JP2012066479A - Method of splitting brittle material substrate with resin - Google Patents
Method of splitting brittle material substrate with resin Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2012066479A JP2012066479A JP2010213157A JP2010213157A JP2012066479A JP 2012066479 A JP2012066479 A JP 2012066479A JP 2010213157 A JP2010213157 A JP 2010213157A JP 2010213157 A JP2010213157 A JP 2010213157A JP 2012066479 A JP2012066479 A JP 2012066479A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- brittle material
- resin
- material substrate
- dividing
- scribe line
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B28—WORKING CEMENT, CLAY, OR STONE
- B28D—WORKING STONE OR STONE-LIKE MATERIALS
- B28D5/00—Fine working of gems, jewels, crystals, e.g. of semiconductor material; apparatus or devices therefor
- B28D5/0005—Fine working of gems, jewels, crystals, e.g. of semiconductor material; apparatus or devices therefor by breaking, e.g. dicing
- B28D5/0011—Fine working of gems, jewels, crystals, e.g. of semiconductor material; apparatus or devices therefor by breaking, e.g. dicing with preliminary treatment, e.g. weakening by scoring
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B43/00—Operations specially adapted for layered products and not otherwise provided for, e.g. repairing; Apparatus therefor
- B32B43/003—Cutting
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Processing Of Stones Or Stones Resemblance Materials (AREA)
- Dicing (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、脆性材料基板を分割する方法に関し、特に、樹脂を接着させたセラミック基板を分割する方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a method for dividing a brittle material substrate, and more particularly to a method for dividing a ceramic substrate to which a resin is bonded.
LTCC(Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics)やHTCC(High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics)などのセラミックスその他の脆性材料を用いて構成された脆性材料基板(主面や内部に電気回路等が形成されたものを含む)を分割し、複数の分割個片に切り出す手法には、種々のものがある。例えば、スクライビングホイールなどを用いて脆性材料基板の分割予定位置にスクライブラインを形成することで、スクライブラインに沿って脆性材料基板の厚み方向に垂直クラックを形成しておき、その後、外力(荷重)を印加することによって垂直クラックを脆性材料基板の厚み方向に伸展させることで、脆性材料基板をブレイクする態様が公知である(例えば、特許文献1参照)。係る場合、スクライブラインに沿って形成される垂直クラックが脆性材料基板の厚み方向に伸展して裏面に到達することによって、脆性材料基板がブレイクされる。あるいは脆性材料基板の製造過程において分割予定位置にあらかじめV字状の溝(V溝などと呼ばれる)が形成され、V溝に沿ってブレイクがなされる場合もある。V溝は、セラミックスの前駆体(セラミックスグリーンシートの積層体)の段階で形成されるのが一般的である。 A brittle material substrate made of ceramics or other brittle materials such as LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics) or HTCC (High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics) There are various methods for dividing the image into a plurality of divided pieces. For example, by forming a scribe line at a planned division position of the brittle material substrate using a scribing wheel or the like, a vertical crack is formed in the thickness direction of the brittle material substrate along the scribe line, and then external force (load) A mode in which a brittle material substrate is broken by applying a vertical crack in the thickness direction of the brittle material substrate by applying is known (for example, see Patent Document 1). In such a case, the vertical crack formed along the scribe line extends in the thickness direction of the brittle material substrate and reaches the back surface, whereby the brittle material substrate is broken. Alternatively, in the process of manufacturing the brittle material substrate, a V-shaped groove (referred to as a V-groove or the like) is formed in advance at a position to be divided, and a break may occur along the V-groove. The V-groove is generally formed at the stage of a ceramic precursor (ceramic green sheet laminate).
脆性材料基板には、主面に形成された回路の保護などを目的として、ガラスエポキシなどの熱硬化性樹脂を該主面に付着させたもの(樹脂付き脆性材料基板)がある。係る樹脂付き脆性材料基板を上述の手法にて脆性材料基板の側からブレイクする場合、脆性材料基板と樹脂とでは材質が異なることが原因で、垂直クラックが樹脂部分まで伸展しない、もしくは樹脂部分を貫通しない、という不具合が生じることがある。あるいは、クラックが垂直に伸展せず、ソゲなどと称される斜め割れが生じてしまう場合もある。 There is a brittle material substrate in which a thermosetting resin such as glass epoxy is attached to the main surface (brittle material substrate with resin) for the purpose of protecting a circuit formed on the main surface. When the brittle material substrate with resin is broken from the side of the brittle material substrate by the above-described method, the vertical crack does not extend to the resin portion because the material is different between the brittle material substrate and the resin, or the resin portion is The problem of not penetrating may occur. Alternatively, the crack may not extend vertically, and an oblique crack called soge may occur.
また、熱硬化性樹脂を付着させる過程において、脆性材料基板に反りが生じてしまうことが原因で、ブレイクによって切り出された分割個片の寸法精度(平坦性)が悪いという問題もある。この問題は、V溝が形成されない脆性材料基板の場合に顕著である。 Further, there is a problem that the dimensional accuracy (flatness) of the divided pieces cut out by the break is poor because the brittle material substrate is warped in the process of attaching the thermosetting resin. This problem is remarkable in the case of a brittle material substrate in which no V-groove is formed.
本発明は上記課題に鑑みてなされたものであり、従来よりも確実性が高く、かつ、寸法精度の向上した樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法を提供することを目的とする。 The present invention has been made in view of the above problems, and an object of the present invention is to provide a method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin having higher reliability and improved dimensional accuracy.
上記課題を解決するため、請求項1の発明は、脆性材料基板の一主面に樹脂が付着してなる樹脂付き脆性材料基板を主面に垂直に分割する方法であって、前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板の樹脂側の分割予定位置に溝部を形成する溝部形成工程と、前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板の脆性材料基板側の分割予定位置にスクライブラインを形成するスクライブライン形成工程と、スクライブラインに沿って前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割するブレイク工程と、を備えることを特徴とする。
In order to solve the above-mentioned problem, the invention of
請求項2の発明は、請求項1に記載の樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法であって、前記ブレイク工程が前記脆性材料基板の主面上であって前記脆性材料基板側の分割予定位置に対して対称な2つの位置と、前記樹脂側の主面であって前記スクライブラインに沿って形成される垂直クラックの前記脆性材料基板の厚み方向の延長線上の位置とに対し、所定の付勢部材にて付勢することによって、前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割するブレイク工程と、を備えることを特徴とする。
Invention of
請求項3の発明は、請求項1または請求項2に記載の樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法であって、前記スクライブライン形成工程が前記脆性材料基板に前記スクライブラインを形成することによって前記スクライブラインに沿って前記脆性材料基板の厚み方向に伸展した垂直クラックを形成させる工程であり、前記ブレイク工程が、前記垂直クラックを前記溝部へと伸展させることによって前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割する工程である、ことを特徴とする。
The invention of
請求項4の発明は、請求項1ないし請求項3のいずれかに記載の樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法であって、前記溝部形成工程がダイサーにより前記溝部を形成する工程である、ことを特徴とする。
Invention of
請求項5の発明は、請求項1ないし請求項4のいずれかに記載の樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法であって、前記脆性材料基板がLTCCまたはHTCCであることを特徴とする。 A fifth aspect of the present invention is the method for dividing a brittle material substrate with a resin according to any one of the first to fourth aspects, wherein the brittle material substrate is LTCC or HTCC.
請求項1ないし請求項5の発明によれば、樹脂付き脆性材料基板をその主面に対して垂直な分割予定位置にて確実に、しかも、優れた寸法精度にて分割することができる。 According to the first to fifth aspects of the present invention, it is possible to divide the brittle material substrate with resin reliably at an expected division position perpendicular to the main surface and with excellent dimensional accuracy.
<樹脂付き脆性材料基板>
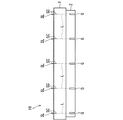
図1は、本実施の形態において分割の対象となる樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を示す模式図である。樹脂付き脆性材料基板10は、LTCC(Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramics)やHTCC(High Temperature Co-fired Ceramics)などのセラミックスその他の脆性材料を用いて構成された脆性材料基板1の一方の主面1aに、ガラスエポキシなどの熱硬化性樹脂(以下、単に樹脂とも称する)2を付着させたものである。なお、本実施の形態において、脆性材料基板1は、主面や内部に電気回路等が形成されたものを含むものとする。樹脂2は、例えば主面に形成された回路の保護などを目的として、設けられてなる。なお、図1においては、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10が水平方向(図面視左右方向)に平坦であるように示しているが、実際には、樹脂2の硬化時の収縮に伴って脆性材料基板1の主面1aに圧縮応力が作用し、脆性材料基板1には図面視上方に凸となる反りが生じている場合がある。
<Brittle substrate with resin>
FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing a
また、図1においては、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の分割予定位置を表す分割予定線Lを破線にて示している。本実施の形態においては、分割予定位置は脆性材料基板1の主面1a、1bに垂直に設定されるものとする。また、分割予定線Lの脆性材料基板1側の端部(主面1bとの交差位置)を特に分割予定位置P1と称し、樹脂2側の端部(主面2aとの交差位置)を分割予定位置P2と称することとする。係る場合において、分割予定位置P1および分割予定位置P2は、紙面に垂直な方向に延在する直線である。
Moreover, in FIG. 1, the division | segmentation planned line L showing the division | segmentation planned position of the brittle material board |
なお、図1における脆性材料基板1と樹脂2とのサイズや、樹脂2の付着態様はあくまで例示に過ぎない。脆性材料基板1および樹脂2のいずれも、それぞれの目的に照らして適宜のサイズが選択されてよい。特に限定されるものではないが、例えば、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の厚みは0.3〜3mm程度、脆性材料基板1の厚みは0.1〜2mm程度、樹脂2の厚みは0.1〜2mm程度とすることができる。また、図1においては(以降の図においても同様)、5箇所の分割予定位置(5本の分割予定線L)が示されているが、これも例示に過ぎない。
In addition, the size of the
<樹脂付き材料基板の分割>
図2は、本実施の形態において樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を分割する処理の手順を示す図である。以降、図2に示す手順に沿って、本実施の形態に係る樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割処理の詳細を説明する。
<Division of material substrate with resin>
FIG. 2 is a diagram showing a processing procedure for dividing the
まず、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を用意する(ステップS1)。係る樹脂付き脆性材料基板10には、図1に示したように、脆性材料基板1の主面1a、1bに垂直な分割予定位置が設定されているものとする。そして、用意した樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の樹脂2側の分割予定位置P2に、溝部形成加工を行う(ステップS2)。溝部形成加工は、ダイサー(ダイシングソー)、レーザービームその他の公知の加工手段の中から、適宜のものを選択して行うことができる。
First, a
図3は、ダイサー100を用いて溝部形成加工を行う様子を示す模式図である。図4は、係る溝部形成加工によって溝部Gが形成された樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を示す図である。
FIG. 3 is a schematic diagram showing a state in which the groove forming process is performed using the
ダイサー100を用いて溝部形成加工を行う場合、まず、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10が、樹脂2の主面2aが被加工面となるように、脆性材料基板1の主面1bを載置面としてダイサー100のステージ101の上に載置固定される。そして、外周部分がダイヤモンドなどを材質とする研削用の刃先となっている円板状のブレード102が溝部Gの深さに見合った高さ位置に調整される。そして、図示しない駆動手段によりブレード102を軸102aを中心に矢印AR1に示すように回転させつつ、分割予定位置P2に沿ってステージ101を矢印AR2に示すように移動させるかあるいはブレード102を矢印AR3に示すように移動させることによって、溝部Gが形成される。全ての分割予定位置P2に対して、同様の加工が行われた状態を示すのが、図4である。
When the groove forming process is performed using the
溝部Gの深さは、脆性材料基板1および樹脂2の材質、硬度、厚みなどによって、適宜に定められてよい。特に限定されるものではないが、例えば、溝部Gの深さは、樹脂2の厚みの30〜90%程度とすることができる。なお、図4においては断面視矩形状に溝部Gが形成されてなるが、溝部Gの断面形状は、必ずしも矩形には限られない。
The depth of the groove G may be appropriately determined depending on the material, hardness, thickness, and the like of the
溝部Gが形成されることで、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10においては、脆性材料基板1の主面1aに作用していた圧縮応力が緩和される。これにより、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の反りが低減される。
By forming the groove part G, the compressive stress acting on the
溝部Gの形成が完了すると、続いて、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の脆性材料基板1側の分割予定位置P1に対し、スクライブ加工を行う(ステップS3)。
When the formation of the groove portion G is completed, a scribing process is subsequently performed on the planned division position P1 on the
図5は、スクライブ加工を行うスクライブ装置200を例示する図である。図6は、スクライブ加工によってスクライブラインSLが形成され、スクライブラインSLに沿って脆性材料基板の厚み方向に伸展した垂直クラックSCが形成された樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を示す図である。
FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating a
スクライブ装置200は、被加工物を載置固定するためのテーブル201と、テーブル201を紙面に垂直な方向に移動自在に案内する一対のガイドレール202と、先端部分にスクライブラインを形成するカッターホイール203を備えるスクライブヘッド204と、スクライブヘッド204を矢印AR4にて示すように、昇降自在に備え、かつ、矢印AR4にて示すように図面視左右方向に摺動自在な態様にてガイドバー205に取り付けられてなる摺動部206と、を主として備える。
The
カッターホイール203は、円周部分の断面が円錐形をなす円板状の部材である。また、カッターホイール203は、その円板状部分の中心をスクライブヘッド204に軸支されてなることで、外力によって回転自在とされてなる。カッターホイール203は、例えば超硬合金、焼結ダイヤモンド、SUS、SKH(工具鋼)、サファイア等などをその材質とする。
The cutter wheel 203 is a disk-shaped member in which a cross section of a circumferential portion forms a conical shape. The cutter wheel 203 is made rotatable by an external force by being pivotally supported by the
スクライブ装置200を用いて樹脂付き脆性材料基板10のスクライブ加工を行う場合は、まず、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10が、脆性材料基板1の主面1bが被加工面となるように、樹脂2の主面2aを載置面としてスクライブ装置200のテーブル201の上に載置固定される。この状態で、カッターホイール203を分割予定位置P1に当接させつつ摺動部206を図面視で左から右、あるいは右から左に移動させると、分割予定位置P1にスクライブラインSLが形成され、スクライブラインSLに沿って脆性材料基板1の厚み方向に垂直クラックSCが伸展する。全ての分割予定位置P1に対して、同様の加工が行われた状態を示すのが、図6である。
When scribing the
図6に示すように、スクライブ加工後の樹脂付き脆性材料基板10は、溝部GとスクライブラインSLおよび垂直クラックSCとが同一の分割予定線L上に形成された状態となっている。
As shown in FIG. 6, the
スクライブラインSLおよび垂直クラックSCの深さの総和は、脆性材料基板1および樹脂2の材質、硬度、厚みや、溝部Gの深さなどにもよるが、少なくとも、脆性材料基板1の厚みの10%程度以上であることが望ましい。係る場合、後段の過程において樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を好適に分割することができる。
The total depth of the scribe lines SL and vertical cracks SC is at least 10 times the thickness of the
スクライブラインSLおよび垂直クラックSCが形成されると、続いて、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10をスクライブラインSLおよび垂直クラックSCに沿ってブレイクするブレイク加工を行う(ステップS4)。
After the scribe line SL and the vertical crack SC are formed, a break process is performed to break the
図7は、ブレイク加工を行うブレイク装置300の様子を示す模式断面図である。図8は、ブレイク加工後の樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を示す図である。
FIG. 7 is a schematic cross-sectional view showing a state of the
ブレイク装置300は、被加工物が粘着固定された弾性フィルム301をその端縁部にて水平に開帳しつつ保持するフレーム302と、被加工物より上側にて上下動する2つの上側ブレイクバー303(303a、303b)と、被加工物より下側にて上下動する1つの下側ブレイクバー304とを主として備える。2つの上側ブレイクバー303a、303bは、水平方向(図面視左右方向)において離間配置されてなる。好ましくは、両者の離間距離は調節可能とされてなる。また、下側ブレイクバー304は、水平方向において2つの上側ブレイクバー303a、303bから等距離の位置に配置されてなる。
The
ブレイク装置300を用いて樹脂付き脆性材料基板10のブレイクを行う場合、まず、樹脂2の主面2aを固定面として樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を弾性フィルム301の粘着面301aに粘着固定する。そして、粘着面301aが上方となる状態で、弾性フィルム301をフレーム302にて開帳する。
In the case where the
続いて、下側ブレイクバー304を弾性フィルム301とは離間させた状態でブレイクの対象となる分割予定線L(以下、対象分割予定線)の延長線上の位置に配置する。そして、2つの上側ブレイクバー303a、303bを脆性材料基板1とは離間させた状態で該分割予定線Lに対して対称となるように、所定の間隔で離間配置する。この状態で、2つの上側ブレイクバー303を下降させてそれぞれの先端303eを脆性材料基板1の主面1bに当接させるとともに、下側ブレイクバー304を上昇させてその先端304eを弾性フィルム301を介して樹脂2の主面2aに当接させる。これによって、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10は、上側ブレイクバー303によって鉛直下向きに、下側ブレイクバー304によって鉛直上向きに付勢される。すると、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10には、対象分割予定線の位置において3点曲げの応力が作用する。係る応力が作用すると、当該位置のスクライブラインSLに沿って形成された垂直クラックSCから該対象分割予定線に沿ったクラック伸展が生じ、直下の溝部Gにまで達する垂直なクラックCRが形成される。このクラックCRの形成によって、対象分割予定線の位置におけるブレイクがなされたことになる。
Subsequently, the
なお、図7においては、上側ブレイクバー303の先端303eと下側ブレイクバー304の先端304eとが断面視鋭角をなしており、脆性材料基板1または弾性フィルム301に線接触する(図7に示す断面においては点接触となっている)態様を例示しているが、これは必須ではなく、先端303eおよび先端304eが断面視矩形状をなしており、脆性材料基板1または弾性フィルム301に面接触する態様であってもよい。
In FIG. 7, the tip 303e of the
全ての分割予定線Lに対して、同様の加工が行われた状態を示すのが、図8である。本実施の形態に係る分割方法を用いた場合、クラックCRは脆性材料基板1に設けたスクライブラインSLに沿って形成された垂直クラックSCから分割予定線Lに沿って樹脂2の溝部Gへと垂直に、しかも確実に(再現性よく)伸展する。なお、ブレイク加工の後においては、図8に示すように複数の分割個片11同士がクラックCRにおいて略接触した状態となっているが、当然ながら、それぞれの分割個片11は物理的には別体のものであって、個別に取り扱うことが可能である。
FIG. 8 shows a state in which the same processing is performed on all the division lines L. When the dividing method according to the present embodiment is used, the crack CR extends from the vertical crack SC formed along the scribe line SL provided on the
図9は、対比のために示す、溝部形成加工を行わなかったほかは上述と同様の手順にて加工を行った樹脂付き脆性材料基板10についての、ブレイク加工後の様子を示す図である。係る場合、図9に示すように、樹脂2において分割予定線Lからずれた斜めのクラック(クラックCR1やクラックCR2)が形成されることで斜め割れが生じたり、樹脂2の途中までしか伸展しないクラック(クラックCR3やクラックCR4)や、あるいは、脆性材料基板1の範囲のみでしか伸展しないクラック(クラックCR5)が形成されるに留まる場合もある。また、仮に良好な分割が行えたとしても、ブレイクに際し、本実施の形態の場合に比してより大きな力を樹脂付き脆性材料基板10に与える必要がある。これらのことは、本実施の形態のように、あらかじめ樹脂2に溝部Gを形成しておくことが、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を良好にブレイクするうえで効果があることを意味している。
FIG. 9 is a view showing a state after the break processing of the
また、本実施の形態においては、上述したように溝部Gの形成によって反りを低減させたうえで、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を分割しているので、それぞれの分割個片11についても、反りが低減されたものとなっている。すなわち、分割個片11は、従来よりも寸法精度(平坦性)が優れたものであるということができる。
Further, in the present embodiment, since the warpage is reduced by forming the groove portion G as described above, the
以上、説明したように、本実施の形態によれば、樹脂側の分割予定位置に溝部を形成しておいたうえで、スクライブ加工とブレイク加工を行うようにすることで、従来よりも高い確実性および優れた寸法精度にて、樹脂付き脆性材料基板をその主面に対して垂直な分割予定位置にて分割することができる。 As described above, according to the present embodiment, the groove portion is formed at the planned division position on the resin side, and then the scribe processing and the break processing are performed, so that the reliability is higher than in the past. Therefore, it is possible to divide the brittle material substrate with resin at a planned division position perpendicular to the main surface with good dimensional accuracy and excellent dimensional accuracy.
<変形例>
ブレイク加工の態様は、上述の実施の形態のものには限られない。例えば、下側ブレイクバーの構成については上述のブレイク装置300と同様であるが、上側ブレイクバーが、比較的幅広で脆性材料基板1の主面1bさらには弾性フィルム301と十分な接触面積で接触する形状を有し、かつ、主面1bとの接触面がラバー等の弾性部材からなる受け部材として設けられてなるブレイク装置を用いる態様であってもよい。係るブレイク装置においては、スクライブラインSLが形成された主面1bに上述の受け部材をあらかじめ接触させた状態で、対象分割予定線の延長線上に配置した下側ブレイクバーを、弾性フィルム301を介して樹脂側の主面2aに対し線接触させ、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10に付勢することで、ブレイクが実現される。
<Modification>
The mode of the break processing is not limited to that of the above-described embodiment. For example, the configuration of the lower break bar is the same as that of the above-described
あるいは、ブレイクバーによってブレイクを行うブレイク装置に代えて、樹脂2側の主面2aをローラーで押圧することにより、樹脂付き脆性材料基板10の厚み方向に垂直クラックを伸展させる形式のブレイク装置を使用してもよい。あるいは、ブレイク装置を使用することなく、スクライブラインSLおよび垂直クラックSCが形成された樹脂付き脆性材料基板10を人間の手で折り割りしてもよい。
Alternatively, instead of a break device that breaks with a break bar, a break device of a type that extends a vertical crack in the thickness direction of the
1 脆性材料基板
1a、1b (脆性材料基板の)主面
2 樹脂
10 樹脂付き脆性材料基板
11 分割個片
100 ダイサー
101 ステージ
102 ブレード
200 スクライブ装置
201 テーブル
202 ガイドレール
203 カッターホイール
204 スクライブヘッド
205 ガイドバー
206 摺動部
300 ブレイク装置
301 弾性フィルム
301a 粘着面
302 フレーム
303(303a、303b) 上側ブレイクバー
303e (上側ブレイクバーの)先端
304 下側ブレイクバー
304e 先端
CR、CR1〜CR5 クラック
G 溝部
L 分割予定線
P1 (脆性材料基板側の)分割予定位置
P2 (樹脂側の)分割予定位置
SC 垂直クラック
SL スクライブライン
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (5)
前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板の樹脂側の分割予定位置に溝部を形成する溝部形成工程と、
前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板の脆性材料基板側の分割予定位置にスクライブラインを形成するスクライブライン形成工程と、
前記クライブラインに沿って前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割するブレイク工程と、を備える、
ことを特徴とする樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法。 A method of dividing a brittle material substrate with a resin in which a resin adheres to one main surface of a brittle material substrate, perpendicularly to the main surface,
A groove portion forming step of forming a groove portion at a planned division position on the resin side of the brittle material substrate with resin;
A scribe line forming step of forming a scribe line at a planned division position on the brittle material substrate side of the brittle material substrate with resin;
Breaking the resin brittle material substrate along the scribe line, and
A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin, characterized in that:
前記ブレイク工程が、前記脆性材料基板の主面上であって前記脆性材料基板側の分割予定位置に対して対称な2つの位置と、前記樹脂側の主面であって前記スクライブラインの延長線上の位置とに対し、所定の付勢部材にて付勢することによって、前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割する工程である、
ことを特徴とする樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法。 A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin according to claim 1,
The breaking step is performed on two main surfaces of the brittle material substrate and symmetrical with respect to a predetermined division position on the brittle material substrate side, and on the resin main surface on the extension line of the scribe line. Is a step of dividing the brittle material substrate with resin by biasing with a predetermined biasing member with respect to the position of
A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin, characterized in that:
前記スクライブライン形成工程が前記脆性材料基板にクラック伸展によって前記スクライブラインを形成する工程であり、
前記ブレイク工程が、前記スクライブラインから前記溝部へとクラックを伸展させることによって前記樹脂付き脆性材料基板を分割する工程である、
ことを特徴とする樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法。 A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with a resin according to claim 1 or 2,
The scribe line forming step is a step of forming the scribe line by crack extension in the brittle material substrate;
The breaking step is a step of dividing the brittle material substrate with resin by extending a crack from the scribe line to the groove.
A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin, characterized in that:
前記溝部形成工程がダイサーにより前記溝部を形成する工程である、
ことを特徴とする樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法。 A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with a resin according to any one of claims 1 to 3,
The groove portion forming step is a step of forming the groove portion with a dicer.
A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin, characterized in that:
前記脆性材料基板がLTCCまたはHTCCであることを特徴とする樹脂付き脆性材料基板の分割方法。 A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with a resin according to any one of claims 1 to 4,
The method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin, wherein the brittle material substrate is LTCC or HTCC.
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010213157A JP5170195B2 (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2010-09-24 | Method for dividing brittle material substrate with resin |
| TW100114720A TWI432305B (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2011-04-27 | A method for dividing a brittle material substrate with resin |
| CN201110165661.6A CN102416672B (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2011-06-14 | The dividing method of attached resin brittle material substrate |
| KR1020110075600A KR101290966B1 (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2011-07-29 | Dividing method of resin-attached brittle material substrate |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010213157A JP5170195B2 (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2010-09-24 | Method for dividing brittle material substrate with resin |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2012066479A true JP2012066479A (en) | 2012-04-05 |
| JP5170195B2 JP5170195B2 (en) | 2013-03-27 |
Family
ID=45941440
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010213157A Active JP5170195B2 (en) | 2010-09-24 | 2010-09-24 | Method for dividing brittle material substrate with resin |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5170195B2 (en) |
| KR (1) | KR101290966B1 (en) |
| CN (1) | CN102416672B (en) |
| TW (1) | TWI432305B (en) |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103786262A (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-14 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | Fracturing method and marking device of laminated ceramic substrate |
| KR20150044367A (en) * | 2013-10-16 | 2015-04-24 | 미쓰보시 다이야몬도 고교 가부시키가이샤 | Breaking apparatus and dividing method |
| JP2015208937A (en) * | 2014-04-28 | 2015-11-24 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Breaking device for brittle material substrate |
| JP2018170474A (en) * | 2017-03-30 | 2018-11-01 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Cutting method and cutting device of resin layer-equipped brittle material substrate |
| CN112740365A (en) * | 2018-09-26 | 2021-04-30 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | Breaking method of substrate with metal film |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6243699B2 (en) * | 2013-10-25 | 2017-12-06 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Fragment material substrate cutting device |
| JP6561565B2 (en) * | 2015-04-30 | 2019-08-21 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Method and apparatus for dividing bonded substrate |
| JP6561566B2 (en) * | 2015-04-30 | 2019-08-21 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Method and apparatus for dividing bonded substrate |
| KR101877462B1 (en) * | 2017-05-16 | 2018-07-13 | 주식회사 이오테크닉스 | Display panel cutting method |
| CN111007686A (en) * | 2019-11-14 | 2020-04-14 | Tcl华星光电技术有限公司 | Array substrate, display panel and preparation method |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002110716A (en) * | 2000-09-29 | 2002-04-12 | Kyocera Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2006192753A (en) * | 2005-01-14 | 2006-07-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for dividing resin mold ceramic substrate |
| JP2007129109A (en) * | 2005-11-04 | 2007-05-24 | Mitsumi Electric Co Ltd | Method for manufacturing electronic module |
| WO2009148073A1 (en) * | 2008-06-05 | 2009-12-10 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Scribing wheel and method for scribing brittle material substrate |
| WO2010087424A1 (en) * | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-05 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Substrate breaking apparatus |
Family Cites Families (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4373980B2 (en) * | 2003-09-24 | 2009-11-25 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Substrate cutting system and substrate cutting method |
-
2010
- 2010-09-24 JP JP2010213157A patent/JP5170195B2/en active Active
-
2011
- 2011-04-27 TW TW100114720A patent/TWI432305B/en active
- 2011-06-14 CN CN201110165661.6A patent/CN102416672B/en active Active
- 2011-07-29 KR KR1020110075600A patent/KR101290966B1/en active IP Right Grant
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002110716A (en) * | 2000-09-29 | 2002-04-12 | Kyocera Corp | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
| JP2006192753A (en) * | 2005-01-14 | 2006-07-27 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Method for dividing resin mold ceramic substrate |
| JP2007129109A (en) * | 2005-11-04 | 2007-05-24 | Mitsumi Electric Co Ltd | Method for manufacturing electronic module |
| WO2009148073A1 (en) * | 2008-06-05 | 2009-12-10 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Scribing wheel and method for scribing brittle material substrate |
| WO2010087424A1 (en) * | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-05 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Substrate breaking apparatus |
| JP2010173251A (en) * | 2009-01-30 | 2010-08-12 | Mitsuboshi Diamond Industrial Co Ltd | Substrate breaking device |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103786262A (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2014-05-14 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | Fracturing method and marking device of laminated ceramic substrate |
| CN110039668A (en) * | 2012-10-30 | 2019-07-23 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | The method for dividing and scoring device of laminated ceramic substrate |
| KR20150044367A (en) * | 2013-10-16 | 2015-04-24 | 미쓰보시 다이야몬도 고교 가부시키가이샤 | Breaking apparatus and dividing method |
| KR102259441B1 (en) | 2013-10-16 | 2021-06-01 | 미쓰보시 다이야몬도 고교 가부시키가이샤 | Breaking apparatus and dividing method |
| JP2015208937A (en) * | 2014-04-28 | 2015-11-24 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Breaking device for brittle material substrate |
| JP2018170474A (en) * | 2017-03-30 | 2018-11-01 | 三星ダイヤモンド工業株式会社 | Cutting method and cutting device of resin layer-equipped brittle material substrate |
| CN112740365A (en) * | 2018-09-26 | 2021-04-30 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | Breaking method of substrate with metal film |
| CN112740365B (en) * | 2018-09-26 | 2024-01-09 | 三星钻石工业股份有限公司 | Breaking method of substrate with metal film |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20120031429A (en) | 2012-04-03 |
| TWI432305B (en) | 2014-04-01 |
| CN102416672A (en) | 2012-04-18 |
| JP5170195B2 (en) | 2013-03-27 |
| TW201213079A (en) | 2012-04-01 |
| KR101290966B1 (en) | 2013-07-30 |
| CN102416672B (en) | 2015-08-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5170195B2 (en) | Method for dividing brittle material substrate with resin | |
| JP5170196B2 (en) | Method for dividing brittle material substrate with resin | |
| TWI583521B (en) | Cracking device of laminated brittle material substrate and cracking method of laminated brittle material substrate | |
| TWI703037B (en) | Dividing method and dividing device for bonded substrate | |
| KR20150048024A (en) | Method and device for dividing brittle material substrate | |
| TWI615365B (en) | Cracking device | |
| TW201605749A (en) | Breaking method of brittle material substrate and breaking device | |
| CN111916356A (en) | Breaking method of metal laminated ceramic substrate | |
| TWI586234B (en) | Disassembly Method and Scribing Device of Laminated Ceramic Substrate | |
| CN105365052B (en) | Cutting device and method for cutting brittle material substrate by cutting device | |
| JPH10209086A (en) | Breaking method for plate-shaped work and its equipment | |
| JP6315882B2 (en) | Method for dividing laminated ceramic substrate | |
| KR20160015145A (en) | Method for dividing bonded subatrate and dividing apparatus | |
| JP6344787B2 (en) | Ceramic substrate cutting method and scribing apparatus | |
| JP6507866B2 (en) | Device and method for manufacturing semiconductor chip with solder ball | |
| CN106079115B (en) | Method and apparatus for dividing bonded substrate | |
| JP6040705B2 (en) | Method for dividing laminated ceramic substrate | |
| CN111438442A (en) | Method and apparatus for dividing SiC substrate | |
| CN110176396B (en) | Cutting device, cutting method and cutting plate | |
| JP5913483B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for dividing brittle material substrate | |
| KR20180012206A (en) | Apparatus for dividing substrate and method of dividing substrate |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120402 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120626 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120820 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20121204 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20121217 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5170195 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |