JP5516043B2 - Travel control device - Google Patents
Travel control device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5516043B2 JP5516043B2 JP2010108914A JP2010108914A JP5516043B2 JP 5516043 B2 JP5516043 B2 JP 5516043B2 JP 2010108914 A JP2010108914 A JP 2010108914A JP 2010108914 A JP2010108914 A JP 2010108914A JP 5516043 B2 JP5516043 B2 JP 5516043B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- vehicle
- light beam
- light
- reflected light
- speed
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Optical Radar Systems And Details Thereof (AREA)
Description
本発明は、走行制御装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a travel control device.
従来から、レーザを、車両方向前方に向けて照射するとともに、車幅方向に走査(前方スキャン)することにより、先行車両や、車両方向前方にある障害物や路面に付された白線(走行路区分線)等を検出する車載レーダ装置が知られている(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 Conventionally, by irradiating a laser beam forward in the vehicle direction and scanning in the vehicle width direction (forward scan), a white line (running road) attached to the preceding vehicle, an obstacle in front of the vehicle direction, or a road surface An in-vehicle radar device that detects a categorization line or the like is known (for example, see Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、上記した車載レーダ装置では、レーザを円弧状に走査しているので、停止線などの道路上を横切る白線に対しては、サンプリング周期を短くしないと検出できない。しかし、サンプリング周期を短くすると、データの処理に時間が掛かり、車両制御に遅れが生じる可能性がある。 However, since the above-described on-vehicle radar device scans the laser in an arc shape, a white line crossing the road such as a stop line cannot be detected unless the sampling cycle is shortened. However, if the sampling period is shortened, it takes time to process the data, which may cause a delay in vehicle control.
本発明は、このような従来の課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、停止線などの道路上を横切る白線に対しても、サンプリング周期を短くすることなく検出可能となり、適切なタイミングで走行制御が可能となる走行制御装置を提供することである。 The present invention has been made in view of such a conventional problem. The object of the present invention is to detect a white line that crosses a road such as a stop line without shortening the sampling period, and is appropriate. It is to provide a travel control device that enables travel control at timing.
本発明の特徴は、車両に搭載された第1のビーム発生手段から光ビームを発生させ、この光ビームを、車両前方に対して第1の角度だけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車両前方に対して第2の角度だけ車幅方向に傾かせて固定し、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査し、車両前方の道路上で反射された光ビームの反射光を受光し、車両の速度を検出し、車両の速度に基づいて反射光の位置を算出し、この反射光の位置に基づいて、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を検出し、この白線と車両の速度に基づいて車両の走行制御を行う走行制御装置であって、第2の角度が走行速度及び光ビームの走査周期により定められることである。 A feature of the present invention is that a light beam is generated from a first beam generating means mounted on a vehicle, and the light beam is tilted vertically downward by a first angle with respect to the front of the vehicle, and with respect to the front of the vehicle. The vehicle is tilted and fixed in the vehicle width direction by the second angle, scanned across the center of the lane width, and the reflected light of the light beam reflected on the road ahead of the vehicle is received to detect the vehicle speed. The position of the reflected light is calculated based on the speed of the vehicle, the white line extending in the vehicle width direction on the road is detected based on the position of the reflected light, and the vehicle travels based on the white line and the speed of the vehicle. In the travel control device that performs control, the second angle is determined by the travel speed and the scanning period of the light beam.
本発明の走行制御装置によれば、停止線などの道路上を横切る白線に対しても、サンプリング周期を短くすることなく検出可能となり、適切なタイミングで走行制御が可能となる。 According to the travel control device of the present invention, it is possible to detect a white line crossing a road such as a stop line without shortening the sampling cycle, and travel control can be performed at an appropriate timing.
以下図面を参照して、本発明の実施の形態を説明する。図面の記載において同一部分には同一符号を付している。 Embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. In the description of the drawings, the same parts are denoted by the same reference numerals.
(第1の実施の形態)
図1を参照して、本発明の第1の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置の構成を説明する。第1の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置は、光ビームを発生する第1の光ビーム発生部(第1の光ビーム発生手段)10と、第1の光ビーム発生部10により発生する光ビームを車両前方の道路上において走査する第1の光ビーム走査部(第1の光ビーム走査手段)15と、車両前方の道路上で反射された光ビームの反射光を受光する第1の受光部(第1の受光手段)20と、車両の速度を検出する車速検出部(車速検出手段)40と、車速検出部40により検出された車両の速度に基づいて第1の受光部20が受光した反射光の位置を算出する反射位置算出部(反射位置算出手段)25と、反射光位置算出部25により算出された反射光の位置を記憶する反射位置記憶部(反射位置記憶手段)30と、反射光位置記憶部30に記憶された反射光の位置に基づいて、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を検出する白線検出部(白線検出手段)50と、白線検出部50で検出した白線と車速検出部40により検出した車両の速度に基づいて車両の走行制御を行う走行制御部(走行制御手段)60とを備える。
(First embodiment)
With reference to FIG. 1, the structure of the traveling control apparatus concerning the 1st Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated. The travel control apparatus according to the first embodiment includes a first light beam generation unit (first light beam generation unit) 10 that generates a light beam, and a light beam generated by the first light
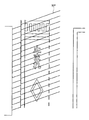
図2(a)は、図1の走行制御装置を搭載した車両SCから車両前方に向けて射出される光ビームLBを示す模式図であり、図2(b)は、車両前方の道路上に照射される光ビームLBの走査領域を示す模式図である。 FIG. 2A is a schematic diagram showing a light beam LB emitted toward the front of the vehicle from the vehicle SC on which the traveling control device of FIG. 1 is mounted, and FIG. It is a schematic diagram which shows the scanning area | region of the irradiated light beam LB.
車両SCの前面部に搭載された第1の光ビーム発生部10により発生する光ビームLBは、図2(a)に示すように鉛直方向において第1の角度αだけ下方に向けて射出される。
The light beam LB generated by the first
第1の光ビーム走査部15は、図2(b)に示すように、水平方向の走査角度範囲γにおいて、光ビームLBを走査する。この時、走査角度範囲γは、走行車線の両端の白線が検出可能な角度範囲が望ましい。
As shown in FIG. 2B, the first light
道路上に照射される光ビームLBの照射位置は、光ビームLBの走査により移動する。光ビームLBの照射位置の軌跡RPは、図2(b)に示すように、車幅方向の中央部を横切り、車幅方向に対して車両前後方向に第2の角度θを成している。第2の角度θは、走行速度及び光ビームLBの走査周期fにより定められる。なお、本発明の実施の形態において軌跡RPは、線分を成しているが、軌跡RPの全体が曲線或いは軌跡RPの一部が曲
線であっても構わない。
The irradiation position of the light beam LB irradiated on the road moves by scanning the light beam LB. As shown in FIG. 2B, the locus RP of the irradiation position of the light beam LB crosses the center portion in the vehicle width direction and forms a second angle θ in the vehicle longitudinal direction with respect to the vehicle width direction. . The second angle θ is determined by the traveling speed and the scanning period f of the light beam LB. In the embodiment of the present invention, the locus RP forms a line segment, but the entire locus RP may be a curved line or a part of the locus RP may be a curved line.
このように、第1の光ビーム走査部15は、先ず、第1の光ビーム発生部10により発生する光ビームLBを、車両前方に対して第1の角度αだけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車両前方に対して第2の角度θだけ車幅方向に傾かせて固定する。そして、車両前方に対して第2の角度θだけ車幅方向に傾かせた方向を走査中心として、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査角度範囲γにおいて光ビームLBを走査する。なお、第2の角度θは、車両の走行速度V及び光ビームの走査周期fにより定められる
In this way, the first light
具体的には、第1の光ビーム発生部10の車載高さをH、走行車線幅をWとすると、(1)式に従って、走査角度範囲γを設定すればよい。これにより、走行車線の両端の白線が検出可能な走査角度範囲γを設定することができる。
Specifically, when the vehicle-mounted height of the first
γ>arctan(Wtanα/2Hcosθ) ・・・(1) γ> arctan (Wtan α / 2H cos θ) (1)
例えば、第1の角度αが0.08[rad](約4.6°)、第2の角度θが0.35[rad](約20°)、光ビーム発生部10の車載高さHが0.5[m]、走行車線幅Wが3[m]である場合、(1)式から、γを、0.25[rad](約14°)以上に設定することができ
る。
For example, the first angle α is 0.08 [rad] (about 4.6 °), the second angle θ is 0.35 [rad] (about 20 °), and the in-vehicle height H of the
第1の受光部20は、光ビームLBの反射光を受光して、少なくとも車両SCに対する反射光の相対的な位置と反射光の強さを検知する。
The first
反射位置算出部25は、車両SCに対する反射光の相対的な位置、車両SCの位置、及び車速検出部40により検出された車両SCの速度Vに基づいて、第1の受光部20が受光した反射光の位置を算出する。反射位置記憶部30は、反射光位置算出部25により算出された反射光の位置及び反射光の強さを関連づけて記憶する。
Based on the relative position of the reflected light with respect to the vehicle SC, the position of the vehicle SC, and the speed V of the vehicle SC detected by the vehicle
白線検出部50は、先ず、射光位置記憶部30に記憶された反射光の位置及び反射光の強さに基づいて、白線を検出する。その後、検出した白線の内、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を、停止線として検出する。
First, the white
図3を参照して、図1の走行制御装置により行われる制御手順の一例を説明する。 With reference to FIG. 3, an example of a control procedure performed by the travel control device of FIG. 1 will be described.
先ず、図3のステップS110では、第1の光ビーム発生部10により光ビームLBを発生するとともに、図2を示したように、第1の光ビーム走査部15により光ビームLBを走査する。これと同時に、第1の受光部20により光ビームLBの反射光を受光し、自車に対する反射光の相対位置と反射光の強さを検知する。
First, in step S110 in FIG. 3, the light beam LB is generated by the first
次に、ステップS120では、車両SCの位置と、ステップS110で検知した車両SCに対する反射光の相対位置と、車速検出部40により検出された車両SCの速度Vとから反射光の位置を算出する。そして、算出された反射光の位置を、ステップS110で検知した反射光の強さと関連付けて反射位置記憶部30に記憶する。なお、車両SCの位置pは初期状態ではp=0でよい。
Next, in step S120, the position of the reflected light is calculated from the position of the vehicle SC, the relative position of the reflected light with respect to the vehicle SC detected in step S110, and the speed V of the vehicle SC detected by the vehicle
次に、ステップS130では、反射位置記憶部30に記憶されている反射光の位置と反射光の強さとから、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線(停止線)を検出する。停止線が検出された場合は、停止線までの距離Lを取得する。ステップS130の停止線検出の詳細な処理手順の一例を図4のフローチャートに示す。
Next, in step S130, a white line (stop line) extending in the vehicle width direction on the road is detected from the position of the reflected light stored in the reflection
先ず、図4のステップS210では、反射位置記憶部30に記憶されている反射光の位置と反射光の強さとから、路面標示の画像を抽出する。アスファルトに比べて路面標示の反射率が高いことを利用し、反射光が強い部分を路面標示の画像として抽出する。これにより、例えば図5に示すような、横断歩道、停止線、横断歩道又は自転車横断帯あり、などの指示表示、規制表示、区画線の画像を得ることができる。図5に記載された平行な複数の斜線は図2(b)の光ビームLBの照射位置の軌跡RPに相当する。
First, in step S210 of FIG. 4, a road marking image is extracted from the position of the reflected light and the intensity of the reflected light stored in the reflection
ステップS220では、ステップS210で抽出した結果から白線を検出する。白線の検出には種種の方法が知られているが、ここでは、ハフ変換により直線(曲線でも良い)を検出し、検出したうち、長さが所定値(例えば10m)以上のものを白線として検出する。 In step S220, a white line is detected from the result extracted in step S210. Various methods are known for detecting a white line. Here, a straight line (or a curved line) is detected by Hough transform, and a detected line having a length of a predetermined value (for example, 10 m) or more is defined as a white line. To detect.
ステップS230では、ステップS210で抽出した画像と、ステップS220で検出した白線とに基づいて停止線を検出する。まず、ステップS210で抽出した画像において、距離が近いスキャン点同士でクラスタリングを行う。次に、クラスタリング結果をステップS220で検出された白線(曲線の場合は接線)に垂直な方向にグルーピングを行う。さらに、各グルーピング結果の白線に平行な方向の所定距離(例えば0.5m)以内に別のグルーピング結果があるは否かを判断し、あった場合には、それらを更にグルーピングする。その結果、例えば、図6に示すような幾つかのグループ結果G1〜G8が抽出される。このグルーピング結果G1〜G8のうち、ステップS220で検出された白線に平行な方向の大きさが所定範囲内(例えば、0.3m以上且つ0.5m以下)のグルーピング結果G2を停止線として検出する。 In step S230, a stop line is detected based on the image extracted in step S210 and the white line detected in step S220. First, clustering is performed between scan points that are close to each other in the image extracted in step S210. Next, the clustering results are grouped in a direction perpendicular to the white line (tangent in the case of a curve) detected in step S220. Further, it is determined whether or not there are other grouping results within a predetermined distance (for example, 0.5 m) in a direction parallel to the white line of each grouping result. As a result, for example, several group results G1 to G8 as shown in FIG. 6 are extracted. Among the grouping results G1 to G8, the grouping result G2 whose magnitude in the direction parallel to the white line detected in step S220 is within a predetermined range (for example, 0.3 m or more and 0.5 m or less) is detected as a stop line. .
図3のステップ140に進み、車速検出部40により自車の速度Vを検出する。
Proceeding to step 140 in FIG. 3, the vehicle
ステップ150では、ステップS130で取得した停止線までの距離Lと、ステップS140で検出した自車の速度Vとに基づいて、走行制御の必要性を判断する。停止線までの距離Lと自車の速度Vが(2)式を満たす場合(S150でYES)、走行制御が必要有ると判断して、ステップ160に進み、(2)式を満たさない場合(S150でNO)、走行制御が必要無いと判断して、ステップ170に進む。ここで、βは停止に必要な減速度に関する係数で、例えばβ=8とする。 In step 150, the necessity of travel control is determined based on the distance L to the stop line acquired in step S130 and the speed V of the host vehicle detected in step S140. When the distance L to the stop line and the speed V of the host vehicle satisfy the equation (2) (YES in S150), it is determined that traveling control is necessary, and the process proceeds to step 160, and the equation (2) is not satisfied ( If NO in S150, it is determined that traveling control is not necessary, and the routine proceeds to step 170. Here, β is a coefficient related to the deceleration required for stopping, for example, β = 8.
L<V2/2β ・・・(2) L <V 2 / 2β (2)
ステップS160では、停止線で停止できるように自車のブレーキを制御する。 In step S160, the brake of the own vehicle is controlled so that it can stop at a stop line.
ステップS170では、イグニッションスイッチ(IGN)がオフされたか否かを判断する。オフされていれば(S170でYES)、図3の処理フローを終了し、オフされていなければ(S170でNO)、ステップS110に戻る。 In step S170, it is determined whether or not the ignition switch (IGN) is turned off. If it is turned off (YES in S170), the process flow of FIG. 3 is terminated. If it is not turned off (NO in S170), the process returns to step S110.
本発明の第1の実施の形態によれば、以下の作用効果が得られる。 According to the first embodiment of the present invention, the following operational effects can be obtained.
第1の光ビーム発生部10により発生する光ビームを、車両前方に対して第1の角度αだけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車幅方向に対して第2の角度θだけ車両前後方向に傾かせて固定し、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査する。これにより、図2(b)に示すように、照射位置の軌跡RP(走査線)が車線幅の中央を横切るので、停止線などの道路上を横切る白線に対してもサンプリング周期を短くすることなく検出可能となり、適切なタイミングで走行制御が可能となる。
The light beam generated by the first
(第2の実施の形態)
第2の実施の形態では、車幅方向に傾かせる第2の角度θを、走行制御を行う最大速度や走査周期に応じて決定する場合について説明する。なお、第2の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置の構成及び処理内容は、第1の実施の形態と同様であり、図示及び説明を省略する。
(Second Embodiment)
In the second embodiment, a case will be described in which the second angle θ to be tilted in the vehicle width direction is determined according to the maximum speed at which traveling control is performed or the scanning cycle. Note that the configuration and processing contents of the travel control apparatus according to the second embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment, and illustration and description thereof are omitted.
第1の光ビーム走査部15が光ビームを走査する周期(走査周期)をfとし、走行制御を行う最大速度をVmaxとすると、(3)式を満たすように、第2の角度θを設定する。
The second angle θ is set so as to satisfy Equation (3), where f is the period (scanning period) at which the first light
ここで、Lは検出すべき対象物の車幅方向の長さの半分の値であり、例えば、検出すべき対象物が第1の実施の形態と同じ停止線である場合は、L=2[m]/2=1とする。δは光ビームの太さなどの特性に応じて調整する調整シロであり、例えばδ=0.1[rad]
程度である。例えば、f=10[Hz]、Vmax=30[km/h]とすると、θ≧約0.59[rad](約34度)で有り、また、白線検出を考慮するとθ≦約0.79[rad](45度)とな
る。白線を検出するためにはθは小さい方が良いことを考えると、例えば、θ=0.59[rad](約34度)と設定することができる。
Here, L is a half value of the length of the object to be detected in the vehicle width direction. For example, when the object to be detected is the same stop line as that of the first embodiment, L = 2. [m] / 2 = 1. δ is an adjustment scale that is adjusted according to characteristics such as the thickness of the light beam. For example, δ = 0.1 [rad]
Degree. For example, if f = 10 [Hz] and Vmax = 30 [km / h], θ ≧ about 0.59 [rad] (about 34 degrees), and θ ≦ about 0.79 considering white line detection. [rad] (45 degrees). Considering that smaller θ is better for detecting the white line, for example, θ = 0.59 [rad] (about 34 degrees) can be set.
なお、第2の角度θは、走行速度V及び光ビームの走査周期fにより定められるため、走行速度を、走行制御を行う最大速度Vmaxに応じて定めることができる。よって、車両前後方向に傾かせる第2の角度θも、走行制御を行う最大速度Vmaxに応じて決定されることになる。よって、停止線などの道路上を横切る白線を検出可能となり、適切なタイミングで走行制御が可能となる。 The second angle θ is determined by the traveling speed V and the light beam scanning period f. Therefore, the traveling speed can be determined according to the maximum speed Vmax at which traveling control is performed. Therefore, the second angle θ tilted in the vehicle front-rear direction is also determined according to the maximum speed Vmax at which traveling control is performed. Therefore, it is possible to detect a white line that crosses the road, such as a stop line, and it is possible to control traveling at an appropriate timing.
第2の実施の形態においては、第2の角度θを走査周期fと走行制御を行う最大速度Vmaxによって決定するので、走行制御を行う速度では停止線の検出精度を高めることがで
きる。
In the second embodiment, since the second angle θ is determined by the scanning period f and the maximum speed Vmax at which travel control is performed, the stop line detection accuracy can be increased at the speed at which travel control is performed.
(第3の実施の形態)
第3の実施の形態では、光ビームを車両前後方向に傾かせる方向(第2の角度θの符号)を車両の通行区分により定める場合について説明する。なお、第3の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置の構成及び処理内容は、第1の実施の形態と同様であり、図示及び説明を省略する。
(Third embodiment)
In the third embodiment, a case will be described in which the direction in which the light beam is tilted in the vehicle front-rear direction (the sign of the second angle θ) is determined by the vehicle traffic classification. The configuration and processing contents of the travel control apparatus according to the third embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment, and illustration and description thereof are omitted.
例えば、通行区分が左側の場合には、図7(a)及び図7(b)に示すように、同じ曲率のカーブを曲がる際、左カーブの場合の方が右カーブの場合に比べて旋回曲率が小さくなる。よって、図7(b)に示す左カーブの場合、図2(b)と反対方向に第2の角度θを与えてしまうと、照射位置の軌跡rpは図7(b)の破線で示すようになり、車線幅の中央を横切ることが難しくなる。このため、白線を検出できなくなってしまう。よって、図2(b)と同じ方向、すなわち通行区分の内側に向かうにつれて車両前方に第2の角度θを与えれば、図7(b)の実線で示す照射位置の軌跡rpが車線幅の中央を横切るので、白線を検出することが可能である。 For example, when the traffic segment is on the left side, as shown in FIGS. 7A and 7B, when turning a curve with the same curvature, the left curve turns compared to the right curve. Curvature decreases. Therefore, in the case of the left curve shown in FIG. 7B, if the second angle θ is given in the opposite direction to FIG. 2B, the irradiation position locus rp is as shown by the broken line in FIG. It becomes difficult to cross the center of the lane width. For this reason, the white line cannot be detected. Therefore, if the second angle θ is given to the front of the vehicle in the same direction as FIG. 2B, that is, toward the inside of the traffic section, the locus rp of the irradiation position indicated by the solid line in FIG. It is possible to detect a white line.
以上説明したように、光ビームを車幅方向に傾かせる方向を通行区分により定めること
により、カーブ路においても停止線等の道路上を横切る白線を検出可能となり、適切なタイミングで走行制御が可能となる。
As described above, by setting the direction of inclining the light beam in the vehicle width direction according to the traffic classification, it is possible to detect white lines that cross over roads such as stop lines even on curved roads, and it is possible to control traveling at appropriate timing It becomes.
(第4の実施の形態)
第4の実施の形態では、2つの光ビームを用いて、停止線の検出を行う場合について説明する。
(Fourth embodiment)
In the fourth embodiment, a case where a stop line is detected using two light beams will be described.
図8を参照して、本発明の第4の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置の構成を説明する。第4の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置は、図1の走行制御装置の構成要素に加えて、更に、第2のビーム発生部(第2のビーム発生手段)12、第2の光ビーム走査部(第2の光ビーム走査手段)17、及び第2の受光部(第2の受光手段)22を備えている。 With reference to FIG. 8, the structure of the traveling control apparatus concerning the 4th Embodiment of this invention is demonstrated. The travel control apparatus according to the fourth embodiment further includes a second beam generation unit (second beam generation means) 12 and a second light beam scanning in addition to the components of the travel control apparatus of FIG. A second light receiving unit (second light receiving unit) 22 and a second light receiving unit (second light receiving unit) 22.
即ち、図8の走行制御装置は、車両に搭載された、光ビームを発生する第2のビーム発生部12と、第2の光ビーム発生部12により発生する光ビームを、車両前方に対して第1の角度αだけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車幅方向に対して第2の角度θの符号を入れ替えた、すなわち第2の角度θの前後方向の傾きに対して逆向きの第3の角度(−θ)だけ車両前後方向に傾かせて固定し、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査する第2の光ビーム走査部17と、車両前方の道路上で反射された光ビームの反射光を受光する第2の受光部22とを更に備える。
In other words, the travel control device of FIG. 8 has a second
そして、反射光位置算出部25は、車速検出部40により検出された車両の速度に基づいて、図3に示す処理フローにしたがって、第2の受光部22が受光した反射光の位置を算出する(S120)。反射光位置記憶部30は、第2の受光部22が受光した反射光の位置を記憶する(S120)。白線検出部50は、第1の受光部20及び第2の受光部22が受光した各反射光の位置に基づいて、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を停止線として検出する(S130)。
The reflected light
なお、第4の実施の形態に係わる走行制御装置のその他の構成及び処理内容は、第1の実施の形態と同様であり、図示及び説明を省略する。 In addition, the other structure and process content of the traveling control apparatus concerning 4th Embodiment are the same as that of 1st Embodiment, and illustration and description are abbreviate | omitted.
図9(a)及び図9(b)に示すように、第1の光ビーム走査部15による光ビームの照射位置の軌跡RP1と、第2の光ビーム走査部17による光ビームの照射位置の軌跡RP2は、それぞれ車幅方向の中央部を横切し、互いに交差している。車幅方向に対して、互いに反対方向に第2の角度θを有している。例えば、θ1=0.35[rad](約20度
)、θ2=0.59[rad](約34度)とする。
9A and 9B, the locus RP1 of the irradiation position of the light beam by the first light
第4の実施の形態においては、2つの光ビームが互いに反対方向に第2の角度θを成しているので、左右どちらのカーブに対しても安定して検出可能であるとともに、記憶されるスキャン結果が格子状となり、より高い速度においても停止線等の検出が可能である。 In the fourth embodiment, since the two light beams form the second angle θ in opposite directions, it is possible to stably detect and store both the left and right curves. The scan result has a lattice shape, and a stop line or the like can be detected even at a higher speed.
(その他の実施の形態)
上記のように、本発明は、4つの実施形態によって記載したが、この開示の一部をなす論述及び図面はこの発明を限定するものであると理解すべきではない。この開示から当業者には様々な代替実施の形態、実施例及び運用技術が明らかとなろう。
(Other embodiments)
As described above, the present invention has been described in terms of four embodiments. However, it should not be understood that the description and drawings that form part of this disclosure limit the present invention. From this disclosure, various alternative embodiments, examples and operational techniques will be apparent to those skilled in the art.
例えば、本発明の実施の形態では、停止線があるところでは停止するものとして説明したが、例えば、一時停止交差点や赤信号情報を取得した場合や、横断者などがいる場合だけに適用するようにしてもよい。 For example, in the embodiment of the present invention, it is described that the vehicle stops when there is a stop line. However, the present invention is applied only when, for example, a temporary stop intersection or red light information is acquired or there is a crossing person or the like. It may be.
また、光ビームを車両に対してヨー角を与えて固定することにより、単路だけでなく交
差点においても適切に路面標示を認識することができる。車載ヨー角は、進行方向に垂直な対象物(例えば、停止線等の道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線)の長さと対象物通過時の最大速度、及び、光ビームの走査周波数から算出することができる。
Further, by fixing the light beam by giving a yaw angle to the vehicle, it is possible to appropriately recognize the road marking not only at the single road but also at the intersection. The in-vehicle yaw angle is calculated from the length of an object perpendicular to the traveling direction (for example, a white line extending in the vehicle width direction on the road such as a stop line), the maximum speed when the object passes, and the scanning frequency of the light beam. be able to.
10 第1の光ビーム発生部(第1の光ビーム発生手段)
12 第2の光ビーム発生部(第2の光ビーム発生手段)
15 第1の光ビーム走査部(第1の光ビーム走査手段)
17 第2の光ビーム走査部(第2の光ビーム走査手段)
20 第1の受光部(第1の受光手段)
22 第2の受光部(第2の受光手段)
25 反射光位置算出部(反射光位置算出手段)
30 反射光位置記憶部(反射光位置記憶手段)
40 車速検出部(車速検出手段)
50 白線検出部(白線検出手段)
60 走行制御部(走行制御手段)
α 第1の角度
θ 第2の角度
10 1st light beam generation part (1st light beam generation means)
12 Second light beam generating section (second light beam generating means)
15 1st light beam scanning part (1st light beam scanning means)
17 Second light beam scanning unit (second light beam scanning means)
20 1st light-receiving part (1st light-receiving means)
22 2nd light-receiving part (2nd light-receiving means)
25 Reflected light position calculating section (reflected light position calculating means)
30 Reflected light position storage unit (reflected light position storage means)
40 Vehicle speed detection unit (vehicle speed detection means)
50 White line detection unit (white line detection means)
60 Travel control unit (travel control means)
α first angle θ second angle
Claims (4)
前記第1の光ビーム発生手段により発生する光ビームを、車両前方に対して第1の角度だけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車幅方向に対して第2の角度だけ車両前後方向に傾かせて固定し、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査する第1の光ビーム走査手段と、
車両前方の道路上で反射された前記光ビームの反射光を受光する第1の受光手段と、
前記車両の速度を検出する車速検出手段と、
前記車速検出手段により検出された前記車両の速度に基づいて前記第1の受光手段が受光した反射光の位置を算出する反射光位置算出手段と、
前記反射光位置算出手段により算出された反射光の位置を記憶する反射光位置記憶手段と、
前記反射光位置記憶手段に記憶された反射光の位置に基づいて、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を検出する白線検出手段と、
前記白線検出手段で検出した前記白線と前記車速検出手段により検出した車両の速度に基づいて車両の走行制御を行う走行制御手段と、を備え、
前記第2の角度は、走行速度及び光ビームの走査周期により定められる
ことを特徴とする走行制御装置。 First beam generating means for generating a light beam mounted on a vehicle;
The light beam generated by the first light beam generating means is tilted vertically downward by a first angle with respect to the front of the vehicle, and tilted in the vehicle front-rear direction by a second angle with respect to the vehicle width direction. First light beam scanning means for fixing and scanning across the center of the lane width;
First light receiving means for receiving reflected light of the light beam reflected on the road ahead of the vehicle;
Vehicle speed detection means for detecting the speed of the vehicle;
Reflected light position calculating means for calculating the position of reflected light received by the first light receiving means based on the speed of the vehicle detected by the vehicle speed detecting means;
Reflected light position storage means for storing the position of the reflected light calculated by the reflected light position calculating means;
A white line detecting means for detecting a white line extending in the vehicle width direction on the road based on the position of the reflected light stored in the reflected light position storage means;
Travel control means for performing travel control of the vehicle based on the white line detected by the white line detection means and the vehicle speed detected by the vehicle speed detection means,
The second angle is determined by a traveling speed and a light beam scanning cycle.
前記第2の光ビーム発生手段により発生する光ビームを、車両前方に対して前記第1の角度だけ鉛直下方に傾かせ、かつ車両前方に対して前記第2の角度の符号を入れ替えた第3の角度だけ車幅方向に傾かせて固定し、車線幅の中央を横切るように走査する第2の光ビーム走査手段と、
車両前方の道路上で反射された前記光ビームの反射光を受光する第2の受光手段と、を更に備え、
前記反射光位置算出手段は、前記車速検出手段により検出された前記車両の速度に基づいて、前記第2の受光手段が受光した反射光の位置を算出し、
前記反射光位置記憶手段は、前記第2の受光手段が受光した反射光の位置を記憶し、
前記白線検出手段は、前記第1の受光手段及び前記第2の受光手段が受光した反射光の位置に基づいて、道路上の車幅方向に伸びる白線を検出する
ことを特徴とする請求項1〜3のいずれか一項に記載の走行制御装置。 A second beam generating means for generating a light beam mounted on the vehicle;
A third light beam generated by the second light beam generating means is tilted vertically downward by the first angle with respect to the front of the vehicle, and the sign of the second angle is changed with respect to the front of the vehicle. A second light beam scanning means that tilts and fixes the vehicle in the vehicle width direction and scans across the center of the lane width;
A second light receiving means for receiving reflected light of the light beam reflected on the road ahead of the vehicle,
The reflected light position calculating means calculates the position of the reflected light received by the second light receiving means based on the speed of the vehicle detected by the vehicle speed detecting means,
The reflected light position storage means stores the position of the reflected light received by the second light receiving means,
The white line detecting means detects a white line extending in a vehicle width direction on a road based on a position of reflected light received by the first light receiving means and the second light receiving means. The travel control device according to any one of?
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010108914A JP5516043B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2010-05-11 | Travel control device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010108914A JP5516043B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2010-05-11 | Travel control device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011238025A JP2011238025A (en) | 2011-11-24 |
| JP5516043B2 true JP5516043B2 (en) | 2014-06-11 |
Family
ID=45325928
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010108914A Active JP5516043B2 (en) | 2010-05-11 | 2010-05-11 | Travel control device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5516043B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018054290A (en) * | 2015-01-29 | 2018-04-05 | 日立建機株式会社 | Obstacle detection device for transportation vehicle |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000147124A (en) * | 1998-11-12 | 2000-05-26 | Denso Corp | On-vehicle radar device |
| JP2000221268A (en) * | 1999-02-02 | 2000-08-11 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Vehicle detecting device |
| DE102004003850A1 (en) * | 2004-01-26 | 2005-08-18 | Ibeo Automobile Sensor Gmbh | Method for detecting markings on a roadway |
| JP2011196916A (en) * | 2010-03-23 | 2011-10-06 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | Measuring vehicle, and road feature measuring system |
-
2010
- 2010-05-11 JP JP2010108914A patent/JP5516043B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011238025A (en) | 2011-11-24 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US8170769B2 (en) | Vehicle speed control system | |
| US7650239B2 (en) | Object recognition apparatus for motor vehicle | |
| US6927699B2 (en) | Object recognition apparatus for vehicle, and inter-vehicle distance control unit | |
| JP3684776B2 (en) | Obstacle recognition device for vehicles | |
| US6738705B2 (en) | Vehicle running control apparatus and map information data recording medium | |
| KR101000229B1 (en) | Radar device for vehicles | |
| JP3405327B2 (en) | Object recognition method and apparatus, recording medium | |
| JP3753932B2 (en) | Vehicle headlight system | |
| US20050219506A1 (en) | Object recognition device for vehicle | |
| JP6301714B2 (en) | Travel route generator | |
| JP4055653B2 (en) | Vehicle speed control device and program | |
| JP4650717B2 (en) | vehicle | |
| JP2004184331A (en) | Object recognition apparatus for motor vehicle | |
| JP2009288099A (en) | Object detector | |
| WO2021187040A1 (en) | Radar device | |
| JP5516043B2 (en) | Travel control device | |
| JP5549272B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP5556317B2 (en) | Object recognition device | |
| JP2004125636A (en) | On-vehicle laser radar device | |
| JP5533763B2 (en) | In-vehicle radar system | |
| JPH09304535A (en) | Apparatus and method for measurement | |
| JP2007240446A (en) | Range finder for vehicle | |
| JP3786094B2 (en) | Vehicle travel control device | |
| JP2020163974A (en) | Vehicle drive assisting system | |
| JPH11110699A (en) | Device and method for recognizing preceding vehicle |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130327 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20140227 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140304 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140317 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 5516043 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |