JP4146298B2 - Coil spring - Google Patents
Coil spring Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4146298B2 JP4146298B2 JP2003183399A JP2003183399A JP4146298B2 JP 4146298 B2 JP4146298 B2 JP 4146298B2 JP 2003183399 A JP2003183399 A JP 2003183399A JP 2003183399 A JP2003183399 A JP 2003183399A JP 4146298 B2 JP4146298 B2 JP 4146298B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- coil
- center line
- coil spring
- terminal
- coil center
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Springs (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、コイルばねに関し、特にその荷重偏心の低減に係る改良に関するものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
通常のコイルばねは、そのコイル中心線が全長に渡って直線となるように形成されている。こうしたコイルばねでは、軸方向の荷重が作用されたときに、その座面の荷重分布が均一とはならないため、軸荷重の作用点がコイル中心線から偏心する荷重偏心が生じ、コイルばねに恒常的な横力やモーメントが発生してしまう。
【0003】
従来、そうした荷重偏心の低減を図る手法として、コイルばねのコイル中心線を湾曲形状化することが知られている(特許文献1,2等)。すなわち図10に示すように、コイルばねC両端の座巻部に対してその軸方向中央の有効巻部を上記荷重偏心の方向と反対側に膨出させるように、コイル中心線Lを湾曲形状化することで、荷重偏心を低減させる手法が知られている。
【0004】
【特許文献1】
特開2000−104772号公報
【特許文献2】
特開2001−208116号公報
【0005】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
ところで内燃機関の吸気弁、排気弁に用いられる弁ばね用のコイルばねでは、コイル径に対する巻線径の比が大きく、ばね指数が小さくなっている。このようなばね指数の小さいコイルばねでは、コイル中心線を所望とする曲率に成形することが非常に困難となっている。
【0006】
すなわちコイル中心線を湾曲形状化するには、コイルばねの巻線のコイル半径をその全長に亘って連続的に変化させる精密な巻線の曲げ加工が必要となる。ところが上記のようなばね指数の小さいコイルばねでは、巻線の曲げ加工度が大きく、また曲げ加工時の巻線のスプリングバックも大きい。そのため、巻線への精密な曲げ加工は施し難く、コイルばねの形状精度が悪化して、図11に示すようにコイルばねCの形状がその上半分(U)と下半分(L)とでアンバランスとなり、場合によっては、かえって荷重偏心を悪化させる虞がある。
【0007】
このようにコイル中心線の湾曲形状化は、たしかに荷重偏心の低減に有効ではあるが、コイルばね形状の精密な成形が必要であり、その製造が困難となっていた。またそのため、精密な巻線の曲げ加工が困難な、弁ばね等のばね指数の小さいコイルばねには、応用し難いものとなっていた。
【0008】
本発明はこうした実情に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることのできるコイルばねを提供することにある。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
以下、上述した目的を達成するための手段及びその作用効果を記載する。
請求項1に記載の発明は、コイル中心線がその全長に亘って直線となるよう形成されたとき、そのコイル中心線に対して、端末からの巻数がN巻の方向に荷重偏心が生じる、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径が等しいコイルばねにおいて、前記端末からの巻数がN巻の位置と同巻数がN+0.5巻の位置との間の、前記座巻部と前記有効巻部との境界部のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、前記座巻部及び前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を直線としたことをその要旨とする。
【0010】
上述のように、コイルばねでは、その座面での荷重分布の非対称性に起因して荷重偏心が発生する。その点、上記構成では、上記境界部のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させることで、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル中心線が直線とされている。このようにコイル中心線を成形することで、有効巻部のコイル中心線を直線としたまま、座巻部のコイル中心線に対して、端末からの巻数がN+0.5巻の方向、すなわち上記荷重偏心の方向と反対方向にオフセットさせることができる。こうしたオフセットの方向は、上記荷重偏心を低減させる方向となる。また上記構成では、有効巻部のコイル中心線には曲率がなく、巻線のスプリングバックが一律となるため、巻線の成形精度、すなわちコイルばねの形状精度を容易に確保することができる。したがって上記構成によれば、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることができる。
上記構成のように座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径を設定すれば、コイルばねの体格の大型化を抑えながらも、コイル中心線のオフセット量を大きくすることが可能となり、大きい荷重偏心の低減効果を確保することができる。
【0011】
また請求項2に記載の発明は、コイル中心線がその全長に亘って直線となるよう形成されたとき、そのコイル中心線に対して、端末からの巻数がN巻の方向に荷重偏心が生じる、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径が等しいコイルばねにおいて、前記端末とその端末からの巻数がN巻の位置との間の前記座巻部のコイル中心線、及び一方及び他方の端末からの巻数がそれぞれN+0.5巻の位置の間の前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を互いに平行な直線としつつ、前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を前記座巻部のコイル中心線に対してオフセットさせたことをその要旨とする。
【0012】
上記構成では、座巻部のコイル中心線と有効巻部のコイル中心線とが互いに平行な直線とされながらも、有効巻部のコイル中心線が座巻部のコイル中心線に対してオフセットされている。すなわち、座巻部と有効巻部との境界部のみで、コイル中心線の曲率が変化されている。したがって上記構成によっても、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることができるようになる。
上記構成のように座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径を設定すれば、コイルばねの体格の大型化を抑えながらも、コイル中心線のオフセット量を大きくすることが可能となり、大きい荷重偏心の低減効果を確保することができる。
【0013】
請求項3に記載の発明は、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径が等しいクローズドエンドのコイルばねであって、端末からの巻数が1巻の位置と同巻数が1.5巻の位置との間の、前記座巻部と前記有効巻部との境界部のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、前記座巻部及び前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を直線としたことをその要旨とする。
【0014】
更に請求項4に記載の発明は、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径が等しいクローズドエンドのコイルばねであって、前記端末とその端末からの巻数が1巻の位置との間の前記座巻部のコイル中心線、及び一方及び他方の端末からの巻数がそれぞれ1.5巻の位置の間の前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を互いに平行な直線としつつ、前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を前記座巻部のコイル中心線に対してオフセットさせたことをその要旨とする。
【0015】
端末と端末からの巻数が1巻の部位とが当接するように座巻部の形成されたクローズドエンドのコイルばねでは、コイル中心線がその全長に亘って直線となるよう形成されたとき、そのコイル中心線に対する荷重偏心の方向は、コイル中心線から見て、端末の位置する方向となる。換言すれば、同コイルばねの上記荷重偏心の方向は、コイル中心線に対して、端末からの巻数が1巻の位置の方向となる。よってクローズドエンドのコイルばねであれば、請求項3、4のように構成することで、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることができる。
上記構成のように座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル径を設定すれば、コイルばねの体格の大型化を抑えながらも、コイル中心線のオフセット量を大きくすることが可能となり、大きい荷重偏心の低減効果を確保することができる。
【0018】
また請求項5に記載の発明は、請求項1〜4のいずれか1項に記載のコイルばねにおいて、当該コイルばねの座面を、前記有効巻部のコイル中心線に対して垂直な面としたことをその要旨とする。
【0019】
上記構成では、コイルばねの座面が、有効巻部のコイル中心線に対して垂直に形成されているため、その組付を容易且つ的確に行うことができる。すなわちコイルばねの組付性、及び組付精度を向上することができる。
【0020】
また請求項6に記載の発明は、請求項1〜5のいずれか1項に記載のコイルばねにおいて、当該コイルばねは、弁ばねとして用いられることをその要旨とする。
【0021】
例えば内燃機関の吸気弁、排気弁等の弁ばねには一般に、ばね指数の小さいコイルばねが用いられている。上記各請求項に記載の構成を適用することで、そうした弁ばね用のコイルばねにおいても、荷重偏心の低減を容易に実現することができるようになる。
【0022】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明をクローズドエンドのコイルばねに適用した一実施形態について、図1〜図5を参照して詳細に説明する。
【0023】
図1に、本実施形態の前提となるコイルばね50の側面構造を示す。
同図に示すように、コイルばね50は、全体の巻数が自然数(同図では巻数5)とされ、その全長に亘ってコイル中心線Lが一直線に形成された通常のクローズドエンドのコイルばねとして構成されている。コイルばね50両端の端末Eはそれぞれ、その端末Eから1巻目の位置Sに当接されている。またコイルばね50両端には、図2にハッチングで示すように、コイル中心線Lに対して垂直な面となるように加工された座面52が形成されている。
【0024】
ちなみに、このコイルばね50の座巻部51のように、巻線の端末Eが、その端末Eから1巻目の位置S0に当接するように形成されたコイルばねの座巻部形状を「クローズドエンド」という。これに対して、巻線の端末Eとその端末Eから1巻目の位置との間に隙間が形成されるコイルばねの座巻部形状を「オープンエンド」という(図6参照)。
【0025】
圧縮状態で配設されたときのコイルばね50の座面52では、軸荷重は、巻線同士が重なった端末Eにほぼ集中して作用する。そのため、図2に示すように、軸荷重の重心位置Pは、コイル中心線Lから見て、端末Eの側にずれることとなる。すなわち、コイル中心線Lが全長に亘って一直線とされた通常のクローズドエンドのコイルばね50では、コイル中心線Lから見て、端末Eの側に向けて、換言すれば端末Eから1巻目の位置S0の側に向けて荷重偏心が生じるようになる。
【0026】
図3に側面構造を示す本実施形態のコイルばね10では、そうした荷重偏心を低減するため、以下のように構成されている。なおこのコイルばね10の座巻部形状も、上記コイルばね50と同様のクローズドエンドとなっており、その両端の端末Eの巻線が、その端末Eからの巻数が1巻の位置S1の巻線に当接されている。
【0027】
同図に示すように、コイルばね10では、その両端の座巻部11のコイル中心線L0、及びその軸方向中央の有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1は、それぞれ直線とされている。また有効巻部12のコイル径は、座巻部11のコイル径と等しくされている。
【0028】
一方、端末Eからの巻数が1巻の上記位置S1と同巻数が1.5巻の位置S2との間の境界部13では、コイル中心線の曲率が変化されている。そのため、このコイルばね10では、有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1は、座巻部11のコイル中心線L0に平行な直線とされながら、そのコイル中心線L0に対して所定のオフセット量ΔLだけ、オフセットされている。こうした有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1のオフセット方向は、座巻部11のコイル中心線L0から見て、端末Eからの巻数が1.5巻の位置S2の方向となっている。
【0029】
コイルばね10の両端には、座面14が形成されている。座面14は、上記有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1に対して垂直な面とされている。
更にこのコイルばね10では、座面14の荷重ベクトル方向が、その両端で一致するように、その全体の巻数が設定されている。すなわち、クローズドエンドとされたこのコイルばね10では、その全体の巻数は、自然数(本実施形態のコイルばね10では巻数5)とされている。
【0030】
以上説明した本実施形態のコイルばね10では、端末Eからの巻数が1巻の位置S1と同巻数が1.5巻の位置S2との間の境界部13のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、それ以外の座巻部11及び有効巻部12のコイル中心線L0,L1は直線とされている。すなわち、コイルばね10では、有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1を、座巻部11のコイル中心線L0と平行な直線としつつ、そのコイル中心線L0に対して、端末Eからの巻数が1.5巻の位置S2の方向にオフセットさせている。このときの上記オフセットの方向は、荷重偏心を低減させる方向となる。ちなみに上記オフセット量ΔLは、荷重偏心を十分に低減可能な適宜な大きさに、予め設定されている。
【0031】
更に有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1には曲率がなく、巻線のスプリングバックが一律となるため、巻線の成形精度、すなわちコイルばね10の形状精度を容易に確保することができる。したがって、このコイルばね10では、上記のような荷重偏心の低減を、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることができる。
【0032】
続いて、以上説明したコイルばね10を、内燃機関の機関バルブである吸気バルブや排気バルブの弁ばねとして適用した場合について説明する。なお、以下の説明では、例として、吸気バルブの弁ばねとしてコイルばね10を用いた場合を説明するが、排気バルブの弁ばねにも同様に適用することができる。
【0033】
図5に、コイルばね10が弁ばねとして用いられた吸気バルブ3及びその周辺部の断面構造を示す。同図に示すように、内燃機関のシリンダヘッド1に形成された吸気ポート2を開閉する吸気バルブ3は、傘部3a及び弁軸3bを備えて構成されている。吸気ポート2の燃焼室1aへの開口部には、上記傘部3aが着座可能な弁座2aが設けられている。吸気ポート2は、傘部3aが弁座2aに着座することで燃焼室1aに対して閉じられ、傘部3aが弁座2aから離座することで燃焼室1aに対して開かれる。また吸気バルブ3の弁軸3bは、シリンダヘッド1に設けられたバルブガイド3cに軸方向に往復動可能に支持されている。
【0034】
シリンダヘッド1の吸気バルブ3上方には、バルブリフタ5が、弁軸3bの軸方向に往復動可能に配設されており、弁軸3bの上端がそのバルブリフタ5に当接されている。更にシリンダヘッド1のバルブリフタ5上方には、カム7の設けられたカムシャフト6が回転可能に支持されている。
【0035】
一方、弁軸3bの上端部にはリテーナ3dが装着されている。そしてシリンダヘッド1に形成されたばね座4と上記リテーナ3dとの間に、コイルばね10が圧縮状態で配設されている。
【0036】
こうした機関バルブの弁ばねとして用いられるコイルばねに、上記のような荷重偏心によって横力が発生すると、その横力が弁軸3bに作用して、弁軸3bとバルブガイド3cとの摺動面の摩擦力が増大されてしまう。その点、そうした弁ばねに本実施形態のコイルばね10を用いれば、上記弁軸3bに作用する横力が低減されて、弁軸3bとバルブガイド3cとの摺動面に作用する摩擦が低減されるため、吸気バルブ3の開閉駆動の円滑化を図ることができる。
【0037】
以上説明した本実施形態のコイルばね10によれば、下記の効果を奏することができる。
(1)コイルばね10の形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心を低減することができる。
【0038】
(2)座巻部11及び有効巻部12のコイル径が等しくされているため、上記コイル中心線L0、L1のオフセット量ΔLを大きく確保しつつも、コイルばね10の体格の大型化を抑えられる。その結果、例えば機関バルブの弁ばねのような、搭載の制約を受ける部位に用いる場合にも、大きい荷重偏心の低減効果を得ることができる。
【0039】
(3)座面14を、有効巻部12のコイル中心線L1に対して垂直な面としているため、コイルばね10の組付性、及び組付精度が向上される。
(4)コイルばね10両端の荷重ベクトルの方向が同一となるように、全体の巻数が設定されているため、コイルばね10両端に生じるモーメントが釣り合うようになり、コイルばね10両端に発生する横力も、好適に低減することができる。
【0040】
(5)コイルばね10を、内燃機関の機関バルブの弁ばねとして用いることで、弁軸3b等の摺動部の摩擦力を低減して、機関バルブの開閉駆動の円滑化を図ることができる。
【0041】
<オープンエンドのコイルばねへの適用例>
続いて、本発明を、オープンエンドのコイルばねに適用した場合について説明する。
【0042】
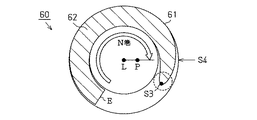
図6は、コイル中心線が全長に亘って一直線に形成された通常のオープンエンドのコイルばね60の側部断面構造を示している。このコイルばね60は、その両端の座巻部61において、巻線の端末Eとその端末Eから1巻目の位置との間に隙間が形成された状態で使用される。またコイルばね60の両端には、そのコイル中心線Lに垂直な面となるように座面62が形成されている。
【0043】
こうしたオープンエンドのコイルばね60が圧縮状態で配設されたとき、その座面62では、巻線がばね座から離間する位置S3で最大となり、その位置S3から端末Eに向かうほど小さくなるように、軸荷重が分布する。そのため、オープンエンドのコイルばね60では、端末Eに軸荷重が集中する上記クローズドエンドのコイルばね50とは異なり、座面62の形状や巻線のピッチ等に応じて、コイル中心線Lに対して軸荷重の重心位置Pがずれる方向、すなわち荷重偏心の方向が変化する。こうしたオープンエンドのコイルばね60における座面62での軸荷重分布の非対称性に起因した荷重偏心の方向は、実験や解析等で予め求めることができる。
【0044】
ここでは図7に示すように、このコイルばね60での荷重偏心の方向が、コイル中心線Lから見て、端末Eからの巻数がN巻の位置S4の方向であるとする。この場合、以下のようにコイルばねを構成することで、形状精度の悪化を招くことなく好適に、荷重偏心の低減を図ることができる。
【0045】
図8に、そうしたコイルばね20の側面構造を示す。このコイルばね20も、上記コイルばね60と同様に、オープンエンドのコイルばねとして構成されている。すなわち、このコイルばね20の座巻部21では、巻線の端末Eが、端末Eからの巻数が1巻の位置の巻線とが離間された状態となっている。
【0046】
同図に示すように、コイルばね20では、端末Eからの巻数が上記N巻の位置S4と同巻数がN+0.5巻の位置S5との間の境界部23のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、それ以外の部分のコイル中心線は直線とされている。すなわち、このコイルばね20では、端末Eと上記位置S4との間の座巻部21のコイル中心線L4、及びコイルばね20上下の上記位置S5の間の有効巻部22のコイル中心線L5は、それぞれ直線とされている。そして上記境界部23でコイル中心線の曲率を変化させることで、有効巻部22のコイル中心線L5は、座巻部21のコイル中心線L4に対して所定のオフセット量ΔLだけオフセットされている。図9に示すように、そうした有効巻部22のコイル中心線L5のオフセット方向は、座巻部21のコイル中心線L4から見て、上記位置S5の方向とされている。
【0047】
このコイルばね20でも、有効巻部22のコイル径と座巻部21のコイル径とは等しくされている。またコイルばね20の両端には、有効巻部22のコイル中心線L5に対して垂直な面とされた座面24が形成されている。
【0048】
なお、このコイルばね20全体の巻数Mは、両端の座面24での荷重ベクトル方向が一致するように設定されている。この場合、上記巻数Nに基づき、M=2N+nとなるようにコイルばね20全体の巻数Mを設定することで、コイルばね20両端の荷重ベクトルの方向を一致させることができる(n:任意の自然数)。
【0049】
このようにコイルばね20を構成すれば、オープンエンドのコイルばねにおいても、上記コイルばね10と同様の作用効果を奏することができる。
なお、上記実施形態は次のように変更して実施することもできる。
【0050】
・コイルばね10,20では、座巻部11,21及び有効巻部12,22のコイル径を等しくしていたが、座巻部及び有効巻部のコイル中心線が直線であれば、それらのコイル径を異ならせたり、或いは座巻部や有効巻部内でコイル径を変化させたりしても、荷重偏心の低減は可能である。
【0051】
・コイルばね10,20では、座面14,24を、有効巻部12,22のコイル中心線L1,L3に対して垂直な面としているが、コイルばねの組付性や組付精度が十分確保できるのであれば、座面14,24をコイル中心線L1,L3に垂直とならないように形成しても良い。
【0052】
・上記実施形態では、コイルばね10の弁ばねとしての使用例を示したが、本発明のコイルばねは、弁ばね以外の用途にも用いることも可能である。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の一実施形態のコイルばねについてその前提となる構成の側面図。
【図2】同じく前提となる構成の平面図。
【図3】本発明の一実施形態に係るコイルばねの側面図。
【図4】同コイルばねの平面図。
【図5】同コイルばねの弁ばねとしての使用状態を示す断面図。
【図6】オープンエンドのコイルばねへの本発明の適用例についてその前提となる構成の側面図。
【図7】同前提となる構成の座巻部の荷重分布を示す図。
【図8】オープンエンドのコイルばねへの本発明の適用例の側面図。
【図9】同コイルばねの平面図。
【図10】コイル中心線の湾曲形状化された従来のコイルばねの側面図。
【図11】形状精度の悪化した従来のコイルばねの側面図。
【符号の説明】
1…シリンダヘッド、2…吸気ポート、2a…弁座、3…吸気バルブ、3a…傘部、3b…弁軸、3c…バルブガイド、3d…リテーナ、4…ばね座、5…バルブリフタ、6…カムシャフト、7…カム、10,20,50,60…コイルばね、11,21,51,61…座巻部、12,22…有効巻部、13,23…境界部、14,24,54,64…座面。[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to a coil spring, and more particularly to an improvement related to reduction of load eccentricity.
[0002]
[Prior art]
A normal coil spring is formed such that its coil center line is a straight line over its entire length. In such a coil spring, when an axial load is applied, the load distribution on the seating surface is not uniform, so that a load eccentricity occurs in which the point of application of the axial load is eccentric from the coil center line, and the coil spring is constantly Side force and moment are generated.
[0003]
Conventionally, as a technique for reducing such load eccentricity, it is known to curve the coil center line of a coil spring (
[0004]
[Patent Document 1]
JP 2000-104772 A [Patent Document 2]
Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 2001-208116
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
By the way, in a coil spring for a valve spring used for an intake valve and an exhaust valve of an internal combustion engine, a ratio of a winding diameter to a coil diameter is large, and a spring index is small. In such a coil spring having a small spring index, it is very difficult to mold the coil center line to a desired curvature.
[0006]
That is, in order to make the coil center line into a curved shape, it is necessary to perform a precise winding bending process in which the coil radius of the coil spring winding is continuously changed over its entire length. However, a coil spring having a small spring index as described above has a large degree of bending of the winding and a large spring back of the winding during bending. Therefore, it is difficult to perform a precise bending process on the winding, and the shape accuracy of the coil spring is deteriorated, and the shape of the coil spring C is divided into an upper half (U) and a lower half (L) as shown in FIG. There is a possibility that the load eccentricity may be worsened in some cases.
[0007]
Thus, the curved shape of the coil center line is effective in reducing the load eccentricity, but requires precise shaping of the coil spring shape, which makes it difficult to manufacture. For this reason, it has been difficult to apply to a coil spring having a small spring index such as a valve spring, which is difficult to bend precisely.
[0008]
The present invention has been made in view of such circumstances, and an object of the present invention is to provide a coil spring that can suitably reduce load eccentricity without causing deterioration in shape accuracy.
[0009]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In the following, means for achieving the above-described object and its operational effects are described.
In the invention according to
[0010]
As described above, in the coil spring, load eccentricity occurs due to the asymmetry of the load distribution on the seat surface. In that respect, in the above configuration, the coil center lines of the end turn portion and the effective winding portion are made straight by changing the curvature of the coil center line only at the boundary portion. By forming the coil center line in this way, the number of turns from the terminal is N + 0.5 turns with respect to the coil center line of the end winding portion while keeping the coil center line of the effective winding portion straight, that is, the above It can be offset in the direction opposite to the direction of load eccentricity. The direction of such an offset is a direction that reduces the load eccentricity. In the above configuration, since the coil center line of the effective winding portion has no curvature and the spring back of the winding is uniform, the winding forming accuracy, that is, the shape accuracy of the coil spring can be easily ensured. Therefore, according to the said structure, reduction of load eccentricity can be aimed at suitably, without causing deterioration of shape accuracy.
If the coil diameters of the end winding part and the effective winding part are set as in the above configuration, it is possible to increase the offset amount of the coil center line while suppressing an increase in the size of the coil spring, and a large load eccentricity. A reduction effect can be secured.
[0011]
In the invention according to
[0012]
In the above configuration, the coil center line of the effective winding portion is offset from the coil center line of the end winding portion while the coil center line of the end winding portion and the coil center line of the effective winding portion are straight lines parallel to each other. ing. That is, the curvature of the coil center line is changed only at the boundary portion between the end winding portion and the effective winding portion. Therefore, even with the above configuration, it is possible to suitably reduce the load eccentricity without causing deterioration of the shape accuracy.
If the coil diameters of the end winding part and the effective winding part are set as in the above configuration, it is possible to increase the offset amount of the coil center line while suppressing an increase in the size of the coil spring, and a large load eccentricity. A reduction effect can be secured.
[0013]
The invention according to
[0014]
Further the invention described in
[0015]
In a closed-end coil spring in which the end winding part is formed so that the terminal and the number of turns from the terminal are in contact with each other, when the coil center line is formed to be a straight line over its entire length, The direction of load eccentricity with respect to the coil center line is the direction in which the terminal is located when viewed from the coil center line. In other words, the direction of the load eccentricity of the coil spring is the direction in which the number of turns from the terminal is one turn with respect to the coil center line. Therefore, if it is a closed-end coil spring, it can reduce load eccentricity suitably, without causing deterioration of a shape precision by comprising like
If the coil diameters of the end winding part and the effective winding part are set as in the above configuration, it is possible to increase the offset amount of the coil center line while suppressing an increase in the size of the coil spring, and a large load eccentricity. A reduction effect can be secured.
[0018]
The invention according to
[0019]
In the said structure, since the seat surface of a coil spring is formed perpendicularly | vertically with respect to the coil centerline of an effective volume part, the assembly | attachment can be performed easily and exactly. That is, the assembling property and the assembling accuracy of the coil spring can be improved.
[0020]
The gist of the invention described in
[0021]
For example, a coil spring having a small spring index is generally used as a valve spring such as an intake valve or an exhaust valve of an internal combustion engine. By applying the configurations described in the above claims, load eccentricity can be easily reduced even in such a coil spring for a valve spring.
[0022]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Hereinafter, an embodiment in which the present invention is applied to a closed-end coil spring will be described in detail with reference to FIGS.
[0023]
In FIG. 1, the side structure of the
As shown in the figure, the
[0024]
By the way, like the
[0025]
In the
[0026]
In order to reduce such load eccentricity, the
[0027]
As shown in the figure, in the
[0028]
On the other hand, at the
[0029]
Seat surfaces 14 are formed at both ends of the
Further, in this
[0030]
In the
[0031]
Furthermore, since the coil center line L1 of the effective winding
[0032]
Next, the case where the
[0033]
FIG. 5 shows a cross-sectional structure of the
[0034]
A
[0035]
On the other hand, a
[0036]
When a lateral force is generated in the coil spring used as a valve spring of such an engine valve due to the load eccentricity as described above, the lateral force acts on the
[0037]
According to the
(1) The load eccentricity can be suitably reduced without deteriorating the shape accuracy of the
[0038]
(2) Since the coil diameters of the
[0039]
(3) Since the
(4) Since the total number of turns is set so that the directions of the load vectors at both ends of the
[0040]
(5) By using the
[0041]
<Application example to open-end coil spring>
Next, the case where the present invention is applied to an open-end coil spring will be described.
[0042]
FIG. 6 shows a side sectional structure of a normal open-
[0043]
When such an open-ended
[0044]
Here, as shown in FIG. 7, it is assumed that the direction of load eccentricity in the
[0045]
FIG. 8 shows a side structure of such a
[0046]
As shown in the figure, in the
[0047]
Even in this
[0048]
The total number M of turns of the
[0049]
If the
In addition, the said embodiment can also be changed and implemented as follows.
[0050]
-In the coil springs 10 and 20, the coil diameters of the
[0051]
-In the coil springs 10 and 20, the seat surfaces 14 and 24 are surfaces perpendicular to the coil center lines L1 and L3 of the effective winding
[0052]
In the above embodiment, the use example of the
[Brief description of the drawings]
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a side view of a precondition of a coil spring according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a plan view of the same underlying configuration.
FIG. 3 is a side view of a coil spring according to an embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a plan view of the coil spring.
FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view showing a use state of the coil spring as a valve spring.
FIG. 6 is a side view of a configuration that is a prerequisite for an application example of the present invention to an open-end coil spring.
FIG. 7 is a view showing a load distribution of an end turn part having the same configuration.
FIG. 8 is a side view of an application example of the present invention to an open-end coil spring.
FIG. 9 is a plan view of the coil spring.
FIG. 10 is a side view of a conventional coil spring in which a coil center line is curved.
FIG. 11 is a side view of a conventional coil spring whose shape accuracy is deteriorated.
[Explanation of symbols]
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
前記端末からの巻数がN巻の位置と同巻数がN+0.5巻の位置との間の、前記座巻部と前記有効巻部との境界部のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、前記座巻部及び前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を直線とした
ことを特徴とするコイルばね。When the coil center line is formed to be a straight line over its entire length, the coil of the end winding part and the effective winding part has a load eccentricity in the direction of N turns from the terminal with respect to the coil center line. In coil springs with the same diameter ,
The position and the number of turns of winding number N winding from terminal between the position of the N + 0.5 vol, to change the curvature of the coil center line only at the boundary portion between the effective winding portion and the end turn portion, said coil springs, characterized in that the linear coil center line of the end turn portion and the useful load unit.
前記端末とその端末からの巻数がN巻の位置との間の前記座巻部のコイル中心線、及び一方及び他方の端末からの巻数がそれぞれN+0.5巻の位置の間の前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を互いに平行な直線としつつ、前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を前記座巻部のコイル中心線に対してオフセットさせた
ことを特徴とするコイルばね。When the coil center line is formed to be a straight line over its entire length, the coil of the end winding part and the effective winding part has a load eccentricity in the direction of N turns from the terminal with respect to the coil center line. In coil springs with the same diameter ,
The effective winding portion between the end turn portions of the coil center line, and one and the number of turns positions of N + 0.5 volumes from the other terminal between the number of turns N positions wound from the terminal and the terminal The coil spring is characterized in that the coil center line of the effective winding portion is offset with respect to the coil center line of the end winding portion while the coil center lines are straight lines parallel to each other.
端末からの巻数が1巻の位置と同巻数が1.5巻の位置との間の、前記座巻部と前記有効巻部との境界部のみでコイル中心線の曲率を変化させ、前記座巻部及び前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を直線とした
ことを特徴とするコイルばね。 A closed-end coil spring in which the coil diameters of the end turn and the effective turn are equal ,
Between turns the position of 1.5 vol position and the number of turns of the winding from the terminal, to change the curvature of the coil center line only at the boundary portion between the effective winding portion and the end turn portion, said seat coil springs, characterized in that a straight line and the winding portion and the coil center line of the effective winding portion.
前記端末とその端末からの巻数が1巻の位置との間の前記座巻部のコイル中心線、及び一方及び他方の端末からの巻数がそれぞれ1.5巻の位置の間の前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を互いに平行な直線としつつ、前記有効巻部のコイル中心線を前記座巻部のコイル中心線に対してオフセットさせた
ことを特徴とするコイルばね。 A closed-end coil spring in which the coil diameters of the end turn and the effective turn are equal ,
The effective winding portion between the end turn portions of the coil center line, and one and the number of turns the position of 1.5 vol each from the other terminal between the number of turns located one reel from the terminal and the terminal The coil spring is characterized in that the coil center line of the effective winding portion is offset with respect to the coil center line of the end winding portion while the coil center lines are straight lines parallel to each other.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003183399A JP4146298B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2003-06-26 | Coil spring |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003183399A JP4146298B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2003-06-26 | Coil spring |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2005016645A JP2005016645A (en) | 2005-01-20 |
| JP4146298B2 true JP4146298B2 (en) | 2008-09-10 |
Family
ID=34183514
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003183399A Expired - Fee Related JP4146298B2 (en) | 2003-06-26 | 2003-06-26 | Coil spring |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP4146298B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109073019A (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2018-12-21 | 新确有限公司 | Helical spring |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4996912B2 (en) * | 2006-11-21 | 2012-08-08 | カヤバ工業株式会社 | Attenuator structure |
| JP5003386B2 (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2012-08-15 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | coil spring |
| JP6350416B2 (en) * | 2015-06-30 | 2018-07-04 | 株式会社デンソー | High pressure pump |
| JP6367256B2 (en) | 2016-04-13 | 2018-08-01 | サンコール株式会社 | Coil spring |
| US10144261B2 (en) * | 2017-01-31 | 2018-12-04 | Nhk Spring Co., Ltd. | Coil spring |
| US10065471B2 (en) * | 2017-01-31 | 2018-09-04 | Nhk Spring Co., Ltd. | Coil spring for vehicle suspension |
| JP7182377B2 (en) | 2018-05-16 | 2022-12-02 | サンコール株式会社 | coil spring |
-
2003
- 2003-06-26 JP JP2003183399A patent/JP4146298B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN109073019A (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2018-12-21 | 新确有限公司 | Helical spring |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2005016645A (en) | 2005-01-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4146298B2 (en) | Coil spring | |
| US6615773B2 (en) | Piston control mechanism of reciprocating internal combustion engine of variable compression ratio type | |
| JP4289192B2 (en) | Variable valve gear for engine | |
| US7819102B2 (en) | Valve driving device for internal combustion engine | |
| JPH02304228A (en) | Spring seat member for coil spring | |
| JPH01305110A (en) | Valve spring for internal combustion engine | |
| JP2002155769A (en) | Variable compression ratio mechanism of reciprocation type internal combustion engine | |
| US20050076866A1 (en) | Electromechanical valve actuator | |
| JP4140029B2 (en) | Internal combustion engine camshaft structure | |
| JP3541730B2 (en) | Valve train | |
| JPH10196333A (en) | Valve lifter structure | |
| JP3125605B2 (en) | Electromagnetically driven valve device for internal combustion engine | |
| JPH06502466A (en) | Improvements regarding drive connections in two rotating bodies | |
| JP2007085293A (en) | Valve gear for engine | |
| US6382153B1 (en) | Partial internal guide for curved helical compression spring | |
| JP6604063B2 (en) | Engine cam structure | |
| JP7225667B2 (en) | Decompression device | |
| JP5617274B2 (en) | Variable valve timing mechanism | |
| JPH068704U (en) | Camshaft bearing device | |
| JP2000055096A (en) | Coil spring for valve spring | |
| JPH07208121A (en) | Valve lifter device with ball bearing | |
| JPH10184750A (en) | Compression coil spring | |
| JP4500228B2 (en) | Variable valve mechanism | |
| JP4192854B2 (en) | Continuously variable valve mechanism | |
| JP2000080908A (en) | Valve lifter supporting structure |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20051031 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20080111 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20080226 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20080418 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080617 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080619 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110627 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |