JP2018022592A - Sample table and electron microscope with the same - Google Patents
Sample table and electron microscope with the same Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2018022592A JP2018022592A JP2016152069A JP2016152069A JP2018022592A JP 2018022592 A JP2018022592 A JP 2018022592A JP 2016152069 A JP2016152069 A JP 2016152069A JP 2016152069 A JP2016152069 A JP 2016152069A JP 2018022592 A JP2018022592 A JP 2018022592A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- sample
- electron detector
- sample stage
- stage according
- detector
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Abstract
Description
本発明は試料台およびそれを備えた電子顕微鏡に関する。 The present invention relates to a sample stage and an electron microscope including the same.
走査型電子顕微鏡(SEM:Scanning Electron Microscope)は、加速された電子線を収束して電子線束として、試料表面上を周期的に走査しながら照射し、照射された試料の局所領域から発生する反射電子および/または二次電子を検出して、それらの電気信号を材料組織像として変換することによって、材料の表面形態および構成組成分布などを観察する装置である。 A scanning electron microscope (SEM) scans a sample surface by periodically irradiating an accelerated electron beam and irradiating it as an electron beam bundle, and a reflection generated from a local region of the irradiated sample. This is an apparatus for observing the surface morphology and composition distribution of materials by detecting electrons and / or secondary electrons and converting their electrical signals as material texture images.
真空中で電子源より引き出された電子線は、直ちに1kV以下の低加速電圧から30kV程度の高加速電圧まで、観察目的に応じて異なるエネルギーで加速される。そして、加速された電子線は、コンデンサレンズおよび対物レンズ等の磁界コイルによって、ナノレベルの極微小径に集束されて電子線束となり、同時に偏向コイルによって偏向することで、試料表面上に収束された電子線束が走査される。また、最近では電子線を集束するに際して、電界コイルも組み合わせるような形式も用いられる。 The electron beam extracted from the electron source in vacuum is immediately accelerated with different energy depending on the observation purpose from a low acceleration voltage of 1 kV or less to a high acceleration voltage of about 30 kV. The accelerated electron beam is focused to a nano-level microscopic diameter by a magnetic field coil such as a condenser lens and an objective lens to form an electron beam bundle, and simultaneously deflected by the deflection coil, thereby being focused on the sample surface. The line bundle is scanned. In addition, recently, a method in which an electric field coil is combined is also used for focusing an electron beam.
従来のSEMにおいては、分解能の制約から、二次電子像によって試料の表面形態を観察し、反射電子像によって組成情報を調べることが主要機能であった。しかしながら、近年、加速された電子線を、高輝度を維持したまま直径数nmという極微小径に集束させることが可能になり、非常に高分解能な反射電子像および二次電子像が得られるようになってきた。 In the conventional SEM, the main function is to observe the surface form of the sample by a secondary electron image and to examine the composition information by a reflected electron image due to the limitation of resolution. However, in recent years, it has become possible to focus an accelerated electron beam on a very small diameter of several nanometers while maintaining high luminance, so that a reflected electron image and a secondary electron image with very high resolution can be obtained. It has become.
反射電子像および二次電子像を得るために、試料から発生した反射電子および二次電子をそれぞれ検出するのが、反射電子検出器および二次電子検出器である。二次電子は、二次電子検出器先端部に数百ボルトの電圧を印加することで引き込み電位場を形成させ、試料表面からたとえ検出器とは異なる方向に向かって放出された場合であっても、検出器に引き込まれることとなる。そのため、高解像度な二次電子像を得る上で、二次電子検出器の配置が大きな問題となることは少ない。一方、エネルギーの高い反射電子は曲げることができず、直進して検出器に入射するため、反射電子検出器の配置の仕方によって反射電子像の見え方が大きく変化する。これまで、試料に対する反射電子検出器の配置方法について様々な検討がなされてきた。 In order to obtain a reflected electron image and a secondary electron image, it is a reflected electron detector and a secondary electron detector that detect the reflected electrons and secondary electrons generated from the sample, respectively. Secondary electrons are generated when a voltage of several hundred volts is applied to the tip of the secondary electron detector to form a drawn potential field and are emitted from the sample surface in a different direction from the detector. Will also be drawn into the detector. For this reason, in obtaining a high-resolution secondary electron image, the placement of the secondary electron detector is rarely a major problem. On the other hand, reflected electrons with high energy cannot be bent and go straight and enter the detector, so that the appearance of the reflected electron image varies greatly depending on the arrangement of the reflected electron detector. Until now, various studies have been made on the method of arranging the backscattered electron detector with respect to the sample.
例えば、特許文献1には、中央に孔のあいた円板状の電子線検出素子を試料ホルダの上部に取り付けた構造の反射電子検出器が開示されている。
For example,
また、特許文献2には、対物レンズの下部磁極片の両側、それも試料傾斜軸に沿って反射電子検出器を2個あるいは4個対にして配置された走査電子顕微鏡が開示されている。
さらに、特許文献3には、試料の観察面を所定の傾斜角にしたとき、この傾斜角に応じて反射電子検出器を駆動して、反射電子検出器の検出面が試料の観察面に対して平行になるよう傾斜させる電子顕微鏡が開示されている。
Further, in
ところで、SEMの特徴として、数mm〜数cmのサイズの大きな試料に対して、局所領域の組織観察ができることが挙げられる。同じように電子線を活用して材料組織を観察する手段として、透過電子顕微鏡(TEM:Transmission Electron Microscope)がある。TEMでは、試料を電子線が透過するために極薄膜試料が必要となり、結果として、試料サイズも直径3mm以下が標準と制約を受けている。観察分解能に関しては、TEMの方が高いため、結晶欠陥の観察はTEM法が主体となる。一方、表面組織形状の観察に関してはSEM法が用いられ、両者は相補的に使われていた。 By the way, as a feature of SEM, it is possible to observe a tissue in a local region with respect to a sample having a large size of several mm to several cm. Similarly, there is a transmission electron microscope (TEM) as means for observing a material structure using an electron beam. In TEM, an ultra-thin film sample is required in order to allow an electron beam to pass through the sample. As a result, the sample size is limited to a standard of 3 mm or less in diameter. Regarding observing resolution, TEM is higher, so TEM method is mainly used for observing crystal defects. On the other hand, the SEM method was used for observation of the surface texture shape, and both were used in a complementary manner.
しかしながら、いくつかの特定方位を満足した結晶粒においては、SEMにおいても反射電子像を活用して、試料表面付近の格子欠陥をTEMと同様の分解能で観察できることが非特許文献1に報告されている。
However, it is reported in
観察された転位コントラストのメカニズムは、まだ必ずしも解明されていないが、入射電子線束が試料に対してチャネリング現象を起こすような結晶方位条件で照射された時に、転位像が観察されることが分かってきた。また、その転位組織は、僅か数度の試料傾斜に対して非常に敏感にコントラストが変化する。鉄鋼をはじめとする金属材料の組織観察においては、観察視野内の結晶粒は種々の方位を有している。したがって、SEM法による転位等の結晶欠陥の観察のためには、個々の結晶粒に対してチャネリング現象を起こす角度に試料の観察面を入射電子方向に対して精密に傾斜させる必要がある。 The mechanism of the observed dislocation contrast has not yet been elucidated, but it has been found that dislocation images are observed when the incident electron beam flux is irradiated under crystal orientation conditions that cause a channeling phenomenon to the sample. It was. Further, the dislocation structure changes in contrast very sensitively to a sample inclination of only a few degrees. In the structure observation of metal materials including iron and steel, the crystal grains in the observation field have various orientations. Therefore, in order to observe crystal defects such as dislocations by the SEM method, it is necessary to precisely tilt the observation surface of the sample with respect to the incident electron direction at an angle causing a channeling phenomenon with respect to individual crystal grains.
非特許文献1では、従来の汎用型SEMでの観察から、チャネリング現象を意図的に起こさせれば、転位などの格子欠陥がSEMでも観察できる可能性が提示されている。しかしながら、非特許文献1では、試料表面から反射した反射電子を効率的に捕獲できるように、反射電子検出器と試料表面との距離を短くすべきことが記載されているのみであり、試料の観察面を入射電子方向に対してチャネリング現象を起こす角度に傾斜させる必要があることについては記載されていない。
また、特許文献1では、そもそも反射電子検出器を取り付けた試料ホルダの傾斜角を調整することについては一切考慮されていない。
In
特許文献2に記載の方法では、一方向のみを軸とする傾斜機構しか存在しないため、転位などの組織を観察しながら傾斜してそのコントラスト変化を観察することはできない。また、空間的な制約から、任意の試料傾斜時に発生する任意の方向の反射電子を検出しようとすると、対物レンズの下に無数で、かつ様々な方向に向いた反射電子検出器を取り付ける必要があり、これは構造的に現実的ではない。さらに、試料ステージを10°以上に傾斜した時には、対物レンズ近傍に設置した反射電子検出器での信号の検出は困難である。
In the method described in
特許文献3に記載の装置は、一方向のみを軸とする傾斜と回転とを組み合わせた傾斜機能しか有していない。回転操作では像組織が回転するだけで、結晶学的条件に対応した求めたい転位コントラストが変化しないため、原理的に、転位などの格子欠陥の観察に適していない。また、観察視野を選んでからその角度を読み取り反射電子検出器を傾斜するまでの時間が非常にかかり、多結晶かつ結晶粒単位で結晶方位が異なる鉄鋼材料などの場合においては、操作上現実的な作業スピードを実現できない。さらに、SEMは既に現場も含め様々な研究箇所におかれている汎用的な装置であるため、特殊なSEMではなく汎用型のSEMにおいて、格子欠陥が観察できることが望まれている。
The device described in
このように、従来の技術においては、SEM法によりTEM法のように一本一本の転位が観察できるような画期的な知見が見出されていなかったため、試料の精密な傾斜制御は要求されてこなかった。そのため、特許文献1〜3に記載の試料台を用いても、結晶粒ごとのチャネリング条件の探索は不可能である。さらに、傾斜角度を大きくした場合に、反射電子検出器の配置が不適切であるために入射電子線が試料に到達しなくなるという問題もあった。
As described above, in the conventional technique, since the epoch-making knowledge that enables observation of individual dislocations by SEM method as in the TEM method has not been found, precise tilt control of the sample is required. It has never been done. Therefore, even if the sample stage described in
また、転位コントラストを観察するためには、試料表面における結晶粒の方位情報を予め把握しておくことが望ましい。SEMには、結晶方位を同時に解析するための電子後方散乱回折(EBSD:Electron Back Scatter Diffraction)装置が、付加的に搭載されることが増えてきた。これによって、試料の表面形状に関する情報、ならびに析出物および第二相等の材料構成物の組成差に関する情報に加えて、試料の結晶方位情報が得られるようになり、その結果、鉄鋼材料およびアルミニウム材料等の金属材料部品分野では、製造プロセス時の結晶粒の集合組織制御、または、部品の変形加工時における結晶塑性挙動制御に対して、従来のX線回折手法と共に、SEM−EBSD法が新しい評価法として、積極的に使われている。 Further, in order to observe the dislocation contrast, it is desirable to grasp in advance crystal grain orientation information on the sample surface. In SEM, an electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD) device for simultaneously analyzing crystal orientation has been additionally installed. This makes it possible to obtain information on the crystal orientation of the sample in addition to information on the surface shape of the sample and information on the compositional differences of the material components such as precipitates and second phases. As a result, steel materials and aluminum materials can be obtained. In the field of metallic material parts such as SEM-EBSD, together with the conventional X-ray diffraction method, a new evaluation is applied to the control of crystal grain texture during the manufacturing process or the control of crystal plastic behavior during deformation of parts. It is actively used as a law.
EBSDにより結晶方位を計測するためには、試料をSEM内で70°程度まで大きく傾斜させる必要がある。そのため、EBSDによる結晶方位測定時においても、反射電子検出器の配置が不適切であると入射電子線が試料に到達しなくなるという問題が発生しうる。このように、非特許文献1および特許文献1〜3では、転位コントラストを観察する上で好適な試料台の構成については検討がなされていない。
In order to measure the crystal orientation by EBSD, it is necessary to greatly tilt the sample to about 70 ° in the SEM. Therefore, even when the crystal orientation is measured by EBSD, there is a problem that the incident electron beam does not reach the sample if the backscattered electron detector is improperly arranged. As described above, in
本発明は、汎用性に優れ、既存の電子顕微鏡に適用することが可能であって、種々の方位を有する個々の結晶粒に対して、結晶欠陥像を観察する条件が得られるよう試料の傾斜角度および反射電子検出器の配置を制御することが可能な試料台を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has excellent versatility and can be applied to existing electron microscopes, and it is possible to incline the sample so that conditions for observing crystal defect images can be obtained for individual crystal grains having various orientations. An object is to provide a sample stage capable of controlling the angle and the arrangement of backscattered electron detectors.
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するためになされたものであり、下記の試料台およびそれを備えた電子顕微鏡を要旨とする。 The present invention has been made in order to solve the above-described problems, and provides the following sample stage and an electron microscope including the sample stage.
(1)一方向に延びる仮想線上を進行する電子線束を試料の表面に入射させる電子顕微鏡内に設置される試料台であって、
前記電子顕微鏡に着脱可能に装着される本体部と、
前記試料を保持する試料保持面を有する試料保持部と、
表面および、前記試料保持面に平行かつ対向しており検出面となる裏面を有する反射電子検出器とを備え、
前記反射電子検出器は、前記表面から前記裏面へ貫通し、かつ、前記電子線束が通過可能な孔を有し、
前記試料保持部は、前記仮想線上の点を中心点として、揺動可能に前記本体部に支持され、
前記反射電子検出器は、
前記試料保持面の法線方向から見た場合に、前記反射電子検出器の外縁が囲う領域と、前記仮想線および前記試料保持面の交点とが重ならない位置まで退避する退避移動可能、かつ、
前記検出面が前記試料保持面に対して平行な状態を維持しつつ、前記電子線束が前記孔を通過可能な範囲に移動する調整移動可能に、前記試料保持部に支持される、
試料台。
(1) A sample stage installed in an electron microscope for causing an electron beam bundle traveling on a virtual line extending in one direction to enter the surface of the sample,
A main body detachably attached to the electron microscope;
A sample holder having a sample holding surface for holding the sample;
A backscattered electron detector having a front surface and a back surface that is parallel to and opposed to the sample holding surface and serves as a detection surface;
The reflected electron detector has a hole penetrating from the front surface to the back surface and allowing the electron beam bundle to pass through,
The sample holding part is supported by the body part so as to be swingable around a point on the imaginary line as a center point,
The backscattered electron detector is
When viewed from the normal direction of the sample holding surface, the retreat movement is possible to retract to a position where the outer edge of the backscattered electron detector surrounds and the intersection of the virtual line and the sample holding surface does not overlap, and
The detection surface is supported by the sample holder so that the electron beam can be adjusted to move to a range where it can pass through the hole while maintaining the detection surface parallel to the sample holding surface.
Sample stage.
(2)前記反射電子検出器は、前記試料保持面の法線方向と平行な軸回りに回転することで退避移動可能に前記試料保持部に支持される、
上記(1)に記載の試料台。
(2) The backscattered electron detector is supported by the sample holder so as to be retractable by rotating around an axis parallel to the normal direction of the sample holding surface.
The sample stage according to (1) above.
(3)前記反射電子検出器は、前記試料保持面の法線方向と垂直な軸周りに回転することで退避移動可能に前記試料保持部に支持される、
上記(1)に記載の試料台。
(3) The backscattered electron detector is supported by the sample holder so as to be retractable by rotating around an axis perpendicular to the normal direction of the sample holding surface.
The sample stage according to (1) above.
(4)前記反射電子検出器は、退避移動できるように着脱可能に前記試料保持部に支持される、
上記(1)に記載の試料台。
(4) The backscattered electron detector is detachably supported by the sample holder so as to be retractable.
The sample stage according to (1) above.
(5)前記試料保持部が、前記試料保持面と平行であり、かつ、前記中心点上で交差する2つの軸の回りを回転可能である、
上記(1)から(4)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(5) The sample holding unit is rotatable around two axes that are parallel to the sample holding surface and intersect on the center point.
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (4) above.
(6)前記2つの軸が直交する、
上記(5)に記載の試料台。
(6) The two axes are orthogonal to each other,
The sample stage according to (5) above.
(7)前記中心点が、前記試料保持部と前記反射電子検出器との間に位置する、
上記(1)から(6)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(7) The center point is located between the sample holder and the backscattered electron detector.
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (6) above.
(8)前記本体部は、高さ調整可能で、かつ、前記試料保持部を支持する3つ以上の支持部を有する、
上記(1)から(7)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(8) The main body part has three or more support parts that are height-adjustable and support the sample holding part.
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (7) above.
(9)前記反射電子検出器を、前記検出面と直交する方向に調整移動させることができる機構をさらに備える、
上記(1)から(8)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(9) The apparatus further includes a mechanism capable of adjusting and moving the backscattered electron detector in a direction orthogonal to the detection surface.
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (8) above.
(10)前記反射電子検出器を、前記検出面と平行で互いに交差する2つの方向に調整移動させることができる機構をさらに備える、
上記(1)から(9)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(10) The apparatus further includes a mechanism capable of adjusting and moving the backscattered electron detector in two directions parallel to the detection surface and intersecting each other.
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (9) above.
(11)前記2つの方向が直交する、
上記(10)に記載の試料台。
(11) The two directions are orthogonal to each other.
The sample stage according to (10) above.
(12)前記試料保持部の揺動を指示する電気信号を受信するための第1コネクタピンと、前記反射電子検出器で得られた電気信号を送信するための第2コネクタピンと、前記反射電子検出器の移動を指示する電気信号を受信するための第3コネクタピンとをさらに備える、
上記(1)から(11)までのいずれかに記載の試料台。
(12) a first connector pin for receiving an electrical signal instructing swinging of the sample holder, a second connector pin for transmitting the electrical signal obtained by the backscattered electron detector, and the backscattered electron detection A third connector pin for receiving an electrical signal instructing movement of the device;
The sample stage according to any one of (1) to (11) above.
(13)上記(12)に記載の試料台と、
前記試料台を設置する設置部と、
前記第1コネクタピン、第2コネクタピンおよび第3コネクタピンと電気的に接続する電気信号コネクタ受取口と、
前記反射電子検出器で得られた反射電子信号を伝播する反射電子伝播装置と、
前記試料保持部の揺動を制御する揺動制御装置と、
前記反射電子検出器の移動を制御する移動制御装置とを備える、電子顕微鏡。
(13) The sample stage according to (12) above,
An installation section for installing the sample stage;
An electrical signal connector receiving port electrically connected to the first connector pin, the second connector pin, and the third connector pin;
A reflected electron propagation device that propagates a reflected electron signal obtained by the reflected electron detector;
A swing control device for controlling the swing of the sample holder;
An electron microscope comprising: a movement control device that controls movement of the reflected electron detector.
本発明の試料台を用いれば、汎用的なSEMに設置することによって、最適なチャネリング現象を満足する入射電子線方位を自在に選ぶことができ、任意の方位の結晶粒に対して、TEM法同様にその転位組織を観察することができる。従来、転位組織観察はTEM法によらなければならなかったが、試料の変形能および延性破壊に影響を及ぼす転位などの結晶欠陥に対して、SEM法により高分解能の反射電子像を得ることができる。 By using the sample stage of the present invention, it is possible to freely select the incident electron beam orientation satisfying the optimum channeling phenomenon by installing it on a general-purpose SEM. Similarly, the dislocation structure can be observed. Conventionally, dislocation structure observation had to be performed by the TEM method, but high-resolution backscattered electron images can be obtained by the SEM method for crystal defects such as dislocations that affect the deformability and ductile fracture of the sample. it can.
添付した図面を参照して、本発明の一実施形態について、詳細に説明する。 An embodiment of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
図1は、本発明に係る試料台を備えた顕微鏡装置の一例を模式的に示した図である。図1では、SEMを例に説明するが、本発明に係る試料台はSEM用に限定されず、電子線マイクロアナライザ(EPMA:Electron Probe Micro Analyser)等の電子線束を試料表面に照射することが可能な装置に設置することが可能である。 FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing an example of a microscope apparatus provided with a sample stage according to the present invention. In FIG. 1, the SEM is described as an example. However, the sample stage according to the present invention is not limited to the SEM, and the sample surface may be irradiated with an electron beam bundle such as an electron probe micro analyzer (EPMA). It can be installed in a possible device.
SEMは、SEM本体100と、外部の駆動装置および制御装置とを備える。SEM本体100は、電子源より電子線を引き出し、加速しながら放出する電子銃20と、その電子線の加速電圧を制御する電子銃制御装置25と、加速された電子線束を集束するコンデンサレンズ30と、その開き角等を制御する集束レンズ系制御装置35と、集束された電子線束を試料上の微小領域に収束させる対物レンズ40と、それを含むポールピース50と、対物レンズ系制御装置45と、電子線束を試料上で走査するための偏向コイル60と、偏向コイル制御装置65とから主に構成される。対物レンズ40で収束された電子線束は、試料の表面に対して、図1に示される一方向に延びる仮想線A上に向かって入射されることとなる。実際の電子線束は微小な幅を有するが、本発明において仮想線Aは、偏向コイルの中心から対物レンズの中心を結ぶ線の延びる方向と同一であるとする。
The SEM includes a SEM
試料表面に電子線束が照射された時に発生する二次電子は、二次電子検出器70に引き込まれることで検出され、二次電子信号伝搬装置75を介して、電子線の走査と同期させることで観察像としての二次電子像を表示装置80で得る。
Secondary electrons generated when the sample surface is irradiated with the electron beam bundle are detected by being drawn into the secondary electron detector 70, and are synchronized with the scanning of the electron beam via the secondary electron
さらに、SEMには、電子後方散乱回折(EBSD)検出器90が装着されている。図1に示す構成においては、電子後方散乱回折検出器90によって得られた信号は、電子後方散乱回折信号伝搬装置92を介して、試料結晶方位表示装置94に送られる。
Further, an electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD)
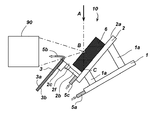
試料台10は、電子顕微鏡内の設置部15に設置される。図2は、試料台10の、試料6を保持した状態における一実施形態を模式的に示した図である。図2に示すように、試料台10は、本体部1と試料保持部2と反射電子検出器3とを備える。上記の構成とすることによって、仮想線A上を進行する電子線束を試料6の表面に照射し、その反射電子を反射電子検出器3で検出することによって、反射電子像を観察することができる。各構成要素について説明する。
The
1.本体部
本体部1は、電子顕微鏡の設置部15に着脱可能に装着されるための部分である。本体部1を設置部15に装着させる方法については従来の方法と同様であり、特別な処理を伴うことはない。そのため、本発明に係る試料台は、汎用的なSEMに取り付けが可能である。設置部15を駆動装置17によって駆動することで、SEM内において試料台10の位置を変化させることができる。
1. Main Body Part The
2.試料保持部
試料保持部2は、試料6を保持する試料保持面2aを有する。試料6は試料保持面2aに対して、導電性カーボンテープ等を用いて接着させることができる。試料表面における転位等に代表される格子欠陥を観察する場合は、試料表面は電解研磨処理などによって平滑になっていることが望ましい。なお、試料保持部2の形状については特に限定されず、試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た場合に、四角形状であってもよいし、多角形、円形、楕円形等であってもよい。
2. Sample Holding Unit The
試料に照射された反射電子像の持つ情報の中で、試料組成を調べる場合は単に試料から反射される反射電子線を収集すればよい。しかしながら、転位および積層欠陥等の試料が持つ格子欠陥については、ブラッグ回折反射に依存した情報であり、入射電子線がどのような角度で試料に入射するかの条件設定が非常に重要である。そのため、仮想線Aに対する試料保持部2の傾斜角度を自在に調整できる必要がある。そこで試料保持部2は、仮想線A上の点Bを中心として、揺動可能に本体部1に支持される構成とする。この際、図2(b)に示すように、試料保持部2が、試料保持面2aと平行であり、かつ、中心点B上で直交する2つの軸の回りを回転可能である構成とすることが望ましい。なお、図2においては、2つの軸は直交しているが、交差していればよい。
In examining the sample composition in the information of the reflected electron image irradiated on the sample, it is only necessary to collect the reflected electron beam reflected from the sample. However, the lattice defects of the sample such as dislocations and stacking faults are information depending on the Bragg diffraction reflection, and it is very important to set conditions for the incident electron beam to enter the sample at what angle. Therefore, it is necessary to freely adjust the inclination angle of the
中心点Bは、仮想線A上であればよいが、試料保持面と検出面との間に位置することが望ましい。また、図2に示すように、中心点Bが試料表面と一致するように調整し、さらに上述の2つの軸がモニター上に現れる反射電子像のX方向およびY方向と一致するように設定すれば、組織像を観察しながら、モニター上でX方向およびY方向の回りに自在に試料を傾斜させる機構を実現させることが可能となる。なお、中心点Bは厳密に仮想線A上に存在する必要はなく、試料保持面を揺動させた際に視野が大きく変化しない程度でのずれは許容される。 The center point B may be on the virtual line A, but is preferably located between the sample holding surface and the detection surface. Further, as shown in FIG. 2, the center point B is adjusted so as to coincide with the sample surface, and further, the above-mentioned two axes are set so as to coincide with the X direction and the Y direction of the reflected electron image appearing on the monitor. For example, it is possible to realize a mechanism for tilting the sample freely around the X and Y directions on the monitor while observing the tissue image. Note that the center point B does not have to be strictly on the imaginary line A, and deviation is allowed to the extent that the field of view does not change significantly when the sample holding surface is swung.
上述の試料保持部2の傾斜機構は、例えば、試料保持部2を本体部1に設けられた直交する二つの円弧上をそれぞれ独立して移動可能な状態で支持することによって実現することができる。また、図2に示すように、本体部1が高さ調整可能で、かつ、試料保持部2を支持する3つ以上の支持部1aを有する構成とすることによっても、傾斜機構を実現することができる。支持部1aがそれぞれの上下方向の位置を相対的に変化させることによって、試料保持部2が中心点Bの周りを揺動可能な状態となるためである。支持部1aとしては、例えば圧電素子等を用いた微小変位冶具を用いることができる。
The above-described tilting mechanism of the
なお、後述するように、EBSDによる結晶方位測定時には、試料をSEM内で70°程度まで大きく傾斜させる必要が生じるが、通常、SEM内で試料台を70°傾斜させることは困難である。しかしながら、上記の傾斜機構を用いて、例えば、試料保持部2の傾斜角度を20°程度にすることによって、試料台自体の傾斜角度を50°程度まで低下させることが可能になる。
As will be described later, when measuring the crystal orientation by EBSD, it is necessary to incline the sample up to about 70 ° in the SEM, but it is usually difficult to incline the sample stage in the SEM by 70 °. However, by using the above tilt mechanism, for example, by setting the tilt angle of the
仮想線Aに対する試料保持部2の傾斜角度は、電気信号によって外部から操作することが可能である。例えば、試料台10の本体部1に第1コネクタピン5aを設け、SEM本体100の電気信号コネクタ受取口82を介してSEMが備える揺動制御装置84と電気的に接続し、電気信号を試料台10に送信することによって、試料保持部の揺動を制御することができる。なお、電気信号の送信は、直接的な接続だけでなく、赤外線または無線等の非接触型の通信を利用することも可能である。
The inclination angle of the
3.反射電子検出器
反射電子検出器3は、表面3aおよび裏面3bを有しており、裏面3bは反射電子の検出面となる部分であって、試料保持面2aに平行かつ対向している。なお、試料保持面2aと裏面3bとは、厳密に平行である必要はなく、略平行であればよい。図2(c)は反射電子検出器3ならびに後述する移動機構2d,2eおよび回転機構2fのみの構成を説明するための斜視図である。図2に示す構成では、反射電子検出器3は、表面3aの法線方向から見た場合に四角形状であるが、形状はこれに限定されず、例えば、多角形、円形、楕円形等であってもよい。
3. Backscattered electron detector The backscattered
反射電子検出器3は、表面3aから裏面3bへ貫通し、かつ、電子線束が通過可能な孔3cを有する。孔3cは試料表面に対して照射された電子線束を通過させるためだけではなく、試料からラザフォード後方散乱したノイズ因子となる反射電子が通過する役割も兼ねている。孔の形状について、特に制限はなく例えば矩形であってもよいが、図2に示すように円形であることが好ましい。
The backscattered
また、孔の大きさについても特に制限は設けない。結晶格子欠陥像を観察する際の反射電子像のノイズ要因となるラザフォード後方散乱は、そのほとんどが仮想線Aの逆方向に放出されるため、電子線束径も考慮し、孔の直径dは0.1mm以上とすることが望ましい。一方、孔の直径dが大きくなりすぎると、反射電子の検出面の面積が小さくなってしまうので、dは2mm以下であることが望ましい。さらに孔の直径dは1mm以下とすることがより望ましい。 Further, there is no particular limitation on the size of the hole. Most of Rutherford backscattering, which is a noise factor in the reflected electron image when observing a crystal lattice defect image, is emitted in a direction opposite to the imaginary line A. Therefore, the hole diameter d is 0 in consideration of the electron beam bundle diameter. It is desirable to set it to 0.1 mm or more. On the other hand, if the diameter d of the hole becomes too large, the area of the detection surface of the reflected electrons becomes small. Therefore, d is preferably 2 mm or less. Further, the diameter d of the hole is more preferably 1 mm or less.
上述のように、結晶の格子欠陥を観察するために、試料への入射電子線の方向が重要である。そして、この技術を駆使するためには、予め試料表面における結晶粒の方位情報が分かっていることが望ましい。すなわち、試料台10は、反射電子像の観察だけでなく、EBSDにより結晶方位の計測にも用いられる。EBSDによる結晶方位測定時には、試料をSEM内で70°程度まで大きく傾斜させるとともに、回折図形を電子後方散乱回折検出器90の検出面に投影する必要があるが、図3(a)に示すように、反射電子検出器3がその障害となりうる。そのため、反射電子検出器3は、退避移動可能に試料保持部2に支持されている必要がある。
As described above, the direction of the incident electron beam on the sample is important for observing crystal lattice defects. And in order to make full use of this technique, it is desirable to know the orientation information of the crystal grains on the sample surface in advance. That is, the
図3(b)を参照して、退避移動可能とは、試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た場合に、反射電子検出器3の外縁が囲う領域と、仮想線Aおよび試料保持面2aの交点Cとが重ならない位置まで、反射電子検出器3が退避することが可能であることを意味する。反射電子検出器3は、試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た場合に、反射電子検出器3の外縁が囲う領域と、試料保持面2a上に配置した試料6とが重ならない位置まで退避可能であることが好ましい。
With reference to FIG. 3B, the retractable movement means that the region surrounded by the outer edge of the backscattered
また、図4に示すように、回折図形をより明瞭に電子後方散乱回折検出器90の検出面に投影するためには、試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た場合に、反射電子検出器3の外縁が囲う領域と、仮想線Aおよび試料6の表面(観察面)の交点Bとが重ならず、かつ点Bから電子後方散乱検出器90の検出面の全面が遮られることなく見通せる位置まで、反射電子検出器3が退避可能であることが好ましい。すなわち、反射電子検出器3が、点Bを頂点、電子後方散乱検出器90の検出面を底面とする略円錐形で囲まれる領域から退避可能であることが好ましい。
Also, as shown in FIG. 4, in order to project the diffraction pattern more clearly on the detection surface of the electron
図5(a)および(b)は、試料台10を試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た図である。例えば、図5(a)に示すように、反射電子検出器3が回転機構2fを中心として試料保持面2aの法線方向と平行な軸回りに90°時計回りに回転することによって、点Bから電子後方散乱検出器90の検出面の全面が遮られることなく見通せる位置まで退避することが可能となる。
5A and 5B are views of the
なお、図5(a)に示す構成では、回転機構2fは試料保持面2aの角部に設けられているが、回転機構2fを設ける位置は特に限定されるものではない。点Bから電子後方散乱検出器90の検出面の全面が遮られることなく見通せる位置まで反射電子検出器3を退避する観点からは、回転機構2fは、試料保持面2aの法線方向から見た場合において、試料保持面2aが有する辺のうち、仮想線Aに交差しない辺に沿う領域に設けることが好ましい。例えば、図5(b)に示すように、仮想線Aに交差しない辺の中央部に設けてもよい。上記の構成を採用した場合には、反射電子検出器3の退避移動に伴い必要となる空間を小さくすることが可能となる。
In the configuration shown in FIG. 5A, the
図3〜5に示す構成では、回転機構2fを有し、反射電子検出器3が、試料保持面2aの法線方向と平行な軸回りに回転することで退避移動が可能となる。反射電子検出器3が、退避移動可能に試料保持部2に支持される構成については、上記の構成には限定されない。例えば、図6(a)に示すように、回転機構2f’を有し、反射電子検出器3が、試料保持面2aの法線方向と垂直な軸周りに回転することで退避移動可能に試料保持部2に支持されていてもよいし、図6(b)に示すように、着脱機構2gを有し、反射電子検出器3が、退避移動できるように着脱可能に試料保持部2に支持されていてもよい。
3 to 5 includes a
さらに、反射電子検出器3は、調整移動可能に試料保持部2に支持される。図2を参照して、調整移動可能とは、反射電子検出器3の検出面が試料保持面2aに対して略平行な状態を維持しつつ、電子線束が孔3cを通過可能な範囲まで、反射電子検出器3の位置を調整することが可能であることを意味する。具体的には、反射電子検出器3を、検出面と直交する方向および平行な方向に移動させることができる機構を備えることが望ましい。
Furthermore, the backscattered
試料保持部2と反射電子検出器3との距離については、試料6の厚さ等に応じて適宜調整すればよい。試料表面から広角に反射した反射電子は、距離Lが大きいと、反射電子検出器2の検出面に到達しない場合がある。そのため、最適な転位等の格子欠陥コントラストを観察できるよう調整するためには、反射電子検出器3を、検出面と直交する方向に移動させることができる機構2bを備えていることが望ましい。距離Lは、10mm以下であることが望ましいが、必ずしも制約はなく、観察条件に依存する。
The distance between the
検出面と直交する方向における微小な移動量を制御する方法としては、圧電素子を用いることができる。なお、図2に示す態様では、試料保持部2が検出面と直交する方向において高さを調整することが可能であり、かつ、反射電子検出器3を保持するための1つの支柱を有する構成となっているが、高精度に高さを調整するために、複数の支柱で反射電子検出器3を保持してもよい。ただし、この構成では、上述の退避移動のための回転機構2fを備えるのは困難となるため、前記複数の支柱がそれぞれ着脱機構2gを有していることが好ましい。
A piezoelectric element can be used as a method for controlling a minute movement amount in a direction orthogonal to the detection surface. In the embodiment shown in FIG. 2, the
図1に示すように、反射電子検出器3に入射した反射電子量は、電流および電圧変動の電気信号に換算されて、反射電子伝播装置88に送られるような構成とすることが望ましい。そのため、電気信号をSEM本体100の電気信号コネクタ受取口82を介して反射電子伝播装置88に送信するための第2コネクタピン5bを、試料台10の試料保持部2に設けることが望ましい。このピンの位置および構造は、汎用的なSEM本体の構成に依存して、適宜、変更すればよい。なお、電気信号の送信は、直接的な接続だけでなく、赤外線または無線等の非接触型の通信を利用することも可能である。
As shown in FIG. 1, it is desirable that the amount of reflected electrons incident on the reflected
ここで、孔の大きさにもよるが、試料保持部2の傾斜角度が大きくなると、試料保持部2と一緒に傾斜する反射電子検出器3の孔3cの位置が仮想線A上からずれ、電子線束が反射電子検出器3の表面3aに衝突し、試料6の表面まで到達しなくなる。そのために、電子線束が孔3cを通過可能な位置まで、反射電子検出器3を移動させる機構2cが必要である。この際、検出面と直交する方向の高さ、すなわち距離Lが変化することは測定条件の変化をもたらすため好ましくない。そこで、図2(c)に示すように、検出面と直交する方向の高さは固定した状態で、反射電子検出器3を、検出面と平行で互いに直交する2つの方向に移動させることができる機構2d,2eを備えることが望ましい。なお、図2(c)においては、2つの方向は直交しているが、交差していればよい。
Here, although depending on the size of the hole, when the inclination angle of the
反射電子検出器3を検出面と平行で互いに直交する2つの方向に移動させる機構については、例えば、圧電素子を応用することで微細化が可能である。また、図2(c)に示すように、上記の2つの方向がモニター上に現れる反射電子像のX方向およびY方向と一致するように設定すれば、組織像を観察しながら、モニター上でX方向およびY方向へ自在に移動させる機構を実現させることが可能となる。
The mechanism for moving the backscattered
反射電子検出器3の検出面に対して、垂直な方向への移動を行う機構2b、平行で互いに直交する2つの方向への移動を行う機構2d,2eおよび反射電子検出器3の退避移動を行う回転機構2fまたは2f’については、電気信号によって外部から操作することが可能である。例えば、試料台10の試料保持部2に、第3コネクタピン5cを設け、SEM本体100の電気信号コネクタ受取口82を介してSEMが備える移動制御装置86と電気的に接続し、電気信号を試料台10に送信することによって、反射電子検出器3の移動を制御することができる。なお、電気信号の送信は、直接的な接続だけでなく、赤外線または無線等の非接触型の通信を利用することも可能である。また、反射電子検出器3の検出面と平行な方向の移動機構2cについては、電子線束と孔の位置関係に応じて、そのずれが極力小さくなるよう制御することが可能な機構としてもよい。
The
1.本体部
1a.支持部
2.試料保持部
2a.試料保持面
2b.直交方向の移動機構
2c.平行方向の移動機構
2d.X方向の移動機構
2e.Y方向の移動機構
2f,2f’.回転機構
2g.着脱機構
3.反射電子検出器
3a.表面
3b.裏面
3c.穴
5a.第1コネクタピン
5b.第2コネクタピン
5c.第3コネクタピン
6.試料
10.試料台
15.設置部
17.駆動装置
20.電子銃
25.電子銃制御装置
30.コンデンサレンズ
35.集束レンズ系制御装置
40.対物レンズ
45.対物レンズ系制御装置
50.ポールピース
60.偏向コイル
65.偏向コイル制御装置
70.二次電子検出器
75.二次電子信号伝搬装置
80.表示装置
82.電気信号コネクタ受取口
84.揺動制御装置
86.移動制御装置
88.反射電子伝播装置
90.電子後方散乱回折検出器
92.電子後方散乱回折信号伝搬装置
94.試料結晶方位表示装置
100.SEM本体
1.
Claims (13)
前記電子顕微鏡に着脱可能に装着される本体部と、
前記試料を保持する試料保持面を有する試料保持部と、
表面および、前記試料保持面に平行かつ対向しており検出面となる裏面を有する反射電子検出器とを備え、
前記反射電子検出器は、前記表面から前記裏面へ貫通し、かつ、前記電子線束が通過可能な孔を有し、
前記試料保持部は、前記仮想線上の点を中心点として、揺動可能に前記本体部に支持され、
前記反射電子検出器は、
前記試料保持面の法線方向から見た場合に、前記反射電子検出器の外縁が囲う領域と、前記仮想線および前記試料保持面の交点とが重ならない位置まで退避する退避移動可能、かつ、
前記検出面が前記試料保持面に対して平行な状態を維持しつつ、前記電子線束が前記孔を通過可能な範囲に移動する調整移動可能に、前記試料保持部に支持される、
試料台。 A sample stage installed in an electron microscope that causes an electron beam bundle traveling on a virtual line extending in one direction to enter the surface of the sample,
A main body detachably attached to the electron microscope;
A sample holder having a sample holding surface for holding the sample;
A backscattered electron detector having a front surface and a back surface that is parallel to and opposed to the sample holding surface and serves as a detection surface;
The reflected electron detector has a hole penetrating from the front surface to the back surface and allowing the electron beam bundle to pass through,
The sample holding part is supported by the body part so as to be swingable around a point on the imaginary line as a center point,
The backscattered electron detector is
When viewed from the normal direction of the sample holding surface, the retreat movement is possible to retract to a position where the outer edge of the backscattered electron detector surrounds and the intersection of the virtual line and the sample holding surface does not overlap, and
The detection surface is supported by the sample holder so that the electron beam can be adjusted to move to a range where it can pass through the hole while maintaining the detection surface parallel to the sample holding surface.
Sample stage.
請求項1に記載の試料台。 The backscattered electron detector is supported by the sample holder so as to be retractable by rotating around an axis parallel to the normal direction of the sample holding surface.
The sample stage according to claim 1.
請求項1に記載の試料台。 The backscattered electron detector is supported by the sample holder so that it can be retracted by rotating around an axis perpendicular to the normal direction of the sample holding surface.
The sample stage according to claim 1.
請求項1に記載の試料台。 The backscattered electron detector is detachably supported by the sample holder so as to be retractable.
The sample stage according to claim 1.
請求項1から請求項4までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 The sample holder is rotatable about two axes parallel to the sample holding surface and intersecting on the center point;
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
請求項5に記載の試料台。 The two axes are orthogonal,
The sample stage according to claim 5.
請求項1から請求項6までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 The center point is located between the sample holder and the backscattered electron detector;
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 6.
請求項1から請求項7までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 The main body part has three or more support parts that are height-adjustable and support the sample holding part,
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 7.
請求項1から請求項8までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 A mechanism capable of adjusting and moving the backscattered electron detector in a direction perpendicular to the detection surface;
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 8.
請求項1から請求項9までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 A mechanism capable of adjusting and moving the backscattered electron detector in two directions parallel to the detection surface and intersecting each other;
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 9.
請求項10に記載の試料台。 The two directions are orthogonal,
The sample stage according to claim 10.
請求項1から請求項11までのいずれかに記載の試料台。 A first connector pin for receiving an electrical signal instructing swinging of the sample holder, a second connector pin for transmitting an electrical signal obtained by the backscattered electron detector, and movement of the backscattered electron detector A third connector pin for receiving an electrical signal indicating
The sample stage according to any one of claims 1 to 11.
前記試料台を設置する設置部と、
前記第1コネクタピン、第2コネクタピンおよび第3コネクタピンと電気的に接続する電気信号コネクタ受取口と、
前記反射電子検出器で得られた反射電子信号を伝播する反射電子伝播装置と、
前記試料保持部の揺動を制御する揺動制御装置と、
前記反射電子検出器の移動を制御する移動制御装置とを備える、電子顕微鏡。 The sample stage according to claim 12,
An installation section for installing the sample stage;
An electrical signal connector receiving port electrically connected to the first connector pin, the second connector pin, and the third connector pin;
A reflected electron propagation device that propagates a reflected electron signal obtained by the reflected electron detector;
A swing control device for controlling the swing of the sample holder;
An electron microscope comprising: a movement control device that controls movement of the reflected electron detector.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016152069A JP6790559B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2016-08-02 | Sample table and electron microscope equipped with it |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016152069A JP6790559B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2016-08-02 | Sample table and electron microscope equipped with it |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2018022592A true JP2018022592A (en) | 2018-02-08 |
| JP6790559B2 JP6790559B2 (en) | 2020-11-25 |
Family
ID=61165667
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016152069A Active JP6790559B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 | 2016-08-02 | Sample table and electron microscope equipped with it |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6790559B2 (en) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018221636A1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-12-06 | 新日鐵住金株式会社 | Inclination angle amount calculation device, sample stand, charged particle beam device, and program |
| WO2019082976A1 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2019-05-02 | 日本製鉄株式会社 | Crystal orientation map generation device, charged particle radiation device, crystal orientation map generation method, and program |
| JP2023503434A (en) * | 2019-11-19 | 2023-01-30 | アイシーティー インテグレーテッド サーキット テスティング ゲゼルシャフト フィーア ハルプライタープリーフテヒニック エム ベー ハー | Charged particle imaging system |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4370554A (en) * | 1979-09-27 | 1983-01-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Alignment system for particle beam lithography |
| JPS58193453U (en) * | 1982-06-14 | 1983-12-22 | 株式会社明石製作所 | Backscattered electron detection device in electron beam equipment |
| JPS594442Y2 (en) * | 1979-11-08 | 1984-02-08 | 日本電子株式会社 | scanning electron microscope |
| JP2007200573A (en) * | 2006-01-23 | 2007-08-09 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Electron microscope and controlling method of the same |
| JP2007207536A (en) * | 2006-02-01 | 2007-08-16 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Test piece base of charged particle beam apparatus |
| JP2011023144A (en) * | 2009-07-14 | 2011-02-03 | Jeol Ltd | Sample observation device |
| WO2012023354A1 (en) * | 2010-08-18 | 2012-02-23 | 株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ | Electron beam apparatus |
-
2016
- 2016-08-02 JP JP2016152069A patent/JP6790559B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4370554A (en) * | 1979-09-27 | 1983-01-25 | International Business Machines Corporation | Alignment system for particle beam lithography |
| JPS594442Y2 (en) * | 1979-11-08 | 1984-02-08 | 日本電子株式会社 | scanning electron microscope |
| JPS58193453U (en) * | 1982-06-14 | 1983-12-22 | 株式会社明石製作所 | Backscattered electron detection device in electron beam equipment |
| JP2007200573A (en) * | 2006-01-23 | 2007-08-09 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Electron microscope and controlling method of the same |
| JP2007207536A (en) * | 2006-02-01 | 2007-08-16 | Hitachi High-Technologies Corp | Test piece base of charged particle beam apparatus |
| JP2011023144A (en) * | 2009-07-14 | 2011-02-03 | Jeol Ltd | Sample observation device |
| WO2012023354A1 (en) * | 2010-08-18 | 2012-02-23 | 株式会社日立ハイテクノロジーズ | Electron beam apparatus |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2018221636A1 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2018-12-06 | 新日鐵住金株式会社 | Inclination angle amount calculation device, sample stand, charged particle beam device, and program |
| KR20200012947A (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2020-02-05 | 닛폰세이테츠 가부시키가이샤 | Inclination angle calculation device, sample stage, charged particle beam device and program |
| US10811218B2 (en) | 2017-05-31 | 2020-10-20 | Nippon Steel Corporation | Tilting parameters calculating device, sample stage, charged particle beam device, and program |
| WO2019082976A1 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2019-05-02 | 日本製鉄株式会社 | Crystal orientation map generation device, charged particle radiation device, crystal orientation map generation method, and program |
| US10811217B2 (en) | 2017-10-25 | 2020-10-20 | Nippon Steel Corporation | Crystal orientation figure creating device, charged particle beam device, crystal orientation figure creating method, and program |
| JP2023503434A (en) * | 2019-11-19 | 2023-01-30 | アイシーティー インテグレーテッド サーキット テスティング ゲゼルシャフト フィーア ハルプライタープリーフテヒニック エム ベー ハー | Charged particle imaging system |
| JP7437501B2 (en) | 2019-11-19 | 2024-02-22 | アイシーティー インテグレーテッド サーキット テスティング ゲゼルシャフト フィーア ハルプライタープリーフテヒニック エム ベー ハー | charged particle imaging system |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6790559B2 (en) | 2020-11-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US5081353A (en) | Combined scanning electron and scanning tunnelling microscope apparatus and method | |
| JP6009862B2 (en) | Scanning probe microscope | |
| WO2010097861A1 (en) | Charged particle beam device | |
| JP5852474B2 (en) | Charged particle beam equipment | |
| KR20160119840A (en) | Method of Performing Electron Diffraction Pattern Analysis Upon a Sample | |
| NL2007475C2 (en) | Particle beam device having a sample holder. | |
| JP2011123998A (en) | Focused ion beam device and focused ion beam processing method | |
| JP2007200573A (en) | Electron microscope and controlling method of the same | |
| JP2018022592A (en) | Sample table and electron microscope with the same | |
| JP6406032B2 (en) | Sample stage and electron microscope equipped with the same | |
| US11282672B2 (en) | Charged particle beam apparatus and sample processing observation method | |
| TWI782958B (en) | Charged Particle Beam Device | |
| US11087953B2 (en) | Moveable detector | |
| KR102559888B1 (en) | Charged particle beam apparatus | |
| US10319561B2 (en) | Object preparation device and particle beam device with an object preparation device and method for operating the particle beam device | |
| TW201822242A (en) | Apparatus for combined STEM and EDS tomography | |
| WO2017186198A1 (en) | Method for characterization of a sample surface by using scanning electron microscope and scanning probe microscope | |
| KR101539738B1 (en) | Scanning Electron Microscope | |
| JP2000277044A (en) | Scanning electron microscope | |
| JP2009193811A (en) | Sample holder, and electron microscope | |
| JPWO2015145706A1 (en) | Sample holder for charged particle beam apparatus and charged particle beam apparatus | |
| JP6316453B2 (en) | Charged particle beam apparatus and observation method using charged particle beam apparatus | |
| JPH05209713A (en) | Scan type electron microscope with scan type tunnel microscope | |
| JP2674993B2 (en) | electronic microscope | |
| JPH1173901A (en) | Sample analysis instrument |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190415 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20200219 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200324 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20201006 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20201019 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6790559 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |