JP2014051222A - Control unit of hybrid vehicle - Google Patents
Control unit of hybrid vehicle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2014051222A JP2014051222A JP2012197741A JP2012197741A JP2014051222A JP 2014051222 A JP2014051222 A JP 2014051222A JP 2012197741 A JP2012197741 A JP 2012197741A JP 2012197741 A JP2012197741 A JP 2012197741A JP 2014051222 A JP2014051222 A JP 2014051222A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- parking
- vehicle
- gear
- electric motor
- engine
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/72—Electric energy management in electromobility
Landscapes
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
- Electric Propulsion And Braking For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、ハイブリッド車両の制御装置に係り、特に、登坂路においてパーキング操作した際に発生するショックの低減に関するものである。 The present invention relates to a control device for a hybrid vehicle, and more particularly to reduction of shock that occurs when a parking operation is performed on an uphill road.
電動機に連結された第1回転要素、エンジンに連結された第2回転要素、および駆動輪に連結された第3回転要素から成る差動機構を備え、パーキングレンジにシフト操作した際には前記第3回転要素に機械的に連結されているパーキングギヤに所定の噛合歯を噛み合わせることで車両を停止させるハイブリッド車両がよく知られている。特許文献1に記載のハイブリッド駆動装置もその一例である。特許文献1のハイブリッド駆動装置では、パーキングロックギヤ70よびパーキングロックポール74を含んで構成されるメカニカルパーキングロック機構68が設けられており、パーキングレンジにシフト操作された場合には、ケーブルやリンク機構等を介してパーキングロックポール74の噛合歯がパーキングギヤ70と噛み合わされることで、第3回転要素に対応するリングギヤ20rおよび駆動輪76が回転停止させられるようになっている。
A differential mechanism comprising a first rotating element connected to the electric motor, a second rotating element connected to the engine, and a third rotating element connected to the drive wheel; A hybrid vehicle is well known in which a vehicle is stopped by meshing predetermined meshing teeth with a parking gear mechanically coupled to a three-rotation element. The hybrid drive device described in Patent Document 1 is an example. In the hybrid drive device of Patent Document 1, a mechanical
ところで、特許文献1のハイブリッド駆動装置において、登坂路でフットブレーキを作動させることで車両を停止し、エンジンを運転させて電動機によるバッテリ充電制御(充電制御)を行っている状態で、運転者がパーキングレンジへのシフト操作を行うことがある。このとき、パーキングギヤ70の回転位置によっては、パーキングギヤ70とパーキングロックポール74とが噛み合わないことがある。具体的には、パーキングレンジにシフト操作されても、パーキングギヤ70の歯先の面とパーキングロックポール74に形成される噛合歯の歯先の面とが接触してしまい、互いの歯車が正常に噛み合わない状態に相当する。この状態で、運転者がブレーキペダルの踏み込みを解除すると、パーキングギヤ70とパーキングロックポール74の噛合歯とが噛み合うまで車両がずり下がり、パーキングギヤ70とパーキングロックポール74とが噛み合った際に車両加速度に比例した大きさのショックが発生する。また、パーキングギヤ70とパーキングロックポール74とが噛み合った際にパーキングロック機構68に車両慣性が入力されるので、パーキングロック機構68の耐久性が低下する可能性も生じる。
By the way, in the hybrid drive device of Patent Document 1, the vehicle is stopped by operating a foot brake on an uphill road, the engine is operated, and the driver performs battery charge control (charge control) using an electric motor. Shifting to the parking range may be performed. At this time, depending on the rotational position of the
これに対して、特許文献1のようなハイブリッド駆動装置にあっては、電動機による充電制御が実行されている間は、出力回転部材である第3回転要素から正転方向に作用するエンジンの直達トルクが出力されているので、ずり下がりが発生したときに直達トルクが駆動輪に伝達され、車両がずり下がったときの車両加速度が低下してショックが低減される。また、これに関連して、パーキングギヤ70とパーキングロックポール74とが噛み合ったときに入力される車両慣性(慣性力)も低減されるので、パーキングロック機構68の耐久性が低下することも抑制される。
On the other hand, in the hybrid drive device as disclosed in Patent Document 1, while the charging control by the electric motor is being executed, the engine directly acting in the normal rotation direction from the third rotating element that is the output rotating member. Since the torque is output, the direct torque is transmitted to the drive wheels when the slippage occurs, and the vehicle acceleration when the vehicle slips decreases and the shock is reduced. In this connection, since the vehicle inertia (inertial force) input when the
ところが、パーキングレンジにシフト操作されて車両がずり下がる際に、バッテリの充電容量が上限値を超えていると電動機による充電制御が実行できない。すなわち、前記直達トルクを発生させることができない。従って、車両のずり下がりを直達トルクによって受けることができなくなってショックが大きくなる可能性があった。また、車両慣性も低減されないので、パーキングロック機構68の耐久性についても低下する可能性があった。
However, when the vehicle is shifted to the parking range and the vehicle is lowered, if the charge capacity of the battery exceeds the upper limit value, the charge control by the electric motor cannot be executed. That is, the direct torque cannot be generated. Therefore, there is a possibility that the vehicle will not be able to receive the sliding down due to the direct torque and the shock will increase. Further, since the vehicle inertia is not reduced, there is a possibility that the durability of the
本発明は、以上の事情を背景として為されたものであり、その目的とするところは、登坂路においてパーキング操作時に発生するショックを確実に低減し、パーキングロック機構の耐久性低下を抑制できるハイブリッド車両の制御装置を提供することにある。 The present invention has been made against the background of the above circumstances, and the object of the present invention is a hybrid capable of reliably reducing shocks generated during parking operation on an uphill road and suppressing deterioration in durability of the parking lock mechanism. It is in providing the control apparatus of a vehicle.
上記目的を達成するための、第1発明の要旨とするところは、(a)電動機に連結された第1回転要素、エンジンに連結された第2回転要素、および駆動輪に動力伝達可能に連結された第3回転要素から成る差動機構と、前記第3回転要素に機械的に連結されているパーキングギヤおよびそのパーキングギヤと噛合可能なパーキングポールを含んで構成されるパーキングロック機構とを、備え、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、前記パーキングギヤと前記パーキングポールとを噛み合わせる信号が出力されるハイブリッド車両の制御装置において、(b)前記エンジンを運転させて前記電動機による充電制御を行っている状態で、車両の車速が予め設定されている所定値以下となると、前記電動機によってバッテリに充電する充電量を、車速がその所定値以下となる前に比べて低減させることを特徴とする。 In order to achieve the above object, the gist of the first invention is that (a) a first rotating element coupled to an electric motor, a second rotating element coupled to an engine, and a drive wheel are coupled to transmit power. A differential mechanism comprising a third rotating element, a parking gear mechanically coupled to the third rotating element, and a parking lock mechanism including a parking pawl that can mesh with the parking gear; In a hybrid vehicle control device that outputs a signal for meshing the parking gear with the parking pole when the shift position is switched to parking, (b) performing charge control by the electric motor by operating the engine. When the vehicle speed of the vehicle is equal to or lower than a predetermined value, the amount of charge charged to the battery by the electric motor, Fast it is characterized by reduced than before to be the predetermined value or less.
このようにすれば、登坂路での停車において車両をずり下げる方向に作用するトルクをエンジンの直達トルクによって受けることで、車両のずり下がりが緩やかになってパーキングロック機構のパーキングギヤとパーキングポールとが噛み合う際のショックが低減される。また、車両のずり下がりが緩やかになるので、パーキングロック機構の耐久性低下も抑制される。ここで、車両がずり下がる際にバッテリの充電容量が上限値を超えていると、電動機による充電制御ができない為に前記直達トルクを発生できず、車両のずり下がりをエンジンの直達トルクで受けることが困難となる。そこで、車両の車速が所定値以下となると、登坂路での停車に備えて予め電動機によってバッテリに充電される充電量を低減させておくことで、バッテリの充電可能な容量に余裕を持たせ、車両がずり下がる際に電動機による充電制御を確実に実施して直達トルクを発生させることができる。これより、車両がずり下がる際に発生するショックを確実に低減し、パーキングロック機構の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。 In this way, when the vehicle stops on the uphill road, the torque acting in the direction of sliding down the vehicle is received by the direct torque of the engine, so that the vehicle slips down gradually, and the parking gear and the parking pole of the parking lock mechanism The shock at the time of meshing is reduced. Further, since the vehicle slides down gradually, the durability of the parking lock mechanism is prevented from being lowered. Here, if the charge capacity of the battery exceeds the upper limit when the vehicle slides down, the direct torque can not be generated because the charge control by the electric motor cannot be performed, and the vehicle slip is received by the engine direct torque. It becomes difficult. Therefore, when the vehicle speed of the vehicle becomes a predetermined value or less, in preparation for stopping on the uphill road, by reducing the amount of charge charged to the battery by the electric motor in advance, the battery has a chargeable capacity, When the vehicle slides down, charging control by the electric motor can be reliably performed to generate direct torque. As a result, it is possible to reliably reduce a shock that occurs when the vehicle slides down and to suppress a decrease in durability of the parking lock mechanism.
また、好適には、上記目的を達成するための第2発明の要旨とするところは、(a)電動機に連結された第1回転要素、エンジンに連結された第2回転要素、および駆動輪に動力伝達可能に連結された第3回転要素から成る差動機構と、前記第3回転要素に機械的に連結されているパーキングギヤおよびそのパーキングギヤと噛合可能なパーキングポールを含んで構成されるパーキングロック機構とを、備え、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、前記パーキングギヤと前記パーキングポールとを噛み合わせる信号が出力されるハイブリッド車両の制御装置において、(b)前記エンジンを運転させて前記電動機による充電制御を行っている状態でシフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、前記電動機によってバッテリに充電する充電量を、そのシフト位置が切り替えられる前に比べて低減させることを特徴とする。 Preferably, the gist of the second invention for achieving the above object is as follows: (a) a first rotating element connected to an electric motor, a second rotating element connected to an engine, and a drive wheel; A parking mechanism comprising a differential mechanism composed of a third rotating element coupled to transmit power, a parking gear mechanically coupled to the third rotating element, and a parking pole meshable with the parking gear. A control device for a hybrid vehicle that outputs a signal for meshing the parking gear and the parking pawl when the shift position is switched to parking; (b) operating the engine to drive the electric motor When the shift position is switched to parking in a state where the charging control is performed by the charging amount, the amount of charge charged in the battery by the electric motor , Wherein the reduced compared to before the shift position is switched.
このようにすれば、登坂路において車両をずり下げる方向に作用するトルクをエンジンの直達トルクによって受けることで、車両のずり下がりが緩やかになってパーキングロック機構のパーキングギヤとパーキングポールとが噛み合う際のショックが低減される。また、車両のずり下がりが緩やかになるので、パーキングロック機構の耐久性低下も抑制される。ここで、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられて、前記パーキングギヤと前記パーキングポールとを噛み合わせる信号が出力された場合であっても、パーキングギヤとパーキングポールとが正常に噛み合わない状態で停止することがある。この状態でフットブレーキペダルの踏み込みを解除した際には車両がずり下がるが、継続的な充電によって既にバッテリの充電容量が上限値を超えていると電動機による充電制御が実行できずに車両のずり下がりをエンジンの直達トルクで受けることが困難となる。そこで、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、電動機による充電量を低減させることで、バッテリの充電可能な容量に余裕を持たせ、車両がずり下がる際に電動機による充電制御を確実に実施して直達トルクを発生させることができる。これより、車両がずり下がる際に発生するショックを確実に低減し、パーキングロック機構の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。 In this way, when the torque that acts in the direction of lowering the vehicle on the uphill road is received by the direct torque of the engine, the vehicle is gradually lowered, and the parking gear and the parking pole of the parking lock mechanism mesh with each other. Shock is reduced. Further, since the vehicle slides down gradually, the durability of the parking lock mechanism is prevented from being lowered. Here, even when the shift position is switched to parking and a signal for meshing the parking gear and the parking pawl is output, the parking gear and the parking pawl are stopped in a state where they are not meshed normally. There is. When the foot brake pedal is released in this state, the vehicle slides down.However, if the battery charge capacity has already exceeded the upper limit due to continuous charging, charging control by the motor cannot be executed and the vehicle slips. It is difficult to receive the drop with the direct torque of the engine. Therefore, when the shift position is switched to parking, the amount of charge by the motor is reduced, so that the capacity of the battery can be charged, and when the vehicle slides down, the charge control by the motor is surely performed and directly reached. Torque can be generated. As a result, it is possible to reliably reduce a shock that occurs when the vehicle slides down and to suppress a decrease in durability of the parking lock mechanism.
また、好適には、前記第3回転要素には、走行用電動機が動力伝達可能に連結され、車両停止中に前記エンジンを運転させて前記電動機による充電制御を行っている状態では、その充電制御によって前記駆動輪に伝達される直達トルクとは反対方向のトルクが前記走行用電動機から出力される。このようにすれば、エンジンを運転させて電動機による充電制御を行っている状態においてエンジンの直達トルクが発生するが、この直達トルクとは反対の方向のトルクを走行用電動機から出力することで駆動輪のトルクが零に制御される。 Preferably, a traveling motor is connected to the third rotating element so that power can be transmitted, and when the vehicle is stopped and the engine is operated and charging control is performed by the motor, the charging control is performed. Thus, torque in the direction opposite to the direct torque transmitted to the drive wheel is output from the traveling motor. In this way, the direct torque of the engine is generated in the state where the engine is operated and the charging control is performed by the electric motor. The torque is driven by outputting the torque in the direction opposite to the direct torque from the traveling motor. The wheel torque is controlled to zero.
ここで、好適には、前記差動機構はシングルピニオン型の遊星歯車装置で構成され、前記電動機に連結される前記第1回転要素がその遊星歯車装置のサンギヤであり、前記エンジンに連結される前記第2回転要素がその遊星歯車装置のキャリヤであり、駆動輪に動力伝達可能に連結される前記第3回転要素がその遊星歯車装置のリングギヤである。 Here, preferably, the differential mechanism is configured by a single pinion type planetary gear device, and the first rotating element connected to the electric motor is a sun gear of the planetary gear device, and is connected to the engine. The second rotating element is a carrier of the planetary gear device, and the third rotating element connected to the drive wheel so as to be able to transmit power is a ring gear of the planetary gear device.
また、好適には、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、パーキングロック機構のパーキングギヤとパーキングポールとを噛み合わせる信号が出力されてパーキングロック機構が作動するが、このときパーキングギヤの歯先の面とパーキングポールに形成されている噛合歯の歯先の面とが当接した状態で停止し、互いの歯車が正常に噛み合わないことがある。この状態で登坂路において車両停止中にフットブレーキペダルの踏み込みが解除されると、パーキングギヤとパーキングロックポールとが正常に噛み合う分だけ、すなわち最大でパーキングギヤが一歯回転する分だけ車両がずり下がることとなる。 Preferably, when the shift position is switched to parking, a signal for meshing the parking gear and parking pole of the parking lock mechanism is output and the parking lock mechanism is activated. And the surface of the teeth of the meshing teeth formed on the parking pole may stop, and the gears may not mesh properly. If the foot brake pedal is released while the vehicle is stopped on the uphill road in this state, the vehicle will slip by the amount that the parking gear and the parking lock pole normally mesh, that is, the maximum amount of rotation of the parking gear by one tooth. Will be lowered.
また、好適には、ハイブリッド車両に対する搭載姿勢は、駆動装置の軸線が車両の幅方向となるFF(フロントエンジン・フロントドライブ)車両などの横置き型でも、駆動装置の軸線が車両の前後方向となるFR(フロントエンジン・リヤドライブ)車両などの縦置き型でも良い。 Preferably, the mounting posture with respect to the hybrid vehicle is a horizontal type such as an FF (front engine / front drive) vehicle in which the axis of the drive device is in the width direction of the vehicle. It may be a vertical installation type such as an FR (front engine / rear drive) vehicle.
また、好適には、前記エンジンと前記差動機構とは作動的に連結されればよく、例えばエンジンと差動機構との間には、脈動吸収ダンパー(振動減衰装置)、直結クラッチ、ダンパー付直結クラッチ、或いは流体伝動装置などが介在させられるものであってもよいが、エンジンと差動機構とが常時連結されたものであってもよい。また、流体伝動装置としては、ロックアップクラッチ付トルクコンバータやフルードカップリングなどが用いられる。 Preferably, the engine and the differential mechanism may be operatively connected. For example, a pulsation absorbing damper (vibration damping device), a direct coupling clutch, and a damper are provided between the engine and the differential mechanism. A direct coupling clutch or a fluid transmission device may be interposed, but an engine and a differential mechanism may be always connected. As the fluid transmission device, a torque converter with a lock-up clutch, a fluid coupling, or the like is used.
以下、本発明の実施例を図面を参照しつつ詳細に説明する。なお、以下の実施例において図は適宜簡略化或いは変形されており、各部の寸法比および形状等は必ずしも正確に描かれていない。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the following embodiments, the drawings are appropriately simplified or modified, and the dimensional ratios, shapes, and the like of the respective parts are not necessarily drawn accurately.
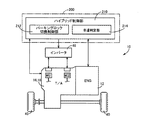
図1は、本発明が適用されるハイブリッド車両10(以下、車両10という)の概略構成を説明する図であると共に、車両10の各部を制御する為に設けられた制御系統の要部を説明するブロック線図である。図1において、車両10は、車体に取り付けられる非回転部材としてのケース34内において、走行用の駆動力源としてのエンジン12と、第1電動機MG1と、エンジン12から出力される動力を第1電動機MG1及び出力歯車14へ分配する動力分配機構16(差動機構)と、出力歯車14に連結される歯車機構18と、出力歯車14に歯車機構18を介して動力伝達可能に連結された第2電動機MG2と、出力歯車14から回転が伝達されるカウンタギヤ対24と、ファイナルギヤ対26と、差動歯車装置(終減速機)28とを、備えて構成されている。このように構成された車両10では、エンジン12の駆動軸32を介して入力されるエンジン12の動力や第2電動機MG2の動力が出力歯車14へ伝達され、その出力歯車14からカウンタギヤ対24、ファイナルギヤ対26、差動歯車装置28、一対の車軸38等を順次介して一対の駆動輪40へ伝達される。すなわち、エンジン12が動力分配機構16等を介して駆動輪40に動力伝達可能に連結されている。
FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating a schematic configuration of a hybrid vehicle 10 (hereinafter, referred to as a vehicle 10) to which the present invention is applied, and also illustrates a main part of a control system provided for controlling each part of the
駆動軸32は、エンジン12によって回転駆動させられる。この駆動軸32の端部には、潤滑油供給装置としてのオイルポンプ44が連結されており駆動軸32が回転駆動されることによりオイルポンプ44が回転駆動させられて、動力分配機構16、歯車機構18、不図示のボールベアリング等に潤滑油が供給されるようになっている。
The
動力分配機構16は、第1サンギヤS1、第1ピニオンギヤP1、その第1ピニオンギヤP1を自転及び公転可能に支持する第1キャリヤCA1、第1ピニオンギヤP1を介して第1サンギヤS1と噛み合う第1リングギヤR1を回転要素(回転部材)として備える公知のシングルピニオン型の遊星歯車装置から構成されており、差動作用を生じる本発明の差動機構として機能する。この動力分配機構16においては、第1キャリヤCA1は駆動軸32すなわちエンジン12に連結され、第1サンギヤS1は第1電動機MG1に連結され、第1リングギヤR1は出力歯車14に連結されている。これより、第1サンギヤS1、第1キャリヤCA1、第1リングギヤR1は、それぞれ相互に相対回転可能となることから、エンジン12の出力が第1電動機MG1及び出力歯車14に分配されると共に、第1電動機MG1に分配されたエンジン12の出力で第1電動機MG1が発電され、その発電された電気エネルギがインバータ46を介して蓄電装置48に蓄電されたりその電気エネルギで第2電動機MG2が回転駆動されるので、動力分配機構16は例えば無段変速状態(電気的CVT状態)とされて、エンジン12の所定回転に拘わらず出力歯車14の回転が連続的に変化させられる電気的な無段変速機として機能する。つまり、動力分配機構16は、差動用電動機として機能する第1電動機MG1の運転状態が制御されることにより、その動力分配機構16の差動状態が制御される電気式差動部(電気式無段変速機)として機能する。これにより、動力分配機構16は、例えば燃費が最もよいエンジン12の動作点(例えばエンジン回転速度NeとエンジントルクTeとで定められるエンジン12の運転点、以下、エンジン動作点という)に沿ってエンジン12を作動させることができる。この種のハイブリッド形式は、機械分配式或いはスプリットタイプと称される。なお、動力分配機構16が本発明の差動機構に対応し、蓄電装置48が本発明のバッテリに対応し、遊星歯車装置のサンギヤS1が本発明の第1回転要素に対応し、キャリヤCA1が本発明の第2回転要素に対応し、リングギヤR1が本発明の第3回転要素に対応している。
The
歯車機構18は、第2サンギヤS2、第2ピニオンギヤP2、その第2ピニオンギヤP2を自転及び公転可能に支持する第2キャリヤCA2、第2ピニオンギヤP2を介して第2サンギヤS2と噛み合う第2リングギヤR2を回転要素として備える公知のシングルピニオン型の遊星歯車装置から構成されている。この歯車機構18においては、第2キャリヤCA2は非回転部材であるケース34に連結されることで回転が阻止され、第2サンギヤS2は第2電動機MG2に連結され、第2リングギヤR2は出力歯車14に連結されている。そして、この歯車機構18は、例えば減速機として機能するように遊星歯車装置自体のギヤ比(歯車比=サンギヤS2の歯数/リングギヤR2の歯数)が構成されており、第2電動機MG2からトルク(駆動力)を出力する力行時には第2電動機MG2の回転が減速させられて出力歯車14に伝達され、そのトルクが増大させられて出力歯車14へ伝達される。なお、この出力歯車14は、動力分配機構16のリングギヤR1及び歯車機構18のリングギヤR2としての機能、及びカウンタドリブンギヤ22と噛み合ってカウンタギヤ対24を構成するカウンタドライブギヤとしての機能が1つのギヤに一体化された複合歯車50となっている。さらに、この複合歯車50には、出力歯車14と軸方向に並ぶようにして、後述するパーキングロック機構86を構成するパーキングギヤ52も形成されている。
The
第1電動機MG1及び第2電動機MG2は、電気エネルギから機械的な駆動力を発生させる発動機としての機能及び機械的な駆動力から電気エネルギを発生させる発電機としての機能のうち少なくとも一方を備えた例えば同期電動機であって、好適には、発動機又は発電機として選択的に作動させられるモータジェネレータである。例えば、第1電動機MG1はエンジン12の反力を受け持つ為のジェネレータ(発電)機能及び運転停止中のエンジン12を回転駆動するモータ(電動機)機能を備え、第2電動機MG2は走行用の駆動力源として駆動力を出力する走行用電動機として機能する為の電動機機能及び駆動輪40側からの逆駆動力から回生により電気エネルギを発生させる発電機能を備える。なお、第1電動機MG1が本発明の電動機に対応している。
The first electric motor MG1 and the second electric motor MG2 have at least one of a function as an engine that generates mechanical driving force from electric energy and a function as a generator that generates electric energy from mechanical driving force. For example, a synchronous motor, preferably a motor generator that is selectively operated as a motor or a generator. For example, the first electric motor MG1 has a generator (power generation) function for taking charge of the reaction force of the
カウンタギヤ対24は、カウンタドライブギヤとしての出力歯車14と、その出力歯車14と噛み合うカウンタドリブンギヤ22とから構成されている。ファイナルギヤ対26は、カウンタドリブンギヤ22と一体回転させられるファイナルドライブギヤ54と、差動歯車装置28のデフケースに形成されファイナルドライブギヤ54と噛み合うファイナルドリブンギヤ56とから構成されている。差動歯車装置28は、よく知られたデファレンシャル装置であり、走行状態に応じて左右の車輪38に差回転を付与するものである。なお、差動歯車装置28の具体的な構成および作動については公知であるため、その説明を省略する。
The
また、車両10には、例えばエンジン12、第1電動機MG1、第2電動機MG2等を制御する車両10の制御装置としての電子制御装置200が備えられている。この電子制御装置200は、例えばCPU、RAM、ROM、入出力インターフェース等を備えた所謂マイクロコンピュータを含んで構成されており、CPUはRAMの一時記憶機能を利用しつつ予めROMに記憶されたプログラムに従って信号処理を行うことにより車両10の各種制御を実行する。例えば、電子制御装置200は、エンジン12、第1電動機MG1、第2電動機MG2などに関するハイブリッド駆動制御等の車両制御を実行するようになっており、必要に応じてエンジン12の出力制御用、動力分配機構16の変速制御用等に分けて構成される。
Further, the
電子制御装置200には、シフト操作装置57においてパーキングポジション(パーキング、Pポジション)以外の非Pポジション(Nポジション、Dポジション、Rポジション等)の何れかへ切り替える為のシフトレバー58のシフトポジション(シフト位置、シフトポジション)Pshを表す信号及びシフトポジション(シフト位置)をPポジション(パーキング)へ切り替える為のPスイッチ60におけるスイッチ操作に応じたPポジションへの切替要求としてのシフトポジションPsh(シフト位置)を表す信号、アクセル開度センサ62により検出された運転者による車両10に対する加速要求量(ドライバ要求量)としてのアクセルペダル64の操作量であるアクセル開度Accを表す信号、ブレーキスイッチ66により検出された常用ブレーキであるフットブレーキの作動中(踏込操作中)を示すフットブレーキペダル68の操作(ブレーキオン)Bonを表す信号、スロットル弁開度センサ70により検出された電子スロットル弁の開度であるスロットル弁開度θthを表す信号、エンジン水温センサ72により検出されたエンジン水温Twを表す信号、クランクポジションセンサ74により検出されたクランク軸の回転角度(位置)Acr及びエンジン12の回転速度であるエンジン回転速度Neを表す信号、出力回転速度センサ78により検出された車速Vに対応する出力歯車14の回転速度である出力回転速度Noutを表す信号、レゾルバ等の第1電動機回転速度センサ80により検出された第1電動機MG1の回転速度である第1電動機回転速度Nm1を表す信号、レゾルバ等の第2電動機回転速度センサ82により検出された第2電動機MG2の回転速度である第2電動機回転速度Nm2を表す信号、バッテリセンサ84により検出された蓄電装置48のバッテリ温度THbatやバッテリ入出力電流(バッテリ充放電電流)Ibatやバッテリ電圧Vbatを表す信号などが、それぞれ供給される。
The
また、電子制御装置200からは、例えばエンジン12の出力制御の為のエンジン出力制御指令信号Seや第1電動機MG1及び第2電動機MG2の駆動制御の為のインバータ46へのモータ制御指令信号などのハイブリッド制御指令信号Smなどが、それぞれ出力される。
Further, the
図2は、図1に示すパーキングロック機構86の具体的な構成を示す図である。パーキングロック機構86は、複合歯車50に形成されているパーキングギヤ52と、そのパーキングギヤ52と選択的に噛合可能な噛合歯88を有して回転支持軸90を中心に回動可能に設けられているパーキングポール92と、パーキングポール92と当接するテーパ部94に挿し通されてテーパ部94を一端部において支持するパーキングロッド96と、パーキングロッド96に設けられてテーパ部94をその小径方向へ付勢するスプリング98と、パーキングロッド96の他端部に回動可能に接続されて節度機構により少なくともパーキングポジション(パーキング、Pポジション)に位置決めされるディテントプレート100と、ディテントプレート100に固設されて一軸まわりに回転可能に支持されたシャフト102と、シャフト102を回転駆動させる電動アクチュエータ104と、シャフト102の回転角θを検出するロータリエンコーダ106と、ディテントプレート100の回転に節度を与えて各シフトポジションに固定するディテントスプリング108およびその先端部に設けられた係合部110とを、備えている。
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a specific configuration of
ディテントプレート100は、シャフト102を介して電動アクチュエータ104の駆動軸に作動的に連結されており、パーキングロッド96と共に電動アクチュエータ104により駆動されてシフトポジション(シフト位置)を切り替えるためのシフトポジション決め部材として機能する。ディテントプレート100の頂部には、第1凹部112および第2凹部114が形成されている。そして、第1凹部112がパーキングロックポジションに対応しており、第2凹部114が非パーキングロックポジションに対応している。また、ロータリエンコーダ106は、電動アクチュエータ104の駆動量すなわち回転量に応じた計数値(エンコーダカウント)を取得するためのパルス信号を出力する。
The
図2は、パーキングロック機構86がパーキングロック状態にある場合を表している。シフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられてパーキングロック機構86がパーキングロック状態にある場合、パーキングポール92の噛合歯88とパーキングギヤ52とが噛み合わされることで、パーキングギヤ52が回転停止させられている。また、パーキングギヤ52は駆動輪40に機械的に連結されているため、パーキングギヤ52が回転停止状態にあると駆動輪40も同様に回転停止させられる。パーキングポール92は、パーキングロッド96の一端に設けられているテーパ部94との当接位置が変化させられることで、その位置が調節される。例えば、パーキングポール92がテーパ部94の大径部と当接する場合、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが噛み合うことで、パーキングロック状態とされる(図2)。一方、パーキングポール92がテーパ部94の小径部と当接する場合、噛合歯88とパーキングギヤ52との噛合いが外れ、パーキングロックが解除される。
FIG. 2 shows a case where the
上記パーキングポール92とテーパ部94との当接位置は、テーパ部94の軸方向位置に基づいて調節される。テーパ部94の軸方向位置は、パーキングロッド96によって変化させられ、それに伴ってパーキングポール92とテーパ部94との当接位置が調節される。例えば、矢印C方向にテーパ部94が移動させられると、パーキングポール92はテーパ部94の小径側と当接することとなる。したがって、パーキングポール92の先端が鉛直下方に移動されるに伴って、パーキングポール92の噛合歯88とパーキングギヤ52との噛合が解除される。すなわちパーキングロックが解除される。
The contact position between the
一方、矢印Cとは逆方向にテーパ部94が移動させられると、パーキングポール92の先端がテーパ部94の大径側と当接することとなる。したがって、パーキングポール92の先端が鉛直上方に移動されるに伴って、パーキングポール92とパーキングギヤ52とが噛み合わされる。すなわち、パーキングロック状態とされる。
On the other hand, when the tapered
また、パーキングロッド96の軸方向への移動は、ディテントプレート100の回動位置すなわちシャフト102の回転位置に応じて調節される。シャフト102は電動アクチュエータ104によって回転させられ、走行レンジを制御する電子制御装置200から出力される電動アクチュエータ104の作動信号に基づいて、その回転位置が制御される。ここで、シャフト102において、ディテントプレート100の第1凹部112とディテントスプリング108に設けられている係合部110とが係合される回転位置がパーキングロック位置、すなわちパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92の噛合歯88とが噛み合う位置に対応している。一方、ディテントプレート100の第2凹部114と係合部110とが係合される回転位置がパーキングロック解除位置、すなわちパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92の噛合歯88との噛合が解除される位置に対応している。
Further, the movement of the
したがって、電子制御装置200からパーキングロック指令が出力されると、電動アクチュエータ104は、シャフト102を上記第1凹部112と係合部110とが係合する回転位置まで回転させる。また、電子制御装置200からパーキングロック解除指令が出力されると、電動アクチュエータ104は、シャフト102を上記第2凹部114と係合部110とが係合する回転位置まで回転させる。なお、シャフト102の回転位置は、予め設定されている基準回転位置よりロータリエンコーダ106によって検出される計数値が、パーキングロック位置およびパーキングロック解除位置に対応する予め設定された回転位置に相当する計数値となるように制御される。
Therefore, when a parking lock command is output from the
図1に戻り、シフト操作装置57は、例えば運転席の近傍に配設され、複数のシフトポジション(シフト位置)Pshへ操作されるモーメンタリ式の操作子すなわち操作力を解くと元位置(初期位置)へ自動的に復帰する自動復帰式の操作子としてのシフトレバー58を備えている。また、本実施例のシフト操作装置57は、シフトレンジをパーキングレンジ(Pレンジ)としてパーキングロックする為のPスイッチ60をシフトレバー58の近傍に別スイッチとして備えている。
Returning to FIG. 1, the
シフトレバー58は、車両の前後方向または上下方向すなわち縦方向に配列された3つのシフトポジション(シフト位置)PshであるRポジション(R位置)、Nポジション(N位置)、Dポジション(D位置)と、それに平行に配列されたMポジション(M位置)、Bポジション(B位置)とへそれぞれ操作されるようになっており、シフトポジションPshに応じた位置信号を電子制御装置200へ出力する。また、シフトレバー58は、RポジションとNポジションとDポジションとの相互間で縦方向に操作可能とされ、MポジションとBポジションとの相互間で縦方向に操作可能とされ、更に、NポジションとMポジションとの相互間で上記縦方向に直交する車両の横方向に操作可能とされている。
The
Pスイッチ60は、例えばモーメンタリ式の押しボタンスイッチであって、運転者により押込み操作される毎にPスイッチ信号を電子制御装置200へ出力する。すなわち、Pスイッチ60が押込み操作されると、シフト位置がPポジション(P位置、パーキング)に切り替えられる。例えばシフトレンジが非PレンジにあるときにPスイッチ60が押されると、車両が停止状態である場合やパーキングロック可能な上限速度Vmaxより低い場合などの所定の条件が満たされていれば、シフトレンジがパーキングレンジとされる。このパーキングレンジは、エンジン12と駆動輪40との間の動力伝達経路が遮断され、且つ、パーキングロック機構86により駆動輪40の回転を機械的に阻止するパーキングロックが実行される駐車レンジである。
The
シフト操作装置57のMポジションはシフトレバー58の初期位置(ホームポジション)であり、Mポジション以外のシフトポジションPsh(R,N,D,Bポジション)へシフト操作されていたとしても、運転者がシフトレバー58を解放すれば、すなわちシフトレバー58に作用する外力が無くなれば、バネなどの機械的機構によりシフトレバー58はMポジションへ戻るようになっている。シフト操作装置57が各シフトポジション(シフト位置)Pshへシフト操作された際には、電子制御装置200によりシフトポジションPsh(シフト位置信号)に基づいてそのシフト操作後のシフトポジションPshに対応したシフトレンジに切り替えられる。
The M position of the
各シフトレンジについて説明すると、シフトレバー58がRポジションへシフト操作されることにより選択されるRレンジは、車両を後進させる駆動力が駆動輪に伝達される後進走行レンジである。また、シフトレバー58がNポジションへシフト操作されることにより選択されるニュートラルレンジ(Nレンジ)は、エンジン12と駆動輪40との間の動力伝達経路が遮断されるニュートラル状態とするための中立レンジである。また、シフトレバー58がDポジションへシフト操作されることにより選択されるDレンジは、車両を前進させる駆動力が駆動輪に伝達される前進走行レンジである。また、シフトレバー58がBポジションへシフト操作されることにより選択されるBレンジは、Dレンジにおいて例えば電動機に回生トルクを発生させるなどによりエンジンブレーキ効果を発揮させ駆動輪の回転を減速させる減速前進走行レンジ(エンジンブレーキレンジ)である。
Explaining each shift range, the R range selected when the
車両10では、シフト操作装置57の操作位置に応じたシフトレバー58のシフト位置信号に応じて、各シフトレンジの切替が電気的に制御される所謂シフトバイワイヤ形式が採用されている。具体的には、シフト操作装置57の操作位置に応じた位置信号に基づいて、Pレンジおよび非Pレンジ(R,N,D,Bレンジ)の切替が、電動アクチュエータ104の回転角制御によって切り替えられる。
The
図3は、電子制御装置200による制御機能の要部を説明する機能ブロック線図である。図3において、ハイブリッド制御部210(ハイブリッド制御手段)は、例えばエンジン12を停止し専ら第2電動機MG2を駆動源とするモータ走行モード、エンジン12の動力に対する反力を第1電動機MG1の発電により受け持つことで出力歯車14(駆動輪40)にエンジン直達トルクを伝達すると共に第1電動機MG1の発電電力により第2電動機MG2を駆動することで出力歯車14にトルクを伝達して走行するエンジン走行モード(定常走行モード)、このエンジン走行モードにおいて蓄電装置48からの電力を用いた第2電動機MG2の駆動力を更に付加して走行するアシスト走行モード(加速走行モード)等を、走行状態に応じて選択的に成立させる。
FIG. 3 is a functional block diagram for explaining a main part of the control function by the
上記エンジン走行モードにおける制御を一例としてより具体的に説明すると、ハイブリッド制御部210は、エンジン12を効率のよい作動域で作動させる一方で、エンジン12と第2電動機MG2との駆動力の配分や第1電動機MG1の発電による反力を最適になるように変化させて動力分配機構16の電気的な無段変速機としての変速比γ0(=エンジン回転速度Ne/出力回転速度Nout)を制御する。例えば、ハイブリッド制御部210は、アクセル開度Accや車速Vから車両10の目標出力を算出し、その目標出力と充電要求値とから必要なトータル目標出力を算出し、そのトータル目標出力が得られるように伝達損失、補機負荷、第2電動機MG2のアシストトルク等を考慮して目標エンジンパワーPe*を算出する。そして、ハイブリッド制御部210は、例えば運転性と燃費性とを両立するように予め実験的に求められた公知のエンジン最適燃費線(燃費マップ)に沿ってエンジン12を作動させつつ目標エンジンパワーPe*が得られるエンジン動作点すなわちエンジン回転速度NeとエンジントルクTeとなるように、エンジン12を制御すると共に第1電動機MG1の発電量を制御する。尚、上記エンジン動作点とは、エンジン回転速度Ne及びエンジントルクTeなどで例示されるエンジン12の動作状態を示す状態量を座標軸とした二次元座標においてエンジン12の動作状態を示す動作点である。また、本実施例では、燃費とは例えば単位燃料消費量当たりの走行距離であったり、車両全体としての燃料消費率(=燃料消費量/駆動輪出力)等である。
More specifically, the control in the engine running mode is described as an example. The
ハイブリッド制御部210は、スロットル制御の為にスロットルアクチュエータにより電子スロットル弁を開閉制御させる他、燃料噴射制御の為に燃料噴射装置による燃料噴射量FUELや噴射時期を制御し、点火時期制御の為に点火装置による点火時期を制御するエンジン出力制御指令信号を出力し、目標エンジンパワーPe*を発生する為のエンジントルクTeが得られるようにエンジン12の出力制御を実行する。また、ハイブリッド制御部210は、第1電動機MG1による発電を制御させる指令をインバータ46に出力して、目標エンジンパワーPe*を発生する為のエンジン回転装度Neが得られるように第1電動機回転速度Nm1を制御する。
The
ハイブリッド制御部210は、パーキングレンジに切り替えるためのPスイッチ60が運転者によって押されると、シフトポジションPshがパーキングポジション(パーキング)に切り替えられたものと判断し、さらに車両が停止状態である場合やパーキングロック可能な上限速度Vmaxより低い場合などの所定の条件が満たされていることを判断した後、パーキングロック機構86を作動させる、すなわちパーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92の噛合歯88とを噛み合わせる信号を出力し、電動アクチュエータ104を駆動させてパーキングロック機構86をパーキングロック状態に切り替えるパーキングロック切換制御部212(パーキングロック切換制御手段)を機能的に備えている。
The
また、ハイブリッド制御部210は、車両停止中であっても、エンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御(バッテリ充電制御)を行うことができる。このとき、第1電動機MG1は、充電制御による反力トルクを出力するので、動力分配機構16の動力分配機能によって出力歯車14からエンジン12の直達トルクが出力される。これに対して、ハイブリッド制御部210は、第2電動機MG2からその直達トルクと反対方向に作用する反力トルクを出力することで、直達トルクを相殺して駆動輪40に伝達されるトルクを零に制御する。なお、ハイブリッド制御部210は、第1電動機MG1から出力される反力トルクに基づいて、駆動輪40の駆動力が零となる第2電動機MG2のトルクを逐次算出して出力する。
Further, the
ここで、登坂路において車両を停止させる場合、一般には運転者がフットブレーキペダル68を踏み込むことで車両が停止させられ、その状態でPスイッチ60が押し込まれてパーキングロック機構86が作動させられる。このときパーキングロック機構86のパーキングポール92が回動させられてその噛合歯88がパーキングギヤ52と噛合可能な位置に移動させられるが、パーキングギヤ52の回転位置によっては図4に示すように、パーキングギヤ52の歯先の面と噛合歯88の歯先の面とが衝突して正常に噛み合わないことがある(非噛合状態)。しかしながら、運転者にはパーキングロック機構86の状態はわからないので、図4のように正常に噛み合っていない状態(非噛合状態)であってもパーキングロック機構86が正常に作動したものと判断してフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを解除する。これより、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92の噛合歯88が噛み合うまで車両がずり下がり、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92の噛合歯88とが噛み合った際にショック(噛合ショック)が発生する。また、パーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが噛み合った際にパーキングロック機構86に大きな車両慣性が入力されるので、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性が低下する可能性も生じる。なお、車両がずり下がる際の移動量は、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが正常に噛み合うまでに回転したパーキングギヤ52の回転量に相関しており、その移動量の最大値は、パーキングギヤ52が一歯分だけ回転したときの車両の移動量となる。
Here, when the vehicle is stopped on the uphill road, the vehicle is generally stopped when the driver depresses the
これに対して、ハイブリッド制御部210が上述したエンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御を行っている場合には、登坂路で停止した状態からフットブレーキペダル68が解除されると駆動輪40側から出力歯車14が回され、同じ回転方向のトルクを出力している第2電動機MG2は反力トルクをとれなくなる。従って、エンジン12の直達トルク分が駆動輪40に伝達される。この直達トルクは、正転方向すなわち登坂路を登る方向に作用するので、登坂路をずり下がろうとしている車両10に対して抵抗となり、車両加速度が抑制されて車両10が緩やかにずり下がる。従って、車両10がずり下がってパーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが噛み合ったときのショックが低減されると共に、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下も抑制される。
On the other hand, when the
しかしながら、車両がずり下がるときに蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが予め設定されている上限値を超えていると、第1電動機MG1による発電が制限される或いは禁止されるので、エンジン12の直達トルクを出力することが困難となる。例えば登坂路において運転者がフットブレーキペダル68を踏み込むことで車両を停止させ、その状態で充電制御が長時間実行されると蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが徐々に増加して蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値に到達する可能性がある。そして、蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値に到達した状態で、運転者がPスイッチ60を押した際に、図4で示したようにパーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが正常に噛み合わないと、運転者がフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを解除した際に車両がずり下がる。このとき、蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値に到達しているので、第1電動機MG1による充電制御が困難となって直達トルクが駆動輪40に出力されず、パーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが噛み合った際に発生するショックが低減されない。そこで、ハイブリッド制御部210は、車両がずり下がる際に第1電動機MG1による充電制御が可能となるように、所定の条件に基づいて第1電動機MG1による充電量を下げる制御を実行する。具体的には、第1電動機MG1による充電量を下げるに際して、ハイブリッド制御部210は、車速Vが予め設定されている所定値以下であるか否かを判定する車速判定部214(車速判定手段)を機能的に備えている。なお、本発明の要部である以下に説明する制御において、エンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御が行われている状態を前提とする。
However, if the charge capacity SOC of the
車速判定部214は、車速Vが予め設定されている所定値α以下であるかを判定し、所定値α以下であると判定されるとハイブリッド制御部210は、第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量を、車速Vが所定値α以下となる前に比べて低減させる指令を第1電動機MG1に出力する。なお、所定値αは、予め実験等に基づいて設定された値であり、車両が略停止しているものと判断されるような極低速の値に設定され、例えば、所定値αがクリープ速度に設定される。言い換えれば、所定値αは、運転者によってパーキングポジションに切り替えられる可能性があると判断される値に設定されている。従って、車速Vが所定値α以下となると、第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量が低減されることとなる。
The vehicle
上記のように制御されることで得られる効果について説明する。登坂路において運転者がフットブレーキペダル68を踏み込むことで車両を停止させると、車速Vが零状態となるので、ハイブリッド制御部210は第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量を、低減させる。従って、仮に運転者がこの状態で長時間待機していた場合であっても蓄電装置48に充電される電力が少なくなるので、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量(空き容量)に余裕が生じる。これより、パーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが正常に噛み合わない状態で停止し、運転者によってPスイッチ60が押し込まれた後にフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みが解除された場合、車両のずり下がりが生じるものの、直達トルクが駆動輪40に出力されるので、ずり下がったときの車両加速度が抑制される、すなわちずり下がりが緩やかとなる。従って、パーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが噛み合ったときに生じるショックが低減され、パーキングロック機構86に入力される車両慣性(慣性力)についても低減されるので、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下が抑制される。なお、第1電動機MG1による充電量の低減量は、予め実験的に求められており、予め設定されている所定時間の充電を許容する、すなわち所定時間充電制御が実行されても蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値に到達しない値に設定される。また、その低減量は必ずしも一定値をとらず、例えば蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCに応じて適宜変更しても構わない。例えば、蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが増加するに従って、第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量がさらに低減される。
The effect obtained by controlling as described above will be described. When the driver stops the vehicle by depressing the
図5は、電子制御装置200の制御作動の要部すなわち登坂路において車両がずり下がっても、それによって発生するショックを低減してパーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下を抑制できる制御作動を説明するためのフローチャートであって、例えば数msec乃至数十msec程度の極めて短いサイクルタイムで繰り返し実行されるものである。なお、以下の説明においても、第1電動機MG1による充電制御が実行されていることを前提とする。
FIG. 5 illustrates a control operation of the
先ず、車速判定部214に対応するステップS1(以下、ステップを省略)において、車両の車速Vが所定値α以下か否かが判断される。S1が否定される場合、本ルーチンは終了させられる。一方、S1が肯定される場合、ハイブリッド制御部210に対応するS2において、第1電動機MG1による充電量が低減されることで、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量に余裕が生じる。従って、車両がずり下がった際に第1電動機MG1による充電制御を確実に実施してエンジン12の直達トルクを駆動輪40に出力することができ、パーキング機構86のギヤの噛合時のショックを低減し、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。
First, in step S1 (hereinafter, step is omitted) corresponding to the vehicle
上述のように、本実施例によれば、登坂路での停車において車両10をずり下げる方向に作用するトルクをエンジン12の直達トルクによって受けることで、車両10のずり下がりが緩やかになってパーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが噛み合う際のショックが低減される。また、車両10のずり下がりが緩やかになるので、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下も抑制される。ここで、車両10がずり下がる際に蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値を超えていると、第1電動機MG1による充電制御ができない為に前記直達トルクを発生できず、車両10のずり下がりをエンジン12の直達トルクで受けることが困難となる。そこで、車両10の車速Vが所定値α以下となると、登坂路での停車に備えて予め第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量を、車速Vが所定値α以下となる前に比べて低減させておくことで、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量に余裕を持たせ、車両10がずり下がる際に第1電動機MG1による充電制御を確実に実施して直達トルクを発生させることができる。これより、車両10がずり下がる際に発生するショックを確実に低減し、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, when the
また、本実施例によれば、第3回転要素であるリングギヤR1には、第2電動機MG2が動力伝達可能に連結され、車両停止中にエンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御を行っている状態では、その充電制御によって駆動輪40に伝達される直達トルクとは反対方向のトルクが第2電動機MG2から出力される。このようにすれば、エンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御を行っている状態においてエンジン12の直達トルクが発生するが、この直達トルクとは反対の方向のトルクを第2電動機MG2から出力することで駆動輪40のトルクが零に制御される。
Further, according to the present embodiment, the second electric motor MG2 is connected to the ring gear R1, which is the third rotating element, so as to be able to transmit power, and the
つぎに、本発明の他の実施例を説明する。なお、以下の説明において前述の実施例と共通する部分には同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。 Next, another embodiment of the present invention will be described. In the following description, parts common to those in the above-described embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof is omitted.
前述した実施例では、車速Vが所定値α以下である場合に第1電動機MG1による充電量を低減したが、運転者がPスイッチ60を押し込むことでシフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられた時点で第1電動機MG1による充電量を低減させることもできる。以下、本実施例の態様について説明する。なお、本実施例においても、エンジン12を運転させて第1電動機MG1による充電制御が行われていることを前提として説明する。
In the above-described embodiment, the amount of charge by the first electric motor MG1 is reduced when the vehicle speed V is equal to or less than the predetermined value α. However, when the driver pushes the
登坂路においてフットブレーキペダル68が踏み込まれて車両が停止した状態で運転者がPスイッチ60を押し込んだ状態にあっても、運転者がフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みをなかなか解除しない場合がある。従って、第1電動機MG1による充電制御が継続されて蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値に到達することがある。ここで、パーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが図4のように正常に噛み合わない状態となっていると、運転者がフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを解除した際に車両がずり下がるが、第1電動機MG1による充電制御ができないので直達トルクが出力されずショックが大きくなる。そこで、本実施例では、Pスイッチ60の押し込み、すなわちシフトポジションPshをパーキングに切り替える信号が出力されたときに、第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量を、シフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられる前に比べて低減させる。
Even when the driver presses the
図6は、本実施例の電子制御装置300による制御作動の要部を説明する機能ブロック線図である。なお、図6のハイブリッド制御部310およびパーキングロック切換制御部320は、前述した実施例のハイブリッド制御部210およびパーキングロック切換制御部212と基本的には変わらないので、その説明を省略し、前述の実施例と異なるパーキング指令判定部330について説明する。
FIG. 6 is a functional block diagram for explaining the main part of the control operation by the
パーキング指令判定部330(パーキング指令判定手段)は、運転者によってPスイッチ60が押し込まれた否か、すなわちシフトポジションPshをパーキングポジション(パーキング)に切り替える信号が出力されたか否かを判定する。Pスイッチ60が押し込まれた場合には、パーキング指令判定部330の判定が肯定され、パーキングレンジに切り換える信号が出力されるに従い、パーキングロック機構86が作動することとなる。ハイブリッド制御部310は、パーキング指令判定部330の判定が肯定されると、第1電動機MG1による充電量を、Pスイッチ60が押し込まれる前に比べて低減する。
The parking command determination unit 330 (parking command determination means) determines whether or not the driver has pushed the
以下、上記ように制御することによって得られる効果について説明する。登坂路において運転者がフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込むことで車両を停止させ、運転者がPスイッチ60を押し込むと、パーキング指令判定部330が肯定されるので、ハイブリッド制御部310は、第1電動機MG1による充電量をPスイッチ60が押し込まれる前に比べて低減させる。従って、運転者がPスイッチ60を押し込んだ後もフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを維持した状態で長時間待機していた場合であっても蓄電装置48に充電される電力が少なくなるので、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量に余裕が生じる。これより、その後に運転者がフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを解除した際に、パーキングロック機構86が正常に噛み合っていないために車両がずり下がった場合であっても、第1電動機MG1による充電制御が実施されて直達トルクが駆動輪40に出力されるので、ずり下がりの車両加速度が抑制されずり下がりが緩やかとなる。従って、パーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52と噛合歯88とが噛み合ったときに生じるショックが低減され、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下も抑制される。
Hereinafter, effects obtained by controlling as described above will be described. When the driver stops the vehicle by depressing the
図7は、電子制御装置300の制御作動の要部すなわち車両がずり下がっても、それによって発生するショックを抑制してパーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下を抑制できる制御作動を説明するためのフローチャートであって、例えば数msec乃至数十msec程度の極めて短いサイクルタイムで繰り返し実行されるものである。
FIG. 7 is a flowchart for explaining a control operation of the
先ず、パーキング指令判定部330に対応するステップS11において、Pスイッチ60が押し込まれたか否か、すなわちシフトポジションPshをパーキングに切り替える信号が出力されたか否かが判定される。S11が否定される場合、本ルーチンは終了させられる。一方、S11が肯定される場合、ハイブリッド制御部310に対応するS22において、第1電動機MG1による充電量が低減されることで、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量に余裕が生じる。従って、車両がずり下がった際に第1電動機MG1による充電制御を確実に実施して直達トルクを出力することができ、パーキング機構86のギヤが噛み合ったときの噛合時のショックが低減され、パーキング機構86の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。
First, in step S11 corresponding to the parking
上述のように、本実施例によれば、登坂路において車両10をずり下げる方向に作用するトルクをエンジン12の直達トルクによって受けることで、車両10のずり下がりが緩やかになってパーキングロック機構86のパーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが噛み合う際のショックが低減される。また、車両10のずり下がりが緩やかになるので、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下も抑制される。ここで、シフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられて、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とを噛み合わせる信号が出力された場合であっても、パーキングギヤ52とパーキングポール92とが正常に噛み合わない状態で停止することがある。この状態でフットブレーキペダル68の踏み込みを解除した際には車両10がずり下がるが、継続的な充電によって既に蓄電装置48の充電容量SOCが上限値を超えていると第1電動機MG1による充電制御が実行できずに車両10のずり下がりをエンジン12の直達トルクで受けることが困難となる。そこで、シフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられると、第1電動機MG1によって蓄電装置48に充電される充電量を、シフトポジションPshがパーキングに切り替えられる前に比べて低減することで、蓄電装置48の充電可能な容量に余裕を持たせ、車両10がずり下がる際に第1電動機MG1による充電制御を確実に実施して直達トルクを発生させることができる。これより、車両10がずり下がる際に発生するショックを確実に低減し、パーキングロック機構86の耐久性低下を抑制することができる。
As described above, according to the present embodiment, by receiving the torque acting in the direction of sliding down the
以上、本発明の実施例を図面に基づいて詳細に説明したが、本発明はその他の態様においても適用される。 As mentioned above, although the Example of this invention was described in detail based on drawing, this invention is applied also in another aspect.
例えば、前述の各実施例では、それぞれ別個の条件に基づいて、第1電動機MG1による充電量を低減させるものであったが、これらの実施例を適宜組み合わせて実施しても構わない。 For example, in each of the above-described embodiments, the amount of charge by the first electric motor MG1 is reduced based on different conditions. However, these embodiments may be combined appropriately.
また、前述の実施例のハイブリッド車両10では、パーキングロック機構86が複合歯車50に設けられているが、パーキングロック機構86が設けられる部位は適宜変更されても構わない。具体的には、パーキングロック機構86は、第3回転要素であるリングギヤR1および駆動輪40の回転を停止させる範囲において、歯車等の機械要素を介して間接的に設けられていても構わない。
Further, in the
また、前述の実施例では、差動機構がシングルピニオン型の遊星歯車装置で構成されているが、ダブルピニオン型の遊星歯車装置であっても構わない。さらに、差動機構は遊星歯車装置に限定されるものではなく、差動作用を生じさせる構成であれば適宜変更しても構わない。 Further, in the above-described embodiment, the differential mechanism is configured by a single pinion type planetary gear device, but may be a double pinion type planetary gear device. Further, the differential mechanism is not limited to the planetary gear device, and may be changed as appropriate as long as it has a differential action.
また、前述の実施例では、第1電動機MG1がサンギヤS1に連結され、エンジン12がキャリヤCA1に連結され、駆動輪40がリングギヤR1に連結されているが、これらの連結構成は適宜変更されても構わない。
In the above-described embodiment, the first electric motor MG1 is connected to the sun gear S1, the
また、前述の実施例において、図5、7に示すステップS2の下に、車両のずり下がりの発生を判定し、車両がずり下がった際には第1電動機MG1による充電量の低減を止める(充電量を元に戻す)というステップをさらに追加して実施しても構わない。 Further, in the above-described embodiment, the occurrence of the vehicle sliding is determined under step S2 shown in FIGS. 5 and 7, and when the vehicle slides down, the reduction of the charge amount by the first electric motor MG1 is stopped ( A step of returning the charge amount to the original state may be added and executed.
また、前述の実施例において、図5、7に示すステップS1の上に、路面が登坂路であるか否かを判定し、登坂路である場合にステップS1以下の制御を実行するというステップをさらに追加して実施しても構わない。 In the above-described embodiment, the step of determining whether or not the road surface is an uphill road on the step S1 shown in FIGS. 5 and 7 and executing the control after the step S1 when the road surface is an uphill road. Furthermore, you may carry out by adding.
なお、上述したのはあくまでも一実施形態であり、本発明は当業者の知識に基づいて種々の変更、改良を加えた態様で実施することができる。 The above description is only an embodiment, and the present invention can be implemented in variously modified and improved forms based on the knowledge of those skilled in the art.
10:ハイブリッド車両
12:エンジン
16:動力分配機構(差動機構)
40:駆動輪
48:蓄電装置(バッテリ)
52:パーキングギヤ
86:パーキングロック機構
92:パーキングポール
200、300:電子制御装置(制御装置)
MG1:第1電動機(電動機)
S1:サンギヤ(第1回転要素)
CA1:キャリヤ(第2回転要素)
R1:リングギヤ(第3回転要素)
10: Hybrid vehicle 12: Engine 16: Power distribution mechanism (differential mechanism)
40: Drive wheel 48: Power storage device (battery)
52: Parking gear 86: Parking lock mechanism 92:
MG1: First motor (motor)
S1: Sun gear (first rotating element)
CA1: Carrier (second rotating element)
R1: Ring gear (third rotating element)
Claims (2)
前記エンジンを運転させて前記電動機による充電制御を行っている状態で、車両の車速が予め設定されている所定値以下となると、前記電動機によってバッテリに充電する充電量を、車速が該所定値以下となる前に比べて低減させることを特徴とするハイブリッド車両の制御装置。 A differential mechanism comprising a first rotating element coupled to the electric motor, a second rotating element coupled to the engine, and a third rotating element coupled to the drive wheel so as to be capable of transmitting power; and mechanically coupled to the third rotating element And a parking lock mechanism including a parking pawl that can mesh with the parking gear, and when the shift position is switched to parking, the parking gear and the parking pawl are engaged. A control device for a hybrid vehicle that outputs a matching signal,
In a state where the engine is operated and charging control is performed by the electric motor, when the vehicle speed of the vehicle is equal to or less than a predetermined value set in advance, the amount of charge charged in the battery by the electric motor is less than the predetermined value. A control device for a hybrid vehicle, characterized in that it is reduced as compared to before.
前記エンジンを運転させて前記電動機による充電制御を行っている状態で、シフト位置がパーキングに切り替えられると、前記電動機によってバッテリに充電する充電量を、該シフト位置が切り替えられる前に比べて低減させることを特徴とするハイブリッド車両の制御装置。 A differential mechanism comprising a first rotating element coupled to the electric motor, a second rotating element coupled to the engine, and a third rotating element coupled to the drive wheel so as to be capable of transmitting power; and mechanically coupled to the third rotating element And a parking lock mechanism including a parking pawl that can mesh with the parking gear, and when the shift position is switched to parking, the parking gear and the parking pawl are engaged. A control device for a hybrid vehicle that outputs a matching signal,
When the shift position is switched to parking while the engine is in operation and charging control is performed by the electric motor, the amount of charge charged to the battery by the electric motor is reduced compared to before the shift position is switched. A control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle characterized by the above.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012197741A JP2014051222A (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-09-07 | Control unit of hybrid vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012197741A JP2014051222A (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-09-07 | Control unit of hybrid vehicle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014051222A true JP2014051222A (en) | 2014-03-20 |
Family
ID=50610117
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012197741A Pending JP2014051222A (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-09-07 | Control unit of hybrid vehicle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2014051222A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017171011A (en) * | 2016-03-22 | 2017-09-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Control device of parking mechanism |
| JP2018131009A (en) * | 2017-02-14 | 2018-08-23 | 株式会社Subaru | Parking lock device |
| CN109572447A (en) * | 2018-11-26 | 2019-04-05 | 吉林大学 | A kind of distributed hybrid power system Anti-slip regulation control method of more wheels |
| CN111791719A (en) * | 2020-07-09 | 2020-10-20 | 中国第一汽车股份有限公司 | P-gear parking control method for vehicle, electronic equipment and storage medium |
-
2012
- 2012-09-07 JP JP2012197741A patent/JP2014051222A/en active Pending
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017171011A (en) * | 2016-03-22 | 2017-09-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Control device of parking mechanism |
| JP2018131009A (en) * | 2017-02-14 | 2018-08-23 | 株式会社Subaru | Parking lock device |
| CN109572447A (en) * | 2018-11-26 | 2019-04-05 | 吉林大学 | A kind of distributed hybrid power system Anti-slip regulation control method of more wheels |
| CN111791719A (en) * | 2020-07-09 | 2020-10-20 | 中国第一汽车股份有限公司 | P-gear parking control method for vehicle, electronic equipment and storage medium |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10166974B2 (en) | Control system of power transmission system of vehicle | |
| JP5158258B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP4215092B2 (en) | Engine starter for hybrid vehicle | |
| US9090247B2 (en) | Control apparatus for vehicular drive system | |
| JP5796382B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| US8197385B2 (en) | Control device for vehicular power transmitting device | |
| JP6791027B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP5174127B2 (en) | Hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5884898B2 (en) | Drive control apparatus for hybrid vehicle | |
| US9096218B2 (en) | Control device of vehicle power transmission device | |
| JP6885256B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| CN104411555A (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2008207690A (en) | Control system of vehicular drive system | |
| CN103201153A (en) | Control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2008296648A (en) | Control device of transmission system for vehicle | |
| JP5724854B2 (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP4501814B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2014051222A (en) | Control unit of hybrid vehicle | |
| US20140148987A1 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5327177B2 (en) | Vehicle control system | |
| EP2730813B1 (en) | Control apparatus and control method of vehicle | |
| US20170166184A1 (en) | Control system for power transmission system | |
| WO2010128561A1 (en) | Parking controller for vehicle | |
| JP2012218622A (en) | Control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2012001186A (en) | Device for control of vehicle |