JP5500354B2 - Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus - Google Patents
Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5500354B2 JP5500354B2 JP2010076773A JP2010076773A JP5500354B2 JP 5500354 B2 JP5500354 B2 JP 5500354B2 JP 2010076773 A JP2010076773 A JP 2010076773A JP 2010076773 A JP2010076773 A JP 2010076773A JP 5500354 B2 JP5500354 B2 JP 5500354B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- shape data
- interface
- film
- surface shape
- measurement target
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 23
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 title description 4
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 claims description 42
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000000691 measurement method Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 16
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004364 calculation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000004069 differentiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000572 ellipsometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005305 interferometry Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Length Measuring Devices By Optical Means (AREA)
- Investigating Or Analysing Materials By Optical Means (AREA)
Description
本発明は、膜構造測定方法及び表面形状測定装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a film structure measuring method and a surface shape measuring apparatus.
プリント基板の表面には、例えば絶縁することを目的に透明な膜(透明膜)が形成されている。このような透明膜に対しては、例えば、白色干渉法を用いた表面形状測定装置を用いることにより、透明膜の表面で反射した測定光から透明膜の表面の形状データを得ることができ、また、透明膜を透過させて、透明膜とプリント基板表面との界面で反射した測定光からこの界面の形状データ(界面形状データ)を得ることができる(例えば、特許文献1参照)。 A transparent film (transparent film) is formed on the surface of the printed board for the purpose of insulation, for example. For such a transparent film, for example, by using a surface shape measuring device using a white interference method, the shape data of the surface of the transparent film can be obtained from the measurement light reflected on the surface of the transparent film, Moreover, the shape data (interface shape data) of this interface can be obtained from the measurement light that is transmitted through the transparent film and reflected at the interface between the transparent film and the printed circuit board surface (see, for example, Patent Document 1).
しかしながら、透明膜を透過した光により測定された界面形状のデータは、表面形状の影響を受けている。すなわち、この透明膜の屈折率により実際の界面形状からずれて観測されてしまう。透明膜の屈折率が正確に分かっている場合には演算により正確な界面形状を求めることができるが、透明膜が形成されたときの条件(透明膜の材料の製造工程や塗布工程等)やその後の経年変化等により屈折率は変化する可能性があるため、正確な界面形状を求めることができないという課題があった。このような膜厚測定としてはエリプソメータが使用されるが、基本的に点の測定であるため、例えば透明膜の不良解析を行う場合のようにその不良部分を探査しなければならない場合には、効率的な解析を行うことができない。 However, the interface shape data measured by the light transmitted through the transparent film is affected by the surface shape. In other words, the crystal is observed with a deviation from the actual interface shape due to the refractive index of the transparent film. When the refractive index of the transparent film is accurately known, an accurate interface shape can be obtained by calculation. However, the conditions when the transparent film is formed (such as the manufacturing process and coating process of the transparent film material) Since the refractive index may change due to subsequent secular change or the like, there is a problem that an accurate interface shape cannot be obtained. An ellipsometer is used as such a film thickness measurement, but basically it is a point measurement. For example, when a defective portion of a transparent film needs to be investigated, such as when performing a failure analysis, An efficient analysis cannot be performed.
本発明はこのような課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、測定対象膜に光を照射して測定される表面形状データ及び界面形状データから、この測定対象膜の屈折率を得ることができる膜構造測定方法、及び、この膜構造測定方法により測定対象膜の膜構造を測定する表面形状測定装置を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of such problems, and a film capable of obtaining the refractive index of the measurement target film from the surface shape data and the interface shape data measured by irradiating the measurement target film with light. It is an object of the present invention to provide a structure measuring method and a surface shape measuring apparatus for measuring the film structure of a measurement target film by the film structure measuring method.
前記課題を解決するために、本発明に係る膜構造測定方法は、物体に形成された測定対象膜に光を照射してこの測定対象膜の膜構造を測定する膜構造測定方法であって、前記光から測定対象膜の表面の形状である表面形状データ及び測定対象膜と物体との界面の形状である界面形状データを測定するステップと、表面形状データに対して当該表面形状データとの差分の平均値がほぼ0となる第1の基準面を算出してこの差分を補正された表面形状データとして算出するとともに、界面形状データに対して当該界面形状データとの差分の平均値がほぼ0となる第2の基準面を算出してこの差分を補正された界面形状データとして算出するステップと、補正された表面形状データ及び補正された界面形状データの相関係数を算出しこの相関係数の絶対値が最小となる条件から、測定対象膜の屈折率を算出するステップと、を有する。 In order to solve the above problems, a film structure measuring method according to the present invention is a film structure measuring method for irradiating light to a measurement target film formed on an object and measuring the film structure of the measurement target film, Measuring surface shape data which is the shape of the surface of the measurement target film from the light and interface shape data which is the shape of the interface between the measurement target film and the object, and a difference between the surface shape data and the surface shape data The first reference surface having an average value of approximately zero is calculated and this difference is calculated as corrected surface shape data. The average value of the difference between the interface shape data and the interface shape data is approximately zero. Calculating a second reference plane and calculating the difference as corrected interface shape data, calculating a correlation coefficient between the corrected surface shape data and the corrected interface shape data , and calculating the correlation coefficient of The condition that pair value is minimized, and a step of calculating a refractive index of the measurement target film.
このような膜構造測定方法において、基準面は直平面であることが好ましい。 In such a film structure measuring method, it is preferable that the reference plane is a straight plane.
また、このような膜構造測定方法において、補正された表面形状データをSCとし、補正された界面形状をKC′としたとき、屈折率nは、次式
また、このような膜構造測定方法は、前記表面形状データ、前記界面形状データ及び前記屈折率から、前記測定対象膜の膜厚分布を算出するステップをさらに有することが好ましい。 Moreover, it is preferable that such a film | membrane structure measuring method further has the step which calculates the film thickness distribution of the said measuring object film | membrane from the said surface shape data, the said interface shape data, and the said refractive index.
また、本発明に係る表面形状測定装置は、物体及び当該物体の表面に形成された測定対象膜に光を照射して測定対象膜の表面の形状である表面形状データ及び測定対象膜と物体との界面の形状である界面形状データを取得する撮像装置と、上述の膜構造測定方法のいずれかにより測定対象膜の膜構造を算出する制御用プロセッサと、を有する。 Further, the surface shape measuring apparatus according to the present invention irradiates light to the object and the measurement target film formed on the surface of the object, and the surface shape data which is the shape of the surface of the measurement target film and the measurement target film and the object An imaging device that acquires interface shape data that is the shape of the interface of the film, and a control processor that calculates the film structure of the measurement target film by any of the above-described film structure measurement methods.
本発明に係る膜構造測定方法及びこの方法を用いた表面形状測定装置によれば、測定対象膜に光を照射して測定される表面形状データ及び界面形状データから、この測定対象膜の屈折率を得ることができ、さらにこの屈折率を用いて、真の界面形状データや膜厚分布を得ることができる。 According to the film structure measuring method and the surface shape measuring apparatus using this method according to the present invention, from the surface shape data and the interface shape data measured by irradiating light to the film to be measured, the refractive index of the film to be measured Further, using this refractive index, true interface shape data and film thickness distribution can be obtained.
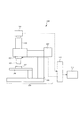
以下、本発明の好ましい実施形態について図面を参照して説明する。まず、図1及び図2を用いて、物体に形成された測定対象膜の表面形状及び界面形状を測定する表面形状測定装置の一例として、白色干渉法を用いた表面形状測定装置の構成について説明する。この表面形状測定装置100は、試料105を走査してこの試料105の画像を取得する撮像装置109と、この撮像装置109の作動の制御及び取得された画像から試料の膜構造(透明膜の屈折率や表面及び界面形状等)を算出する制御用プロセッサ110と、この制御用プロセッサ110による処理結果を表示するディスプレイ装置111と、を有して構成される。
Hereinafter, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings. First, using FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the configuration of a surface shape measuring apparatus using a white light interferometry will be described as an example of a surface shape measuring apparatus that measures the surface shape and interface shape of a measurement target film formed on an object. To do. The surface
撮像装置109は、撮像素子14が内蔵された撮像カメラ101と、光学系が格納された顕微鏡鏡筒装置102と、ピエゾ素子16を有し対物レンズユニット15を駆動して試料105を垂直走査するピエゾ駆動装置103と、対物レンズユニット15が格納された顕微鏡対物レンズ104と、試料105が載置される顕微鏡用試料台106と、白色光を放射して試料105を照明する光源1が格納された顕微鏡用照明装置107と、顕微鏡鏡筒装置102や顕微鏡照明装置107を支持する顕微鏡ベース108と、を有して構成される。なお、ピエゾ素子16の駆動制御及び撮像素子14から出力される信号の処理は上述の制御用プロセッサ110により行われる。
The
また、この表面形状測定装置100の光学系は、光源1から放射された光を集光して試料105に照射する照明光学系2と、試料105からの光を集光してこの試料105の像を撮像素子14の撮像面上に結像する結像光学系3と、を有して構成される。
Further, the optical system of the surface
照明光学系2は、光源1側から順に、この光源1から放射された光を略平行光に変換する集光レンズ4と、この略平行光を一旦結像してさらに略平行光としてリレーする第1リレーレンズ6及び第2リレーレンズ8と、第2リレーレンズ8から出射した略平行光の一部を試料105の方向へ反射するハーフミラー(若しくはハーフプリズム)9と、このハーフミラー9で反射された光を試料105上に集光して照射する対物レンズユニット15と、から構成されている。なお、第1リレーレンズ6と第2リレーレンズ8との間に開口絞り7が設けられており、また、第2リレーレンズ8とハーフミラー9との間に視野絞り5が設けられている。
The illumination
一方、結像光学系3は、試料105側から順に、この試料105で反射した光を集光する対物レンズユニット15と、対物レンズユニット15からの光の一部を透過するハーフミラー9と、ハーフミラー9を透過した光を集光して撮像素子14の撮像面上に結像する結像レンズ13と、から構成されている。
On the other hand, the imaging optical system 3 includes, in order from the
ここで、対物レンズユニット15は、対物レンズ10と、対物レンズ10から出射した光の一部を透過して試料105に導き、残りの光を反射するハーフミラー(若しくはハーフプリズム)11と、対物レンズ10の試料105側の焦点と共役な位置に配置され、ハーフミラー11で反射した光を反射する参照ミラー12とが一体に構成されている。なお、この対物レンズユニット15は、ピエゾ素子16により対物レンズ10の光軸に沿って振動される。
Here, the
このような構成の表面形状測定装置100によると、光源1から放射された光は照明光学系2により対物レンズユニット15に導かれ対物レンズ10で集光される。この対物レンズ10で集光された光はハーフミラー11に入射し、一部の光は透過して試料105上に集光され、残りの光は反射して参照ミラー12上に集光される。そして、試料105で反射した光(この光を「測定光」と呼ぶ)はハーフミラー11に再度入射してその一部が透過し、また、参照ミラー12で反射した光(この光を「参照光」と呼ぶ)もハーフミラー11に再度入射してその一部が撮像素子14側に反射するため、これらの測定光及び参照光が重畳されて対物レンズ10に入射し、結像光学系3により撮像素子14の撮像面上に試料105の像として結像される。
According to the surface
対物レンズユニット15において、対物レンズ10の焦点面と参照ミラー12の反射面とは上述したように共役であるので、ハーフミラー11で重畳された測定光と参照光とは干渉する。そのため、この対物レンズユニット15をピエゾ素子16で光軸方向に振動させると、対物レンズ10の焦点面にある試料105から出射した測定光は強められ、それ以外から出射した測定光は弱められるため、撮像素子14で得られる試料105の像は、対物レンズ10の焦点面にある部分が明るくなり、それ以外の部分が暗くなる(干渉縞を形成する)。そのため、この像から試料105の高さ情報を算出してその形状を測定することができる。なお、本実施形態に係る表面形状測定装置100の対物レンズユニット15においては、測定光と参照光との干渉をマイケルソン型としているが、ミラウ型やリンニク型の構成とすることも可能である。
In the
ここで、試料105が、図3(a)に示すように、プリント基板(物体)105aの表面に透明膜(測定対象膜)105bが形成されている場合であって、この透明膜105bの表面105c、及び、プリント基板105aの表面、すなわち、プリント基板105aと透明膜105bとの界面105dの形状を測定する場合について説明する。なお、説明を簡単にするために、界面105dは、直平面であって、対物レンズ10の光軸と直交するように配置されているものとする。
Here, as shown in FIG. 3A, the
表面形状測定装置100の撮像素子14から出力される試料105の画像を用いて算出される透明膜105bの表面105cの形状の測定値(以下、「表面形状データ」と呼ぶ)をS(i,j)とし、界面105dの形状の測定値(以下、「界面形状データ」と呼ぶ)をK′(i,j)とすると、測定で得られる界面形状データK′(i,j)は透明膜105bの屈折率nの影響を受けているため、真の界面形状データK(i,j)は次式(1)で求められる。なお、(i,j)は撮像素子14の撮像面(若しくは、この撮像素子14で撮像される試料105の像)の座標である。ここで、撮像素子14の撮像面は、対物レンズ10の光軸に直交するように配置されているものとする。また、図3(b)に示すように、表面形状データS(i,j)、界面形状データK(i,j),K′(i,j)は、対物レンズ10の光軸方向で、試料105に対して照射される光の進む方向を正として表すものとする。
A measured value (hereinafter referred to as “surface shape data”) of the shape of the
この式(1)において、第2項の(K′(i,j)−S(i,j))は、試料105において、座標(i,j)に相当する場所の表面105cと界面105dとの光学距離を表している。この式(1)より、座標(i,j)における真の界面形状データK及び透明膜105bの厚さを計算するためには、透明膜105bの屈折率nの正確な値が必要となる。透明膜105bの屈折率nの正確な値を測定するためには、上述のように、例えば、エリプソメトリの原理に基づく専用の装置で計測する方法があるが、表面形状の測定箇所毎に、別の装置により屈折率を測定することは煩雑であり、測定作業の効率が低下する。そこで、表面形状測定装置100により得られる表面形状データS(i,j)及び測定された界面形状データK′(i,j)からその箇所の透明膜105bの屈折率nを求める膜構造測定方法について図4に示すフローチャートに基づいて以下に説明する。なお、以降の説明では座標(i,j)は省略する。また、以下の処理は、本実施形態の場合、制御用プロセッサ110で実行される。
In this equation (1), the second term (K ′ (i, j) −S (i, j)) is expressed by the
まず、制御用プロセッサ110は、ピエゾ素子16を作動させて試料105の表面を光軸方向に走査(ピエゾ走査)して撮像素子14により試料105の画像を取得する(ステップS200)。そして、この画像から表面形状データSを算出し(ステップS210)、さらに界面形状データK′を算出する(ステップS220)。
First, the
次に、測定で得られた表面形状データS及び界面形状データK′の各々を基準となる面により補正して補正された表面形状データSC及び界面形状データKC′を算出する(ステップS230)。具体的には、図5(a)に示すように、基準面として補正された結果の平均値がほぼ0となるような直平面S0,K0′を最小二乗法などで求め、図5(b)に示すように、表面形状データS及び界面形状データK′と直平面S0,K0′との差分から、補正された表面形状データSC及び界面形状データKC′を求める。なお、図5(b)は、直平面Oに対する補正された表面形状データSC及び界面形状データKC′との関係を示している。 Next, the corrected surface shape data S C and interface shape data K C ′ are calculated by correcting each of the surface shape data S and interface shape data K ′ obtained by measurement with a reference surface (step S230). ). Specifically, as shown in FIG. 5A, straight planes S 0 and K 0 ′ whose average value corrected as a reference plane is almost 0 are obtained by the least square method or the like, and FIG. As shown in (b), the corrected surface shape data S C and interface shape data K C ′ are obtained from the difference between the surface shape data S and interface shape data K ′ and the plane planes S 0 and K 0 ′. FIG. 5B shows the relationship between the corrected surface shape data S C and interface shape data K C ′ with respect to the plane O.
ここで、補正された表面形状データSCと同様の方法で補正された真の界面形状データKCとの相関係数Cを求めると、次式(2)のように表される。なお、この式(2)において、バー付のSC及びバー付のKCはそれぞれ、補正された表面形状データSC及び真の界面形状データKCの平均値である。また、Σは、座標(i,j)で表されるデータの総和を示している。 Here, when the correlation coefficient C between the corrected surface shape data S C and the true interface shape data K C corrected by the same method is obtained, it is expressed by the following equation (2). In Equation (2), S C with a bar and K C with a bar are average values of the corrected surface shape data S C and true interface shape data K C , respectively. Further, Σ indicates the total sum of data represented by coordinates (i, j).
この式(2)において、真の界面形状データKを上述の式(1)で置き換えてK′で表すと相関係数Cは、次式(3)のように表される。なお、この式(3)において、補正された表面形状データSC及び界面形状データKC,KC′の平均値は、上述のように0である。 In this equation (2), when the true interface shape data K is replaced by the above equation (1) and represented by K ′, the correlation coefficient C is represented by the following equation (3). In this equation (3), the average value of the corrected surface shape data S C and interface shape data K C , K C ′ is 0 as described above.
ここで、図6に示すように,透明膜105bの表面105cが、対物レンズ10側に向かって凸であるとすると、透明膜の屈折率nと表面形状データS及び測定された界面形状データK′とから式(1)により算出される界面形状データは、屈折率nが真の値の場合に真の界面形状データKと一致するが、屈折率nが真の値より大きい場合には表面105c側に凸となり(図6におけるK+)、反対に屈折率nが真の値より小さい場合には表面105cと反対側に凸となって算出される(図6におけるK−)。これにより、補正された表面形状SCと補正された真の界面形状KCとの相関係数Cの絶対値は、透明膜105bの屈折率nが真の値のときに最小となることが判る。したがって、式(3)で示される相関係数Cの二乗が最小になる屈折率nの値を求めれば、透明膜105bの真の屈折率を求めることができる。具体的には、次式(4)に示すように、相関係数Cの二乗を屈折率nで偏微分した値が0となるときである。
Here, as shown in FIG. 6, assuming that the
上述のように、屈折率nを真の値を挟んで変化させると相関係数Cは変化するため、この相関係数Cの屈折率nによる偏微分の値(∂C/∂n)は0ではない。よって、式(4)において、相関係数Cが0になる屈折率nが真の値ということになる。すなわち、式(3)の相関係数Cを0として、次式(5)のように表される。 As described above, since the correlation coefficient C changes when the refractive index n is changed across the true value, the partial differential value (∂C / ∂n) of the correlation coefficient C by the refractive index n is 0. is not. Therefore, in formula (4), the refractive index n at which the correlation coefficient C is 0 is a true value. That is, it is expressed as the following equation (5) with the correlation coefficient C of equation (3) set to 0.
そして、この式(5)から屈折率nを求めると、次式(6)のように表される。 And if refractive index n is calculated | required from this Formula (5), it will represent like following Formula (6).
以上より、直平面補正された表面形状データSC及び界面形状データKC′を式(6)に代入することにより、撮像素子14で撮像された領域の透明膜105bの屈折率nを求めることができる(ステップS240)。そして、このようにして求められた屈折率nから、透明膜105bの膜厚分布や、真の界面形状Kを算出し(ステップS250)、その結果が、例えば制御用プロセッサ110によりディスプレイ装置111に表示される(ステップS260)。
As described above, the refractive index n of the
図3(b)に示すように、表面形状データSが対物レンズ10側に凸形状を有すると、直平面の界面105dに対して測定される界面形状データK′は対物レンズ10と反対側に凸になる。すなわち、表面形状データの補正値SCが負になるときは測定された界面形状データの補正値KC′は正になり、反対に、表面形状データの補正値SCが正になるときは測定された界面形状データの補正値KC′は負になるため、式(6)における第2項の分子は負になる。そのため、この式(6)の第2項全体も負となるので、式(6)から求められる屈折率nは1よりも大きくなる。すなわち、物質の屈折率は1より大きいため、この式(6)はこの特性に合致していると言える。
As shown in FIG. 3B, when the surface shape data S has a convex shape on the
なお、以上の説明では白色干渉を用いて表面形状及び界面形状を測定する場合について説明したが、本発明がこの構成の表面形状測定装置に限定されることはなく、例えば、コンフォーカル顕微鏡等にも適用することができる。また、膜構造測定方法において、測定で得られた表面形状データS及び界面形状データK′を直平面で補正する場合について説明したが、4次曲面で補正することも可能である。 In the above description, the case where the surface shape and the interface shape are measured using white interference has been described. However, the present invention is not limited to the surface shape measuring apparatus having this configuration. For example, the present invention is applied to a confocal microscope or the like. Can also be applied. Further, in the film structure measuring method, the case where the surface shape data S and the interface shape data K ′ obtained by the measurement are corrected with a straight plane has been described. However, it is also possible to correct with a quartic curved surface.
105a プリント基板(物体) 105b 透明膜(測定対象膜)
109 撮像装置 110 制御用プロセッサ
105a Printed circuit board (object) 105b Transparent film (measuring film)
109
Claims (5)
前記光から前記測定対象膜の表面の形状である表面形状データ及び前記測定対象膜と前記物体との界面の形状である界面形状データを測定するステップと、
前記表面形状データに対して当該表面形状データとの差分の平均値がほぼ0となる第1の基準面を算出して前記差分を補正された表面形状データとして算出するとともに、前記界面形状データに対して当該界面形状データとの差分の平均値がほぼ0となる第2の基準面を算出して前記差分を補正された界面形状データとして算出するステップと、
前記補正された表面形状データ及び前記補正された界面形状データの相関係数を算出し前記相関係数の絶対値が最小となる条件から、前記測定対象膜の屈折率を算出するステップと、を有する膜構造測定方法。 A film structure measuring method for measuring the film structure of the measurement target film by irradiating light to the measurement target film formed on the object,
Measuring surface shape data that is the shape of the surface of the measurement target film from the light and interface shape data that is the shape of the interface between the measurement target film and the object;
A first reference surface with an average difference between the surface shape data and the surface shape data of approximately zero is calculated to calculate the difference as corrected surface shape data, and to the interface shape data On the other hand, calculating a second reference surface in which the average value of the difference with the interface shape data is approximately 0 and calculating the difference as corrected interface shape data ;
Calculating a correlation coefficient between the corrected surface shape data and the corrected interface shape data , and calculating a refractive index of the measurement target film from a condition in which an absolute value of the correlation coefficient is minimized. A method for measuring a film structure.
請求項1〜4のいずれか一項に記載の膜構造測定方法により前記測定対象膜の膜構造を算出する制御用プロセッサと、を有する表面形状測定装置。 Irradiating light to an object and a measurement target film formed on the surface of the object, surface shape data that is a shape of the surface of the measurement target film and interface shape data that is a shape of an interface between the measurement target film and the object An imaging device for acquiring
A surface shape measurement apparatus comprising: a control processor that calculates a film structure of the measurement target film by the film structure measurement method according to claim 1.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010076773A JP5500354B2 (en) | 2010-03-30 | 2010-03-30 | Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010076773A JP5500354B2 (en) | 2010-03-30 | 2010-03-30 | Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011209098A JP2011209098A (en) | 2011-10-20 |
| JP5500354B2 true JP5500354B2 (en) | 2014-05-21 |
Family
ID=44940322
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010076773A Active JP5500354B2 (en) | 2010-03-30 | 2010-03-30 | Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5500354B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2955478B1 (en) * | 2014-06-13 | 2019-08-21 | Mitutoyo Corporation | Calculating a height map of a body of transparent material with an inclined or curved surface |
| JP2018125769A (en) * | 2017-02-02 | 2018-08-09 | パイオニア株式会社 | Imaging apparatus, imaging method, program, and recording medium |
| JP2019152570A (en) * | 2018-03-05 | 2019-09-12 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | measuring device |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3459327B2 (en) * | 1996-06-17 | 2003-10-20 | 理化学研究所 | Method and apparatus for measuring layer thickness and refractive index of laminated structure |
| JP3582311B2 (en) * | 1996-08-04 | 2004-10-27 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | Medium measuring method and measuring device |
| JP5057848B2 (en) * | 2007-05-17 | 2012-10-24 | 東レエンジニアリング株式会社 | Method and apparatus for measuring refractive index of transparent film and method and apparatus for measuring film thickness of transparent film |
-
2010
- 2010-03-30 JP JP2010076773A patent/JP5500354B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011209098A (en) | 2011-10-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5168168B2 (en) | Refractive index measuring device | |
| US9869852B2 (en) | Microscopy system with auto-focus adjustment by low-coherence interferometry | |
| JP4939304B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring film thickness of transparent film | |
| JP2017530341A (en) | Optical evaluation of lenses and lens molds | |
| WO2013084557A1 (en) | Shape-measuring device | |
| KR102341678B1 (en) | Optical characteristic measuring apparatus and optical characteristic measuring method | |
| JP5459944B2 (en) | Surface shape measuring device, stress measuring device, surface shape measuring method and stress measuring method | |
| JP5871242B2 (en) | Film thickness measuring apparatus and film thickness measuring method | |
| JP5500354B2 (en) | Membrane structure measuring method and surface shape measuring apparatus | |
| JP5057848B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring refractive index of transparent film and method and apparatus for measuring film thickness of transparent film | |
| JP2016109670A (en) | Refractive index distribution measurement method, refractive index distribution measurement device, and optical element manufacturing method | |
| WO2022145391A1 (en) | Scanning confocal microscope and adjustment method for scanning confocal microscope | |
| JP4192038B2 (en) | Surface shape and / or film thickness measuring method and apparatus | |
| JP4810693B2 (en) | Lightwave interference measurement device | |
| JP4100663B2 (en) | Absolute thickness measuring device | |
| KR100942236B1 (en) | Measurement error correcting method for the thick of glass panel | |
| JP5983881B2 (en) | V-block type refractive index measuring apparatus, refractive index calculating apparatus and refractive index calculating method used therefor | |
| JP2002005631A (en) | Method and apparatus for measuring characteristics of plate | |
| JPH01145504A (en) | Optically measuring apparatus | |
| KR100942235B1 (en) | Thickness measuring method for a plate glass | |
| JP2008256504A (en) | Shape measuring apparatus | |
| JP5430473B2 (en) | Surface shape measuring device | |
| JP4639808B2 (en) | Measuring apparatus and adjustment method thereof | |
| CZ2006350A3 (en) | Method of measuring non-stationary thin layers and optical thickness gauge | |
| JP6407000B2 (en) | Refractive index measuring method, refractive index measuring apparatus, and optical element manufacturing method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130327 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131119 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20131120 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20140117 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140213 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140226 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5500354 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |