JP2020173155A - Target motion estimating device and target motion estimating method - Google Patents
Target motion estimating device and target motion estimating method Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2020173155A JP2020173155A JP2019074719A JP2019074719A JP2020173155A JP 2020173155 A JP2020173155 A JP 2020173155A JP 2019074719 A JP2019074719 A JP 2019074719A JP 2019074719 A JP2019074719 A JP 2019074719A JP 2020173155 A JP2020173155 A JP 2020173155A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- target
- passive sensor
- motion estimation
- passive
- doppler
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 19
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 28
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 230000002194 synthesizing effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 7
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Landscapes
- Radar Systems Or Details Thereof (AREA)
- Measurement Of Velocity Or Position Using Acoustic Or Ultrasonic Waves (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、目標運動推定装置及び目標運動推定方法に関し、特にドップラーシフトを用いて目標運動を推定する技術に関する。 The present invention relates to a target motion estimation device and a target motion estimation method, and particularly to a technique for estimating a target motion using Doppler shift.
受動型センサを用いて、目標となる物体の位置・速度を推定する目標運動推定装置が提案されている。能動型センサは信号を発射して反射等を観測するのに対し、受動型センサは、信号を発射せず、対象が放射する信号を観測する。受信する信号の種類により、パッシブソーナー、パッシブレーダー、赤外線センサ等の種類がある。 A target motion estimation device that estimates the position and velocity of a target object using a passive sensor has been proposed. The active sensor emits a signal and observes reflections, etc., whereas the passive sensor does not emit a signal and observes the signal emitted by the target. Depending on the type of signal received, there are types such as passive sonar, passive radar, and infrared sensor.
特許文献1は、無指向性のパッシブソーナー装置を用いてドップラーシフト量から目標運動を推定する技術を開示している。本方法によれば、目標が放射する信号のドップラーシフトに基づいて、目標の針路と目標の存在する方位のなす角度を算出することができる。ここで、3個以上の無指向性パッシブソーナー装置を用いることにより、目標の位置及び針路が一つに定まる。
また、指向性を備えた受動型センサを用いると、1つのセンサで目標の方位を検出することができる。したがって、2つの受動型センサを用いて目標の存在する方位を検出すると、センサを起点とした方位線の交点から目標の存在位置を求めることができる。
そして、時間間隔を置いた後に、同様の方法で再度目標の存在位置を得て、存在位置の変化から目標の速度を推定することができる。
Further, if a passive sensor having directivity is used, the target direction can be detected by one sensor. Therefore, when the direction in which the target exists is detected by using the two passive sensors, the position where the target exists can be obtained from the intersection of the direction lines starting from the sensor.
Then, after the time interval is set, the target existing position can be obtained again in the same manner, and the target speed can be estimated from the change in the existing position.
受動型センサを用いて、目標となる物体の位置・速度を推定する目標運動推定方法において短時間で目標の運動を推定できないという問題があった。 There is a problem that the target motion cannot be estimated in a short time in the target motion estimation method for estimating the position and velocity of the target object using a passive sensor.
特許文献1の方法は、目標がCPA(Closest Point of Approach:最接近点)を通過する際に予め目標速度を取得する場合を想定している。したがって、速度が未知の目標について、短時間で目標運動を推定することはできない。
The method of
また、指向性を備えた受動型センサを用いた場合は、所定の時間間隔を置いて2回存在位置を求めなければならない。したがって、短時間で目標運動を推定することはできない。 Further, when a passive sensor having directivity is used, the existence position must be obtained twice at a predetermined time interval. Therefore, the target movement cannot be estimated in a short time.
本開示は上記課題を解決するためにされたものであって、目標が放射する信号のドップラーシフトを用いて、短時間で目標運動を推定することができる目標運動推定装置及び目標運動推定方法を提供することを目的とする。 This disclosure is made to solve the above-mentioned problems, and provides a target motion estimation device and a target motion estimation method capable of estimating a target motion in a short time by using a Doppler shift of a signal radiated by a target. The purpose is to provide.
本開示にかかる目標運動推定装置は、2以上の受動型センサ装置と、目標運動推定手段とを備え、前記受動型センサ装置は、指向性を備えた受動型センサと、前記受動型センサが受信した信号から目標が放射した放射信号を検出信号として検出し、目標が存在する目標方位と前記検出信号の周波数を特定する信号検出手段と、を備え、前記目標運動推定手段は、第1の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第1の目標方位と、第2の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第2の目標方位とに基づいて、前記目標の目標位置を推定する位置推定手段と、前記周波数と前記放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、第1の受動型センサ及び第2の受動型センサから見た前記目標のドップラ速度を、それぞれ第1及び第2のドップラ速度として算出する相対運動推定手段と、前記第1のドップラ速度と前記第2のドップラ速度を合成することにより、前記目標の運動を推定する運動推定手段と、を備えたものである。 The target motion estimation device according to the present disclosure includes two or more passive sensor devices and a target motion estimation means, and the passive sensor device receives a passive sensor having directionality and the passive sensor. The target motion estimation means includes a signal detecting means for detecting a radiation signal radiated by a target from the resulting signal as a detection signal and specifying a target direction in which the target exists and a frequency of the detected signal, and the target motion estimating means is a first passive A position estimating means for estimating the target position of the target based on the first target azimuth starting from the position of the type sensor and the second target azimuth starting from the position of the second passive sensor. Based on the Doppler shift between the frequency and the frequency of the radiation signal, the target Doppler speeds seen from the first passive sensor and the second passive sensor are calculated as the first and second Doppler speeds, respectively. The relative motion estimation means is provided, and the motion estimation means for estimating the target motion by synthesizing the first Doppler velocity and the second Doppler velocity.
本開示にかかる目標運動推定方法は、2以上の受動型センサ装置を用いる方法であって、指向性を備えた受動型センサを用いて周囲の信号を受信し、前記受動型センサが受信した信号から目標が放射した放射信号を検出信号として検出し、目標が存在する目標方位と前記検出信号の周波数を特定し、第1の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第1の目標方位と、第2の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第2の目標方位と、に基づいて前記目標の目標位置を推定し、前記周波数と前記放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、第1の受動型センサ及び第2の受動型センサから見た前記目標のドップラ速度を、それぞれ第1及び第2のドップラ速度として算出し、前記第1のドップラ速度と前記第2のドップラ速度を合成することにより、前記目標の運動を推定する、ものである。 The target motion estimation method according to the present disclosure is a method using two or more passive sensor devices, in which an ambient signal is received by using a passive sensor having directional properties, and the signal received by the passive sensor. The radiation signal radiated from the target is detected as a detection signal, the target direction in which the target exists and the frequency of the detection signal are specified, and the first target direction starting from the position of the first passive sensor and the first The target position of the target is estimated based on the second target orientation starting from the position of the passive sensor of 2, and the first passive is based on the Doppler shift between the frequency and the frequency of the radiation signal. By calculating the target Doppler speed as seen from the type sensor and the second passive sensor as the first and second Doppler speeds, respectively, and synthesizing the first Doppler speed and the second Doppler speed. , The movement of the target is estimated.
本開示によれば、短時間で目標運動を推定することが可能となり、より早く目標の運動を認識することが可能となる。 According to the present disclosure, it is possible to estimate the target movement in a short time, and it is possible to recognize the target movement earlier.
<第1実施形態>
図1を用いて、本発明の実施の形態にかかる目標運動推定装置の構成について説明する。この目標運動推定装置は、図1に示されるように、複数の受動型センサ装置10A、10B、目標運動推定部20を備えている。
<First Embodiment>
The configuration of the target motion estimation device according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIG. As shown in FIG. 1, this target motion estimation device includes a plurality of
受動型センサ装置10Aは、受動型センサ11A、信号検出部12Aを備えている。受動型センサ装置10Bは、受動型センサ11B、信号検出部12Bを備えている。受動型センサ11A、11Bは指向性を備えている。
The
受動型センサ11A、11Bは、周囲から到来する信号を受信して電気信号に変換し、信号検出部12A、12Bに出力する。受動型センサ11A、11Bとしては、パッシブソーナー、パッシブレーダー、赤外線センサなどを用いることができる。
受動型センサ11A、11Bの動作は同期しており、同一時刻において受信した信号に対して以下の処理が施される。
The
The operations of the
信号検出部12A、12Bは、受動型センサ11A、11Bが出力した電気信号から、目標が放射する放射信号を検出する。信号検出部12A、12Bで検出した信号を検出信号とする。検出信号の検出には、目標が放射する放射信号の周波数特性を使用することができる。目標となる移動体は、例えば、車両、船舶、航空機である。目標毎に放射信号の周波数特性をデータベースとして備えてもよい。検出信号と放射信号には、ドップラーシフトによる周波数のずれが生じている。
そして、信号検出部12A、12Bは、検出信号の周波数を特定し、目標運動推定部20に出力する。
また、信号検出部12A、12Bは、受動型センサ11A、11Bが出力した電気信号から、受動型センサ11A、11Bを起点として目標が存在する目標方位を算出し、目標運動推定部20に出力する。受動型センサ11Aを起点とする目標方位を第1の目標方位とし、受動型センサ11Bを起点とする目標方位を第2の目標方位とする。
受動型センサ装置10A、10Bの両者が情報を出力するため、出力信号に識別番号を付加する必要がある。また、受動型センサ装置10A、10Bごとに、固有の通信チャネルを用いても良い。
The
Then, the
Further, the
Since both the
目標運動推定部20は、位置推定部21、相対運動推定部22、運動推定部23を備えている。
The target
位置推定部21は、受動型センサ11A、11Bの位置情報を有している。受動型センサ装置10A、10Bが移動する場合には、受動型センサ装置10A、10Bとの間で通信を行う等の方法により、位置情報を更新しても良い。
位置推定部21は、目標を検出した受動型センサ11A、11Bの位置と、信号検出部12A、12Bから出力された第1及び第2の目標方位に基づいて、目標の位置を推定する。
目標の位置を推定する方法としては、受動型センサ11Aの位置を起点とした第1の目標方位と、受動型センサ11Bの位置を起点とした第2の目標方位の交点を、目標の位置と推定する方法がある。
位置推定部21は、推定した目標の位置を運動推定部23に出力する。
The
The
As a method of estimating the target position, the intersection of the first target direction starting from the position of the
The
相対運動推定部22は、目標の放射信号の周波数に関する情報を有している。
相対運動推定部22は、受動型センサ11Aにおいて検出された検出信号の周波数と、目標の放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、受動型センサ11Aから見た目標のドップラ速度を算出する。これを第1のドップラ速度とする。また、相対運動推定部22は、受動型センサ11Bにおいて検出された検出信号の周波数と、目標の放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、受動型センサ11Bから見た目標のドップラ速度を算出する。これを第2のドップラ速度とする。
相対運動推定部22は、算出した第1及び第2のドップラ速度を運動推定部23に出力する。
The relative
The relative
The relative
運動推定部23は、位置推定部21において推定された目標の目標位置を起点として、第1のドップラ速度と第2のドップラ速度を合成することにより、目標運動を推定する。目標運動は、例えば、移動速度及び移動方向の情報を含んでいる。
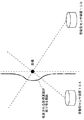
図2に、推定される目標運動と受動型センサ11A、11Bから見た目標の相対運動との関係を示す。
The
FIG. 2 shows the relationship between the estimated target motion and the relative motion of the target as seen from the
本実施の形態にかかる目標運動推定装置は、複数の受動型センサ11A、11Bから見た目標のドップラ速度を合成することによって目標の速度を推定するため、より短時間の検出で目標の運動を推定することができる。
Since the target motion estimation device according to the present embodiment estimates the target speed by synthesizing the target Doppler speeds seen from the plurality of
なお、本実施形態の内容は上述した説明に限定されない。
本発明は、最小で2つの受動型センサ装置10A、10Bを用いることで実施できるが、3つ以上の受動型センサ装置を用いることで目標運動の推定結果の精度を高めることができる。
The contents of the present embodiment are not limited to the above description.
The present invention can be carried out by using at least two
<第2実施形態>
第2実施形態は、目標の放射信号の周波数が特定されていない場合である。かかる状況でも目標運動の取り得る範囲を限定することが可能である。
なお、装置の構成は図1と同じであり、受動型センサ装置10A、10Bと位置推定部21の動作は共通しているため、説明を省略する。
<Second Embodiment>
The second embodiment is a case where the frequency of the target radiation signal is not specified. Even in such a situation, it is possible to limit the range in which the target movement can be taken.
Since the configuration of the device is the same as that in FIG. 1 and the operations of the
目標の放射信号の周波数が特定されていない場合、目標運動推定部20は放射信号の周波数を変数として扱い、変数が取り得る範囲で、目標運動を推定する。放射信号の周波数に関する情報がない場合は、変数の下限を十分小さな値とし、変数の上限を十分に大きな値とする必要がある。
When the frequency of the target radiation signal is not specified, the target
目標の放射信号の周波数を表す変数をfとする。
相対運動推定部22は、受動型センサ11Aにおいて検出された信号の周波数と、周波数fとのドップラーシフトに基づいて、受動型センサ11Aから見た目標のドップラ速度を算出する。また、相対運動推定部22は、受動型センサ11Bにおいて検出された信号の周波数と、周波数fとのドップラーシフトに基づいて、受動型センサ11Bから見た目標のドップラ速度を算出する。
Let f be a variable representing the frequency of the target radiation signal.
The relative
運動推定部23は、位置推定部21において推定された目標の位置を起点として、受動型センサ11Aから見た目標のドップラ速度と、受動型センサ11Bから見た目標のドップラ速度と、を合成することにより、周波数fについての目標運動を推定する。
The
運動推定部23が、周波数fを取り得る値で動かすことにより、目標運動が取り得る範囲を限定することができる。
図3に目標運動が取り得る範囲の例を示す。受動型センサ装置10Aでの検出周波数が、受動型センサ装置10Bでの検出周波数よりも高い場合の例である。目標運動、つまり単位時間後の目標の位置は鎖線上に限定される。
このことにより、目標の移動方向を指定すると目標の移動速度を推定でき、目標の移動速度を指定すると、目標の移動方向を推定することが可能となる。
By moving the
FIG. 3 shows an example of the range in which the target movement can be taken. This is an example in which the detection frequency of the
As a result, if the moving direction of the target is specified, the moving speed of the target can be estimated, and if the moving speed of the target is specified, the moving direction of the target can be estimated.
本実施の形態にかかる目標運動推定装置は、目標の放射信号の周波数が特定されていない状況においても、短時間の検出で目標の運動を限定することができる。 The target motion estimation device according to the present embodiment can limit the target motion by detecting the target motion in a short time even in a situation where the frequency of the target radiation signal is not specified.
10A,10B 受動型センサ装置
11A,11B 受動型センサ
12A,12B 信号検出部
20 目標運動推定部
21 位置推定部
22 相対運動推定部
23 運動推定部
10A, 10B
Claims (10)
前記受動型センサ装置は、
指向性を備えた受動型センサと、
前記受動型センサが受信した信号から目標が放射した放射信号を検出信号として検出し、目標が存在する目標方位と前記検出信号の周波数を特定する信号検出手段と、を備え、
前記目標運動推定手段は、
第1の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第1の目標方位と、第2の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第2の目標方位とに基づいて、前記目標の目標位置を推定する位置推定手段と、
前記周波数と前記放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、第1の受動型センサ及び第2の受動型センサから見た前記目標のドップラ速度を、それぞれ第1及び第2のドップラ速度として算出する相対運動推定手段と、
前記第1のドップラ速度と前記第2のドップラ速度を合成することにより、前記目標の運動を推定する運動推定手段と、を備える、
目標運動推定装置。 It is equipped with two or more passive sensor devices and a target motion estimation means.
The passive sensor device is
Passive sensor with directivity and
A signal detecting means for detecting a radiation signal radiated by a target from a signal received by the passive sensor as a detection signal and specifying a target direction in which the target exists and a frequency of the detection signal is provided.
The target motion estimation means is
A position for estimating the target position of the target based on the first target direction starting from the position of the first passive sensor and the second target direction starting from the position of the second passive sensor. Estimating means and
Based on the Doppler shift between the frequency and the frequency of the radiation signal, the target Doppler speeds seen from the first passive sensor and the second passive sensor are calculated as the first and second Doppler speeds, respectively. Relative motion estimation means and
A motion estimation means for estimating the motion of the target by synthesizing the first Doppler velocity and the second Doppler velocity is provided.
Target motion estimation device.
前記運動推定手段は、前記変数が取り得る範囲で前記目標の運動を推定し、前記目標の運動が取り得る範囲を限定する、
請求項1に記載の目標運動推定装置。 The relative motion estimation means calculates the first and second Doppler velocities with the frequency of the radiation signal as a variable.
The motion estimation means estimates the target motion within the range that the variable can take, and limits the range that the target motion can take.
The target motion estimation device according to claim 1.
指向性を備えた受動型センサを用いて周囲の信号を受信し、
前記受動型センサが受信した信号から目標が放射した放射信号を検出信号として検出し、目標が存在する目標方位と前記検出信号の周波数を特定し、
第1の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第1の目標方位と、第2の受動型センサの位置を起点とした第2の目標方位と、に基づいて前記目標の位置を推定し、
前記周波数と前記放射信号の周波数とのドップラーシフトに基づいて、第1の受動型センサ及び第2の受動型センサから見た前記目標のドップラ速度を、それぞれ第1及び第2のドップラ速度として算出し、
前記第1のドップラ速度と前記第2のドップラ速度を合成することにより、前記目標の運動を推定する、
目標運動推定方法。 It is a method using two or more passive sensor devices.
Receives ambient signals using a directional passive sensor
The radiation signal radiated by the target from the signal received by the passive sensor is detected as a detection signal, the target direction in which the target exists and the frequency of the detection signal are specified.
The position of the target is estimated based on the first target direction starting from the position of the first passive sensor and the second target direction starting from the position of the second passive sensor.
Based on the Doppler shift between the frequency and the frequency of the radiation signal, the target Doppler speeds seen from the first passive sensor and the second passive sensor are calculated as the first and second Doppler speeds, respectively. And
By synthesizing the first Doppler velocity and the second Doppler velocity, the motion of the target is estimated.
Target motion estimation method.
前記変数が取り得る範囲で前記目標の運動を推定し、前記目標の運動の取り得る範囲を限定する、
請求項6に記載の目標運動推定方法。 Using the frequency of the target radiation signal as a variable, the first and second Doppler velocities are calculated.
Estimate the target motion within the range that the variable can take, and limit the range that the target motion can take.
The target motion estimation method according to claim 6.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019074719A JP7306030B2 (en) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-04-10 | Target motion estimation device and target motion estimation method |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019074719A JP7306030B2 (en) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-04-10 | Target motion estimation device and target motion estimation method |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2020173155A true JP2020173155A (en) | 2020-10-22 |
| JP7306030B2 JP7306030B2 (en) | 2023-07-11 |
Family
ID=72830997
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019074719A Active JP7306030B2 (en) | 2019-04-10 | 2019-04-10 | Target motion estimation device and target motion estimation method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP7306030B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115390077A (en) * | 2022-07-28 | 2022-11-25 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Underwater maneuvering target instantaneous navigational speed analytic solution method under double-element condition |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013044602A (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2013-03-04 | Nec Corp | Target movement estimation system and method |
| JP2016215908A (en) * | 2015-05-22 | 2016-12-22 | 防衛装備庁長官 | Sensor laying device, system and method for estimating sound source object |
-
2019
- 2019-04-10 JP JP2019074719A patent/JP7306030B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013044602A (en) * | 2011-08-23 | 2013-03-04 | Nec Corp | Target movement estimation system and method |
| JP2016215908A (en) * | 2015-05-22 | 2016-12-22 | 防衛装備庁長官 | Sensor laying device, system and method for estimating sound source object |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN115390077A (en) * | 2022-07-28 | 2022-11-25 | 哈尔滨工程大学 | Underwater maneuvering target instantaneous navigational speed analytic solution method under double-element condition |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP7306030B2 (en) | 2023-07-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10222463B2 (en) | Systems and methods for 4-dimensional radar tracking | |
| US10175348B2 (en) | Use of range-rate measurements in a fusion tracking system via projections | |
| JP5919328B2 (en) | Vehicle collision warning device and vehicle collision warning method | |
| JP5835243B2 (en) | Target recognition device | |
| US9479867B2 (en) | Method and circuitry for direction of arrival estimation using microphone array with a sharp null | |
| CN109716157B (en) | Shaft offset estimation device | |
| WO2020072041A1 (en) | Systems and methods for stereo radar tracking | |
| US11131768B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for automotive parking assistance using radar sensors | |
| KR102437345B1 (en) | Method and radar apparatus for determining radial relative acceleration of one or more targets | |
| JP6892600B2 (en) | Object detection method and object detection device | |
| CN112119330B (en) | Object detection device and object detection method | |
| CN111386476B (en) | Determining object motion and acceleration vectors in a vehicle radar system | |
| CN111801718B (en) | Object detection device, object detection method, and recording medium | |
| JP2020173155A (en) | Target motion estimating device and target motion estimating method | |
| US11726178B2 (en) | LIDAR sensor apparatus and control method thereof | |
| KR101837845B1 (en) | System and method for obtaining information of underwater target | |
| TW202020476A (en) | Obstacle detection method and device thereof achieving a good obstacle angle detection effect by using sensors with relatively lower costs | |
| CN115698764B (en) | Doppler based velocity direction determination | |
| JP2001083232A (en) | Apparatus for determining passive target position | |
| WO2024174174A1 (en) | Data processing method of radar sensor, and related apparatus | |
| JP2006329829A (en) | Radar device | |
| JP6311230B2 (en) | Target detection apparatus, target detection method, program, and recording medium | |
| US20210231799A1 (en) | Object detection device, object detection method and program | |
| JP2012202698A (en) | Time difference orientation detection device | |
| JP2007093542A (en) | Method and instrument for measuring position |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20220304 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20230116 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20230131 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20230322 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20230530 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20230612 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 7306030 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |