電気負荷200は、消費電力の比較的大きな負荷であるため、アクセサリ系統電源ACCがオフの場合にバッテリ140の電力を消費しないように、リレー41を介してアクセサリ系統電源ACCと接続され、リレー41のオン/オフを切り替えることにより、バッテリ140からの電力の供給と停止とが制御される。
As described above, since the
第4実施形態における自動運転制御処理は、電気負荷検出処理の手順において第1実施形態における電気負荷検出処理と異なり、他の処理手順は第1実施形態と同じである。 The automatic operation control process in the fourth embodiment is different from the electric load detection process in the first embodiment in the procedure of the electric load detection process, and the other processing procedures are the same as those in the first embodiment.
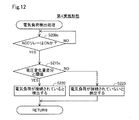
図12に示す第4実施形態における電気負荷検出処理は、ステップS200に代えてステップS200cを実行する点と、ステップS205およびステップS210を省略する点と、ステップS215に代えてステップS215cを実行する点とにおいて、図3に示す第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と異なる。第4実施形態の電気負荷検出処理におけるその他の手順は、第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と同じであるので、同一の手順には同一の符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 In the electric load detection process according to the fourth embodiment shown in FIG. 12, a point where step S200c is executed instead of step S200, a point where step S205 and step S210 are omitted, and a point where step S215c is executed instead of step S215. Is different from the electric load detection process of the first embodiment shown in FIG. Since the other procedures in the electric load detection process of the fourth embodiment are the same as those of the electric load detection process of the first embodiment, the same procedures are designated by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
第4実施形態の電気負荷検出処理では、リレー41がオンにされたときに電気負荷200とバッテリ140とが電気的に接続されることを前提として、リレー41がオンにされたときの電圧変化量と、電気負荷200が接続されていない場合におけるリレー41がオンにされたときの電圧変化量と、を比較することにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出する。以下、詳細に説明する。
In the electric load detection process of the fourth embodiment, it is assumed that the
図12に示すように、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、リレー41がオンであるか否かを判定する(ステップS200c)。リレー41がオンでないと判定された場合(ステップS200c:NO)、ステップS200cの実行前に戻り、リレー41がオンにされたと判定されるまで繰り返しステップS200cを実行する。
As shown in FIG. 12, the second voltage change
上述のステップS200cにおいて、リレー41がオンであると判定された場合(ステップS200c:YES)、負荷接続検出部17は、電圧変化量差分が閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS215c)。具体的には、まず、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、リレー41のオン前後における電流センサ152の示す電流値を利用して、バッテリ140の電圧変化量を特定する。次に、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、特定された電圧変化量と、予めマップに記憶されている電気負荷200が接続されていない場合におけるリレー41がオンにされたときの電圧変化量と、の差分(以下、「電圧変化量差分」と呼ぶ)を算出する。負荷接続検出部17は、かかる差分が所定の閾値以上であるか否かを判定する。かかる差分が所定の閾値以上であることは、バッテリ140に予め想定しているよりも大きな電圧変動がある、すなわち、消費電流が多いことを意味する。
When it is determined in step S200c described above that the
電圧変化量差分が閾値以上であると判定されると(ステップS215c:YES)、上述のステップS220が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていると検出される。他方、電圧変化量差分が閾値以上でないと判定されると(ステップS215c:NO)、上述のステップS225が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていないと検出される。
When it is determined that the voltage change amount difference is equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S215c: YES), the above-mentioned step S220 is executed, and it is detected that the
図13において、横軸は、時間を示している。図13において、最上段はアクセサリ系統電源ACCのオン/オフの状態を示している。上から2段目は第1イグニッション系統電源IG1のオン/オフの状態を、上から3段目は第2イグニッション系統電源IG2のオン/オフの状態を、それぞれ示している。上から4段目は、バッテリ電流[A]を示しており、実際の電流値を一点鎖線で、電流センサ152の示す値を実線で、それぞれ示している。上から5段目は、バッテリ電圧[V]を示しており、電流センサ152の示す電流値から推定される電圧を二点鎖線で、電圧センサ151の示す電圧を実線で、それぞれ示している。最下段は、電圧変化量差分を示している。
In FIG. 13, the horizontal axis represents time. In FIG. 13, the uppermost stage shows the on / off state of the accessory system power supply ACC. The second stage from the top shows the on / off state of the first ignition system power supply IG1, and the third stage from the top shows the on / off state of the second ignition system power supply IG2. The fourth row from the top shows the battery current [A], the actual current value is shown by the alternate long and short dash line, and the value indicated by the
図13に示すように、時間T1において、アクセサリ系統電源ACCがオフの状態からオンの状態になると、バッテリ電流は、増加する。また、バッテリ電圧は、バッテリ電流の消費分(放電分)だけ低下する。時間T1において、上述のステップS215cが実行されて、バッテリ電圧が検出される。ここで、電気負荷200が接続されている場合、電流センサ152は電気負荷200の消費電流を検出できないため、実線で示す電圧センサ151の示すバッテリ電圧は、二点鎖線で示す電流センサ152の示す電流値から推定される電圧に比べて大きい。この2つの電圧の差が電圧変化量差分ΔVとして算出される。上述のステップS215cでは、かかる電圧変化量差分ΔVが所定の閾値以上である場合、電気負荷200が接続されたことが検出される。
As shown in FIG. 13, at time T 1, the accessory system power supply ACC is turned on from off, the battery current increases. In addition, the battery voltage is reduced by the amount of battery current consumed (discharged). At time T 1, the above-described step S215c is performed, the battery voltage is detected. Here, when the
その後、時間T2において第1イグニッション系統電源IG1がオンにされると、バッテリの電流はさらに増加するとともに、バッテリ電圧はさらに低下する。その後、時間T3において第2イグニッション系統電源IG2がオンにされると、バッテリの電流はさらに増加するとともに、バッテリ電圧はさらに低下する。但し、第1イグニッション系統電源IG1、第2イグニッション系統電源IG2がオンしたときの電圧変化量差分ΔVは、アクセサリ系統電源ACCがオンしたときの電圧変化量差分ΔVから変化していない。 Thereafter, when the first ignition system power supply IG1 is turned on at time T 2, together with the battery current is further increased, the battery voltage is further reduced. Thereafter, when the second ignition system power supply IG2 is turned on at time T 3, with the battery current is further increased, the battery voltage is further reduced. However, the voltage change amount difference ΔV when the first ignition system power supply IG1 and the second ignition system power supply IG2 are turned on does not change from the voltage change amount difference ΔV when the accessory system power supply ACC is turned on.
以上の構成を有する第4実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、負荷接続検出部17は、リレー41がオフからオンに切り替わる際の、電圧センサ151により検出されるバッテリの電圧変化量と、第2電圧変化量特定部14により特定された電圧変化量との差である電圧変化量差分が、予め定められた変化量よりも大きい場合に、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出するので、リレー41がオフからオンに切り替わる際、すなわち、車両のエンジンが始動する際に電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出できる。このため、車両の走行中に電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出する構成に比べて、より早いタイミングで電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出できるので、バッテリ140の過放電や瞬低の発生をより早いタイミングから抑制できる。
According to the automatic
E.第5実施形態:
第5実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10と同様であるため、その詳細な説明は省略する。第5実施形態における自動運転制御処理は、電気負荷検出処理の手順において第1実施形態における電気負荷検出処理と異なり、他の処理手順は第1実施形態と同じである。
E. Fifth embodiment:
Since the automatic
図14に示す第5実施形態における電気負荷検出処理は、ステップS200に代えてステップS200dを実行する点と、ステップS205およびステップS210を省略する点と、ステップS215に代えてステップS215dを実行する点とにおいて、図3に示す第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と異なる。第5実施形態の電気負荷検出処理におけるその他の手順は、第1実施形態の電気負荷検出処理と同じであるので、同一の手順には同一の符号を付し、その詳細な説明は省略する。 The electrical load detection process according to the fifth embodiment shown in FIG. 14 is a point where step S200d is executed instead of step S200, a point where step S205 and step S210 are omitted, and a point where step S215d is executed instead of step S215. Is different from the electric load detection process of the first embodiment shown in FIG. Since the other procedures in the electric load detection process of the fifth embodiment are the same as those of the electric load detection process of the first embodiment, the same procedures are designated by the same reference numerals, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
第5実施形態の電気負荷検出処理では、バッテリ140の充放電電流量の増加に伴ってバッテリ140の発熱量が増加するためにバッテリ140の温度が上昇するという特性を利用して、車両の走行開始時から所定時間の間におけるバッテリ140の温度を検出し、検出した温度と、外気温度や運転状態から推定されるバッテリ140の温度とを比較することにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出する。以下、詳細に説明する。
In the electric load detection process of the fifth embodiment, the running of the vehicle utilizes the characteristic that the temperature of the
図14に示すように、温度推定部16は、外気温度および運転状態に基づき、車両の走行開始時から所定時間の間におけるバッテリ温度を推定する(ステップS200d)。例えば、低速走行では風による冷却が少なくバッテリ温度は上昇する。また、外気温度が高いとバッテリ温度は上昇する。このような外気温度や運転状態に応じたバッテリ温度を予めマップに記憶しておき、かかるマップを参照して特定された外気温度や運転状態に対応するバッテリ温度を推定する。ステップS200dの実行後、負荷接続検出部17は、温度センサ153により検出される実際のバッテリ温度とステップS200dにおいて推定されたバッテリ温度との差が閾値以上であるか否かを判定する(ステップS215d)。かかる差が所定の閾値以上であることは、予め想定される電流量よりも多くの放電が行われたことによりバッテリ140の発熱量が増加したことを意味する。
As shown in FIG. 14, the temperature estimation unit 16 estimates the battery temperature during a predetermined time from the start of traveling of the vehicle based on the outside air temperature and the operating state (step S200d). For example, at low speeds, the cooling by the wind is small and the battery temperature rises. Further, when the outside air temperature is high, the battery temperature rises. Such a battery temperature corresponding to the outside air temperature and the operating state is stored in a map in advance, and the battery temperature corresponding to the specified outside air temperature and the operating state is estimated by referring to the map. After executing step S200d, the load
実際のバッテリ温度と推定したバッテリ温度との差が閾値以上であると判定された場合(ステップS215d:YES)、上述のステップS220が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていると検出される。他方、実際のバッテリ温度と推定したバッテリ温度との差が閾値以上でないと判定された場合(ステップS215d:NO)、上述のステップS225が実行されて、電気負荷200が接続されていないと検出される。
When it is determined that the difference between the actual battery temperature and the estimated battery temperature is equal to or greater than the threshold value (step S215d: YES), the above-mentioned step S220 is executed, and it is detected that the
図15において、横軸は、時間を示している。図15において、最上段はバッテリ温度[℃]を、上から2段目はバッテリ充電量SOC[%]を、上から3段目はバッテリ電流[A]を、上から4段目はエンジン回転数[rpm]を、最下段は車速[km/h]を、それぞれ示している。バッテリ温度、バッテリSOCおよびバッテリ電流は、電気負荷200が接続されている場合を実線で、電気負荷200が接続されていない場合を1点鎖線で、それぞれ示している。
In FIG. 15, the horizontal axis represents time. In FIG. 15, the uppermost stage is the battery temperature [° C.], the second stage from the top is the battery charge amount SOC [%], the third stage from the top is the battery current [A], and the fourth stage from the top is the engine rotation. The number [rpm] is shown, and the vehicle speed [km / h] is shown at the bottom. The battery temperature, battery SOC, and battery current are shown by a solid line when the
時間T0において車両は停車状態である。なお、このとき、車両は、アイドリングストップ状態である。したがって、車速は0km/hであり、エンジン回転数は0rpmである。車両の停車状態(時間T0〜時間T1)では、アイドリングストップによりエンジン130が停止状態であるためにオルタネータ131が発電できず、バッテリ140から電力をまかなう。このとき、例えば、車両に搭載されたナビゲーション装置等の機器の負荷により、バッテリ140から放電が行われる。したがって、図15に示すように、バッテリSOCは徐々に低下している。バッテリ温度は、バッテリ140からの放電に伴う発熱により、徐々に上昇している。
Vehicle is stopped state at time T 0. At this time, the vehicle is in the idling stop state. Therefore, the vehicle speed is 0 km / h and the engine speed is 0 rpm. When the vehicle is stopped (time T 0 to time T 1 ), the
時間T1においてアイドリングストップが解除されてエンジンが始動され車両の走行が開始されると、エンジン回転数は上昇して車速が増加する。エンジン回転数の上昇に伴いオルタネータ131での発電量が増加して、オルタネータ131によって発電された電力がバッテリ140に充電されて、バッテリSOCは増加している。
When the time T 1 is the running of the start-up idling stop is released engine vehicle is started, the engine speed rises and the vehicle speed is increased. As the engine speed increases, the amount of power generated by the
電気負荷200が接続されていない場合は、一点鎖線に示すように、時間T2においてバッテリSOCの充電が完了し、バッテリSOCは略一定となる。他方、電気負荷200が接続されている場合、実線で示すように、時間T2よりも遅い時間T3においてバッテリSOCの充電が完了する。すなわち、電気負荷200が接続されている場合、バッテリ140の充電に要する時間が長くなり、その分、バッテリ140での発熱量が増加するため、図15に示すように、バッテリ温度の上昇量が増加する。したがって、時間T1から時間T3におけるバッテリ温度を検出して、所定の閾値と比較することにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出できる。
If an
以上の構成を有する第5実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、負荷接続検出部17は、車両の走行開始時から予め定められた時間の間における温度センサ153の示すバッテリ140の実測温度が推定温度よりも予め定められた閾値以上大きい場合に、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことを検出する。このため、車両に予め搭載された温度センサ153を利用して電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出でき、かかる検出に要するコストを抑えることができる。
According to the automatic
F.第6実施形態:
第6実施形態における自動運転制御装置10は、図1に示す第1実施形態における自動運転制御装置10と同様であるため、その詳細な説明は省略する。第6実施形態における自動運転制御処理は、自動運転機能を制限して自動運転を行う際に(上述のステップS115)、制限する自動運転機能を決定する処理(以下、「自動運転機能制限処理」と呼ぶ)を追加して実行する点において、第1実施形態における自動運転制御処理と異なる。
F. Sixth Embodiment:
Since the automatic
図16に示す第6実施形態における自動運転機能制限処理の概要を説明する。電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出した場合に、第1実施形態ではすべての自動運転機能が所定の制約を受けながら自動運転を実行し、かかる所定の制約とは、各機能を全く実行しないという制約であった。これに対して、第6実施形態では、「所定の制約を受けながら自動運転を実行する」とは、自動運転機能の段階を下げて自動運転を実行することを意味する。自動運転機能の段階を下げる際、電圧変化量の差分と、バッテリ140の内部抵抗値とを利用して、自動運転の機能制限レベルを決定する。以下、詳細に説明する。
The outline of the automatic operation function limiting process in the sixth embodiment shown in FIG. 16 will be described. When it is detected that the
図16に示すように、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、電圧変化量差分ΔVを検出する(ステップS300)。具体的には、上述のステップS215cと同様に、リレー41のオンの前後におけるバッテリ140の電圧変化量の差分を検出する。
As shown in FIG. 16, the second voltage change
ステップS300の実行後、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、算出した電圧変化量差分ΔVとバッテリ140の内部抵抗値とを利用して電気負荷200の消費電流Iaddを算出する(ステップS305)。具体的には、第2電圧変化量特定部14は、下記式(3)を用いて、電気負荷200の消費電流Iaddを算出する。
Iadd=ΔV/Ri・・・(3)
上記式(3)において、Riは、バッテリ140の内部抵抗値である。
After the execution of step S300, the second voltage change amount specifying unit 14 calculates the current consumption Iadd of the
I add = ΔV / Ri ... (3)
In the above formula (3), Ri is the internal resistance value of the
ここで、内部抵抗値Riは、公知の方法により求めることができ、例えば、特開2007−223530号公報に記載の方法により求めてもよい。具体的には、バッテリ140の電圧および電流のペアを所定のタイミングにて複数サンプリングし、サンプリングした電圧および電流の複数のペア群を利用して内部抵抗値Riを算出する。より具体的には、サンプリングした電圧および電流を二次元プロットして回帰直線を求め、かかる回帰直線の傾きを内部抵抗値Riとして算出する。
Here, the internal resistance value Ri can be obtained by a known method, and may be obtained, for example, by the method described in JP-A-2007-223530. Specifically, a plurality of voltage and current pairs of the
ステップS305の実行後、自動運転制御部10bは、算出した消費電流Iaddから自動運転の機能制限レベルを決定する(ステップS310)。具体的には、予め消費電流の値に応じて電圧変動が大きくなりやすいと想定される装置とを対応づけておき、算出した消費電流Iaddに基づいて、電圧変動が大きくなりやすいと想定される装置により実現される自動運転機能を制限する。例えば、算出された消費電流Iaddが所定の閾値よりも大きい場合に電圧変動が大きくなりやすいと予め想定される自動運転部10cとしてEPS110が特定された場合には、自動運転制御部10bは、自動操舵の機能を制限する。また、算出された消費電流Iaddが所定の閾値よりも大きい場合に電圧変動が大きくなりやすいと予め想定される自動運転部10cとしてECB120が特定された場合には、自動運転制御部10bは、自動制動の機能を制限してもよい。また、算出された消費電流Iaddが所定の閾値よりも大きい場合には、自動運転制御部10bは、自動駆動用の装置の動作を制限してもよい。この場合、例えば、エンジン回転数を高く維持することで制限される電圧を下回らない場合、エンジン回転数の下限を制限してもよい。
After step S305, the automatic
ステップS310の実行後、自動運転機能制限処理は終了し、決定された機能制限レベルに応じて自動運転機能が制限されて自動運転が実行される。 After the execution of step S310, the automatic operation function restriction process ends, the automatic operation function is restricted according to the determined function restriction level, and the automatic operation is executed.
なお、第6実施形態における電気負荷検出処理は、図3に示す第1実施形態における電気負荷検出処理と同様であるため、その詳細な説明は省略する。 Since the electric load detection process in the sixth embodiment is the same as the electric load detection process in the first embodiment shown in FIG. 3, detailed description thereof will be omitted.
以上の構成を有する第6実施形態における自動運転制御装置10によれば、電圧変化量差分ΔVとバッテリ140の内部抵抗値Riとを利用して電気負荷200の消費電流Iaddを算出し、算出された消費電流Iaddに応じて自動運転機能の機能制限レベルを決定するので、消費電流Iaddがより大きい場合に自動運転機能をより制限することができる。このため、消費電流Iaddが大きいために電圧変動が大きくなることによる自動運転への悪影響を低減できる。
According to the automatic
G.変形例:
G1.変形例1:
上記第1実施形態において、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出された場合にすべての自動運転機能を制限して自動運転を実行していなかったが、本発明はこれに限定されない。
G. Modification example:
G1. Modification 1:
In the first embodiment, when it is detected that the
図17に示す各自動運転機能の機能制限の有無の組み合わせには、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵のいずれも機能制限がない第1状態と、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵のうちの少なくとも1つに機能制限がある第2状態とがある。第1状態は、電気負荷200が接続されていないことを検出された場合における自動運転の実行状態である。第2状態は、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出された場合における自動運転の実行状態である。
The combination of the presence or absence of functional restrictions of each automatic driving function shown in FIG. 17 includes the first state in which none of automatic driving, automatic braking, and automatic steering has functional restrictions, and at least one of automatic driving, automatic braking, and automatic steering. One is the second state, which has functional restrictions. The first state is the execution state of the automatic operation when it is detected that the
本変形例において、「機能制限がある」(図17における「×」)とは、自動駆動、自動制動および自動操舵の各機能が所定の制約を受けながら実行することを意味する。例えば、自動駆動の機能制限があるとは、車速が時速50kmを超えないように制御されることであってもよい。また、例えば、自動制動の機能制限があるとは、前方車両との車間距離を機能制限がない場合と比べて大きくすることであってもよい。このように自動制動の機能制限が設けられるのは、減速度が小さくなるように制限されるからである。また、例えば、自動操舵の機能制限があるとは、ハンドルをきることができる角度が所定の範囲内に制限されることであってもよい。このように自動操舵の機能制限が設けられるのは、EPS110の備えるモータの出力が制限されるからである。なお、機能制限の例は、上述の例に限られず、各機能に対して所定の制約をして実行することにより車両が安定して走行できる構成であれば、他の任意の機能制限を設けてもよい。
In this modification, "there is a function limitation" ("x" in FIG. 17) means that each function of automatic driving, automatic braking, and automatic steering is executed while being subject to predetermined restrictions. For example, the limitation of the automatic drive function may mean that the vehicle speed is controlled so as not to exceed 50 km / h. Further, for example, the function limitation of automatic braking may mean that the inter-vehicle distance to the vehicle in front is made larger than that in the case where there is no function limitation. The reason why the automatic braking function is restricted in this way is that the deceleration is restricted to be small. Further, for example, the function limitation of automatic steering may mean that the angle at which the steering wheel can be turned is limited within a predetermined range. The reason why the function limitation of the automatic steering is provided in this way is that the output of the motor included in the
図17に示すように、第2状態は、例えば、自動駆動および自動制動は「機能制限なし」(○)であり、かつ、自動操舵は「機能制限あり」(×)である場合や、自動駆動および自動操舵は「機能制限なし」(○)であり、かつ、自動制動は「機能制限あり」(×)である場合や、自動駆動は「機能制限なし」(○)であり、自動制動および自動操舵は「機能制限あり」(×)である場合等が該当する。本変形例では、電気負荷200が接続されていることが検出された場合に、第2状態のいずれかの態様で自動運転が実行される構成であれば、上記第1実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。すなわち、一般には、バッテリ140に電気負荷200が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、自動運転部10cにより実現される自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる構成であれば、上記第1実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。なお、第2状態に掲げる機能制限の有無の組み合わせのうち、いずれの実行状態で自動運転を実行するかは、例えば、上記第6実施形態で述べたように、電圧変化量差分ΔVとバッテリ140の内部抵抗値Riとを利用して決定してもよい。
As shown in FIG. 17, the second state is, for example, when automatic driving and automatic braking are "no function limitation" (○) and automatic steering is “function limitation” (×), or when automatic steering is performed. Drive and automatic steering are "no function restrictions" (○), automatic braking is "function restrictions" (x), and automatic drive is "no function restrictions" (○), and automatic braking And automatic steering corresponds to the case where "function is limited" (x). In this modification, if it is detected that the
G2.変形例2:
上記各実施形態において、自動運転部10cの動作電圧を考慮せずに自動運転機能の機能制限の有無を決定していたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。
G2. Modification 2:
In each of the above embodiments, the presence or absence of functional limitation of the automatic driving function has been determined without considering the operating voltage of the
図18において、横軸はエンジン回転数[rpm]を、縦軸はオルタネータ最大出力[A]を、それぞれ示している。図18に示すように、エンジン回転数がアイドル回転数であるときに、オルタネータ最大出力は最小である。エンジン回転数が増加するにつれて、オルタネータ最大出力も増加する。したがって、オルタネータ最大出力は、オルタネータ131の性能と、エンジン回転数とで決定されると言える。本変形例では、このようなオルタネータ最大出力の特性を利用することにより消費電流を特定して、電気負荷200が接続された場合に動作に影響がある装置の稼働を停止する。以下、詳細に説明する。
In FIG. 18, the horizontal axis represents the engine speed [rpm], and the vertical axis represents the alternator maximum output [A]. As shown in FIG. 18, the maximum output of the alternator is the minimum when the engine speed is the idle speed. As the engine speed increases, so does the maximum alternator output. Therefore, it can be said that the maximum output of the alternator is determined by the performance of the
図19において、上段は負荷電流[A]とオルタネータ出力電流[A]との特性を、下段は負荷電流[A]とバッテリ電圧[V]との特性を、それぞれ示している。まず、バッテリ140に接続される全ての負荷でそれぞれ予め定められている負荷電流に基づいて、バッテリ140に接続される全ての負荷の負荷電流の最大値Imを算出する。図19上段および下段には、算出された負荷電流の最大値Imを示している。上述のように、オルタネータ最大出力は、エンジン回転数により決定されるので、図18に示す特性を利用することにより、図19上段に示すオルタネータ最大出力Altmが決定する。ここで、負荷電流Iαは、オルタネータ最大出力Altmと同じ値である。負荷電流Iαは、図8に示す負荷電流I1と同様に、バッテリ140の充電から放電に切り替えられる負荷電流である。
In FIG. 19, the upper row shows the characteristics of the load current [A] and the alternator output current [A], and the lower row shows the characteristics of the load current [A] and the battery voltage [V]. First, based on the load current is predetermined respectively at all loads connected to the
一般に、バッテリ140の電圧は、充電から放電に切り替えられる際に低下することから、図19下段に示すような関係が得られる。このとき、バッテリ140に接続される全ての負荷の負荷電流の最大値Imに対応するバッテリ電圧Vαを求めることができる。そして、例えば、EPS110のポンプの動作電圧や、ECB120のモータの動作電圧が、算出されたバッテリ電圧Vαよりも下回っている場合に、自動駆動や自動操舵の機能を制限してもよい。したがって、このような構成においても、上記各実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
In general, the voltage of the
G3.変形例3:
上記各実施形態において、自動運転制御装置10はガソリンを燃料とする車両に搭載されていたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、自動運転制御装置10は、燃料電池車両に搭載されてもよい。また、例えば、ハイブリッド車両や電気自動車に搭載されてもよい。この構成では、オルタネータ131に代えて、DC/DCコンバータを備えることにより、上記各実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
G3. Modification 3:
In each of the above embodiments, the automatic
G4.変形例4:
上記第3実施形態において、電圧変動幅の予測上限値ΔVestは電圧変動幅ΔV1に所定の閾値を加算した値であったが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、電圧変動幅ΔV1を予測上限値ΔVestとしてもよい。このような構成においても、上記第3実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
G4. Modification 4:
In the third embodiment, the predicted upper limit value ΔVest of the voltage fluctuation width is a value obtained by adding a predetermined threshold value to the voltage fluctuation width ΔV 1, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, a voltage fluctuation width [Delta] V 1 may be predicted upper limit value [Delta] V est. Even in such a configuration, the same effect as that of the third embodiment is obtained.
G5.変形例5:
上記各実施形態において、電気負荷検出処理(ステップS100)は自動運転制御処理において一度実行された後、再び実行されなかったが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、所定時間経過ごとに実行してもよい。また、例えば、車両のエンジンが稼働している間、繰り返し自動運転制御処理を実行することにより、電気負荷検出処理を繰り返し実行してもよい。このような構成においても、上記各実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
G5. Modification 5:
In each of the above embodiments, the electric load detection process (step S100) is executed once in the automatic operation control process and then not executed again, but the present invention is not limited thereto. For example, it may be executed every predetermined time elapses. Further, for example, the electric load detection process may be repeatedly executed by repeatedly executing the automatic driving control process while the engine of the vehicle is running. Even in such a configuration, the same effect as that of each of the above-described embodiments can be obtained.
G6.変形例6:
上記第2実施形態において、ステップS200aは消費電流の変化量が閾値以上であると判定された場合に実行されていたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、自動運転制御装置10が、ブレーキやパワーステアリングで用いられるアクチュエータが起動した旨の通知を自動運転部10cから受信可能な構成においては、かかる通知を受信したことを契機としてステップS215aを実行してもよい。このような構成においても、上記第2実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。加えて、消費電流の変化量が閾値以上であるか否かを判定する処理(ステップS200a)を省略できるので、電気負荷検出処理に要する時間および処理負荷を削減できる。
G6. Modification 6:
In the second embodiment, the step S200a is executed when it is determined that the amount of change in the current consumption is equal to or greater than the threshold value, but the present invention is not limited to this. For example, in a configuration in which the automatic
G7.変形例7:
実施形態および各変形例において、ソフトウェアによって実現された機能及び処理の一部又は全部は、ハードウェアによって実現されてもよい。また、ハードウェアによって実現された機能及び処理の一部又は全部は、ソフトウェアによって実現されてもよい。ハードウェアとしては、例えば、集積回路、ディスクリート回路、または、それらの回路を組み合わせた回路モジュールなど、各種回路を用いてもよい。また、本発明の機能の一部または全部がソフトウェアで実現される場合には、そのソフトウェア(コンピュータプログラム)は、コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体に格納された形で提供することができる。「コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体」とは、フレキシブルディスクやCD−ROMのような携帯型の記録媒体に限らず、各種のRAMやROM等のコンピュータ内の内部記憶装置や、ハードディスク等のコンピュータに固定されている外部記憶装置も含んでいる。すなわち、「コンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体」とは、データパケットを一時的ではなく固定可能な任意の記録媒体を含む広い意味を有している。
G7. Modification 7:
In the embodiments and each modification, some or all of the functions and processes realized by the software may be realized by the hardware. In addition, some or all of the functions and processes realized by the hardware may be realized by the software. As the hardware, various circuits such as an integrated circuit, a discrete circuit, or a circuit module combining these circuits may be used. Further, when a part or all of the functions of the present invention are realized by software, the software (computer program) can be provided in a form stored in a computer-readable recording medium. "Computer readable recording medium" is not limited to portable recording media such as flexible disks and CD-ROMs, but is fixed to internal storage devices in computers such as various RAMs and ROMs, and computers such as hard disks. It also includes external storage devices that have been installed. That is, the term "computer-readable recording medium" has a broad meaning including any recording medium in which data packets can be fixed rather than temporarily.
G8.変形例8:
上記第4実施形態において、電気負荷200はアクセサリ系統電源ACCに接続されていたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、電気負荷200は、第1イグニッション系統電源IG1に接続されていてもよい。この構成では、リレー42がオフからオンに切り替わる際の電圧変化量差分が予め定められた変化量よりも大きい場合に、電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出できる。また、例えば、電気負荷200は、第2イグニッション系統電源IG2に接続されていてもよい。この構成では、リレー43がオフからオンに切り替わる際の電圧変化量差分が予め定められた変化量よりも大きい場合に、電気負荷200が接続されたことを検出できる。このような構成においても、上記第4実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
G8. Modification 8:
In the fourth embodiment, the
G9.変形例9:
上記第4実施形態および変形例8において、各電源系統ACC、IG1およびIG2の起動はリレー41、42、43のオンとオフとを切り替えることにより行っていたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、リレーを用いない構成においては、キーシリンダによるメカニカルなスイッチを用いることにより、各電源系統を起動してもよい。このような構成においても、上記第4実施形態および変形例8と同様な効果を奏する。
G9. Modification 9:
In the fourth embodiment and the eighth modification, the power supply systems ACC, IG1 and IG2 are started by switching the
G10.変形例10:
上記第1実施形態において、開放端電圧OCVから推定した2回分の充電量SOC(SOC1、SOC2)の変化量は求めず、上記式(2)の演算を行うことにより、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出していたが、本発明はこれに限定されない。例えば、推定した2回分の充電量SOC(SOC1、SOC2)の変化量を求めて、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出してもよい。具体的には、推定した2回分の充電量SOC(SOC1、SOC2)から充電量SOCの変化量を求める。また、電流センサ152の示す電流値の積算値からバッテリ140の充電量SOCの変化量を求める。これら2つの充電量SOCの変化量の差が所定の閾値(上述のK)よりも小さい場合に、電気負荷200が接続されていることを検出してもよい。このような構成においても、上記第1実施形態と同様な効果を奏する。
G10. Modification 10:
In the first embodiment, the change amount of the charge amount SOC (SOC 1 , SOC 2 ) for two times estimated from the open end voltage OCV is not obtained, and the
本発明は、上述の実施形態および変形例に限られるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の構成で実現することができる。例えば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部又は全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部又は全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiments and modifications, and can be realized with various configurations without departing from the spirit of the present invention. For example, the embodiments corresponding to the technical features in each of the embodiments described in the column of the outline of the invention, the technical features in the modified examples are used to solve some or all of the above-mentioned problems, or the above-mentioned above. It is possible to replace or combine them as appropriate to achieve some or all of the effects. Further, if the technical feature is not described as essential in the present specification, it can be deleted as appropriate.
10…自動運転制御装置、10b…自動運転制御部、10c…自動運転部、17…負荷接続検出部、140…バッテリ、200…電気負荷 10 ... Automatic operation control device, 10b ... Automatic operation control unit, 10c ... Automatic operation unit, 17 ... Load connection detection unit, 140 ... Battery, 200 ... Electric load
Claims (9)
前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、
を備え、
前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路(Cp1)において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する電流検出部(152)と、 前記バッテリの開放端電圧を推定する開放端電圧推定部(11)と、
推定された前記開放端電圧を利用して前記バッテリの充電量を推定する充電量推定部(12)と、
を、さらに備え、
前記負荷接続検出部は、予め定められた時間における推定された前記充電量の変化量と、検出された前記電流の前記予め定められた時間における積算値と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、
自動運転制御装置。 An automatic driving control device (10) that controls the automatic driving of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140).
A load connection detection unit (17) for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery, and a load connection detection unit (17).
When it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery, it is realized by an automatic operation unit (10c) that is supplied with power from the battery and has an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation. An automatic operation control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions, and
Equipped with a,
In the power path (Cp1) between the battery and the automatic operation unit, the current detection unit (152) that detects a current at a position closer to the automatic operation unit than the connection point with the electric load, and the battery. The open-end voltage estimation unit (11) that estimates the open-end voltage,
A charge amount estimation unit (12) that estimates the charge amount of the battery using the estimated open-end voltage, and a charge amount estimation unit (12).
To prepare for
In the load connection detection unit, the difference between the estimated change amount of the charge amount in the predetermined time and the integrated value of the detected current in the predetermined time is from a predetermined threshold value. Is also large, it detects that the electrical load is electrically connected to the battery.
Automatic operation control device.
前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、
を備え、
前記車両に搭載され、前記バッテリの電圧を測定する電圧センサ(151)と、
測定された前記バッテリの電圧を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する第1電圧変化量特定部(13)と、
を、さらに備え、
前記負荷接続検出部は、前記車両に搭載された予め定められた装置が起動する前と、前記予め定められた装置が起動した後と、における特定された前記バッテリの電圧の変化量が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、
自動運転制御装置。 An automatic driving control device (10) that controls the automatic driving of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140).
A load connection detection unit (17) for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery, and a load connection detection unit (17).
When it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery, it is realized by an automatic operation unit (10c) that is supplied with power from the battery and has an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation. An automatic operation control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions, and
With
A voltage sensor (151) mounted on the vehicle and measuring the voltage of the battery,
The first voltage change amount specifying unit (13) for specifying the change amount of the battery voltage by using the measured voltage of the battery, and
To prepare for
In the load connection detection unit, the amount of change in the voltage of the specified battery before the activation of the predetermined device mounted on the vehicle and after the activation of the predetermined device is predetermined. Detects that the electrical load is electrically connected to the battery if it is greater than the threshold.
Automatic operation control device.
前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、
を備え、
前記車両に搭載され、前記バッテリの電圧を測定する電圧センサと、
前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する電流検出部と、
検出された前記電流を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する第2電圧変化量特定部(14)と、
少なくとも前記電気負荷を含む前記車両に搭載された装置に対して前記バッテリの給電の実行と停止とを切り替えるリレー(41)と、
を備え、
前記負荷接続検出部は、前記リレーがオフからオンに切り替わる際の、前記電圧センサにより検出される前記バッテリの電圧の変化量と、前記第2電圧変化量特定部により特定された前記変化量と、の差である電圧変化量差分が、予め定められた量よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、
自動運転制御装置。 An automatic driving control device (10) that controls the automatic driving of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140).
A load connection detection unit (17) for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery, and a load connection detection unit (17).
When it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery, it is realized by an automatic operation unit (10c) that is supplied with power from the battery and has an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation. An automatic operation control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions, and
With
A voltage sensor mounted on the vehicle and measuring the voltage of the battery,
A current detection unit that detects a current at a position closer to the automatic operation unit than a connection point with the electric load in the power path between the battery and the automatic operation unit.
A second voltage change amount specifying unit (14) that specifies the amount of change in the voltage of the battery by using the detected current, and
A relay (41) that switches between executing and stopping the power supply of the battery to the device mounted on the vehicle including at least the electric load.
With
The load connection detection unit includes the amount of change in the voltage of the battery detected by the voltage sensor when the relay is switched from off to on, and the amount of change specified by the second voltage change amount identification unit. When the voltage change amount difference, which is the difference between, is larger than a predetermined amount, it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery.
Automatic operation control device.
前記電圧変化量差分と、前記バッテリの内部抵抗値と、を利用して、前記電気負荷の消費電流量を推定する消費電流量推定部(15)を、さらに備え、
前記自動運転制御部は、推定された前記電気負荷の消費電流量に応じたレベルで、前記自動運転機能の少なくとも一部の機能を、制限して実行させる、
自動運転制御装置。 The automatic operation control device according to claim 3.
Further, a current consumption amount estimation unit (15) for estimating the current consumption amount of the electric load by using the voltage change amount difference and the internal resistance value of the battery is further provided.
The automatic operation control unit limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions at a level corresponding to the estimated current consumption of the electric load.
Automatic operation control device.
前記バッテリに電気負荷(200)が電気的に接続されたことを検出する負荷接続検出部(17)と、
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記バッテリから給電され、前記自動運転を実行するための自動運転機能を有する自動運転部(10c)により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる自動運転制御部(10b)と、
を備え、
前記バッテリは、前記バッテリの温度を検出する温度センサ(153)を有し、
外気温度および前記車両の運転状態に基づいて前記バッテリの温度を推定する温度推定部(16)を、さらに備え、
前記負荷接続検出部は、前記車両の走行開始時から予め定められた時間経過後における推定された前記バッテリの温度と、検出された前記バッテリの温度と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する、
自動運転制御装置。 An automatic driving control device (10) that controls the automatic driving of a vehicle equipped with a battery (140).
A load connection detection unit (17) for detecting that an electric load (200) is electrically connected to the battery, and a load connection detection unit (17).
When it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery, it is realized by an automatic operation unit (10c) that is supplied with power from the battery and has an automatic operation function for executing the automatic operation. An automatic operation control unit (10b) that limits and executes at least a part of the automatic operation functions, and
With
The battery has a temperature sensor (153) that detects the temperature of the battery.
A temperature estimation unit (16) for estimating the temperature of the battery based on the outside air temperature and the operating state of the vehicle is further provided.
In the load connection detection unit, the difference between the estimated battery temperature and the detected battery temperature after a lapse of a predetermined time from the start of traveling of the vehicle is larger than a predetermined threshold value. When it is large, it detects that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery.
Automatic operation control device.
前記バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する第1工程と、
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記自動運転部により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる第2工程と、
を備え、
前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路(Cp1)において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する工程と、
前記バッテリの開放端電圧を推定する工程と、
推定された前記開放端電圧を利用して前記バッテリの充電量を推定する工程と、
を、さらに備え、
前記第1工程は、予め定められた時間における推定された前記充電量の変化量と、検出された前記電流の前記予め定められた時間における積算値と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する工程を含む、
自動運転制御方法。 It is an automatic driving control method in a vehicle having a battery and an automatic driving unit having an automatic driving function for executing automatic driving supplied from the battery.
The first step of detecting that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, and
The second step of limiting and executing at least a part of the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. When,
Equipped with a,
A step of detecting a current at a position closer to the automatic driving unit than a connection point with the electric load in the power path (Cp1) between the battery and the automatic driving unit.
The process of estimating the open end voltage of the battery and
A step of estimating the charge amount of the battery using the estimated open end voltage, and
To prepare for
In the first step, the difference between the estimated change amount of the charge amount in the predetermined time and the integrated value of the detected current in the predetermined time is larger than the predetermined threshold value. In the case of a large amount, the step of detecting that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery is included.
Automatic operation control method.
前記バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する第1工程と、 The first step of detecting that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, and
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記自動運転部により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる第2工程と、 The second step of limiting and executing at least a part of the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. When,
を備え、 With
前記車両に搭載された電圧センサ(151)により前記バッテリの電圧を測定する工程と、 The process of measuring the voltage of the battery by the voltage sensor (151) mounted on the vehicle, and
測定された前記バッテリの電圧を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する工程と、 A process of specifying the amount of change in the voltage of the battery by using the measured voltage of the battery, and
を、さらに備え、 To prepare for
前記第1工程は、前記車両に搭載された予め定められた装置が起動する前と、前記予め定められた装置が起動した後と、における特定された前記バッテリの電圧の変化量が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する工程を含む、 In the first step, the amount of change in the voltage of the specified battery before the activation of the predetermined device mounted on the vehicle and after the activation of the predetermined device is predetermined. A step of detecting that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery when the voltage is larger than the threshold value is included.
自動運転制御方法。 Automatic operation control method.
前記バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する第1工程と、 The first step of detecting that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, and
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記自動運転部により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる第2工程と、 The second step of limiting and executing at least a part of the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. When,
を備え、 With
前記車両に搭載された電圧センサ(151)により前記バッテリの電圧を測定する工程と、 The process of measuring the voltage of the battery by the voltage sensor (151) mounted on the vehicle, and
前記バッテリと前記自動運転部との間の電力経路において、前記電気負荷との接続点よりも前記自動運転部に近い位置における電流を検出する工程と、 A step of detecting a current at a position closer to the automatic driving unit than a connection point with the electric load in the power path between the battery and the automatic driving unit.
検出された前記電流を利用して、前記バッテリの電圧の変化量を特定する第3工程と、 The third step of specifying the amount of change in the voltage of the battery by using the detected current, and
リレーを用いて、少なくとも前記電気負荷を含む前記車両に搭載された装置に対して前記バッテリの給電の実行と停止とを切り替える工程と、 A step of switching between execution and stop of power supply of the battery to a device mounted on the vehicle including at least the electric load by using a relay.
を、さらに備え、 To prepare for
前記第1工程は、前記リレーがオフからオンに切り替わる際の、前記電圧センサにより検出される前記バッテリの電圧の変化量と、前記第3工程により特定された前記変化量と、の差である電圧変化量差分が、予め定められた量よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する工程を含む、 The first step is the difference between the amount of change in the voltage of the battery detected by the voltage sensor and the amount of change specified by the third step when the relay is switched from off to on. A step of detecting that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery when the voltage change amount difference is larger than a predetermined amount is included.
自動運転制御方法。 Automatic operation control method.
前記バッテリに電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する第1工程と、 The first step of detecting that an electric load is electrically connected to the battery, and
前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことが検出された場合に、前記自動運転部により実現される前記自動運転機能のうち、少なくとも一部の機能を制限して実行させる第2工程と、 The second step of limiting and executing at least a part of the automatic driving functions realized by the automatic driving unit when it is detected that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery. When,
を備え、 With
前記バッテリは、前記バッテリの温度を検出する温度センサ(153)を有し、 The battery has a temperature sensor (153) that detects the temperature of the battery.
外気温度および前記車両の運転状態に基づいて前記バッテリの温度を推定する工程を、さらに備え、 A step of estimating the temperature of the battery based on the outside air temperature and the operating state of the vehicle is further provided.
前記第1工程は、前記車両の走行開始時から予め定められた時間経過後における推定された前記バッテリの温度と、検出された前記バッテリの温度と、の差が予め定められた閾値よりも大きい場合に、前記バッテリに前記電気負荷が電気的に接続されたことを検出する工程を含む、 In the first step, the difference between the estimated battery temperature and the detected battery temperature after a lapse of a predetermined time from the start of traveling of the vehicle is larger than a predetermined threshold value. In the case, the step of detecting that the electric load is electrically connected to the battery is included.
自動運転制御方法。 Automatic operation control method.
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017109634A JP6962006B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2017-06-02 | Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method |
| JP2021166763A JP7334769B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2021-10-11 | AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL DEVICE, VEHICLE, AND AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL METHOD |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017109634A JP6962006B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2017-06-02 | Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2021166763A Division JP7334769B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2021-10-11 | AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL DEVICE, VEHICLE, AND AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL METHOD |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018202989A JP2018202989A (en) | 2018-12-27 |
| JP6962006B2 true JP6962006B2 (en) | 2021-11-05 |
Family
ID=64956151
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017109634A Active JP6962006B2 (en) | 2017-06-02 | 2017-06-02 | Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6962006B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP7143354B2 (en) * | 2020-01-24 | 2022-09-28 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle control device and control program |
| JP6989631B2 (en) * | 2020-01-24 | 2022-01-05 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Vehicle control device and control program |
| CN111301393B (en) * | 2020-03-26 | 2022-10-11 | 东风柳州汽车有限公司 | Automobile man-machine driving mode-shared braking control system and control method |
| KR102476870B1 (en) * | 2020-10-30 | 2022-12-13 | 주식회사 비엔씨테크 | Apparatus And Method For Predicting Failure Of Last Mile Mobility |
| WO2023112985A1 (en) * | 2021-12-16 | 2023-06-22 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | Battery status detection device, information processing system, and data collection method |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3731258B2 (en) * | 1996-09-03 | 2006-01-05 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Vehicle travel control device |
| WO2006137316A1 (en) * | 2005-06-22 | 2006-12-28 | Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., Ltd. | Power supply stabilizing apparatus and vehicle using the same |
| WO2012086555A1 (en) * | 2010-12-24 | 2012-06-28 | 株式会社リブ技術研究所 | Trapping determination device for opening/closing section, vehicle with same, and trapping determination method for opening/closing section |
| JP6266491B2 (en) * | 2014-11-06 | 2018-01-24 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | Automatic operation control device |
-
2017
- 2017-06-02 JP JP2017109634A patent/JP6962006B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2018202989A (en) | 2018-12-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6962006B2 (en) | Automatic operation control device and automatic operation control method | |
| US10381695B2 (en) | Cooling system for secondary battery | |
| US10059286B2 (en) | Electric power source system | |
| JP4228760B2 (en) | Battery charge state estimation device | |
| US10403942B2 (en) | Cooling system for vehicle-mounted secondary battery | |
| JP4866187B2 (en) | Battery control device, electric vehicle, and program for causing computer to execute processing for estimating charge state of secondary battery | |
| JP4306746B2 (en) | Vehicle power supply | |
| KR101589395B1 (en) | Vehicle control device, vehicle, and vehicle control method | |
| JP5928177B2 (en) | Torque assist control device | |
| JP4416802B2 (en) | Power management device | |
| JPWO2013072976A1 (en) | Driving environment prediction device, vehicle control device, and methods thereof | |
| JP2005037230A (en) | Battery degradation detection device and method | |
| JP2007245818A (en) | Battery state control system | |
| JP6287938B2 (en) | In-vehicle secondary battery cooling system | |
| JP4489101B2 (en) | Power supply control device and power supply control method | |
| JP2016199153A (en) | Cooling system for on-vehicle secondary battery | |
| JP2019118204A (en) | Management device and management method for power storage element | |
| JP6627694B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2008172908A (en) | Vehicular power supply unit | |
| JP7334769B2 (en) | AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL DEVICE, VEHICLE, AND AUTOMATIC DRIVING CONTROL METHOD | |
| JP5887493B2 (en) | Power supply | |
| JP7295915B2 (en) | vehicle power system | |
| JP2007239526A (en) | Control device for vehicle | |
| JP2010081732A (en) | Method of controlling battery of automobile and its apparatus | |
| JP4735523B2 (en) | Power storage device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20200513 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20210511 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20210712 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20210914 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20210927 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6962006 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |