JP3956252B2 - Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method - Google Patents
Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3956252B2 JP3956252B2 JP10659098A JP10659098A JP3956252B2 JP 3956252 B2 JP3956252 B2 JP 3956252B2 JP 10659098 A JP10659098 A JP 10659098A JP 10659098 A JP10659098 A JP 10659098A JP 3956252 B2 JP3956252 B2 JP 3956252B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- obstacle
- transmission
- overlapping
- reception
- transducers
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Measurement Of Velocity Or Position Using Acoustic Or Ultrasonic Waves (AREA)
Description
【0001】
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、例えば、超音波等を用いて、車両等の物体の周囲に存在する障害物の有無や位置を検出する障害物検出装置及び障害物の検出方法に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
近年、代表的な車両である自動車のうち、一部の自動車においては、その自動車の車庫入れ、或いは縦列駐車等を行うのに際して周囲の障害物に接触することを防止すべく、障害物の有無や位置を検出可能な障害物検出装置を備えるものがある。このような障害物検出装置においては、一般に、障害物の有無や位置を検出する手段として超音波を使用したトランスデューサが用いられている。
【0003】
また、例えば特開平8−301029号には、2つの超音波センサ(トランスデューサ)が形成する検出範囲を重複させることによって3つの検出範囲を形成し、これにより障害物を検出する際の分解能を向上する手法が提案されている。
【0004】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、上記2つの超音波センサを利用する従来例においては、検出可能な領域が3つであり、例えば縦列駐車等のように狭い領域内で車両を操作しなければならないとき等には、十分な分解能であるとは言えない。
【0005】
そこで本発明は、少ないトランスデューサにより、高精度に障害物を検出する障害物検出装置及び障害物の検出方法の提供を目的とする。
【0006】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上記の目的を達成するため、本発明に係る障害物検出装置は、以下の構成を特徴とする。
【0007】
即ち、請求項1は、少なくとも2つのトランスデューサの検出領域により、2つの非重複領域とそれら2つの非重複領域に挟まれる1つの重複領域とを形成し、それらの領域内に存在する障害物の有無及び位置を検出する検出手段を備える障害物検出装置であって、前記2つのトランスデューサのうち、少なくとも第1のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とは異なっており、前記重複領域は、前記第1のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第1の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第2の重複領域とを構成しており、且つそれら第1及び第2の重複領域は、第2のトランスデューサの検出領域に含まれるとき、前記検出手段は、前記2つの非重複領域、並びに前記第1及び第2の重複領域の4つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする。
これにより、2つのトランスデューサによって4つの領域を形成し、その領域内の障害物を高精度に検出する。
【0008】
また、請求項2として、更に、前記第2のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とが異なっており、前記第1の重複領域は、前記第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第3の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第4の重複領域とを構成しているとき、前記検出手段は、前記2つの非重複領域、前記第2から第4の重複領域の5つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする。これにより、2つのトランスデューサによって5つの領域を形成し、その領域内の障害物を高精度に検出する。
【0009】
尚、上記の構成を備える障害物検出装置において、前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサが、例えば超音波式の場合には、その送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とは異なっており、送信有効範囲は受信有効範囲より小さい(請求項9)。
【0010】
また、更に、前記検出手段によって検出した障害物が、前記4つまたは5つの領域のうち何れの領域内に存在するかを識別可能に報知する報知手段を備え(請求項3)、
好ましくは、前記報知手段は表示手段であって、その表示手段は、前記検出した障害物が存在する領域を表わす表示パターンを表示するとき、その表示パターンと共に、該障害物の存在する領域に対して前記4つまたは5つの領域の反中央側に位置する他の領域がある場合には当該他の領域を表わす表示パターンをも表示するとよい(請求項4)。
これにより、その時点では検出できない他の障害物や、複数の領域に渡って存在するかもしれない大きな障害物をユーザに認識させる。
【0011】
また、好ましくは、前記2つのトランスデューサは、それぞれ送信機構と受信機構とを備えており、前記検出手段は、該送信機構による送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信させ、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、該受信機構の両方に行わせることを特徴とする(請求項5)。
これにより、上記の4つまたは5つの領域を効率よく検出する。
【0012】
このとき、前記検出手段は、少なくとも前記第1のトランスデューサの送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の一部を、前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサが受信したとき、前記第1の重複領域に障害物が存在すると判断すればよい(請求項6)。
【0013】
また、請求項7として、前記2つのトランスデューサは、前記非重複領域と重複領域との2つの境界線が、車両側方の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上と、前記車両前端及び/または後端の近傍であって、その車両前端及び/または後端に平行な線の延長線上とに位置するように、所定の開角をなして車両のコーナに近接配置されているとよい。
これにより、運転操作に必要な情報を、ドライバの車両感覚に合った形態で提供する。
【0014】
また、請求項8として、前記2つのトランスデューサは、前記第2の重複領域と第3の重複領域との境界線が、前記車両側方の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上に位置するように、前記第3の重複領域と第4の重複領域との境界線が、前記車両前端及び/または後端の近傍であって、その車両前端及び/または後端に平行な線の延長線上に位置するように、所定の開角をなして車両のコーナに近接配置されているとよい。
これにより、運転操作に必要な情報を、ドライバの車両感覚に合った形態で提供する。
【0015】
または、上記の目的を達成するため、本発明に係る障害物の検出方法は、以下の構成を特徴とする。
【0016】
即ち、請求項10は、少なくとも2つのトランスデューサの検出領域により、2つの非重複領域とそれら2つの非重複領域に挟まれる1つの重複領域とを形成し、それらの領域内に存在する障害物の有無及び位置を検出する障害物の検出方法であって、前記2つのトランスデューサのうち、少なくとも第1のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とは異なっており、前記重複領域は、前記第1のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第1の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第2の重複領域とを構成しており、且つそれら第1及び第2の重複領域は、第2のトランスデューサの検出領域に含まれるとき、前記2つのトランスデューサによる送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信し、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、それらトランスデューサの両方で行うことにより、前記2つの非重複領域、並びに前記第1及び第2の重複領域の4つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする。
これにより、2つのトランスデューサによって4つの領域を形成し、その領域内の障害物を高精度に検出する。
【0017】
また、請求項11は、更に、前記第2のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とが異なっており、前記第1の重複領域は、前記第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第3の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第4の重複領域とを構成しているとき、前記2つのトランスデューサによる送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信し、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、それらトランスデューサの両方で行うことにより、前記2つの非重複領域、前記第2から第4の重複領域の5つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする。
これにより、2つのトランスデューサによって5つの領域を形成し、その領域内の障害物を高精度に検出する。
【0018】
また、上記の方法において、少なくとも前記第1のトランスデューサの送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の一部を、前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサが受信したときには、前記第1の重複領域に障害物が存在すると判断すればよい(請求項12)。
【0019】
好ましくは、前記障害物の検出方法において、更に、前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲は、受信有効範囲より小さくされており、前記2つのトランスデューサを、所定の開角をなして予め近接配置し、前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲のうち、それらトランスデューサ側の略半分の範囲を用いるとよい(請求項13)。
これにより、2つのトランスデューサの検出範囲を略扇型に形成し、ユーザによる認識を容易にする。
【0020】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明に係る障害物検出装置を、代表的な車両である自動車に適用した実施形態として、図面を参照して詳細に説明する。
【0021】
[第1の実施形態]
<ハードウエア>
はじめに、本実施形態における障害物検出装置のハードウエアの構成について説明する。
【0022】
図1は、本発明の第1の実施形態としての障害物検出装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
【0023】
同図において、1は、超音波の発信(以下、便宜上送信と称する)と受信とを行う検出ユニットである。この検出ユニット1には、2つのトランスデューサTr1及びTr2が設けられており、それぞれのトランスデューサには、所定の超音波を送信する送信モジュールと、外部からの超音波を受信する受信モジュールとが設けられている。本実施形態に係る障害物検出装置は、図6に示すように、4つの検出ユニット1を備える。
【0024】
8は、4つの検出ユニット1とコントローラ2との入出力信号の切り替えを行うマルチプレクサ回路である。9は、マルチプレクサ回路8が出力する検出信号を増幅し、その増幅した信号に所定のフィルタをかけると共に、コントローラ1から出力される信号に対しては増幅を行うフィルタ・アンプ回路である。10は、フィルタ・アンプ回路9が出力する信号を所定の基準電圧と比較するコンパレータである。
【0025】
3は、自動車の車速を検出する車速センサである。4は、自動車のシフト(変速)ポジションを検出するシフトポジションセンサである。5は、自動車の前輪の操舵角度を検出する舵角センサである。6は、当該障害物検出装置が検出した結果を、ドライバに画像によって報知する表示器である。そして、7は、当該障害物検出装置が検出した結果を、ドライバに警報音によって報知するブザー(チャイムを含む)である(尚、音声出力装置であってもよいことは言うまでもない)。
【0026】
コントローラ2は、CPU21、RAM22、ROM23、そして車速センサ3等の出力信号や表示器6への入力信号をインタフェースする不図示の入出力インタフェース等を備えている。CPU21は、RAM22を各種データの一時記憶エリア、ワークエリアとして使用しながら、予めROM23に記憶されている、後述する障害物検出・判定処理プログラム等に従って、本実施形態における障害物検出装置の動作を、後述の如く制御する。
【0027】
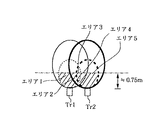
次に、検出ユニット1の構成について、図2から図8を参照して説明する。検出ユニット1は、図3の正面図、図4の上面図、そして図5の背面図に示すような形状を有する。Tr1及びTr2は、同図に示すように、一例として70度の開角をなして隣接配置されている。Tr1及びTr2の配置角度は、個々のトランスデューサが発信する超音波の覆角(本実施形態では120度程度)、そして後述する2つのトランスデューサの送受信エリアの重複領域の設定の仕方等によって決定されるものであり、70度に限られるものではない。このような形状を有する検出ユニット1が、図6に示すように、自動車11の4つのコーナに設けられ、それぞれの検出ユニット1は、自動車11のコーナの周辺に送受信エリア12を形成する。
【0028】
図2は、本発明の第1の実施形態における検出ユニット内のトランスデューサが形成する送受信エリアを説明する図である。尚、同図においては、説明の便宜上、Tr1及びTr2を、並行に隣接させて表現している。尚、実際の送受信エリア12は、例えば、後述する図23のような形状を有する。
【0029】
Tr1は、Tr1が出力する所定の超音波に対する反射波の一部(以下、便宜上単に反射波という)を、そのTr1自身が受信可能な、同図に細線の実線で示す受信有効領域と、Tr1についての反射波に限らず何らかの超音波を外部より受信可能な、同図に細線の破線で示す送信有効領域とを有する。同様に、Tr2は、同図に太線の実線で示す受信有効領域と、同図に太線の破線で示す送信有効領域とを有する。尚、Tr1とTr2とは、後述するように送信タイミングが異なる。
【0030】
このような送信及び受信有効領域を有するTr1及びTr2は、図3から図5に示したように検出ユニット1の内部で隣接して配置されているため、これらの領域は5つの領域(エリア1からエリア5)を形成する。ここで、これらの5つの領域について説明する。
【0031】
エリア1:Tr1が超音波を送信したとき、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1によってのみ受信可能な領域であって、Tr2が超音波を送信したときには、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1は受信できない領域である。
【0032】
エリア2:Tr1が超音波を送信したとき、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1及びTr2によって計測可能な領域であって、Tr2が超音波を送信したときには、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1は受信できない領域である。
【0033】
エリア3:Tr1が超音波を送信したとき、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1及びTr2によって計測可能な領域であって、Tr2が超音波を送信したときにも、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1及びTr2によって計測可能な領域である。
【0034】
エリア4:Tr2が超音波を送信したとき、その超音波の反射波を、Tr1及びTr2によって計測可能な領域であって、Tr1が超音波を送信したときには、その超音波の反射波を、Tr2は受信できない領域である。
【0035】
エリア5:Tr2が超音波を送信したとき、その超音波の反射波を、Tr2によってのみ受信可能な領域であって、Tr1が超音波を送信したときには、その超音波の反射波を、Tr2は受信できない領域である。
【0036】
また、本実施形態に係る障害物検出装置は、上述した5つの領域において、図7に示す斜線部分ように、Tr1及びTr2の送信有効領域の半分程度の領域を障害物の検出に使用し、これにより、図8に概略的な形状で示すように、自動車11のコーナの周辺に、上記のエリア1からエリア5からなる扇型の送受信エリア12を形成する(尚、一例としてフロント右側のコーナの送受信エリアだけを示している)。
【0037】
尚、本実施形態では、この障害物検出に使用する領域は、車庫入れや縦列駐車を行う際の障害物を検出するという観点から、例えばTr1及びTr2の前方0.75m程度としているが、より遠方の障害物を検出する場合には、トランスデューサから送出する超音波の出力を大きくすればよいことは言うまでもない。
【0038】
<ソフトウエア>
コントローラ2のCPU21が、予めROM23に記憶されているプログラムに従って実行するところの、障害物検出・判定処理について図9から図12を参照して説明する。この障害物検出・判定処理は、運転者がイグニッションキースイッチをオンすることにより開始される。
【0039】
図9は、本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物検出・判定処理を示すフローチャートである。同図において、
ステップS1,ステップS2:CPU21は、内部のバッファやカウンタ等を所定の状態に初期化し(ステップS1)、所定時間割り込み待ちを行う(ステップS2)。
【0040】
ステップS3,ステップS4:CPU21は、車速センサ3の出力信号に基づいて現在の自動車11の車速を検出し(ステップS3)、その検出した車速が所定の車速より遅いか否かを判断する(ステップS4)。
【0041】
ステップS5:ステップS4の判断においてNO(所定の速度より速い)のとき、CPU21は、現時点では障害物検出・判定処理を行う必要が無いと判断して、表示器6の表示及びブザー7の警報をオフにする。
【0042】
ステップS6,ステップS7:ステップS4の判断においてYES(所定の速度より遅い)のとき、CPU21は、ステップS7の障害物検出処理により、自動車11が備える全てのトランスデューサについて最新の計測値を得られたか否かを判断し(ステップS6)、その判断がNO(今回車速が所定の速度より遅くなった時点から、全てのトランスデューサについて最新の計測値を検出する途中)のときには、後述する障害物検出処理を行う(ステップS7)。
【0043】
ステップS8:ステップS6の判断においてYES(今回車速が所定の速度より遅くなった時点から、全てのトランスデューサについて最新の計測値を検出完了)のとき、CPU21は、後述する障害物判定処理を行う(ステップS8)。
尚、上述した図9のステップS7及びステップS8では、4つのコーナのそれぞれの検出ユニット1について障害物検出処理と判定処理を行ったが、例えば、シフトポジションセンサ4の出力信号によって自動車11の進行方向を検出し、そして、舵角センサ5の出力信号によって自動車11の操舵角度を検出し、その検出した進行方向及び操舵角度に応じて、4つのコーナの検出ユニット1の一部だけを処理対象とすることによって計測時間を短縮し、これによりドライバへの警報を迅速に行い、且つコントローラ2の負荷を軽減してもよいことは言うまでもない。
【0044】
図10は、本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートであり、この処理は、検出ユニット1毎に行われる。同図において、
ステップS71,ステップS72:CPU21は、Tr1から超音波を送信し(ステップS71)、その超音波の反射波をTr1及びTr2によって受信する(ステップS72)。ここで、ステップS72において、Tr1から送信した超音波の反射波をTr1で受信することによって計測された距離を「受信距離R11」とする。また、Tr1から送信した超音波の反射波をTr2で受信することによって計測された距離を「受信距離R12」とする。このとき、反射波は検出できない場合が有ることは言うまでもない。
【0045】
ステップS73,ステップS74:CPU21は、Tr2から超音波を送信し(ステップS73)、その超音波の反射波をTr1及びTr2によって受信する(ステップS74)。ここで、ステップS74において、Tr2から送信した超音波の反射波をTr2で受信することによって計測された距離を「受信距離R22」とする。また、Tr2から送信した超音波の反射波をTr1で受信することによって計測された距離を「受信距離R21」とする。このとき、反射波は検出できない場合が有ることは言うまでもない。
【0046】
ステップS75:CPU21は、ステップS72及びステップS74で計測した受信距離R11,12,21,そして22の4種類の距離に基づいて、一般的な方法を用いて、自動車11から障害物までの距離と位置とを算出する。ここで、位置とは、自動車11を基準とした障害物の存在位置である。
【0047】
ステップS76:CPU21は、ステップS72及びステップS74の検出状況に従って、表示器6への表示パターンを決定し、その決定したパターンを表示器6に表示する。
【0048】
ステップS76における表示パターンの決定方法については、ステップS76の表に示すように、「受信距離R11」等の検出状況と、その検出状況に応じた表示パターンを、ルックアップテーブルとして予めROM23等に登録しておけばよい。ここで、ステップS76に示す表示パターンの組み合わせ表について説明すれば、ステップS72及びステップS74において、
「受信距離R11」だけを検出したとき:障害物は、図8に示すエリア1に存在するため、エリア1を表わす表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0049】
「受信距離R11」と「受信距離R12」だけを検出したとき:検出結果としては、障害物が図8に示すエリア2に存在することになるが、実際にはエリア1にも障害物が存在することも予想されるため、エリア1及び2を表わす表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0050】
「受信距離R11」から「受信距離R22」の全てを検出したとき:検出結果としては、障害物が図8に示すエリア3に存在することになるが、実際にはエリア3の左右の各エリアにも障害物が存在することも予想されるため、エリア1からエリア5までを表わす表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0051】
「受信距離R22」と「受信距離R21」だけを検出したとき:検出結果としては、障害物が図8に示すエリア4に存在することになるが、実際にはエリア5にも障害物が存在することも予想されるため、エリア4及び5を表わす表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0052】
「受信距離R22」だけを検出したとき:障害物は、図8に示すエリア5に存在するため、エリア5を表わす表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0053】
このように、本実施形態では、検出した障害物の位置が5つのエリアの中心に有るときほど、複数のエリアを同時に点灯させる。これにより、検出した障害物が存在するエリアの左右のエリアに、検出が不可能な他の障害物(大きな障害物が複数のエリアに渡って存在する場合を含む)が存在することを考慮に入れた報知(表示)をドライバに対して行えるため、車庫入れ等の運転操作に対するドライバへの精神的な負担を軽減することができる。
【0054】
図12は、本発明の第1の実施形態における表示器の表示画面を示す図であり、自動車11に相当する表示パターンの4つのコーナには、図8に示す5つのエリアに相当する表示パターンがそれぞれ設けられている。CPU21は、上記の障害物検出処理の検出結果に応じて、この図12の各表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0055】
図11は、本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物判定処理を示すフローチャートである。この処理も検出ユニット1毎に行われるが、一例として、自動車11のフロント右側の検出ユニット1についての障害物判定処理を示している。同図において、
ステップS81:CPU21は、ステップS75で算出した障害物までの距離の中に、10cm程度の至近距離の値が有るか否かを判断する。この判断において、YES(至近距離に障害物が有る)のときにはステップS87に進む。
【0056】
ステップS82,ステップS83:ステップS81の判断においてNO(至近距離には障害物は無い)のとき、CPU21は、舵角センサ5の出力信号に基づいて現在の前輪の操舵角度を検出し(ステップS82)、その検出した操舵角度に応じて、ステップS84からステップS86の何れかのステップに進む(ステップS83)。
【0057】
ステップS84:ステップS83の判断において操舵角度が「右最大舵角の近辺」のとき、CPU21は、障害物がエリア4及び5に存在するか否かに関わらずに、エリア1から3に障害物が存在するか否かを判断する。この判断には、上述の障害物検出処理の結果を用いる。ステップS84の判断においてNO(存在しない)のときには、警報は出力する必要が無いのでステップS2に戻り、YES(存在する)のときには、ステップS87に進む。これは、操舵角度が「右最大舵角の近辺」であれば、現時点において自動車1はエリア4及び5の方向には前進しないからである。
【0058】
ステップS85:ステップS83の判断において操舵角度が「舵角0の近辺」のとき、CPU21は、障害物がエリア3から5に存在するか否かに関わらずに、エリア1または2に障害物が存在するか否かを判断する。ステップS85の判断においてNO(存在しない)のときには、警報は出力する必要が無いのでステップS2に戻り、YES(存在する)のときには、ステップS87に進む。これは、操舵角度が「舵角0の近辺」であれば、現時点において自動車1はエリア3から5の方向には前進しないからである。
【0059】
ステップS86:ステップS83の判断において操舵角度が「左最大舵角の近辺」のとき、CPU21は、障害物がエリア2から5に存在するか否かに関わらずに、エリア1に障害物が存在するか否かを判断する。ステップS85の判断においてNO(存在しない)のときには、警報は出力する必要が無いのでステップS2に戻り、YES(存在する)のときには、ステップS87に進む。これは、操舵角度が「左最大舵角の近辺」であれば、現時点において自動車1はエリア2から5の方向には前進しないからである。
【0060】
ステップS87:CPU21は、障害物が有る旨を報知する警報を表示器6及びまたはブザー7を用いて行い、ステップS2に戻る。
【0061】
尚、ステップS84からステップS86の判断要素は、対象とする検出ユニット1の位置に応じて異なることは言うまでもない。
【0062】
上述したように、本実施形態によれば、検出ユニット1にTr1及びTr2を図4等に示すように配置し、それら2つのトランスデューサの送信タイミングをずらすことにより、2つのトランスデューサでありながら、エリア1からエリア5までの5つのエリア内の障害物の有無及びその障害物までの距離を正確に検出することができる。これにより、障害物検出装置における障害物検出の分解能を向上することができる。
【0063】
[第2の実施形態]
本実施形態では、表示器6への表示パターンを、検出した障害物までの距離をも判別可能にすることにより、ドライバの利便性を向上する。本実施形態における障害物検出装置も、基本的な構成は第1の実施形態と同様なため、重複する説明は省略し、特徴的な部分を説明する。
【0064】
尚、以下の説明において、反射波R11は、障害物に反射したTr1の送信波のうち、Tr1に受信されたものをいう。反射波R12は、障害物に反射したTr1の送信波のうち、Tr2に受信されたものをいう。反射波R21は、障害物に反射したTr2の送信波のうち、Tr1に受信されたものをいう。そして、反射波R22は、障害物に反射したTr2の送信波のうち、Tr2に受信されたものをいう。
【0065】
まず、本実施形態では、図13に示すように、表示するエリアをエリアAからエリアCまでの3つのエリアとする。
【0066】
図14は、本発明の第2の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートである。同図において、
ステップS71からステップS75までの処理は第1の実施形態と同様である。
【0067】
ステップS701:CPU21は、ステップS72にて反射波R11を検出できたか否かを判断し、NO(検出しない)のときにはステップS703に進む。
【0068】
ステップS702:ステップS701の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアBに障害物が有ると判断し、「受信距離R11」に相当するエリアB内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0069】
ステップS703:CPU21は、ステップS74にて反射波R22を検出できたか否かを判断し、NO(検出しない)のときにはステップS705に進む。
【0070】
ステップS704:ステップS703の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアCに障害物が有ると判断し、「受信距離R22」に相当するエリアC内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0071】
ステップS705:CPU21は、ステップS72またはステップS74にて反射波R12またはR21を検出できたか否かを判断し、NO(検出しない)のときにはステップS2に進む。
【0072】
ステップS706:ステップS705の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアAに障害物が有ると判断し、「受信距離R12」または「受信距離R21」に相当するエリアA内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0073】
図15は、本発明の第2の実施形態における表示器の表示画面を示す図であり、自動車11に相当する表示パターンの4つのコーナには、図13に示す3つのエリアに分けて、複数の表示パターンがそれぞれ設けられている。CPU21は、上記の障害物検出処理の検出結果に応じて、この図15の各表示パターンを点灯させる。ここで、各エリア内の3つの表示パターンについて説明すれば、例えば、aは、0.6m<(コーナと障害物との距離)≦0.8m,bは、0.4m<(コーナと障害物との距離)≦0.6m,そしてcは、(コーナと障害物との距離)≦0.4mとし、これらの3つのパターンを、「受信距離Rnn」(nは1または2)に応じて表示すればよい。
【0074】
図16及び図17は、本発明の第2の実施形態における5つのエリアの設定例を説明する図であり、一例として、自動車11のフロント右側の場合を示している。
【0075】
本実施形態では、Tr1及びTr2によって形成される送受信エリア12の5つのエリアを、表示器6への表示のために、図13に示すように3つのエリアAからCに分けて使用している。このとき、検出ユニット1内の2つのトランスデューサTr1及びTr2の配置角度を予め調整することにより、エリア1からエリア5の設定の仕方を、図16及び図17に示すようにする。即ち、図16の例では、エリア1とエリア2との境界線が自動車11の車両側方に沿った線の延長線上に、そしてエリア4とエリア5との境界線が自動車11の車両前端に沿った線の延長線上にある。一方、図17の例では、エリア2とエリア3との境界線が自動車11の車両側方に沿った線の延長線上に、そしてエリア3とエリア4との境界線が自動車11の車両前端に沿った線の延長線上にある。
【0076】
図16及び図17に示す各エリアの設定例は、それぞれ特有の効果を有しており、図16の設定は、例えば検出ユニット1が自動車11のフロントの場合、駐車場や車庫からの脱出、或いはクランク状の狭い路地でのすり抜け等に有効である。これは、トランスデューサを図16の設定とすれば、ドライバにとって死角となり易い領域であって、駐車場や車庫からの脱出等を行う際にドライバが最も障害物との接触に注意を払うエリア2からエリア4の領域における当該障害物検出装置の検出分解能を向上できるからである。また、図17の設定は、例えば検出ユニット1が自動車11のリアの場合、縦列駐車を行う場合に有効である。これは、トランスデューサを図17の設定とすれば、ドライバにとって死角となり易い領域であって、縦列駐車を行う際にドライバが最も障害物との接触に注意を払うエリア1及び2、エリア4及び5の領域における当該障害物検出装置の検出分解能を向上できるからである。
【0077】
尚、検出ユニット1に3つ以上のトランスデューサを設け、その中の2つをCPU21によって選択して使用する制御を行い、図16及び図17の両方の設定を適宜使用できるように構成してもよい。
【0078】
以上説明した本実施形態では、障害物が存在する位置を、表示器6にて点灯している表示パターンによって表現し、且つ2つのトランスデューサTr1及びTr2によって形成される5つのエリアの境界線のうち何れか2つの境界線を、自動車11の車両側方に沿った線の延長線上と、車両前端(後端)に沿った線の延長線上になるように設定し、更に表示器6の表示パターンも、図15に示すように同様な設定としている。これにより、ドライバは、自動車11と障害物との位置関係を、表示器6の表示により、感覚的に容易に認識できる。
【0079】
<第2の実施形態の変形例>
また、図18は、本発明の第2の実施形態の変形例における5つのエリアの設定例を説明する図である。また、図19は、本発明の第2の実施形態の変形例における表示パターンの設定例を説明する図である。
【0080】
上述した第1及び第2の実施形態では、自動車11の4つのコーナが略直角であり、表示パターンも同様な設定としているが、図18に示す自動車11’のように、コーナがラウンドしている形状の場合は、5つのエリアの境界線のうち何れか2つの境界線と表示パターンとを、図18及び図19に示すように、当該自動車の車両側方内側の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上と、車両前端(後端)内側の近傍であって、その車両前端(後端)に平行な線の延長線上とに合わせて設定するときにも、コーナが略直角の場合と略同様な効果が得られる。また、当該自動車の車両側方または前端(後端)の近傍であれば、内側でなく外側であってもよい。
【0081】
即ち、上記の第2の実施形態及びその変形例において、2つのトランスデューサが形成する5つのエリアの境界線のうち何れか2つの境界線と表示パターンとは、自動車の車両側方の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上と、該自動車の車両前端及び/または後端の近傍であって、その車両前端及び/または後端に平行な線の延長線上とに合わせればよい。
【0082】
尚、自動車11の車室内において、表示器6による表示位置としては、例えば、本願出願人が先行する特願平9−266483号(本願出願時点では未公開である)で提案しているように、進行方向に応じて、計器パネル、車室後方、ルームミラー、或いはサイドミラーに適宜表示するように構成すればよい。
【0083】
[第3の実施形態]
本実施形態では、第1及び第2の実施形態と比較して更にコーナから至近距離に存在する障害物を検出し、その旨を報知することにより、ドライバの利便性を向上する。本実施形態における障害物検出装置も、基本的な構成は第1及び第2の実施形態と同様なため、重複する説明は省略し、特徴的な部分を説明する。
【0084】
図24は、一般的な単一の超音波トランスデューサによる送信有効領域とその反射波により障害物を計測可能な領域とを説明する図である。同図に示すように、トランスデューサ31による障害物の計測可能領域は、そのトランスデューサから30cm程度の至近距離の位置には存在しない。これは、至近距離に障害物が存在する場合、トランスデューサの送信波に対する反射波は短時間でそのトランスデューサに到達するため、トランスデューサの送信波に対する反射波が、その送信波を送出終了した後に当該トランスデューサ内の振動子の残留振動によって生じる残響波に埋もれてしまい、その反射波を、当該トランスデューサにて検出することができないからである。
【0085】
そこで、本実施形態では、第1及び第2の実施形態と同様に、2つのトランスデューサTr1及びTr2の配置と、それらのトランスデューサからの送信タイミングをずらすことを基本として、トランスデューサと障害物との距離が至近距離にあるため、障害物までの距離が正確に検出できない場合であっても、反射波R12またはR21が検出されたときには、自動車11のコーナの至近距離に障害物が存在すると判断し、その旨を報知する。これは、図21に示すように、トランスデューサと障害物との距離が至近距離にあるために、送信波を出力した送受信ch側のトランスデューサが、その送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波(反射波の一部)を検出できなくても、もう一方の受信ch側のトランスデューサにより、その反射波の一部を受信することができたときには、障害物が存在すると判断できるからである。
【0086】
尚、本実施形態においても、表示するエリアは、図13に示すようにエリアAからエリアCまでの3つのエリアとする。
【0087】
図20は、本発明の第3の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートである。同図において、
ステップS71からステップS75までの処理は第1の実施形態と同様である。
【0088】
ステップS711:CPU21は、ステップS72にて反射波R11を検出できたか否かを判断する。
【0089】
ステップS712:ステップS711の判断にてNO(検出しない)のとき、CPU21は、ステップS74にて反射波R22を検出できたか否かを判断する。
【0090】
ステップS713:ステップS712の判断にてNO(検出しない)のとき、CPU21は、ステップS72またはステップS74にて反射波R12またはR21を検出できたか否かを判断し、NO(検出しない)のときには、当該検出ユニット1の周辺には障害物は存在しないと判断してステップS2に戻る。
【0091】
ステップS714:ステップS713の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアA内の至近距離に障害物が存在すると判断し、表示器6に表示エリアAに相当する表示パターンを点灯させると共に、例えば、至近距離を表わす数字0の表示や、他の表示パターン、表示色の変更等によってドライバの注意を喚起する。
【0092】
ステップS715:ステップS712の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアC内に障害物が存在すると判断し、「受信距離R22」に相当するエリアC内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0093】
ステップS716:ステップS711の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、ステップS74にて反射波R22を検出できたか否かを判断する。
【0094】
ステップS717:ステップS716の判断にてNO(検出しない)のとき、CPU21は、エリアB内に障害物が存在すると判断し、「受信距離R11」に相当するエリアB内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0095】
ステップS718:ステップS716の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、エリアB及びC内に障害物が存在すると判断し、「受信距離R11」及び「受信距離R22」に相当するエリアB及びC内の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0096】
ステップS719:CPU21は、ステップS72またはステップS74にて反射波R12またはR21を検出できたか否かを判断し、NO(検出しない)のときには、当該検出ユニット1の周辺には障害物は存在しないと判断してステップS2に戻る。
【0097】
ステップS720:ステップS719の判断にてYES(検出した)のとき、CPU21は、ステップS717またはステップS718にて点灯させた表示パターンに加え、更に、エリアA内に障害物が存在すると判断し、「受信距離R12」または「受信距離R21」に相当するエリアA内の表示パターンより内側の表示パターンを点灯させる。
【0098】
これにより、本実施形態では、2つのトランスデューサTr1及びTr2の配置と、図20に示す障害物検出処理とにより、実質的な計測可能領域を、図22に示すように大きく広げることができ、自動車11のコーナの至近距離に位置する障害物をも検出することができる。
【0099】
また、トランスデューサの送信波によって生じる所謂サイドローブを、検出ユニット1におけるトランスデューサ取り付け位置の形状を工夫することにより、図23に示すように、自動車11のコーナの形状に沿うようにしている。
【0100】
このように、本実施形態によれば、実質的な計測可能領域を、より大きく広げることができ、更に、サイドローブを有効に利用することによってコーナから至近距離に存在する障害物の検出可能な領域も広げることができるため、ドライバの利便性を向上することができる。
【0101】
【発明の効果】
以上説明したように、本発明によれば、少ないトランスデューサにより、高精度に障害物を検出する障害物検出装置及び障害物の検出方法の提供が実現する。
【0102】
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の第1の実施形態としての障害物検出装置の構成を示すブロック図である。
【図2】本発明の第1の実施形態における検出ユニット内のトランスデューサが形成する送受信エリアを説明する図である。
【図3】本発明の第1の実施形態における検出ユニットの正面図である。
【図4】本発明の第1の実施形態における検出ユニットの上面図である。
【図5】本発明の第1の実施形態における検出ユニットの背面図である。
【図6】本発明の第1の実施形態における自動車に取り付けられた検出ユニットの位置を示す図である。
【図7】本発明の第1の実施形態において実際に使用するトランスデューサが形成する送受信エリアを説明する図である。
【図8】本発明の第1の実施形態における2つのトランスデューサが形成する検出エリアを説明する図である。
【図9】本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物検出・判定処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図10】本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図11】本発明の第1の実施形態における障害物判定処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図12】本発明の第1の実施形態における表示器の表示画面を示す図である。
【図13】本発明の第2の実施形態における表示エリアの分け方を説明する図である。
【図14】本発明の第2の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図15】本発明の第2の実施形態における表示器の表示画面を示す図である。
【図16】本発明の第2の実施形態における5つのエリアの設定例を説明する図である。
【図17】本発明の第2の実施形態における5つのエリアの設定例を説明する図である。
【図18】本発明の第2の実施形態の変形例における5つのエリアの設定例を説明する図である。
【図19】本発明の第2の実施形態の変形例における表示パターンの設定例を説明する図である。
【図20】本発明の第3の実施形態における障害物検出処理を示すフローチャートである。
【図21】本発明の第3の実施形態における至近距離に位置する障害物の検出方法を説明するタイムチャートである。
【図22】本発明の第3の実施形態において2つのトランスデューサによる送信有効領域とその反射波により障害物を計測可能な領域とを示す図である。
【図23】本発明の第3の実施形態においてサイドローブを利用して自動車のコーナに沿って形成された送受信エリアを示す図である。
【図24】一般的な単一の超音波トランスデューサによる送信有効領域とその反射波により障害物を計測可能な領域とを示す図である。
【符号の説明】
1:検出ユニット,
2:コントローラ,
3:車速センサ,
4:シフトポジションセンサ,
5:舵角センサ,
6:表示器,
7:ブザー,
8:マルチプレクサ回路,
9:フィルタ・アンプ回路,
10:コンパレータ,
11,32:自動車,
12:送受信エリア,
21:CPU,
22:RAM,
23:ROM,
Tr1,Tr2,31:トランスデューサ,[0001]
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
The present invention relates to an obstacle detection apparatus and an obstacle detection method for detecting the presence and position of an obstacle present around an object such as a vehicle using, for example, ultrasonic waves.
[0002]
[Prior art]
In recent years, some automobiles, which are representative vehicles, have obstacles in order to prevent them from coming into contact with surrounding obstacles when entering the car garage or parallel parking. And an obstacle detection device capable of detecting the position. In such an obstacle detection device, generally, a transducer using ultrasonic waves is used as means for detecting the presence or absence and position of an obstacle.
[0003]
Also, for example, in JP-A-8-301029, three detection ranges are formed by overlapping the detection ranges formed by two ultrasonic sensors (transducers), thereby improving the resolution when detecting an obstacle. A technique has been proposed.
[0004]
[Problems to be solved by the invention]
However, in the conventional example using the above two ultrasonic sensors, there are three detectable areas, which is sufficient when the vehicle must be operated in a narrow area such as parallel parking. It cannot be said that the resolution is high.
[0005]
Therefore, an object of the present invention is to provide an obstacle detection device and an obstacle detection method for detecting an obstacle with high accuracy by using a small number of transducers.
[0006]
[Means for Solving the Problems]
In order to achieve the above object, an obstacle detection apparatus according to the present invention is characterized by the following configuration.
[0007]
That is, claim 1 forms two non-overlapping regions and one overlapping region sandwiched between the two non-overlapping regions by the detection regions of at least two transducers, and obstacles existing in these regions An obstacle detection apparatus comprising detection means for detecting presence / absence and position, wherein at least the transmission effective range and the reception effective range in the detection range of the first transducer of the two transducers are different, and the overlapping region Comprises a first overlapping region included in the effective transmission range and the effective reception range of the first transducer, and a second overlapping region included in either the effective transmission range or the effective reception range. And when the first and second overlapping regions are included in the detection region of the second transducer, the detection means Multiple area, and characterized by detecting whether an obstacle to any region of the four regions of the first and second overlapping region exists.
Thus, four areas are formed by the two transducers, and obstacles in the areas are detected with high accuracy.
[0008]
Further, as a second aspect of the present invention, the effective transmission range and the effective reception range in the detection range of the second transducer are different from each other, and the first overlapping area is different from the effective transmission range and the reception of the second transducer. When the third overlapping area included in the effective range and the fourth overlapping area included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range are configured, the detection means includes the two non-existing areas. It is characterized by detecting in which of the five areas of the overlapping area and the second to fourth overlapping areas an obstacle exists. Thus, five regions are formed by the two transducers, and obstacles in the regions are detected with high accuracy.
[0009]
In the obstacle detection device having the above-described configuration, when the first and second transducers are, for example, an ultrasonic type, the transmission effective range and the reception effective range are different, and the transmission effective range is It is smaller than the effective reception range (claim 9).
[0010]
Further, the information processing apparatus further comprises notification means for notifying which of the four or five areas the obstacle detected by the detection means exists (Claim 3).
Preferably, the notification means is a display means, and when the display means displays a display pattern representing an area where the detected obstacle exists, together with the display pattern, If there is another area located on the opposite side of the four or five areas with respect to the area where the obstacle exists, It is preferable to display a display pattern representing another area.
This allows the user to recognize other obstacles that cannot be detected at that time, or large obstacles that may exist across multiple areas.
[0011]
Preferably, each of the two transducers includes a transmission mechanism and a reception mechanism, and the detection means transmits the transmission waves transmitted by the transmission mechanism while shifting the transmission waves so that the transmission waves are obstructed. The reception of the reflected wave generated by the reflection is performed by both of the reception mechanisms (claim 5).
As a result, the above four or five regions are efficiently detected.
[0012]
At this time, when the first and second transducers receive at least a part of the reflected wave generated when the transmission wave of the first transducer is reflected by an obstacle, First What is necessary is just to judge that an obstruction exists in an overlapping area | region (Claim 6).
[0013]
Further, as claimed in
Thus, information necessary for driving operation is provided in a form suitable for the driver's sense of vehicle.
[0014]
Further, according to an eighth aspect of the present invention, in the two transducers, a boundary line between the second overlap region and the third overlap region is in the vicinity of the side of the vehicle and is parallel to the side of the vehicle. A boundary line between the third overlap region and the fourth overlap region is located in the vicinity of the vehicle front end and / or rear end and parallel to the vehicle front end and / or rear end so as to be located on the extension line. It is good to arrange | position close to the corner of a vehicle at a predetermined opening angle so that it may be located on the extended line of a straight line.
Thus, information necessary for driving operation is provided in a form suitable for the driver's sense of vehicle.
[0015]
Or in order to achieve said objective, the detection method of the obstruction which concerns on this invention is characterized by the following structures.
[0016]
That is, claim 10 forms two non-overlapping regions and one overlapping region sandwiched between the two non-overlapping regions by the detection regions of at least two transducers, and obstructions existing in these regions. An obstacle detection method for detecting presence / absence and position, wherein at least a transmission effective range and a reception effective range in a detection range of a first transducer of the two transducers are different, and the overlapping region is A first overlapping region included in the transmission effective range and the reception effective range of the first transducer, and a second overlapping region included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range; When the first and second overlapping regions are included in the detection region of the second transducer, the transmission waves of the two transducers The transmission timing is shifted and reception of the reflected waves generated by the reflected waves being reflected by the obstacle is performed by both of the transducers, so that the two non-overlapping regions and the first and second It is characterized by detecting in which of the four areas of the overlapping area an obstacle is present.
Thus, four areas are formed by the two transducers, and obstacles in the areas are detected with high accuracy.
[0017]
Further, according to
Thus, five regions are formed by the two transducers, and obstacles in the regions are detected with high accuracy.
[0018]
Further, in the above method, when the first and second transducers receive at least a part of a reflected wave generated when the transmission wave of the first transducer is reflected by an obstacle, First What is necessary is just to judge that an obstruction exists in an overlapping area | region (Claim 12).
[0019]
Preferably, in the obstacle detection method, Further, the effective transmission range of the first and second transducers is smaller than the effective reception range, The two transducers are preliminarily arranged close to each other with a predetermined opening angle, and the first and second transducers Out of transmission range It is preferable to use a substantially half range on the transducer side.
As a result, the detection range of the two transducers is formed in a substantially fan shape to facilitate recognition by the user.
[0020]
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
DESCRIPTION OF EMBODIMENTS Hereinafter, an obstacle detection device according to the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings as an embodiment in which the obstacle detection device is applied to an automobile which is a typical vehicle.
[0021]
[First Embodiment]
<Hardware>
First, the hardware configuration of the obstacle detection apparatus in the present embodiment will be described.
[0022]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing the configuration of an obstacle detection apparatus as a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0023]
In the figure,
[0024]
[0025]
[0026]
The
[0027]
Next, the configuration of the
[0028]
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a transmission / reception area formed by the transducer in the detection unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention. In the figure, for convenience of explanation, Tr1 and Tr2 are expressed adjacently in parallel. The actual transmission /
[0029]
Tr1 is a reception effective area indicated by a thin solid line in the figure, in which Tr1 itself can receive a part of a reflected wave (hereinafter simply referred to as a reflected wave for convenience) outputted from Tr1. In addition to the reflected wave, a transmission effective region indicated by a thin broken line in FIG. Similarly, Tr2 has a reception effective area indicated by a thick solid line in the figure and a transmission effective area indicated by a thick broken line in the figure. Tr1 and Tr2 have different transmission timings as will be described later.
[0030]
Since Tr1 and Tr2 having such transmission and reception effective areas are arranged adjacent to each other in the
[0031]
Area 1: When Tr1 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave can be received only by Tr1, and when Tr2 transmits an ultrasonic wave, Tr1 returns the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave. It is an area that cannot be received.
[0032]
Area 2: When Tr1 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave can be measured by Tr1 and Tr2. When Tr2 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave is Tr1. Is an area that cannot be received.
[0033]
Area 3: When Tr1 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave can be measured by Tr1 and Tr2, and when Tr2 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave is also transmitted. , Tr1 and Tr2 are measurable areas.
[0034]
Area 4: When Tr2 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave can be measured by Tr1 and Tr2. When Tr1 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave is Tr2 Is an area that cannot be received.
[0035]
Area 5: When Tr2 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave can be received only by Tr2, and when Tr1 transmits an ultrasonic wave, the reflected wave of the ultrasonic wave is Tr2 It is an area that cannot be received.
[0036]
Further, the obstacle detection apparatus according to the present embodiment uses, in the five areas described above, an area that is about half of the effective transmission area of Tr1 and Tr2 for the detection of the obstacle, as shown by the hatched portion in FIG. Thus, as shown in a schematic shape in FIG. 8, a fan-shaped transmission /
[0037]
In the present embodiment, the area used for the obstacle detection is, for example, about 0.75 m in front of Tr1 and Tr2 from the viewpoint of detecting an obstacle when performing garage entry or parallel parking. Needless to say, when detecting a distant obstacle, the output of the ultrasonic wave transmitted from the transducer may be increased.
[0038]
<Software>
The obstacle detection / determination process executed by the
[0039]
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing obstacle detection / determination processing in the first embodiment of the present invention. In the figure,
Step S1, Step S2: The
[0040]
Steps S3 and S4: The
[0041]
Step S5: When the determination in step S4 is NO (faster than a predetermined speed), the
[0042]
Step S6, Step S7: If YES in step S4 (slower than the predetermined speed), has the
[0043]
Step S8: When the determination in step S6 is YES (detection of the latest measured values for all transducers has been completed from the time when the current vehicle speed is lower than the predetermined speed), the
In step S7 and step S8 of FIG. 9 described above, the obstacle detection process and the determination process are performed for the
[0044]
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing the obstacle detection process according to the first embodiment of the present invention, and this process is performed for each
Step S71, Step S72: The
[0045]
Step S73, Step S74: The
[0046]
Step S75: The
[0047]
Step S76: The
[0048]
As for the display pattern determination method in step S76, as shown in the table of step S76, the detection status such as “reception distance R11” and the display pattern corresponding to the detection status are registered in advance in the
When only “reception distance R11” is detected: Since the obstacle exists in
[0049]
When only “reception distance R11” and “reception distance R12” are detected: As a result of the detection, an obstacle exists in
[0050]
When all of “reception distance R11” to “reception distance R22” are detected: As a detection result, an obstacle is present in
[0051]
When only “reception distance R22” and “reception distance R21” are detected: As a result of the detection, an obstacle is present in area 4 shown in FIG. Therefore, the display patterns representing the
[0052]
When only “reception distance R22” is detected: Since the obstacle exists in
[0053]
Thus, in this embodiment, a plurality of areas are lit simultaneously as the detected obstacle is located at the center of the five areas. This takes into account that other obstacles that cannot be detected (including cases where large obstacles exist across multiple areas) exist in the left and right areas of the area where the detected obstacles exist. Since the entered notification (display) can be made to the driver, the mental burden on the driver for driving operations such as garage entry can be reduced.
[0054]
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a display screen of the display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. In the four corners of the display pattern corresponding to the
[0055]
FIG. 11 is a flowchart showing an obstacle determination process in the first embodiment of the present invention. Although this process is also performed for each
Step S81: The
[0056]
Step S82, Step S83: When the determination in step S81 is NO (no obstacle at close range), the
[0057]
Step S84: When the steering angle is “in the vicinity of the maximum right steering angle” in the determination in Step S83, the
[0058]
Step S85: When the steering angle is “near the
[0059]
Step S86: When the steering angle is “near the left maximum steering angle” in the determination in step S83, the
[0060]
Step S87: The
[0061]
Needless to say, the determination elements from step S84 to step S86 differ depending on the position of the
[0062]
As described above, according to the present embodiment, Tr1 and Tr2 are arranged in the
[0063]
[Second Embodiment]
In the present embodiment, the convenience of the driver is improved by enabling the display pattern on the
[0064]
In the following description, the reflected wave R11 means a wave received by Tr1 among the transmitted waves of Tr1 reflected by an obstacle. The reflected wave R12 is a wave received by Tr2 among the transmitted waves of Tr1 reflected by the obstacle. The reflected wave R21 is a wave received by Tr1 among the transmitted waves of Tr2 reflected by the obstacle. The reflected wave R22 is a wave received by Tr2 among the transmitted waves of Tr2 reflected by the obstacle.
[0065]
First, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 13, the areas to be displayed are three areas from area A to area C.
[0066]
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing obstacle detection processing in the second embodiment of the present invention. In the figure,
The processing from step S71 to step S75 is the same as in the first embodiment.
[0067]
Step S701: The
[0068]
Step S702: When the determination in step S701 is YES (detected), the
[0069]
Step S703: The
[0070]
Step S704: If YES (detected) in the determination in step S703, the
[0071]
Step S705: The
[0072]
Step S706: When the determination in step S705 is YES (detected), the
[0073]
FIG. 15 is a diagram showing a display screen of the display device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. The four corners of the display pattern corresponding to the
[0074]
FIGS. 16 and 17 are diagrams illustrating an example of setting five areas according to the second embodiment of the present invention. As an example, the case of the front right side of the
[0075]
In this embodiment, five areas of the transmission /
[0076]
The setting example of each area shown in FIGS. 16 and 17 has a unique effect. The setting in FIG. 16 is, for example, when the
[0077]
It should be noted that the
[0078]
In the present embodiment described above, the position where the obstacle is present is expressed by the display pattern that is lit on the
[0079]
<Modification of Second Embodiment>
FIG. 18 is a diagram for explaining a setting example of five areas in a modification of the second embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 19 is a diagram for explaining a display pattern setting example in a modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0080]
In the first and second embodiments described above, the four corners of the
[0081]
That is, in the second embodiment and the modification thereof, any two of the five area boundary lines formed by the two transducers and the display pattern are in the vicinity of the vehicle side of the automobile. The extension of the line parallel to the side of the vehicle and the extension of the line near the front end and / or rear end of the automobile and parallel to the front end and / or rear end of the vehicle. Good.
[0082]
In addition, as the display position of the
[0083]
[Third Embodiment]
In the present embodiment, as compared with the first and second embodiments, an obstacle existing at a close distance from the corner is further detected, and notification to that effect is made, thereby improving the convenience of the driver. Since the basic configuration of the obstacle detection apparatus according to this embodiment is the same as that of the first and second embodiments, a redundant description will be omitted, and a characteristic part will be described.
[0084]
FIG. 24 is a diagram for explaining a transmission effective area by a general single ultrasonic transducer and an area where an obstacle can be measured by its reflected wave. As shown in the figure, the obstacle measurable area by the transducer 31 does not exist at a position as close as 30 cm from the transducer. This is because when there is an obstacle at a close distance, the reflected wave with respect to the transmission wave of the transducer reaches the transducer in a short time. This is because it is buried in the reverberation wave generated by the residual vibration of the inner vibrator, and the reflected wave cannot be detected by the transducer.
[0085]
Therefore, in this embodiment, as in the first and second embodiments, the distance between the transducer and the obstacle is based on shifting the arrangement of the two transducers Tr1 and Tr2 and the transmission timing from these transducers. Even if the distance to the obstacle cannot be accurately detected because the distance is close, when the reflected wave R12 or R21 is detected, it is determined that there is an obstacle at the close distance of the corner of the
[0086]
In this embodiment as well, the areas to be displayed are three areas from area A to area C as shown in FIG.
[0087]
FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing an obstacle detection process in the third embodiment of the present invention. In the figure,
The processing from step S71 to step S75 is the same as in the first embodiment.
[0088]
Step S711: The
[0089]
Step S712: When the determination in step S711 is NO (not detected), the
[0090]
Step S713: When the determination in step S712 is NO (not detected), the
[0091]
Step S714: When the determination in step S713 is YES (detected), the
[0092]
Step S715: When the determination in step S712 is YES (detected), the
[0093]
Step S716: If YES (detected) in the determination in step S711, the
[0094]
Step S717: When the determination in step S716 is NO (not detected), the
[0095]
Step S718: When the determination in step S716 is YES (detected), the
[0096]
Step S719: The
[0097]
Step S720: When the determination in step S719 is YES (detected), the
[0098]
Thereby, in this embodiment, the substantial measurable area can be greatly expanded as shown in FIG. 22 by the arrangement of the two transducers Tr1 and Tr2 and the obstacle detection processing shown in FIG. Obstacles located at a close distance of 11 corners can also be detected.
[0099]
Further, so-called side lobes generated by the transmission waves of the transducers are adapted to the shape of the corner of the
[0100]
As described above, according to the present embodiment, the substantial measurable region can be further expanded, and further, obstacles existing at a close distance from the corner can be detected by effectively using the side lobe. Since the area can be expanded, the convenience of the driver can be improved.
[0101]
【The invention's effect】
As described above, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide an obstacle detection apparatus and an obstacle detection method for detecting an obstacle with high accuracy by using a small number of transducers.
[0102]
[Brief description of the drawings]
FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration of an obstacle detection apparatus according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 2 is a diagram illustrating a transmission / reception area formed by a transducer in the detection unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 3 is a front view of the detection unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 4 is a top view of the detection unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 5 is a rear view of the detection unit according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 6 is a diagram showing the position of a detection unit attached to the automobile in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating a transmission / reception area formed by a transducer actually used in the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 8 is a diagram illustrating a detection area formed by two transducers in the first embodiment of the invention.
FIG. 9 is a flowchart showing obstacle detection / determination processing in the first embodiment of the present invention;
FIG. 10 is a flowchart showing obstacle detection processing according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 11 is a flowchart illustrating obstacle determination processing according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 12 is a diagram showing a display screen of the display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 13 is a diagram for explaining how to divide display areas according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 14 is a flowchart showing an obstacle detection process in the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 15 is a diagram showing a display screen of a display device according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 16 is a diagram illustrating an example of setting five areas in the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 17 is a diagram illustrating an example of setting five areas in the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating a setting example of five areas in a modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 19 is a diagram illustrating a display pattern setting example according to a modification of the second embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 20 is a flowchart showing obstacle detection processing according to the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 21 is a time chart for explaining a method of detecting an obstacle located at a close distance in the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 22 is a diagram showing a transmission effective area by two transducers and an area where an obstacle can be measured by the reflected wave in the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 23 is a diagram showing a transmission / reception area formed along a corner of an automobile using side lobes in the third embodiment of the present invention.
FIG. 24 is a diagram showing a transmission effective area by a general single ultrasonic transducer and an area where an obstacle can be measured by its reflected wave.
[Explanation of symbols]
1: detection unit,
2: Controller,
3: Vehicle speed sensor,
4: Shift position sensor,
5: Rudder angle sensor,
6: Display,
7: Buzzer,
8: Multiplexer circuit,
9: Filter / amplifier circuit,
10: Comparator,
11, 32: car,
12: Transmission / reception area,
21: CPU,
22: RAM,
23: ROM,
Tr1, Tr2, 31: Transducer,
Claims (13)
前記2つのトランスデューサのうち、少なくとも第1のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とは異なっており、
前記重複領域は、前記第1のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第1の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第2の重複領域とを構成しており、且つそれら第1及び第2の重複領域は、第2のトランスデューサの検出領域に含まれるとき、
前記検出手段は、前記2つの非重複領域、並びに前記第1及び第2の重複領域の4つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする障害物検出装置。Detection in which detection regions of at least two transducers form two non-overlapping regions and one overlapping region sandwiched between the two non-overlapping regions and detect the presence and position of obstacles present in these regions An obstacle detection device comprising means,
Of the two transducers, at least the transmission effective range and the reception effective range in the detection range of the first transducer are different,
The overlapping area includes a first overlapping area included in a transmission effective range and a reception effective range of the first transducer, and a second overlapping area included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range. And the first and second overlapping regions are included in the detection region of the second transducer,
The detection means detects an obstacle in which of the two non-overlapping areas and the four areas of the first and second overlapping areas. apparatus.
前記第1の重複領域は、前記第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第3の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第4の重複領域とを構成しているとき、
前記検出手段は、前記2つの非重複領域、前記第2から第4の重複領域の5つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする請求項1記載の障害物検出装置。Further, the effective transmission range and the effective reception range in the detection range of the second transducer are different,
The first overlapping area includes a third overlapping area included in the transmission effective range and the reception effective range of the second transducer, and a fourth overlapping area included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range. When configuring the overlap area,
2. The detection unit according to claim 1, wherein the detection unit detects in which of the two non-overlapping regions and the five regions of the second to fourth overlapping regions an obstacle exists. Obstacle detection device.
前記検出手段は、該送信機構による送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信させ、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、該受信機構の両方に行わせることを特徴とする請求項1または請求項2記載の障害物検出装置。Each of the two transducers includes a transmission mechanism and a reception mechanism,
The detection means is characterized in that transmission timings of transmission waves transmitted by the transmission mechanism are shifted and transmission of reception of reflected waves caused by reflection of the transmission waves on an obstacle is performed by both of the reception mechanisms. The obstacle detection device according to claim 1 or 2.
前記非重複領域と重複領域との2つの境界線が、車両側方の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上と、前記車両前端及び/または後端の近傍であって、その車両前端及び/または後端に平行な線の延長線上とに位置するように、
所定の開角をなして車両のコーナに近接配置されていることを特徴とする請求項1記載の障害物検出装置。The two transducers are
Two boundary lines between the non-overlapping region and the overlapping region are in the vicinity of the side of the vehicle, on the extension line of the line parallel to the side of the vehicle, and in the vicinity of the front end and / or the rear end of the vehicle. So as to be located on an extension of a line parallel to the front end and / or rear end of the vehicle,
The obstacle detection device according to claim 1, wherein the obstacle detection device is disposed close to a corner of the vehicle at a predetermined opening angle.
前記第2の重複領域と第3の重複領域との境界線が、車両側方の近傍であって、その車両側方に平行な線の延長線上に位置するように、
前記第3の重複領域と第4の重複領域との境界線が、前記車両前端及び/または後端の近傍であって、その車両前端及び/または後端に平行な線の延長線上に位置するように、
所定の開角をなして車両のコーナに近接配置されていることを特徴とする請求項2記載の障害物検出装置。The two transducers are
The boundary line between the second overlapping region and the third overlapping region is located in the vicinity of the vehicle side and on the extension line of the line parallel to the vehicle side,
A boundary line between the third overlapping region and the fourth overlapping region is located in the vicinity of the front end and / or rear end of the vehicle and on an extension of a line parallel to the front end and / or rear end of the vehicle. like,
The obstacle detection device according to claim 2, wherein the obstacle detection device is disposed close to a corner of the vehicle at a predetermined opening angle.
前記2つのトランスデューサのうち、少なくとも第1のトランスデューサの検出範囲における送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とは異なっており、
前記重複領域は、前記第1のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第1の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第2の重複領域とを構成しており、且つそれら第1及び第2の重複領域は、第2のトランスデューサの検出領域に含まれるとき、
前記2つのトランスデューサによる送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信し、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、それらトランスデューサの両方で行うことにより、前記2つの非重複領域、並びに前記第1及び第2の重複領域の4つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする障害物の検出方法。Obstacles that form two non-overlapping regions and one overlapping region sandwiched between the two non-overlapping regions and detect the presence and position of obstacles in those regions by the detection regions of at least two transducers A method for detecting an object,
Of the two transducers, at least the transmission effective range and the reception effective range in the detection range of the first transducer are different,
The overlapping area includes a first overlapping area included in a transmission effective range and a reception effective range of the first transducer, and a second overlapping area included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range. And the first and second overlapping regions are included in the detection region of the second transducer,
The transmission timing of the transmission waves transmitted by the two transducers is shifted, and the reception of the reflected waves caused by the reflection of the transmission waves to the obstacle is performed by both of the transducers. An obstacle detection method comprising: detecting an obstacle in any one of the four areas of the first and second overlapping areas.
前記第1の重複領域は、前記第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲と受信有効範囲とに含まれる第3の重複領域と、その送信有効範囲または受信有効範囲の何れか一方に含まれる第4の重複領域とを構成しているとき、
前記2つのトランスデューサによる送信波の送信タイミングをずらして送信し、それら送信波が障害物に反射することによって生じる反射波の受信は、それらトランスデューサの両方で行うことにより、前記2つの非重複領域、前記第2から第4の重複領域の5つの領域のうち何れの領域内に障害物が存在するかを検出することを特徴とする請求項10記載の障害物の検出方法。Further, the effective transmission range and the effective reception range in the detection range of the second transducer are different,
The first overlapping area includes a third overlapping area included in the transmission effective range and the reception effective range of the second transducer, and a fourth overlapping area included in either the transmission effective range or the reception effective range. When configuring the overlap area,
The transmission timing of the transmission waves transmitted by the two transducers is shifted, and the reception of the reflected waves caused by the reflection of the transmission waves to the obstacle is performed by both of the transducers. The obstacle detection method according to claim 10, wherein an obstacle is present in any one of the five areas of the second to fourth overlapping areas.
前記2つのトランスデューサを、所定の開角をなして予め近接配置し、
前記第1及び第2のトランスデューサの送信有効範囲のうち、それらトランスデューサ側の略半分の範囲を用いることを特徴とする請求項11記載の障害物の検出方法。 Further, the effective transmission range of the first and second transducers is smaller than the effective reception range,
The two transducers are preliminarily arranged close to each other with a predetermined opening angle,
12. The obstacle detection method according to claim 11, wherein, within the transmission effective ranges of the first and second transducers, a range approximately half of the transducer side is used.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP10659098A JP3956252B2 (en) | 1998-04-16 | 1998-04-16 | Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP10659098A JP3956252B2 (en) | 1998-04-16 | 1998-04-16 | Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH11304919A JPH11304919A (en) | 1999-11-05 |
| JP3956252B2 true JP3956252B2 (en) | 2007-08-08 |
Family
ID=14437409
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP10659098A Expired - Fee Related JP3956252B2 (en) | 1998-04-16 | 1998-04-16 | Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP3956252B2 (en) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3956251B2 (en) * | 1998-04-16 | 2007-08-08 | マツダ株式会社 | Obstacle detection device for vehicle and arrangement method of transducer for obstacle detection |
| JP2005056336A (en) * | 2003-08-07 | 2005-03-03 | Denso Corp | Device for supervising area around vehicle |
| WO2013118772A1 (en) * | 2012-02-10 | 2013-08-15 | 日産自動車株式会社 | Travel control device and travel control method |
| KR101892763B1 (en) * | 2013-10-08 | 2018-08-28 | 주식회사 만도 | Method for detecting obstacle, apparatus for detecting obstacle and method and system for parking assistant |
| JP6467748B2 (en) * | 2014-04-08 | 2019-02-13 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | Object detection device |
| KR101513198B1 (en) * | 2014-09-24 | 2015-04-17 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | Parking Asist Apparatus and vehicle |
| JP6557958B2 (en) * | 2014-10-22 | 2019-08-14 | 株式会社Soken | Obstacle detection device for vehicle |
| JP6645416B2 (en) * | 2016-12-20 | 2020-02-14 | 株式会社デンソー | Occupant detection device, occupant detection system, occupant detection method |
| JP2021139692A (en) * | 2020-03-04 | 2021-09-16 | 株式会社豊田自動織機 | Obstacle detector for moving body |
-
1998
- 1998-04-16 JP JP10659098A patent/JP3956252B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JPH11304919A (en) | 1999-11-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US7248153B2 (en) | Method for parking a vehicle | |
| US7388474B2 (en) | Vehicular obstacle detection system | |
| JP4880712B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device | |
| US7095361B2 (en) | Radar sensor platform | |
| JP2000028717A (en) | Device for detecting obstacle | |
| JP6557958B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device for vehicle | |
| JP6528382B2 (en) | Vehicle Obstacle Detection Device | |
| JP3956252B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method | |
| JP3608432B2 (en) | Obstacle monitoring device for vehicles | |
| JP2006317186A (en) | Obstruction detector | |
| CN106662642A (en) | Detection system | |
| JP3956251B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device for vehicle and arrangement method of transducer for obstacle detection | |
| JP3956253B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device and obstacle detection method | |
| JP4370813B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device for vehicle | |
| JP4742803B2 (en) | Vehicle periphery monitoring device | |
| JP3145592B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device for vehicles | |
| JPH06331742A (en) | On-board ultrasonic sensor unit | |
| JPH07159531A (en) | Obstacle detecting device of vehicle | |
| JPH0683509U (en) | Obstacle detecting control device of vehicle | |
| JP2001273595A (en) | Device for detecting obstacle for automobile | |
| JP5780159B2 (en) | Obstacle detection device | |
| JP2018087772A (en) | Object detection device | |
| JP2009236492A (en) | Obstacle monitoring device for vehicle | |
| JP2007276559A (en) | Obstacle detection device | |
| JP2024135753A (en) | Driving assistance device, driving assistance method, and computer program |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20050124 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7426 Effective date: 20050124 |
|
| RD03 | Notification of appointment of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7423 Effective date: 20050124 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20061212 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20061215 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070213 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20070413 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20070426 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110518 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110518 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120518 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |