JP2017196659A - Press metal dies and press machine, and method for checking metal die formation - Google Patents
Press metal dies and press machine, and method for checking metal die formation Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2017196659A JP2017196659A JP2016099096A JP2016099096A JP2017196659A JP 2017196659 A JP2017196659 A JP 2017196659A JP 2016099096 A JP2016099096 A JP 2016099096A JP 2016099096 A JP2016099096 A JP 2016099096A JP 2017196659 A JP2017196659 A JP 2017196659A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- molding
- die height
- reference block
- press
- overload protector
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Presses And Accessory Devices Thereof (AREA)
- Control Of Presses (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、自動車のプレス部品製造におけるプレス金型を用いた加工において、解析結果を実現するプレス機械と、その機械を用いた金型の成形確認方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a press machine that realizes an analysis result in processing using a press die in manufacturing a press part of an automobile, and a mold forming confirmation method using the machine.
自動車用プレス部品を生産するプレス金型(以下、金型という)は、電子計算機による解析技術とNC加工等を用いて設計、製作されるが、実際には解析結果と一致する成形結果が得られず、成形結果を熟練技能者が判定して成形調整として金型の修正を行っている。 Press dies that produce automotive stamping parts (hereinafter referred to as dies) are designed and manufactured using computer analysis technology and NC processing, but in practice, molding results that match the analysis results are obtained. However, the skilled technician determines the molding result and corrects the mold as a molding adjustment.
金型の解析技術は、大きく分けて成形解析と構造解析(剛性解析とも言う)の2種類がある。成形解析は、被成形物の「応力−歪」特性に基づく非線形領域の塑性変形解析が主体であり、金型がプレス機械から受ける加圧力が均一であることを前提に、意図した塑性変形に必要な加圧力と変形量を被成形物に印加可能な形状面を決定する。構造解析は、成形解析結果の加圧力分布に対して、成形に影響を及ぼさない剛性を有する構造を解析し決定している。 There are two types of mold analysis techniques: molding analysis and structural analysis (also referred to as rigidity analysis). Molding analysis mainly consists of plastic deformation analysis in the non-linear region based on the “stress-strain” characteristics of the workpiece. A shape surface capable of applying a necessary pressure and deformation amount to the molding is determined. In the structural analysis, a structure having rigidity that does not affect the forming is analyzed and determined with respect to the pressure distribution of the forming analysis result.
金型の成形調整作業は、実際の成形結果物や、光明丹や圧力測定フィルム等を用いた面当り状態や、ヒューズや粘土等を用いた上下成形面間等の隙の確認や測定によって、熟練技能者が成形時の状態を推測し、金型の修正を行っている。これらの調整用具は、調整範囲とその調整量を定量的に明示すものではないため、技能者が、自身の技能と経験に基づいて独自の判定を行っている。このため、技能者毎に修正方針は異なるが、修正と確認を何度も繰り返すことは共通する。実際に生産を開始する以前、金型の組付け完成直後から、トライプレスと呼ぶ金型の成形調整用プレスで何度も成形調整を行い、その後も、生産ラインで、成形確認と調整を行うため、金型の成形調整には長期を費やしている。近年の測定技術の発達に伴い、成形結果物と金型の成形部形状を測定し、その結果を元に成形解析を再実行して金型を調整加工する方法も行われている。この方法は、熟練技能者の不足や技能者間の能力差の緩和に効果はあるが、金型すなわち成形の初期品質の劇的な向上には至っていない。 Mold adjustment work of the mold is performed by checking and measuring the actual molding result, the surface contact state using Komyotan, pressure measurement film, etc., and the gap between the upper and lower molding surfaces using fuse, clay, etc. A skilled technician guesses the state at the time of molding and corrects the mold. Since these adjustment tools do not quantitatively clarify the adjustment range and the adjustment amount, the technician makes an independent determination based on his skill and experience. For this reason, although a correction policy differs for every technician, it is common to repeat correction and confirmation many times. Immediately before the start of production, immediately after the assembly of the mold is completed, the mold is adjusted many times with a press for mold adjustment called a tri-press. After that, the mold is checked and adjusted on the production line. Therefore, it takes a long time to adjust the molding of the mold. Along with the development of measurement technology in recent years, a method of adjusting a mold by measuring a molding result and a molding part shape of a mold and re-executing molding analysis based on the result is performed. This method is effective in reducing the shortage of skilled technicians and the ability difference between technicians, but has not led to a dramatic improvement in the initial quality of the mold, that is, molding.
技能者による成形調整では、成形面の形状の調整に加え、上下型の位置関係についても、被成形物の厚みのばらつきも考慮して調整する。上下型の位置関係の調整には、完全に上下型を押切った状態で、過剰押下を防止し、かつ上下成形面の位置関係を決定する押切りブロックが用いられている。この押切りブロックは、上型全体と下型全体の鉛直方向の位置関係を決定するものであり、成形調整の過程で成形調整の一部として調整され、成形および押切り状態の調整結果として、最後に完成される。 In the molding adjustment by the technician, in addition to the adjustment of the shape of the molding surface, the positional relationship between the upper and lower molds is adjusted in consideration of the variation in the thickness of the molding. For adjusting the positional relationship between the upper and lower molds, a pressing block that prevents excessive pressing and determines the positional relationship between the upper and lower molding surfaces while the upper and lower molds are completely pressed is used. This pressing block determines the vertical positional relationship between the entire upper mold and the entire lower mold, and is adjusted as part of the molding adjustment in the process of molding adjustment. Finally completed.
光明丹や圧力測定フィルムに代わる金型内の成形状態を知る工学的方法として、成形面もしくはその内部に歪ゲージを取付けて歪を測定する方法(特許文献1)が発明されている。しかし、歪は無次元で物理量を持たないため、自身の経過変化のような相対比較としては有効であるが、他と相対比較するためには、物理量への変換が必要であり、この点で、実用化には多くの課題がある。 As an engineering method for knowing the molding state in a mold in place of Komyotan or a pressure measurement film, a method of measuring strain by attaching a strain gauge on the molding surface or inside thereof (Patent Document 1) has been invented. However, since distortion is dimensionless and has no physical quantity, it is effective as a relative comparison such as its own change, but in order to make a relative comparison with others, it needs to be converted into a physical quantity. There are many problems in practical application.
成形に関わる主要装置であるプレス機械のダイハイト調整装置とオーバーロードプロテクタ装置を説明する。なお、説明は、以降も含め、自動車用プレス部品の生産現場で最も一般的な4ポイントのプレス機械、すなわち、スライドが4本のプランジャロッドで駆動装置と連結されたプレス機械を例にする。 A die height adjusting device and an overload protector device of a press machine, which are main devices related to molding, will be described. In addition, the description will exemplify a four-point press machine, which is the most common on the production site of press parts for automobiles, that is, a press machine in which a slide is connected to a drive device by four plunger rods.
ダイハイト調整装置を説明する。ダイハイト調整装置は、プレス機械のダイハイト、すなわちスライド下死点におけるポルスタプレート(もしくはベッド)上面からスライド底面までの、金型の押切り高さを調整する装置である。ダイハイト調整装置は、プランジャロッド毎に組付けられたダイハイト調整機を全て機械的に連結し、1台のモータで同期運転する。ダイハイト調整機は、ウォームネジとウォームホイールネジを対として構成される。ウォームネジは他のダイハイト調整機と駆動モータとに機械的に連結され、ウォームホイールネジは、プランジャロッドに組付けられ、ダイハイト調整機本体はスライドに固定されている。ウォームホイールネジは、ウォームネジにより回転され、プランジャロッドに対する位置が調整され、これによりスライド調整機が固定されたスライド位置が上下し、ダイハイトが調整される。 A die height adjusting device will be described. The die height adjusting device is a device for adjusting the die cut height of the die from the die height of the press machine, that is, the top surface of the Porstag plate (or bed) to the bottom surface of the slide at the slide bottom dead center. The die height adjusting device mechanically connects all the die height adjusting devices assembled for each plunger rod, and operates synchronously with one motor. The die height adjusting machine is constituted by a pair of a worm screw and a worm wheel screw. The worm screw is mechanically connected to another die height adjuster and a drive motor, the worm wheel screw is assembled to the plunger rod, and the die height adjuster main body is fixed to the slide. The worm wheel screw is rotated by the worm screw, and the position with respect to the plunger rod is adjusted, whereby the slide position to which the slide adjuster is fixed moves up and down, and the die height is adjusted.
ダイハイトとスライド平行度の関係を説明する。一般にダイハイト調整量は、数十〜数百[mm]であり、前項説明のように、1台のモータで機械的に同期運転される。スライド平行度は、ダイハイト調整機の組付け状態により決定され、任意調整はできない。スライド平行度は成形に影響するため、JISにて精度等級の一部として制定されている。自動車用プレス部品用のプレス機械は、通常、JIS等級の1級であり、例えば、ダイスペース長4[m]のスライド平行度の許容差は、0.44[mm]である。スライド平行度の金型への影響の一例として、下死点でダイハイト調整装置を駆動する際に平行度が許容値を外れると、上下型の水平方向の位置関係を規制するガイド等の規制部で、干渉不具合の原因となる。以上、ダイハイト調整装置とスライド平行度は密接に関係し、ダイハイトの調整運転中においても、スライド平行度を許容値内に保つ必要がある。 The relationship between die height and slide parallelism will be described. In general, the die height adjustment amount is several tens to several hundreds [mm], and is mechanically operated synchronously with one motor as described in the previous section. The slide parallelism is determined by the assembled state of the die height adjuster and cannot be arbitrarily adjusted. Since slide parallelism affects molding, it is established as a part of accuracy grade by JIS. A press machine for press parts for automobiles is normally a
一部のプレス機械において、スライドの平行度を調整する方法として、各々のダイハイト調整機を個別のモータで独立して調整する方法(特許文献2)や油圧シリンダを用いた平行度調整装置(特許文献3)が発明されている。しかし、両発明とも各調整軸間の機械的な同期構造を有せず、ダイハイトの調整の過程で平行度を許容値内に保つ制御等の付加的な機構を必要とする。また、個別モータ方式(特許文献2)は、広い設置スペースを必要とする。油圧シリンダ方式(特許文献3)は、構造が複雑である上、オーバーロードプロテクタ装置に能動的な伸縮機能を付加したものであり、プレス加圧時の圧縮時の補正や油の粘度の温度変化等に対して、さらに高度の制御を必要とする。 In some press machines, as a method of adjusting the parallelism of the slide, a method of adjusting each die height adjuster independently with an individual motor (Patent Document 2) and a parallelism adjusting device using a hydraulic cylinder (Patent) Document 3) has been invented. However, both inventions do not have a mechanical synchronization structure between the adjustment axes, and require an additional mechanism such as control for keeping the parallelism within an allowable value in the process of adjusting the die height. The individual motor system (Patent Document 2) requires a large installation space. The hydraulic cylinder method (Patent Document 3) has a complicated structure and an active expansion / contraction function added to the overload protector device. Correction during compression during press pressurization and temperature change of oil viscosity Etc., more sophisticated control is required.
また、近年、プレス機械の駆動源としてサーボモータを使った、通称、サーボプレスが実用化されていて、一部のサーボプレスでは、加圧点毎に設けたサーボモータを同期させて下死点停止させている。この形態のサーボプレスにおいても、個別のモータで独立して調整する方法(特許文献2)と同様に、同期性が不安定で動作中の平行度の保持が課題である。加えて、下死点位置自体と下死点位置での平行度の双方が、サイクル毎で精度差を有し再現性がない。サーボプレスの平行度に関しては、その平行度の維持機構が数多く発明されているが、発明の多さが平行度に関する課題の大きさの査証でもある。 In recent years, the so-called servo press, which uses a servo motor as a drive source for press machines, has been put into practical use. In some servo presses, the servo motor provided for each pressurizing point is synchronized with the bottom dead center. Stopped. Even in this form of servo press, as in the method of independent adjustment with individual motors (Patent Document 2), the problem is that the synchronization is unstable and the parallelism during operation is maintained. In addition, both the bottom dead center position itself and the parallelism at the bottom dead center position have accuracy differences from cycle to cycle and are not reproducible. Regarding the parallelism of the servo press, many mechanisms for maintaining the parallelism have been invented, but the number of inventions is also a visa for the magnitude of the problem related to parallelism.
オーバーロードプロテクタ装置を説明する。プレス機械の加圧点である各プランジャロッドの直下にオーバーロードプロテクタと呼ぶ油圧室が存在する。オーバーロードプロテクタ(油圧室)は、油圧ダンパーと同等の機構であり、下死点での押切り時に圧縮による反力を発生するのみで、能動的な伸縮機能は有しない。オーバーロードプロテクタ装置は、オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧室を全て油圧配管で接続し、共通の油圧が供給される。オーバーロード発生時には、この油圧供給が停止され、かつ、オーバーロードプロテクタ内の油圧が排出され、圧縮による反力が減じられる。オーバーロードプロテクタ装置は、ダイハイト調整装置と密接に関連しており、金型のダイハイト(上下型押切り時の高さ)よりプレス機械のダイハイト(下死点でのスライド高さ)を低く設定することで、下死点でオーバーロードプロテクタが圧縮され反力が発生し、この反力がプレス機械の加圧力である。一般に、プレス機械は汎用機と位置付けられ、金型に対しては均等な加圧力を発生する前提で設計され、全てのオーバーロードプロテクタは、前述のように油圧配管で相互に接続され、かつ油圧源も同一であり、全オーバーロードプロテクタの反力である加圧力はその圧縮量に関係なく均等となる。 An overload protector device will be described. A hydraulic chamber called an overload protector exists directly under each plunger rod, which is a pressurizing point of the press machine. The overload protector (hydraulic chamber) is a mechanism equivalent to a hydraulic damper, and only generates a reaction force due to compression at the time of pressing at the bottom dead center, and does not have an active expansion / contraction function. In the overload protector device, all of the overload protector hydraulic chambers are connected by hydraulic piping, and a common hydraulic pressure is supplied. When overload occurs, this hydraulic pressure supply is stopped, and the hydraulic pressure in the overload protector is discharged, and the reaction force due to compression is reduced. The overload protector device is closely related to the die height adjustment device, and sets the die height (slide height at the bottom dead center) of the press machine lower than the die height of the die (height at the time of vertical die pressing). As a result, the overload protector is compressed at the bottom dead center and a reaction force is generated, and this reaction force is the pressing force of the press machine. In general, the press machine is positioned as a general-purpose machine, and is designed on the premise that uniform pressure is generated on the mold. All overload protectors are interconnected by hydraulic piping as described above, and hydraulic The source is also the same, and the applied pressure that is the reaction force of all overload protectors is equal regardless of the amount of compression.
オーバーロードプロテクタ装置の油圧調整は、類似発明として、オーバーロードプロテクタによる平行度調整装置(特許文献4)やシリンダによる平行度調整装置(特許文献5)が発明されている。両発明ともスライド平行度調整を目的とするが、プレス加圧点の油圧を調整する技術を共通とする。両発明とも、能動的な油圧調整方式であるため、高額な油圧装置を必要とし、かつ油圧の粘度の温度変化や圧縮量によるばらつきが大きく、高精度の制御を必要とする。 For the hydraulic adjustment of the overload protector device, as a similar invention, a parallelism adjusting device using a overload protector (Patent Document 4) and a parallelism adjusting device using a cylinder (Patent Document 5) have been invented. Both inventions aim at adjusting the slide parallelism, but share the same technique for adjusting the hydraulic pressure at the press pressure point. Since both inventions are active hydraulic pressure adjustment systems, an expensive hydraulic device is required, and the variation in the viscosity of the hydraulic pressure due to temperature changes and compression amounts is large, requiring high-precision control.
以上は、金型の製作から調整まで、実際の生産に移行する前の技術背景である。生産に移行後は、金型の成形調整過程で得られたダイハイト値等のプレス機械の調整結果を生産要件として、生産段取り時に、プレス機械を調整している。しかし、生産移管等によりプレス機械を変更した場合や、プレス機械もしくは金型の保全内容によっては、再度の成形確認と調整を必要としている。 The above is the technical background before shifting to actual production from mold production to adjustment. After shifting to production, the press machine is adjusted at the time of production setup using the adjustment result of the press machine such as the die height value obtained in the mold adjustment process as a production requirement. However, if the press machine is changed due to production transfer, etc., or depending on the maintenance content of the press machine or the mold, it is necessary to confirm and adjust the molding again.
解析技術とNC加工等を用いて設計、製作した金型を用いた実際のプレス成形において、解析結果と一致した成形結果が得られない。この主たる原因は、解析技術の中で簡略化や単純化した因子、すなわちプレス機械や金型の精度差等の因子が、実際には成形に影響するためである。これら因子の成形への影響に対しての定量的な要因分析も不十分で、この部分の解析技術が確立していない。また、成形結果の解析技術への帰還も不完全であり、解析技術の性能の向上も限定される。以上により、本発明は、前提条件や演算過程を含めた解析技術と比較可能な成形の実態を検知する手段を提供し、その手段を用いてプレス機械と金型の成形影響因子を排除もしくは極小化する手段を提供することが課題である。 In actual press molding using a die designed and manufactured using analysis technology and NC machining, a molding result that matches the analysis result cannot be obtained. The main cause is that factors that are simplified or simplified in the analysis technique, that is, factors such as accuracy differences between the press machine and the die actually affect the forming. Quantitative factor analysis of the influence of these factors on molding is insufficient, and the analysis technology for this part has not been established. Further, the return of the molding result to the analysis technology is incomplete, and the improvement of the performance of the analysis technology is limited. As described above, the present invention provides means for detecting the actual state of molding that can be compared with analysis techniques including preconditions and calculation processes, and eliminates or minimizes molding influencing factors of the press machine and the mold using the means. It is a problem to provide means for realizing the above.
本発明の嵌合基準ブロックは、上下型の嵌合面、すなわち下型上面もしくは上型下面の何れか一方に固定され、上下型の嵌合時の相手型との接触面を、成形の正の基準と一対一に関連付けた接触基準として形成することにより、上下型の成形面を成形解析結果と一致する位置関係に規制し、かつ、上下型の間の縦歪を加圧力へ変換可能な面積精度を有する構造体を成し、その構造体側面に歪ゲージを取付けて成り、この嵌合基準ブロックを金型内の要所に配置し、上下型の嵌合押切り状態において、上下型の成形面の位置関係を成形解析結果と一致するよう規制し、かつ加圧力分布を成形解析結果と一致させる指標とすることを特徴とする。 The fitting reference block of the present invention is fixed to the upper and lower mold fitting surfaces, that is, either the upper surface of the lower mold or the lower surface of the upper mold, and the contact surface with the mating mold when the upper and lower molds are fitted to each other. By forming it as a contact reference that has a one-to-one relationship with the standard of the upper and lower molds, it is possible to restrict the molding surface of the upper and lower molds to a positional relationship that matches the molding analysis result, and to convert the vertical strain between the upper and lower molds into a pressure A structure with area accuracy is formed, and a strain gauge is attached to the side of the structure. This fitting reference block is placed at a key point in the mold. The positional relationship of the molding surface is regulated so as to match the molding analysis result, and the pressure distribution is used as an index for matching the molding analysis result.
本発明の多点ダイハイト調整装置は、プレス機械と金型の成形影響因子を排除もしくは影響を極小化して、成形解析結果と一致する嵌合押切り状態を実現することを目的とし、嵌合基準ブロックから得られる加圧力情報である実測値と、当該嵌合基準ブロック部の加圧力の成形解析結果である設定値とを比較し、仮に実測値が設定値より低い部分に対しては、当該部分のダイハイト調整機のみのクラッチを接続し、かつ対となるブレーキを解放して、調整モータを駆動して、実測値が設定値の許容範囲内に入るまでダイハイトを下降させ、仮に、実測値が設定値より高い部位に対しては、同様にクラッチとブレーキとモータの操作を用いて必要箇所のみを駆動し、実測値が設定値の許容範囲内に入るまでダイハイトを上昇させる機能を有することを特徴とする。 The multi-point die height adjusting device of the present invention aims to eliminate a molding machine influence factor between a press machine and a mold or minimize the influence, and to realize a fitting press-cut state that matches a molding analysis result. Compare the measured value, which is the pressure information obtained from the block, with the set value, which is the molding analysis result of the pressure of the fitting reference block, and for the part where the measured value is lower than the set value, Connect the clutch of only the part die height adjuster and release the paired brake, drive the adjustment motor, lower the die height until the measured value is within the allowable range of the set value, tentatively measured value For parts where is higher than the set value, similarly, only the necessary parts are driven using the operation of the clutch, brake and motor, and the die height is raised until the measured value falls within the allowable range of the set value. And wherein the door.
本発明の多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置は、プレス機械と金型の成形影響因子を排除もしくは影響を極小化して、成形解析結果と一致する嵌合押切り状態を実現することを目的とし、偏荷重に対応してプレス機械の出力バランスを変更する場合において、嵌合基準ブロックから得られる加圧力情報である実測値と、当該嵌合基準ブロック部の加圧力の成形解析結果である設定値とを比較し、変更が必要なオーバーロードプロテクタと対となるパイロット操作逆止弁の逆止機能を有効として当該オーバーロードプロテクタを他油圧室から遮断し、かつ、当該オーバーロードプロテクタ部の上記ダイハイト調整機を用いて、仮に増圧が必要な場合は、実測値が設定値の許容範囲内に一致するまでダイハイトを下降し、仮に減圧が必要な場合は、実測値が設定値の許容範囲内に入るまでダイハイトを上昇させて、金型内の加圧力分布を成形解析結果と一致させる調整機能を有するパイロット操作逆止弁を用いたことを特徴とする。 The multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device of the present invention aims to eliminate a molding influencing factor of the press machine and the mold or minimize the influence, and realize a fitting press-cut state that matches the molding analysis result, When changing the output balance of the press machine in response to the unbalanced load, the measured value that is the pressure information obtained from the fitting reference block and the setting value that is the molding analysis result of the pressure of the fitting reference block , The check function of the pilot operated check valve that is paired with the overload protector that needs to be changed is enabled to shut off the overload protector from the other hydraulic chambers, and the above-mentioned die height of the overload protector section If pressure increase is necessary using the adjuster, the die height is lowered until the measured value is within the allowable range of the set value, and pressure reduction is required. In this case, a pilot-operated check valve having an adjustment function for increasing the die height until the measured value falls within the allowable range of the set value and matching the pressure distribution in the mold with the molding analysis result is used. And
本発明のプレス機械は、上記嵌合基準ブロックと、上記多点ダイハイト調整装置と、上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を有する2点以上の加圧ポイントを有するプレス機械であって、上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージからの歪ゲージ信号を受取れるインターフェース機能を有することを特徴とする。 The press machine of the present invention is a press machine having two or more pressurizing points including the fitting reference block, the multi-point die height adjusting device, and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device. It has an interface function for receiving a strain gauge signal from the strain gauge of the reference block.
本発明の制御装置は、上記プレス機械に用いる制御装置であって、上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージからの上記歪ゲージ信号を加圧力へ変換し、当該加圧力を、成形解析結果の加圧力と一致させるように、上記多点ダイハイト調整装置と上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を調整することを特徴とする。 The control device of the present invention is a control device used in the press machine, which converts the strain gauge signal from the strain gauge of the fitting reference block into a pressurizing force, and applies the pressurizing force to the molding analysis result. The multi-point die height adjusting device and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device are adjusted so as to coincide with the pressure.
詳細には、本発明の制御装置は、上記嵌合基準ブロックに対し上記嵌合基準ブロック毎に対応する管理番号を付与し、当該管理番号と、当該管理番号毎に、上記歪ゲージからの上記歪ゲージ信号を加圧力に変換する変換係数と、成形解析結果もしくは上記プレス機械で実測した全ての上記嵌合基準ブロックの加圧力における、成形調整および成形品質確認時に設定値として用いる、実負荷時の成形余裕加圧力上限値および下限値と、それら成形余裕加圧力上下限値の中央範囲の加圧力中央上限値および下限値と、成形調整および金型段取り時に設定値として用いる、無負荷時の無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値と、同じく成形調整および成形品質確認時に設定値として用いる、実負荷時の加圧力分布が成形解析結果の加圧力分布と一致する時の全ての加圧点の上記多点ダイハイト調整装置の実測値から得られるダイハイト設定上限値および下限値と、全ての上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の上記パイロット操作逆止弁の逆止機能の設定状態と、上記多点ダイハイト調整装置が実負荷時の加圧力分布を成形解析結果の加圧力分布と一致させるダイハイト値である時の、実負荷時と無負荷時双方の全ての加圧点のオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧の実測値から得られる実負荷出力上限値および下限値と無負荷出力上限値および下限値とを、生産要件として金型毎に記憶する機能を有し、かつ、上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージからの上記歪ゲージ信号を、上記嵌合基準ブロックに対応する管理番号毎に、加圧力に変換する演算機能を有し、かつ、生産時において、全ての上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージからの上記歪ゲージ信号を変換して得られる加圧力である実測値を、上記嵌合基準ブロックに対応する管理番号毎に、記憶情報である生産要件の成形余裕加圧力上下限値と比較し、仮に実測値が成形余裕加圧力上限値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と過剰加圧警報を出力し、仮に実測値が成形余裕加圧力下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と加圧不足警報を出力し、仮に実測値が成形余裕加圧力上下限値内であれば、さらに記憶情報である生産要件の成形余裕加圧力上下限値の中央範囲の加圧力中央上下限値とも比較し、仮に実測値が加圧力中央上下限値内であれば成形状態を良好と判定出力し、仮に実測値が加圧力中央上値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と過剰加圧注意報を出力し、仮に実測値が加圧力中央下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と加圧不足注意報を出力する機能を有し、かつ、金型を装着する際に、装着直前の上死点では、上記多点ダイハイト調整装置の全ての上記ダイハイト調整機のダイハイト値である実測値を、記憶情報である生産要件のダイハイト設定上下限値と個別に比較し、仮に実測値がダイハイト設定下限値より低ければ当該ダイハイトを上昇し、仮に実測値がダイハイト設定上限値より高ければ当該ダイハイトを下降して生産要件のダイハイト設定上下限値内に調整し、かつ、上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の上記パイロット操作逆止弁の逆止機能の有効もしくは無効を記憶情報である生産要件と一致した状態に設定し、装着時の下死点では、上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の全ての上記オーバーロードプロテクタの油圧値である実測値を、記憶情報である生産用件の無負荷出力圧上下限値と個別に比較し、仮に実測値が無負荷出力圧上限値を超えた場合は、当該オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧が設定範囲内となるまで対となるダイハイトを上昇し、仮に実測値が無負荷出力圧下限値に満たない場合は、同様に当該オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧が設定範囲内となるまで対となるダイハイトを下降し、仮に実測値が設定範囲内であれば、さらに上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージからの歪ゲージ信号を変換して得られる加圧力を実測値として、生産要件である無負荷加圧力上下限値とを比較し、仮に実測値が無負荷加圧力上限値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号とダイハイト過剰下降警報を出力し、仮に実測値が無負荷加圧力下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号とダイハイト下降不足警報を出力し、仮に実測値が生産要件である無負荷加圧力上下限値内である場合は、装着正常信号を出力する機能を有することを特徴とする。 Specifically, the control device of the present invention assigns a management number corresponding to each of the fitting reference blocks to the fitting reference block, and the management number and the management number from the strain gauge for each of the management numbers. At the time of actual load, used as a set value when checking the molding adjustment and molding quality in the conversion coefficient for converting the strain gauge signal into the pressing force and the pressing analysis force of all the fitting reference blocks measured by the molding analysis result or the press machine Upper limit value and lower limit value of molding margin pressure, and upper limit value and lower limit value of the central range of the upper and lower limits of molding margin pressure, and set values for molding adjustment and mold setup. When the load distribution at the actual load matches the pressure distribution in the molding analysis result, which is also used as the set value for molding adjustment and molding quality confirmation The die height setting upper limit value and lower limit value obtained from the measured values of the multipoint die height adjusting device at all the pressurizing points, and the check function of the pilot operated check valve of all the multipoint overload protector hydraulic adjusting devices All pressurization points at both actual load and no load when the set state and the above-mentioned multi-point die height adjustment device are die height values that match the pressure distribution at the actual load with the pressure distribution of the molding analysis result The actual load output upper limit value and lower limit value and no-load output upper limit value and lower limit value obtained from the actual measured values of the overload protector hydraulic pressure of each mold are stored as production requirements for each mold, and the above-mentioned fitting It has a calculation function for converting the strain gauge signal from the strain gauge of the reference block into a pressurizing force for each control number corresponding to the fitting reference block, and at the time of production, An actual measurement value obtained by converting the strain gauge signal from the strain gauge of the fitting reference block is stored for each management number corresponding to the fitting reference block according to the production requirements. Compared with the upper and lower limit values of the forming margin pressure, if the measured value exceeds the upper limit value of the molding margin pressure, the control number of the fitting reference block and the over-pressurization alarm are output, and the measured value is temporarily set to the molding margin. If the lower limit of the applied pressure is not reached, the control number of the fitting reference block and the insufficient pressurization alarm are output. If the measured value is within the upper and lower limits of the molding allowance applied pressure, the production requirement that is further stored information Compared with the median upper / lower limit of the pressurization center pressure range, if the measured value is within the median upper / lower limit value, the molding condition is judged to be good and the measured value is temporarily added. If the upper pressure median value is exceeded, the mating standard Outputs block control number and overpressurization warning, and if the measured value is less than the median lower limit of pressurization, it has a function to output the control number of the fitting reference block and underpressurization warning In addition, when mounting the mold, at the top dead center immediately before mounting, the measured height values of all the die height adjusters of the multi-point die height adjusting device are set to the die height of the production requirements as stored information. Compared with the upper and lower limit values, if the measured value is lower than the die height setting lower limit value, the die height is increased, and if the measured value is higher than the die height setting upper limit value, the die height is lowered and the die height setting upper and lower limits of the production requirements Adjust the value within the range, and match the production requirement as the stored information with the check function of the pilot operated check valve of the multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device. At the bottom dead center at the time of installation, the measured values, which are the hydraulic values of all the overload protectors of the multipoint overload protector hydraulic adjustment device, are stored as no-load output of production information If the measured value exceeds the upper limit value of the no-load output pressure, the die height of the pair is raised until the overload protector hydraulic pressure is within the set range. If the lower limit of the no-load output pressure is not reached, the corresponding die height is lowered until the overload protector hydraulic pressure is within the set range. Using the applied pressure obtained by converting the strain gauge signal from the strain gauge of the block as an actual measurement value, it compares the upper and lower limits of the no-load applied pressure that is a production requirement, and the actual measured value is assumed to be no-load applied pressure. If the limit value is exceeded, the control number of the fitting reference block and the die height excessive descent warning are output, and if the measured value is less than the no-load pressure lower limit value, the control number of the fitting reference block is A die height descent insufficient alarm is output, and if the actually measured value is within the upper and lower limits of the no-load applied pressure that is a production requirement, it has a function of outputting a mounting normal signal.
本発明のプレス金型の成形確認方法は、上記制御装置を用いたプレス金型の成形確認方法であって、上記嵌合基準ブロックの上記歪ゲージの上記歪ゲージ信号を変換して得られる上記加圧力を、成形解析結果の加圧力と一致させるように、上記多点ダイハイト調整装置と上記多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を調整することを特徴とする。 The press mold forming confirmation method of the present invention is a press mold forming confirmation method using the control device, and is obtained by converting the strain gauge signal of the strain gauge of the fitting reference block. The multi-point die height adjusting device and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device are adjusted so that the pressurizing force coincides with the pressurizing force of the molding analysis result.
プレス金型の成形状態を成形解析結果と一致させることができる。例えば、本発明を用いれば、プレス機械と金型の精度差の影響の修正と、金型製作直後のトライプレスによる金型調整過程が不要となり、期間短縮が可能となる。 The molding state of the press die can be matched with the molding analysis result. For example, if the present invention is used, the correction of the influence of accuracy difference between the press machine and the die and the die adjustment process by the tri-press immediately after the die production are unnecessary, and the period can be shortened.
成形解析結果と実際の成形結果との差異の原因を、プレス機械と金型の精度差の影響を排除した解析技術だけの要因に絞り込んだ良質のデータとして、解析技術に帰還することが可能となり、解析技術の性能が向上する。 It is possible to return to the analysis technology as high-quality data that narrows down the cause of the difference between the molding analysis result and the actual molding result to the factor of only the analysis technology that eliminates the influence of accuracy difference between the press machine and the mold. , Analysis technology performance will improve.
副次的な波及効果として人材の有効活用が可能となる。従来、量産開始後も含め金型調整には、一定以上の技能と経験年数を有する熟練者が必用であった。本発明により、成形状態が数値管理可能となるため、熟練者の作業の大部分が代行可能となる。従って、熟練者を、従来の後追い仕事から、金型製作および成形プロセス革新等の先取り仕事へ振り向けることが可能となる。 Effective utilization of human resources becomes possible as a secondary ripple effect. Conventionally, skilled workers with a certain level of skill and years of experience are necessary for mold adjustment, including after the start of mass production. According to the present invention, the molding state can be numerically managed, so that most of the work of skilled workers can be performed. Therefore, it is possible to turn the skilled person from the conventional follow-up work to the advance work such as mold production and molding process innovation.
金型設計における解析技術には、成形解析と構造解析とがある。成形解析は、被成形物の「応力−歪」特性に基づき、意図した塑性変形に必要な加圧力と変形量を被成形物に印加できる成形形状を解析し決定する。この成形形状は、被成形物に対し、意図した形状を実現する変形量を決定する「型」となる形状を有する成形面と、被成形物をその「型」に沿わせ、かつ必要な応力を印加するための成形面とが、被成形物を間に挟んで対を成す。構造解析は、成形に必要なプレス機械からの加圧力と金型内の成形荷重の双方に対して、成形に影響しない十分な剛性を有する構造を決定する。これら成形、構造の両解析技術とNC加工を用いて製作した金型において、実際の成形結果が、解析結果と一致しない。この原因は、解析技術の性能に起因するだけでなく、プレス機械の精度差や、金型の製作精度差にも起因する。従って、解析結果と一致する成形結果を得るには、成形結果に影響する因子を、解析技術の性能に関わる因子と、プレス機械と金型に関わる因子とに分離し、解析技術以外の後者の影響を排除もしくは影響を無視できる程度まで極小化することが必要であり、前提条件と演算過程を含む解析技術と比較可能な成形の実態を検知する手段と、その手段を用いたプレス機械と金型の成形影響因子を排除もしくは極小化する手段が必要である。なお、被成形物の厚み等の形状と応力特性のばらつきは、成形余裕の問題として、解析技術の性能の一部に含むべきものである。 Analysis techniques in mold design include molding analysis and structural analysis. The molding analysis is based on the “stress-strain” characteristic of the molding, and analyzes and determines a molding shape that can apply the pressure and deformation necessary for the intended plastic deformation to the molding. This molded shape has a molding surface that has a shape that is a “mold” that determines the amount of deformation that achieves the intended shape of the molded product, and that the molded product conforms to the “mold” and has the necessary stress. And a molding surface for applying a pair of materials with a molding object in between. In the structural analysis, a structure having sufficient rigidity that does not affect the molding is determined with respect to both the pressing force from the press machine necessary for molding and the molding load in the mold. In a mold manufactured using both the molding and structural analysis techniques and NC machining, the actual molding results do not match the analysis results. The cause of this is not only due to the performance of the analysis technique, but also due to the difference in accuracy of the press machine and the difference in manufacturing accuracy of the mold. Therefore, in order to obtain a molding result that matches the analysis result, the factors affecting the molding result are separated into factors relating to the performance of the analysis technology and factors relating to the press machine and the die, and the latter factors other than the analysis technology. It is necessary to eliminate the influence or minimize it to the extent that the influence can be ignored, a means for detecting the actual condition of the molding that can be compared with the analysis technology including the preconditions and the calculation process, and the press machine and the gold using the means. There is a need for means to eliminate or minimize the mold influencing factors. Note that variations in the shape and stress characteristics of the workpiece, such as the thickness, should be included as part of the performance of the analysis technique as a problem of molding margin.
成形解析結果における、変形量を決定する「型」となる成形面を正の基準(面)とする正の成形面とし、被成形物をその「型」に沿わせ、かつ必要な応力を印加する成形面を従の成形面とする。成形解析結果と一致した成形結果を得るには、プレス成形時の加圧状態、すなわち上下型の嵌合押切り状態において、正と従の両成形面間の位置関係と両成形面間の加圧力分布の双方が、成形解析結果と一致する必要がある。以上より、嵌合押切り状態下で、正と従の両成形面間の位置関係を規制し、かつ両成形面間の加圧力分布を測定する手段として、本発明である嵌合基準ブロック(10)を用いる。 In the molding analysis result, the molding surface that is the “mold” that determines the amount of deformation is the positive molding surface with the positive reference (surface), the workpiece is placed along the “mold”, and the necessary stress is applied. The molding surface to be used is the secondary molding surface. In order to obtain a molding result that matches the molding analysis result, the positional relationship between the positive and secondary molding surfaces and the addition between the molding surfaces in the pressurized state during press molding, that is, the upper and lower molds are fitted and cut off. Both pressure distributions need to match the molding analysis results. From the above, as a means for regulating the positional relationship between both the primary and secondary molding surfaces and measuring the pressure distribution between the molding surfaces in the fitted push-off state, the fitting reference block according to the present invention ( 10) is used.
嵌合基準ブロック(10)の構造について、図1の嵌合基準ブロック(10)の説明図と、図2の嵌合基準ブロック(10)を用いた上下型の嵌合押切り状態の説明図とを用いて説明する。なお、嵌合基準ブロックは、上下型の何れに取付けても良いが、加圧測定用配線の処理等、段取り性が良い下型への取付けを前提に説明する。図1に示す嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、図2に示す上下型の嵌合押切り状態おいて、正の成形面(21a、22a)と被成形物(23)を挟んで対面する従の成形面(21aに対しては22b、22aに対しては21b)の位置関係を成形解析結果と一致するよう規制する構造体である。従って、嵌合基準ブロックの上面(10a)および同上面(10a)に接触する上型の接触面の双方を、成形の正の基準と一対一に関連付けた嵌合時の接触基準として定め、成形解析にて嵌合基準面として形成する。詳しくは、仮に正の成形面(21a、22a)が上下型に存在する場合には、双方の位置関係が成形解析結果と一致する位置関係に、仮に上下型の一方にしか正の成形面(21aもしくは22a)が存在しない場合でも、正の成形面(21aもしくは22a)と対面する従の成形面(21aに対して22b、22aに対して21b)が成形解析結果と一致する位置関係に規制可能な、正の基準(面)と一対一に関連付けた精度保証された嵌合基準(面)として解析する。嵌合基準面を精度保証する手段例として、嵌合基準ブロックを組付け後に成形の正の基準と一対一に関連付けた嵌合基準面として機械加工を施す。 About the structure of a fitting reference | standard block (10), explanatory drawing of the fitting reference | standard block (10) of FIG. 1, and explanatory drawing of the upper and lower type fitting push-off state using the fitting reference | standard block (10) of FIG. And will be described. The fitting reference block may be attached to any of the upper and lower molds, but the description will be made on the assumption that the fitting reference block is attached to the lower mold with good set-up characteristics such as processing of pressure measurement wiring. The mating reference block (10) shown in FIG. 1 is a slave that faces the positive molding surfaces (21a, 22a) and the molding (23) with the upper and lower molds shown in FIG. This is a structure that regulates the positional relationship of the molding surface (22b for 21a, 21b for 22a) to coincide with the molding analysis result. Therefore, both the upper surface (10a) of the fitting reference block and the contact surface of the upper die that contacts the upper surface (10a) are determined as the contact reference at the time of fitting in a one-to-one relationship with the positive reference of molding, and molding is performed. It is formed as a fitting reference plane by analysis. Specifically, if the positive molding surfaces (21a, 22a) are present in the upper and lower molds, the positive molding surface (only on one of the upper and lower molds) Even if 21a or 22a) does not exist, the secondary molding surface (22b for 21a, 21b for 22a) facing the positive molding surface (21a or 22a) is restricted to a positional relationship that matches the molding analysis result. Analyzes are made as possible fitting standards (surfaces) with guaranteed accuracy in a one-to-one relationship with the positive standard (surface). As an example of means for assuring the accuracy of the fitting reference surface, machining is performed as a fitting reference surface associated with the molding positive reference one-to-one after the fitting reference block is assembled.
嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、正と従の両成形面間の加圧力分布を測定する手段としても用いる。嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、ボルトによる取付け部(10c)と測定部(10b)とで構成し、測定部(10b)の側面に歪ゲージ(11)を取付ける。嵌合基準ブロック(10)の上面(10a)は平面とし、その上面(10a)と測定部(10b)の側面は垂直を成す。かつ、測定部(10b)における、嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)と平行な断面の面積精度を保証する。歪ゲージ(11)は、その面積保証された測定部(10b)の側面に、嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)と垂直方向の縦歪を測定するよう取付ける。嵌合基準ブロック(10)の金型内への取付けは、その上面(10a)が、常に加圧力を垂直に受けるように、取付け部(10c)をボルト固定する。例えば、加圧力が鉛直であれば、嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)を水平とし、例えば、加圧力が水平であれば、嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)を鉛直とする等、常に、加圧力の方向が嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)と垂直を成すように取付ける。成形面の可動方向は加圧力の方向と一致し、その可動は横ずれに対しガイド構造にて規制されているから、嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、嵌合基準ブロック上面(10a)に対して加圧力の方向である垂直方向の位置関係を規制するのみで良い。 The fitting reference block (10) is also used as a means for measuring the pressure distribution between the positive and secondary molding surfaces. The fitting reference block (10) includes a mounting portion (10c) using a bolt and a measuring portion (10b), and a strain gauge (11) is attached to the side surface of the measuring portion (10b). The upper surface (10a) of the fitting reference block (10) is a flat surface, and the upper surface (10a) and the side surface of the measurement unit (10b) are perpendicular to each other. And the area accuracy of a cross section parallel to the fitting reference block upper surface (10a) in a measurement part (10b) is ensured. The strain gauge (11) is attached to the side surface of the measurement portion (10b) whose area is guaranteed so as to measure the vertical strain in the direction perpendicular to the upper surface of the fitting reference block (10a). When the fitting reference block (10) is mounted in the mold, the mounting portion (10c) is bolted so that the upper surface (10a) always receives the applied pressure vertically. For example, if the applied pressure is vertical, the fitting reference block upper surface (10a) is horizontal, and if the applied pressure is horizontal, for example, the fitting reference block upper surface (10a) is always vertical, etc. The mounting direction is perpendicular to the upper surface (10a) of the fitting reference block. Since the movable direction of the molding surface coincides with the direction of the applied pressure, and its movement is restricted by the guide structure against lateral displacement, the fitting reference block (10) is located on the fitting reference block upper surface (10a). It is only necessary to regulate the positional relationship in the vertical direction, which is the direction of the applied pressure.
歪ゲージ(11)の出力信号εは無次元のため、物理量である力[N]へ変換し、成形解析結果と比較する。嵌合基準ブロックの測定部(10b)の弾性係数[Pa]と水平断面積[m2]とを乗ずるか、もしくは嵌合基準ブロック(10)をロードセルとして校正し、物理量である力[N]として扱う。嵌合基準ブロックの材質については、耐荷重性と弾性係数の均一性を除いて制約は無く、仮に一般鋼で製作する場合、鋼材の弾性係数は約206GPa(軟鋼で201〜206GPa)であるから、嵌合基準ブロックの水平断面積の製作精度を管理すれば、ロードセル用の校正を行わなくとも、5%以内の精度で加圧力を測定可能である。Since the output signal ε of the strain gauge (11) is dimensionless, it is converted to a force [N], which is a physical quantity, and compared with the molding analysis result. Multiplying the elastic modulus [Pa] and horizontal cross-sectional area [m 2 ] of the measurement part (10b) of the fitting reference block, or calibrating the fitting reference block (10) as a load cell, and the force [N] which is a physical quantity Treat as. There is no restriction on the material of the fitting reference block except for the load resistance and the uniformity of the elastic coefficient, and if manufactured with general steel, the elastic coefficient of the steel is about 206 GPa (201 to 206 GPa for mild steel). If the manufacturing accuracy of the horizontal sectional area of the fitting reference block is managed, the applied pressure can be measured with an accuracy of 5% or less without performing calibration for the load cell.
嵌合基準ブロック(10)に対応するプレス機械の制御装置は、歪ゲージ(11)信号を加圧力へ変換し、成形解析結果の加圧力分布と比較する機能を有する。詳しくは、嵌合基準ブロック(10)へ付与した管理番号と、当該管理番号毎に、弾性係数と水平断面積の積、もしくはロードセルとしての校正係数を、歪ゲージ信号を加圧力へ変換する変換係数として、金型毎に生産要件として記憶する機能を有す。かつ、当該管理番号毎に、当該変換係数と対応する歪ゲージ信号(11)を用いて加圧力へ変換する図1の演算機能(12)も有す。当該管理番号毎に、実際に嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力と、当該嵌合基準ブロック(10)に対する加圧力の成形解析結果とを比較し、嵌合押切り時の加圧力分布を検知、判定する。従って、当発明の嵌合基準ブロック(10)を成形の実態を検知する手段とし、後述の多点ダイハイト装置や多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を、プレス機械と金型の成形影響因子を排除もしくは影響を極小化する手段として用い、嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させる。 The control device of the press machine corresponding to the fitting reference block (10) has a function of converting the strain gauge (11) signal into the applied pressure and comparing it with the applied pressure distribution of the forming analysis result. Specifically, the control number assigned to the fitting reference block (10), and the conversion of the product of the elastic coefficient and the horizontal cross-sectional area or the calibration coefficient as a load cell for each management number, to convert the strain gauge signal into the applied pressure As a coefficient, each die has a function of storing it as a production requirement. In addition, for each management number, the calculation function (12) shown in FIG. 1 for converting into a pressurizing force using the strain gauge signal (11) corresponding to the conversion coefficient is also provided. For each control number, the pressure actually obtained from the fitting reference block (10) is compared with the molding analysis result of the pressure applied to the fitting reference block (10), and the pressure applied at the time of fitting push-off Detect and judge the distribution. Therefore, the fitting reference block (10) of the present invention is used as a means for detecting the actual condition of molding, and a multi-point die height device and a multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device, which will be described later, are excluded from molding influencing factors of the press machine and the mold. Alternatively, it is used as a means for minimizing the influence, and the fitted and cut-off state is matched with the molding analysis result.
仮に、上下成形面間の嵌合押切り状態が成形解析結果と一致した状態下でも、意図した成形結果が得られない場合は、成形解析もしくは構造解析もしくはその双方の解析技術の性能の問題であるから、嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力の分布と実際の成形結果の双方を、解析技術に帰還する。前述の「成形結果品と金型の成形部形状を測定比較する方法」は、プレス機械と金型の精度差等の影響を含み、かつ差異の定量的な要因分析にも至っていない。対して、当発明で得られるデータは、プレス機械の精度差等の影響を排除した解析技術だけの要因に絞り込んだ良質のデータである。また、仮に上下成形面間の嵌合押切り状態が成形解析結果と一致せず、部分的に、加圧実測値が設計加圧力の許容下限値に満たない場合は、金型の加工もしくは組付け時の製作上の不良、もしくはその加圧不足部の近傍の剛性不足であり、仮に、加圧実測値が設計加圧力の許容上限値を超える場合は、金型の加工もしくは組付け時の製作上の不良、もしくはその加圧不足部の近傍以外の剛性不足である。仮に剛性不足の場合は、嵌合基準ブロックから得られる加圧力分布の実測値を構造解析に帰還する。以上、本発明の帰還データは、解析技術の要因に限定した良質のものであり、かつ「応力−歪」と比較可能な「力」の数値データであるため、解析技術の向上にも寄与する。 If the intended molding results cannot be obtained even when the upper and lower molding surfaces are in the same state as the molding analysis results, it may be due to performance problems in the molding analysis and / or structural analysis techniques. Therefore, both the pressure distribution obtained from the fitting reference block (10) and the actual molding result are fed back to the analysis technique. The above-mentioned “method for measuring and comparing the molding result product and the shape of the molded part of the mold” includes the influence of accuracy difference between the press machine and the mold, and has not led to quantitative factor analysis of the difference. On the other hand, the data obtained by the present invention is high-quality data narrowed down to the factor of only the analysis technique that eliminates the influence of the accuracy difference of the press machine. If the press-fit state between the upper and lower molding surfaces does not match the molding analysis result, and the measured pressure value partially does not meet the allowable lower limit value of the design pressure, the mold is processed or assembled. If there is a manufacturing defect at the time of mounting, or insufficient rigidity in the vicinity of the under-pressurized part, and if the actual measured pressure value exceeds the allowable upper limit value of the design pressure, if the mold is processed or assembled, It is a manufacturing defect or a rigidity other than the vicinity of the insufficiently pressurized portion. If the rigidity is insufficient, the measured value of the pressure distribution obtained from the fitting reference block is fed back to the structural analysis. As described above, the feedback data of the present invention is high-quality data limited to the factors of the analysis technique, and is numerical data of “force” that can be compared with “stress-strain”, and thus contributes to improvement of the analysis technique. .
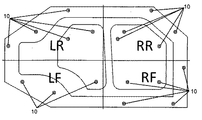
嵌合基準ブロック(10)を用いる形態を、図3の嵌合基準ブロックの配置例を用いて説明する。なお、図3の中のLF、RF、LR、RRの記号は、以降の図4と図5も含め、4ポイントのプレス機械において、プレス機械の機械中心で前後左右に4分割し、各ポイントすなわち加圧点に対応する区画をプレス機械の呼び名称に合せ、LF=左前、RF=右前、LR=左後、RR=右後と示す。嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、後述の多点ダイハイト調整装置や多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いて、プレス機械と金型の成形に影響する因子を排除もしくは影響を極小化するための指標でもあるため、LF、RF、LR、RRの各加圧ポイントにおける区画の調整指標となるよう全区画に配置する。かつ、正と従の両成形面間の位置関係が、嵌合押切り時に安定を保つよう、バランス良く配置する。取付け位置に関しては、成形面を有する金型の構造体が、構造解析にて成形に影響しない十分な剛性を有することを前提にすれば、嵌合基準ブロック(10)を被成形物と干渉する成形面内に配置する必要は無く、被成形物と干渉しない成形面の近傍に配置する。むしろ、被成形物の厚みのばらつきの影響を受けないよう、被成形物と干渉しない成形面の近傍が望ましい。ただし、クッションパッドやプレッサーパッド等のスプリング機能による押圧構造部で、かつ被成形物の流動に影響しない場合は、この限りでない。なお、特に重点管理が必要な成形部位の近傍に数多く嵌合基準ブロック(10)を配置し、また嵌合基準ブロック(10)をロードセルと同様に校正して用いれば、成形管理の精度向上も可能である。 The form using a fitting reference | standard block (10) is demonstrated using the example of arrangement | positioning of the fitting reference | standard block of FIG. In addition, the symbols LF, RF, LR, and RR in FIG. 3 are divided into four parts in the four-point press machine including the subsequent FIG. 4 and FIG. That is, the section corresponding to the pressurizing point is matched to the name of the press machine, and LF = front left, RF = front right, LR = back left, and RR = back right. The fitting reference block (10) uses a multi-point die height adjusting device and a multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device, which will be described later, to eliminate factors that affect the molding of the press machine and the mold or minimize the influence. Since it is also an index, it is arranged in all the sections so as to be an adjustment index of the sections at the pressurization points of LF, RF, LR, and RR. And it arrange | positions with sufficient balance so that the positional relationship between both the positive and sub molding surfaces may maintain stability at the time of fitting and cutting. Assuming that the mold structure having the molding surface has sufficient rigidity that does not affect the molding in the structural analysis, the fitting reference block (10) interferes with the workpiece. It is not necessary to arrange in the molding surface, and it is arranged in the vicinity of the molding surface that does not interfere with the workpiece. Rather, the vicinity of the molding surface that does not interfere with the molding object is desirable so as not to be affected by variations in the thickness of the molding object. However, this is not the case when the pressing structure is a spring function such as a cushion pad or a presser pad and does not affect the flow of the molding. In addition, if many fitting reference blocks (10) are arranged in the vicinity of a molding part that particularly requires priority management, and the fitting reference block (10) is calibrated and used in the same manner as the load cell, the accuracy of molding management can be improved. Is possible.
嵌合基準ブロックを(10)を用いるに当たり、全ての嵌合基準ブロック(10)に対し管理番号を付与し、プレス機械の制御装置は、当該管理番号と、当該管理番号毎に、成形解析もしくは実測にて得た、被成形物を成形する負荷時における成形余裕加圧力上限値および下限値と、それら成形余裕加圧力上下限値の中央範囲の加圧力中央上限値および下限値と、さらには、無負荷時の嵌合押切り状態の許容範囲の無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値を、金型毎に生産要件としてプレス機械の制御装置に記憶保管する機能を有す。なお、これらの値は、上下型の嵌合時の加圧分布もしくは実際の成形結果において、成形解析結果と一致しない場合は、嵌合基準ブロックから得られる実際の加圧分布を成形解析もしくは構造解析に帰還し、解析技術の性能の向上を図ると共に、再計算し常に最新に保つ。 In using the fitting reference block (10), a management number is assigned to all the fitting reference blocks (10), and the control device of the press machine performs molding analysis or The molding upper and lower limits of the molding allowance pressure at the time of molding the molded article obtained by actual measurement, the median upper and lower limits of the pressing margin in the middle range of the molding margin pressing force upper and lower limits, and In addition, it has a function of storing and storing the no-load pressurization upper limit value and lower limit value of the allowable range of the fitting push-off state at no load as a production requirement for each die in the control device of the press machine. If these values do not agree with the molding analysis results in the pressure distribution at the time of fitting the upper and lower molds or the actual molding results, the actual pressure distribution obtained from the mating reference block is determined from the molding analysis or structure. Return to analysis, improve the performance of analysis technology, and recalculate to keep it up to date.
歪ゲージを成形面に取付けて歪を測定する方法(特許文献1)が発明されている。しかし、歪は無次元で物理量を持たないため、自身の経過変化のような相対比較としては有効であるが、成形部全体をロードセルと同等の校正を行わない限り、物理量への変換が困難である。物理量として取扱えなければ、他部位との相対比較も被成形物の「応力−歪」特性との関連付け、すなわち成形解析結果との比較が出来ない。また、同発明は、上下型の成形面間の位置関係を規制する構造を有しないため、被成形物の無い無負荷時には測定不能である。負荷時においても、特に歪ゲージを成形部の表面に取付ける場合は、被成形物の板厚のばらつきの影響や、例えば絞り成形における材料流入のような成形中の被成形物の挙動が測定と成形の双方に相互に影響し合い、測定値にも影響する。特に十数[μm]以上の突起、異物は被成形物の外観の品質不良となるため、外板部品用の金型へは適用できない。加えて、歪ゲージは取付け部と密着して一体化する必要があり、成形面の表面処理や歪ゲージの補修が困難である上、内部に取付ける場合は、取付けスペースによる成形面の剛性への影響等の課題が残る。 A method of measuring strain by attaching a strain gauge to a molding surface (Patent Document 1) has been invented. However, since distortion is dimensionless and has no physical quantity, it is effective as a relative comparison such as its own change, but it is difficult to convert it into a physical quantity unless the entire molded part is calibrated in the same way as a load cell. is there. If it cannot be handled as a physical quantity, the relative comparison with other parts cannot be correlated with the “stress-strain” characteristic of the molded product, that is, compared with the molding analysis result. Further, since the present invention does not have a structure that regulates the positional relationship between the molding surfaces of the upper and lower molds, it cannot be measured when there is no object to be molded. Even when a load is applied, especially when a strain gauge is attached to the surface of the molded part, the effects of variations in the plate thickness of the molded object, and the behavior of the molded object during molding, such as material inflow during drawing, are measured. It affects both the molding and the measurement value. In particular, since protrusions and foreign matters having a size of more than a dozen [μm] cause poor quality of the appearance of the molded object, they cannot be applied to a mold for an outer plate part. In addition, the strain gauge needs to be closely integrated with the mounting part, and it is difficult to treat the molding surface and repair the strain gauge. Issues such as impact remain.
前項の発明(特許文献1)に対し、本発明の嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、成形面間の位置関係を成形解析結果と一致させる規制構造体であるため、無負荷時の測定も可能である。また、物理量である力[N]へ換算可能な形状も有す。加えて、嵌合基準ブロック(10)は単体の構造物として金型へのボルト組付けを前提とし、金型の表面処理や補修、歪ゲージの補修やロードセルとしての校正も容易である。 Compared to the invention of the previous paragraph (Patent Document 1), the fitting reference block (10) of the present invention is a restricting structure that matches the positional relationship between the molding surfaces with the molding analysis result, so that measurement at no load is also possible. It is. Moreover, it has a shape that can be converted into a force [N] that is a physical quantity. In addition, the fitting reference block (10) is premised on assembling bolts to the mold as a single structure, and it is easy to perform surface treatment and repair of the mold, repair of the strain gauge, and calibration as a load cell.
また、嵌合基準ブロックの(10)は、従来の押切りブロックとは、特に思想的に異なる。押切りブロックが、成形調整と共に調整される成形調整の従属結果であるのに対し、嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、成形面間の位置関係を規制する構造体であり、かつ他を調整するための指標でもある。例えば、従来の嵌合状態の調整では、光明丹や被成形物や粘土等を使い、何度もスライドを昇降させ、成形調整と成形確認を繰り返し、その都度、成形調整の一環として押切りブロックも調整する。対して、本発明である嵌合基準ブロック(10)は、嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させる規制構造体を成す正の基準であり、同時に他を調整する指標でもあるから、嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力情報を基に、プレス機械の多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いることで、スライドを下死点へ一度降ろすのみで、嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させることが可能となる。このように、本発明を用いれば、金型の成形調整が効率化できる。特に、実際に生産するプレス機械に於いて、成形解析結果と一致した成形状態を実現できるため、従来のトライプレスを使った成形調整は意味を持たなくなり、廃止も可能である。 Further, the fitting reference block (10) is particularly different in concept from the conventional press-cut block. The press-cut block is a dependent result of the molding adjustment that is adjusted together with the molding adjustment, whereas the fitting reference block (10) is a structure that regulates the positional relationship between the molding surfaces and adjusts the others. It is also an indicator for. For example, in the conventional adjustment of the mating state, the slide block is moved up and down many times by using Komyotan, moldings, clay, etc., and the molding adjustment and the molding confirmation are repeated. Also adjust. On the other hand, the fitting reference block (10) according to the present invention is a positive reference for forming a restricting structure that matches the fitting push-cut state with the molding analysis result, and at the same time is an index for adjusting others. Based on the applied pressure information obtained from the combined reference block (10), the multi-point die height adjusting device and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device of the press machine can be used to lower the slide once to the bottom dead center. It is possible to make the mating cut state coincide with the molding analysis result. Thus, if this invention is used, the shaping | molding adjustment of a metal mold | die can be made efficient. In particular, in a press machine that is actually produced, a molding state that matches the molding analysis result can be realized. Therefore, molding adjustment using a conventional tri-press has no meaning and can be abolished.
図4に多点ダイハイト調整装置、図5に多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の説明図を示す。LF、RF、LR、RRの各区画において、同一区画内の嵌合基準ブロックとダイハイト調整機とオーバーロードプロテクタ装置は同一のグループとして管理する。 FIG. 4 is an explanatory view of a multipoint die height adjusting device, and FIG. 5 is an explanatory view of a multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device. In each of the LF, RF, LR, and RR sections, the fitting reference block, the die height adjuster, and the overload protector device in the same section are managed as the same group.
図4の多点ダイハイト調整装置の説明図を用いて、同装置の構成を説明する。多点ダイハイト調整装置は、ダイハイト調整機(43)に、1対のクラッチ(40a)とブレーキ(40b)を、当該ダイハイト調整機(43)に対として加えたことを特徴とする。ダイハイト調整機(43)は、1対のウォームネジ(43a)とウォームホイールネジ(43b)を主要構成とし、本体はスライド(46)に固定されている。ウォームネジ(43a)は他のダイハイト調整機(43)と駆動モータ(41)とに駆動シャフト(44)で機械的に連結される。本発明では、ウォームネジ(43a)の駆動側、駆動シャフト(44)との間にクラッチ(40a)を設け、かつ当該ウォームネジ(43a)の反駆動側に当該クラッチ(40a)の対となるブレーキ(40b)を設ける。ダイハイトの調整には、調整するダイハイト調整機(43)と対となるクラッチ(40a)を接続し、かつ対となるブレーキ(40b)を開放し、駆動モータ(41)を駆動し、当該ダイハイト調整機(43)のウォームネジ(43a)を介して対となるウォームホイールネジ(43b)を回転させる。当該ウォームホイールネジ(43b)の回転を以て、当該ウォームホイールネジ(43b)が組込まれたプランジャロッド(45)に対する当該ウォームホイールネジ(43b)の位置が調整され、結果、当該ウォームホイールネジ(43b)と機械構造的に一体であるダイハイト調整機(43)と当該ダイハイト調整機(43)が固定されたスライド(46)の位置が調整される。ダイハイトの調整を要しない場合は、ダイハイト調整機(43)の対となるクラッチ(40a)を開放し、かつ対となるブレーキ(40b)を接続することにより、駆動モータ(41)の駆動力が当該ダイハイト調整機(43)のウォームネジ(43a)に伝達されず、かつ、当該ダイハイト調整機(43)は当該ブレーキ(40b)にてその位置が保持され、ダイハイトは調整されない。以上の機構により、スライドの平行度と金型内の加圧力分布を調整し、成形解析結果と一致する嵌合押切り状態を実現する。なお、金型内の偏荷重に対応してプレス機械の出力バランスを変更する場合、もしくはスライドの平行度がプレス機械の許容値を超える場合は、多点ダイハイト調整装置に加え、後述の多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いる必要がある。先ず、多点ダイハイト調整装置について説明し、多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置については後述する。 The configuration of the multi-point die height adjusting device shown in FIG. The multipoint die height adjusting device is characterized in that a pair of clutches (40a) and a brake (40b) are added to the die height adjusting machine (43) as a pair to the die height adjusting machine (43). The die height adjuster (43) mainly includes a pair of worm screws (43a) and a worm wheel screw (43b), and the main body is fixed to the slide (46). The worm screw (43a) is mechanically connected to another die height adjuster (43) and a drive motor (41) by a drive shaft (44). In the present invention, the clutch (40a) is provided between the drive side of the worm screw (43a) and the drive shaft (44), and the clutch (40a) is paired on the non-drive side of the worm screw (43a). A brake (40b) is provided. For adjusting the die height, the die height adjuster (43) to be adjusted is connected to the clutch (40a) as a pair, the brake (40b) as a pair is released, and the drive motor (41) is driven to adjust the die height. A pair of worm wheel screws (43b) are rotated via a worm screw (43a) of the machine (43). The rotation of the worm wheel screw (43b) adjusts the position of the worm wheel screw (43b) with respect to the plunger rod (45) in which the worm wheel screw (43b) is incorporated. As a result, the worm wheel screw (43b) And the position of the slide (46) to which the die height adjusting machine (43) is fixed. When the adjustment of the die height is not required, the driving force of the driving motor (41) can be increased by opening the clutch (40a) as a pair of the die height adjusting machine (43) and connecting the brake (40b) as a pair. It is not transmitted to the worm screw (43a) of the die height adjuster (43), and the position of the die height adjuster (43) is held by the brake (40b), and the die height is not adjusted. With the above mechanism, the parallelism of the slide and the pressure distribution in the mold are adjusted, and a fitting push-off state that matches the molding analysis result is realized. When changing the output balance of the press machine corresponding to the uneven load in the mold, or when the parallelism of the slide exceeds the allowable value of the press machine, in addition to the multi-point die height adjustment device, the multi-point described later It is necessary to use an overload protector hydraulic adjustment device. First, the multipoint die height adjusting device will be described, and the multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device will be described later.
本発明の特徴である、嵌合基準ブロックと多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いる形態を説明する。スライド下死点で上下型を嵌合押切り状態とし、嵌合基準ブロック(10)の加圧力に関して、仮に無負荷の場合は記憶情報である無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値を設定上下限値とし、仮に実負荷の場合は記憶情報である成形解析結果の加圧力中央上限値および下限値を設定上下限値とし、金型内の嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力である実測値と、LF、RF、LR、RRの区画毎に比較し判定する。その結果、仮に実測値が設定下限値に満たない場合は、当該区画のダイハイト調整装置のクラッチ(40a)を接続し、かつ対となるブレーキ(40b)を解放し、調整モータ(41)を駆動して当該区画のダイハイトを下降し、加圧力の実測値が設定上下限内に入るまでオーバーロードプロテクタ(51)の圧縮量を増加し、仮に実測値が設定上限値を超える場合は、当該区画のダイハイト調整装置のクラッチ(40a)を接続し、かつ対となるブレーキ(40b)を解放し、調整モータ(41)を駆動して当該区画のダイハイトを上昇し、加圧力の実測値が設定上下限内に入るまでオーバーロードプロテクタ(51)の圧縮量を軽減し、仮に実測値が設定上下限値内の場合は、当該区画のダイハイト調整装置のクラッチ(40a)を解放し、かつ対となるブレーキ(40b)を接続してダイハイトを調整せず、結果、スライド平行度と金型内の加圧力分布を成形解析結果と一致させる。そして、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布である状態での多点ダイハイト調整装置のダイハイト検出器(42)の実測値を、生産用件として制御装置に記憶保存する。従って、プレス機械の制御装置は、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布である状態でのダイハイト値において、その許容範囲であるダイハイト設定上限値および下限値を、生産用件として記憶する機能を有す。 An embodiment using a fitting reference block and a multipoint die height adjusting device, which is a feature of the present invention, will be described. Set the upper and lower molds at the bottom dead center of the slide, and set the upper and lower limits of the no-load force upper limit and lower limit values that are stored information if there is no load, with regard to the force applied to the fitting reference block (10). Value, and in the case of an actual load, it is the pressure obtained from the fitting reference block (10) in the mold, with the median upper limit value and lower limit value of the molding analysis result that is stored information as the set upper and lower limit values. Judgment is made by comparing the actual measurement value with each of LF, RF, LR, and RR sections. As a result, if the actually measured value is less than the set lower limit value, the clutch (40a) of the die height adjusting device in the section is connected, the paired brake (40b) is released, and the adjusting motor (41) is driven. Then, the die height of the section is lowered and the compression amount of the overload protector (51) is increased until the measured value of the applied pressure falls within the set upper and lower limits. If the measured value exceeds the set upper limit value, The clutch (40a) of the die height adjusting device is connected, the paired brake (40b) is released, the adjusting motor (41) is driven to raise the die height of the section, and the measured value of the applied pressure is set. The amount of compression of the overload protector (51) is reduced until it falls within the lower limit, and if the measured value is within the set upper and lower limit values, the clutch (40a) of the die height adjusting device in the section is released. And without adjusting the die height by connecting a brake (40b) forming a pair, the result causes the pressure distribution of the slide in the parallelism and the mold is consistent with forming analysis results. Then, the actual measurement value of the die height detector (42) of the multipoint die height adjusting device in a state where the applied pressure distribution matches the molding analysis result is stored and saved in the control device as a production requirement. Therefore, the control device of the press machine has a function of storing the die height setting upper limit value and lower limit value, which are allowable ranges, as the production requirements in the die height value in a state where the pressure distribution is consistent with the molding analysis result. The
スライドの平行度の調整方法として、個別モータ方式(特許文献2)や油圧シリンダ方式(特許文献3)が発明されている。一般に、ダイハイト調整量は数十〜数百[mm]、平行度の許容値は1[mm]未満であるが、両発明とも、スライドの平行度調整時以外のダイハイト調整における長距離駆動において、各調整軸間の同期性の保証がなく平行度が不安定となる。加えて、モータや油圧装置等の高額の機器や設置スペースも必要とする。対して、本発明では、通常のダイハイト調整時は、全クラッチ(40a)を接続し、かつ全ブレーキ(40b)を解放し同期運転し、スライドの平行度調整時のみクラッチ(40a)と対となるブレーキ(40b)を操作して平行度調整を行うことが可能である。かつ、複数のモータや油圧装置等の高額の機器を必要としない上、省スペースである。 As a method for adjusting the parallelism of the slide, an individual motor system (Patent Document 2) and a hydraulic cylinder system (Patent Document 3) have been invented. In general, the die height adjustment amount is several tens to several hundreds [mm], and the allowable value of parallelism is less than 1 [mm]. However, in both inventions, long distance driving in die height adjustment other than during slide parallelism adjustment, There is no guarantee of synchronism between the adjustment axes, and the parallelism becomes unstable. In addition, expensive equipment such as motors and hydraulic devices and installation space are also required. On the other hand, in the present invention, during normal die height adjustment, all clutches (40a) are connected, all brakes (40b) are released and synchronized operation is performed, and only when adjusting the parallelism of the slide, the clutch (40a) is paired. It is possible to adjust the parallelism by operating the brake (40b). In addition, it does not require expensive equipment such as a plurality of motors and hydraulic devices, and is space-saving.
図5の多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の説明図を用い、同装置の構成を説明する。なお、同装置の主要構成物であるオーバーロードプロテクタは、油圧ダンパー構造であるため、オーバーロードプロテクタとオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧室は同義である。多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置は、オーバーロードプロテクタ(51)にその対となるオーバーロードプロテクタ遮断装置(50)を加え、当該オーバーロードプロテクタ(51)をその対とするオーバーロードプロテクタ遮断装置(50)を介し、油圧配管で他のオーバーロードプロテクタと接続して構成する。オーバーロードプロテクタ遮断装置(50)は、パイロット操作逆止弁(50a)とパイロット操作弁(50b)を基本構成とする。油圧検出器(52)は、以降に説明するが、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いた生産時における段取り時の調整時の指標として用いる。 The configuration of the multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device shown in FIG. In addition, since the overload protector which is a main component of the apparatus has a hydraulic damper structure, the overload protector and the overload protector hydraulic chamber are synonymous. The multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device includes an overload protector cutoff device (50) as a pair added to the overload protector (51), and the overload protector cutoff device (51) as a pair. 50), and connected to another overload protector by hydraulic piping. The overload protector shut-off device (50) basically includes a pilot operated check valve (50a) and a pilot operated valve (50b). As will be described later, the oil pressure detector (52) is used as an index at the time of setup during production using the multi-point die height adjusting device.
本発明の特徴である、嵌合基準ブロックと多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いる形態を説明する。多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置は、金型内の偏荷重に対応してプレス機械出力バランスを変更する場合、もしくはスライドの平行度がプレス機械の許容を超える場合に、前述の多点ダイハイト調整装置と共に用いる。先ず、オーバーロードプロテクタ(51)に圧縮力が作用する前、例えば上死点で、他の区画から遮断するオーバーロードプロテクタ(51)の対となるパイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能を有効とする。次に、上下型を嵌合押切り状態とし、嵌合基準ブロック(10)の加圧力に関して、仮に無負荷の場合は記憶情報である無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値を設定上下限値とし、仮に実負荷の場合は記憶情報である加圧力中央上限値および下限値を設定上下限値とし、金型内の嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力である実測値と、LF、RF、LR、RRの区画毎に比較し判定する。その結果、仮に実測値が設定下限値に満たない場合は、当該区画のダイハイト調整装置を前項記載の様に操作してダイハイトを下降し、加圧力の実測値が設定範囲内に入るまでオーバーロードプロテクタ(51)の圧縮量を増加し、仮に実測値が設定上限値を超える場合は、当該区画のダイハイト調整装置を前項記載の様に操作してダイハイトを上昇し、加圧力の実測値が設定範囲内に入るまでオーバーロードプロテクタ(51)の圧縮量を軽減し、結果、オーバーロードプロテクタの反力であるプレス機械の出力をポイント毎に調整し、金型内の加圧力分布を成形解析結果と一致させる。そして、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布である状態での多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置における、パイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能の設定状態と油圧検出器(52)の実測値を、生産用件として用いるために、制御装置に記憶保存する。従って、プレス機械の制御装置は、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布である状態での多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の状態において、パイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能の設定状態とオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧の許容範囲である実負荷出力上限値および下限値を、生産用件として記憶する機能を有す。加えて、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布である状態を実現するダイハイトである状態下で、生産段取り用の生産用件として、被成形物の無い無負荷時のオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置の油圧検出器(52)の実測値も制御装置に記憶保存する。従って、プレス機械の制御装置は、成形解析結果と一致する嵌合押切り状態を実現するダイハイトの設定状態下において、無負荷時のオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧の許容範囲である無負荷出力上限値および下限値も、生産用件として記憶する機能を有す。なお、パイロット操作弁(50b)の作動形態として、パイロット操作弁(50b)の励磁状態とパイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能との関係における技術的規定はない。同逆止機能を多用する環境下では、パイロット操作弁(50b)の消磁時にパイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能を有効とし、逆に同逆止機能を多用しない環境下では、当該パイロット操作弁の消磁時に当該パイロット操作逆止弁の逆止機能を無効とすることが合理的であるが、必要条件ではない。 An embodiment using a fitting reference block, a multipoint die height adjusting device, and a multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device, which are features of the present invention, will be described. The multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjuster adjusts the press machine output balance in response to the uneven load in the mold, or the multi-point die height adjustment described above when the slide parallelism exceeds the tolerance of the press machine. Used with the device. First, before the compressive force acts on the overload protector (51), for example, at the top dead center, the check function of the pilot operated check valve (50a) that is a pair of the overload protector (51) that shuts off from other sections. Is valid. Next, when the upper and lower molds are in the fitted push-off state, and the applied pressure of the fitting reference block (10) is assumed to be no load, the no-load applied pressure upper limit value and the lower limit value, which are stored information, are set as upper and lower limit values. In the case of an actual load, the pressurization median upper limit value and lower limit value, which are stored information, are set as upper and lower limit values, an actual measurement value obtained from the fitting reference block (10) in the mold, LF, Comparison is made for each section of RF, LR, and RR. As a result, if the measured value does not reach the set lower limit value, operate the die height adjustment device for the section as described in the previous section to lower the die height, and overload until the measured value of the applied pressure falls within the set range. If the amount of compression of the protector (51) is increased and the actual measured value exceeds the set upper limit value, the die height adjustment device for that section is operated as described in the previous section to raise the die height, and the measured value of the applied pressure is set. The amount of compression of the overload protector (51) is reduced until it falls within the range, and as a result, the output of the press machine, which is the reaction force of the overload protector, is adjusted point by point, and the pressure distribution in the mold is the result of molding analysis. To match. Then, in the multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device in a state where the applied pressure distribution matches the molding analysis result, the setting state of the check function of the pilot operated check valve (50a) and the actual measurement of the hydraulic pressure detector (52). The value is stored and stored in the control device for use as a production requirement. Accordingly, the control device of the press machine sets the check function setting state of the pilot operated check valve (50a) in the state of the multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device in a state where the pressure distribution is consistent with the molding analysis result. And the actual load output upper limit value and lower limit value that are the allowable range of overload protector hydraulic pressure are stored as production requirements. In addition, under the condition of a die height that realizes the pressure distribution that matches the molding analysis results, the overload protector hydraulic adjustment device at the time of no load without molding is used as a production requirement for production setup. The measured value of the hydraulic pressure detector (52) is also stored and saved in the control device. Therefore, the control device of the press machine has the no-load output upper limit value and the lower limit that are the allowable range of the overload protector hydraulic pressure when there is no load under the setting state of the die height that realizes the fitting push-off state that matches the molding analysis result. The value also has a function to memorize as production requirements. In addition, there is no technical regulation regarding the relationship between the excited state of the pilot operated valve (50b) and the check function of the pilot operated check valve (50a) as the operation mode of the pilot operated valve (50b). In an environment where the check function is frequently used, the check function of the pilot operated check valve (50a) is enabled when the pilot operated valve (50b) is demagnetized. Conversely, in an environment where the check function is not frequently used, Although it is reasonable to disable the check function of the pilot operated check valve when the pilot operated valve is demagnetized, it is not a necessary condition.
なお、オーバーロードプロテクタ装置の油圧調整は、類似形態(特許文献4および特許文献5)が発明されている。両発明とも、プレス加圧点の油圧を能動的に調整する方式のため、高額の油圧発生および調整装置を追加もしくは従来に比べ高機能である油圧装置を必要とする。対して、本発明は、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いて受動的に油圧を調整する簡易な方法であり、高額の油圧装置の追加も高機能化も必要としない。 Similar forms (Patent Document 4 and Patent Document 5) have been invented for adjusting the hydraulic pressure of the overload protector device. Both of the inventions require a hydraulic device that actively adjusts the hydraulic pressure at the pressurizing point, adding a high-priced hydraulic pressure generating and adjusting device, or having a higher function than conventional ones. On the other hand, the present invention is a simple method for passively adjusting the hydraulic pressure using a multi-point die height adjusting device, and does not require the addition of a high-priced hydraulic device or the enhancement of functionality.
本発明の特徴である、嵌合基準ブロックと多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いた、生産時における成形確認の形態を説明する。生産時における成形確認の形態には、生産時における嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させる形態と、生産中の品質確認の形態とがある。 The form of forming confirmation at the time of production using the fitting reference block, the multi-point die height adjusting device and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device, which is a feature of the present invention, will be described. Forms for forming confirmation at the time of production include a form for matching the fitting / cut-off state at the time of production with the result of the forming analysis, and a form for quality confirmation during production.
生産時における嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させる形態として、生産段取り時の金型装着時において、嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と一致させ、生産における品質の安定化を実現する。従来の金型装着では、上死点においてスライド全体のダイハイトを調整するのみで、成形解析結果との一致性を確認していない。本発明のプレス機械の制御装置は、成形解析結果と一致する嵌合押切り状態、すなわち成形結果を得られるLF、RF、LR、RRの各区画における、ダイハイト設定上限値および下限値と、多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置のパイロット操作逆止弁(50a)の逆止機能の有効か無効かの設定状態と、無負荷での嵌合押切り時のオーバーロードプロテクタ油圧の無負荷出力圧上限値および下限値と、全ての嵌合基準ブロックの無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値とを、生産要件として記憶保管する機能を有し、かつ、上死点においては、多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いて、LF、RF、LR、RRの各区画のダイハイト調整を行い、かつオーバーロードプロテクタの遮断が必要な区画を遮断し、下死点においては、嵌合基準ブロックと多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置を用いて、成形解析結果と一致する加圧力分布を実現する。 As a form to match the mating press-cut state during production with the molding analysis result, when fitting a mold during production setup, the mating press-cut state is matched with the molding analysis result to achieve stable production quality. . In the conventional mold mounting, only the die height of the entire slide is adjusted at the top dead center, and the consistency with the molding analysis result is not confirmed. The control device for the press machine of the present invention includes a die height setting upper limit value and lower limit value in each of the LF, RF, LR, and RR sections that can obtain a molding result, that is, a fitting and cutting state that matches the molding analysis result, Point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device pilot operation check valve (50a) check function enable / disable setting state and overload protector hydraulic no-load output pressure upper limit at the time of mating push-off without load Value and lower limit value, and the no-load pressure upper limit value and lower limit value of all mating reference blocks are stored and stored as production requirements, and at the top dead center, a multipoint die height adjusting device Use the multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device to adjust the die height of each of the LF, RF, LR, and RR sections, and to block the overload protector. Blocked In the bottom dead center, with a fitting reference block and multi-point die height adjusting device and the multi-point overload protector hydraulic adjustment device, to realize the pressurizing force distribution consistent with forming analysis results.
詳しくは、先ず、金型の装着直前の上死点において、LF、RF、LR、RRの各区画のダイハイトを、区画毎にダイハイト検出器(図4の42)の実測値とダイハイト設定上限値および下限値とを比較し、仮に実測値が設定上限値を超えている場合は、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いて、当該区画のダイハイトを下降し、仮に実測値が設定下限値に満たない場合は、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いて、当該区画のダイハイトを上昇して、全ての区画のダイハイトを設定上下限内に調整する。また、各区画の多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置のパイロット操作逆止弁(図5の50a)の逆止機能の有効か無効かを生産要件と一致した状態に設定する。 Specifically, first, at the top dead center just before the mold is mounted, the die heights of the LF, RF, LR, and RR sections are measured for each section, and the measured values of the die height detector (42 in FIG. 4) and the die height setting upper limit value. If the measured value exceeds the set upper limit value, the die height of the section is lowered using the multi-point die height adjustment device, and the measured value does not reach the set lower limit value. Uses a multi-point die height adjusting device to raise the die height of the section and adjust the die heights of all sections within the upper and lower limits. In addition, whether the check function of the pilot check valve (50a in FIG. 5) of the multi-point overload protector hydraulic regulator of each section is valid or invalid is set to a state that matches the production requirements.
次に、スライドを下死点へ降ろし、嵌合押切り状態とし、LF、RF、LR、RRの各区画のオーバーロードプロテクタにおいて、記憶情報である無負荷出力圧上限値と下限値を設定上下限値とし、オーバーロードプロテクタの油圧検出器(図5の52)の実測値と比較し、仮に実測値が設定上限値を超えている場合は、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いて、実測値が無負荷出力圧上下限値内に入るまで当該ダイハイトを上昇し、仮に実測値が設定下限値に満たない場合は、多点ダイハイト調整装置を用いて、実測値が無負荷上下限値内に入るまで当該ダイハイトを下降する。さらに、この状態で、記憶情報である生産用件の各嵌合基準ブロックの無負荷加圧力上限値および下限値を設定上下限値とし、嵌合基準ブロック(10)から得られる加圧力である実測値と、嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号毎に比較し、仮に実測値が設定上限値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号とダイハイト過剰下降警報を出力し、仮に実測値が設定下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号とダイハイト下降不足警報を出力し、仮に実測値が設定上下限内の場合は、段取り時の装着正常信号を出力する。 Next, the slide is lowered to the bottom dead center to be in the fitted push-off state, and the no-load output pressure upper limit value and lower limit value, which are stored information, are set in the overload protector in each of the LF, RF, LR, and RR sections. Compared with the actual value of the overload protector's oil pressure detector (52 in FIG. 5), if the actual value exceeds the set upper limit value, use the multi-point die height adjustment device to The die height is increased until it falls within the no-load output pressure upper / lower limit value. If the measured value is less than the set lower limit value, the measured value falls within the no-load upper / lower limit value using a multipoint die height adjustment device. Lower the die height until Further, in this state, the no-load applied pressure upper limit value and the lower limit value of each fitting reference block of the production requirements that are stored information are set as upper and lower limit values, and the pressure is obtained from the fitting reference block (10). Compare the actual measurement value with each management number of the mating reference block.If the actual measurement value exceeds the set upper limit value, the management number of the mating reference block and the die height excessive descent warning are output. When the set lower limit value is not reached, a management number of the fitting reference block and a die height descent deficiency warning are output. If the measured value is within the set upper and lower limits, a normal mounting signal at the time of setup is output.
生産時における成形確認の形態のうち、生産中の品質確認の形態を説明する。生産時の品質検査において、嵌合押切り状態を成形解析結果と比較し、自動での品質検査を実現する。本発明のプレス機械の制御装置は、全ての嵌合基準ブロック(10)に対し、被成形物を成形する際の成形余裕加圧力上限値および下限値と、それら成形余裕加圧力上下限値の中央範囲の加圧力中央上限値および下限値を、生産要件として金型毎に記憶保管する機能を有し、かつ、それら生産要件と嵌合基準ブロック(10)より得られる加圧力である実測値とを比較し、生産時の成形品質を自動で検査する。 Of the form confirmation forms during production, the form of quality confirmation during production will be described. In the quality inspection at the time of production, the mating press-cut state is compared with the molding analysis result, and automatic quality inspection is realized. The control device for a press machine according to the present invention includes a molding margin pressure upper limit value and a lower limit value, and upper and lower limits of molding margin pressure when molding a molding, for all fitting reference blocks (10). Measured value that has the function of storing and storing the median upper limit value and lower limit value of the central range for each mold as production requirements, and is the pressure obtained from these production requirements and the fitting reference block (10) And automatically inspecting the molding quality during production.
詳しくは、プレス機械の生産稼働中において、全ての嵌合基準ブロック(10)より得られる加圧力である実測値と、記憶情報である生産要件の成形余裕加圧力上下限値を、嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号毎に比較し、仮に実測値が成形余裕加圧力上限値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と過剰加圧警報を出力し、仮に実測値が成形余裕加圧力下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と加圧不足警報を出力し、仮に成形余裕加圧力上下限値内であれば、さらに、記憶情報である生産要件の成形余裕加圧力上下限値の中央範囲の加圧力中央上下限値とも比較する。比較の結果、仮に加圧力中央上下限内であれば成形状態を良好と判定出力し、仮に加圧力中央上限値を超えた場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と過剰加圧注意報を出力し、仮に加圧力中央下限値に満たない場合は、当該嵌合基準ブロックの管理番号と加圧不足注意報を出力する。 Specifically, during the production operation of the press machine, the actual value that is the applied pressure obtained from all the fitting reference blocks (10) and the upper and lower limits of the molding allowance pressing force of the production requirements that are stored information are the fitting criteria. Compared to each block control number, if the measured value exceeds the upper limit of the molding allowance pressure, the control number of the fitting reference block and an over-pressurization alarm are output, and the measured value is assumed to be the molding margin pressure If the lower limit value is not reached, the control number of the fitting reference block and the insufficient pressurization alarm are output. Also compare with the median upper / lower limit value of the pressure in the middle range of the upper / lower pressure value. As a result of comparison, if it is within the upper and lower limits of the pressurizing force, the molding state is judged to be good, and if the upper limit of the pressurizing force is exceeded, the control number of the fitting reference block and the overpressurization warning are displayed. If it is less than the pressurization median lower limit value, the management number of the fitting reference block and the insufficient pressurization warning are output.
嵌合基準ブロックは、金型を用いたプレス成形一般に適用できる。 The fitting reference block can be applied to general press molding using a mold.
多点ダイハイト調整装置と多点オーバーロードプロテクタ油圧調整装置は、2ポイント以上のプレス機械に適用できる。 The multipoint die height adjusting device and the multipoint overload protector hydraulic pressure adjusting device can be applied to a press machine having two or more points.
10 嵌合基準ブロック
10a 嵌合基準ブロック上面(上型接触面)
10b 嵌合基準ブロック測定部
10c 嵌合基準ブロック取付け部
11 歪ゲージ
12 歪ゲージ信号から加圧力への変換器(機能)
21 上型(成形面を有するブロック)
21a 上型の正の成形面(正の基準)
21b 上型の従の成形面
22 下型(成形面を有するブロック)
22a 下型の正の成形面(正の基準)
22b 下型の従の成形面
23 被成形物
40a クラッチ
40b ブレーキ
41 モータ
42 ダイハイト検出器
43 ダイハイト調整装置
43a ウォームネジ
43b ウォームホイールネジ
44 駆動シャフト
45 プランジャロッド(ネジ部)
46 スライド
50 オーバーロードプロテクタ遮断装置
50a パイロット操作逆止弁
50b パイロット操作弁
51 オーバーロードプロテクタ(油圧室)
52 油圧検出器10
10b Fitting reference block measuring section 10c Fitting reference
21 Upper mold (block with molding surface)
21a Positive molding surface of upper mold (positive reference)
21b Secondary molding surface of upper mold 22 Lower mold (block having molding surface)
22a Positive molding surface of lower mold (positive reference)
22b Secondary mold
46
52 Oil pressure detector
Claims (6)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016099096A JP6710406B2 (en) | 2016-04-25 | 2016-04-25 | Press mold, press machine, and mold confirmation method |
| JP2020058952A JP6932882B2 (en) | 2016-04-25 | 2020-02-28 | Multi-point overload protector hydraulic regulator for press machines |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016099096A JP6710406B2 (en) | 2016-04-25 | 2016-04-25 | Press mold, press machine, and mold confirmation method |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020058952A Division JP6932882B2 (en) | 2016-04-25 | 2020-02-28 | Multi-point overload protector hydraulic regulator for press machines |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017196659A true JP2017196659A (en) | 2017-11-02 |
| JP6710406B2 JP6710406B2 (en) | 2020-06-17 |
Family
ID=60237073
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016099096A Active JP6710406B2 (en) | 2016-04-25 | 2016-04-25 | Press mold, press machine, and mold confirmation method |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6710406B2 (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113118397A (en) * | 2021-03-15 | 2021-07-16 | 上海二十冶建设有限公司 | Integral base of vertical continuous casting machine light pressure module and adjusting method thereof |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01139933U (en) * | 1988-03-15 | 1989-09-25 | ||
| JPH01172499U (en) * | 1988-02-19 | 1989-12-06 | ||
| JP2005131671A (en) * | 2003-10-30 | 2005-05-26 | Komatsu Ltd | Die height adjusting device of press machine |
-
2016
- 2016-04-25 JP JP2016099096A patent/JP6710406B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01172499U (en) * | 1988-02-19 | 1989-12-06 | ||
| JPH01139933U (en) * | 1988-03-15 | 1989-09-25 | ||
| JP2005131671A (en) * | 2003-10-30 | 2005-05-26 | Komatsu Ltd | Die height adjusting device of press machine |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113118397A (en) * | 2021-03-15 | 2021-07-16 | 上海二十冶建设有限公司 | Integral base of vertical continuous casting machine light pressure module and adjusting method thereof |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6710406B2 (en) | 2020-06-17 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US4918956A (en) | Monitorable and compensatable feedback tool and control system for a press using a solid tool backup element | |
| KR0180523B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for optimizing press operating condition based operating environment and/or physical condition of blank | |
| US4939918A (en) | Monitorable and compensatable feedback tool and control system for a press | |
| US4945742A (en) | Monitorable and compensatable feedback tool and control system for a press | |
| CN111822580B (en) | Method for operating a fine blanking system | |
| CN110753590A (en) | Method for operating a forming press | |
| CN104014628A (en) | Numerical control telescopic cushion with error compensation function | |
| JP6710406B2 (en) | Press mold, press machine, and mold confirmation method | |
| KR101791401B1 (en) | Method for operating electric stamping machine | |
| JPH01127118A (en) | Drawing press for sheet metal part | |
| JP6932882B2 (en) | Multi-point overload protector hydraulic regulator for press machines | |
| KR19990035990A (en) | Blank-holder force-adjustment system in press | |
| EP1555116B1 (en) | Press forming method | |
| CN109482740A (en) | A kind of material tooling template flexible forming mold and manufacturing process again | |
| US7165490B2 (en) | Press forming method | |
| JP5267842B2 (en) | Press machine and adjustment method | |
| KR101919922B1 (en) | Intelligent Numerical Control Hydraulic Metal Powder Press and Control Method Thereof | |
| KR20150028012A (en) | Cushion pin device for press | |
| JP2007326135A (en) | Press die apparatus | |
| JP2921342B2 (en) | Adjustment method of slide height of press machine | |
| KR20180067010A (en) | Method for forming various curve on the plate | |
| US20190084026A1 (en) | Press molding method and press molding apparatus | |
| CN118847792A (en) | High-precision accurate stamping forming device and method | |
| CN211101108U (en) | High-precision stamping die | |
| JP2013086165A (en) | Press forming apparatus |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A711 Effective date: 20181225 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20190228 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20200123 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200204 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200228 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20200421 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20200428 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6710406 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |