JP4835518B2 - Probe information collection system - Google Patents
Probe information collection system Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4835518B2 JP4835518B2 JP2007154969A JP2007154969A JP4835518B2 JP 4835518 B2 JP4835518 B2 JP 4835518B2 JP 2007154969 A JP2007154969 A JP 2007154969A JP 2007154969 A JP2007154969 A JP 2007154969A JP 4835518 B2 JP4835518 B2 JP 4835518B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- information
- probe
- quality
- data
- unit
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 title claims description 242
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 claims description 47
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 claims description 32
- 238000013500 data storage Methods 0.000 description 37
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 29
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 24
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 14
- 230000010365 information processing Effects 0.000 description 12
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
Description
本発明は、プローブ情報収集システムに関する。 The present invention relates to a probe information collection system .
従来、複数の車両にそれぞれ搭載された複数のプローブ装置から、搭載先の車両の走行状況の情報(以下、プローブ情報という)が、プローブ情報センタに送信され、プローブ情報センタにおいて、当該プローブ情報が加工されて配信データとなり、作成した配信データがプローブ情報センタから通信装置に配信されるという、プローブ情報収集システムの技術が知られている(例えば特許文献1参照)。このような技術を実用化する方法として、タクシー、バス等の既存の配車システムで用いられる車両にプローブ装置を搭載することが考えられている。
しかし、プローブ情報を送信する側の車両の業務形態は様々なので、各車両から送信されるプローブデータの内容間にばらつきが生じる。したがって、プローブ情報センタ側が必要としている情報が、プローブセンタに効率的に提供されない場合が多い。 However, since the business forms of the vehicle on the probe information transmission side are various, variations occur between the contents of the probe data transmitted from each vehicle. Therefore, the information required by the probe information center is often not efficiently provided to the probe center.
本発明は上記点に鑑み、プローブ情報収集システムにおいて、プローブ情報センタが、必要とする情報を効率的に取得できるようにすることを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above points, and an object of the probe information collection system is to enable a probe information center to efficiently acquire necessary information.
上記目的を達成するための本発明の第1の特徴は、それぞれ異なる車両に搭載された複数のプローブ装置が検出した搭載先の車両の走行状況の情報を受信し、それら受信した走行状況の情報を加工した結果の加工情報を、複数の通信装置に配信するプローブ情報センタについてのものである。このプローブ情報センタが、受信した走行状況の情報のうち、情報の提供者を示す提供者識別情報と関連付けられた状態で送信された走行状況の情報の品質を特定し、当該提供者識別情報に対応する提供者に、特定した品質が高いほど高い対価を提供するための処理を行う。 In order to achieve the above object, the first feature of the present invention is that it receives information on the driving situation of a mounting destination vehicle detected by a plurality of probe devices mounted on different vehicles, and receives the information on the received driving situation. This is for a probe information center that distributes processing information obtained as a result of processing to a plurality of communication devices. The probe information center identifies the quality of the driving situation information transmitted in a state associated with the provider identification information indicating the provider of the information among the received driving situation information, and includes the provider identification information. The corresponding provider is processed to provide higher consideration as the identified quality is higher.
このようになっていることで、プローブ情報センタに送信される走行状況の情報の品質が、当該第1品質指標において高いほど、その提供者への対価が向上する。これによって、情報提供者に、プローブ情報センタの第1品質指標によって高く評価される情報を提供しようというインセンティブが働き、その結果、プローブ情報センタは、必要となる情報を効率的に取得できるようになる。 In this way, the higher the quality of the traveling state information transmitted to the probe information center in the first quality index, the higher the consideration for the provider. As a result, an incentive to provide the information provider with information highly evaluated by the first quality index of the probe information center works, and as a result, the probe information center can efficiently acquire necessary information. Become.
ここで、走行状況の情報とは、走行時の外部環境(例えば勾配)、および、走行時の車両挙動(例えば電力消費量、車速)のうちいずれかまたは両方の情報をいう。また、車両の走行状況の情報は、プローブ装置からプローブ情報センタへ無線通信等を介して送信されるようになっていてもよいし、人がプローブ装置から車両の走行状況の情報を記録している記憶媒体を搬出し、他の通信装置に当該記憶媒体を接続したときに、当該通信装置からプローブ情報センタへ無線通信等を介して送信されるようになっていてもよい。すなわち、プローブ情報センタは、プローブ装置が検出した車両の走行状況の情報を最終的に受信すれば足りるのであって、その受信経路はどのようなものであってもよい。 Here, the information on the traveling state refers to information on one or both of the external environment (for example, gradient) during traveling and the vehicle behavior (for example, power consumption, vehicle speed) during traveling. In addition, the vehicle travel status information may be transmitted from the probe device to the probe information center via wireless communication or the like, or a person records the vehicle travel status information from the probe device. When the storage medium is unloaded and the storage medium is connected to another communication apparatus, the communication medium may be transmitted from the communication apparatus to the probe information center via wireless communication or the like. That is, the probe information center only needs to finally receive information on the traveling state of the vehicle detected by the probe device, and any reception path may be used.
また、ここでいう「所定の」とは、「あらかじめ定められた」という意味である。そして、この「あらかじめ」とは、その所定の品質指標が実際に用いられる前にという意味である。したがって、あらかじめ定められる時期は、このプローブ情報センタの製造時でもよいし、その品質指標が用いられる直前であってもよい。また、「対価」とは、金銭的対価のみをいうのではなく、配信するデータの付加価値の高さ等であってもよい。 The “predetermined” here means “predetermined”. The term “in advance” means that the predetermined quality index is not actually used. Therefore, the predetermined time may be at the time of manufacturing the probe information center, or may be just before the quality index is used. Further, “consideration” does not mean only monetary consideration but may be high added value of data to be distributed.
また、「提供者識別情報に対応する提供者に、特定した品質が高いほど高い対価を提供するための処理」としては、具体的には、当該提供者識別情報に対応する通信装置に配信する加工情報を、特定した品質が高いほどその加工情報の所定の第2品質指標に基づいた品質が高くなるよう決定し、さらに、決定したこの加工情報を、当該提供者識別情報に対応する通信装置に配信する処理であってもよい。このようになっていることで、走行状況の情報の提供者は、提供した当該情報の品質が第1品質指標に照らして高ければ高いほど、より高い品質の加工データの配信を受けることができる。 In addition, as “a process for providing higher value to the provider corresponding to the provider identification information as the specified quality is higher”, specifically, the process is delivered to the communication device corresponding to the provider identification information. The processing information is determined such that the higher the specified quality is, the higher the quality is based on a predetermined second quality index of the processing information, and the processing information thus determined is a communication device corresponding to the provider identification information. It may be a process of delivering to. In this way, the provider of the travel status information can receive higher quality processed data as the quality of the provided information is higher in light of the first quality index. .
また、プローブ情報センタは、第1品質指標として、過去の基準時間範囲内において受信された同一の提供者識別情報を有するすべての走行状況の情報についての総データ量またはデータ受信頻度が多いほど高品質であるという指標を用いるようになっていてもよい。 In addition, the probe information center, as the first quality index, increases as the total data amount or the data reception frequency increases with respect to all travel status information having the same provider identification information received within the past reference time range. An indicator of quality may be used.
このようになっていることで、ある提供者がプローブ装置が搭載された車両を多数有している場合、それらプローブ装置が検出した走行状況の情報に同一の提供者識別情報を関連付ければ、プローブ情報センタにおいては、当該提供者から受ける走行状況の情報の量および頻度が、他の提供者に比べて増大する。したがって、いわゆる大口の提供者が優遇される。 In this way, when a certain provider has a large number of vehicles equipped with probe devices, if the same provider identification information is associated with the information on the driving situation detected by the probe devices, In the probe information center, the amount and frequency of travel situation information received from the provider is increased compared to other providers. Therefore, so-called large providers are favored.
また、本発明の第2の特徴は、送信装置が、それぞれ異なる車両に搭載された複数のプローブ装置が検出した搭載先の車両の走行状況の情報を取得し、それら取得した走行状況の情報のそれぞれに、同一の提供者識別情報を関連付け、また、関連付けた結果の走行状況の情報を、上述のような第1品質指標を採用するプローブ情報センタに送信することである。 In addition, according to a second feature of the present invention, the transmission device acquires information on a traveling state of a mounting destination vehicle detected by a plurality of probe devices mounted on different vehicles, and the acquired information on the traveling state is acquired. The same provider identification information is associated with each other, and the information on the traveling status as a result of the association is transmitted to the probe information center that employs the first quality index as described above.
このようになっていることで、装置が搭載される車両を複数台有する大口の提供者の提供者識別情報の、車両の状況情報への関連付けは、プローブ装置で個々に行われるのではなく、送信装置で一括して行われる。したがって、提供者識別情報を個々のプローブ装置が有する必要がなくなる。 In this way, the association of the provider identification information of the large provider having a plurality of vehicles on which the device is mounted with the vehicle status information is not individually performed by the probe device, It is performed in a lump in the transmission device. Therefore, it is not necessary for each probe apparatus to have provider identification information.
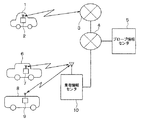
以下、本発明の一実施形態について説明する。図1に、本実施形態に係るプローブ情報収集システムの一例を概略的に示す。プローブ情報収集システムにおいては、車両1、6、8のそれぞれに搭載されたプローブ装置2、7、9が、搭載先の車両のプローブ情報を検出し、その検出されたプローブ情報を最終的にプローブ情報センタ5が受信する。
Hereinafter, an embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 1 schematically shows an example of a probe information collection system according to this embodiment. In the probe information collection system, the
ここで、車両のプローブ情報とは、当該車両の走行状況の情報をいう。走行状況の情報とは、走行時の外部環境および走行時の車両挙動のうちいずれかまたは両方の情報をいう。車両の走行状況の情報としては、例えば、当該車両の所在位置情報、走行速度情報、路面勾配情報、および、これらのプローブ情報を取得した時刻の情報等がある。各プローブ装置2、7、9は、これらの情報を、車両に搭載された各種センサ(例えば、GPS受信機、車速センサ、傾斜センサ等)を用いて検出する。また、プローブ装置2、7、9は、カーナビゲーション装置等で広く利用されているマップマッチング処理を行うことができる場合、マップマッチングの結果の位置を自車両の所在位置として検出してもよい。また、プローブ情報には、所在位置の検出のためにマップマッチングを利用したか否かを示す情報を含める。
Here, the probe information of the vehicle refers to information on the traveling state of the vehicle. The information on the traveling state refers to information on either or both of the external environment during traveling and the vehicle behavior during traveling. Examples of the vehicle travel status information include location information of the vehicle, travel speed information, road surface gradient information, and information on the time at which these probe information is acquired. Each
個人の有する車両である車両1に搭載されたプローブ装置2で検出されたプローブ情報は、プローブ装置2から携帯電話網3までの無線通信路および通信網4を介してプローブ情報センタ5に送信される。通信網4は、インターネット等の広域ネットワークであってもよいし、プローブ情報の提供のためだけの専用回線であってもよい。
Probe information detected by the
また、同じ1つの業者の所有する業者車両6、8に搭載されたプローブ装置7、9で検出されたプローブ情報は、プローブ装置7、9から業者情報センタ10に渡される。そして業者情報センタ10は、受けたプローブ情報を通信網4を介してプローブ情報センタ5に送信する。なお、プローブ装置7、9から業者情報センタ10へのプローブ情報の提供は、図1に示すような無線通信によって実現してもよいし、あるいは、プローブ装置7、9からプローブ情報が記録された記憶媒体を人が業者情報センタ10まで運び、その上で当該記憶媒体を業者情報センタ10に接続することで実現してもよい。
Further, probe information detected by the
ここで、プローブ装置2、7、9から無線によって送信されるプローブ情報の送信形態について説明する。プローブ装置2、7、9は、所定の時間区間(例えば長さ1分の時間区間)毎に、当該時間区間において検出したプローブ情報を、1まとまりのプローブデータフレームとして送信する。そして、当該プローブデータフレームには、検出時刻および検出時の自車両の位置の情報を1つ付加する。また、個人車両1に搭載されたプローブ装置2は、当該プローブデータフレームに、個人車両1の所有者の提供者識別情報を付加する。この提供者識別情報は、あらかじめプローブ装置2に登録されている。したがって、プローブ装置2、7、9から無線で送信されるデータは、基本的にリアルタイム性を有している。
Here, a transmission form of probe information transmitted from the
しかし、車両が地下、トンネル内等、無線通信が不能な位置を走行している期間は、プローブデータフレームを送信できないので、その期間中のプローブデータフレームは、無線通信が回復して後送信する。このような場合のプローブデータフレームは、リアルタイム性を有していない場合がある。 However, since the probe data frame cannot be transmitted while the vehicle is traveling in a position where wireless communication is not possible, such as underground or in a tunnel, the probe data frame during that period is transmitted after the wireless communication is recovered. . The probe data frame in such a case may not have real-time characteristics.
また、業者車両6、8に搭載されたプローブ装置7、9から業者情報センタ10まで運ばれる記憶媒体中のプローブ情報について説明する。記憶媒体中のプローブ情報は、1日、半日、数日等、無線送信するデータよりも長い期間内に複数回検出された情報の集合体となっており、各回に検出されたデータには、その検出時時刻および検出位置の情報が付加されている。
The probe information in the storage medium carried from the
プローブ情報センタ5は、このようにして受信した各車両2、5、7からのプローブ情報に対して統計処理等を行うことで、当該プローブデータを加工し、その加工結果の情報を、プローブ装置2、業者情報センタ10、および他の通信装置に配信する。そしてこの配信時に、その配信先から過去に提供されたプローブ情報の品質の高低に基づいて、どのような品質の加工情報を当該配信先に送信するかを決定する。
The
図2に、業者情報センタ10の構成を概略的に示す。業者情報センタ10は、無線部11、ネットワークI/F部12、外部データ読取部13、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部14、過去データ蓄積部15、および制御部16を有している。
FIG. 2 schematically shows the configuration of the
無線部11は、業者車両6、8と無線通信することでプローブ情報を受信する装置である。ネットワークI/F部12は、通信網4に接続し、プローブ情報センタ5とのデータの授受を実現するためのインターフェースである。外部データ読取部13は、プローブ装置によって検出されたプローブ情報が記録されている記憶媒体から、当該プローブ情報を読み取る装置である。リアルタイムデータ蓄積部14は、無線部11が受信したプローブ情報のうち、リアルタイム性のある情報をリアルタイムデータとして記憶するための記憶媒体を有する装置である。過去データ蓄積部15は、無線部11が受信したプローブ情報のうちリアルタイム性のない情報、および、外部データ読取部13が読み取ったプローブ情報を、過去データとして記憶するための記憶媒体を有する装置である。
The
制御部16は、これら各部11〜15の作動を制御する装置である。具体的には、制御部16は、無線部11が受信したプローブデータフレームの個々について、リアルタイム性があるか否かを判定し、リアルタイム性があれば当該プローブデータフレームをリアルタイムデータ蓄積部14に記憶させ、リアルタイム性がなければ当該プローブデータフレームを過去データ蓄積部15に記憶させる。なお、リアルタイム性があると判定する場合は、当該プローブデータフレームに含まれる、プローブ情報の検出時刻の情報が、現在から基準時間幅(例えば5分、10分)未満の過去を示している場合である。また、リアルタイム性がないと判定する場合は、当該プローブデータフレームに含まれる、プローブ情報の検出時刻の情報が、現在から基準時間幅(例えば5分、10分)以上の過去を示している場合である。
The
また、制御部16は、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部14に記録されたプローブデータフレームのうち、時間が経過したことによってリアルタイム性が失われたプローブデータフレームを、過去データとして、過去データ蓄積部15に移動させる。
Also, the
また、制御部16は、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部14中のプローブデータフレームについては、それがリアルタイムデータ蓄積部14中に記録されるとすぐに(例えば10秒以内に)、プローブ情報センタ5へ送信する。また、制御部16は、過去データ蓄積部15中の過去データについては、所定のタイミング(例えば1時間間隔のタイミング)で、前回のタイミングから今回のタイミングまでに取得した過去データをまとめて1つのプローブデータフレームとして、プローブ情報センタ5へ送信する。
The
また、制御部16は、プローブデータフレームを送信するとき、各プローブデータフレームに、そのプローブデータフレームがどの車両のプローブ装置によって検出されたかに関らず、同一の提供者識別情報を付加した上で、ネットワークI/F部12を用いてプローブ情報センタ5に送信する。ここで付加する提供者識別情報は、業者情報センタ10を有する業者に、あらかじめ契約時に割り当てられた提供者識別情報である。
Further, when transmitting the probe data frame, the
なお、プローブ装置2、7、業者情報センタ10、および他の通信装置は、ユーザの操作に基づいて、プローブ情報センタ5に対して配信要求を送信するようになっていてもよい。
Note that the
図3に、プローブ情報センタ5の構成を概略的に示す。プローブ情報センタ5は、ネットワークI/F部52、個別データ記憶部53、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部54、過去データ蓄積部55、リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部56、統計渋滞情報加工部57、配信用渋滞情報分配部58、リアルタイムデータ送信部59、統計データ送信部60、および制御部61を有している。
FIG. 3 schematically shows the configuration of the
ネットワークI/F部52は、通信網4に接続し、業者情報センタ10とのデータの授受を実現するためのインターフェースである。個別データ記憶部53は、ネットワークI/F部52を介して受けたプローブ情報を一時的に記録するための記憶媒体を有する装置である。リアルタイムデータ蓄積部54は、個別データ記憶部53に蓄積されたデータのうち、リアルタイム性のあるデータをリアルタイムデータとして記憶するための記憶媒体を有する装置である。過去データ蓄積部55は、個別データ記憶部53に蓄積されたデータのうち、リアルタイム性のないデータを過去データとして記憶するための記憶媒体を有する装置である。
The network I /
リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部56は、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部54中のリアルタイムデータを加工することで、速報性のある渋滞情報を生成する装置である。統計渋滞情報加工部57は、過去データ蓄積部55中の過去データを加工することで、過去の渋滞の統計を示す統計渋滞情報を生成する装置である。
The real-time traffic jam
配信用渋滞情報分配部58は、リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部56で生成された情報のうち、配信する必要がある情報をリアルタイムデータ送信部59に出力し、また、統計渋滞情報加工部57で生成された情報のうち、配信する必要がある情報を統計データ送信部60に出力する。配信する必要があるか否かは、ネットワークI/F部52を介して、プローブ装置2、7、9または他の通信装置から、限定された(例えば特定の地域に限定された)配信対象についての配信要求があった場合、その限定内容に基づいて判定する。
The distribution traffic
リアルタイムデータ送信部59は、配信用渋滞情報分配部58から受けたリアルタイムデータを、ネットワークI/F部52を用いて、配信要求の送信元に配信する。統計データ送信部60は、配信用渋滞情報分配部58から受けた過去データを、ネットワークI/F部52を用いて、配信要求の送信元に配信する。リアルタイムデータ送信部59および統計データ送信部60は、配信用渋滞情報分配部58から受けたデータを、どの通信装置に宛てて送信するかについては、後述する通り制御部61によって登録された送信先のデータに従って決定する。
The real-time
制御部61は、プローブ情報センタ5の各部52〜60を制御する。具体的には、制御部61は、図4に示すプローブ情報受信処理100、および図5に示す情報提供処理200を必要に応じて繰り返し実行するようになっている。
The
具体的には、制御部61は、プローブ情報受信処理100を実行しておらず、かつネットワークI/F部52がプローブデータフレームを受信したことに基づいて、プローブ情報受信処理100の実行を開始する。そして、プローブ情報受信処理100の1回の実行において、現在時刻と、受信したプローブデータフレーム中の検出時刻とを比較することで、検出時刻に対する現在時刻の遅れが許容幅(例えば5分、10分)を超えているか否かを判定し(ステップ110)、許容幅以下であれば、プローブデータフレーム中のリアルタイムフラグ(以下、Rフラグという)をオンにセットする(ステップ115)。
Specifically, the
図6に、プローブデータフレーム70のデータフォーマットを概略的に示す。この図に示すように、プローブ装置2、業者情報センタ10等から送信され、プローブ情報センタ5が受信するプローブデータフレーム70は、提供者識別情報部71、プローブ情報部72、Rフラグ部73、Mフラグ部74、Tフラグ部75、Dフラグ部76を有している。提供者識別情報部71は、提供者識別情報が記録されている部分である。プローブ情報部72は、検出された情報(検出時刻、車速、勾配等、)が記録されている部分である。Rフラグ部73、Mフラグ部74、Tフラグ部75、Dフラグ部76は、それぞれ、Rフラグ、マップマッチングフラグ(以下、Mフラグという)、収集頻度フラグ(以下、Tフラグという)、データ量フラグ(以下、Dフラグという)を記録するための部分である。なお、プローブ装置2、業者情報センタ10当からプローブデータフレーム70が送信された時点では、Rフラグ部73、Mフラグ部74、Tフラグ部75、Dフラグ部76の値はオフとなっている。
FIG. 6 schematically shows the data format of the
続いて制御部61は、プローブデータフレーム70の所在位置情報がマップマッチングを行ったものであるか否かをプローブ情報部72中の情報に基づいて判定し(ステップ120)、マップマッチングを行っていればMフラグをオンにセットする(ステップ125)。
Subsequently, the
続いて、当該プローブデータフレーム70を個別データ記憶部53に記録する(ステップ130)。その後、このプローブ情報受信処理100の今回の開始時以降、基準時間(例えば10分)が経過するまで(ステップ140)、別のプローブデータフレームの受信を待ち(ステップ135)、その受信がある度に、受信したプローブデータフレームに対して、先に受信したプローブデータフレームと同様の処理を施す(ステップ110〜130)。
Subsequently, the
基準時間経過後、制御部61は、今回のプローブ情報受信処理100の開始以降個別データ記憶部53に記録されたプローブデータフレームを、それらの提供者識別情報に基づいてグループ分けし(ステップ145)、それらグループ毎に、プローブデータフレームの数が基準数(例えば、1、2、5)を超えているか否かを判定し(ステップ150)、基準数以上であればTフラグをオンにセットする(ステップ155)。さらに、それらグループ毎に、全プローブデータフレームの総データ量が基準量を超えているか否かを判定し(ステップ160)、超えていればDフラグをオンにセットする(ステップ165)。
After the reference time elapses, the
このように、収集頻度および受信データ量については、提供者識別情報別にまとめて計測および判定を行うので、1つの提供者識別情報に多くのプローブ装置を対応させている提供者、すなわち大口の提供者の方が、1つの提供者識別情報に1つのプローブ装を割り当てている個人の提供者よりも、その計測結果が大きくなり易く、かつ、TフラグおよびDフラグがオンになる可能性が高い。 As described above, since the collection frequency and the amount of received data are measured and determined collectively for each provider identification information, a provider in which many probe devices are associated with one provider identification information, that is, a large provision The measurement result is likely to be larger and the T flag and the D flag are more likely to be turned on than the individual provider who assigns one probe device to one provider identification information. .
以上のような処理100を制御部61が実行することで、プローブ情報センタ5は、受信したプローブデータフレームの時刻がリアルタイム性を有しているか否か、(ステップ110参照)、および、マップマッチングが為されたデータであるか否か(ステップ120参照)について判定し、その判定結果を当該プローブデータフレームにフラグとして付加する(ステップ115、125参照)。そして、基準時間範囲内で取得した(ステップ135、140参照)プローブデータフレームを提供者識別情報別に分け、各提供者識別情報毎に、プローブデータフレームの収集頻度が基準より高いか否か(ステップ150参照)、および、プローブデータフレームの総受信データ量が基準より多いか否か(ステップ160参照)を判定し、その判定結果を、当該提供者識別情報を有するプローブデータフレームにフラグとして付加する(ステップ155、165参照)。その結果、個別データ記憶部53には、図7に示すように、提供者識別情報毎にフラグ値が異なる複数のプローブデータフレームが格納された状態となる。
When the
また、制御部61は、プローブ情報受信処理100の実行直後に情報提供処理200の実行を開始し、まず、直前のプローブ情報受信処理100によって個別データ記憶部53に格納されたプローブデータフレーム(以下、新規プローブデータフレームという)のそれぞれについて、それがリアルタイム性を有しているか否かを、Rフラグの値に基づいて判定し(ステップ205)、リアルタイムデータであればリアルタイムデータ蓄積部54に追加蓄積(ステップ220)した後に、リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部56を制御するこことで、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部54中の全データを加工して渋滞情報を生成する(ステップ225)。また、当該プローブデータフレームがリアルタイムデータでなければ過去データ蓄積部55に追加蓄積(ステップ210)した後に、統計渋滞情報加工部57を制御するこことで、過去データ蓄積部55中のデータを加工して渋滞情報を生成する(ステップ215)。なお、渋滞情報とは、どの程度の長さの渋滞があるか等を示す情報をいう。
Also, the
さらに制御部61は、個別データ記憶部53中の新規プローブデータフレームを参照することで(ステップ230)、新規プローブデータフレームのそれぞれについて、そのRフラグおよびDフラグのうち少なくともいずれか一方がオンとなっているか、あるいはそうでないかを判定する(ステップ235)。そして、その判定が肯定的となったプローブデータフレーム中の提供者識別情報を、品質の高いデータを提供した提供者として、リアルタイムデータ送信部59に登録し(ステップ240)、その判定が否定的となったプローブデータフレーム中の提供者識別情報を、品質の低いデータを提供した提供者として、リアルタイムデータ送信部59に登録する(ステップ245)。
Further, the
このとき、配信用渋滞情報分配部58は、リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部56で生成されたデータをリアルタイムデータ送信部59に渡し、統計渋滞情報加工部57で生成されたデータを統計データ送信部60に渡す。配信用渋滞情報分配部58からデータを受けたリアルタイムデータ送信部59および統計データ送信部60は、自己に登録された提供者識別情報に対応する送信先の通信装置(携帯電話機であれば電話番号、業者情報センタのような装置であればネットワーク上のアドレス)に、受けたデータの送信を行う。
At this time, the distribution traffic
したがって、プローブ情報センタ5において決められたステップ235の品質指標(第1品質指標の一例に相当する)によって品質が高いと判定されたプローブ情報を送信した提供者は、リアルタイム性のある高品質の渋滞情報の配信を受けることができ、当該品質指標によって品質が低いと判定されたプローブ情報を送信した提供者は、リアルタイム性のない低品質の渋滞情報の配信を受けることになる。なお、配信するデータの品質の高低の指標(第2品質指標の一例に相当する)も、プローブ情報センタ5によってあらかじめ決められている。
Therefore, the provider who has transmitted the probe information determined to have high quality according to the quality index of
以上のような情報提供処理200を制御部61が繰り返し実行することで、プローブ情報センタ5は、個別データ記憶部53に記録されたプローブデータフレームのそれぞれについて、それがリアルタイムデータであるか過去データであるかによって格納先を分け(ステップ205参照)、さらに仕分けされたデータをそれぞれリアルタイム渋滞情報および統計渋滞情報として加工する(ステップ215、225参照)。そして、これらプローブデータフレーム中の提供者識別情報とフラグとの対応関係に応じて、提供者識別情報毎に、当該提供者に高品質の(具体的にはリアルタイムの)加工データを送信するか、低品質の(具体的にはリアルタイムでない過去の)加工データを送信するかを決定し(ステップ235参照)、その決定に従った配信を行う(ステップ240、245参照)。
When the
また、制御部16は、リアルタイムデータ蓄積部54に記録されたプローブデータフレームのうち、時間が経過したことによってリアルタイム性が失われたプローブデータフレームを、過去データとして、過去データ蓄積部55に移動させる。リアルタイム性が失われたか否かは、プローブデータフレーム中のプローブ情報部のデータと、現在時刻との比較に基づいて判定する。
Also, the
以上のように、プローブ情報センタ5が、受信したプローブ情報のうち、情報の提供者を示す提供者識別情報と関連付けられた状態で送信されたプローブ情報の品質を特定し、特定した品質が高いほど配信の品質が高くなるよう、当該提供者識別情報に対応する通信装置に配信する加工情報を決定する。
As described above, the
このようになっていることで、プローブ情報センタ5に送信されるプローブ情報の品質が、所定の品質指標において高いほど、そのプローブ情報の提供者への配信品質が向上する。これによって、情報提供者に、プローブ情報センタ5の決めた品質指標によって高く評価される情報を提供しようというインセンティブが働き、その結果、プローブ情報センタ5は、必要となる情報を効率的に取得できるようになる。
In this way, the higher the quality of the probe information transmitted to the
また、プローブ情報センタ5は、受信するプローブ情報に適用する品質指標として、過去の基準時間範囲内において受信された同一の提供者識別情報を有するすべての走行状況の情報についての総データ量が多いほど高品質であるという指標を用いるようになっている。
In addition, the
このようになっていることで、ある提供者が、プローブ装置が搭載された車両を多数有している場合、それらプローブ装置が検出したプローブ情報に同一の提供者識別情報を関連付ければ、プローブ情報センタ5においては、当該提供者から受ける走行状況の情報の量および頻度が、他の提供者に比べて増大する。したがって、いわゆる大口の提供者が優遇される。
In this way, when a certain provider has a large number of vehicles equipped with probe devices, the probe information detected by the probe devices can be associated with the same provider identification information. In the
また、業者情報センタ10が、それぞれ異なる車両に搭載された複数のプローブ装置7、9が検出した搭載先の車両6、8のプローブ情報を取得し、それら取得したプローブ情報のそれぞれに、同一の提供者識別情報を関連付け、また、関連付けた結果のプローブ情報をプローブ情報センタ5に送信するようになっている。
Further, the
このようになっていることで、プローブ装置が搭載される車両を複数台有する大口の提供者の提供者識別情報の、プローブ情報への関連付けは、プローブ装置で個々に行われるのではなく、業者情報センタ10で一括して行われる。したがって、提供者識別情報を個々のプローブ装置が有する必要がなくなる。
In this way, the association of the provider identification information of the large provider having a plurality of vehicles on which the probe device is mounted with the probe information is not performed individually in the probe device, but a contractor. It is performed at the
なお、上記の実施形態において、業者情報センタ10が送信装置の一例に相当し、プローブ装置2、業者情報センタ10が通信装置の一例に相当する。また、制御部61が、処理100を実行することで受信品質特定手段の一例として機能し、処理200を実行すること、配信品質決定手段の一例として機能する。また、リアルタイムデータ送信部59および統計データ送信部60のそれぞれが、配信手段の一例に送信する。また、ネットワークI/F部12が送信手段の一例に相当し、また、制御部16が関連付け手段の一例に相当する。
In the above embodiment, the
また、上記したプローブ情報センタ5および業者情報センタ10の各部11〜16、52〜61は、それらの機能を実現する専用の回路を有したハードウェアとして実現されていてもよいし、それらの機能を実現するためのプログラムを実行するコンピュータとして実現されていてもよい。
Moreover, each part 11-16, 52-61 of the above-mentioned
(他の実施形態)
以上、本発明の実施形態について説明したが、本発明の範囲は、上記実施形態のみに限定されるものではなく、本発明の各発明特定事項の機能を実現し得る種々の形態を包含するものである。
(Other embodiments)
As mentioned above, although embodiment of this invention was described, the scope of the present invention is not limited only to the said embodiment, The various form which can implement | achieve the function of each invention specific matter of this invention is included. It is.
例えば、上記の実施形態においては、高品質配信がリアルタイム渋滞情報の送信となり、低品質配信が統計渋滞情報の送信となっているが、必ずしもこのようになっておらずともよい。例えば、高品質配信がリアルタイム渋滞情報を示す簡易図形+リアルタイム渋滞情報の詳細文字データ(例えば渋滞の総距離等)であり、低品質配信が上記簡易図形のみの配信であってもよい。すなわち、第2品質指標はどのようなものでもよい。 For example, in the above embodiment, high-quality distribution is transmission of real-time traffic jam information and low-quality distribution is transmission of statistical traffic jam information. However, this need not be the case. For example, high-quality distribution may be simple graphics showing real-time traffic jam information + detailed character data of real-time traffic jam information (for example, the total distance of traffic jams), and low-quality delivery may be delivery of only the simple graphics. That is, the second quality index may be anything.
また、上記の実施形態においては、ある提供者からのプローブ情報の品質を判定するための第1品質指標として、当該提供者からのプローブデータフレームがリアルタイム性を有しているか否か、および、当該提供者からのデータ量が多いか否かを採用している。しかし、これら以外にも、当該提供者からのプローブデータフレームがマップマッチングを行っているか否か(すなわちMフラグがオンか否か)、および、当該提供者のプローブ情報の収集頻度が高いか否か(すなわちTフラグがオンか否か)を、第1品質指標として採用してもよい。 In the above embodiment, as a first quality indicator for determining the quality of probe information from a certain provider, whether or not the probe data frame from the provider has real-time characteristics, and Whether the amount of data from the provider is large is adopted. However, in addition to these, whether or not the probe data frame from the provider performs map matching (that is, whether or not the M flag is on) and whether the probe information collection frequency of the provider is high. (That is, whether or not the T flag is on) may be adopted as the first quality index.
また、配信サービスの種別ごとに求められるプローブ情報のデータ項目やデータ量、収集頻度は異なる。したがって、より多くの種別の配信サービスに提供できるプローブデータフレームほど品質が高くなるような指標を、第1品質指標として採用してもよい。 Further, the data items, data amount, and collection frequency of probe information required for each type of distribution service are different. Therefore, an index that increases the quality of probe data frames that can be provided to more types of distribution services may be adopted as the first quality index.
また、上記の実施形態においては、プローブ情報センタ5が配信する情報は、渋滞情報のみとなっているが、プローブ情報センタ5は、複数種類の情報(例えば、渋滞情報および事故情報)を配信するようになっていてもよい。この場合、配信する情報の種類毎に、異なる第1品質指標を設定し、受信したプローブ情報に、それぞれの第1品質指標を適用して品質判定を行い、それら品質判定の結果を複合的に利用して配信データの品質を決定するようになっていてもよい。
In the above embodiment, the information distributed by the
また、上記実施形態においては、直前に受信したプローブデータフレームの提供者に対して、加工した情報を配信するようになっている。しかし、必ずしもこのように、提供元からのプローブデータフレームの受信と加工データの当該提供元への配信とが1対1の連動関係となっている必要はない。例えば、プローブ情報センタ5は、過去にプローブデータフレームを提供したことがある提供元から加工データの配信の要求があったとき、その要求の直前に当該提供元からプローブデータフレームを受けているといないとに関わらず、加工データを配信するようになっていてもよい。
In the above embodiment, the processed information is distributed to the provider of the probe data frame received immediately before. However, it is not always necessary that the reception of the probe data frame from the provider and the distribution of the processed data to the provider have a one-to-one relationship. For example, when the
この場合、当該提供元からプローブ情報の提供があった時点においては、プローブ情報センタ5は、リアルタイムデータ送信部59、統計データ送信部60に提供者識別情報を登録しておき、後に当該提供元から配信要求があったときに初めて、登録内容に応じた品質の配信を行うようになっていてもよい。なお、プローブ情報センタ5は、提供者識別情報と提供者の通信装置との対応情報を有しているので、提供者の通信装置から配信要求に提供者識別情報が含まれていなくても、プローブ情報センタ5は、その対応情報に基づいて、当該通信装置に対応する提供者識別情報を特定することができる。
In this case, at the time when the probe information is provided from the provider, the
また、上記の実施形態においては、プローブ情報センタ5は、配信データの付加価値に変化をつけることで、プローブ情報の品質が高いほど高い対価を提供者に提供するようになっている。しかし、配信についてはこの方法以外にも、プローブ情報を送信するだけでデータの配信を受けない提供者に対して、提供されたプローブ情報の品質が高いほど高い金銭的対価を支払うようになっていてもよい。例えば、プローブ情報センタ5からのデータの配信に対して、配信を受ける側からデータ利用料を(例えば電子マネー等の技術を用いて)受け取り、受け取った利用料を、プローブ情報の提供者に、提供されたプローブ情報の品質の高低に応じて分配するようになっていてもよい。
In the above embodiment, the
1…個人車両、2、7、9…プローブ装置、3…携帯電話網、4…通信網、
5…プローブ情報センタ、6、8…業者車両、10…業者情報センタ、11…無線部、
12…ネットワークI/F部、13…外部データ読取部、
14…リアルタイムデータ蓄積部、15…過去データ蓄積部、16…制御部、
52…ネットワークI/F部、53…個別データ記憶部、
54…リアルタイムデータ蓄積部、55…過去データ蓄積部、
56…リアルタイム渋滞情報加工部、57…統計渋滞情報加工部、
58…配信用渋滞情報分配部、59…リアルタイムデータ送信部、
60…統計データ送信部、61…制御部、70…プローブデータフレーム、
71…提供者識別情報部、72…プローブ情報部、73…Rフラグ部、
74…Mフラグ部、75…Tフラグ部、76…Dフラグ部、
81…プローブデータフレーム、82…プローブデータフレーム、
83…プローブデータフレーム、84…プローブデータフレーム、
100…プローブ情報受信処理、200…情報提供処理。
DESCRIPTION OF
5 ... Probe information center, 6, 8 ... Trader vehicle, 10 ... Trader information center, 11 ... Radio unit,
12 ... Network I / F unit, 13 ... External data reading unit,
14 ... Real time data storage unit, 15 ... Past data storage unit, 16 ... Control unit,
52 ... Network I / F unit, 53 ... Individual data storage unit,
54 ... Real-time data storage unit, 55 ... Past data storage unit,
56 ... Real-time traffic jam information processing unit, 57 ... Statistical traffic jam information processing unit,
58 ... Congestion information distribution unit for distribution, 59 ... Real-time data transmission unit,
60 ... statistical data transmission unit, 61 ... control unit, 70 ... probe data frame,
71 ... provider identification information part, 72 ... probe information part, 73 ... R flag part,
74 ... M flag part, 75 ... T flag part, 76 ... D flag part,
81: Probe data frame, 82: Probe data frame,
83: Probe data frame, 84: Probe data frame,
100: Probe information reception processing, 200: Information provision processing.
Claims (3)
前記複数のプローブ装置が検出した搭載先の車両の走行状況のうち、個人が所有する個人車両の走行状況の情報であり、プローブ装置毎に割り当てられる提供者識別情報と関連付けられた状態で送信された走行状況の情報を、受信する受信手段と、
前記複数のプローブ装置が検出した搭載先の車両の走行状況のうち、同じ1つの業者が所有する複数の業者車両の走行状況の情報を受信し、それら受信した走行状況の情報のそれぞれに、同一の提供者識別情報を関連付ける関連付け手段と、
前記受信手段が受信した前記個人車両の走行状況の情報の品質と、前記関連付け手段によって同一の提供者識別情報が関連付けられた複数の業者車両の走行状況の情報の品質とを、所定の第1品質指標を用いて特定する受信品質特定手段と、
前記提供者識別情報に対応する提供者に、前記品質特定手段が特定した前記品質が高いほど高い対価を提供するための処理を行う対価提供手段と、を備えたプローブ情報収集システム。 Receiving information on the traveling status of the mounting destination vehicle detected by a plurality of probe devices mounted on different vehicles, and distributing processing information obtained as a result of processing the received traveling status information to a plurality of communication devices A probe information collecting system ,
Of the traveling status of the mounting-destination vehicles detected by the plurality of probe devices, this is information on the traveling status of an individual vehicle owned by an individual, and is transmitted in a state associated with provider identification information assigned to each probe device. Receiving means for receiving the information on the traveling state ,
Among the traveling conditions of the mounted vehicles detected by the plurality of probe devices, the information on the traveling conditions of a plurality of dealer vehicles owned by the same dealer is received, and the same information is received for each of the received traveling situation information. Means for associating the provider identification information of
The quality of the information on the travel status of the personal vehicle received by the receiving means and the quality of the information on the travel status of a plurality of dealer vehicles associated with the same provider identification information by the association means A reception quality specifying means for specifying using a quality index;
A probe information collection system comprising: a fee providing unit that performs processing for providing a higher price as the quality specified by the quality specifying unit is higher to a provider corresponding to the provider identification information.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154969A JP4835518B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2007-06-12 | Probe information collection system |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154969A JP4835518B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2007-06-12 | Probe information collection system |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008310396A JP2008310396A (en) | 2008-12-25 |
| JP4835518B2 true JP4835518B2 (en) | 2011-12-14 |
Family
ID=40237969
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007154969A Expired - Fee Related JP4835518B2 (en) | 2007-06-12 | 2007-06-12 | Probe information collection system |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4835518B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN101908274B (en) * | 2010-07-19 | 2013-02-13 | 北京世纪高通科技有限公司 | Method and device for processing road traffic accident information |
| JP6657637B2 (en) * | 2015-07-29 | 2020-03-04 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Information generation system, information generation device, information generation method, information generation program, probe information collection device, probe information collection method, and probe information collection program |
| WO2019159429A1 (en) * | 2018-02-14 | 2019-08-22 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Management device, in-vehicle device, data collection system, data collection method and data collection program |
| JP7070516B2 (en) * | 2019-07-29 | 2022-05-18 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | Information generation system, information generation device, information generation method, information generation program, probe information collection device, probe information collection method, and probe information collection program |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3613275B2 (en) * | 1994-12-28 | 2005-01-26 | オムロン株式会社 | Traffic information system |
| JP4387555B2 (en) * | 2000-05-02 | 2009-12-16 | 日本信号株式会社 | Traffic information system and information system |
| JP2002150467A (en) * | 2000-11-15 | 2002-05-24 | Toshiba Corp | Detection method for traffic conditions |
| JP2003279358A (en) * | 2002-03-26 | 2003-10-02 | Fujitsu Ltd | Method for updating road map data |
| JP2004132830A (en) * | 2002-10-10 | 2004-04-30 | Clarion Co Ltd | Information gathering system |
| JP4026520B2 (en) * | 2003-03-14 | 2007-12-26 | 株式会社日立製作所 | Traffic information display device |
-
2007
- 2007-06-12 JP JP2007154969A patent/JP4835518B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2008310396A (en) | 2008-12-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11615433B2 (en) | Vehicle dispatch device | |
| CN108765933B (en) | Method, device, equipment and storage medium for recommending boarding points | |
| US20180122155A1 (en) | Determining vehicle occupancy using sensors | |
| US6711495B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for gathering vehicle information | |
| US9495813B2 (en) | Vehicle data collection system, vehicle data collection method, vehicle-mounted device, program, and recording medium | |
| CN102682394A (en) | Learning driver demographics from vehicle trace data | |
| US20100321206A1 (en) | Road-vehicle communication system | |
| US10668930B1 (en) | Determining acceptable driving behavior based on vehicle specific characteristics | |
| CN107908644A (en) | The recommendation method, apparatus and computer-readable medium of trip mode | |
| JP4835518B2 (en) | Probe information collection system | |
| CN107392672A (en) | A kind of advertisement broadcast method and vehicle arrangement | |
| JP2011198334A (en) | Information providing device and information processor | |
| US11511769B2 (en) | Data collecting system, server, and data processing apparatus | |
| JP2003248898A (en) | Information management system | |
| JP4862804B2 (en) | Information acquisition device | |
| JP2003196791A (en) | Vehicle operation support system | |
| JP5456444B2 (en) | Travel information collection system and server device | |
| CN114724262A (en) | Data checking method, device, system and computer readable storage medium | |
| JP7219650B2 (en) | Information processing device and vehicle driving situation data collection system | |
| JP2002092104A (en) | Fare-calculating and presenting method | |
| WO2016054700A1 (en) | Online booking system | |
| JP2009048445A (en) | Taximeter | |
| JP2002208094A (en) | Traffic information collection/service system | |
| JP2021026669A (en) | Information processor, method for processing information, and program | |
| WO2022123897A1 (en) | Tire management system, and tire management method |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100112 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110614 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20110615 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20110809 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20110830 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20110912 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20141007 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4835518 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |