JP2013086612A - Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle - Google Patents
Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2013086612A JP2013086612A JP2011227825A JP2011227825A JP2013086612A JP 2013086612 A JP2013086612 A JP 2013086612A JP 2011227825 A JP2011227825 A JP 2011227825A JP 2011227825 A JP2011227825 A JP 2011227825A JP 2013086612 A JP2013086612 A JP 2013086612A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- gear
- target
- input shaft
- rotational speed
- gear stage
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/62—Hybrid vehicles
Landscapes
- Hybrid Electric Vehicles (AREA)
- Control Of Transmission Device (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、変速機の入力軸にトルクを付加可能な電動機を備えたハイブリッド車両の変速制御装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a shift control device for a hybrid vehicle including an electric motor capable of adding torque to an input shaft of a transmission.
内燃機関と駆動輪との間の動力伝達経路中に設けられて入力軸にクラッチを介して内燃機関が接続され、かつ変速比が手動で変更されるマニュアル式の変速機と、変速機の入力軸にトルクを付加可能な電動機とが搭載された車両が知られている。このような車両の変速制御装置として、変速操作が行われた場合にまず予測した変速比に基づいて目標回転数を設定し、続いて実際の入力軸の回転数が目標回転数になるように電動機を制御し、その後予測した変速比が実際に変更された変速比と一致しない場合には電動機と入力軸との間のクラッチを解放する装置が知られている(特許文献1参照)。その他、本発明に関連する先行技術文献として特許文献2、3が存在する。
A manual transmission that is provided in a power transmission path between the internal combustion engine and the drive wheel, is connected to the input shaft via a clutch, and the transmission ratio is manually changed, and the input of the transmission A vehicle equipped with an electric motor capable of applying torque to a shaft is known. As a shift control device for such a vehicle, when a shift operation is performed, first, a target rotation speed is set based on the predicted gear ratio, and then the actual rotation speed of the input shaft becomes the target rotation speed. An apparatus is known that controls an electric motor and then releases a clutch between the electric motor and an input shaft when the predicted gear ratio does not coincide with the actually changed gear ratio (see Patent Document 1). In addition,
特許文献1の装置では、予測した変速比が実際の変速比と一致しない場合に変速機の入力軸と電動機とを切り離す。そのため、その後入力軸に電動機のトルクを付加する必要が生じた場合に入力軸と電動機とを再接続する必要があるため、入力軸へのトルクの付加が開始されるまで時間が掛かる可能性がある。また、特許文献1の装置では、予測した変速比が実際の変速比と一致しない場合には変速機に設けられているシンクロ機構にて回転数差が補償される。そのため、シンクロ機構に大きな負荷が掛かる可能性がある。
In the device of
そこで、本発明は、電動機のトルクを入力軸に迅速に付加でき、かつ変速機に設けられているシンクロ機構の負荷を低減可能なハイブリッド車両の変速制御装置を提供することを目的とする。 SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION An object of the present invention is to provide a shift control device for a hybrid vehicle that can quickly add torque of an electric motor to an input shaft and can reduce the load on a synchro mechanism provided in the transmission.
本発明のハイブリッド車両の変速制御装置は、互いに大きさが異なる変速比が設定された複数のギア段を有し、シフトレバーの操作にてギア段が切り替えられるマニュアル式の変速機と、前記変速機の入力軸にクラッチ手段を介して接続された電動機と、前記変速機の出力軸と動力伝達可能に接続された駆動輪と、を備え、前記変速機には、ギア段の切替時に切替後に使用されるギアとそのギアが設けられた軸とを摩擦力を利用して同期させるシンクロ機構が設けられているハイブリッド車両に適用される変速制御装置において、前記変速機に対してギア段の切り替えが要求された場合に、まず前記複数のギア段のうち変速比が最も小さいギア段を目標ギア段に設定するとともに設定した目標ギア段の変速比及び前記出力軸の回転数に基づいて目標回転数を設定する初期値設定処理を実行し、次に前記クラッチ手段を前記入力軸と前記電動機とが係合される係合状態に切り替えるとともに前記入力軸の回転数が前記目標回転数に調整されるように前記電動機から前記入力軸にトルクを付加するトルク付加処理を実行し、その後前記目標ギア段が前記変速機に対して要求されたギア段である要求ギア段と一致しているか否か判定する判定処理を実行し、前記判定処理にて前記目標ギア段と前記要求ギア段が不一致と判定された場合には前記クラッチ手段を前記係合状態に維持し、かつ前記複数のギア段のうち前記判定処理の実行時に前記目標ギア段に設定されていたギア段の次に変速比が小さいギア段を前記目標ギア段に再設定するとともに再設定した目標ギア段と前記出力軸の回転数に基づいて前記目標回転数を再設定する再設定処理を実行し、前記判定処理にて前記目標ギア段と前記要求ギア段とが一致していると判定されるまで前記トルク付加処理、前記判定処理、及び前記再設定処理を繰り返し実行する制御手段を備えている(請求項1)。 A shift control apparatus for a hybrid vehicle according to the present invention includes a manual transmission that has a plurality of gear stages having different gear ratios set to different sizes, and that can be switched by operating a shift lever. An electric motor connected to the input shaft of the machine via clutch means, and drive wheels connected to the output shaft of the transmission so as to be able to transmit power, the transmission after switching at the time of gear stage switching In a shift control device applied to a hybrid vehicle provided with a synchro mechanism that synchronizes a gear used and a shaft provided with the gear by using a frictional force, the gear stage is switched with respect to the transmission. First, the gear stage having the smallest gear ratio among the plurality of gear stages is set as the target gear stage, and based on the set gear ratio of the target gear stage and the rotation speed of the output shaft. An initial value setting process for setting a target rotational speed is executed, and then the clutch means is switched to an engaged state in which the input shaft and the electric motor are engaged, and the rotational speed of the input shaft is set to the target rotational speed. A torque addition process for adding torque from the electric motor to the input shaft so as to be adjusted, and then the target gear stage matches a requested gear stage that is a required gear stage for the transmission A determination process for determining whether or not the target gear and the required gear are inconsistent in the determination process, the clutch means is maintained in the engaged state, and the plurality of gears Of the stages, the gear stage having the next smallest gear ratio is reset to the target gear stage after the gear stage that has been set to the target gear stage when the determination process is executed, and the reset target gear stage and the output shaft rotation A reset process for resetting the target rotational speed based on the torque, and the torque adding process and the determination until it is determined in the determination process that the target gear stage and the requested gear stage match. And a control means for repeatedly executing the process and the resetting process (claim 1).
本発明の変速制御装置によれば、目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが不一致の場合にはクラッチ手段を係合状態に維持するので、再度電動機のトルクを入力軸に付加する必要が生じた場合に迅速にトルクを付加することができる。また、本発明によれば、目標ギア段が要求ギア段と一致するまで電動機のトルクを入力軸に付加するので、シンクロ機構の負荷を低減できる。 According to the speed change control device of the present invention, when the target gear stage and the required gear stage do not match, the clutch means is maintained in the engaged state, so that it becomes necessary to add the torque of the motor to the input shaft again. Torque can be quickly applied to the. Further, according to the present invention, since the torque of the electric motor is applied to the input shaft until the target gear stage matches the required gear stage, the load on the synchronization mechanism can be reduced.
本発明の変速制御装置の一形態において、前記制御手段は、前記判定処理において前記入力軸の回転数が前記目標回転数より低い所定の判定値以上になったときに前記電動機による前記入力軸へのトルクの付加を停止するとともに前記入力軸の回転数と前記目標回転数との差である回転数差の時間微分値が所定の傾き判定値以下か否か判定し、前記再設定処理では前記判定処理にて前記回転数差の時間微分値が前記傾き判定値以下と判定された場合に前記目標ギア段及び前記目標回転数をそれぞれ再設定してもよい(請求項2)。周知のようにギア段の切り替えが行われるときには、シンクロ機構を介して出力軸の回転が入力軸に伝達されて入力軸の回転数同期が行われる。この際に目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが不一致の場合には入力軸の回転数は目標回転数を超えてさらに増加する。この場合、入力軸の回転数が目標回転数に近くても単位時間当たりの回転数差の変化量、いわゆる回転数差の傾きは大きいままである。周知のように回転数差の傾きは、回転数差の時間微分値である。一方、目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが一致している場合には入力軸の回転数は目標回転数とほぼ同じになる。そのため、回転数差の時間微分値は小さくなる。従って、回転数差の時間微分値に基づいて目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが一致しているか否か判定することができる。 In one form of the speed change control device according to the present invention, the control means applies to the input shaft by the electric motor when the rotation speed of the input shaft becomes equal to or higher than a predetermined determination value lower than the target rotation speed in the determination process. And the time differential value of the rotational speed difference, which is the difference between the rotational speed of the input shaft and the target rotational speed, is determined to be less than or equal to a predetermined inclination determination value. When it is determined in the determination process that the time differential value of the rotation speed difference is equal to or less than the inclination determination value, the target gear stage and the target rotation speed may be reset (claim 2). As is well known, when the gear stage is switched, the rotation of the output shaft is transmitted to the input shaft via the synchro mechanism, and the rotation speed of the input shaft is synchronized. At this time, if the target gear stage and the required gear stage do not match, the rotational speed of the input shaft further increases beyond the target rotational speed. In this case, even if the rotational speed of the input shaft is close to the target rotational speed, the change amount of the rotational speed difference per unit time, that is, the gradient of the so-called rotational speed difference remains large. As is well known, the gradient of the rotational speed difference is a time differential value of the rotational speed difference. On the other hand, when the target gear stage and the required gear stage match, the rotational speed of the input shaft is substantially the same as the target rotational speed. Therefore, the time differential value of the rotational speed difference becomes small. Therefore, it is possible to determine whether or not the target gear stage and the required gear stage match based on the time differential value of the rotational speed difference.
この形態において、前記制御手段は、前記判定処理において前記回転数差の時間微分値が前記傾き判定値以下か否か判定するとともに前記回転数差の2階時間微分値が0未満か否か判定し、前記再設定処理では前記回転数差の時間微分値が前記傾き判定値以下と判定され、かつ前記回転数差の2階時間微分値が0未満と判定された場合に前記目標ギア段及び前記目標回転数をそれぞれ再設定してもよい(請求項3)。周知のように回転数制御では、回転数が目標回転数に到達した後暫くの間目標回転数を挟んで振動することが知られている。このように回転数が振動した場合、回転数と目標回転数との間の回転数差が増加から減少に転じる変曲点が生じる。そして、この変曲点では回転数差の2階時間微分値が0になる。また、回転数差が減少する場合には回転数差の2階時間微分値が0より大きくなる。そのため、目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが一致している場合には入力軸の回転数が目標回転数を挟んで振動し、回転数差の2階時間微分値が0以上になる。これに対して目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが不一致の場合には、上述したように入力軸の回転数は目標回転数を超えてさらに増加するので、回転数差の2階時間微分値は0未満になる。このように回転数差の2階時間微分値を用いても目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが一致しているか否か判定できる。この形態では、回転数差の時間微分値及び回転数差の2階時間微分値の両方を用いて目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが一致しているか否か判定するので、判定精度を向上させることができる。 In this embodiment, the control means determines whether the time differential value of the rotation speed difference is equal to or less than the inclination determination value in the determination process, and determines whether the second-order time differential value of the rotation speed difference is less than 0. In the resetting process, when the time differential value of the rotation speed difference is determined to be equal to or less than the inclination determination value and the second-order time differential value of the rotation speed difference is determined to be less than 0, the target gear stage and Each of the target rotational speeds may be reset (claim 3). As is well known, in the rotational speed control, it is known that the rotational speed vibrates across the target rotational speed for a while after the rotational speed reaches the target rotational speed. When the rotational speed vibrates in this way, an inflection point occurs at which the rotational speed difference between the rotational speed and the target rotational speed turns from increasing to decreasing. At this inflection point, the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference becomes zero. When the rotational speed difference decreases, the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference becomes greater than zero. Therefore, when the target gear stage and the required gear stage match, the rotational speed of the input shaft vibrates across the target rotational speed, and the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference becomes 0 or more. On the other hand, when the target gear stage and the required gear stage do not match, the rotational speed of the input shaft further increases beyond the target rotational speed as described above, so the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference is It becomes less than 0. In this way, it is possible to determine whether or not the target gear stage and the required gear stage match even using the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference. In this embodiment, since it is determined whether or not the target gear stage and the required gear stage match using both the time differential value of the rotational speed difference and the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference, the determination accuracy is improved. be able to.
以上に説明したように、本発明の変速制御装置によれば、目標ギア段と要求ギア段とが不一致の場合にはクラッチ手段を係合状態に維持するので、迅速にトルクを付加することができる。また、目標ギア段が要求ギア段と一致するまで入力軸にトルクを付加するので、シンクロ機構の負荷を低減できる。 As described above, according to the speed change control device of the present invention, when the target gear stage and the required gear stage do not match, the clutch means is maintained in the engaged state, so that the torque can be quickly applied. it can. Further, since torque is applied to the input shaft until the target gear stage matches the required gear stage, the load on the synchro mechanism can be reduced.
図1は、本発明の一形態に係る変速制御装置が組み込まれた車両を模式的に示している。この車両1は、走行用動力源として内燃機関(以下、エンジンと称することがある。)2及び電動機としてのモータ・ジェネレータ(以下、MGと略称することがある。)3を備えている。すなわち、この車両1はハイブリッド車両として構成されている。エンジン2は、4つの気筒を有する周知の火花点火式内燃機関である。エンジン2には、エンジン2を始動するためのスタータ2aが設けられている。MG3は、ハイブリッド車両に搭載されて電動機及び発電機として機能する周知のものである。MG3は、バッテリ4と電気的に接続されている。車両1には変速機10が搭載され、エンジン2及びMG3は変速機10と接続されている。また、変速機10には、車両1の駆動輪5に動力を出力するための出力部6も接続されている。出力部6は、出力ギア7と、駆動輪5に連結されたデファレンシャル機構8とを備えている。出力ギア7は、変速機10の出力軸12に一体回転するように取り付けられている。また、出力ギア7は、デファレンシャル機構8のケースに設けられたリングギア8aと噛み合っている。デファレンシャル機構8は、伝達された動力を左右の駆動輪5に分配する周知のものである。
FIG. 1 schematically shows a vehicle in which a shift control device according to an embodiment of the present invention is incorporated. The
変速機10は、入力軸11と、出力軸12とを備えている。入力軸11と出力軸12との間には、第1〜第5変速ギア対G1〜G5及び後進ギア群GRが設けられている。第1変速ギア対G1は互いに噛み合う第1ドライブギア13及び第1ドリブンギア14にて構成され、第2変速ギア対G2は互いに噛み合う第2ドライブギア15及び第2ドリブンギア16にて構成されている。第3変速ギア対G3は互いに噛み合う第3ドライブギア17及び第3ドリブンギア18にて構成され、第4変速ギア対G4は互いに噛み合う第4ドライブギア19及び第4ドリブンギア20にて構成されている。第5変速ギア対G5は互いに噛み合う第5ドライブギア21及び第5ドリブンギア22にて構成されている。第1〜第5変速ギア対G1〜G5は、ドライブギアとドリブンギアとが常時噛み合うように設けられている。各変速ギア対G1〜G5には互いに異なる変速比が設定されている。変速比は、第1変速ギア対G1、第2変速ギア対G2、第3変速ギア対G3、第4変速ギア対G4、第5変速ギア対G5の順に小さくなるように設定されている。後進ギア群GRは、後進ドライブギア23、中間ギア24、及び後進ドリブンギア25にて構成されている。
The
第1〜第5ドライブギア13、15、17、19、21は、入力軸11に対して相対回転可能なように入力軸11に支持されている。後進ドライブギア23は、入力軸11と一体に回転するように入力軸11に固定されている。この図に示したようにこれらのギアは、後進ドライブギア23、第1ドライブギア13、第2ドライブギア15、第3ドライブギア17、第4ドライブギア19、第5ドライブギア21の順番で軸線方向に並ぶように配置されている。第1〜第5ドリブンギア14、16、18、20、22及び後進ドリブンギア25は、出力軸12と一体に回転するように出力軸12に固定されている。
The first to fifth drive gears 13, 15, 17, 19, and 21 are supported on the input shaft 11 so as to be rotatable relative to the input shaft 11. The
入力軸11には第1〜第4スリーブ26〜29が設けられている。第1〜第3スリーブ26〜28は、入力軸11と一体に回転し、かつ軸線方向に移動可能なように入力軸11に支持されている。第4スリーブ29は、入力軸11に対して相対回転可能かつ軸線方向に移動可能なように入力軸11に支持されている。第1スリーブ26及び第4スリーブ29は、第1ドライブギア13と後進ドライブギア23との間に設けられている。第2スリーブ27は、第2ドライブギア15と第3ドライブギア17との間に設けられている。第3スリーブ28は、第4ドライブギア19と第5ドライブギア21との間に設けられている。
The input shaft 11 is provided with first to
第1スリーブ26は、入力軸11と第1ドライブギア13とが一体に回転するように第1ドライブギア13と噛み合う1速位置と、その噛み合いが解除される解放位置とに切り替え可能に設けられている。第2スリーブ27は、入力軸11と第2ドライブギア15とが一体に回転するように第2ドライブギア15と噛み合う2速位置と、入力軸11と第3ドライブギア17とが一体に回転するように第3ドライブギア17と噛み合う3速位置と、第2ドライブギア15及び第3ドライブギア17のいずれとも噛み合わない解放位置とに切り替え可能に設けられている。第3スリーブ28は、入力軸11と第4ドライブギア19とが一体に回転するように第4ドライブギア19と噛み合う4速位置と、入力軸11と第5ドライブギア21とが一体に回転するように第5ドライブギア21と噛み合う5速位置と、第4ドライブギア19及び第5ドライブギア21のいずれとも噛み合わない解放位置とに切り替え可能に設けられている。なお、図示は省略したが入力軸11には、第1〜第3スリーブ26〜28と第1〜第5ドライブギア13、15、17、19、21とを噛み合わせる際にこれらの回転を同期させる複数のシンクロ機構が設けられている。これらシンクロ機構には、摩擦係合により回転を同期させるシンクロ機構、例えば周知のキー式シンクロメッシュ機構を用いればよい。そのため、シンクロ機構の詳細な説明は省略する。
The
第4スリーブ29は、中間ギア24を回転可能に支持している。中間ギア24は、第4スリーブ29とともに軸線方向に移動する。第4スリーブ29は、中間ギア24が後進ドライブギア23及び後進ドリブンギア25のそれぞれと噛み合うリバース位置と、中間ギア24と各ギア23、25との噛み合いが解除される解放位置とに切り替え可能に設けられている。
The
この図に示すように入力軸11には、第1クラッチ30を介してエンジン2が接続されている。第1クラッチ30は、エンジン2と入力軸11との間で動力が伝達される係合状態と、その動力伝達が遮断される解放状態とに切り替え可能な周知のものである。第1クラッチ30はクラッチペダル9にて操作される。第1クラッチ30は、クラッチペダル9が踏まれた場合に解放状態に切り替わり、その踏み込みが解除されると係合状態に切り替わる。
As shown in this figure, the
MG3のロータ軸3aには、クラッチ手段としての第2クラッチ31と、中間部材32とが設けられている。中間部材32は、ロータ軸3aに相対回転可能に支持されている。中間部材32と出力軸12との間には、常時噛み合い式のギア対33が設けられている。ギア対33は、出力軸12に固定された第1ギア34と、中間部材32に固定されて第1ギア34と噛み合う第2ギア35とを備えている。第2クラッチ31は、ロータ軸3aと入力軸11とが一体に回転するようにこれらを係合する入力軸係合状態と、ロータ軸3aと中間部材32とが一体に回転するようにこれらを係合する出力軸係合状態と、ロータ軸3aが入力軸11及び出力軸12のいずれとも係合しない解放状態とに切り替え可能に構成されている。第2クラッチ31としては、例えばロータ軸3aに一体回転するスリーブを設け、そのスリーブの位置を切り替えて係合先を切り替える周知のクラッチを使用すればよい。
The
変速機10の各スリーブ26〜29は、ドライバが操作するシフトレバー36と接続されている。図2は、シフトレバー36のシフトパターン37を示している。シフトパターン37は、この図の左右方向に延びるセレクト経路38と、そのセレクト経路38から図の上下方向に延びる7つのシフト経路39とを備えている。シフトレバー36は、これらセレクト経路38及び各シフト経路39を移動可能に設けられている。この図に示すように7つのシフト経路39には、1速〜5速、後進R、及びEV走行EVが設定されている。なお、1速〜5速については周知のシフトパターンと同様に数字のみを示す。セレクト経路38には、ニュートラルNが設定されている。
Each
このシフトパターン37において、シフトレバー36が1速に操作された場合、第1スリーブ26が1速位置に、第2〜第4スリーブ27〜29がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36が2速に操作された場合、第2スリーブ27が2速位置に、第1、第3、第4スリーブ26、28、29がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36が3速に操作された場合、第2スリーブ27が3速位置に、第1、第3、第4スリーブ26、28、29がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36が4速に操作された場合、第3スリーブ28が4速位置に、第1、第2、第4スリーブ26、27、29がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36が5速に操作された場合、第3スリーブ28が5速位置に、第1、第2、第4スリーブ26、27、29がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36が後進Rに操作された場合、第4スリーブ29がリバース位置に、第1〜第3スリーブ26〜28がそれぞれ解放位置に切り替わる。シフトレバー36がEV走行EV又はニュートラルNに操作された場合、第1〜第4スリーブ26〜29が解放位置に切り替わる。このようにシフトレバー36と各スリーブ26〜29とは連動するように接続されている。そのため、変速機10はドライバがシフトレバー36を操作して変速を行う、いわゆるマニュアル式変速機として構成されている。
In the
この車両1では、エンジン2、MG3、及び第2クラッチ31の動作を制御することにより複数の走行モードが実現される。複数の走行モードとしては、エンジン2の動力で走行するエンジン走行モード、エンジン2及びMG3の両方の動力で走行するHV走行モード、MG3の動力のみで走行するEV走行モードが設定されている。エンジン走行モード及びHV走行モードは、シフトレバー36が1速〜5速又は後進Rに操作された場合に実行される。なお、エンジン走行モードとHV走行モードの切り替えは、車両1に要求される速度やトルク等に応じて適宜に行われる。EV走行モードは、シフトレバー36がEV走行EVの位置に操作された場合に実行される。
In the
エンジン走行モードでは、エンジン2が運転状態に切り替えられ、第2クラッチ31が解放状態に切り替えられる。そして、変速機10がドライバによって1速〜5速又は後進Rに適宜に切り替えられる。HV走行モードでは、エンジン走行モードの状態から第2クラッチ31が入力軸係合状態又は出力軸係合状態に切り替えられる。そして、MG3を電動機として機能させる。EV走行モードでは、シフトレバー36がEV走行EVに操作されるため上述したように第1〜第4スリーブ26〜29が解放位置に切り替えられる。また、エンジン2を停止させる。第2クラッチ31は出力軸係合状態に切り替えられ、MG3を電動機として機能させる。
In the engine travel mode, the
エンジン2、MG3、及び第2クラッチ31の動作は、制御装置50にて制御される。制御装置50は、マイクロプロセッサ及びその動作に必要なRAM、ROM等の周辺機器を含んだコンピュータユニットとして構成されている。制御装置50は、車両1を適切に走行させるための各種制御プログラムを保持している。制御装置50は、これらのプログラムを実行することによりエンジン2、MG3等の制御対象に対する制御を行っている。制御装置50には、車両1に係る情報を取得するための種々のセンサが接続されている。例えば、クラッチペダル9が踏み込まれているときに信号を出力するクラッチペダルセンサ51、車両1の速度に対応した信号を出力する車速センサ52、及び入力軸11の回転数に対応した信号を出力する入力軸回転数センサ53等が接続されている。また、図2に示すように制御装置50には、シフトレバー36がニュートラルNにあるか否かに対応した信号を出力するニュートラルセンサ54、シフトレバー36がEV走行EVにあるか否かに対応した信号を出力するEV走行センサ55、及びシフトレバー36が後進Rにあるか否かに対応した信号を出力する後進センサ56も接続されている。この他にも制御装置50には種々のセンサが接続されているが、それらの図示は省略した。
Operations of the
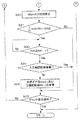
制御装置50は、変速機10に対して変速が要求された場合にその変速を補助する制御を実行する。周知のように変速時にはシンクロ機構にて入力軸11の回転数と変速後に使用されるドライブギアの回転数との同期が行われる。この制御では、変速時にMG3から入力軸11にトルクを付加し、この回転数の同期を補助する。図3及び図4は、制御装置50がこのように変速を補助するために実行する変速補助制御ルーチンを示している。なお、図4は図3に続くフローチャートである。この制御ルーチンは車両1の走行中に所定の周期で繰り返し実行される。また、この制御ルーチンは、制御装置50が実行する他のルーチンと並行に実行される。
The
この制御ルーチンにおいて制御装置50は、まずステップS11で車両1の走行状態を取得する。車両1の走行状態としては、例えば入力軸11の回転数及び車両1の速度等が取得される。次のステップS12において制御装置50は、車両1がフリーラン走行中か否か判定する。フリーラン走行とは、変速機10の各スリーブ26〜29が解放位置であるとともに第2クラッチ31が入力軸接続状態又は解放状態であり、駆動輪5がエンジン2及びMG3から切り離されて車両1が惰性で走行している走行状態を示す。フリーラン走行中ではないと判定した場合には、今回の制御ルーチンを終了する。
In this control routine, the
一方、フリーラン走行中と判定した場合にはステップS13に進み、制御装置50はクラッチペダル9が踏み込まれるクラッチ遮断操作が行われたか否か判定する。この判定は、クラッチペダルセンサ51の出力信号を参照して行えばよい。クラッチ遮断操作が行われていないと判定した場合には今回の制御ルーチンを終了する。一方、クラッチ遮断操作が行われたと判定した場合にはステップS14に進み、制御装置50は所定の入力軸接続条件が成立したか否か判定する。入力軸接続条件は、例えばMG3を出力軸12と接続できず、かつシフトレバー36がニュートラルN、EV走行EV、又は後進Rの位置に無い場合に成立したと判定される。MG3を出力軸12と接続できない場合とは、例えば車両1が高速で走行中の場合等が設定される。また、シフトレバー36がニュートラルN、EV走行EV、又は後進Rの位置に無い場合とは、シフトレバー36が1速〜5速のいずれかのシフト経路39に動かされたことを示す。すなわち、変速機10に対して1速〜5速のいずれかへの変速が要求されたことを示している。入力軸接続条件が不成立と判定した場合には、今回の制御ルーチンを終了する。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the vehicle is in free-running, the process proceeds to step S13, and the
一方、入力軸接続条件が成立したと判定した場合にはステップS15に進み、制御装置50は第2クラッチ31を入力軸係合状態に切り替えてMG3と入力軸11とを接続する。続くステップS16において制御装置50は、目標ギア段Gear_t及び目標回転数Nin_tのそれぞれの初期値を設定する。目標回転数Nin_tは、変速時にMG3で制御すべき入力軸11の回転数である。なお、目標ギア段Gear_tには、初期値として変速機10の最高段すなわち5速が設定される。また、目標回転数Nin_tは、出力軸12の回転数及び5速の変速比に基づいて算出される。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the input shaft connection condition is satisfied, the process proceeds to step S15, and the
次のステップS17において制御装置50は、入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_tから目標補正値N1を引いた値(以下、この値を判定値と称することがある。)未満か否か判定する。目標補正値N1は、入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_tに到達する前にMG3から入力軸11へのトルクの付加を停止するために設定される値である。目標補正値N1は、現在の車速及び目標ギア段Gear_tに基づいて設定される。なお、目標補正値N1は、例えば予め実験や数値計算等により車速及び目標ギア段Gear_tと目標補正値N1との関係を求めて制御装置50のROMにマップとして記憶させておき、そのマップを用いて設定すればよい。入力軸回転数Ninが判定値以上と判定した場合にはステップS18及びS19をスキップしてステップS20に進む。一方、入力軸回転数Ninが判定値未満と判定した場合にはステップS18に進み、制御装置50はMG正トルク付加制御を実行する。このMG正トルク付加制御では、入力軸回転数Ninが上述した判定値になるようにMG3から入力軸11に正トルクを付加する。なお、正トルクとはエンジン2の回転方向に入力軸11が回転するトルクである。次のステップS19において制御装置50は、入力軸回転数Ninが判定値以上か否か判定する。入力軸回転数Ninが判定値未満と判定した場合にはステップS17に戻る。
In the next step S17, the
一方、入力軸回転数Ninが判定値以上と判定した場合にはステップS20に進み、制御装置50はMG3から入力軸11へのトルクの付加を停止する。次のステップS21において制御装置50は、目標回転数Nin_tから現在の入力軸回転数Ninを引いた値である回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値が傾き判定値N2以下か否か判定する。図5は、この変速補助制御ルーチンを実行して変速を行っているときの回転数差sub(Nin)の時間変化の一例を示している。この図には、変速機10が5速に変速されたとき、及び変速機10が4速に変速されたときの回転数差sub(Nin)の時間変化をそれぞれ示す。なお、実線が5速に変速されたときの時間変化を示し、破線が4速に変速されたときの時間変化を示している。この図では時刻T1において変速機10の変速が行われる。上述したようにこの制御では、目標ギア段には初期値として5速が設定される。そのため、実際に5速に変速された場合には、入力軸回転数Ninが判定値未満になったときには実線で示したように回転数差sub(Nin)の単位時間当たりの変化量が小さくなる。これに対して実際には4速に変速された場合には、入力軸回転数Ninが判定値未満になっても破線で示したように回転数差sub(Nin)の単位時間当たりの変化量は大きいままである。回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値とは、この回転数差sub(Nin)の傾きである。そのため、この図から明らかなように実際のギア段と目標ギア段とが一致していた場合には回転数差sub(Nin)の微分値は小さくなり、実際のギア段と目標ギア段とが異なっていた場合には回転数差sub(Nin)の微分値は大きくなる。傾き判定値N2は、実際のギア段と目標ギア段とが一致しているか否かを判定するために設定される。傾き判定値N2は、現在の車速及び目標ギア段Gear_tに基づいて設定される。なお、傾き判定値N2は、例えば予め実験や数値計算等により車速及び目標ギア段Gear_tと傾き判定値N2との関係を求めて制御装置50のROMにマップとして記憶させておき、そのマップを用いて設定すればよい。
On the other hand, if it is determined that the input shaft rotational speed Nin is greater than or equal to the determination value, the process proceeds to step S20, and the
回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値が傾き判定値N2より大きいと判定した場合にはステップS22をスキップしてステップS23に進む。一方、回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値が傾き判定値N2以下と判定した場合にはステップS22に進み、制御装置50は目標ギア段Gear_t及び目標回転数Nin_tを変更する。なお、この処理では、目標ギア段Gear_tをそれまで設定していたギア段よりも1つ小さいギア段に変更する。例えば、それまで5速が設定されていた場合には4速に変更される。目標回転数Nin_tは、変更後の目標ギア段Gear_tと出力軸12の回転数とに基づいて設定される。
If it is determined that the time differential value of the rotational speed difference sub (Nin) is greater than the inclination determination value N2, step S22 is skipped and the process proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, when it is determined that the time differential value of the rotation speed difference sub (Nin) is equal to or smaller than the inclination determination value N2, the process proceeds to step S22, and the
次のステップS23において制御装置50は、クラッチペダル9の踏み込みが解除されるクラッチ係合操作が行われたか否か判定する。クラッチ係合操作が行われていないと判定した場合にはステップS17に戻り、クラッチ係合操作が行われるまでステップS17〜S23の処理を繰り返し実行する。一方、クラッチ係合操作が行われたと判定した場合には今回の制御ルーチンを終了する。
In the next step S23, the
以上に説明したように本発明によれば、まず5速を目標ギア段に設定するので、MG3から入力軸11に付加すべきトルクを低減できる。そして、実際のギア段が目標ギア段Gear_tと異なる場合には第2クラッチ31を解放せず、目標ギア段Gear_tを変更して入力軸11にさらにトルクを付加する。そのため、入力軸11に迅速にトルクを付加することができる。また、目標ギア段Gear_tが実際のギア段と一致するまで入力軸11の回転数同期を補助することができる。従って、シンクロ機構に掛かる負荷を低減できる。
As described above, according to the present invention, since the fifth gear is first set as the target gear stage, the torque to be applied from the
周知のように入力軸11の回転数が目標回転数Nin_tに到達するまでトルクを付加すると、入力軸11の回転数が目標回転数Nin_tに到達した後にさらに大きくなる可能性がある。この場合、入力軸11の回転数を目標回転数Nin_tに合わせようとして回転数が振動する。これに対して本発明では、入力軸11の回転数が目標回転数Nin_tに到達する前に入力軸11へのトルクの付加を停止する。そのため、入力軸11の回転数が目標回転数Nin_tに到達した後に回転数が振動することを軽減できる。 As is well known, if torque is applied until the rotational speed of the input shaft 11 reaches the target rotational speed Nin_t, the rotational speed of the input shaft 11 may further increase after reaching the target rotational speed Nin_t. In this case, the rotational speed vibrates so as to match the rotational speed of the input shaft 11 with the target rotational speed Nin_t. On the other hand, in the present invention, the application of torque to the input shaft 11 is stopped before the rotational speed of the input shaft 11 reaches the target rotational speed Nin_t. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the vibration of the rotation speed after the rotation speed of the input shaft 11 reaches the target rotation speed Nin_t.
なお、変速補助制御ルーチンを実行することにより制御装置50が本発明の制御手段として機能する。また、ステップS16が本発明の初期値設定処理に相当し、ステップS18が本発明のトルク付加処理に相当する。さらにステップS19〜S21が本発明の判定処理に相当し、ステップS22が再設定処理に相当する。
The
図6を参照して変速補助制御ルーチンの変形例について説明する。なお、図6ではこの変形例の制御ルーチンの一部を示す。この変形例では、上述した変速補助制御ルーチンと比較してステップS21とステップS22との間にステップS30、S31が追加されている点が異なり、その以外は同じである。そのため、同じ処理には同じ符号を付して説明を省略する。この図ではステップS20以降の処理を示す。この変形例でもステップS20より前の処理は図3が参照される。 A modification of the shift assist control routine will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 6 shows a part of the control routine of this modification. This modification is different from the above-described shift assist control routine in that steps S30 and S31 are added between step S21 and step S22, and the rest is the same. For this reason, the same processes are denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof is omitted. In this figure, the process after step S20 is shown. Also in this modification, FIG. 3 is referred to for the process before step S20.
上述したように変速機10の各スリーブ26〜29はシフトレバー36と連動するように接続されている。そのため、各スリーブ26〜29が動く速度はドライバがシフトレバー36を操作する力(以下、シフト操作力と称することがある。)の大きさや操作する速度(以下、シフト操作速度と称することがある。)に応じて変化する。図7は、変速時における入力軸11の回転数の時間変化の一例を示している。なお、この図の実線SL1〜SL3はシフト操作力が小さいときの入力軸11の回転数の時間変化を示し、破線BL1〜BL3はシフト操作力が大きいときの入力軸11の回転数の時間変化を示している。また、この図の回転数Nin_5thは目標ギア段が5速のときの目標回転数を、回転数Nin_4thは目標ギア段が4速のときの目標回転数を、回転数Nin_3rdは目標ギア段が3速のときの目標回転数をそれぞれ示している。
As described above, the
シフト操作力が大きい場合は、シンクロ機構のシンクロリングがドライブギアのコーン部に押し付けられる力(以下、押付力と称することがある。)が大きい。そのため、この図に破線BL1〜BL3で示したように入力軸回転数が速やかに上昇する。一方、シフト操作力が小さい場合はこの押付力が小さいため、図に実線SL1〜SL3で示したように入力軸回転数がゆっくりと上昇する。このように変速時における入力軸回転数の時間変化は、シフト操作力に応じて変化する。シフト操作力が大きく入力軸11の回転数が速やかに上昇した場合、目標ギア段Gear_tと実際のギア段とが一致していても回転数差sub(Nin)の傾きが大きくなる可能性がある。そのため、目標ギア段Gear_tと実際のギア段とが一致しているか否かを回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値のみで判定すると誤判定するおそれがある。そこで、この変形例ではシフト操作力やシフト操作速度を考慮して目標ギア段を変更すべきか否か判定する。 When the shift operation force is large, the force (hereinafter sometimes referred to as pressing force) by which the synchro ring of the synchro mechanism is pressed against the cone portion of the drive gear is large. As a result, the input shaft speed rapidly increases as indicated by broken lines BL1 to BL3 in this figure. On the other hand, when the shift operation force is small, the pressing force is small, so that the input shaft rotational speed slowly increases as indicated by solid lines SL1 to SL3 in the figure. Thus, the time change of the input shaft rotation speed at the time of shifting changes according to the shift operation force. When the shift operation force is large and the rotation speed of the input shaft 11 rapidly increases, the inclination of the rotation speed difference sub (Nin) may increase even if the target gear stage Gear_t matches the actual gear stage. . For this reason, if it is determined only by the time differential value of the rotational speed difference sub (Nin) whether or not the target gear stage Gear_t and the actual gear stage coincide with each other, there is a risk of erroneous determination. Therefore, in this modification, it is determined whether or not the target gear stage should be changed in consideration of the shift operation force and the shift operation speed.
この変形例の変速補助制御ルーチンにおいて制御装置50は、ステップS21までは図3に示した制御ルーチンと同様に処理を進める。ステップS21において回転数差sub(Nin)の時間微分値が傾き判定値N2以下と判定した場合にはステップS30に進み、制御装置50は入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_t以上か否か判定する。入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_t未満の場合には入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_t以上になるまでこの処理を繰り返し実行する。入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_t以上の場合にはステップS31に進み、制御装置50は入力軸回転数Ninが振動しているか否か判定する。図8は図7の範囲Aを拡大して示している。なお、この図では実線SL3の図示を省略した。この図に示したように目標ギア段と実際のギア段とが一致している場合、入力軸回転数Ninは目標回転数Nin_tに到達した後に振動する。この振動は1速〜5速のいずれのギア段においても同様に生じる。そのため、この振動が検出された場合には目標ギア段と実際のギア段とが一致していると判断できる。入力軸回転数Ninが振動している場合には、入力軸回転数Ninが増加から減少に転じる変曲点が生じる。そこで、この処理では入力軸回転数Ninが目標回転数Nin_t以上の所定の回転数範囲内にあるときに以下の式(1)を用いて入力軸回転数Ninが振動しているか否か判定する。
In the shift assist control routine of this modification, the
この式(1)に示すように、回転数差sub(Nin)の2階時間微分値が0未満の場合は変曲点が生じていない。そのため、入力軸回転数Ninが振動していないと判定できる。なお、所定の回転数範囲としては例えば図8に示すように目標回転数Nin_tとその目標回転数Nin_tに所定値αを加えた範囲上限値Nin_t+αとの間が設定される。所定値αには、範囲上限値Nin_t+αが入力軸回転数Ninの振動時の上限値よりも若干高くなるように適宜に設定すればよい。 As shown in this equation (1), when the second-order time differential value of the rotation speed difference sub (Nin) is less than 0, no inflection point has occurred. Therefore, it can be determined that the input shaft speed Nin is not vibrating. As the predetermined rotation speed range, for example, as shown in FIG. 8, a range between a target rotation speed Nin_t and a range upper limit value Nin_t + α obtained by adding a predetermined value α to the target rotation speed Nin_t is set. The predetermined value α may be set appropriately so that the range upper limit value Nin_t + α is slightly higher than the upper limit value during vibration of the input shaft rotational speed Nin.
入力軸回転数Ninが振動していると判定した場合にはステップS23に進む。一方、入力回転数Ninが振動していないと判定した場合にはステップS22に進む。ステップS22又はS23以降は、図3、図4に示した変速補助制御ルーチンと同様に処理を進める。 If it is determined that the input shaft speed Nin is vibrating, the process proceeds to step S23. On the other hand, when it determines with the input rotation speed Nin not vibrating, it progresses to step S22. After step S22 or S23, the process proceeds in the same manner as the shift assist control routine shown in FIGS.
この変形例では、目標ギア段が実際のギア段と一致しているか否かを回転数差sub(Nin)の2階時間微分値を用いても判定する。そのため、ドライバのシフト操作力の大小のバラツキに基づく目標ギア段の誤判定を防止できる。このように判定精度を向上させることによりシンクロ機構の負荷をさらに軽減することができる。 In this modification, it is also determined using the second-order time differential value of the rotational speed difference sub (Nin) whether or not the target gear stage matches the actual gear stage. Therefore, it is possible to prevent erroneous determination of the target gear stage based on the variation in the shift operation force of the driver. Thus, by improving the determination accuracy, the load on the synchro mechanism can be further reduced.
なお、この変形例では、ステップS19〜21、S30、及びS31が本発明の判定処理に相当する。 In this modification, steps S19 to S21, S30, and S31 correspond to the determination process of the present invention.
本発明は、上述した形態に限定されることなく、種々の形態にて実施することができる。例えば、本発明が適用される変速機は最高段が5速の変速機に限定されない。本発明は4速又は6速が最高段の変速機に適用してもよい。この場合、目標ギア段の初期値にはそれらの変速機の最高段が設定される。すなわち、最高段が6速の変速機であれば目標ギア段の初期値には6速が設定される。 The present invention is not limited to the above-described form and can be implemented in various forms. For example, the transmission to which the present invention is applied is not limited to a transmission having a maximum speed of 5 speeds. The present invention may be applied to a transmission in which the fourth speed or the sixth speed is the highest. In this case, the highest stage of these transmissions is set as the initial value of the target gear stage. That is, if the highest gear is a six-speed transmission, the initial value of the target gear is set to sixth.
本発明に設けられる変速機のシンクロ機構は、キー式シンクロメッシュ機構に限定されない。本発明に設けられる変速機には、変速時に摩擦力を利用して回転軸とギアとの同期を行う種々のシンクロ機構を設けてよい。また、変速機は、シンクロ機構が入力軸に設けられた変速機に限定されない。例えば、各ドライブギアが入力軸に一体回転するように設けられるとともに各ドリブンギアが出力軸に相対回転可能に支持され、かつ出力軸とドリブンギアとの間にシンクロ機構が設けられた変速機であってもよい。 The synchromesh mechanism of the transmission provided in the present invention is not limited to the key type synchromesh mechanism. The transmission provided in the present invention may be provided with various synchro mechanisms that synchronize the rotating shaft and the gear by using frictional force during shifting. Further, the transmission is not limited to a transmission in which a synchronization mechanism is provided on the input shaft. For example, a transmission in which each drive gear is provided to rotate integrally with an input shaft, each driven gear is supported so as to be relatively rotatable with respect to an output shaft, and a synchro mechanism is provided between the output shaft and the driven gear. There may be.
1 車両
3 モータ・ジェネレータ(電動機)
5 駆動輪
10 変速機
11 入力軸
12 出力軸
31 第2クラッチ(クラッチ手段)
36 シフトレバー
50 制御装置(制御手段)
N2 傾き判定値
1
5 Drive
36
N2 inclination judgment value
Claims (3)
前記変速機には、ギア段の切替時に切替後に使用されるギアとそのギアが設けられた軸とを摩擦力を利用して同期させるシンクロ機構が設けられているハイブリッド車両に適用される変速制御装置において、
前記変速機に対してギア段の切り替えが要求された場合に、まず前記複数のギア段のうち変速比が最も小さいギア段を目標ギア段に設定するとともに設定した目標ギア段の変速比及び前記出力軸の回転数に基づいて目標回転数を設定する初期値設定処理を実行し、次に前記クラッチ手段を前記入力軸と前記電動機とが係合される係合状態に切り替えるとともに前記入力軸の回転数が前記目標回転数に調整されるように前記電動機から前記入力軸にトルクを付加するトルク付加処理を実行し、その後前記目標ギア段が前記変速機に対して要求されたギア段である要求ギア段と一致しているか否か判定する判定処理を実行し、前記判定処理にて前記目標ギア段と前記要求ギア段が不一致と判定された場合には前記クラッチ手段を前記係合状態に維持し、かつ前記複数のギア段のうち前記判定処理の実行時に前記目標ギア段に設定されていたギア段の次に変速比が小さいギア段を前記目標ギア段に再設定するとともに再設定した目標ギア段と前記出力軸の回転数に基づいて前記目標回転数を再設定する再設定処理を実行し、前記判定処理にて前記目標ギア段と前記要求ギア段とが一致していると判定されるまで前記トルク付加処理、前記判定処理、及び前記再設定処理を繰り返し実行する制御手段を備えている変速制御装置。 A manual type transmission having a plurality of gear stages with different speed ratios set to each other, the gear stage being switched by operating a shift lever, and a clutch means connected to the input shaft of the transmission A drive wheel connected to the output shaft of the transmission so as to be able to transmit power,
Shift control applied to a hybrid vehicle provided with a synchro mechanism that synchronizes a gear used after switching at the time of switching of a gear stage and a shaft provided with the gear by using frictional force in the transmission. In the device
When the transmission is requested to change gear positions, the gear stage having the smallest gear ratio among the plurality of gear stages is first set as the target gear stage, and the gear ratio of the set target gear stage and the An initial value setting process for setting a target rotational speed based on the rotational speed of the output shaft is performed, and then the clutch means is switched to an engaged state in which the input shaft and the electric motor are engaged, and the input shaft Torque addition processing for adding torque from the electric motor to the input shaft is executed so that the rotation speed is adjusted to the target rotation speed, and then the target gear stage is a gear stage requested for the transmission. A determination process is performed to determine whether or not the required gear stage matches, and if the target gear stage and the required gear stage are determined to be inconsistent in the determination process, the clutch means is brought into the engaged state. Wei And, among the plurality of gear stages, the gear stage having the next smallest gear ratio after the gear stage that has been set as the target gear stage at the time of execution of the determination process is reset to the target gear stage and reset. A reset process for resetting the target rotational speed is executed based on the gear speed and the rotational speed of the output shaft, and it is determined in the determination process that the target gear speed and the required gear speed are the same. A shift control apparatus comprising control means for repeatedly executing the torque addition process, the determination process, and the resetting process until a predetermined time is reached.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011227825A JP2013086612A (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2011-10-17 | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011227825A JP2013086612A (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2011-10-17 | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013086612A true JP2013086612A (en) | 2013-05-13 |
Family
ID=48530972
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011227825A Pending JP2013086612A (en) | 2011-10-17 | 2011-10-17 | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2013086612A (en) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020515790A (en) * | 2017-04-04 | 2020-05-28 | ツェットエフ、フリードリッヒスハーフェン、アクチエンゲゼルシャフトZf Friedrichshafen Ag | Vehicle drive train |
-
2011
- 2011-10-17 JP JP2011227825A patent/JP2013086612A/en active Pending
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020515790A (en) * | 2017-04-04 | 2020-05-28 | ツェットエフ、フリードリッヒスハーフェン、アクチエンゲゼルシャフトZf Friedrichshafen Ag | Vehicle drive train |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5962780B2 (en) | Hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5648698B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2014058286A (en) | Control unit of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5198645B1 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2012187962A (en) | Vehicle control device | |
| JP5811262B2 (en) | Hybrid vehicle start control device | |
| JP5812181B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2013035403A (en) | Hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2013060043A (en) | Power transmission device for vehicle | |
| JP2013141938A (en) | Start control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5353820B2 (en) | Drive control device | |
| JP2013151261A (en) | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2013086612A (en) | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5929738B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2014094596A (en) | Gear shift controller for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5836048B2 (en) | transmission | |
| JP6036328B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5890154B2 (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2013086542A (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP5712938B2 (en) | Vehicle transmission control device | |
| JP2013103655A (en) | Control device for hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2011133032A (en) | Controller for vehicular stepped transmission | |
| JP2018039430A (en) | Power transmission system and control device | |
| JP2016164069A (en) | Speed change control device of hybrid vehicle | |
| JP2018105316A (en) | Display control device |