JP5234218B1 - Light emitting diode element - Google Patents
Light emitting diode element Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5234218B1 JP5234218B1 JP2012268708A JP2012268708A JP5234218B1 JP 5234218 B1 JP5234218 B1 JP 5234218B1 JP 2012268708 A JP2012268708 A JP 2012268708A JP 2012268708 A JP2012268708 A JP 2012268708A JP 5234218 B1 JP5234218 B1 JP 5234218B1
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- gan
- emitting diode
- substrate
- light emitting
- diode element
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Led Devices (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】発光効率に優れ、白色LED用の励起光源に適したGaN系発光ダイオード素子を提供することを目的とする。
【解決手段】GaN系発光ダイオード素子は、n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が20mAのときの順方向電圧が4.0V以下である。
【選択図】図1An object of the present invention is to provide a GaN-based light emitting diode element that is excellent in luminous efficiency and suitable as an excitation light source for white LEDs.
A GaN-based light-emitting diode element includes an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light-emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on a front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and the m-plane GaN substrate. It has a flat portion provided on the back surface of the surface GaN substrate and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the flat portion of the rough processed portion, and a forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 20 mA. In this case, the forward voltage is 4.0 V or less.
[Selection] Figure 1
Description
本発明は発光ダイオード素子に関し、とりわけ、GaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造を有するGaN系発光ダイオード素子に関する。GaN系半導体は、一般式AlaInbGa1−a−bN(0≦a≦1、0≦b≦1、0≦a+b≦1)で表される化合物半導体であり、窒化物半導体、窒化物系化合物半導体などとも呼ばれる。 The present invention relates to a light-emitting diode element, and more particularly to a GaN-based light-emitting diode element having a light-emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor. A GaN-based semiconductor is a compound semiconductor represented by the general formula Al a In b Ga 1-ab N (0 ≦ a ≦ 1, 0 ≦ b ≦ 1, 0 ≦ a + b ≦ 1), and is a nitride semiconductor. It is also called a nitride compound semiconductor.
GaN系半導体を用いて形成されたダブルヘテロpn接合型の発光構造をm面GaN基板上に有する半導体発光素子が公知である(非特許文献1〜4)。
Semiconductor light emitting devices having a double hetero pn junction type light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on an m-plane GaN substrate are known (Non-Patent
非特許文献1〜3に開示されているのは発光ダイオード素子であり、いずれの素子においても、m面GaN基板上にエピタキシャル成長により形成されたn型のSiドープGaN層上にn側オーミック電極が形成されている。非特許文献4に開示されているのはレーザダイオード素子であり、m面GaN基板の裏面にn側オーミック電極が形成されている。このレーザダイオード素子の閾値電流はCW駆動時で36mA、パルス駆動時で28mAであり、閾値電圧は約7〜8Vとなっている。
Non-Patent
GaN基板上に発光構造を形成した発光素子においては、GaN基板の裏面に良好なn側オーミック電極を形成することが難しいといわれている(特許文献1〜6)。そこで、特許文献2に記載された方法では、GaN基板の裏面を粒径10μm以上の研磨剤で研磨して粗くすることにより、該裏面上に形成するn側オーミック電極の接触抵抗の低減が図られている。また、特許文献3に記載された方法では、同じ目的のために、GaN基板の裏面をウェットエッチングまたはドライエッチングで粗くしている。一方、特許文献4によれば、GaN基板の厚さを落とすためにその裏面をグラインディング、ラッピングまたはポリッシングしたときにダメージ層が形成され、これが良好なオーミック電極の形成を阻害するとのことである。そこで、該特許文献4に記載の方法では、研磨加工後のGaN基板の裏面をドライエッチングまたはウェットエッチングで削っている。しかし、特許文献5には、ウェットエッチングではこの目的は達成できなかったと記載されている。特許文献6に記載された方法では、GaN基板の裏面をドライエッチングして、機械研磨により発生した結晶欠陥を含む部分を削り取ることにより、GaN基板とn側オーミック電極との接触抵抗の低減が図られている。なお、これら特許文献1〜6に記載された知見や発明は、基本的にはc面GaN基板に関するものである。
In a light emitting device having a light emitting structure formed on a GaN substrate, it is said that it is difficult to form a good n-side ohmic electrode on the back surface of the GaN substrate (
金属ワイヤ、金属バンプまたはハンダのような給電部材が接合される部品として発光ダイオードに必須なのが、素子表面に金属材料を用いて形成される電極パッドである。電極パッドは光透過性を有さないので、発光構造を流れる電流が光取出し方向から見て電極パッドの影となる部位に集中する発光ダイオードは、発光効率の低いものとなる。なぜなら、この部位で発生する光は電極パッドによる遮蔽と吸収を受けるので、素子外部に効率的に取り出せないからである。そこで、電流がこの部位に集中しないように、電極パッドと発光構造の間に電流ブロック構造として高抵抗膜(絶縁膜)または高抵抗領域を設けて、素子内を流れる電流の経路を制御することが行われている(特許文献7〜9)。 An electrode pad formed using a metal material on the element surface is essential for a light emitting diode as a part to which a power feeding member such as a metal wire, a metal bump, or solder is bonded. Since the electrode pad does not have optical transparency, a light emitting diode in which the current flowing through the light emitting structure is concentrated in a portion that is a shadow of the electrode pad when viewed from the light extraction direction has low light emission efficiency. This is because the light generated at this site is shielded and absorbed by the electrode pad and cannot be extracted efficiently outside the device. Therefore, to prevent the current from concentrating on this part, a high resistance film (insulating film) or a high resistance region is provided as a current block structure between the electrode pad and the light emitting structure to control the path of the current flowing in the element. (Patent Documents 7 to 9).
m面GaN基板上に発光構造を形成したGaN系発光ダイオード素子は、QCSE(Quantum-confined Stark effect)が生じないので、印加電流の増加に伴う発光波長の変動
が小さいことが要求される白色LED用の励起光源に適している。しかし、発光ダイオード素子の発熱量が大きかったり、その放熱性が良好でない場合には、該発光ダイオード素子が放出する熱で蛍光体の温度が大きく変動することとなり、期待通りの効果が得られなくなる。また、発熱量が大きく放熱性が良好でない発光ダイオード素子は、印加電流を増やすにつれてそれ自体の温度も大きく上昇するので、発光効率の低いものとなる。
A GaN-based light-emitting diode element in which a light-emitting structure is formed on an m-plane GaN substrate does not cause QCSE (Quantum-confined Stark effect), and therefore a white LED that is required to have a small variation in emission wavelength with an increase in applied current Suitable for excitation light source. However, if the heat generation amount of the light emitting diode element is large or its heat dissipation is not good, the temperature of the phosphor largely fluctuates due to the heat emitted by the light emitting diode element, and the expected effect cannot be obtained. . Further, a light emitting diode element having a large amount of heat generation and poor heat dissipation has a low luminous efficiency because its own temperature greatly increases as the applied current is increased.
本発明は上記事情に鑑みなされたものであり、その主たる目的は、白色LED用の励起光源に適したGaN系発光ダイオード素子を提供することである。
本発明の他の目的は、m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側電極を有する、発光効率の改善されたGaN系発光ダイオード素子を提供することである。
本発明の更に他の目的は、m面GaN基板の裏面に形成された低接触抵抗のn側電極を有するGaN系発光ダイオード素子を製造する方法を提供することである。
This invention is made | formed in view of the said situation, The main objective is to provide the GaN-type light emitting diode element suitable for the excitation light source for white LED.
Another object of the present invention is to provide a GaN-based light emitting diode device with improved luminous efficiency, having an n-side electrode formed on the back surface of an m-plane GaN substrate.
Still another object of the present invention is to provide a method of manufacturing a GaN-based light emitting diode device having a low contact resistance n-side electrode formed on the back surface of an m-plane GaN substrate.
本発明の一態様によれば以下のGaN系発光ダイオード素子が提供される。
(1) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導
体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が20mAのときの順方向電圧が4.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(2) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導
体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が60mAのときの順方向電圧が4.5V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(3) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導
体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が120mAのときの順方向電圧が5.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(4) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導
体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側
オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が200mAのときの順方向電圧が5.5V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(5) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導
体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が350mAのときの順方向電圧が6.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(6) 前記発光ダイオード構造が、GaN系半導体からなる活性層と、該活性層と前記
m面GaN基板との間に配置されたn型GaN系半導体層と、該n型GaN系半導体層とで該活性層を挟むp型GaN系半導体層と、を含む、前記(1)〜(5)のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(7) 前記m面GaN基板の裏面の面積が0.0012cm2以上である、前記(1)
〜(6)のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(8) 前記n側オーミック電極の面積が0.0012cm2以上、前記m面GaN基板
の裏面の面積以下である、前記(7)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(9) 前記m面GaN基板の裏面は、少なくとも前記n側オーミック電極と接触する部
分において、10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下である、前記(1)〜(8)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
(10) 前記n側オーミック電極はパターニングされている、前記(1)〜(9)のい
ずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
According to one aspect of the present invention, the following GaN-based light emitting diode device is provided.
(1) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. A GaN-based light emitting diode device having a forward voltage of 4.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the light emitting diode device is 20 mA.
(2) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 4.5 V or less when a forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 60 mA.
(3) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 5.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 120 mA.
(4) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 5.5 V or less when a forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 200 mA.
(5) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 6.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 350 mA.
(6) The light emitting diode structure includes an active layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer disposed between the active layer and the m-plane GaN substrate, and the n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer. And a p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer sandwiching the active layer. The GaN-based light-emitting diode element according to any one of (1) to (5).
(7) The area of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate is 0.0012 cm 2 or more (1)
The GaN-type light emitting diode element in any one of-(6).
(8) The GaN-based light emitting diode device according to (7), wherein an area of the n-side ohmic electrode is 0.0012 cm 2 or more and not more than an area of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate.
(9) The back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate has an arithmetic average roughness Ra in a range of 10 μm square of 0.1 nm or less at least in a portion in contact with the n-side ohmic electrode. The semiconductor light-emitting device according to any one of the above.
(10) The GaN-based light emitting diode element according to any one of (1) to (9), wherein the n-side ohmic electrode is patterned.
本発明の一態様によれば以下のGaN系発光ダイオード素子が提供される。
(11) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半
導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が20mAのときの順方向電圧が4.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(12) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半
導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が60mAのときの順方向電圧が4.5V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(13) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半
導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が120mAのときの順方向電圧が5.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(14) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半
導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が200mAのときの順方向電圧が5.5V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(15) n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半
導体を用いて形成された発光ダイオード構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に設けられた平坦な部分と粗く加工された部分のうちの平坦な部分に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が350mAのときの順方向電圧が6.0V以下である、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(16) 前記粗く加工された部分が、サブミクロンサイズの凹凸が形成されるように加
工されている部分である、前記(11)〜(15)のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
According to one aspect of the present invention, the following GaN-based light emitting diode device is provided.
(11) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. The forward voltage when the forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 20 mA is 4 A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a voltage of 0.0 V or less.
(12) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. And the n-side ohmic electrode formed on the flat portion of the rough processed portion, and the forward voltage when the forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 60 mA is 4 A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a voltage of 5 V or less.
(13) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light-emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. And the n-side ohmic electrode formed on the flat portion of the rough processed portion, and the forward voltage when the forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 120 mA is 5 A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a voltage of 0.0 V or less.
(14) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. And the n-side ohmic electrode formed on the flat portion of the rough processed portion, and the forward voltage when the forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 200 mA is 5 A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a voltage of 5 V or less.
(15) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light-emitting diode structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and a back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. And the n-side ohmic electrode formed on the flat portion of the rough processed portion, and the forward voltage when the forward current applied to the light emitting diode element is 350 mA is 6 A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a voltage of 0.0 V or less.
(16) The GaN-based light-emitting diode element according to any one of (11) to (15), wherein the rough processed portion is a portion processed so as to form submicron-sized irregularities.
本発明の他の一態様によれば以下のGaN系発光ダイオード素子が提供される。
(17) n型導電性のm面GaN基板である基板と、該基板上にエピタキシャル成長し
たGaN系半導体からなりpn接合型の発光構造を含むエピ層と、該基板の裏面に形成されたn側電極と、該エピ層の上面に形成された透光性のp側オーミック電極と、該p側オーミック電極上の一部に形成されたp側電極パッドとを有し、
前記基板の裏面のうち前記n側電極に覆われた領域には、ポリッシング仕上げされた領域である低接触抵抗領域と、ドライエッチング仕上げされた領域である高接触抵抗領域とが含まれ、
前記基板の裏面への前記p側電極パッドの正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領域に含まれる、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(18) 前記p側オーミック電極上に、前記p側電極パッドに接続された補助電極が形
成されており、前記基板の裏面への前記補助電極の正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領域に含まれない、前記(17)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(19) n型導電性のm面GaN基板である基板と、該基板上にエピタキシャル成長し
たGaN系半導体からなりpn接合型の発光構造を含むエピ層と、該基板の裏面に形成された透光性のn側オーミック電極と、該n側オーミック電極上の一部に形成されたn側電極パッドと、該エピ層の上面に形成されたp側電極とを有し、前記基板の裏面のうち前記n側オーミック電極に覆われた領域には、ポリッシング仕上げされた領域である低接触抵抗領域と、ドライエッチング仕上げされた領域である高接触抵抗領域とが含まれ、
前記基板の裏面への前記n側電極パッドの正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領域に含まれる、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(20) 前記n側オーミック電極上に、前記n側電極パッドに接続された補助電極が形
成されており、前記基板の裏面への前記補助電極の正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領域に含まれない、前記(19)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(21) n型導電性のm面GaN基板である基板と、該基板上にエピタキシャル成長し
たGaN系半導体からなりpn接合型の発光構造を含むエピ層と、該基板の裏面に部分的に形成されたn側電極と、該エピ層の上面に形成されたp側電極とを有し、
前記n側電極は、パッド部と、該パッド部に接続された補助部とを有し、
基板の裏面のうち前記n側電極に覆われた領域には、ポリッシング仕上げされた領域である低接触抵抗領域と、ドライエッチング仕上げされた領域である高接触抵抗領域とが含まれ、
前記基板の裏面への前記パッド部の正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領域に含まれる、GaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(22) 前記基板の裏面への前記補助部の正射影の全部または一部が前記高接触抵抗領
域に含まれない、前記(21)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(23) 前記基板のキャリア濃度が1017cm−3である、前記(19)〜(22)
のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
According to another aspect of the present invention, the following GaN-based light emitting diode device is provided.
(17) A substrate, which is an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, an epi layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor epitaxially grown on the substrate and including a pn junction type light emitting structure, and an n-side formed on the back surface of the substrate An electrode, a translucent p-side ohmic electrode formed on the upper surface of the epi layer, and a p-side electrode pad formed on a part of the p-side ohmic electrode,
Of the back surface of the substrate, the region covered with the n-side electrode includes a low contact resistance region that is a polished region and a high contact resistance region that is a dry-etched region,
A GaN-based light emitting diode element, wherein all or part of the orthogonal projection of the p-side electrode pad on the back surface of the substrate is included in the high contact resistance region.
(18) An auxiliary electrode connected to the p-side electrode pad is formed on the p-side ohmic electrode, and all or a part of the orthogonal projection of the auxiliary electrode to the back surface of the substrate is the high contact resistance. The GaN-based light emitting diode device according to (17), which is not included in the region.
(19) A substrate which is an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, an epi layer comprising a pn-junction light-emitting structure epitaxially grown on the substrate, and a light transmission formed on the back surface of the substrate An n-side ohmic electrode, an n-side electrode pad formed on a part of the n-side ohmic electrode, and a p-side electrode formed on the upper surface of the epi layer, The region covered with the n-side ohmic electrode includes a low contact resistance region that is a polished region and a high contact resistance region that is a dry etched region,
A GaN-based light emitting diode element, wherein all or part of an orthogonal projection of the n-side electrode pad on the back surface of the substrate is included in the high contact resistance region.
(20) An auxiliary electrode connected to the n-side electrode pad is formed on the n-side ohmic electrode, and all or a part of the orthogonal projection of the auxiliary electrode to the back surface of the substrate is the high contact resistance. The GaN-based light emitting diode device according to (19), which is not included in the region.
(21) A substrate which is an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, an epitaxial layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor epitaxially grown on the substrate and including a pn junction type light emitting structure, and partially formed on the back surface of the substrate An n-side electrode and a p-side electrode formed on the upper surface of the epi layer,
The n-side electrode has a pad part and an auxiliary part connected to the pad part,
Of the back surface of the substrate, the region covered with the n-side electrode includes a low contact resistance region that is a polished region and a high contact resistance region that is a dry etched region,
A GaN-based light emitting diode element, wherein all or part of the orthogonal projection of the pad portion on the back surface of the substrate is included in the high contact resistance region.
(22) The GaN-based light-emitting diode element according to (21), wherein all or part of the orthogonal projection of the auxiliary portion on the back surface of the substrate is not included in the high contact resistance region.
(23) Said (19)-(22) whose carrier concentration of the said board | substrate is 10 < 17 > cm <-3 >.
A GaN-based light emitting diode device according to any one of the above.
本発明の更に他の一態様によれば以下のGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法が提供される。
(24) (i)n型導電性のm面GaN基板である基板と、該基板上にエピタキシャル成長したGaN系半導体からなりpn接合型の発光構造を含むエピ層と、を有するエピウェハを準備する第1ステップと、
(ii)前記エピウェハに含まれる前記基板の裏面をポリッシングする第2ステップと、
(iii)前記第2ステップでポリッシュされた前記基板の裏面全体にn側オーミック電極
を形成する第3ステップと、
(iv)前記第3ステップで形成された前記n側オーミック電極をエッチングによりパターニングする第4ステップと、
を有するGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法。
(25) 前記第4ステップで露出した前記基板の裏面を粗く加工する第5ステップを更
に有する、前記(24)に記載の製造方法。
(26) 前記第5ステップでは、前記第4ステップで露出した前記基板の裏面に周期性
を有する凹凸パターンを形成する、前記(25)に記載の製造方法。
(27) 前記n側オーミック電極が多結晶質の透明導電性酸化物膜であり、前記第4ス
テップでは前記n側オーミック電極の一部をその残渣が前記基板上に残るようにエッチングし、更に、前記第5ステップでは、該残渣をエッチングマスクとして利用してドライエッチングすることにより前記基板の露出した裏面を粗く加工する、前記(25)に記載の製造方法。
(28) 前記第4ステップで露出した前記基板の裏面に反射膜を形成する第6ステップ
を更に有する、前記(24)に記載の製造方法。
(29) 前記反射膜が誘電体反射膜である、前記(28)に記載の製造方法。
(30) 前記第2ステップでポリッシングする前記基板の裏面を、前記第2ステップの
直前にラッピングする、前記(24)〜(29)のいずれかに記載の製造方法。
(31) 前記基板のキャリア濃度が1017cm−3である、前記(24)〜(30)
のいずれかに記載の製造方法。
According to still another aspect of the present invention, the following method for manufacturing a GaN-based light emitting diode element is provided.
(24) (i) preparing an epi-wafer having a substrate which is an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate and an epi layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor epitaxially grown on the substrate and including a pn junction type light emitting structure One step,
(Ii) a second step of polishing the back surface of the substrate included in the epi-wafer;
(Iii) a third step of forming an n-side ohmic electrode over the entire back surface of the substrate polished in the second step;
(Iv) a fourth step of patterning the n-side ohmic electrode formed in the third step by etching;
The manufacturing method of the GaN-type light emitting diode element which has this.
(25) The manufacturing method according to (24), further including a fifth step of roughly processing the back surface of the substrate exposed in the fourth step.
(26) The manufacturing method according to (25), wherein in the fifth step, an uneven pattern having periodicity is formed on the back surface of the substrate exposed in the fourth step.
(27) The n-side ohmic electrode is a polycrystalline transparent conductive oxide film, and in the fourth step, a part of the n-side ohmic electrode is etched so that the residue remains on the substrate. In the fifth step, the exposed back surface of the substrate is roughly processed by dry etching using the residue as an etching mask.
(28) The manufacturing method according to (24), further including a sixth step of forming a reflective film on the back surface of the substrate exposed in the fourth step.
(29) The manufacturing method according to (28), wherein the reflective film is a dielectric reflective film.
(30) The manufacturing method according to any one of (24) to (29), wherein the back surface of the substrate to be polished in the second step is lapped immediately before the second step.
(31) The above-mentioned (24) to (30), wherein the carrier concentration of the substrate is 10 17 cm −3.
The manufacturing method in any one of.
本発明の実施形態に係る上記(1)〜(16)に記載の半導体系発光素子は、m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極を有するので、金属電極上にハンダを用いて固定することができる。つまり、放熱性が良好となる形態で実装することができる。また、順方向電圧が低く抑えられているので発熱量が小さく、白色LED用の励起光源に極めて適している。 Since the semiconductor light emitting element according to the above (1) to (16) according to the embodiment of the present invention has an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, solder is used on the metal electrode. Can be fixed. That is, it can be mounted in a form with good heat dissipation. Moreover, since the forward voltage is kept low, the amount of heat generation is small, and it is extremely suitable as an excitation light source for white LEDs.
本発明の実施形態に係る上記(17)〜(23)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子では、素子内を流れる電流の経路を制御することにより、n側電極とp側電極の少なくともいずれかに含まれる電極パッドによる光の遮蔽または吸収を抑制することができる。また、素子内を流れる電流の経路を制御し、発光構造を流れる電流の密度を均一化することにより、ドループ現象による発光効率の低下を抑制することができる。 In the GaN-based light emitting diode device according to any one of (17) to (23) according to the embodiment of the present invention, by controlling a path of a current flowing in the device, at least one of the n-side electrode and the p-side electrode The shielding or absorption of light by the included electrode pad can be suppressed. Further, by controlling the path of the current flowing in the element and making the density of the current flowing in the light emitting structure uniform, it is possible to suppress a decrease in light emission efficiency due to the droop phenomenon.
本発明の実施形態に係る上記(24)〜(31)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子製造方法によれば、m面GaN基板の裏面に形成された低接触抵抗のn側電極を有するGaN系発光ダイオードを製造することができる。 According to the GaN-based light-emitting diode element manufacturing method according to the above (24) to (31) according to the embodiment of the present invention, a GaN-based light source having a low contact resistance n-side electrode formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. Light emitting diodes can be manufactured.
本発明者等によるGaN系発光ダイオード素子(以下では「LED素子」ともいう)の試作および評価の結果を以下に記す。 The results of trial manufacture and evaluation of a GaN-based light emitting diode element (hereinafter also referred to as “LED element”) by the present inventors are described below.
1.試作したLED素子の基本構造
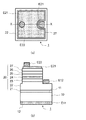
図1に、試作したLED素子の基本構造を模式的に示す。図1(a)は上面図、図1(b)は図1(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。図1(a)に示すように、LED素子1の平面形状は矩形であり、サイズは350μm×340μmである。
1. Basic Structure of Prototype LED Element FIG. 1 schematically shows the basic structure of the prototype LED element. 1A is a top view, and FIG. 1B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line XX in FIG. 1A. As shown to Fig.1 (a), the planar shape of the
図1(b)に示すように、LED素子1は、基板10の上にGaN系半導体からなる半導体積層体20を有している。基板10はm面GaN基板であり、半導体積層体20は該
基板10のおもて面11上に配置されている。半導体積層体20は基板10側から順に、第1のアンドープGaN層21、Siドープされたn型GaNコンタクト層22、第2のアンドープGaN層23、Siドープされたn型GaNクラッド層24、MQW活性層25、Mgドープされたp型Al0.1Ga0.9Nクラッド層26、Mgドープされたp型Al0.03Ga0.97Nコンタクト層27を有している。
As shown in FIG. 1B, the
MQW活性層25は、交互に積層されたアンドープIn0.04Ga0.96Nバリア層とアンドープIn0.16Ga0.84Nウェル層とを有している。アンドープInGaNバリア層の数は4層、アンドープInGaNウェル層の数は3層であり、ゆえに、MQW活性層25の最下層と最上層はいずれもバリア層である。ウェル層の組成は発光ピーク波長が445〜465nmの範囲内に入るように調整されたものである。
The MQW
LED素子1は2つのn側電極と1つのp側電極を有している。n側電極のひとつは第1のn側メタルパッドE11であり、基板10の裏面12全体を覆うように設けられている。もうひとつは第2のn側メタルパッドE12であり、半導体積層体20を一部除去することにより露出したn型GaNコンタクト層22の表面上に形成されている。第1のn側メタルパッドE11と第2のn側メタルパッドE12は、どちらもオーミック電極を兼用している。p側電極を構成するのは、p型AlGaNコンタクト層27の上面に形成されたオーミック性の透光性電極E21と、該透光性電極E21上の一部に形成されたp側メタルパッドE22である。MQW活性層25への電流印加は、第1のn側メタルパッドE11とp側メタルパッドE22を通して行うこともできるし、第2のn側メタルパッドE12とp側メタルパッドE22を通して行うこともできる。
The
第1のn側メタルパッドE11は多層膜であり、基板10側から順にTiW層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層を有している。第2のn側メタルパッドE12も同様の積層構造を備える多層膜であり、n型GaNコンタクト層22側から順にTiW層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層を有している。透光性電極E21はITO(インジウム錫酸化物)膜である。p側メタルパッドE12は第1のn側メタルパッドE11および第2のn側メタルパッドE12と同様の積層構造を備える多層膜であり、透光性電極E21側から順にTiW層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層、Pt層、Au層を有している。
The first n-side metal pad E11 is a multilayer film, and includes a TiW layer, an Au layer, a Pt layer, an Au layer, a Pt layer, an Au layer, a Pt layer, and an Au layer in order from the
2.LED素子の試作
LED素子1を次の手順により作製した。
2−1.エピタキシャル成長
サイズが7mm(c軸方向)×15mm(a軸方向)×330μm(厚さ)、おもて面(半導体積層体を設ける側の主面)のオフ角が0±0.5°の範囲内で、n型不純物としてSiが添加されたn型導電性のm面GaN基板を準備した。ホール測定により調べた該m面GaN基板のキャリア濃度は1.3×1017cm−3であった。
2. Prototyping of LED Element
2-1. Epitaxial growth Size is 7 mm (c-axis direction) x 15 mm (a-axis direction) x 330 μm (thickness), and the off-angle of the front surface (main surface on which the semiconductor laminate is provided) is 0 ± 0.5 ° The n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate to which Si was added as an n-type impurity was prepared. The carrier concentration of the m-plane GaN substrate examined by hole measurement was 1.3 × 10 17 cm −3 .
このm面GaN基板のおもて面上に、常圧MOVPE法を用いて複数のGaN系半導体層をエピタキシャル成長させて半導体積層体を形成した。III族原料にはTMG(トリメチルガリウム)、TMI(トリメチルインジウム)およびTMA(トリメチルアルミニウム)、V族原料にはアンモニア、Si原料にはシラン、Mg原料にはビスエチルシクロペンタジエニルマグネシウム((EtCp)2Mg)を用いた。 A plurality of GaN-based semiconductor layers were epitaxially grown on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate using the atmospheric pressure MOVPE method to form a semiconductor laminate. TMG (trimethylgallium), TMI (trimethylindium) and TMA (trimethylaluminum) for Group III materials, ammonia for Group V materials, silane for Si materials, bisethylcyclopentadienylmagnesium ((EtCp) for Mg materials ) 2 Mg) was used.
各層の成長温度および膜厚を表1に示す。 Table 1 shows the growth temperature and film thickness of each layer.
n型GaNコンタクト層、n型GaNクラッド層、p型AlGaNクラッド層およびp型AlGaNコンタクト層に添加した不純物の濃度は表2に示す通りである。 Table 2 shows the concentration of impurities added to the n-type GaN contact layer, n-type GaN clad layer, p-type AlGaN clad layer, and p-type AlGaN contact layer.
p型AlGaNクラッド層およびp型AlGaNコンタクト層に添加したMgの活性化は、p型AlGaNコンタクト層を所定時間成長させた後、MOVPE装置の成長炉内で基板温度が室温まで降下する間に、該成長炉内に流す窒素ガスおよびアンモニアガスの流量を制御する方法を用いて行った。 The activation of Mg added to the p-type AlGaN cladding layer and the p-type AlGaN contact layer is performed while the p-type AlGaN contact layer is grown for a predetermined time and then the substrate temperature is lowered to room temperature in the growth furnace of the MOVPE apparatus. This was carried out using a method for controlling the flow rates of nitrogen gas and ammonia gas flowing into the growth furnace.
2−2.p側電極および第2のn側メタルパッドの形成
上記エピタキシャル成長により形成した半導体積層体の表面(p型AlGaNコンタクト層の表面)に、電子ビーム蒸着法によりITO膜を210nmの厚さに形成した。続いて、フォトリソグラフィとエッチングの技法を用いて、このITO膜を所定の形状にパターニングして、透光性電極を形成した。パターニング後、反応性イオンエッチング(RIE)加工により半導体積層体の一部を除去して、第2のn側メタルパッドを形成すべき部位にn型GaNコンタクト層を露出させるとともに、メサ形成を行った。RIE加工においては、エッチングガスとしてCl2を用い、アンテナ/バイアスを100W/20W、
チャンバー内圧力を0.3Paと設定した。
2-2. Formation of p-side electrode and second n-side metal pad An ITO film having a thickness of 210 nm was formed on the surface of the semiconductor laminate formed by the epitaxial growth (surface of the p-type AlGaN contact layer) by electron beam evaporation. Subsequently, the ITO film was patterned into a predetermined shape using photolithography and etching techniques to form a translucent electrode. After patterning, a part of the semiconductor stacked body is removed by reactive ion etching (RIE) processing to expose the n-type GaN contact layer at the site where the second n-side metal pad is to be formed, and perform mesa formation. It was. In RIE processing, Cl 2 is used as an etching gas, the antenna / bias is 100 W / 20 W,
The pressure in the chamber was set to 0.3 Pa.
RIE加工に続いて、上記作製したITO膜に対し、大気雰囲気中、520℃で20分間の熱処理を施した。更に続けて、RTA(Rapid Thermal Annealing)装置を用いて、
このITO膜に対し、窒素ガス雰囲気中、500℃で1分間の熱処理を施した。
Subsequent to the RIE process, the produced ITO film was heat-treated at 520 ° C. for 20 minutes in the air atmosphere. Furthermore, using an RTA (Rapid Thermal Annealing) device,
This ITO film was heat-treated at 500 ° C. for 1 minute in a nitrogen gas atmosphere.
ITO膜の熱処理後、リフトオフ法を用いて、第2のn側メタルパッドとp側メタルパッドを同時に所定のパターンに形成した。第2のn側メタルパッドとp側メタルパッドを構成するメタル多層膜に含まれる全ての層(TiW層、Au層およびPt層)は、スパッタリング法で形成した。TiW膜を形成する際は、ターゲットにTi含有量が10wt%のTi−Wターゲット、スパッタガスにAr(アルゴン)を使用し、スパッタ条件はRF電力800W、Ar流量50sccm、スパッタガス圧2.2×10−1Paとした。最
下層であるTiW層とその直上に積層するAu層の厚さは108nmとし、それ以外のPt層およびAu層の厚さはいずれも89nmとした。
After the heat treatment of the ITO film, a second n-side metal pad and a p-side metal pad were simultaneously formed in a predetermined pattern using a lift-off method. All layers (TiW layer, Au layer, and Pt layer) included in the metal multilayer film constituting the second n-side metal pad and the p-side metal pad were formed by sputtering. When forming a TiW film, a Ti-W target having a Ti content of 10 wt% is used as a target, Ar (argon) is used as a sputtering gas, sputtering conditions are RF power 800 W, Ar flow rate 50 sccm, sputtering gas pressure 2.2. × 10 −1 Pa. The thickness of the lowermost TiW layer and the Au layer laminated immediately above it was 108 nm, and the thicknesses of the other Pt layers and Au layers were all 89 nm.
第2のn側メタルパッドとp側メタルパッドを形成した後、露出した半導体積層体の表面および透光性電極の表面に、SiO2からなるパッシベーション膜を213nmの厚さに形成した。 After forming the second n-side metal pad and p-side metal pad, a passivation film made of SiO 2 was formed to a thickness of 213 nm on the exposed surface of the semiconductor stacked body and the surface of the translucent electrode.
2−3.m面GaN基板の裏面の加工
上記パッシベーション膜の形成後、m面GaN基板の裏面に対し、以下に加工a〜加工fとして記す6通りの異なる加工を行った。
2-3. Processing of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate After the formation of the passivation film, six different processes described below as processing a to processing f were performed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate.
加工a:m面GaN基板の裏面にラッピングおよびポリッシングをこの順に施すことにより、該基板の厚さを200μmに減じた。 Process a: The thickness of the substrate was reduced to 200 μm by lapping and polishing the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate in this order.
ラッピング工程では、定法に従い、使用するダイヤモンド砥粒の粒径を段階的に小さくしていった。 In the lapping process, the grain size of the diamond abrasive used was gradually reduced in accordance with a conventional method.
ポリッシング工程では、酸性コロイダルシリカ(粒径70〜100nm)に酸を添加してpHを2未満に調整したCMPスラリーを用い、ポリッシングレートが0.5μm/hとなるように荷重を調整し、ポリッシング加工時間は約14時間とした。この条件でポリッシュされたm面GaN基板の表面は、AFM(例えばDIGITALINSTRUMENTS社製 DIMENSION 5000)を用いて測定される10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下と
なる。
In the polishing step, a CMP slurry in which acid is added to acidic colloidal silica (particle size 70-100 nm) and the pH is adjusted to less than 2 is used, and the load is adjusted so that the polishing rate is 0.5 μm / h. The processing time was about 14 hours. The surface of the m-plane GaN substrate polished under these conditions has an arithmetic average roughness Ra in the range of 10 μm square measured using AFM (for example, DIMENSION 5000 manufactured by DIGITALINSTRUMENTS) of 0.1 nm or less.
ポリッシングされた面(m面GaN基板の裏面)は水で洗った後、更に室温のIPAおよびアセトンを用いて洗浄し、乾燥後に5分間の紫外線オゾン洗浄(110℃、酸素流量5L/分)を施した。 The polished surface (the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate) is washed with water, further washed with IPA and acetone at room temperature, and then dried with ultraviolet ozone cleaning (110 ° C., oxygen flow rate 5 L / min) for 5 minutes. gave.
加工b:加工aを行った後、更に、RIEによってm面GaN基板の裏面から表層部分を削り取った。RIE条件は上記2−2.で半導体積層体に対してRIE加工を施したときの条件と同じとし、エッチング深さが0.1μmとなるよう、エッチング時間を60秒に設定した。RIE加工後の表面の粗さを触針式段差計(株式会社小坂研究所製ET3000)で測定したところ、算術平均粗さRaは0.02μm、最大高さRzは0.04μmであった。 Process b: After process a, the surface layer portion was further removed from the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate by RIE. The RIE condition is the above 2-2. The etching time was set to 60 seconds so that the etching depth was 0.1 μm under the same conditions as when the RIE processing was performed on the semiconductor laminate. When the roughness of the surface after RIE processing was measured with a stylus type step gauge (ET3000 manufactured by Kosaka Laboratory Ltd.), the arithmetic average roughness Ra was 0.02 μm, and the maximum height Rz was 0.04 μm.
加工c:加工aを行った後、更に、RIEによってm面GaN基板の裏面から表層部分を削り取った。RIE条件は上記2−2.で半導体積層体に対してRIE加工を施したときの条件と同じとし、エッチング深さが1.0μmとなるよう、エッチング時間を610
秒に設定した。RIE加工後の表面の粗さを触針式段差計で測定したところ、算術平均粗さRaは0.06μm、最大高さRzは0.55μmであった。
Processing c: After processing a, the surface layer portion was further scraped off from the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate by RIE. The RIE condition is the above 2-2. The etching time is set to 610 so that the etching depth is 1.0 μm under the same conditions as when the RIE processing is performed on the semiconductor stacked body.
Set to seconds. When the surface roughness after RIE processing was measured with a stylus profilometer, the arithmetic average roughness Ra was 0.06 μm, and the maximum height Rz was 0.55 μm.
加工d:加工aを行った後、更に、RIEによってm面GaN基板の裏面から表層部分を削り取った。RIE条件は上記2−2.で半導体積層体に対してRIE加工を施したときの条件と同じとし、エッチング深さが2.0μmとなるよう、エッチング時間を1220秒に設定した。RIE加工後の表面の粗さを触針式段差計で測定したところ、算術平均粗さRaは0.07〜0.12μm、最大高さRzは1.30μmであった。 Processing d: After processing a, the surface layer portion was further scraped off from the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate by RIE. The RIE condition is the above 2-2. The etching time was set to 1220 seconds so that the etching conditions were the same as those when the RIE processing was performed on the semiconductor laminate. When the surface roughness after RIE processing was measured with a stylus profilometer, the arithmetic average roughness Ra was 0.07 to 0.12 μm, and the maximum height Rz was 1.30 μm.
加工e:加工aを行った後のm面GaN基板の裏面に、ノボラック樹脂を用いたポジ型フォトレジスト(住友化学株式会社製 スミレジストPFI−34AL)を1.6μmの厚さにコーティングし、フォトリソグラフィ技法を用いて該フォトレジストをパターニングすることによって、図2に示すマスクパターンを形成した。すなわち、複数の円形エッチングマスクが三角格子の格子位置に配置されたマスクパターンである。各円形マスクの直径(図2中のR)は2μm、隣り合う円形マスク間のスペース(図2中のS)は2.5μmとした。マスクパターンの方向は、図3に示すように、三角格子の6つの格子位置を頂点とする正六角形ABCDEFの2つの辺BC、EFが、m面GaN基板のc軸と直交するように定めた。 Process e: A positive photoresist (Sumiresist PFI-34AL manufactured by Sumitomo Chemical Co., Ltd.) using a novolac resin is coated on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate after the process a to a thickness of 1.6 μm. The mask pattern shown in FIG. 2 was formed by patterning the photoresist using a photolithography technique. That is, it is a mask pattern in which a plurality of circular etching masks are arranged at the lattice positions of a triangular lattice. The diameter of each circular mask (R in FIG. 2) was 2 μm, and the space between adjacent circular masks (S in FIG. 2) was 2.5 μm. As shown in FIG. 3, the direction of the mask pattern was determined so that the two sides BC and EF of the regular hexagon ABCDEF having the six lattice positions of the triangular lattice as vertices were orthogonal to the c-axis of the m-plane GaN substrate. .
上記のように形成したマスクパターンをエッチングマスクに用いてRIEを行うことにより、m面GaN基板の裏面を凹凸状に加工した。エッチングガスとしてCl2を用い、アンテナ/バイアスを100W/20W、チャンバー内圧力を0.3Paと設定して、エッチング選択比が約1となるようにした。なお、ここでいうエッチング選択比は、エッチング時間が約800秒以下であるときの、〔GaNのエッチングレート〕/〔マスクのエッチングレート〕である。この条件で、1500秒間、RIE加工を行った。マスクパターンは、エッチング時間が約800秒に達したところで殆ど消失した。RIE加工後、有機溶剤を用いてウェハを洗浄し、続けて、RIE加工された面に5分間の紫外線オゾン洗浄(110℃、酸素流量5L/分)を施した。 The back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate was processed into a concavo-convex shape by performing RIE using the mask pattern formed as described above as an etching mask. Cl 2 was used as an etching gas, the antenna / bias was set to 100 W / 20 W, the pressure in the chamber was set to 0.3 Pa, and the etching selectivity was about 1. The etching selectivity here is [GaN etching rate] / [mask etching rate] when the etching time is about 800 seconds or less. Under these conditions, RIE processing was performed for 1500 seconds. The mask pattern almost disappeared when the etching time reached about 800 seconds. After the RIE processing, the wafer was cleaned using an organic solvent, and then the surface subjected to the RIE processing was subjected to ultraviolet ozone cleaning (110 ° C., oxygen flow rate 5 L / min) for 5 minutes.
加工eを施したm面GaN基板の裏面のSEM像を図4に示す。図4において(a)は平面図、(b)は断面方向から見た図、(c)は斜視図である。 図4(a)〜(c)のいずれにおいても紙面内で右から左に向かう方向が、GaNの[0001]方向(c+方向)であり、左から右に向かう方向がGaNの[000−1]方向(c−方向)である。m面GaN基板の裏面に形成された突起の高さは1.5μmであった。 FIG. 4 shows an SEM image of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate subjected to the processing e. 4A is a plan view, FIG. 4B is a diagram viewed from the cross-sectional direction, and FIG. 4C is a perspective view. 4A to 4C, the direction from right to left in the drawing is the [0001] direction (c + direction) of GaN, and the direction from left to right is [000-1] of GaN. ] Direction (c-direction). The height of the protrusion formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate was 1.5 μm.
加工f:加工aを行った後のm面GaN基板の裏面に、加工eと同じ手順でマスクパターンを形成した。しかし、RIEチャンバー内に設置した後、薄いサファイア板でm面GaN基板の裏面を覆うことにより、該裏面がRIE加工を受けないように保護した。このことを除いて、加工fで行った処理は、加工eと同じである。すなわち、加工fを施したm面GaN基板の裏面には、フォトレジストを用いてマスクパターンを形成する処理、該マスクパターンを有機溶剤を用いて取り除く処理、及び、該マスクパターン除去後の紫外線オゾン洗浄処理が行われている。 Process f: A mask pattern was formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate after process a by the same procedure as process e. However, after being installed in the RIE chamber, the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate was covered with a thin sapphire plate to protect the back surface from being subjected to RIE processing. Except for this, the process performed in process f is the same as process e. That is, on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate subjected to processing f, a process of forming a mask pattern using a photoresist, a process of removing the mask pattern using an organic solvent, and an ultraviolet ozone after removing the mask pattern A cleaning process is being performed.
2−4.第1のn側メタルパッドの形成
上記加工a〜fのいずれかを行ったm面GaN基板の裏面に、第1のn側メタルパッドとなるメタル多層膜を形成した。このメタル多層膜に含まれる全ての層(TiW層、Au層およびPt層)は、スパッタリング法で形成した。TiW膜を形成する際は、ターゲットにTi含有量が10wt%のTi−Wターゲット、スパッタガスにAr(アルゴン)を使用し、スパッタ条件はRF電力800W、Ar流量50sccm、スパッタガス圧2.2×10−1Paとした。最下層であるTiW層とその直上に積層するAu層の厚さは1
08nmとし、それ以外のPt層およびAu層の厚さはいずれも89nmとした。
2-4. Formation of first n-side metal pad A metal multilayer film serving as a first n-side metal pad was formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate subjected to any of the above processes a to f. All layers (TiW layer, Au layer, and Pt layer) included in this metal multilayer film were formed by sputtering. When forming a TiW film, a Ti-W target having a Ti content of 10 wt% is used as a target, Ar (argon) is used as a sputtering gas, sputtering conditions are RF power 800 W, Ar flow rate 50 sccm, sputtering gas pressure 2.2. × 10 −1 Pa. The thickness of the lowermost TiW layer and the Au layer stacked immediately above it is 1
The thickness of the other Pt layer and Au layer was 89 nm.
上記メタル多層膜の形成後、スクライブおよびブレーキングを行うことによりウェハを分断し、LED素子をチップにした。上記メタル多層膜はこの工程でGaN基板と共に分断した。従って、第1のn側メタルパッドの平面形状はm面GaN基板の裏面の形状と同じとなった。また、第1のn側メタルパッドのサイズはチップサイズと略同じ350μm×340μmとなった。 After the metal multilayer film was formed, the wafer was divided by scribing and breaking to form LED elements as chips. The metal multilayer film was cut together with the GaN substrate in this step. Therefore, the planar shape of the first n-side metal pad is the same as the shape of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. The size of the first n-side metal pad was 350 μm × 340 μm, which was substantially the same as the chip size.
2−5.順方向電圧の評価
上記手順にて得たLEDチップに対して、第1のn側メタルパッドとp側メタルパッドを通して電流を印加したときの順方向電圧(Vf1)と、第2のn側メタルパッドとp側メタルパッドを通して電流を印加したときの順方向電圧(Vf2)を比較した。印加電流はパルス幅1msec、パルス周期100msecのパルス電流とし、電流値は20mAおよび60mAの2通りとした。結果を表3に示す。
2-5. Evaluation of forward voltage Forward voltage (Vf 1 ) when current is applied through the first n-side metal pad and p-side metal pad to the LED chip obtained by the above procedure, and the second n-side The forward voltage (Vf 2 ) when current was applied through the metal pad and the p-side metal pad was compared. The applied current was a pulse current having a pulse width of 1 msec and a pulse period of 100 msec, and the current value was 20 mA and 60 mA. The results are shown in Table 3.
表3に示すように、m面GaN基板の裏面に加工aのみを行ったLEDチップではVf1とVf2は一致したのに対し、加工b〜fを行ったLEDチップではいずれもVf1がVf2よりも大きくなった。特に、RIE加工を含む加工b〜eを行ったLEDチップでは、その差は数V以上にもなった。 As shown in Table 3, Vf 1 and Vf 2 coincided with the LED chip in which only the processing a was performed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, whereas Vf 1 was all in the LED chips subjected to processing b to f. It becomes larger than the vf 2. In particular, the difference between the LED chips subjected to processing b to e including RIE processing was several V or more.
また、m面GaN基板の裏面に加工aのみを行ったLEDチップに、パルス幅1msec、パルス周期100msecの順方向電流を20mA、60mA、100mA、120mA、180mA、240mAおよび350mA印加したときのVf1を表4に示す。表4には、それぞれの場合の、第1のn側メタルパッドにおける平均電流密度を併せて示している。この平均電流密度は順方向電流をn側メタルパッドの面積(350μm×340μm)で除した値であり、n側メタルパッドとm面GaN基板の裏面との界面を横切って流れる電流の平均的な密度を表している。 Further, Vf 1 when forward current of 20 mA, 60 mA, 100 mA, 120 mA, 180 mA, 240 mA, and 350 mA is applied to an LED chip that has been processed only on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate with a pulse width of 1 msec and a pulse period of 100 msec. Is shown in Table 4. Table 4 also shows the average current density in the first n-side metal pad in each case. This average current density is a value obtained by dividing the forward current by the area of the n-side metal pad (350 μm × 340 μm), and is an average of the current flowing across the interface between the n-side metal pad and the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate. Represents density.
以上の結果から、下記(I)〜(XI)の半導体発光素子が実現可能であると考えられる。
(I)n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該素子に印加される順方向電流が20mAのときの順方向電圧が4.0V以下である半導体発光素子。
(II)n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該素子に印加される順方向電流が60mAのときの順方向電圧が4.5V以下である半導体発光素子。
(III)n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該素子に印加される順方向電流が120mAのときの順方向電圧が5.0V以下である半導体発光素子。
(IV)n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該素子に印加される順方向電流が200mAのときの順方向電圧が5.5V以下である半導体発光素子。
(V)n型導電性のm面GaN基板と、該m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体を用いて形成された発光構造と、該m面GaN基板の裏面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該素子に印加される順方向電流が350mAのときの順方向電圧が6.0V以下である半導体発光素子。
(VI)前記発光構造が、GaN系半導体からなる活性層と、該活性層と前記m面GaN基板との間に配置されたn型GaN系半導体層と、該n型GaN系半導体層とで該活性層を挟むp型GaN系半導体層と、を含む、前記(I)〜(V)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
(VII)発光ダイオード素子である、前記(I)〜(VI)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
(VIII)前記m面GaN基板の裏面の面積が0.0012cm2以上である、前記(I)〜(VII)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
(IX)前記n側オーミック電極の面積が0.0012cm2以上、前記m面GaN基板の裏面の面積以下である、前記(VII)に記載の半導体発光素子。
(X)前記m面GaN基板のキャリア濃度が1×1017cm−3である、前記(I)〜(IX)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
(XI)前記m面GaN基板の裏面は、少なくとも前記n側オーミック電極と接触する部分において、10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下である、前記(I)〜(X)のいずれかに記載の半導体発光素子。
From the above results, it is considered that the following semiconductor light emitting devices (I) to (XI) can be realized.
(I) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate A semiconductor light emitting device having an n-side ohmic electrode and having a forward voltage of 4.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the device is 20 mA.
(II) an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate A semiconductor light emitting device having an n-side ohmic electrode and having a forward voltage of 4.5 V or less when a forward current applied to the device is 60 mA.
(III) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate A semiconductor light emitting device having an n-side ohmic electrode and having a forward voltage of 5.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the device is 120 mA.
(IV) An n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate A semiconductor light emitting device having an n-side ohmic electrode and having a forward voltage of 5.5 V or less when a forward current applied to the device is 200 mA.
(V) an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate, a light emitting structure formed using a GaN-based semiconductor on the front surface of the m-plane GaN substrate, and formed on the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate A semiconductor light emitting device having an n-side ohmic electrode and having a forward voltage of 6.0 V or less when a forward current applied to the device is 350 mA.
(VI) The light emitting structure includes an active layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer disposed between the active layer and the m-plane GaN substrate, and the n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer. A semiconductor light emitting device according to any one of (I) to (V), comprising a p-type GaN-based semiconductor layer sandwiching the active layer.
(VII) The semiconductor light-emitting device according to any one of (I) to (VI), which is a light-emitting diode device.
(VIII) The semiconductor light-emitting device according to any one of (I) to (VII), wherein an area of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate is 0.0012 cm 2 or more.
(IX) The semiconductor light emitting element according to (VII), wherein an area of the n-side ohmic electrode is 0.0012 cm 2 or more and not more than an area of the back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate.
(X) The semiconductor light-emitting device according to any one of (I) to (IX), wherein the carrier concentration of the m-plane GaN substrate is 1 × 10 17 cm −3 .
(XI) The back surface of the m-plane GaN substrate has an arithmetic average roughness Ra in a range of 10 μm square of 0.1 nm or less in at least a portion in contact with the n-side ohmic electrode. The semiconductor light-emitting device according to any one of the above.
本発明は、以上に記したLED素子の試作および評価から得られた知見に基づき完成されたものである。ただし、いうまでもないことであるが、本発明は、試作されたLED素
子や、試作で用いられた方法に限定されるものではない。
The present invention has been completed based on the knowledge obtained from the trial manufacture and evaluation of the LED elements described above. However, it goes without saying that the present invention is not limited to a prototype LED element or a method used in the trial production.
以下では、本発明の実施形態に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子並びにGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法について説明する。 Below, the manufacturing method of the GaN-type light emitting diode element which concerns on embodiment of this invention, and a GaN-type light emitting diode element is demonstrated.
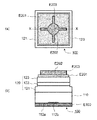
(実施形態1)
実施形態1に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図5に模式的に示す。GaN系発光ダイオード素子100は基板110と、その上にエピタキシャル成長したGaN系半導体からなるエピ層120とを有している。図5(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100をエピ層120側から見た平面図であり、図5(b)は図5(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 1)
The structure of the GaN-based light emitting diode element according to
基板110はn型導電性のm面GaN基板である。エピ層120はpn接合を構成するn型層121とp型層123を含んでいる。ダブルヘテロ構造が形成されるように、n型層121とp型層123との間には活性層122が設けられている。基板110の裏面にはオーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するn側電極E100が設けられ、エピ層120上には、透光性電極であるp側オーミック電極E201が設けられている。n側電極E100と、p側オーミック電極E201上の一部に形成されたp側電極パッドE202とを通してエピ層120に順方向電圧を印加することにより、活性層122で発光が生じる。この光は、p側オーミック電極E201を透過してGaN系発光ダイオード素子の外部に放出される。また、この光の一部は、基板110の端面およびエピ層120の端面からも放出される。
The
n側電極E100は好ましくは積層構造とされる。その場合、基板110と接触する部分はAl、Ti、Cr、V、W、ITOのような、n型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料を用いて形成し、その他部分はAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属を用いて形成する。
The n-side electrode E100 preferably has a laminated structure. In that case, the portion in contact with the
p側オーミック電極E201は、ITOのような透明導電性酸化物(TCO;Transparent Conductive Oxide)を用いて形成される。p側オーミック電極E201は、p型層123の上面の全体を覆うように形成することが好ましい。p側電極パッドE202は金属を用いて形成され、好ましくは積層構造とされる。p側電極パッドE202を積層構造とする場合、p側オーミック電極E201と接する部分はCr、Ti、Ni、Pt、Rhのような、TCOとの密着性に優れた金属で形成し、その他の部分はAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属を用いて形成する。TCOで形成されるp側オーミック電極E201の厚さは好ましくは0.1μm〜0.5μmであり、金属で形成されるp側電極パッドE202の厚さは好ましくは0.5μm〜5μmである。
The p-side ohmic electrode E201 is formed using a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) such as ITO. The p-side ohmic electrode E201 is preferably formed so as to cover the entire upper surface of the p-
n側電極E100は基板110の裏面を全面的に覆っている。その基板110の裏面には、n側電極E100との接触抵抗が相対的に低い低接触抵抗領域112aと、該接触抵抗が相対的に高い高接触抵抗領域112bとが存在している。低接触抵抗領域112aはポリッシング仕上げされている。すなわち、n側電極E100を形成する前に低接触抵抗領域112aに行われた最後の加工(洗浄は含まない)は、ポリッシング加工である。一方、高接触抵抗領域112bはドライエッチング仕上げされている。すなわち、n側電極E100を形成する前に高接触抵抗領域112bに行われた最後の加工は、反応性イオンエッチング(RIE)のようなドライエッチング加工である。
The n-side electrode E100 covers the entire back surface of the
前述したLED素子の試作および評価結果から判明したように、n型導電性のm面GaN基板を、酸性のCMPスラリーを用いて、0.5μm/h以下という低いポリッシングレートでポリッシング加工することにより得られる表面(m面)には、低接触抵抗の電極
を形成することができる。一方、ポリッシング加工後に更にドライエッチング加工を施したm面GaN基板の表面に形成した電極は、より高い接触抵抗を示す。
As proved from the LED device prototype and evaluation results described above, by polishing an n-type conductive m-plane GaN substrate with an acidic CMP slurry at a polishing rate as low as 0.5 μm / h or less. An electrode having a low contact resistance can be formed on the obtained surface (m-plane). On the other hand, an electrode formed on the surface of an m-plane GaN substrate that has been further subjected to dry etching after polishing exhibits higher contact resistance.
高接触抵抗領域112bは、基板110の裏面へのp側電極パッドE202の正射影の少なくとも一部を含んでいればよいが、好ましくは全部を含むように形成する。この構成によって、基板110およびエピ層120の内部を流れる電流が、p側電極パッドE202とn側電極E100とを最短距離で結ぶ経路(図5(b)中に矢印で示す経路)に集中することが防止される。その結果として、この領域に電流が集中した場合と比べて、活性層122で発生する光がp側電極パッドE202により受ける遮蔽および吸収が低減される。加えて、活性層122を横切って流れる電流の密度がより均一となるので、ドループ現象(GaN系発光ダイオード素子に特有の、電流密度が高くなるにつれて発光効率が低下する現象)による発光効率低下が抑制される。
The high
(実施形態2)
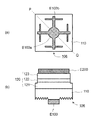
実施形態2に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図6に模式的に示す。図6では、実施形態1のGaN系発光ダイオード素子と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図6(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100をエピ層120側から見た平面図であり、図6(b)は図6(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 2)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 2 is schematically shown in FIG. In FIG. 6, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting diode element of the first embodiment. FIG. 6A is a plan view of the GaN-based light emitting
図6に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、p側電極パッドE202に4つの補助電極E203が接続されている。したがって、金属ワイヤなどからp側電極パッドE202に供給される電流は、ライン状の補助電極E203によって横方向(エピ層120の厚さ方向に直交する方向)に拡げられたうえ、p側オーミック電極E201に流れることになる。
In the GaN-based light emitting
基板110の裏面のうち、n側電極E100に覆われた領域には、高接触抵抗領域112bがp側電極パッドE202の正射影の少なくとも一部、好ましくは全部を含むように形成されている。従って、基板110およびエピ層120の内部を流れる電流が、p側電極パッドE202とn側電極E100とを最短距離で結ぶ経路に集中することが防止される。更に、p側電極パッドE202に補助電極E203が接続されているので、エピ層120内を流れる電流はp側電極パッドE202から横方向に十分に離れた領域まで広げられる。
In the region covered with the n-side electrode E100 on the back surface of the
図6のGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、補助電極E203の基板110の裏面への正射影が高接触抵抗領域112bに含まれていない。従って、補助電極E203からは直下の方向にも電流が流れるが、補助電極E203はp側電極パッドE202と異なり細長く形成されているので、その直下で起こる発光に及ぼす影響(遮蔽および吸収)は比較的小さい。一実施形態では、補助電極E203の基板110の裏面への正射影の全部または一部を含むように、高接触抵抗領域112bを形成することもできる。
In the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態3)
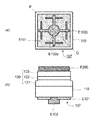
実施形態3に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図7に模式的に示す。図7では、実施形態1のGaN系発光ダイオード素子と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図7(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100をエピ層120側から見た平面図であり、図7(b)は図7(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 3)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 3 is schematically shown in FIG. In FIG. 7, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting diode element of the first embodiment. FIG. 7A is a plan view of the GaN-based light emitting
図7に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、エピ層120とp側オーミック電極E201との間の、p側パッド電極E100の直下の位置に、絶縁膜Z100が形成されている。基板110の裏面に設けられた高接触抵抗領域112bと絶縁膜Z100という2つの電流ブロック構造が設けられることにより、基板110およびエピ層120の内
部を流れる電流がp側電極パッドE202とn側電極E100とを最短距離で結ぶ経路に集中することが、効果的に防止される。
In the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態4)
実施形態4に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図8に模式的に示す。図8では、実施形態1のGaN系発光ダイオード素子と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図8(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100を基板110側から見た平面図であり、図8(b)は図8(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 4)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 4 is schematically shown in FIG. In FIG. 8, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting diode element of the first embodiment. FIG. 8A is a plan view of the GaN-based light emitting
図8に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、基板110の裏面に透光性電極であるn側オーミック電極E101が設けられ、エピ層120上にオーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するp側電極E200が設けられている。n側オーミック電極E101上の一部に形成されたn側電極パッドE102と、p側電極E200とを通してエピ層120に順方向電圧を印加することにより、活性層122で発光が生じる。この光は、n側オーミック電極E101を透過してGaN系発光ダイオード素子の外部に放出される。また、この光の一部は、基板110の端面およびエピ層120の端面からも放出される。
In the GaN-based light emitting
n側オーミック電極E101は、ITOのような透明導電性酸化物(TCO;Transparent Conductive Oxide)を用いて形成される。n側電極パッドE102は金属を用いて形成され、好ましくは積層構造とされる。n側電極パッドE102を積層構造とする場合、n側オーミック電極E201と接する部分はCr、Ti、Ni、Pt、Rhのような、TCOとの密着性に優れた金属で形成し、その他の部分はAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属を用いて形成する。TCOで形成されるn側オーミック電極E101の厚さは好ましくは0.1μm〜0.5μmであり、金属で形成されるn側電極パッドE102の厚さは好ましくは0.5μm〜5μmである。 The n-side ohmic electrode E101 is formed using a transparent conductive oxide (TCO) such as ITO. The n-side electrode pad E102 is formed using a metal, and preferably has a laminated structure. When the n-side electrode pad E102 has a laminated structure, the portion in contact with the n-side ohmic electrode E201 is formed of a metal having excellent adhesion to TCO, such as Cr, Ti, Ni, Pt, and Rh, and other portions. Is formed using a highly conductive metal such as Au, Al, Cu, or Ag. The thickness of the n-side ohmic electrode E101 formed of TCO is preferably 0.1 μm to 0.5 μm, and the thickness of the n-side electrode pad E102 formed of metal is preferably 0.5 μm to 5 μm.
p側電極E200は好ましくは積層構造とされる。その場合、p型層123と接触する部分はNi、Au、Pt、Pd、Co、ITOのような、p型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料を用いて形成し、その他の部分はAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属を用いて形成する。p側電極E200は、p型層123の上面の全体を覆うように形成することが好ましい。
The p-side electrode E200 is preferably a laminated structure. In that case, the portion that contacts the p-
n側オーミック電極E101は基板110の裏面を全面的に覆っている。その基板110の裏面には、n側オーミック電極E101との接触抵抗が相対的に低い低接触抵抗領域112aと、該接触抵抗が相対的に高い高接触抵抗領域112bとが存在している。低接触抵抗領域112aはポリッシング仕上げされた領域であり、高接触抵抗領域112bはドライエッチング仕上げされた領域である。
The n-side ohmic electrode E101 covers the entire back surface of the
高接触抵抗領域112bはn側電極パッドE102の直下に設けられる。高接触抵抗領域112bは、基板110の裏面へのn側電極パッドE102の正射影の少なくとも一部を含んでいればよいが、好ましくは全部を含むように形成する。この構成によって、基板110およびエピ層120の内部を流れる電流が、p側電極E200とn側電極パッドE102とを最短距離で結ぶ経路(図8(b)中に矢印で示す経路)に集中することが防止される。その結果として、この領域に電流が集中した場合と比べて、活性層122で発生する光がn側電極パッドE102により受ける遮蔽および吸収が低減される。加えて、活性層122を横切って流れる電流の密度がより均一となるので、ドループ現象(GaN系発光ダイオード素子に特有の、電流密度が高くなるにつれて発光効率が低下する現象)による発光効率低下が抑制される。
The high
(実施形態5)
実施形態5に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図9に模式的に示す。図9では、実施形態1のGaN系発光ダイオード素子と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図9(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100を基板110側から見た平面図であり、図9(b)は図9(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 5)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 5 is schematically shown in FIG. In FIG. 9, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting diode element of the first embodiment. FIG. 9A is a plan view of the GaN-based light emitting
図9に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、n側電極パッドE102に4つの補助電極E103が接続されている。したがって、金属ワイヤなどからn側電極パッドE102に供給される電流は、ライン状の補助電極E103によって横方向(基板層110の厚さ方向に直交する方向)に拡げられたうえ、n側オーミック電極E101に流れることになる。
In the GaN-based light emitting
基板110の裏面のうち、n側オーミック電極E101に覆われた領域には、高接触抵抗領域112bがn側電極パッドE102の正射影の少なくとも一部、好ましくは全部を含むように形成されている。従って、基板110およびエピ層120の内部を流れる電流が、p側電極E200とn側電極パッドE102とを最短距離で結ぶ経路に集中することが防止される。更に、n側電極パッドE102に補助電極E103が接続されているので、エピ層120内を流れる電流はn側電極パッドE102から横方向に十分に離れた領域まで広げられる。
In the region covered with the n-side ohmic electrode E101 on the back surface of the
図9のGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、補助電極E103の基板110の裏面への正射影が高接触抵抗領域112bに含まれていない。従って、補助電極E103からは直下の方向にも電流が流れるが、補助電極E103はn側電極パッドE202と異なり細長く形成されているので、その直下で起こる発光に及ぼす影響(遮蔽および吸収)は比較的小さい。一実施形態では、補助電極E103の基板110の裏面への正射影の全部または一部を含むように、高接触抵抗領域112bを形成することもできる。
In the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態6)
実施形態6に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図10に模式的に示す。図10では、実施形態1のGaN系発光ダイオード素子と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図10(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子100を基板110側から見た平面図であり、図10(b)は図10(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。
(Embodiment 6)
The structure of the GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 6 is schematically shown in FIG. In FIG. 10, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting diode element of the first embodiment. FIG. 10A is a plan view of the GaN-based light emitting
図10に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子100では、パッド部を含むn側電極E100が、基板110の裏面に直接形成されている。n側電極E100は、電極パッドを兼用するパッド部E100aと、該パッド部E100aに接続され、十文字パターン(枝分かれした線状パターンともいえる)を呈する補助部E100bとを有している。
In the GaN-based light emitting
n側電極E100は、好ましくは、基板110と接触する部分をAl、Ti、Cr、V、W、ITOのような、n型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料を用いて形成し、その他部分をAu、Al、Cu、Agのような、導電性の高い金属を用いて形成する。 The n-side electrode E100 is preferably formed by using a material that forms ohmic contact with an n-type GaN-based semiconductor, such as Al, Ti, Cr, V, W, ITO, etc. The portion is formed using a highly conductive metal such as Au, Al, Cu, or Ag.
基板110の裏面のうち、n側電極E100に覆われた領域には、高接触抵抗領域112bがn側電極のパッド部E100aの正射影の少なくとも一部、好ましくは全部を含むように形成されている。従って、n側電極E100から基板110に注入されるキャリア(電子)は、パッド部E100aから直接ではなく、補助部E100bによって横方向に拡げられたうえで基板110に注入される。従って、高接触抵抗領域112bを設けない場合に比べて、エピ層120内の発光構造を流れる電流の密度が均一となる。なお、補助部E100bからは直下の方向にも電流が流れるが、補助部E100bはパッド部E10
0aと異なり細長く形成されているので、その直下で起こる発光に及ぼす影響(遮蔽および吸収)は小さい。
In the region covered with the n-side electrode E100 in the back surface of the
Since it is formed in an elongated shape unlike 0a, the influence (shielding and absorption) on the light emission that occurs immediately below it is small.
(実施形態7)
実施形態7に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図11に模式的に示す。図11に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子101は、基板110と、その上にエピタキシャル成長したGaN系半導体からなるエピ層120とを有している。図11(a)はGaN系発光ダイオード素子101をエピ層120側から見た平面図であり、図11(b)は図11(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。図12には、GaN系発光ダイオード素子101を基板110側から見た平面図を示す。
(Embodiment 7)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 7 is schematically shown in FIG. A GaN-based light emitting
基板110はn型導電性のm面GaN基板である。エピ層120はpn接合を構成するn型層121とp型層123を含んでいる。ダブルヘテロ構造が形成されるように、n型層121とp型層123との間には活性層122が設けられている。基板110の裏面にはオーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するn側電極E100が形成されている。エピ層120上には、透光性電極であるp側オーミック電極E201が形成されている。n側電極E100と、p側オーミック電極E201上の一部に形成されたp側電極パッドE202とを通して、エピ層120に順方向電圧を印加することにより活性層122で発光が生じる。この光は、p側オーミック電極E201の表面、エピ層120の端面、基板110の端面などから、GaN系発光ダイオード素子101の外部に放出される。
The
n側電極E100は、少なくとも基板110と接触する部分がAl、Ti、Cr、V、W、ITOのような、n型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料で形成される。好ましい実施形態において、n側電極E100は、基板110と接触する部分がAl、Ti、Cr、V、W、ITOなどで形成され、その上にAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属からなる層が積層された、多層構造とされる。
The n-side electrode E100 is formed of a material that forms an ohmic contact with an n-type GaN-based semiconductor, such as Al, Ti, Cr, V, W, or ITO, at least at a portion in contact with the
p側オーミック電極E201は、ITOのような透明導電性酸化物(TCO;TransparentConductive Oxide)で形成される。好ましくは、p側オーミック電極E201は、p
型層123の上面全体を覆うように設けられる。p側電極パッドE202は金属を用いて形成される。好ましい実施形態において、p側電極パッドE202は、p側オーミック電極E201と接する部分がCr、Ti、Ni、Pt、Rhのような、TCOとの密着性に優れた金属で形成され、その上にAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属からなる層が積層された、多層構造とされる。TCOからなるp側オーミック電極E201の厚さは好ましくは0.1μm〜0.5μmであり、金属からなるp側電極パッドE202の厚さは好ましくは0.5μm〜5μmである。
The p-side ohmic electrode E201 is formed of a transparent conductive oxide (TCO; Transparent Conductive Oxide) such as ITO. Preferably, the p-side ohmic electrode E201 is p
It is provided so as to cover the entire top surface of the
図12に示すように、基板110の裏面上に形成されたn側電極E100は特定の形状にパターニングされている。n側電極E100の中央部には、基板110の裏面へのp側電極パッドE202の正射影と重なる位置に、円形の開口部が設けられている。この開口部があるために、p側電極パッドE202からエピ層120に流れる電流はp側電極パッドE202の真下に集中することがない。つまり、電流が図11(b)中に矢印で示す経路に集中することがない。その結果として、この経路に電流が集中した場合と比べて、活性層122で発生する光がp側電極パッドE202により受ける遮蔽および吸収が低減される。加えて、活性層122を横切って流れる電流の密度がより均一となるので、ドループ現象(GaN系発光ダイオード素子に特有の、電流密度が高くなるにつれて発光効率が低下する現象)による発光効率低下が抑制される。
As shown in FIG. 12, the n-side electrode E100 formed on the back surface of the
(実施形態8)
実施形態8に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の断面構造を図13に模式的に示す。図
13では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図13に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子102では、基板110の裏面のn側電極E100に覆われていない部分に、活性層122で生じる光を乱反射させ得る凹凸パターンが設けられている。この凹凸パターンは、例えば、ドット状の凹部または凸部が周期的に配列されたパターンであり、フォトリソグラフィとドライエッチングによって形成することができる。凹凸パターンは、凹部の深さまたは凸部の高さとパターンの周期が1μm以上であれば、活性層122で生じる近紫外〜可視波長の光を乱反射させることができる。乱反射を発生させ得る凹凸パターンの形成によって多重反射が抑制され、光取出し効率が改善される。周期性を有する凹凸パターンの形成に代えて、ランダムエッチングマスクを用いたドライエッチングあるいはサンドブラストによって、同様の効果を奏する、周期性を有さない粗面を形成することもできる。
(Embodiment 8)
FIG. 13 schematically shows a cross-sectional structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to the eighth embodiment. In FIG. 13, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態9、10)
実施形態9、10に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の断面構造を図14に模式的に示す。図14では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図14(a)に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子103および図14(b)に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子104では、オーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するn側電極E100に代えて、パターニングされたn側オーミック電極E101と、それを覆うn側電極パッドE102が、基板110の裏面上に形成されている。基板110の裏面上でn側オーミック電極E101が呈するパターンは、図15(a)に一例を示すドットパターンや、図15(b)に一例を示すネットパターンなどとすることができる。n側オーミック電極E101は、好ましくはサブトラクティブ法によってパターニングされる。
(Embodiments 9 and 10)
FIG. 14 schematically shows a cross-sectional structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to the ninth and tenth embodiments. In FIG. 14, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting
図14(a)のGaN系発光ダイオード素子103では、n側電極パッドE102が基板110の露出した裏面と接するように設けられているが、図14(b)のGaN系発光ダイオード素子104では、基板110の裏面とn側電極パッドE102との間に誘電体反射膜R100が介在している。誘電体反射膜Rの好適例はブラッグ反射膜(DBR)であるが、限定されるものではなく、基板110より屈折率の低い誘電体からなる単層膜であってもよい。
In the GaN-based light emitting
GaN系発光ダイオード素子103、104において、n側オーミック電極E101は、Al、Ti、Cr、V、W、ITOのような、n型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料を用いて、蒸着、スパッタ、CVDのような気相法により、好ましくは0.05μm〜0.5μmの厚さに形成される。n側電極パッドE102は、Au、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属からなる厚さ0.5μm〜5μmの層を含むことが望ましい。また、n側電極パッドE102は基板110側に、Ag、Al、Rh、Ptのような近紫外〜可視波長域における反射率の高い金属からなる高反射部を含むことが望ましい。
In the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態11)
実施形態11に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図16に模式的に示す。図16(a)は基板側から見た平面図、図16(b)は図16(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。図16では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図16に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子105では、p型層123上に設けられる電極が、オーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するp側電極E200とされるとともに、活性層122で生じる光が基板110の裏面からGaN系発光ダイオード素子100の外部に放出されるように、n側電極E100の面積が小さくされている。好ましい実施形態においては、p側電極E200は、p型層123と接触する部分がp型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料で形成され、そ
の上にAu、Al、Cu、Agのような導電性の高い金属からなる層が積層された、多層構造とされる。p型GaN系半導体とオーミック接触を形成する材料としては、Ni、Au、Pd、Rh、Pt、Coなどの金属が挙げられる他、ITO、亜鉛添加酸化インジウム、酸化亜鉛、酸化錫、酸化チタン、酸化ガリウムなどの透明導電性酸化物が挙げられる。導電性の高い金属からなる層は、好ましくは0.5μm〜5μmの厚さに形成される。
(Embodiment 11)
The structure of the GaN-based light emitting diode element according to
(実施形態12)
実施形態12に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図17に模式的に示す。図17では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図17に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子106は、図16に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子105の変形例である。相違点として、平面図である図17(a)に示すように、GaN系発光ダイオード素子106ではn側電極E100が、ボンディングワイヤ等が接続される部分である接続部E100aと、電流を横方向(基板110の厚さ方向と直交する方向)に拡げるための延長部E100bとから構成されている。加えて、GaN系発光ダイオード素子106では、図17(a)のP−Q線の位置における断面図である図17(b)に示すように、基板110の裏面の露出した部分が粗く加工されている。この粗く加工された部分には、活性層122で生じる光を乱反射させ得るミクロンサイズの凹凸、活性層122で生じる光を回折させ得るサブミクロンサイズの周期的凹凸パターン、あるいは、活性層122で生じる光の全反射を抑制し得るサブミクロンサイズの微細な凹凸が形成される。サブミクロンサイズの凹凸は、ポリマー微粒子やシリカ微粒子をマスクに用いて基板110をエッチング加工する方法を用いて形成することができる。
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to
(実施形態13)
実施形態12に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図18に模式的に示す。図18(a)は基板側から見た平面図、図18(b)は図18(a)のP−Q線の位置における断面図である。図18では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図18に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子107は、図16に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子105の別の変形例である。相違点として、図18(a)(b)に示すように、GaN系発光ダイオード素子107では、オーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するn側電極E100に代えて、ITOのような透明導電性酸化物で形成された透光性のn側オーミック電極E101と、その一部上に設けられたn側電極パッドE102が、基板110の裏面上に形成されている。
(Embodiment 13)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to
n側電極パッドE102は、図17のGaN系発光ダイオード素子106におけるn側電極E100と同様に、ボンディングワイヤ等が接続される部分である接続部E102aと、電流を横方向に拡げるための延長部E102bとから構成されている。透光性のn側オーミック電極E101はパターニングされており、n側電極パッドE102aの直下の部分に円形の開口部を有している。
Similarly to the n-side electrode E100 in the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態14)
実施形態14に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図19に模式的に示す。図19(a)は基板側から見た平面図、図19(b)は図19(a)のX−X線の位置における断面図である。図19では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図19に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子108は、図16に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子105の更に別の変形例である。相違点として、図19(a)(b)に示すように、発光ダイオード108では、オーミック電極と電極パッドを兼用するn側電極E100に代えて、ITOのような透明導電性酸化物で形成された透光性のn側オーミック電極E101と、その一部上に設けられたn側電極パッドE102が、基板110の裏面上に形成されている。ただし、図18のGaN
系発光ダイオード素子107とは異なり、n側オーミック電極E101は基板110の裏面を広く覆っておらず、その面積はn側電極パッドE102よりも僅かに大きいだけである。加えて、GaN系発光ダイオード素子108では、図16のGaN系発光ダイオード素子105と異なり、基板110の裏面のうちn側オーミック電極E101に覆われていない部分が粗面とされている。
(Embodiment 14)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 14 is schematically shown in FIG. FIG. 19A is a plan view seen from the substrate side, and FIG. 19B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line XX of FIG. 19A. In FIG. 19, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting
Unlike the system light emitting
(実施形態15)
実施形態15に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の構造を図20に模式的に示す。図20(a)は基板側から見た平面図、図20(b)は図20(a)のP−Q線の位置における断面図である。図20では、実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101と共通する構成要素については同一の符号を付している。図20に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子109は、図19に示すGaN系発光ダイオード素子108の変形例である。相違点として、GaN系発光ダイオード素子109では図20(a)(b)に示すように、n側電極パッドE102が、ボンディングワイヤ等が接続される部分である接続部E102aと、電流を横方向(基板110の厚さ方向と直交する方向)に拡げるための、グリッド状の延長部E102bとから構成されている。n側電極パッドE102とp型層123との間に介在されたn側オーミック電極E101は、n側電極パッドE102と略同じ形状だが少し幅広にパターニングされている。
(Embodiment 15)
The structure of a GaN-based light emitting diode element according to Embodiment 15 is schematically shown in FIG. 20A is a plan view seen from the substrate side, and FIG. 20B is a cross-sectional view taken along the line PQ in FIG. 20A. In FIG. 20, the same reference numerals are given to components common to the GaN-based light emitting
(実施形態7のGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法)
次に、本発明の実施形態に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法を、前述の実施形態7に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子101を製造する場合を例に挙げて説明する。GaN系発光ダイオード素子101は以下に記す(A)〜(G)のステップを順次実行することにより製造することができる。
(Method for Manufacturing GaN-Based Light Emitting Diode Device of Embodiment 7)
Next, a method for manufacturing a GaN-based light-emitting diode element according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described by taking as an example the case of manufacturing the GaN-based light-emitting
(A)エピウェハの準備
最初のステップでは、図21(a)に示すように、n型導電性のm面GaN基板110上に、GaN系半導体からなるn型層121、活性層122およびp型層123を含むエピ層120が形成されたエピウェハを準備する。この段階における基板110の厚さは、典型的には300μm〜1mmである。
(A) Preparation of Epi Wafer In the first step, as shown in FIG. 21A, an n-
(B)エピ層の加工
このステップでは、図21(b)に示すように、エピ層120をドライエッチング加工して素子分離溝G100を形成する。そして、素子分離溝G100によって区画される各発光ダイオード部のp型層123上に、p側オーミック電極E201とp側電極パッドE202を順次形成する。素子分離溝G100とp側オーミック電極E201の形成の順序に限定はなく、素子分離溝G100を形成する前にp側オーミック電極E201を形成してもよい。また、この例では、素子分離溝G100はn型層121に達する深さとされているが、基板110の表面または内部に達する深さに形成することもできる。好ましくは、素子分離溝G100、p側オーミック電極E201およびp側電極パッドE202を形成した後、p側オーミック電極E201の表面とエピ層120の露出面をSiO2、SiNxのような透明材料からなる絶縁性の保護膜(図示せず)で被覆する。
(B) Process of Epi Layer In this step, as shown in FIG. 21B, the
(C)基板の薄肉化
このステップでは、基板110の裏面をグラインディングまたはラッピングして、図21(c)に示すように基板110の厚さを減じる。グラインディングを行った場合には、続けてラッピングを行って、加工された面の粗さを減じる。このラッピングの際には、使用するダイヤモンド砥粒の粒径を段階的に小さくしていくことが好ましい。
このステップ(C)は、必要に応じて行えばよく、省略することも可能である。
(C) Substrate Thinning In this step, the back surface of the
This step (C) may be performed as necessary, and may be omitted.
(D)基板の裏面のポリッシング
このステップでは、酸性のCMPスラリーを用いて、0.5μm/h以下という低いポリッシングレートで基板110の裏面をポリッシングし、AFMを用いて測定される10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaを0.1nm以下とする。CMPスラリーのpHは好ましくは2未満である。ポリッシング前の基板110の裏面がグラインドされたままの表面のような荒れた面である場合は、予備加工としてラッピングを行って粗さを減じてから、ポリッシングを行う。このラッピングの際には、使用するダイヤモンド砥粒の粒径を段階的に小さくしていくことが望ましい。ポリッシング後は基板110に付着したスラリーを水で洗い流し、乾燥させる。水洗の後に、有機洗浄や紫外線オゾン洗浄を行ってもよい。
(D) Polishing of Backside of Substrate In this step, an acidic CMP slurry is used to polish the backside of the
(E)n側電極の形成
このステップでは、図22(d)に示すように、基板110の裏面全体にn側電極E100を、蒸着、スパッタ、CVDなどの気相法を用いて薄膜状に形成する。このように、酸性スラリーを用いて低いレートで基板110の表面をポリッシングした後に、そのポリッシュされたままの表面にn側電極E100を形成することによって、n側電極E100の接触抵抗を低くすることができる。
(E) Formation of n-side electrode In this step, as shown in FIG. 22 (d), the n-side electrode E100 is formed on the entire back surface of the
(F)n側電極のパターニング
このステップでは、必要な部分をマスクで保護したうえで不要部分をエッチングにより除去する方法、すなわちサブトラクティブ法によって、図22(e)に示すようにn側電極E100を所定形状にパターニングする。マスクのパターニングは、よく知られたフォトリソグラフィ技法を用いて行うことができる。エッチング方法は、ウェットエッチングとドライエッチングのいずれでもよい。ウェットエッチングで用いるエッチャント、ドライエッチングで用いるエッチングガスについては、公知技術を適宜参照して選択すればよい。好ましい実施形態においては、n側電極E100のパターニング後、基板110の露出面をSiO2、SiNxのような透明材料からなる絶縁性の保護膜(図示せず)で被覆する。
(F) Patterning of n-side electrode In this step, as shown in FIG. 22 (e), an n-side electrode E100 is formed by a method of protecting unnecessary portions with a mask and removing unnecessary portions by etching, that is, a subtractive method. Is patterned into a predetermined shape. Mask patterning can be performed using well-known photolithography techniques. The etching method may be either wet etching or dry etching. An etchant used in wet etching and an etching gas used in dry etching may be selected by appropriately referring to known techniques. In a preferred embodiment, after patterning the n-side electrode E100, the exposed surface of the
(G)ダイシング
最後のステップとして、図22(f)に示すように、エピ層120に形成した素子分離溝G100の位置でエピウェハを切断し、チップ状のGaN系発光ダイオード素子101を得る。
(G) Dicing As the last step, as shown in FIG. 22F, the epi-wafer is cut at the position of the element isolation groove G100 formed in the
(実施形態8のGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法)
実施形態8に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子102(図13参照)を製造する場合、基板110の裏面を凹凸状に加工するステップが必要となる。このステップは、n側電極E100をパターニングするステップの後に行う。
(Method for Manufacturing GaN-Based Light Emitting Diode Device of Embodiment 8)
When manufacturing the GaN-based light-emitting diode element 102 (see FIG. 13) according to Embodiment 8, a step of processing the back surface of the
(実施形態14のGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法)
実施形態8に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子108(図19参照)を製造するには、まず、n型導電性のm面GaN基板110上に、GaN系半導体からなるn型層121、活性層122およびp型層123を含むエピ層120が形成されたエピウェハを準備する。そして、エピ層120をドライエッチング加工して素子分離溝G100を形成するとともに、素子分離溝G100によって区画される各発光ダイオード部のp型層123上に、p側電極E200を形成する。
(Method for Manufacturing GaN-Based Light Emitting Diode Device of Embodiment 14)
In order to manufacture the GaN-based light emitting diode device 108 (see FIG. 19) according to the eighth embodiment, first, an n-
p側電極E200の形成後、基板110の裏面をグラインディングまたはラッピングして、基板110の厚さを減じる。グラインディングを行った場合には、続けてラッピングを行って、加工された面の粗さを減じる。その後、酸性のCMPスラリーを用いて、0.5μm/h以下という低いポリッシングレートで基板110の裏面をポリッシングし、A
FMを用いて測定される10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaを0.1nm以下とする。ポリッシング後は基板110に付着したスラリーを水で洗い流し、乾燥させる。水洗の後に、有機洗浄や紫外線オゾン洗浄を行ってもよい。
After forming the p-side electrode E200, the back surface of the
The arithmetic average roughness Ra in the range of 10 μm square measured using FM is set to 0.1 nm or less. After polishing, the slurry adhering to the
次に、ポリッシュされたままの基板110の裏面全体にITOからなるn側オーミック電極E101を、蒸着、スパッタ、CVDなどの気相法を用いて薄膜状に形成する。このステップまで完了したエピウェハの断面図が図23(a)である。
Next, an n-side ohmic electrode E101 made of ITO is formed in a thin film shape on the entire back surface of the
次のステップでは、必要な部分をレジストマスクで保護したうえで不要部分をエッチングにより除去する方法、すなわちサブトラクティブ法によって、図23(b)に示すようにn側オーミック電極E101を所定形状にパターニングする。レジストマスクのパターニングは、通常のフォトリソグラフィ技法を用いて行うことができる。ITOのエッチングは、好ましくは、エッチャントに塩化鉄水溶液または塩酸を用いて、ウェット法により行う。このウェットエッチングの際には、ITOの不要部分を完全に取り除かないで、その残渣が基板110上に残るようにエッチング時間などを調節する。
In the next step, the n-side ohmic electrode E101 is patterned into a predetermined shape as shown in FIG. 23B by a method of removing unnecessary portions by etching after protecting necessary portions with a resist mask, that is, a subtractive method. To do. Patterning of the resist mask can be performed using a normal photolithography technique. Etching of ITO is preferably performed by a wet method using an aqueous iron chloride solution or hydrochloric acid as an etchant. In this wet etching, the etching time or the like is adjusted so that the unnecessary portion of ITO is not completely removed and the residue remains on the
ITOのような多結晶質のTCO薄膜は、成膜後にアニールして結晶部分の結晶性を向上させることによって、ウェットエッチング時の結晶部分と粒界部分とのエッチングレート差を大きくすることができる。従って、n側オーミック電極E101をITOのような多結晶質のTCO膜とする場合には、これを熱処理することによって、ウェットエッチング後にTCOの残渣が基板110上に残留し易くすることができる。
A polycrystalline TCO thin film such as ITO can increase the etching rate difference between the crystal part and the grain boundary part during wet etching by annealing after film formation to improve the crystallinity of the crystal part. . Therefore, when the n-side ohmic electrode E101 is a polycrystalline TCO film such as ITO, the TCO residue can be easily left on the
次のステップでは、前のステップでn側オーミック電極E101の保護に用いたレジストマスクを引き続きマスクとして残したまま、露出した基板110の裏面を塩素ガスをエッチングガスに用いてドライエッチングする。このとき、残留したITOの残渣が微細マスクとして働くことによって、図23(c)に示すように、基板110のドライエッチされた部分には微細な凹凸が無数に形成される。
In the next step, the exposed back surface of the
ドライエッチング後、図24(d)に示すようにn側オーミック電極E101上にn側電極パッドE102を形成する。好ましい実施形態においては、この後、基板110の露出面をSiO2、SiNxのような透明材料からなる絶縁性の保護膜(図示せず)で被覆する。そして、最後のステップとして、図24(e)に示すように、エピ層120に形成した素子分離溝G100の位置でエピウェハを切断し、チップ状のGaN系発光ダイオード素子108を得る。
After dry etching, an n-side electrode pad E102 is formed on the n-side ohmic electrode E101 as shown in FIG. In a preferred embodiment, thereafter, the exposed surface of the
(変形実施形態)
上述の各実施形態と同様に、m面GaN基板のおもて面上にGaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層を含むエピ層が形成されたエピウェハを準備し、該p型層の上面にp側電極を形成した後、変形実施形態に係るGaN系発光ダイオード素子の製造方法では、該p側電極を挟んで、該エピウェハのエピ層側に支持基板を接合する。
次いで、該m面GaN基板を裏面側からグラインディングまたはラッピングして磨滅させ、エピ層に含まれるn型層を露出させる。
次いで、該n型層の露出面を酸性のCMPスラリー(好ましくはpH2未満)を用いて、0.5μm/h以下という低いポリッシングレートでポリッシングし、AFMを用いて測定される10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaを0.1nm以下とする。ポリッシング後、ポリッシュされたn型層表面に付着したスラリーを水で洗い流し、乾燥させる。水洗の後に、有機洗浄や紫外線オゾン洗浄を行ってもよい。
その後は、上述の実施形態に係る製造方法と同様の手順で、該ポリッシュされたn型層露出面上にn側電極を形成し、次いで、そのパターニングを行う。
このようにして形成したn側電極は、n型層に対する接触抵抗の低いものとなると考え
られる。
(Modified embodiment)
Similar to each of the above-described embodiments, an epi-wafer in which an n-type layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are formed on the front surface of an m-plane GaN substrate is prepared, and the p After forming the p-side electrode on the upper surface of the mold layer, in the method for manufacturing a GaN-based light emitting diode device according to the modified embodiment, a support substrate is bonded to the epilayer side of the epiwafer with the p-side electrode interposed therebetween.
Next, the m-plane GaN substrate is ground or lapped from the back side to expose the n-type layer included in the epi layer.
Then, the exposed surface of the n-type layer is polished with an acidic CMP slurry (preferably less than pH 2) at a polishing rate as low as 0.5 μm / h or less, and in the range of 10 μm square measured using AFM. Arithmetic average roughness Ra shall be 0.1 nm or less. After polishing, the slurry adhering to the polished n-type layer surface is washed away with water and dried. After washing with water, organic cleaning or ultraviolet ozone cleaning may be performed.
Thereafter, an n-side electrode is formed on the polished n-type layer exposed surface in the same procedure as the manufacturing method according to the above-described embodiment, and then the patterning is performed.
The n-side electrode formed in this way is considered to have a low contact resistance with respect to the n-type layer.
(その他の発明の開示)
当業者であれば、以下に記載する表面処理方法、半導体素子の製造方法またはGaN系発光ダイオード素子に関する発明が、本明細書に開示されていることを理解するであろう。
(a1)m面GaN基板の表面を、酸性のCMPスラリーを用いて0.5μm/h以下のポリッシングレートでポリッシングする第1工程と、該第1工程に続いて該m面GaN基板の該表面を水洗する第2工程と、を有するm面GaN基板の表面処理方法。
(a2)前記CMPスラリーのpHが2未満である、前記(a1)に記載の表面処理方法。
(a3)前記第1工程では前記m面GaN基板の表面をポリッシュ後の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下となるようにポリッシングする、前記(a1)または(a2)に記載の表面処理方法。
(a4)n型導電性を有するm面GaN基板の表面にオーミック電極を形成する電極形成工程を有するとともに、該電極形成工程の前に、該表面の仕上げ工程として前記(a1)〜(a3)のいずれかに記載の表面処理方法を用いた表面処理を該表面に施す表面処理工程を有する、半導体素子の製造方法。
(a5)前記n型導電性を有するm面GaN基板のキャリア濃度が1×1017cm−3である、半導体素子の製造方法。
(Disclosure of other inventions)
Those skilled in the art will understand that the invention relating to the surface treatment method, semiconductor device manufacturing method, or GaN-based light-emitting diode device described below is disclosed herein.
(A1) A first step of polishing the surface of the m-plane GaN substrate using an acidic CMP slurry at a polishing rate of 0.5 μm / h or less, and the surface of the m-plane GaN substrate following the first step And a second step of washing the surface with water.
(A2) The surface treatment method according to (a1), wherein the pH of the CMP slurry is less than 2.
(A3) The surface treatment method according to (a1) or (a2), wherein in the first step, the surface of the m-plane GaN substrate is polished so that the arithmetic average roughness Ra after polishing is 0.1 nm or less. .
(A4) An electrode forming step of forming an ohmic electrode on the surface of an n-type GaN substrate having n-type conductivity, and (a1) to (a3) as the surface finishing steps before the electrode forming step. A method for manufacturing a semiconductor element, comprising a surface treatment step of performing a surface treatment on the surface using the surface treatment method according to any one of the above.
(A5) The method for manufacturing a semiconductor element, wherein the m-plane GaN substrate having n-type conductivity has a carrier concentration of 1 × 10 17 cm −3 .
(b1)n型GaN系半導体の露出したm面を、酸性のCMPスラリーを用いて0.5μm/h以下のポリッシングレートでポリッシングする第1工程と、該第1工程に続いて該m面を水洗する第2工程と、を有する表面処理方法。
(b2)前記CMPスラリーのpHが2未満である、前記(b1)に記載の表面処理方法。
(b3)前記第1工程では前記m面をポリッシュ後の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下となるようにポリッシングする、前記(b1)または(b2)に記載の表面処理方法。
(b4)n型GaN系半導体の露出したm面上にオーミック電極を形成する電極形成工程を有するとともに、該電極形成工程の前に、該m面の仕上げ工程として前記(b1)〜(b3)のいずれかに記載の表面処理方法を用いた表面処理を該m面に施す表面処理工程を有する、半導体素子の製造方法。
(b5)前記n型GaN系半導体が、m面GaN基板を用いてエピタキシャル成長により形成されたn型GaN系半導体層である、前記(b4)に記載の製造方法。
(B1) A first step of polishing the exposed m-plane of the n-type GaN-based semiconductor using an acidic CMP slurry at a polishing rate of 0.5 μm / h or less, and the m-plane following the first step. A surface treatment method comprising: a second step of washing with water.
(B2) The surface treatment method according to (b1), wherein the pH of the CMP slurry is less than 2.
(B3) The surface treatment method according to (b1) or (b2), wherein in the first step, the m-plane is polished so that the arithmetic average roughness Ra after polishing is 0.1 nm or less.
(B4) An electrode forming step of forming an ohmic electrode on the exposed m-plane of the n-type GaN-based semiconductor, and the steps (b1) to (b3) as finishing steps of the m-plane before the electrode forming step. A method for producing a semiconductor element, comprising a surface treatment step of performing surface treatment on the m-plane using the surface treatment method according to any one of the above.
(B5) The manufacturing method according to (b4), wherein the n-type GaN-based semiconductor is an n-type GaN-based semiconductor layer formed by epitaxial growth using an m-plane GaN substrate.
(c1)GaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層がこの順に積層され、その積層方向が該GaN系半導体のm軸と平行である半導体積層体と、該p型層に接続されたp側電極と、該n型層の該活性層側の表面とは反対側の表面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が20mAのときの順方向電圧が4.0V以下であるGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c2)GaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層がこの順に積層され、その積層方向が該GaN系半導体のm軸と平行である半導体積層体と、該p型層に接続されたp側電極と、該n型層の該活性層側の表面とは反対側の表面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が60mAのときの順方向電圧が4.5V以下であるGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c3)GaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層がこの順に積層され、その積層方向が該GaN系半導体のm軸と平行である半導体積層体と、該p型層に接続されたp側電極と、該n型層の該活性層側の表面とは反対側の表面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が120mAのときの順方向電圧が5.0V以下であるGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c4)GaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層がこの順に積層され、その積層方向が該GaN系半導体のm軸と平行である半導体積層体と、該p型層に接続されたp側電極と、該n型層の該活性層側の表面とは反対側の表面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が200mAのときの順方向電圧が5.5V以下であるGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c5)GaN系半導体からなるn型層、活性層およびp型層がこの順に積層され、その積層方向が該GaN系半導体のm軸と平行である半導体積層体と、該p型層に接続されたp側電極と、該n型層の該活性層側の表面とは反対側の表面に形成されたn側オーミック電極とを有し、当該発光ダイオード素子に印加される順方向電流が350mAのときの順方向電圧が6.0V以下であるGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c6)前記n型層の前記n側オーミック電極が形成された側の表面の面積が0.0012cm2以上である、前記(c1)〜(c5)のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c7)前記n側オーミック電極の面積が0.0012cm2以上、前記前記n型層の前記n側オーミック電極が形成された側の表面の面積以下である、前記(c6)に記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(c8)前記n型層の表面は、少なくとも前記n側オーミック電極と接触する部分において、10μm角の範囲の算術平均粗さRaが0.1nm以下である、前記(c1)〜(c7)のいずれかに記載のGaN系発光ダイオード素子。
(C1) An n-type layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are stacked in this order, and the stacking direction is parallel to the m-axis of the GaN-based semiconductor and connected to the p-type layer A p-side electrode and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the surface of the n-type layer opposite to the active layer side, and a forward current applied to the light-emitting diode element is 20 mA. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 4.0 V or less at
(C2) An n-type layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are stacked in this order, and the stacking direction is parallel to the m-axis of the GaN-based semiconductor and connected to the p-type layer A p-side electrode and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the surface of the n-type layer opposite to the surface on the active layer side, and a forward current applied to the light-emitting diode element is 60 mA. A GaN-based light-emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 4.5 V or less at the time.
(C3) An n-type layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are stacked in this order, and the stacking direction is parallel to the m-axis of the GaN-based semiconductor and connected to the p-type layer A p-side electrode and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the surface of the n-type layer opposite to the surface on the active layer side, and a forward current applied to the light-emitting diode element is 120 mA. A GaN-based light-emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 5.0 V or less at the time.
(C4) An n-type layer made of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are stacked in this order, and the stacking direction is parallel to the m-axis of the GaN-based semiconductor and connected to the p-type layer A p-side electrode and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the surface of the n-type layer opposite to the active layer side, and a forward current applied to the light-emitting diode element is 200 mA. A GaN-based light-emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 5.5 V or less at the time.
(C5) An n-type layer composed of a GaN-based semiconductor, an active layer, and a p-type layer are stacked in this order, and the stacking direction is parallel to the m-axis of the GaN-based semiconductor and connected to the p-type layer A p-side electrode and an n-side ohmic electrode formed on the surface of the n-type layer opposite to the surface on the active layer side, and a forward current applied to the light-emitting diode element is 350 mA. A GaN-based light emitting diode element having a forward voltage of 6.0 V or less at
(C6) The GaN-based light-emitting diode element according to any one of (c1) to (c5), wherein an area of a surface of the n-type layer on which the n-side ohmic electrode is formed is 0.0012 cm 2 or more. .
(C7) The GaN-based material according to (c6), wherein an area of the n-side ohmic electrode is 0.0012 cm 2 or more and an area of a surface of the n-type layer on the side where the n-side ohmic electrode is formed. Light emitting diode element.
(C8) The surface of the n-type layer has an arithmetic average roughness Ra in the range of 10 μm square of 0.1 nm or less in at least a portion in contact with the n-side ohmic electrode, according to (c1) to (c7) The GaN-based light emitting diode element according to any one of the above.
100、101、102、103、104、105、106、107、108、109 GaN系発光ダイオード素子
110 基板
112a 低接触抵抗領域
112b 高接触抵抗領域
120 エピ層
121 n型層
122 活性層
123 p型層
E100 n側電極
E101 n側オーミック電極
E102 n側電極パッド
E103 補助電極
E200 p側電極
E201 p側オーミック電極
E202 p側電極パッド
E203 補助電極
G100 素子分離溝
R100 誘電体反射膜
100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109 GaN-based light emitting
Claims (5)
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012268708A JP5234218B1 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-12-07 | Light emitting diode element |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| WOPCT/JP2012/072922 | 2012-09-07 | ||
| PCT/JP2012/072922 WO2013039003A1 (en) | 2011-09-12 | 2012-09-07 | Light-emitting diode element |
| JP2012268708A JP5234218B1 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-12-07 | Light emitting diode element |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP5234218B1 true JP5234218B1 (en) | 2013-07-10 |
| JP2014053578A JP2014053578A (en) | 2014-03-20 |
Family
ID=48913994
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012268708A Active JP5234218B1 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-12-07 | Light emitting diode element |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5234218B1 (en) |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004115305A (en) * | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-15 | Showa Denko Kk | Gallium nitride single crystal substrate, method of manufacturing the same, gallium nitride-based semiconductor device and light emitting diode |
| JP2008258503A (en) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Nitride-based semiconductor light emitting element, and method of fabricating nitride-based semiconductor light emitting element |
| JP2009123969A (en) * | 2007-11-15 | 2009-06-04 | Tohoku Univ | Ultraviolet nitride semiconductor light-emitting element and its manufacturing method |
| WO2011083551A1 (en) * | 2010-01-06 | 2011-07-14 | パナソニック株式会社 | Nitride semiconductor light-emitting element and process for production thereof |
-
2012
- 2012-12-07 JP JP2012268708A patent/JP5234218B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004115305A (en) * | 2002-09-26 | 2004-04-15 | Showa Denko Kk | Gallium nitride single crystal substrate, method of manufacturing the same, gallium nitride-based semiconductor device and light emitting diode |
| JP2008258503A (en) * | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | Nitride-based semiconductor light emitting element, and method of fabricating nitride-based semiconductor light emitting element |
| JP2009123969A (en) * | 2007-11-15 | 2009-06-04 | Tohoku Univ | Ultraviolet nitride semiconductor light-emitting element and its manufacturing method |
| WO2011083551A1 (en) * | 2010-01-06 | 2011-07-14 | パナソニック株式会社 | Nitride semiconductor light-emitting element and process for production thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014053578A (en) | 2014-03-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2013039003A1 (en) | Light-emitting diode element | |
| KR100967841B1 (en) | Gallium nitride-based compound semiconductor light-emitting device | |
| JP5556657B2 (en) | Group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device manufacturing method, group III nitride semiconductor light emitting device, and lamp | |
| JP5232968B2 (en) | LIGHT EMITTING ELEMENT, ITS MANUFACTURING METHOD, AND LAMP | |
| US7947995B2 (en) | Gallium nitride-based compound semiconductor light emitting device | |
| US8173461B2 (en) | Process for fabrication of nitride semiconductor light emitting device | |
| US20150014702A1 (en) | Light-emitting diode having improved light extraction efficiency and method for manufacturing same | |
| JP2004281863A (en) | Nitride semiconductor element and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2007220972A (en) | Semiconductor light-emitting element, manufacturing method thereof, and lamp | |
| JP2005268581A (en) | Gallium nitride family compound semiconductor light emitting device | |
| JP4626306B2 (en) | Nitride semiconductor light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP5234219B1 (en) | Light emitting diode element and light emitting device | |
| JP2013084750A (en) | Method of manufacturing gan-based light-emitting diode | |
| JP5640398B2 (en) | Nitride semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof | |
| JP2014053614A (en) | Light emitting diode element | |
| JP4959184B2 (en) | Method for manufacturing nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device | |
| JP2013258207A (en) | Semiconductor light-emitting element and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP5234218B1 (en) | Light emitting diode element | |
| JP5234220B1 (en) | Light emitting diode element | |
| JP2009094108A (en) | MANUFACTURING METHOD OF GaN-BASED LED DEVICE | |
| JP5163970B1 (en) | Light emitting diode element | |
| JP5398937B1 (en) | Nitride semiconductor light emitting chip, nitride semiconductor light emitting device, and method of manufacturing nitride semiconductor chip | |
| JP2013074071A (en) | GaN-BASED LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE | |
| JP2013062542A (en) | SURFACE TREATMENT METHOD OF m-SURFACE GaN SUBSTRATE | |
| JP2011091442A (en) | Semiconductor light emitting diode of gallium nitride compound |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160405 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313111 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |