JP5590292B2 - Manufacturing method of resin laminate - Google Patents
Manufacturing method of resin laminate Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5590292B2 JP5590292B2 JP2009299074A JP2009299074A JP5590292B2 JP 5590292 B2 JP5590292 B2 JP 5590292B2 JP 2009299074 A JP2009299074 A JP 2009299074A JP 2009299074 A JP2009299074 A JP 2009299074A JP 5590292 B2 JP5590292 B2 JP 5590292B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sheet
- mold
- pair
- resin
- extrusion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 title claims description 70
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 title claims description 70
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 31
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 54
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 claims description 50
- 229920005992 thermoplastic resin Polymers 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 18
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000011218 segmentation Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 10
- -1 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 10
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229920000728 polyester Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000000071 blow moulding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000013585 weight reducing agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Styrene Natural products C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 PPBRXRYQALVLMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000297 Rayon Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004566 building material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000000155 melt Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L Calcium carbonate Chemical compound [Ca+2].[O-]C([O-])=O VTYYLEPIZMXCLO-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 2
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229920006127 amorphous resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920005669 high impact polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004797 high-impact polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010445 mica Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052618 mica group Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002964 rayon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 150000003440 styrenes Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 229920002994 synthetic fiber Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000012209 synthetic fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- SAAZSCOLNCGLKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylbuta-1,3-diene;pent-1-ene Chemical compound CCCC=C.CC(=C)C=C SAAZSCOLNCGLKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- JMMZCWZIJXAGKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-methylpent-2-ene Chemical compound CCC=C(C)C JMMZCWZIJXAGKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N Acrylonitrile Chemical compound C=CC#N NLHHRLWOUZZQLW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 244000025254 Cannabis sativa Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000012766 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. sativa Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000012765 Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa var. spontanea Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229920000049 Carbon (fiber) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000742 Cotton Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004793 Polystyrene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002978 Vinylon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000001336 alkenes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000002216 antistatic agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000004323 axial length Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- NTXGQCSETZTARF-UHFFFAOYSA-N buta-1,3-diene;prop-2-enenitrile Chemical compound C=CC=C.C=CC#N NTXGQCSETZTARF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTAZNLWOLGHBHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N butadiene-styrene rubber Chemical class C=CC=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 MTAZNLWOLGHBHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000019 calcium carbonate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 235000009120 camo Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000004917 carbon fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000005607 chanvre indien Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- QKSIFUGZHOUETI-UHFFFAOYSA-N copper;azane Chemical compound N.N.N.N.[Cu+2] QKSIFUGZHOUETI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002537 cosmetic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005034 decoration Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- BXOUVIIITJXIKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N ethene;styrene Chemical group C=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 BXOUVIIITJXIKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000003063 flame retardant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004088 foaming agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011487 hemp Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001903 high density polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004700 high-density polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001519 homopolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011256 inorganic filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910003475 inorganic filler Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002649 leather substitute Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N olefin Natural products CCCCCCCC=C JRZJOMJEPLMPRA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005022 packaging material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008188 pellet Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000088 plastic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002223 polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005996 polystyrene-poly(ethylene-butylene)-polystyrene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004064 recycling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920006132 styrene block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920003048 styrene butadiene rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000004381 surface treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000454 talc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052623 talc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007666 vacuum forming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000002268 wool Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Blow-Moulding Or Thermoforming Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Description
本発明は、樹脂積層板の製造方法に関し、より詳細には、製造効率および製品品質を確保しつつ、十分な軽量化、薄肉化を達成可能な樹脂積層板の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a method for producing a resin laminate, and more particularly, to a method for producing a resin laminate capable of achieving sufficient weight reduction and thinning while ensuring production efficiency and product quality.
従来から、自動車の内装材や建材、物流・包装材として、いわゆる樹脂積層板が採用されている。
樹脂積層板は、樹脂製の表面材と樹脂製の裏面材とを有し、裏面材には先端部が表面材の内面に突き合わされる凹部が設けられる。特に、外観が重視される自動車の内装材や建材の場合には、表面材の表側には不織布が貼着される。
この樹脂積層板の製造方法には、従来から種々の方法が採用されている。
第1に、溶融樹脂を用いて一体押出中空成形により製造する技術が採用されている。
このような方法により製造された樹脂積層板によれば、単に内部に中空部を有するだけの二重壁中空構造に比べ、表面材と裏面材とを連結する凹部により、剛性、特に面材に対して鉛直方向の荷重に対する圧縮剛性を確保することが可能である。
Conventionally, so-called resin laminates have been used as interior materials, building materials, logistics and packaging materials for automobiles.
The resin laminate has a resin surface material and a resin back material, and the back material is provided with a recess whose tip is abutted against the inner surface of the surface material. In particular, in the case of automobile interior materials and building materials where the appearance is important, a nonwoven fabric is stuck on the front side of the surface material.
Conventionally, various methods have been adopted as a method for producing the resin laminate.
First, a technique of manufacturing by integral extrusion hollow molding using a molten resin is employed.
According to the resin laminate produced by such a method, compared to a double-walled hollow structure that simply has a hollow portion inside, a concave portion that connects the front surface material and the back surface material provides rigidity, particularly a surface material. On the other hand, it is possible to ensure the compressive rigidity against the load in the vertical direction.
第2に、特許文献1に開示されているように、一方が表面に多数の突起部が千鳥模様状に配置されたロールである一対のロールの間に、個別に押出された2枚の溶融状態のシートを所定押圧力のもとで通して、一方のシートに凹部を形成するとともに、凹部の底面を他方のシートの内面に突き合わせる形態で2枚のシートを溶着し、さらに一方のシートの凹部の開口が形成された側の面に別のシートを溶着させる技術であり、凹部を形成したシートの表側および裏側それぞれに対してシートを溶着させる3層構造をなす。 Secondly, as disclosed in Patent Document 1, two melts extruded individually between a pair of rolls, one of which is a roll having a large number of protrusions arranged on the surface in a staggered pattern. The sheet in the state is passed under a predetermined pressing force to form a recess in one sheet, and the two sheets are welded in such a form that the bottom surface of the recess is abutted against the inner surface of the other sheet. This is a technique in which another sheet is welded to the surface on the side where the opening of the recess is formed, and has a three-layer structure in which the sheet is welded to each of the front side and the back side of the sheet in which the recess is formed.
第3に、特許文献2に開示されているように、第2の方法と異なり、それぞれ表面に多数の突起部が千鳥模様状に配置されたロールである一対のロールの間に、個別に押出された2枚の溶融状態のシートを所定押圧力のもとで通して、それぞれのシートに凹部を形成するとともに、それぞれのシートの対応する凹部の底面同士を溶着する形態で2枚のシートを溶着し、さらにそれぞれシートの反対側の面に別のシートを溶着させる技術であり、シートそれぞれの凹部の開口が形成された側の面に対してシートを溶着させる4層構造をなす。
以上のような溶融状態のシートを押出して樹脂積層板を製造する技術には、以下のような技術的問題点が存する。
Thirdly, as disclosed in Patent Document 2, unlike the second method, the extrusion is individually performed between a pair of rolls each having a plurality of protrusions arranged on the surface in a zigzag pattern. The two melted sheets are passed under a predetermined pressing force to form recesses in the respective sheets, and the two sheets in a form in which the bottom surfaces of the corresponding recesses of the respective sheets are welded to each other. It is a technique of welding and further welding another sheet to the opposite surface of each sheet, and has a four-layer structure in which the sheet is welded to the surface of the sheet on which the recess opening is formed.
The following technical problems exist in the technology for producing a resin laminate by extruding a molten sheet as described above.
すなわち、製造効率を確保しつつ、方向性のない十分な強度を有する樹脂積層板を得ることが困難な点である。より詳細には、第1の方法ないし第3の方法に共通の押し出し成形特有の問題として、シートの押出し方向の端部は開放状態となることから、熱シール処理等の端面処理が必須となるため、その分余分な工程が必要となり、全体の製造効率が低下する。さらに、千鳥状に凹部が形成されるシートと別のシートとの溶着、または、それぞれ千鳥状に凹部が形成されるシート同士の溶着はそれぞれ、一対のローラーの間をローラーにより送り出されながら通過する際の押圧力により行われるに過ぎず、十分な溶着時間を確保することが難しく、それによる溶着不足が原因で樹脂積層板として十分な強度を確保することが困難となり、品質劣化を引き起こす。
この点、連続的な押出成形ではなく、ブロー成形によれば、上記のような端面処理に伴う製造効率の低下、および溶着不足に伴う強度不足を回避することが可能である。
特許文献3は、このようなブロー成形による方法を開示する。
特許文献3によれば、溶融状態の筒状のパリソンを用いて、裏面壁には先端部が表面壁の内面に突合せ溶着される凹部を設けるとともに、表面壁の外表面には、表装材を貼着する点が開示されている。
しかしながら、このように筒状のパリソンを用い吹き込み圧をかけて成形するブロー成形によれば、別の技術的問題点が引き起こされる。
すなわち、周方向に肉厚の均一な筒状のパリソンを用い吹き込み圧をかけて成形することに起因して、樹脂積層板の十分な軽量化、薄肉化が困難な点である。
That is, it is difficult to obtain a resin laminate having sufficient strength without directionality while ensuring manufacturing efficiency. More specifically, as a problem peculiar to extrusion molding common to the first method to the third method, the end portion in the extrusion direction of the sheet is in an open state, so that end surface treatment such as heat sealing treatment is essential. For this reason, an extra step is required, and the overall manufacturing efficiency is lowered. Further, the welding between the sheet having the concave portions formed in a zigzag pattern and another sheet, or the welding between the sheets having the concave portions formed in a zigzag pattern, respectively, passes while being fed by a roller between the pair of rollers. However, it is difficult to ensure a sufficient welding time, and it is difficult to ensure sufficient strength as a resin laminate due to insufficient welding, resulting in quality deterioration.
In this respect, according to blow molding rather than continuous extrusion molding, it is possible to avoid a decrease in manufacturing efficiency due to the end face treatment as described above and a lack of strength due to insufficient welding.
Patent Document 3 discloses a method by such blow molding.
According to Patent Document 3, using a molten cylindrical parison, the back wall is provided with a recess whose front end is butt welded to the inner surface of the front wall, and the outer surface of the front wall is provided with a cover material. The point to stick is disclosed.
However, blow molding using a cylindrical parison and applying blow pressure causes another technical problem.
That is, it is difficult to sufficiently reduce the thickness and thickness of the resin laminate due to molding by applying blowing pressure using a cylindrical parison having a uniform thickness in the circumferential direction.
より詳細には、筒状のパリソンは、通常ダイコア間の環状のスリットから押し出しされることからその厚みは周方向に略一様であり、一方、分割形式の一対の金型を型締めした際、金型内の密閉空間から吹き込み圧をかけることからパリソンの金型に対する押圧力はパリソンの全面に亘って一様であるところ、凹部を形成する一方の金型に押圧されるパリソンは、凹部の深さ、開口径に応じたブロー比との関係でパリソンが引き伸ばされて局所的な薄肉部が生じる一方、他方の金型には凹部を形成しないことから、このような薄肉部が生じない。
この点から、筒状パリソンの厚みは、一方の金型の側の薄肉部に合わせて設定する必要があり、それにより他方の金型の側には、余分な厚みのシートが形成されることになる。
このように、周方向の肉厚が略均一な筒状パリソンを利用する場合は、ブロー成形後に複数の凹部を有する壁面と凹部が形成されない壁面とで不可避的に厚みの違いを生じ、これに起因して、樹脂積層板の十分な軽量化、薄肉化を達成することができない。
この点、特許文献4によれば、筒状のパリソンに基づく2枚の溶融状態のシートを用いて、内部に空洞部を有するとともに、互いに対向する二面に、複数の凹部がその底面部が互いに背向するように形成される熱可塑性樹脂の板状体を製造する方法が開示されている。
しかしながら、特に、おもて面の外観が重視される自動車の内装材や建材向けの樹脂積層板の場合には、おもて面を形成する一方のシートには、不織布等の化粧材を貼着する必要があることから、一方のシートに凹部を形成する凹部を設けて表面に多数の凹部の開口を形成するのは避けるのが好ましい。
From this point, it is necessary to set the thickness of the cylindrical parison according to the thin part on the side of one mold, thereby forming a sheet with an extra thickness on the side of the other mold. become.
As described above, when a cylindrical parison having a substantially uniform thickness in the circumferential direction is used, a difference in thickness inevitably occurs between a wall surface having a plurality of recesses and a wall surface where no recesses are formed after blow molding. As a result, it is impossible to achieve sufficient weight reduction and thinning of the resin laminate.
In this regard, according to Patent Document 4, two sheets in a molten state based on a cylindrical parison are used to have a hollow portion inside, and a plurality of concave portions on the two surfaces facing each other have a bottom surface portion thereof. A method of manufacturing a plate of thermoplastic resin formed so as to face each other is disclosed.
However, in particular, in the case of automobile laminates and building resin laminates for building materials where the appearance of the front surface is important, a decorative material such as a nonwoven fabric is applied to one sheet forming the front surface. Since it is necessary to wear, it is preferable to avoid forming the opening of many recessed parts in the surface by providing the recessed part which forms a recessed part in one sheet | seat.
以上の技術的問題点にかんがみ、本発明の目的は、製造効率および製品品質を確保しつつ、十分な軽量化、薄肉化を達成可能な樹脂積層板の製造方法を提供する。 In view of the above technical problems, an object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing a resin laminate capable of achieving sufficient weight reduction and thinning while ensuring production efficiency and product quality.
上記課題を達成するために、本発明の樹脂積層板の製造方法は、
一方の金型のキャビティに対して、他方の金型に向かって突起する複数の突起体を設けた分割形式の一対の金型を設けるとともに、それぞれの厚みを調整した2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを準備する段階と、
2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを互いに所定間隔を隔てて、環状ピンチオフ部のまわりにはみ出す形態で、分割形式の一対の金型の間に位置決めする段階と、
一方のシートと、一方のシートの外表面に対向する一方の金型のキャビティとの間に密閉空間を形成する段階と、
一方の金型の側から前記密閉空間を吸引して、一方の金型のキャビティに対して一方のシートの外表面を押し当てることにより、一方のシートを賦形して、凹部を形成する段階と、
一対の金型を型締めして、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートの周縁同士を、および一方のシートに形成された凹部の頂部を他方のシートの内表面に、それぞれ溶着する段階と、を有し、
それにより、両シートの厚みが実質的に等しい樹脂積層板を製造する構成としている。
In order to achieve the above object, the method for producing a resin laminate of the present invention comprises:
A pair of split molds having a plurality of protrusions projecting toward the other mold is provided in the cavity of one mold, and two melted heats each adjusted in thickness are provided. Preparing a plastic resin sheet; and
Positioning two molten thermoplastic resin sheets between a pair of split molds in a form that protrudes around an annular pinch-off portion at a predetermined interval from each other;
Forming a sealed space between one sheet and the cavity of one mold facing the outer surface of the one sheet;
The step of sucking the sealed space from the side of one mold and pressing the outer surface of the one sheet against the cavity of the one mold to shape one sheet and form a recess When,
Clamping a pair of molds and welding the peripheral edges of two molten thermoplastic resin sheets and the tops of the recesses formed in one sheet to the inner surface of the other sheet, respectively And having
Thereby, it is set as the structure which manufactures the resin laminated board in which the thickness of both sheets is substantially equal.
以上の構成を有する樹脂積層板の製造方法によれば、それぞれ厚み調整をした2枚の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを分割形式の金型の間に位置決めしたうえで、一方の樹脂製シートとそれに対向する金型のキャビティとの間に密閉空間を形成して、金型の側から密閉空間内を吸引することにより、従来のブロー成形によれば円筒状のパリソンを用いて吹き込み圧によりキャビティに沿った形状に賦形するところ、一方の金型のキャビティのみに複数の突起体が設けられているため、突起体を有するキャビティ側でパリソンが大きく引き伸ばされる反面、突起体を有しないキャビティ側では比較的パリソンが引き伸ばされずにそれぞれの肉厚に差が生じるという問題が引き起こされていたところ、このような問題を解決することにより、必要な強度を確保する限度で2枚の樹脂製シートそれぞれの厚みを個別に最大限まで薄肉化することが可能であり、それにより製造効率および製品品質を確保しつつ、十分な軽量化、薄肉化を達成可能である。
また、前記型締め段階後に、型締めされた一対の金型内に形成された密閉空間から吹き込み圧をかけることにより、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートそれぞれを対応する金型のキャビティに対して押し当てて、両シートを賦形することができる。
さらに、溶融状態のシート状の2条のパリソンを下方に垂下する形態で、一対の分割形式の金型の間に向かって押し出す段階を有するのでもよい。
さらに、前記突起体は、上下方向に互いに所定の間隔を隔ててキャビティの表面に複数列設けられ、それぞれの列の突起体の少なくとも一部は、キャビティの表面において水平方向に亘って延びる帯状をなすのがよい。
また、前記突起体は、キャビティ上で千鳥模様状に配置されているのがよい。
さらにまた、前記突起体は、他方の金型に向かって先細の正六角形の角錐台形状を有するのがよい。
加えて、前記他方のシートは、その外表面に化粧材が貼着されたシートであるのがよい。
さらに、前記吸引段階は、前記一方の金型の周縁に型締め方向に移動自在に外嵌する外枠を前記一方のシートの外表面に向かって移動させる段階を有し、前記一方のシートの外表面、前記外枠の内周面および前記一方の金型のキャビティにより密閉空間を構成するのがよい。
さらにまた、一対の金型を型締めを通じて、それぞれのピンチオフ部同士を当接させることにより、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートの周縁同士を溶着させてパーティングラインを形成するとともに、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートの間に密閉中空部を形成するのがよい。
According to the method for manufacturing a resin laminate having the above-described configuration, after positioning two thermoplastic resin sheets each having a thickness adjusted between the molds of the split type, one resin sheet is opposed to the resin sheet. A sealed space is formed between the mold cavity and the inside of the sealed space is sucked from the mold side. According to conventional blow molding, a cylindrical parison is used to blow the cavity along the cavity. When a shape is formed, a plurality of protrusions are provided only in the cavity of one mold, so the parison is greatly stretched on the cavity side with the protrusions, but on the cavity side without the protrusions The problem was that the parison would not be stretched and there would be a difference in the thickness of each wall. By solving such a problem, the required strength was increased. It is possible to reduce the thickness of each of the two resin sheets to the maximum as long as they are maintained, thereby achieving sufficient weight reduction and thinning while ensuring manufacturing efficiency and product quality. It is.
In addition, after the mold clamping step, by applying blowing pressure from a sealed space formed in the pair of molds clamped, two molten thermoplastic resin sheets respectively correspond to the mold cavities. To form both sheets.
Furthermore, you may have a step which extrudes between a pair of division | segmentation type | mold metal mold | die by the form which hangs down the sheet-like parison of a molten state downward.
Further, the protrusions are provided in a plurality of rows on the surface of the cavity at predetermined intervals in the vertical direction, and at least a part of the protrusions in each row has a strip shape extending in the horizontal direction on the surface of the cavity. It should be made.
The protrusions may be arranged in a staggered pattern on the cavity.
Furthermore, it is preferable that the protrusion has a regular hexagonal truncated pyramid shape that is tapered toward the other mold.
In addition, the other sheet may be a sheet having a decorative material attached to the outer surface thereof.
Further, the suction step includes a step of moving an outer frame that is fitted around a peripheral edge of the one mold so as to be movable in a mold clamping direction toward an outer surface of the one sheet, It is preferable that a sealed space is constituted by the outer surface, the inner peripheral surface of the outer frame, and the cavity of the one mold.
Furthermore, through clamping the pair of molds, the respective pinch-off portions are brought into contact with each other, thereby welding the peripheral edges of two molten thermoplastic resin sheets to form a parting line, It is preferable to form a sealed hollow portion between two molten thermoplastic resin sheets.
本発明に係る樹脂積層板100の製造方法の実施形態を図面を参照しながら、以下に詳細に説明する。
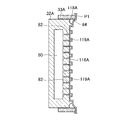
図1ないし図3に示すように、樹脂積層板100は、おもて面側シート120Aと裏面側シート120Bと、おもて面側シート120Aの外表面150に貼り合わされた化粧材シート140とから構成され、樹脂積層板100は、化粧材シート140、おもて面側シート120A、および裏面側シート120Bの3層の積層構造である。なお、図1において、樹脂積層板100の内部構造を明瞭に示すために、樹脂積層板100の周端部まわりを省略して示している。
An embodiment of a method for producing a
As shown in FIGS. 1 to 3, the
おもて面側シート120Aおよび裏面側シート120Bそれぞれの厚み(肉厚)、および車両用内装品100としての全体厚み(板厚)は、車両用内装品100の用途に応じて適宜定めればよい。軽量性の観点から肉厚は1.5mm以下、好ましくは1.0mm以下であり、板厚は15mm以下、好ましくは10mm以下である。
裏面側シート120Bは、それぞれの底部が、おもて面側シート120Aの化粧材シート140が接着される外表面150と反対側の面である内表面170に接着される多数の凹部200を有し、多数の凹部200の深さが、積層構造板100の厚みを実質的に構成する。多数の凹部200それぞれは、裏面側シート120Bの内表面180とおもて面側シート120Aの内表面170との間を延びるリブ122により、内表面側で突出するように内方に向かって先細に構成され、複数の凹部200はそれぞれ、有底であり、最先細部に突き合わせ面240を有し、突き合わせ面240がおもて面側シート120Aの内表面170に接着されるようにしている。
複数の凹部200の数は、樹脂積層板100の用途により適宜設定すればよいが、数が多いほど重量に比して高い剛性を得ることができる。
Each thickness (thickness) of the front side sheet 120 </ b> A and the back side sheet 120 </ b> B and the overall thickness (plate thickness) as the vehicle
The
The number of the plurality of
図1に示すように、複数の凹部200はそれぞれ、裏面側シート120Bの外表面220における開口260が正六角形の角錐台であり、外表面220上で開口260がハニカム状に配置されていることが好ましい。すなわち、外表面220上で、隣り合う開口260の対向する辺同士が平行となるように配置されている。これにより、外表面220に最も密に複数の凹部200を配置することが可能である。また、外表面200上で、隣り合う正六角形の角錐台形状の開口260の角同士が近接するように配置することも可能である。開口260の角同士が近接するように均等に配置することで、このような金型を製作するうえで切削加工が容易となる。複数の凹部200それぞれの開口260の大きさ、凹部200の深さおよび隣り合う凹部200同士の間隔について、開口260の大きさが小さく、凹部200の深さが深く、隣合う凹部200同士の間隔が小さいほど、積層板100全体としての重量に比して高い剛性を得ることができる。
図3に示すように、おもて面側シート120Aと裏面側シート120Bとの間には、密閉中空部280が形成されており、密閉中空部280が積層構造板100の周端面において、裏面側シート120Bの外周壁により閉じられている。
変形例として、複数の凹部200は、外表面220において均等に分散配置させるのが好ましいが、その形状は、円錐形状、円錐台形状、円筒形状、角柱形状、角錐形状、半球形状など多種の形状から適宜選択すればよい。
As shown in FIG. 1, in each of the plurality of
As shown in FIG. 3, a sealed
As a modified example, the plurality of
裏面側シート120Bが、後に説明するように、2つの分割形式の金型50の間に位置決めした溶融状態の2枚のシート状パリソンPを2つの分割形式の金型50を型締することにより成形される場合、積層板100の用途に応じて、おもて面側シート120Aと裏面側シート120Bとの間の所望の位置に密閉中空部280を有するとともに所望の表面形状を呈するように形成する一方、おもて面側シート120Aと裏面側シート120Bとを溶着し、積層板100の用途に応じた外形あるいは表面形状および内部構造を所望に実現可能な積層板100を提供することが可能である。特に、おもて面側シート120Aおよび裏面側シート120B同士の周縁面が互いに溶着することにより、パーティングラインPLが形成される。
次に、このような積層板100の成形装置について、以下に説明する。
As will be described later, the back-
Next, an apparatus for forming such a
図4に示すように、積層板100の成形装置10は、押出装置12と、押出装置12の下方に配置された型締装置14とを有し、押出装置12から押出された溶融状態のシート状パリソンPを型締装置14に送り、型締装置14により溶融状態のシート状パリソンPを成形するようにしている。ここに、2枚の熱可塑性樹脂それぞれを押し出して、型締装置14まで送るまでの装置は、同様であるので、一方のみ説明し、他方については同様な参照番号を付することによりその説明は省略する。
As shown in FIG. 4, the
押出装置12は、従来既知のタイプであり、その詳しい説明は省略するが、ホッパー16が付設されたシリンダー18と、シリンダー18内に設けられたスクリュー(図示せず)と、スクリューに連結された油圧モーター20と、シリンダー18と内部が連通したアキュムレータ22と、アキュムレータ22内に設けられたプランジャー24とを有し、ホッパー16から投入された樹脂ペレットが、シリンダー18内で油圧モーター20によるスクリューの回転により溶融、混練され、溶融状態の樹脂がアキュムレータ室22に移送されて一定量貯留され、プランジャー24の駆動によりTダイ28に向けて溶融樹脂を送り、押出スリット34を通じて所定の長さの連続的なシート状パリソンPが押し出され、間隔を隔てて配置された一対のローラー30によって挟圧されながら下方へ向かって送り出されて分割金型32の間に垂下される。これにより、後に詳細に説明するように、シート状パリソンPが上下方向(押出方向)に一様な厚みを有する状態で、分割金型32の間に配置される。
The extruding
押出装置12の押出の能力は、成形する樹脂成形品の大きさ、シート状パリソンPのドローダウンあるいはネックイン発生防止の観点から適宜選択する。より具体的には、実用的な観点から、間欠押出における1ショットの押出量は好ましくは1〜10kgであり、押出スリット34からの樹脂の押出速度は、数百kg/時以上、より好ましくは700kg/時以上である。また、シート状パリソンPのドローダウンあるいはネックイン発生防止の観点から、シート状パリソンPの押出工程はなるべく短いのが好ましく、樹脂の種類、MFR値、メルトテンション値に依存するが、一般的に、押出工程は40秒以内、より好ましくは10〜20秒以内に完了するのがよい。このため、熱可塑性樹脂の押出スリット34からの単位面積、単位時間当たりの押出量は、50kg/時cm2以上、より好ましくは150kg/時cm2以上である。
The extrusion capability of the
一対のローラー30の回転により一対のローラー30間に挟み込まれたシート状パリソンPを下方に送り出すことで、シート状パリソンPを延伸薄肉化することが可能であり、押し出されるシート状パリソンPの押出速度と一対のローラー30によるシート状パリソンPの送り出し速度との関係を調整することにより、ドローダウンあるいはネックインの発生を防止することが可能であるから、樹脂の種類、特にMFR値およびメルトテンション値、あるいは単位時間当たりの押出量に対する制約を小さくすることが可能である。 By feeding the sheet-like parison P sandwiched between the pair of rollers 30 by the rotation of the pair of rollers 30 downward, the sheet-like parison P can be stretched and thinned, and the extruded sheet-like parison P is extruded. By adjusting the relationship between the speed and the delivery speed of the sheet-like parison P by the pair of rollers 30, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of drawdown or neck-in, so the type of resin, particularly the MFR value and melt tension. It is possible to reduce the restriction on the value or the extrusion amount per unit time.
図4に示すように、Tダイ28に設けられる押出スリット34は、鉛直下向きに配置され、押出スリット34から押し出されたシート状パリソンPは、そのまま押出スリット34から垂下する形態で、鉛直下向きに送られるようにしている。押出スリット34は、その間隔を可変とすることにより、シート状パリソンPの厚みを変更することが可能である。 As shown in FIG. 4, the extrusion slit 34 provided in the T-die 28 is arranged vertically downward, and the sheet-like parison P extruded from the extrusion slit 34 is suspended from the extrusion slit 34 as it is vertically downward. I am trying to send it. The extrusion slit 34 can change the thickness of the sheet-like parison P by making the interval variable.
一対のローラー30について説明すれば、一対のローラー30は、押出スリット34の下方において、各々の回転軸が互いに平行にほぼ水平に配置され、一方が回転駆動ローラー30Aであり、他方が被回転駆動ローラー30Bである。より詳細には、図3に示すように、一対のローラー30は、押出スリット34から下方に垂下する形態で押し出されるシート状パリソンPに関して、線対称となるように配置される。 The pair of rollers 30 will be described. In the pair of rollers 30, the rotation axes of the pair of rollers 30 are arranged substantially horizontally in parallel with each other, one is the rotation drive roller 30A, and the other is driven to rotate. The roller 30B. More specifically, as shown in FIG. 3, the pair of rollers 30 are arranged so as to be line-symmetric with respect to the sheet-like parison P extruded in a form that hangs downward from the extrusion slit 34.
それぞれのローラーの直径およびローラーの軸方向長さは、成形すべきシート状パリソンPの押出速度、シートの押出方向長さおよび幅、ならびに樹脂の種類等に応じて適宜設定すればよいが、後に説明するように、一対のローラー30間にシート状パリソンPを挟み込んだ状態で、ローラーの回転によりシート状パリソンPを円滑に下方に送り出す観点から、回転駆動ローラー30Aの径は、被回転駆動ローラー30Bの径より若干大きいのが好ましい。ローラーの径は50〜300mmの範囲であることが好ましく、シート状パリソンPとの接触においてローラーの曲率が大きすぎてもまた、小さすぎてもシート状パリソンPがローラーへ巻き付く不具合の原因となる。
一方、型締装置14も、押出装置12と同様に、従来既知のタイプであり、その詳しい説明は省略するが、2つの分割形式の金型32A,Bと、金型32A,Bを溶融状態のシート状パリソンPの供給方向に対して略直交する方向に、開位置と閉位置との間で移動させる金型駆動装置とを有する。
The diameter of each roller and the axial length of the roller may be appropriately set according to the extrusion speed of the sheet-like parison P to be molded, the length and width of the sheet in the extrusion direction, and the type of resin. As will be described, from the viewpoint of smoothly feeding the sheet-like parison P downward by rotation of the roller with the sheet-like parison P sandwiched between the pair of rollers 30, the diameter of the rotation drive roller 30A is the rotation-driven roller. It is preferably slightly larger than the diameter of 30B. The diameter of the roller is preferably in the range of 50 to 300 mm. If the curvature of the roller is too large or too small in contact with the sheet-like parison P, the sheet-like parison P may be wound around the roller. Become.
On the other hand, the
図4に示すように、2つの分割形式の金型32A,Bは、キャビティ116を対向させた状態で配置され、それぞれキャビティ116が略鉛直方向沿うように配置される。それぞれのキャビティ116の表面には、溶融状態のシート状パリソンPに基づいて成形される成形品の外形、および表面形状に応じて突起体119が設けられる。
より詳細には、裏面側シート120Bを成形する一方の金型32Aのキャビティ116Aの表面には、裏面側シート120Bの外表面に凹部200を形成するように、凹部200と相補形状の突起体119が、他方の金型32Bのキャビティ116Bに向かって突出するように設けられている。
複数の突起体119のキャビティ116Aの表面上における配置として、上下方向に互いに所定の間隔を隔ててキャビティ116Aの表面に複数列設け、それぞれの列の突起体119は、キャビティ116Aの表面において水平方向に亘って延びる帯状をなしてもよい。これにより、凹部200が凹溝として形成される。また、複数の突起体119は、キャビティ116Aの表面において千鳥模様状に配置されていてもよい。
As shown in FIG. 4, the two divided molds 32 </ b> A and 32 </ b> B are arranged with the cavities 116 facing each other, and the cavities 116 are arranged along the substantially vertical direction.
More specifically, a
As the arrangement of the plurality of
2つの分割形式の金型32A,Bそれぞれにおいて、キャビティ116のまわりには、ピンチオフ部118が形成され、このピンチオフ部118は、キャビティ116のまわりに環状に形成され、対向する金型32A,Bに向かって突出する。これにより、2つの分割形式の金型32A,Bを型締する際、それぞれのピンチオフ部118の先端部が当接し、2枚の溶融状態のシート状パリソンP1、P2は、その周縁にパーティングラインPLが形成されるように溶着され、中空部を閉塞する外周壁が形成される。
In each of the two divided
金型32Aの外周部には、型枠33Aが密封状態で摺動可能に外嵌し、図示しない型枠移動装置により、型枠33Aが、金型32Aに対して相対的に移動可能としている。より詳細には、型枠33Aは、金型32Aに対して金型32Bに向かって突出することにより、金型32A,B間に配置されたシート状パリソンP1の側面に当接可能である。
A
金型駆動装置については、従来と同様のものであり、その説明は省略するが、2つの分割形式の金型32A,Bはそれぞれ、金型駆動装置により駆動され、開位置において、2つの分割金型32A,Bの間に、2枚の溶融状態のシート状パリソンPが配置可能なようにされ、一方閉位置において、2つの分割金型32A,Bのピンチオフ部118が当接し、環状のピンチオフ部118が互いに当接することにより、2つの分割金型32A,B内に密閉空間が形成されるようにしている。開位置から閉位置への各金型32A,Bの移動について、閉位置、すなわち、ピンチオフ部118同士が互いに当接する位置は、2枚の溶融状態のシート状パリソンP1、P2間で、両シート状パリソンP1、P2から等距離の位置とし、各金型32A,Bが金型駆動装置により駆動されてその位置に向かって移動するようにしている。
なお、一方のシート状パリソンP1用の押出装置および一対のローラーと、他方の一方のシート状パリソンP2用の押出装置および一対のローラーとは、この閉位置に関して対称に配置されている。
The mold driving device is the same as the conventional one, and the description thereof is omitted. However, the two divided
Note that the extrusion device and the pair of rollers for one sheet-like parison P1 and the extrusion device and the pair of rollers for the other sheet-like parison P2 are arranged symmetrically with respect to this closed position.
図6に示すように、分割金型32Aの内部には、真空吸引室80が設けられ、真空吸引室80は吸引穴82を介してキャビティ116Aに連通し、真空吸引室80から吸引穴82を介して吸引することにより、キャビティ116Aに向かってシート状パリソンP1を吸着させて、キャビティ116Aの外表面に沿った形状に賦形するようにしている。より詳細には、キャビティ116Aの外表面に設けた突起体119により、裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1の外表面117に凹部200を形成するようにしている。
一方、分割金型32Bには、金型32A、Bを型締したときに両金型により形成される密閉空間内から吹き込み圧をかけることが可能なように、従来既知のブローピン(図示せず)が設置されている。
As shown in FIG. 6, a
On the other hand, a conventionally known blow pin (not shown) is applied to the divided
おもて面側シート120Aおよび裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1、P2は、ポリエチレン、ポリプロピレン等のオレフィン系樹脂、または非晶性樹脂などから形成されたシートからなる。より詳細には、シート状パリソンP1、P2は、ドローダウン、ネックインなどにより肉厚のバラツキが発生することを防止する観点から溶融張力の高い樹脂材料を用いることが好ましく、一方で金型への転写性、追従性を良好とするため流動性の高い樹脂材料を用いることが好ましい。
The sheet-like parisons P1 and P2 which are materials of the
より具体的にはエチレン、プロピレン、ブテン、イソプレンペンテン、メチルペンテン等のオレフィン類の単独重合体あるいは共重合体であるポリオレフィン(例えば、ポリプロピレン、高密度ポリエチレン)であって、230℃におけるMFR(JIS K−7210に準じて試験温度230℃、試験荷重2.16kgにて測定)が3.0g/10分以下、さらに好ましくは0.3〜1.5g/10分のもの、またはアクリロニトリル・ブタジエン・スチレン共重合体、ポリスチレン、高衝撃ポリスチレン(HIPS樹脂)、アクリロニトリル・スチレン共重合体(AS樹脂)等の非晶性樹脂であって、200℃におけるMFR(JIS K−7210に準じて試験温度200℃、試験荷重2.16kgにて測定)が3.0〜60g/10分、さらに好ましくは30〜50g/10分でかつ、230℃におけるメルトテンション(株式会社東洋精機製作所製メルトテンションテスターを用い、余熱温度230℃、押出速度5.7mm/分で、直径2.095mm、長さ8mmのオリフィスからストランドを押し出し、このストランドを直径50mmのローラーに巻き取り速度100rpmで巻き取ったときの張力を示す)が50mN以上、好ましくは120mN以上のものを用いて形成される。 More specifically, it is a polyolefin (for example, polypropylene, high density polyethylene) which is a homopolymer or copolymer of an olefin such as ethylene, propylene, butene, isoprene pentene, methyl pentene, etc., and has an MFR (JIS) at 230 ° C. According to K-7210, measured at a test temperature of 230 ° C. and a test load of 2.16 kg) of 3.0 g / 10 min or less, more preferably 0.3 to 1.5 g / 10 min, or acrylonitrile butadiene Amorphous resin such as styrene copolymer, polystyrene, high impact polystyrene (HIPS resin), acrylonitrile / styrene copolymer (AS resin), MFR at 200 ° C. (test temperature 200 according to JIS K-7210) ℃, measured at a test load of 2.16 kg) is 3.0 to 60 g / 10 min More preferably, the melt tension at 30 to 50 g / 10 min and at 230 ° C. (using a melt tension tester manufactured by Toyo Seiki Seisakusho Co., Ltd., preheating temperature 230 ° C., extrusion speed 5.7 mm / min, diameter 2.095 mm, A strand is extruded from an orifice having a length of 8 mm, and a tension when the strand is wound around a roller having a diameter of 50 mm at a winding speed of 100 rpm) is 50 mN or more, preferably 120 mN or more.
また、シート状パリソンP1、P2には衝撃により割れが生じることを防止するため、水素添加スチレン系熱可塑性エラストマーが30wt%未満、好ましくは15wt%未満の範囲で添加されていることが好ましい。具体的には水素添加スチレン系熱可塑性エラストマーとしてスチレン−エチレン・ブチレン−スチレンブロック共重合体、スチレン−エチレン・プロピレン−スチレンブロック共重合体、水添スチレン−ブタジエンゴムおよびその混合物が好適であり、スチレン含有量が30wt%未満、好ましくは20wt%未満であり、230℃におけるMFR(JIS K−7210に準じて試験温度230℃、試験荷重2.16kgにて測定)は1.0〜10g/10分、好ましくは5.0g/10分以下で、かつ1.0g/10分以上あるものがよい。
さらに、シート状パリソンP1、P2には、添加剤が含まれていてもよく、その添加剤としては、シリカ、マイカ、タルク、炭酸カルシウム、ガラス繊維、カーボン繊維等の無機フィラー、可塑剤、安定剤、着色剤、帯電防止剤、難燃剤、発泡剤等が挙げられる。
具体的にはシリカ、マイカ、ガラス繊維等を成形樹脂に対して50wt%以下、好ましくは30〜40wt%添加する。
In addition, in order to prevent the sheet-like parisons P1 and P2 from cracking due to impact, it is preferable that a hydrogenated styrene-based thermoplastic elastomer is added in a range of less than 30 wt%, preferably less than 15 wt%. Specifically, a styrene-ethylene / butylene-styrene block copolymer, a styrene-ethylene / propylene-styrene block copolymer, a hydrogenated styrene-butadiene rubber and a mixture thereof are suitable as the hydrogenated styrene-based thermoplastic elastomer. The styrene content is less than 30 wt%, preferably less than 20 wt%, and the MFR at 230 ° C. (measured at a test temperature of 230 ° C. and a test load of 2.16 kg according to JIS K-7210) is 1.0 to 10 g / 10. Minute, preferably 5.0 g / 10 min or less and 1.0 g / 10 min or more.
Further, the sheet-like parisons P1 and P2 may contain an additive. Examples of the additive include inorganic fillers such as silica, mica, talc, calcium carbonate, glass fiber, and carbon fiber, plasticizer, and stability. Agents, colorants, antistatic agents, flame retardants, foaming agents and the like.
Specifically, silica, mica, glass fiber or the like is added in an amount of 50 wt% or less, preferably 30 to 40 wt%, based on the molding resin.
おもて面側シート120Aの材料であるシート状パリソンP2の表面に化粧材シート140を設ける場合において、化粧材シート140とは、外観性向上、装飾性、成形品と接触する物(例えば、カーゴフロアボードの場合、ボード上面に載置される荷物など)の保護を目的として構成されるものである。化粧材シート140の材質は、繊維表皮材、シート状表皮材、フィルム状表皮材等が適用される。かかる繊維表皮材の素材としては、ポリエステル、ポリプロピレン、ポリアミド、ポリウレタン、アクリル、ビニロン等の合成繊維、アセテート、レーヨン等の半合成繊維、ビスコースレーヨン、銅アンモニアレーヨン等の再生繊維、綿、麻、羊毛、絹等の天然繊維、又はこれらのブレンド繊維が挙げられる。
In the case where the
これらの中でも、触感、耐久性及び成形性の観点から、ポリプロピレン又はポリエステルであることが好ましく、ポリエステルであることがより好ましい。繊維表皮材に用いられる糸は、例えば、ポリエステル:(3〜5)デニール×(50〜100)mm等の繊度が3〜15デニール、繊維長さが2〜5インチ程度のステープルの紡績糸と、細い柔軟なフィラメントを束にしたポリエステル:約150〜1000デニール/30〜200フィラメント=約5デニール×30〜200本等のマルチフィラメント、又は、ポリエステル:400〜800デニール/1フィラメント等の太いモノ・フィラメントと、を組み合わせて用いることが好ましい。 Among these, polypropylene or polyester is preferable and polyester is more preferable from the viewpoints of touch, durability, and moldability. The yarn used for the fiber skin material is, for example, polyester: (3-5) denier × (50-100) mm or other fineness of 3-15 denier, and a staple spun yarn having a fiber length of about 2-5 inches Polyester in a bundle of thin flexible filaments: about 150 to 1000 denier / 30 to 200 filaments = about 5 denier × 30 to 200 multifilaments, or polyester: 400 to 800 deniers per filament -It is preferable to use in combination with a filament.
化粧材シート140の組織としては、不織布、織物、編物、それらを起毛した布地等が挙げられる。なお、織物には、織組織が縦糸、横糸が順次上下に交絡する平組織のほか、何本かの糸を跳び越して交絡する種々の変化織も含まれる。これらの中でも、伸びに対する方向性がないため、立体形状に成形し易く、且つ表面の触感、風合いに優れることから、不織布であることが好ましい。ここで、不織布とは、繊維を平行に又は交互させて積上げるか又はランダムに散布してウエブを形成し、次いでウエブとなった繊維を接合してなる布状品を意味する。これらの中でも、成形品の立体形状再現性及び外観特性の観点から、ニードルパンチ法により製造された不織布であることが好ましい。また、ニードルパンチ法にて得られた不織布は、織物に比べて強度が小で伸度が大であり任意方向に対する変形度合いが大きいので、不織布としての強度を向上させると共に寸法の安定化を図るために、織布にバインダーを付着させる、又は、ウエブと不織布を重ね針でパンチさせておくことがより好ましい。これらのことから、化粧材シート140は、ポリプロピレン不織布又はポリエステル不織布であることがより好ましい。この場合、化粧材シート140自体が熱可塑性であるので、剥離回収後、加熱して変形させることによって、別の用途に用いることも可能である。例えば主体樹脂層をポリプロピレンにて構成し、化粧材シート140をポリプロピレン不織布で構成すると、成形品の主体樹脂層と化粧材シート140とが同じ素材であることから、リサイクルが容易になる。
Examples of the structure of the
一方、化粧材シート140がポリエステル不織布であると、ポリプロピレンにて構成した主体樹脂層と繊維表皮材との融点が異なるので、成形品に化粧材シート140を接着する際、熱により変質、変形したり、正しい位置に接着できない等の不具合が生じるのを抑制できる。また、この場合、成形性、剛性、外観及び耐久性にも優れる。また、化粧材シート140の引張強度は、立体形状再現性及び成形性の観点から、15kg/cm
2以上であることが好ましく、伸度は、30%以上であることが好ましい。なお、かかる引張強度及び伸度の値は、温度20℃においてJIS−K−7113に準拠して測定したものである。シート状表皮材、フィルム状表皮材としては、熱可塑性エラストマ−、エンボス加工された樹脂層、印刷層が外面に付された樹脂層、合成皮革、滑り止め用メッシュ形状の表皮層等が使用できる。
On the other hand, if the
It is preferably 2 or more, and the elongation is preferably 30% or more. In addition, the value of this tensile strength and elongation is measured based on JIS-K-7113 at the temperature of 20 degreeC. As the sheet-like skin material and film-like skin material, thermoplastic elastomer, embossed resin layer, resin layer with printed layer attached to the outer surface, synthetic leather, non-slip mesh-shaped skin layer, etc. can be used. .
以上の構成を有する積層板100の成形装置10を利用した積層板100の製造方法について、図面を参照しながら以下に説明する。
まず、図4において、溶融混練した熱可塑性樹脂をアキュムレータ22内に所定量貯留し、Tダイ28に設けられた所定間隔の押出スリット34から、貯留された熱可塑性樹脂を単位時間当たり所定押出量で間欠的に押し出すことにより、熱可塑性樹脂はスウェルし、溶融状態のシート状に下方に垂下するように所定の厚みにて所定押出速度で押し出される。
A method for manufacturing the
First, in FIG. 4, a predetermined amount of the melt-kneaded thermoplastic resin is stored in the accumulator 22, and the stored thermoplastic resin is discharged from the extrusion slits 34 provided at predetermined intervals on the T die 28. In this case, the thermoplastic resin swells and is extruded at a predetermined extrusion speed with a predetermined thickness so as to hang downward into a molten sheet.
次いで、一対のローラー30を開位置に移動し、押出スリット34の下方に配置された一対のローラー30同士の間隔をシート状パリソンPの厚みより広げることにより、下方に押し出された溶融状態のシート状パリソンPの最下部が一対のローラー30間に円滑に供給されるようにする。なお、ローラー30同士の間隔をシート状パリソンPの厚みより広げるタイミングは、押し出し開始後でなく、ワンショットごとに二次成形が終了時点で行ってもよい。
次いで、一対のローラー30同士を互いに近接させて閉位置に移動し、一対のローラー30同士の間隔を狭めてシート状パリソンPを挟み込み、ローラーの回転によりシート状パリソンPを下方に送り出す。
次いで、図4に示すように、押出方向に一様な厚みを形成したシート状パリソンPを一対のローラー30の下方に配置された分割金型32A,B間に配置する。これにより、シート状パリソンPは、ピンチオフ部118のまわりにはみ出す形態で位置決めされる。
以上の工程を、2枚のシート状パリソンP1、P2それぞれについて行い、おもて面側シート120Aの材料であるシート状パリソンP2と、裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1とを互いに間隔を隔てた状態で、分割金型32A,B間に配置する。
この場合、2枚のシート状パリソンP1、P2はそれぞれ、互いに独立に、押し出しスリット34の間隔、あるいは一対のローラー30の回転速度を調整することにより、分割金型32A,B間に配置される際の厚みを調整可能である。
Next, the pair of rollers 30 is moved to the open position, and the gap between the pair of rollers 30 disposed below the extrusion slit 34 is widened from the thickness of the sheet-like parison P, so that the molten sheet is pushed downward. The lowermost part of the parison P is smoothly supplied between the pair of rollers 30. In addition, the timing which makes the space | interval of the rollers 30 wider than the thickness of the sheet-like parison P may be performed after the end of the secondary molding for each one shot, not after the start of extrusion.
Next, the pair of rollers 30 are moved closer to each other and moved to the closed position, the sheet-like parison P is sandwiched by narrowing the interval between the pair of rollers 30, and the sheet-like parison P is sent downward by the rotation of the rollers.
Next, as shown in FIG. 4, the sheet-like parison P having a uniform thickness in the extrusion direction is disposed between the divided molds 32 </ b> A and 32 </ b> B disposed below the pair of rollers 30. Thereby, the sheet-like parison P is positioned in a form that protrudes around the pinch-off portion 118.
The above process is performed for each of the two sheet-like parisons P1 and P2, and the sheet-like parison P2 that is the material of the
In this case, the two sheet-like parisons P1 and P2 are arranged between the divided
より詳細には、裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1については、複数の凹部200が形成されることから成形時に金型キャビティの突起体に沿って引き伸ばされて、凹部200を設けないおもて面側シート120Aの材料であるシート状パリソンP2に比べて薄肉化される傾向にあるところ、後に説明するように、分割金型32A,Bを型締めすることにより、裏面側シート120Bとおもて面側シート120Aとを溶着して積層板100を完成した際、裏面側シート120Bの厚みとおもて面側シート120Aの厚みとが実質的に同じとなるように、裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1については、たとえば押し出しスリット34Aの間隔を押し出しスリット34Bの間隔より広げることにより、より厚くしておくことが可能である。
次いで、図5に示すように、型枠33Aを金型32Aに対して、裏面側シート120Bの材料であるシート状パリソンP1に向かって、金型32Aに対向するシート状パリソンP1の外表面117に当たるまで移動させる。
なお、化粧材シート14は、適宜金型上方に保持させてキャビティ面に沿って予め垂下させておけばよい。この化粧材シート14の配置のタイミングは、金型32を型締するまでに行えばよい。
More specifically, the sheet-like parison P1 that is the material of the back-
Next, as shown in FIG. 5, the
The
次いで、図5および図6に示すように、金型32Aのキャビティ116A、型枠33Aの内周面102、および金型32Aに対向するシート状パリソンP1の外表面117により構成された第1密閉空間84を通じて、真空吸引室80から吸引穴82を介して吸引することにより、シート状パリソンP1をキャビティ116Aに対して押し付けて、キャビティ116Aの凹凸表面に沿った形状にシート状パリソンP1を賦形する。これにより、裏面側シート120Bとして、複数の凹部200を形成する。
Next, as shown in FIGS. 5 and 6, a first hermetic seal formed by the
次いで、図7に示すように、シート状パリソンP1の外表面117に当接する型枠33Aをそのままの位置に保持した状態でシート状パリソンP1を吸引保持しつつ、それぞれの環状のピンチオフ部118A,B同士が当接するまで両金型32A,Bを互いに近づく向きに移動させる。この場合、ピンチオフ部118A,B同士の型締方向の当接位置は、互いに離間する2枚のシート状パリソンP1,P2の間となるところ、図7に示すように、ピンチオフ部118A,B同士が当接することにより、2枚のシート状パリソンP1,P2は互いの周縁部同士が溶着固定されるとともに、裏面側シート120Bの表面に形成された多数の凹部200の突き合わせ平面部240がおもて面側シート120Aの内表面に溶着される。
これにより、裏面側シート120Bとおもて面側シート120Aとの間に密閉中空部280を形成する。
次いで、図8に示すように、分割金型32A,Bを型開きして、成形された積層板100を取り出し、ピンチオフ部118A,Bの外側のバリ部分Bを切断し、これで成形が完了する。
Next, as shown in FIG. 7, each annular pinch-
Thereby, the sealed
Next, as shown in FIG. 8, the
以上のように、溶融状態のシート状パリソンPを間欠的に押し出すたびに、以上のような工程を繰り返すことにより、シート状の積層板100を次々に成形することが可能であり、押出成形により熱可塑性樹脂を間欠的に溶融状態のシート状パリソンPとして押し出し、真空成形または圧空成形により押し出されたシート状パリソンPを金型を用いて所定の形状に賦形することが可能である。
As described above, each time the molten sheet-like parison P is extruded intermittently, the sheet-like
以上の構成を有する樹脂積層板100の製造方法によれば、従来技術、例えば円筒状のパリソンを用いたブロー成形のように円筒状パリソンの円周方向の肉厚を調整することが困難な場合に、金型の型締め後にパリソン内に吹き込み圧を付加すると、ブロー比に応じて成形後のシートの厚みが局所的に薄肉化される問題が引き起こされてしまうという問題を解消することが可能である。つまり、それぞれ独立に厚み調整をした2枚の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを分割形式の金型32A、Bの間に位置決めしたうえで、一方の樹脂製シートとそれに対向する金型のキャビティ116との間に密閉空間を形成して、金型の側から密閉空間内を吸引することにより、熱可塑性樹脂シートがそれぞれのキャビティ形状に沿って引き伸ばされる程度に応じて、必要な強度および成形性を確保する限度で2枚の樹脂製シートそれぞれの厚みを個別に最大限まで薄肉化することが可能であり、それにより製造効率および製品品質を確保しつつ、十分な軽量化、薄肉化を達成可能である。
According to the manufacturing method of the
以上、本発明の実施形態を詳細に説明したが、本発明の範囲から逸脱しない範囲内において、当業者であれば種々の修正あるいは変更が可能である。たとえば、本実施形態においては、分割金型の型締前の吸引により賦形する、ものとして説明したが、それに限定されることなく、たとえばシートの表面に賦形する模様の態様に応じて、分割金型の型締後に吹き込み圧をかけてもよいし、金型32Aと金型32Bとにより内部に形成された第2密閉空間86を通じてシート状パリソンP1,P2を加圧するとともに、第1密閉空間84を通じて金型32Aの側からシート状パリソンP1を引き続き吸引するものとしてもよい。
Although the embodiments of the present invention have been described in detail above, various modifications or changes can be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the scope of the present invention. For example, in the present embodiment, it has been described that it is formed by suction before mold clamping of the divided mold, but is not limited thereto, for example, depending on the mode of the pattern to be formed on the surface of the sheet, Blowing pressure may be applied after the molds of the divided molds are clamped, and the sheet-like parisons P1 and P2 are pressurized through the second sealed
また、本実施形態においては、押し出された溶融状態のシート状パリソンを利用して、積層板100としてダイレクトに賦形・成形するものとして説明したが、それに限定されることなく、賦形・成形するのに必要な溶融状態を実現する限り、いったん押出成形し、冷却した熱可塑性樹脂製シートを再度加熱して溶融状態とした材料を利用して賦形・成形を行ってもよい。
Moreover, in this embodiment, although demonstrated as what shape | molds and shape | molds directly as the
さらに、本実施形態においては、おもて面側シート120Aを一対の金型の間に配置する際、金型上方に保持させてキャビティ面に沿って垂下させるものとして説明したが、それに限定されることなく、化粧材シート140をたとえば金型Bから吸引することによりキャビティ116B内に配置した状態で金型を型締めするものでもよいし、おもて面側シート120Aに化粧材シート140が予め接着された状態で配置されるものとしてもよい。
Further, in the present embodiment, when the
P シート状パリソンP
PL パーティングライン
10 成形装置
12 押出装置
14 型締装置
16 ホッパー
18 シリンダー
20 油圧モーター
22 アキュムレータ
24 プランジャー
28 Tダイ
30 ローラー
32 分割金型
33 型枠
34 押出スリット
80 真空吸引室
82 真空吸引穴
84 第1密閉空間
86 第2密閉空間
100 積層板
102 内周面
116 キャビティ
117 外表面
118 ピンチオフ部
119 突起体
120 シート
140 化粧材シート
150 おもて面側シートの外表面
170 おもて面側シートの内表面
180 裏面側シートの内表面
200 凹部
220 裏面側シートの外表面
240 突き合わせ面
260 開口
280 密閉中空部
P sheet parison P
102 Inner peripheral surface 116
Claims (10)
それぞれ、対応する押出ダイから押し出され、対応する一対のローラー間を通過した2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを互いに所定間隔を隔てて、環状ピンチオフ部のまわりにはみ出す形態で、分割形式の一対の金型の間に位置決めする段階と、
一方のシートと、一方のシートの外表面に対向する一方の金型のキャビティとの間に密閉空間を形成する段階と、
一方の金型の側から前記密閉空間を吸引して、一方の金型のキャビティに対して一方のシートの外表面を押し当てることにより、一方のシートを賦形して、突起体に沿うように引き伸ばす段階と、
一対の金型を型締めして、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートの周縁同士を、および一方のシートの突起体先端に対応する頂部を他方のシートの内表面に、それぞれ溶着する段階と、を有し、
2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートを準備する段階において、両熱可塑性樹脂製シート間のブロー比の相対差による製造後の両シート間の厚み差を低減するように、2枚の溶融状態の熱可塑性樹脂製シートについて、押出ダイの押し出しスリットの間隔及び/又は一対のローラーの回転速度を調整して、それぞれ独立に厚みを調整することにより、樹脂積層板を製造することを特徴とする樹脂積層板の製造方法。 A pair of split molds provided with a plurality of protrusions projecting toward the other mold only in the cavity of one mold, and extrusion of the pair of molds downstream in the extrusion direction of the extrusion die A pair of rollers provided on the upstream side in the direction, each having a pair of rollers in which the respective rotation axes are arranged in parallel to each other, and two molten thermoplastic resin sheets each having a adjusted thickness And the stage of preparing
Each of the two molten thermoplastic resin sheets extruded from the corresponding extrusion dies and passed between the corresponding pair of rollers protrudes around the annular pinch-off portion at a predetermined interval from each other. Positioning between a pair of molds;
Forming a sealed space between one sheet and the cavity of one mold facing the outer surface of the one sheet;
By sucking the sealed space from the side of one mold and pressing the outer surface of one sheet against the cavity of one mold, one sheet is shaped so that it follows the projection The stage of stretching to,
A pair of molds are clamped, and the peripheral edges of two molten thermoplastic resin sheets are welded to the inner surface of the other sheet, and the tops corresponding to the protrusion tips of one sheet are welded to each other. And having a stage
In the stage of preparing two molten thermoplastic resin sheets, the two sheets were melted so as to reduce the difference in thickness between the two sheets after production due to the relative difference in the blow ratio between the two thermoplastic resin sheets. About the thermoplastic resin sheet in a state, the distance between the extrusion slits of the extrusion die and / or the rotation speed of the pair of rollers is adjusted, and the resin laminate is manufactured by independently adjusting the thickness. A method for manufacturing a resin laminate.
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009299074A JP5590292B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2009-12-29 | Manufacturing method of resin laminate |
| PCT/JP2011/050018 WO2011081224A1 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2011-01-04 | Method for manufacturing a resin laminate |
| KR1020127017272A KR101579520B1 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2011-01-04 | Method for manufacturing a resin laminate |
| CN201180005229.9A CN102686379B (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2011-01-04 | The manufacture method of resin bed lamination |
| EP11728534.6A EP2520410B1 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2011-01-04 | Method for manufacturing a resin laminate |
| US13/132,024 US8926784B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2011-02-09 | Resin laminate manufacturing method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009299074A JP5590292B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2009-12-29 | Manufacturing method of resin laminate |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011136523A JP2011136523A (en) | 2011-07-14 |
| JP5590292B2 true JP5590292B2 (en) | 2014-09-17 |
Family
ID=44348428
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009299074A Active JP5590292B2 (en) | 2009-12-29 | 2009-12-29 | Manufacturing method of resin laminate |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5590292B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5604997B2 (en) * | 2010-06-07 | 2014-10-15 | キョーラク株式会社 | Manufacturing method of resin laminate having inner rib |
| KR102082989B1 (en) * | 2011-11-24 | 2020-02-28 | 교라꾸 가부시끼가이샤 | Resin panel and forming method |
| JP5963473B2 (en) * | 2012-02-28 | 2016-08-03 | キョーラク株式会社 | Resin panel and molding method |
| JP5871689B2 (en) * | 2012-03-29 | 2016-03-01 | キョーラク株式会社 | Resin panel and manufacturing method thereof |
| WO2013099828A1 (en) * | 2011-12-28 | 2013-07-04 | 東レ株式会社 | Thermoplastic resin molded article having hollow portion and method for manufacturing same |
| US9597854B2 (en) * | 2013-09-02 | 2017-03-21 | Kyoraku Co., Ltd. | Resin laminated plate |
| JP6657551B2 (en) * | 2016-03-03 | 2020-03-04 | キョーラク株式会社 | Method for manufacturing resin molded body |
| JP6206549B2 (en) * | 2016-06-28 | 2017-10-04 | キョーラク株式会社 | Resin panel and molding method |
| JP6721834B2 (en) | 2016-09-29 | 2020-07-15 | キョーラク株式会社 | Mold and its manufacturing method, and molded body manufacturing method |
| JP6761985B2 (en) * | 2016-09-30 | 2020-09-30 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Surface decorative panel, decorative panel equipped with this, and surface decorative panel manufacturing method |
| JP6916982B2 (en) * | 2017-06-30 | 2021-08-11 | キョーラク株式会社 | Manufacturing method of laminated structure and laminated structure |
| JP7453518B2 (en) * | 2020-02-28 | 2024-03-21 | キョーラク株式会社 | Method for manufacturing molds and molded bodies |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2748994B2 (en) * | 1991-05-24 | 1998-05-13 | 宇部興産株式会社 | Parison thickness control |
| JPH07156255A (en) * | 1993-12-06 | 1995-06-20 | Showa Denko Kk | Forming method for panel blown product |
| JPH11254509A (en) * | 1998-03-11 | 1999-09-21 | Yoshikatsu Kono | Blow molding method and apparatus therefor |
| JP4662321B2 (en) * | 2001-08-31 | 2011-03-30 | キョーラク株式会社 | Blow molding die and blow molding method |
| JP4763933B2 (en) * | 2001-08-31 | 2011-08-31 | キョーラク株式会社 | Blow molding method for hollow resin molded products |
| JP5204480B2 (en) * | 2005-03-31 | 2013-06-05 | キョーラク株式会社 | Interior parts for automobile and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP4919840B2 (en) * | 2007-03-06 | 2012-04-18 | 株式会社アイテック | panel |
| US8609015B2 (en) * | 2008-06-25 | 2013-12-17 | Kyoraku Co., Ltd. | Method for forming resin molded articles, apparatus for forming resin molded articles, and apparatus for adjusting thickness of thermoplastic resin sheet |
-
2009
- 2009-12-29 JP JP2009299074A patent/JP5590292B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011136523A (en) | 2011-07-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5590292B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of resin laminate | |
| WO2011081224A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing a resin laminate | |
| JP5556805B2 (en) | Molding method and molding apparatus for resin molded product, and apparatus for adjusting thickness of thermoplastic resin sheet | |
| KR102051679B1 (en) | Molding method and molding apparatus of resin molded article | |
| JP5004371B2 (en) | Sandwich panel core, sandwich panel core molding method, and sandwich panel and sandwich panel molding method | |
| WO2013002366A1 (en) | Resin laminated plate | |
| WO2016171156A1 (en) | Molten resin extrusion device and extrusion method as well as molten resin molding apparatus and molding method | |
| JP5720439B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of resin laminate and molding die of resin laminate | |
| JP6424653B2 (en) | Resin panel | |
| JP5345026B2 (en) | Molding method and molding apparatus for resin molded product, and apparatus for adjusting thickness of thermoplastic resin sheet | |
| JP5604997B2 (en) | Manufacturing method of resin laminate having inner rib | |
| JP6751504B2 (en) | Molding method of resin molded products and molding equipment for thermoplastic resin | |
| JP5772300B2 (en) | Resin laminate |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20121024 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20140327 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140524 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140605 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140702 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140715 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5590292 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |