JP2011053058A - Vehicle inspection device - Google Patents
Vehicle inspection device Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2011053058A JP2011053058A JP2009201638A JP2009201638A JP2011053058A JP 2011053058 A JP2011053058 A JP 2011053058A JP 2009201638 A JP2009201638 A JP 2009201638A JP 2009201638 A JP2009201638 A JP 2009201638A JP 2011053058 A JP2011053058 A JP 2011053058A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wheel
- reference mark
- image
- vehicle inspection
- feature amount
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Length Measuring Devices By Optical Means (AREA)
- Investigating Materials By The Use Of Optical Means Adapted For Particular Applications (AREA)
- Image Processing (AREA)
- Image Analysis (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、車輪の側面について特徴量を画像処理により自動的に検出する車両検査装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a vehicle inspection apparatus that automatically detects a feature amount of a side surface of a wheel by image processing.
鉄道車輪の検査は、従来目視により、きず等の特徴量を検出し、劣化を判断していた。しかし、目視の検査では停止中の車輪の見えている部分しか行えず、また車輪全周を検査するためには、車輪を取り外して検査する必要がある。そのため、走行中に撮影した画像による検査の自動化が望まれていた。 In the inspection of railway wheels, conventionally, visual observation has detected feature quantities such as scratches and judged deterioration. However, the visual inspection can be performed only on the visible portion of the stopped wheel, and in order to inspect the entire circumference of the wheel, it is necessary to remove the wheel for inspection. For this reason, it has been desired to automate inspections using images taken during traveling.
一方、特徴量の成長来歴を把握することで、寿命の予測や走行条件との照合などの予防保全の用途に活用するニーズがあるが、来歴管理のためには、異なる検査間で、同一車輪の座標系の照合が必要である。 On the other hand, by grasping the growth history of features, there is a need to utilize it for preventive maintenance applications such as life prediction and collation with driving conditions, but for history management, the same wheel is used between different inspections. It is necessary to check the coordinate system.
これらのニーズを満たすためには、走行中に撮影した画像から、動的に変わる基準位置を検出する必要がある。 In order to satisfy these needs, it is necessary to detect a dynamically changing reference position from an image taken during traveling.
車輪の検査の自動化に関する従来技術として、特開平7-174672が知られている。この特許文献では、線路脇にカメラを設置し、車輪の通過を検知するセンサからの信号に基づいて車輪踏面の画像を取得し、画像処理を用いて特徴量を検出する。 Japanese Patent Application Laid-Open No. 7-14672 is known as a prior art relating to automation of wheel inspection. In this patent document, a camera is installed beside a track, an image of a wheel tread is acquired based on a signal from a sensor that detects the passage of a wheel, and a feature amount is detected using image processing.
上記の特許文献に開示の従来技術では、車輪踏面の特徴量を検出しているが、本発明では車輪側面に生じた特徴量を画像処理により自動的に検出することを意図している。
また従来技術では、異なったタイミングで撮影した画像上のきず位置を照合する手段がないため、きずの成長や、変化を追跡することができない。
In the prior art disclosed in the above patent document, the feature amount of the wheel tread is detected. However, the present invention intends to automatically detect the feature amount generated on the wheel side surface by image processing.
Further, in the prior art, since there is no means for collating the positions of flaws on images taken at different timings, it is impossible to track flaw growth or changes.
さらに、従来技術では車輪側面を画像処理するに適した処理、あるいは表示について、検討されていない。 Further, in the prior art, processing or display suitable for image processing of the wheel side surface is not studied.
以上のことから、本発明の第一の目的は、車輪側面のきず等の特徴量を検出するに当たり、その存在する位置を絶対位置との関係で特定するための基準マーク検出手法を備えた車両検査装置を提供することにある。 In view of the above, the first object of the present invention is to provide a vehicle equipped with a reference mark detection method for specifying the position where the feature exists in relation to the absolute position in detecting a feature amount such as a flaw on a wheel side surface. It is to provide an inspection device.
本発明の第2の目的は、位置が特定された特徴量について、異なる時間関係での複数の車輪側面画像から同一の特徴量を同定し、その来歴管理を行うことのできる車両検査装置を提供することにある。 A second object of the present invention is to provide a vehicle inspection apparatus that can identify the same feature quantity from a plurality of wheel side surface images in different time relationships and manage the history of the feature quantity for which the position is specified. There is to do.
さらに本発明の第3の目的は、車輪側面を画像処理するに適した処理、あるいは表示の手法を備える車両検査装置を提供することにある。 A third object of the present invention is to provide a vehicle inspection apparatus provided with a process suitable for image processing of a wheel side surface or a display technique.
請求項1に記載の発明では、特徴量の位置を検出する車両検査装置を実現するという第一の目的達成のために、
入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪中心の座標を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から基準マークを検出してその座標を決定し、車輪中心の座標と基準マークの座標を基準として決定された特徴量の位置を記憶する。
In the first aspect of the present invention, in order to achieve the first object of realizing the vehicle inspection device that detects the position of the feature amount,
Detect feature values on the wheels from the image of the side of the railcar wheel that was input, detect the coordinates of the wheel center from the image of the side of the railcar wheel that was input, and detect the reference mark from the image of the railroad wheel side that was input The coordinates are determined, and the position of the feature amount determined based on the coordinates of the wheel center and the coordinates of the reference mark is stored.
また、基準マーク検出は、基準マークについてのテンプレートを保持しており入力した画像からテンプレートマッチングで相関値が高い領域を検出して行う。 The reference mark detection is performed by detecting a region having a high correlation value by template matching from an input image that holds a template for the reference mark.
また、基準マークについてのテンプレートは、車輪の回転に応じて回転させた複数のテンプレートとして保持され、複数のテンプレートごとに入力した画像から、テンプレートマッチングで、相関値が高い領域を検出し、基準マークを検出する。 Further, the template for the reference mark is held as a plurality of templates rotated according to the rotation of the wheel, and an area having a high correlation value is detected by template matching from images input for each of the plurality of templates. Is detected.
基準マークマッチングについては、1種類のテンプレートによりマッチング検出して相関値が高い基準マーク候補領域を複数選出し、撮影条件の異なる複数のテンプレートにより選出した基準マーク候補領域をマッチングして、相関値の最も高い位置を基準マーク位置とする。 For reference mark matching, a plurality of reference mark candidate areas having a high correlation value are detected by matching detection using one type of template, and the reference mark candidate areas selected by a plurality of templates having different shooting conditions are matched, The highest position is the reference mark position.
基準マーク検出は、入力した画像から、文字候補を切り出し、車輪上に存在する複数の文字列の文字間の間隔をルールとして格納し、文字列の並び間隔のルールを用いて切り出した文字列候補のうちから、ルールと一致する文字列候補を検出し、基準マークの位置を推定する。 In the reference mark detection, character candidates are cut out from the input image, the intervals between the characters of the plurality of character strings existing on the wheel are stored as rules, and the character string candidates cut out using the rule of the arrangement interval of the character strings Among them, a character string candidate that matches the rule is detected, and the position of the reference mark is estimated.
文字候補切り出しは、複数の異なる閾値を用いて切り出した文字列候補それぞれについて、マーク位置を推定し、基準マーク位置とする。 In the character candidate cutout, the mark position is estimated for each of the character string candidates cut out using a plurality of different threshold values, and set as the reference mark position.
基準マーク検出は、基準マークについてのテンプレートを保持しており入力した画像からテンプレートマッチングで相関値が高い領域を検出して基準マークとし、入力した画像から、文字候補を切り出し、車輪上に存在する複数の文字列の文字間の間隔をルールとして格納し、文字列の並び間隔のルールを用い文字列候補のうちから、ルールと一致する文字列候補を検出し、基準マークと文字列候補のマーク位置候補から最終的にマーク位置を決定する。 In the reference mark detection, a template for a reference mark is held, and a region having a high correlation value is detected from the input image by template matching to be used as a reference mark. Character candidates are cut out from the input image and exist on the wheel. The interval between characters of multiple character strings is stored as a rule, and the character string candidate that matches the rule is detected from the character string candidates using the rule of the character string arrangement interval, and the reference mark and the character string candidate mark The mark position is finally determined from the position candidates.
また、マーク位置決定は、基準マーク位置候補の相関値が十分高い場合、マーク位置決定で推定した基準マーク位置候補より優先して基準マーク位置とする。 In addition, when the correlation value of the reference mark position candidate is sufficiently high, the mark position determination has priority over the reference mark position candidate estimated by the mark position determination as the reference mark position.
さらにマーク位置決定は、基準マークマッチングで検出した基準マーク位置候補、およびマーク位置決定で推定した基準マーク位置候補が複数存在する場合、同一の位置を検出、もしくは推定した件数が多い位置を優先して基準マーク位置として決定してもよい。 In addition, when there are multiple reference mark position candidates detected by reference mark matching and multiple reference mark position candidates estimated by mark position determination, the mark position determination gives priority to the position where the same position is detected or estimated. The reference mark position may be determined.
さらに、文字並び間隔ルールの複数の異なるルールについて重み付けをして、重み付に基づき、マーク位置決定のときに複数の基準マーク位置候補から基準マーク位置を決定する際に優先度を決定する。 Further, a plurality of different rules of the character arrangement interval rule are weighted, and based on the weighting, the priority is determined when determining the reference mark position from the plurality of reference mark position candidates when determining the mark position.
また基準マークマッチングにより検出した基準マーク位置候補、およびマーク位置決定で推定した基準マーク位置候補が複数存在する場合、マーク位置決定は、近傍に複数推定位置が存在する場合に、複数推定位置の平均、もしくは、複数ルールの重み付けをしている場合には、加重平均をとって算出した位置をマーク位置として決定する。 In addition, when there are a plurality of reference mark position candidates detected by the reference mark matching and a plurality of reference mark position candidates estimated by the mark position determination, the mark position determination is an average of a plurality of estimated positions when there are a plurality of estimated positions in the vicinity. Alternatively, when a plurality of rules are weighted, the position calculated by taking the weighted average is determined as the mark position.
請求項12に記載の発明では、特徴量の来歴を記録する車両検査装置を実現するという第二の目的達成のために、
入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪中心の座標を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から基準マークを検出してその座標を決定し、鉄道車両を撮影するときに撮影車輪を識別する車輪識別情報の対応を格納し、車輪中心の座標と基準マークの座標を基準として決定された特徴量の位置を車輪識別情報に対応づけて記憶し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から得られた特徴量について、同じ車輪識別情報を有する車輪の情報の中に特徴量位置情報から同一と考えられる特徴量があった場合は、同一特徴量を示す識別情報を付与して追記憶する。
In the invention according to
Detect feature values on the wheels from the image of the side of the railcar wheel that was input, detect the coordinates of the wheel center from the image of the side of the railcar wheel that was input, and detect the reference mark from the image of the railroad wheel side that was input Stores the correspondence of the wheel identification information that determines the coordinates and identifies the shooting wheel when shooting the railway vehicle, and the position of the feature amount determined with reference to the coordinates of the wheel center and the coordinates of the reference mark as the wheel identification information If the feature value obtained from the image of the side surface of the railroad vehicle wheel that is stored in association with the input image is the same as the feature value that is considered identical from the feature value position information in the wheel information having the same wheel identification information Is additionally stored with identification information indicating the same feature amount.
また、異なる日付に撮影した同じ車輪の画像を同じ特徴量が画像比較できるよう並べて表示する。 In addition, images of the same wheels taken on different dates are displayed side by side so that the same feature amount can be compared.
また、編成運行情報と、統計情報から、車輪の走行に関する情報と、特徴量に関する情報の関係を対比して表示する。 Moreover, the relationship between the information regarding the traveling of the wheel and the information regarding the feature amount is displayed in comparison with the train operation information and the statistical information.
請求項16に記載の発明では、車輪側面を画像処理するに適した処理、あるいは表示の手法を備える車両検査装置を実現するという第三の目的達成のために、
入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について車輪上の特徴量を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について車輪中心の座標を検出し、入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について基準マークを検出してその座標を決定し、隣接する位置で撮影された画像について対応する位置を求めて連結することにした。
In the invention according to
Detect feature values on wheels for multiple images of the input railcar wheel side, detect wheel center coordinates for the input railcar wheel side images, and mark reference marks for the input railcar wheel side images. The coordinates are determined by detection, and the corresponding positions of images taken at adjacent positions are obtained and connected.
また、画像間位置照合は、画像上の車輪の中心と、車輪の弧を検出することで車輪の摩耗量を求め、隣り合う画像同士の対応点を算出する。 Further, the inter-image position collation calculates the wear amount of the wheel by detecting the center of the wheel on the image and the arc of the wheel, and calculates the corresponding point between the adjacent images.
さらに、検出した車輪中心を基準とし極座標変換した画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出する。 Further, the feature amount on the wheel is detected from the image obtained by polar coordinate conversion with the detected wheel center as a reference.
本発明によれば、車輪側面の特徴量位置を絶対位置との関係で特定するための基準マークを車輪側面画像から検出する手法を提供できる。 ADVANTAGE OF THE INVENTION According to this invention, the method of detecting the reference mark for specifying the feature-value position of a wheel side surface by a relationship with an absolute position from a wheel side surface image can be provided.
本発明によれば、異なる時間関係での複数の車輪側面画像から同一の特徴量を同定し、その来歴管理を行うことができる。 According to the present invention, it is possible to identify the same feature amount from a plurality of wheel side surface images in different time relations and manage their history.
さらに本発明によれば、車輪側面を画像処理するに適した処理、あるいは表示の手法を提供することができる。 Furthermore, according to the present invention, it is possible to provide a processing or display technique suitable for image processing of the wheel side surface.
以下に本発明の実施例を説明する。 Examples of the present invention will be described below.
以下、図1〜図30を参照して、本発明の車両検査装置について説明する。 Hereinafter, the vehicle inspection apparatus of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
実施例1は、本発明に掛かる車両検査装置の基本的な構成、機能を説明するものであり、図1乃至図11を用いて説明を行う。 The first embodiment describes the basic configuration and functions of the vehicle inspection apparatus according to the present invention, and will be described with reference to FIGS.
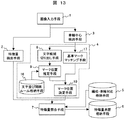
まず、図1は、本発明の車両検査装置の第一の実施例の概略装置構成を示すブロック図である。図1の車両検査装置は、画像入力手段1と、特徴量検出手段2と、車輪中心検出手段3と、基準マーク検出手段4と、編成・車輪対応格納手段5と、特徴量来歴格納手段6と、特徴量照合手段7とからなる。 First, FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a schematic apparatus configuration of a first embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus of the present invention. The vehicle inspection apparatus of FIG. 1 includes an image input means 1, a feature quantity detection means 2, a wheel center detection means 3, a reference mark detection means 4, a composition / wheel correspondence storage means 5, and a feature quantity history storage means 6 And feature amount matching means 7.
第一の実施例の構成要素について順に詳細に説明する。尚、以下の説明では、理解を容易にするために日付、長さ、角度等、具体的な数値を用いて説明しているが、これらは全て例として挙げたものであり、数値自体に格別の意味はない。 The components of the first embodiment will be described in detail in order. In the following description, for ease of understanding, the explanation is made using specific numerical values such as date, length, angle, etc., but these are all given as examples, and the numerical values themselves are exceptional. There is no meaning.
まず、本発明において処理の対象とする車輪側面を撮影した画像の例を図2に示す。 図2は同一車輪について、異なる検査時期で撮影した画像の例を示す。同図(a)は、検査時期1で撮影した画像21、同図(b)は、その後の検査時期2で撮影した画像22である。車輪23と、車輪23’は、異なる時期の同一の車輪である。25、および25’に示すマークは、全ての車輪中の一箇所に必ず存在するマークとする。
First, FIG. 2 shows an example of an image obtained by photographing the wheel side surface to be processed in the present invention. FIG. 2 shows an example of images taken at different inspection times for the same wheel. FIG. 5A shows an
ここで、画像21で撮影した車輪23上には特徴量26が存在する。この特徴量26の位置は、24を車輪の中心とし、マーク25を基準としてなす角27により、定義することができる。ここで、角度27をx°とする。
Here, a
画像22のその後に撮影した車輪23’上には特徴量28と特徴量29が存在する。ここで、画面上での車輪の位置は、回転により画像22と21では相違するのが通常である。具体的には、画像21の基準マーク25が画面22ではマーク25’へ、画面上の位置が移動している。
A
しかしながら、基準マーク25’と中心24のなす角度2aが画像21のときの既値の角度x°に相当することから、この位置にある画面21上の特徴量26と同一の特徴量は、画面22上の特徴量28であると同定できる。なお特徴量29について、基準マークからの角度2bがy°とすると、この位置に対応する位置に画像21上には特徴量がないので、新たな特徴量として今後継続監視されることになる。
However, since the
以上のように、人間であれば目視により、回転する検査対象物である車輪を、任意のタイミングで撮影しても、車輪上の位置を照合可能である。しかしながら、これを自動的に実施するには、画面上で動的に変わる車輪の中心を検出する車輪中心検出手段3と、全ての車輪に必ず一箇所あるマーク位置を検出して円周上の角度の基準位置とする基準マーク検出手段4を備え、車輪上に発生する特徴量位置を同定し、同一特徴量の大きさや形状の変更を比較することが必要となる。なお、基準として想定するマークは、車輪の製造メーカのマークなど、車輪毎に一箇所必ず存在するユニークなマークとする。 As described above, if a human is visually inspecting a wheel, which is a rotating inspection object, at an arbitrary timing, the position on the wheel can be collated. However, in order to perform this automatically, the wheel center detecting means 3 that detects the center of the wheel that dynamically changes on the screen and the mark position that is always in one place on all the wheels are detected and It is necessary to provide the reference mark detection means 4 as the reference position of the angle, identify the feature amount position generated on the wheel, and compare the change in size and shape of the same feature amount. It should be noted that a mark assumed as a reference is a unique mark that always exists at one place for each wheel, such as a mark of a wheel manufacturer.
以上の前提に基づき、第一の実施例の構成要素について順に説明する。図1の画像入力手段1は、検査対象の画像を撮影し、入力する手段である。図2の21、22に示すような画像を入力する。
Based on the above assumptions, the components of the first embodiment will be described in order. The
特徴量検出手段2は、画像入力手段1で撮影した画像から、特徴量を検出する手段である。この実現手段については、例えば、特徴量が車輪面より輝度が低く(黒く)撮影されるとすると、車輪面の平均輝度と特徴量の平均輝度の間に設定した閾値による二値化により、特徴量領域を黒く抽出するなどの方法を用いる。
The feature
図3は特徴量検出手段2の処理内容を説明するための図である。このうち同図(a)は、画像入力手段1から入力した画像31の例であるが、車輪32上に特徴量32と33がある。これを特徴量検出手段2で抽出し、同図(b)の35で示すように画面上の例えば左下の点39を基準とし、各特徴量について、画面上での始点、終点座標を取得する。例えば特徴量37については始点3a、終点3bの座標、特徴量38については始点3c、終点3dの座標を取得し、画面上で管理できる座標を取得する。ここで、図3で述べた座標とはあくまでもこの画像の上での座標であり、図2で述べた基準マークや車輪中心から求められる絶対位置の座標位置でないことはいうまでもない。
FIG. 3 is a diagram for explaining the processing contents of the feature amount detection means 2. FIG. 2A shows an example of the
尚、図3において取得した画像範囲の中には、本来特徴量検出の必要のない車輪中の3eに示す車軸の領域なども写っている。この処理不要領域については、予め処理の必要ない領域としてマスク処理を実施し、特徴量検出処理の対象としない、などの処理を施して、不要な領域の誤検出を防ぐ。車軸領域の範囲の求め方は、後述する車輪中心検出手段3で求める画像中での車輪の中心と、既知の車軸領域の半径から求めることができる。 In the image range acquired in FIG. 3, the axle region indicated by 3e in the wheel that does not need to detect the characteristic amount is also shown. The processing unnecessary area is subjected to mask processing as an area that does not need to be processed in advance and is not subjected to feature amount detection processing, thereby preventing erroneous detection of unnecessary areas. The method of obtaining the range of the axle region can be obtained from the center of the wheel in the image obtained by the wheel center detecting means 3 described later and the radius of the known axle region.
車輪中心検出手段3は、検出した特徴量の車輪上の位置を一意に求めるために、画像上の車輪の中心座標を求める手段である。この手段は、例えば特許文献特開平6-167313に開示があるように、車輪の弧のエッジを画像処理で検出し、円の弧との近似から中心位置を求める、等の手段で求めることができる。図4は、車輪中心検出手段3の処理内容を説明するための図であり、この図に示すように、求めた中心位置43は、特徴量検出手段2で検出された特徴量の位置と同様、画像中の始点44からの相対座標で把握され、メモリ上に保持する。
The wheel
基準マーク検出手段4は、車輪の円周方向の基準位置として、車輪上に存在する特定マークを検出する手段である。基準マーク検出手段4を実現する実施例の一つは、例えばパターンマッチングを用いて、テンプレートと最もテクスチャの類似した位置を求める方法である。 The reference mark detection means 4 is a means for detecting a specific mark present on the wheel as a reference position in the circumferential direction of the wheel. One of the embodiments for realizing the reference mark detection means 4 is a method for obtaining a position where the texture is most similar to the template by using, for example, pattern matching.
図5は、基準マーク検出手段4の処理内容を説明するための図であり、先のパターンマッチングを用いる方法は、仮に、特定マークを図5の51のようなテクスチャのマークとすると、51をテンプレートとして保有し、画像上の情報とのマッチングにより、相関値の大きい位置をマーク位置として検出する手法である。52の画像中で、51と一致度の高い位置は図中53を中心とする位置であるので、車輪中心位置、特徴量位置と同様に、画像中の左下基準点54を基準とした相対座標で基準マークの位置を把握し、メモリに格納する。
FIG. 5 is a diagram for explaining the processing contents of the reference mark detection means 4. If the specific mark is a texture mark such as 51 in FIG. This is a method of detecting a position having a large correlation value as a mark position by matching with information on an image held as a template. In the image of 52, the position having a high degree of coincidence with 51 is the position centered on 53 in the figure, so that the relative coordinates based on the lower
尚、車輪のような円盤状の対象物の場合、マークは、車輪中心を中心とする円弧に沿って付いている場合が多いと考えられ、画像中でのマークの方向は360°回転する可能性があると考えられる。そのため、パターンマッチングの手段としては、テンプレート51について、360°の範囲で少しずつ回転させた複数テンプレートを作成しておき、全てのテンプレートでマッチングして最大相関値の位置を採用するなどの手段を用いることができる。
In the case of a disk-like object such as a wheel, the mark is often attached along an arc centered on the center of the wheel, and the direction of the mark in the image can be rotated 360 °. It is thought that there is sex. Therefore, as a means of pattern matching, for
次に、編成・車輪対応格納手段5について説明する。編成・車輪対応格納手段5は、編成を識別するIDと、編成に組み込まれている車輪のIDの対応を格納する手段である。編成・車輪対応格納手段5に格納されるデータの例を図6に示す。図6の列方向は格納項目を示し、行方向がデータレコードの例とする。 Next, the knitting / wheel correspondence storage means 5 will be described. The knitting / wheel correspondence storing means 5 is a means for storing the correspondence between the ID for identifying the knitting and the ID of the wheel incorporated in the knitting. An example of data stored in the knitting / wheel correspondence storage means 5 is shown in FIG. In FIG. 6, the column direction indicates storage items, and the row direction is an example of a data record.
図6において、列61は一続きの編成を特定できる編成IDであり、編成を一意に特定できるIDとする。列62は、車輪が付いている側面(左/右)を識別するコードであり、仮に左をL,右をRとする。列63は、配列番号であり、列62で特定された側面の、先頭から数えた配列番号を示す。列64は、車輪IDで、車輪を一意に特定できる番号である。
In FIG. 6, a
また、車輪が編成から取り外されて交換されることもありうるため、6bに示す「開始日」に編成にその車輪が取り付けられた日付と、6cの「終了日」に車輪がその編成から取り外された日付も格納しておく。このようにすることである位置に取り付けられていた車輪の来歴も参照することができる。最新の編成と車輪の対応は、「終了日」が空欄のレコードを参照することで取得できる。 Also, because the wheel may be removed from the train and replaced, the date the wheel was attached to the train on the “start date” shown in 6b and the wheel removed from the train on the “end date” in 6c. The stored date is also stored. It is also possible to refer to the history of the wheels that have been attached to the position in this way. The correspondence between the latest knitting and the wheel can be acquired by referring to a record in which the “end date” is blank.
編成・車輪対応格納手段5には、例えば以上のような約束の下に各種データが格納されており、行65から70には個別にデータが格納されている。このうち、例えば行65に示すデータレコードは、編成ID“1”の編成の、左側の一番前の車輪は、車輪IDが“AAA”であることを示す。同様に、行70に示すデータレコードは、編成ID“1”の編成の、右側の先頭から3番目の車輪はID“BBD”であることを示す。以上のように、編成・車輪対応格納手段5では、列車の編成IDと、左右の側面と、配列番号をキーに、車輪のIDを取得することができる。
For example, various data are stored in the knitting / wheel correspondence storage means 5 under the above-mentioned promise, and data are individually stored in the
特徴量来歴格納手段6は、車輪上に発生した特徴量の来歴に関する情報を格納する手段である。図7に、特徴量来歴格納手段6に格納する情報の例を示す。図中、一行目の71〜78に示すのが格納項目の例であり7a、7bの行がデータの例である。
The feature quantity history storage means 6 is means for storing information relating to the history of the feature quantity generated on the wheel. FIG. 7 shows an example of information stored in the feature amount history storage means 6. In the figure, 71 to 78 in the first row are examples of storage items, and the
図7において、列71が、特徴量を検出した日付である。列72は特徴量の存在する車輪IDである。列73は、特徴量を特定するための特徴量IDである。列74は、特徴量の位置を特定するための、基準マークからの特徴量の角度である。列75は、特徴量の位置を特定するための、中心からの位置である。列76は、特徴量の長さである。列77は、画像上での特徴量の始点座標である。列78は、画像上での特徴量の終点座標である。列79は、特徴量の撮影された画像名である。
In FIG. 7, a
特徴量来歴格納手段6には、例えば以上のような約束の下に各種データが格納されており、例えば、行7aのデータでは、「2008年12月10日」に撮影(列71)された画像で、車輪ID「AAA」上に(列72)基準からの角度が33°(列74)、中心からの位置が256mm(列75)の位置に、長さ30mm(列76)の特徴量があることを示している。列73より、この特徴量は、「AAA-1」というユニークなIDで管理する。また、列77〜列79より、この特徴量は、画像名「img090210AAA」上の始点座標(520,200)、終点座標(523,215)上にある、という情報を示す。
In the feature quantity history storage means 6, various data are stored under the promise as described above. For example, in the data of the
以上のように、特徴量来歴格納手段6に格納する情報は、車輪の特徴量が検出された日付と位置・大きさを管理し、また、撮影した画像を管理する格納手段(図示せず)がある場合は、その特徴量が写っている位置を特定することもできる手段である。 As described above, the information stored in the feature quantity history storage means 6 is the storage means (not shown) for managing the date and position / size when the feature quantity of the wheel is detected, and for managing the photographed image. If there is, there is a means for specifying the position where the feature amount is reflected.
特徴量照合手段7は、特徴量検出手段2で検出した特徴量を、過去の検査で検出した特徴量と、位置情報を使って同定し、同一と考えられる特徴量があった場合は、同一IDを付与する手段である。 The feature quantity matching means 7 identifies the feature quantity detected by the feature quantity detection means 2 using the positional information and the feature quantity detected in the past examination, and if there is a feature quantity that is considered to be the same, it is the same It is a means to give ID.
特徴量照合手段7の処理の流れを、図8を用いて説明する。この処理においては、編成・車輪対応格納手段5の情報と、特徴量来歴格納手段6の情報とを使用する。
A processing flow of the feature
このフロー図において、処理81では、編成・車輪対応格納手段5から、車輪IDを取得する。この処理では、車輪画像が入力される際に、予め編成IDを入力しておく。もしくは編成が、この検査場等の画像取得位置に入ってくるときの、ダイヤスケジュールデータを予め持っていて、画像入力を開始したタイミングで、当該時刻に検査場に入ってくる編成のID、および、車輪の配列から、撮影された画像毎に車輪IDを取得する。ここで、車輪IDをxとする。
In this flowchart, in a
処理82では、特徴量数のカウンタIを0クリアする。処理83では、I番目の特徴量の基準からの角度を算出する。処理84では特徴量のカウンタIを1進める。処理85では、全ての特徴量を処理したか否かの判定を行い、全ての特徴量を処理していれば処理86に、未処理の特徴量があれば処理82に戻り、すべての特徴量の角度算出処理が完了するまで繰返し処理を行う。
In the
以上の一連の循環処理の間に、処理83では特徴量の基準マークからの角度を算出し、その結果を特徴量来歴格納手段6に格納している。図9は画像入力手段から得た画像の例であり、処理83の処理内容につき図9を用いて説明する。図9の車輪91の画像の例では処理83によって、特徴量検出手段2により検出した特徴量の位置92,93と、車輪中心検出手段3により検出した車輪の中心94と、基準マーク検出手段4により検出した基準マークの位置95を導出し、角度を演算している。
During the above-described series of cyclic processes, the
なお、処理83において、画像上の位置関係から角度を求めるに当たり、カメラの向きが車輪面に対し垂直であることを前提とするが、多くの場合はカメラと車輪面は垂直でなく傾きがあると考えられる。その場合は、カメラと車輪の角度情報から、カメラキャリブレーションにより座標変換し、カメラの向きが車輪面に対して垂直な、正対化した画像に変換しておき正対化した画像上で、基準マークと特徴量の角度を求めることが有効である。
In the
処理86では、車輪xの前回の検査で検出した特徴量の情報を特徴量来歴格納手段6から抽出する。処理87では、車輪xの前回の検査で検出した特徴量をカウントするカウンタJを0クリアする。処理88では、前回の検査で検出の特徴量jと一致する特徴量Iを、今回検出したものから検索する。処理89では、特徴量jと一致する特徴量Iに、特徴量jの特徴量IDを設定する。処理8aでは、前回の検査で検出した特徴量が全て処理されたか否かを判定し、全ての特徴量の処理が終了していれば処理8bに、未処理の特徴量があれば処理88に戻る。処理8bでは、今回検出した特徴量のうち、処理88〜処理8aで、特徴量IDが付与されなかった、新規の特徴量につき、新規の特徴量IDを付与する。
In the
なお、処理88において、特徴量が一致するか否かの判定は、特徴量来歴格納手段6に格納される列74の基準マークからの角度、および、列75の中心からの位置の比較により、一致もしくは値が最も近いものを一致として判定する。
In the
以上の図8の一連の処理の流れにつき、具体的なデータを用いて説明する。図9は、画像入力手段1から入力した先述の画像の例であり、この画像は、編成ID「1」の編成の左側で撮影された一番目の画像とする。図中、91は車輪、92と93は検出された特徴量、94は車輪の中心であり、95は検出した基準マークである。 The above-described series of processing flow in FIG. 8 will be described using specific data. FIG. 9 is an example of the above-described image input from the image input means 1, and this image is the first image taken on the left side of the composition having the composition ID “1”. In the figure, 91 is a wheel, 92 and 93 are detected feature quantities, 94 is the center of the wheel, and 95 is a detected reference mark.
処理81で、編成・車輪対応格納手段5から、車輪IDを取得する。図6の編成・車輪対応格納手段5の例から、編成IDが「1」の、左側に設置の、配列が1番目の車輪は、行65のデータであるので、車輪IDは「AAA」を取得する。
In
処理83で、0番目の特徴量の角度を算出する。この際、特徴量を代表する点を決める必要があるが、特徴量の始終点から求められる重心などを用いる。求めた特徴量92の基準マークとのなす角を33°、中心からの位置を254mmとし、また始終点の座標等を特徴量来歴格納手段6に追加する。図7には2008年12月10日付で検出した車輪ID「AAA」の特徴量が記録されているが、2009年2月10日に実施した車両検査の結果を追加したレコードを図10中の行101に示す。情報を取得した時刻から、日付を登録し、また、車輪IDと、入力した画像名を登録する。
In
図9の例では特徴量数が「2」なので、処理85の判定で処理83に戻る。同様に、図9中の特徴量93の基準マークとのなす角、中心からの距離を算出し、始終点の座標等を特徴量来歴格納手段6に追加する。追加したレコードは102である。この時点では、特徴量IDはまだ付与されていない。
In the example of FIG. 9, since the number of feature quantities is “2”, the process returns to process 83 in the determination of
車輪「AAA」の全ての特徴量の処理が終了したので、処理86に移る。車輪「AAA」の前回検査の特徴量を特徴量来歴格納手段6から抽出する。図10から、車輪「AAA」の前回の検査の特徴量のレコードを抽出すると、行7aの1件となる。
Since the processing of all the feature values of the wheel “AAA” has been completed, the processing shifts to
処理88で、前回の検査時の車輪「AAA」の特徴量である行7aの特徴量「AAA-1」について、一致する特徴量を検索する。今回の画像から検出された特徴量は、特徴量来歴格納手段6の行101、102に登録されているが、角度が66°で一致するのは行101のレコードであるので、これを行7aのレコードと一致する特徴量であるとして、特徴量IDを「AAA-1 」と付与する。
In
前回の検査時の特徴量のレコードはこの1件であるので、図10の行102に該当する特徴量は、前回は検出されず、今回新規に検出されたものとして、新規の特徴量ID「AAA-2」を付与する。
Since the record of the feature quantity at the time of the previous inspection is this one, the feature quantity corresponding to the
以上の、特徴量照合手段7の処理が終了した時の特徴量来歴格納手段6の状態を図11に示す。図10との相違は特徴量IDが新たに賦与された点である。この結果、基準位置として求めたマークの位置と、中心の位置から、その車輪に不変的な位置を求めることにより、異なる検査時に、画像中での基準位置が異なる際に検出した特徴量との照合をすることができる。
FIG. 11 shows the state of the feature amount
以上が車両検査装置の第一の実施例である。この実施例に拠れば、車輪中心検出手段3と、基準マーク検出手段4により、画像中の車輪位置が変化しても、基準となる中心からの位置と、基準マークからの角度により、車輪上の座標系をいつも一意に決められるため、画像撮影時に車輪の向きを意識することなく、特徴量来歴管理をすることができる。
The above is the first embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus. According to this embodiment, even if the wheel position in the image is changed by the wheel
次に、車両検査装置の第二の実施例について説明する。第二の実施例では図12から図22を用いて、特徴量の絶対位置を決定する上で必要となる基準マーク位置を精度よく検出するための各種の工夫について紹介する。 Next, a second embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus will be described. In the second embodiment, various devices for accurately detecting the reference mark position necessary for determining the absolute position of the feature amount will be introduced with reference to FIGS.
車両検査装置の第二の実施例では、パターンマッチングによるマーク検出以外に、基準マークの含まれる文字列の並び間隔のルールを使って、基準マークの位置を推定する点で工夫がされている。本実施例の説明として、鉄道車両の車輪に刻印された製造情報の文字列の並びを検出することにより、基準マークの位置を推定する処理を例にとり説明する。 The second embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus is devised in that the position of the reference mark is estimated using a rule for the arrangement interval of the character strings including the reference mark, in addition to the mark detection by pattern matching. As an explanation of the present embodiment, a process for estimating the position of a reference mark by detecting the arrangement of character strings of manufacturing information stamped on the wheels of a railway vehicle will be described as an example.
本第2の実施例の前提として、想定する製造情報の文字列の例を、図12のようなものであると仮定する。本実施例の前提は、円周上の位置に基準となるユニークなマークが一箇所あること、また、文字列の桁数が一定であることである。図12(a)は、車輪Aに打刻された文字列121、図12(b)は、車輪Bに打刻された文字列124の例を示す。これらは車輪についての製造情報であるので、車輪により文字の内容は異なるが、一箇所以上、かならずユニークなマークもしくは文字が含まれることを前提とする。図の例では、文字列121および文字列124中で、それぞれ122と125のマークは同一の形状で、どの車輪にも打刻される、例えば製造メーカのマークなどである。これに対し、123、126に示す文字列は、製造日時・製造番号など、車輪により可変であることが多い。
As a premise of the second embodiment, it is assumed that an example of a character string of manufacturing information to be assumed is as shown in FIG. The premise of the present embodiment is that there is one reference unique mark at a position on the circumference and that the number of digits in the character string is constant. 12A shows an example of a
本発明の車両検査では、メンテナンス時の検査を想定しているため、検査対象である車輪は汚れなどのノイズが付着し、また、画像取得時の照明環境も適切にコントロールしにくいなどが考えられ、画像上で製造情報の文字列が全て克明に取得するのが困難な状況である。そこで、製造情報の文字列の内容を認識できなくても、製造情報の文字列中のユニークなマークの位置を検出するための方法をこの実施例で説明する。 In the vehicle inspection of the present invention, since inspection at the time of maintenance is assumed, noise such as dirt adheres to the wheels to be inspected, and the lighting environment at the time of image acquisition is difficult to control appropriately. This is a situation where it is difficult to obtain all the character strings of the manufacturing information on the image. Therefore, a method for detecting the position of a unique mark in the character string of the manufacturing information even if the content of the character string of the manufacturing information cannot be recognized will be described in this embodiment.
本実施例では、車輪毎に一箇所の、図12の122、125のマークの位置を推定することを例に挙げ説明する。図13は実施例2の構成を示すブロック図である。図1の実施例1の構成の、基準マーク検出手段4の構成として、文字候補切り出し手段8と、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16と、マーク位置推定手段9と、マーク位置決定手段10と、基準マークマッチング手段17とを追加した構成である。
In the present embodiment, description will be given by taking as an example the estimation of the positions of the
以下第二の実施例の説明では、新規に追加された構成を主体として順に説明する。まず、文字候補切り出し手段8は、画像入力手段1から入力した画像から、文字または特定パタンを切り出す手段である。尚、以降、「文字候補」として説明するが、数種類の特定し得るパタンでもよい。
In the following description of the second embodiment, the newly added configuration will be described in order. First, the character
この際、入力した画像をそのまま処理することも可能であるが、画像処理時の座標管理を容易にするため、入力した円形の車輪画像を、極座標変換して展開画像に変換した上で処理することが有効である。。この変換処理は、入力された画像の位置座標(x,y)を、画像中の円系の中心を基準に(r,θ)(rは円の半径、θは円周の角度)に変換し、θをx軸、rをy軸の直行座標系に変換することで実行できる。 At this time, it is possible to process the input image as it is. However, in order to facilitate coordinate management during image processing, the input circular wheel image is converted into a developed image by polar coordinate conversion and then processed. It is effective. . This conversion process converts the input image position coordinates (x, y) to (r, θ) (r is the radius of the circle and θ is the angle of the circumference) with reference to the center of the circle in the image. Then, it can be executed by converting θ into an orthogonal coordinate system of x-axis and r as y-axis.
図14に極座標変換前後の画像の例を示す。図14(a)において、141は極座標変換前の画像であり、図14(b)の146は極座標変換後の画像である。画像141中の車輪142で、車輪中心検出手段3で検出した車輪の中央143から、車輪の外周方向を結ぶ半径方向の長さを144とする。これは変換前の座標系中の、円形の系方向の長さrに相当する。また、145は143を中心とした角度であり、変換前の座標系中の、円形の角度θに相当する。
FIG. 14 shows examples of images before and after polar coordinate conversion. In FIG. 14A, 141 is an image before polar coordinate conversion, and 146 in FIG. 14B is an image after polar coordinate conversion. With the
変換後の画像146は、車輪の中心143を中心とした、144であらわす径方向の長さrをx軸とし、角度145をy軸とした座標系に変換したものである。画像処理は通常xy平面座標系で扱うことが多いため、画像処理前に極座標変換してxy座標系にすることで、画像処理結果の座標データが扱いやすくなるメリットがある。実施例2の処理は極座標変換を実施した仮定で行うが、説明中のx座標を角度、y座標を径方向の長さと読み替えることで、変換しない場合も同様に処理できることはいうまでもない。
The converted
文字候補切り出し手段8の処理の説明に戻る。図15に、文字候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字列候補の例を示す。図15(a)の151が入力画像、15(b)の152が文字列切り出し手段で切り出した文字列候補とする。文字列切り出し方法としては、例えば文字が車輪の色より輝度が低い(黒い)とすると、車輪の背景色の平均値と、文字の色の平均値の間の値を閾値として適切に決定し、二値化することで、背景領域から文字列領域を抽出する等の処理で実現できる。また、単に二値化のみでは、文字が途切れたり、またノイズとの区別が不明瞭であるため、膨張・収縮処理などを実施して、孤立点などのノイズを除去し、文字領域の輪郭を明確に抽出する。 Returning to the description of the processing of the character candidate cutout means 8. FIG. 15 shows an example of character string candidates cut out by the character candidate cutout means 8. In FIG. 15A, 151 is an input image, and 15 in FIG. 15B is a character string candidate cut out by the character string cutting means. As a character string cut-out method, for example, if the character is lower in brightness than the wheel color (black), a value between the average value of the wheel background color and the average value of the character color is appropriately determined as a threshold, By binarizing, it can be realized by processing such as extracting a character string area from the background area. In addition, since binarization alone is used, characters are interrupted and the distinction from noise is unclear. Therefore, noise such as isolated points is removed by performing expansion / contraction processing, and the outline of the character area is defined. Extract clearly.
次に文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16につき説明する。図16に、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16に格納する文字並び間隔ルールの例を示す。本実施例は、製造情報などの文字列が等間隔であることを前提とする。 Next, the character arrangement interval rule storage means 16 will be described. FIG. 16 shows an example of the character arrangement interval rule stored in the character arrangement interval rule storage means 16. This embodiment is based on the premise that character strings such as manufacturing information are equally spaced.
図16の161に示すのが、本実施例での製造情報の文字並びルールの例である。図12で説明したように、図16中の16aが基準マークであり、すべての車輪に必ず1つ存在するマークとする。これに対し、後ろの文字列16bは、車輪毎に異なる数字もしくは記号の並びである。
文字並びルールの例として、図16中16cの文字を基準とした左右8文字の文字並びのルール(16d)を示す。16cの文字の中心を基準とし、右隣の文字との間隔162、左隣の文字との間隔163、間隔164‥と、168までの8桁全ての文字との間隔を定義する。間隔は、極座標変換前の度数、もしくは、極座標変換後の画素数などで定義する。また、基準文字16cと、基準マーク16aとの間隔169も定義する。ルールとする桁並び相互の位置関係が定義できれば、基準文字の選定方法など必ずしもこの例によらない。
As an example of the character arrangement rule, a rule (16d) for character arrangement of 8 characters on the left and right with reference to the
また、ルールとして選定する文字並びは、製造情報全文字列中でユニークなものであれば何でも良く、16bに示す製造情報文字列全てであっても、16dに示すように部分的な並びであってもいずれでも構わない。製造文字列中の位置を一意に特定できる文字間隔の並びであるとする。不適切な例としては、例えば16eに示す4桁の並びであると、16dの8桁の並びと部分的に一致してしまうので、このような文字並びは避けるとする。 In addition, the character sequence selected as a rule may be anything unique as long as it is unique among all manufacturing information character strings, and even the entire manufacturing information character string shown in 16b is a partial sequence as shown in 16d. But it doesn't matter. It is assumed that the character spacing is a sequence that can uniquely identify the position in the manufacturing character string. As an inappropriate example, for example, the 4-digit arrangement shown in 16e partially matches the 8-digit arrangement of 16d, so such a character arrangement is avoided.
以上のように定義した一種類または複数種類の文字並び間隔ルールを文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16に格納する。 One or more types of character arrangement interval rules defined as described above are stored in the character arrangement interval rule storage means 16.
次に、マーク位置推定手段9の処理に付き説明する。マーク位置推定手段9は、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16に格納した文字列の並び間隔のルールを用い、文字列候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字列候補のうちから、ルールと一致する文字列候補を検出し、ルール文字列と、基準マークとの間隔から、基準マークの位置を推定する手段である。文字列候補切り出し手段8により切り出した文字列候補のうち、図16の文字間隔162〜168に間隔が一致する文字並びを検出し、文字並びと基準マークとの間隔169により、基準マークの位置を推定するのがマーク位置推定手段9である。
Next, the process of the mark position estimating means 9 will be described. The mark
マーク位置推定手段9の処理の流れに付き図17を用いて説明する。 The process flow of the mark position estimating means 9 will be described with reference to FIG.
処理171では、ルールの種類数をカウントするカウンタIを0クリアする。処理172では、文字候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字数をカウントするカウンタJを0クリアする。処理173では、文字候補切り出し手段8で切り出した、j番目の文字候補を基準とした文字並びと、ルールIの並びを比較し、x方向の位置の誤差を算出する。処理174では、文字候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字数のカウンタjを1進める。処理175では、文字候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字数のカウンタjが、文字列候補文字数を超えたか否かを判定する。超えていれば全ての文字候補を基準としたルールIとの比較が終了したので処理176に進み、超えていなければ処理173に戻り、j番目の文字列につき処理をする。
In
処理176では、ルールIに対して、誤差最小の文字候補の位置を取得する処理を行い、処理173で、j番目の文字候補を基準とした場合のうち、誤差最小となるjの値を求める。処理177では、処理176で求めた誤差最小になる文字候補の位置から、相対位置で基準マークの位置を推定する。処理178では、ルールの種類数をカウントするカウンタiを1進めて次のルールの処理に移る。処理179では、ルールの種類数をカウントするカウンタIが、ルール種類数を超えたか否かを判定する。超えていれば全てのルールについての処理が終了したとし、処理を終了する。超えていなければ処理172に戻り、次のルールについて処理を行う。
In
以上がマーク位置推定手段9の処理の流れであるが、処理の内容を具体例を用い説明する。図18は、文字及び間隔ルールと、切り出した文字列の位置の比較方法を示す図である。図中、181は文字並びルールの例であり、182がルール中の基準文字であり、183が、このルール中で、基準文字182との相対位置で推定される基準マークの位置である。
The above is the processing flow of the mark position estimating means 9. The content of the processing will be described using a specific example. FIG. 18 is a diagram illustrating a method of comparing the character and interval rule and the position of the extracted character string. In the figure, 181 is an example of a character arrangement rule, 182 is a reference character in the rule, and 183 is a reference mark position estimated in a relative position to the
これに対し、文字列候補切り出し手段8で切り出した文字候補を152に示す。図中、説明の便宜のため、文字候補の下部に(0)から(14)の配列番号を表示しているが、これら(0)乃至(14)の各文字候補を基準位置とし、181に示す文字並びルールの並びと順に比較していくのが処理173、処理174の処理の内容である。
On the other hand, the character candidates cut out by the character string candidate cut-out means 8 are shown at 152. In the figure, for convenience of explanation, the sequence numbers (0) to (14) are displayed at the bottom of the character candidates.The character candidates (0) to (14) are used as reference positions, and The contents of the
図18の例では、ルールの基準文字182と、配列(5)の文字候補184の中心x座標を合わせて、他の7桁の文字のx座標を、文字候補のうち最も近いものと比較し、誤差の絶対値を7桁分累積して、ルールIの、j番目の文字候補を基準とした誤差を算出する。この173の処理を、基準位置をjのカウンタで0から14まで進めながら算出していく。
In the example of FIG. 18, the
181の文字並びルールは、8桁の等間隔の文字並びであるので、ルールの基準文字182を、文字候補(0)から(14)まで順に合わせて誤差評価した場合、図18に示す、配列(5)、184と合わせた場合が最も誤差が小さくなる。そこで、j=5の位置が181のルールに一致する位置とし、この位置を基準として、基準マークの位置を推定する。
Since the character arrangement rule of 181 is an 8-digit uniform character arrangement, when error evaluation is performed by matching the
図18図中、169で示す間隔が、ルール181の基準文字182と基準マーク183との間隔であるので、この位置を切り出した文字候補の並びに重ねると、推定位置は図中185の位置となる。185の位置を、ルール181による基準マークの推定位置とする。
In FIG. 18, the interval indicated by 169 is the interval between the
同様に、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16に、複数ルールが存在する場合は、上記の処理をルール数分繰り返して、ルール毎に誤差最小となる推定位置を求める。
Similarly, when there are a plurality of rules in the character arrangement interval
尚、上記実施例では、推定位置は誤差最小の位置としたが、場合によっては、影の影響、ノイズ、文字のかすれ等の原因で、切り出した文字候補が欠けており、図18の152に示すような文字列として切り出せない場合がある。そのような場合には誤差最小でも異なる文字並びを検出する恐れもあるので、誤差の閾値を設け、誤差が閾値以下で、且つ最小値の位置を、推定の確信度が高いとして採用するなどの実施例をとることもできる。 In the above embodiment, the estimated position is the position with the smallest error, but in some cases, the extracted character candidate is missing due to the influence of shadow, noise, blurred character, etc. It may not be cut out as a character string as shown. In such a case, there is a possibility of detecting different character arrangements even with the smallest error, so an error threshold is set, and the error is below the threshold, and the position of the minimum value is adopted as having a high certainty of estimation. Examples can also be taken.
基準マークマッチング手段17は、実施例1の基準マーク検出手段4と同様に、基準マークの位置をパターンマッチングにより相関値の高い位置を求める処理である。実施例1では、入力画像に対してテンプレートマッチングするため、円周方向の位置により向きの異なる基準マークのテンプレートを複数用意しマッチングする例を挙げたが、車輪画像の極座標変換により、図14(b)の146のように円周上の文字列は水平方向に並ぶ文字列画像に変換できる。極座標変換後の車輪画像を対象にパターンマッチングする場合には、基準マークの向きは画像上のどこにあっても一定であるので、マッチングのテンプレートは1種類でも実施可能である。
The reference
一方で、基準マークが車輪に打刻された刻印である場合には、刻印の位置が変わると照明の当たる角度が変わるため、刻印の影のできる向きも変わる。同じ刻印でも、テンプレートと影の向きが異なるとマッチングの相関値も低下するため、基準マークの位置によらずマッチングで高い相関値を得るためには、画面上の様々な位置にある複数のマーク画像をテンプレートとし、マッチングする実施例をとることもできる。 On the other hand, when the reference mark is an inscription stamped on the wheel, the illumination angle changes when the position of the inscription changes, so the direction in which the shadow of the inscription changes. Even if the stamp is the same, the correlation value of matching also decreases if the direction of the shadow of the template is different. Therefore, in order to obtain a high correlation value by matching regardless of the position of the reference mark, multiple marks at various positions on the screen are used. An embodiment in which an image is used as a template and matching is also possible.
図19に、複数テンプレートの作成方法を示す。図19中、311、313、315は車輪の極座標変換後の画像であり、それぞれ、基準マークは画像中のx方向の異なる位置に存在する。これらの基準マーク領域312、314、316を切り出して、317に示すように複数のテンプレートとして予め作成する。
FIG. 19 shows a method for creating a plurality of templates. In FIG. 19, 311, 313, and 315 are images after the polar coordinate conversion of the wheel, and the reference marks exist at different positions in the x direction in the image. These
このように作成した複数のテンプレートで、マッチングを行い、相関値最大となった位置をマッチングによる基準マーク候補位置とする。この際、全てのテンプレートで、全検知領域をサーチしても良いが、テンプレートの数が多くなると処理負荷が大きくなるため、例えば、画像中の中心付近から採用したテンプレートにより検知領域全体をサーチし、マッチング相関値の高い候補位置を複数選出して、選出した候補位置につき、複数のテンプレートそれぞれでマッチングして相関値を算出する方法などを採ることもできる。 Matching is performed using the plurality of templates created in this way, and the position where the correlation value is maximized is set as a reference mark candidate position by matching. At this time, the entire detection area may be searched for all templates, but the processing load increases as the number of templates increases.For example, the entire detection area is searched using the template adopted from the vicinity of the center in the image. Alternatively, a method of selecting a plurality of candidate positions having a high matching correlation value and calculating a correlation value by matching each of the selected candidate positions with a plurality of templates may be employed.
次に、実施例2の構成の、マーク位置決定手段10に付き説明する。マーク位置決定手段は、基準マーク検出手段4と、マーク位置推定手段9により求めた複数のマーク位置候補から、最終的にマーク位置を決定する手段である。
Next, the mark position determining means 10 having the configuration of the second embodiment will be described. The mark position determining means is a means for finally determining the mark position from the plurality of mark position candidates obtained by the reference
本手段では、基準マーク検出手段4の検出位置と、マッチングの相関値、および、マーク位置推定手段9により求めた複数のルールによる推定位置と、推定誤差、等から、最も確からしい基準マークの位置を決定する処理である。 In this means, the most probable reference mark position from the detection position of the reference mark detection means 4, the correlation value of the matching, the estimated position by a plurality of rules obtained by the mark position estimation means 9, the estimation error, etc. It is a process to determine.
複数のマーク位置候補から、マーク位置を決定する判定条件として、例えば以下のような方法がある。
マッチングによる相関値は、マークのテクスチャの類似度を示すため、マッチングによる相関値が高い位置は、基準マークである確信度が高いとし、基準マーク検出手段4による検出位置の相関値が閾値以上の場合には、無条件で検出位置をマーク位置として採用する。複数のマーク候補位置が同一位置であった場合には、その位置をマーク位置として採用する。
複数の推定ルールがある場合は、各推定ルールの間に優先度による重み付けをする。優先度をつける方法としては、文字並びルールのパターンが特徴的であり、誤推定が少ないものは重みを高くする、一方、ノイズなどの影響で、誤検出しやすい文字並びルールは、重みを低くする、等の方法とする。複数ルール間でマークの推定位置が異なる場合は、これらの重みと、誤差を考慮し、最も確からしい基準マーク位置を判定する。
As a determination condition for determining a mark position from a plurality of mark position candidates, for example, there are the following methods.
Since the correlation value by matching indicates the degree of similarity of the texture of the mark, a position where the correlation value by matching is high has a high certainty that it is a reference mark, and the correlation value of the detection position by the reference mark detection means 4 is greater than or equal to a threshold value. In some cases, the detection position is unconditionally adopted as the mark position. If a plurality of mark candidate positions are the same position, that position is adopted as the mark position.
When there are a plurality of estimation rules, weighting is performed between the estimation rules by priority. As a method of assigning priorities, character arrangement rule patterns are characteristic, and those with few false estimates increase the weight, while character arrangement rules that are easily misdetected due to noise or the like have a low weight. And so on. If the estimated positions of the marks differ among the plurality of rules, the most probable reference mark position is determined in consideration of these weights and errors.
以上のように、マッチングによるマーク候補位置と、推定によるマーク候補位置を求め、最終的にマーク位置を判定することで、マークが画像上ではっきり顕在化している場合にはマッチングによる候補位置を採用することができる。また、マークが照明の陰に入っていたり、かすれて薄いなどで、画像上で顕在化しない場合には、マーク以外の文字列の並びから推定することで、マーク位置として確からしい位置を推定し採用することができる。 As described above, if the mark candidate position by matching and the estimated mark candidate position are obtained and the mark position is finally determined, the candidate position by matching is adopted when the mark is clearly visible on the image. can do. Also, if the mark is in the shade of lighting or is faint and faint, it does not become obvious on the image, so the estimated position is estimated by estimating from the sequence of character strings other than the mark. Can be adopted.
また、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16中に、推定ルールを複数準備する実施例の効果としては、図20の文字列201中の202に示すように、製造情報の文字列が部分的に薄い、影による隠れがあるなどで見えない場合、203に示すルールでは8桁の桁数の一部が文字候補として切り出せないのでルールによる推定が失敗する。
Further, as an effect of the embodiment in which a plurality of estimation rules are prepared in the character arrangement interval rule storage means 16, as indicated by 202 in the
準備しているルールが203のみであると、推定による基準マーク検出も失敗することになるが、204に示すルールも準備しており、これによる推定が成功すると、基準マーク位置を特定できることになる。以上のように、ルールを複数準備することで、製造情報文字列の一部が隠れた場合も、推定による基準マーク位置特定の成功確率を高めることができる。 If the only prepared rule is 203, the reference mark detection by estimation will also fail, but the rule shown in 204 is also prepared, and if the estimation by this is successful, the reference mark position can be specified. . As described above, by preparing a plurality of rules, even when a part of the manufacturing information character string is hidden, the success probability of specifying the reference mark position by estimation can be increased.
また、文字並び間隔ルール格納手段16中に複数ルールを準備する効果として、複数の推定位置が一致するマーク候補位置を採用する効果が挙げられる。図21に示すように、211に示す製造情報の文字列から、文字候補切り出し手段8で切出した文字候補を212とする。
Further, as an effect of preparing a plurality of rules in the character arrangement interval rule storage means 16, there is an effect of adopting a mark candidate position where a plurality of estimated positions match. As shown in FIG. 21, the character candidate cut out by the character
これに対し、文字並びールを仮に図中213、214、215の3種類とする。それぞれ、ルール213は、文字候補216を基準とした位置で誤差最小になり、基準マーク推定位置は219となる。ルール214は、文字候補217を基準とした位置で誤差最小になり、基準マーク推定位置は21aとなる。ルール215は、文字候補218を基準とした位置で誤差最小になり、基準マーク推定位置は21bとなる。この例では、文字候補が正しく切り出せているため、各ルールが適切な位置に一致し、結果として219、21a、21bの複数の推定位置が一致する。
In contrast, the character arrangement rules are assumed to be three
これは推定が成功した例であるが、図22は、製造情報以外に傷などノイズが存在し、誤推定が発生する例である。図22中、221は製造情報の文字列であるが、222は製造情報であるのに対し、223は傷であるとする。これを文字列候補切り出し手段8で切り出したものが224であるが、真の文字以外の傷も、文字と色が似ていると22eのように切り出される。 This is an example in which the estimation is successful, but FIG. 22 is an example in which noise such as a flaw exists in addition to the manufacturing information and an erroneous estimation occurs. In FIG. 22, 221 is a character string of manufacturing information, and 222 is manufacturing information, whereas 223 is a flaw. The character string candidate cutout means 8 cuts this out 224, but a scratch other than a true character is cut out as in 22e if the character and color are similar.
224の文字候補に対し、図21と同様にルール225、226、227の3種類で誤差最小の位置を求めると、ルール225、ルール226については、正しい位置に一致し、基準マーク推定位置がそれぞれ22b、22cと、一致した位置を推定している。これに対しルール227は、本来、文字候補22fに一致するのが正解であるが、切り出した文字候補22gが4桁の文字並び22eに似ているため、22aを基準とした文字候補並びのほうが誤差が小さくなる場合が発生する。
For the 224 character candidates, the position with the smallest error is obtained with the three types of
この場合、基準マークの推定位置が22dとなり、これは他の2ルールの推定位置とは一致しない。しかし、前述の基準マーク位置の判定条件より、複数の推定位置が同一位置であった場合には、その位置をマーク位置として採用するため、この際のマーク位置の判定は22b、22cの位置が優先されるとする。
In this case, the estimated position of the reference mark is 22d, which does not match the estimated positions of the other two rules. However, when the plurality of estimated positions are the same position based on the above-described reference mark position determination conditions, the positions are adopted as the mark positions. In this case, the mark positions are determined by the
また、以上の説明では、複数推定位置が「同一位置になったとき」としたが、文字切り出し処理などの過程で、文字の幅、中心位置などに誤差が発生する場合があるため、ルールに正しく一致しても、推定位置に誤差が発生する場合がある。 In the above description, the multiple estimated positions are assumed to be “when they are the same position”. However, there are cases where errors occur in the character width, center position, etc. Even if they match correctly, an error may occur in the estimated position.
このため、同一位置として判定する際に、誤差を考慮した幅を設け、例えば一文字分くらい推定位置に誤差が発生する場合も、同一位置と判定するなどの運用も考えられる。また、その場合には、複数の推定位置のいずれかを採用するのではなく、平均値をとるなどの運用もある。また、ルールごとに優先度の重み付けをしている場合には、重みを考慮した加重平均を取るなどの運用も考えられる。 For this reason, when determining as the same position, a range in which an error is taken into consideration is provided. For example, even when an error occurs in the estimated position for one character, an operation such as determining the same position is also conceivable. In that case, there is an operation such as taking an average value instead of adopting any of a plurality of estimated positions. In addition, when priority is weighted for each rule, an operation such as taking a weighted average considering the weight may be considered.
また、文字候補切り出し手段8で、二値化により文字候補を切り出すときに、複数の閾値により二値化して文字候補を切り出し、それぞれの閾値による切り出し結果からマーク位置推定手段9で推定を行い、基準マーク推定位置候補を求めることもできる。
In addition, when character candidates are cut out by binarization by the character
この場合、マーク位置推定手段9では、「ルール種類数×閾値数」種類の基準マーク位置候補が求まる可能性があるが、これらの複数候補位置から、マーク位置決定手段10で、一箇所の基準マーク位置を決定する。このように、閾値を変えて文字列候補を切り出すことで、文字列が画像上で薄いような場合にも、低い閾値による二値化で文字列候補として切り出せたり、またノイズが多い場合に、高い閾値でノイズを切り出さないようにするなどの効果がある。一方でノイズも多く切り出す可能性も増えるが、図22に示すように、複数のルールによる推定結果を優先することで、単独のノイズによる誤推定は除去できる。 In this case, there is a possibility that the mark position estimating means 9 may obtain the reference mark position candidates of “number of rule types × threshold number” types. From these multiple candidate positions, the mark position determining means 10 uses one reference position. Determine the mark position. In this way, by cutting out character string candidates by changing the threshold, even when the character string is thin on the image, it can be cut out as a character string candidate by binarization with a low threshold, or when there is a lot of noise, There is an effect of not cutting out noise at a high threshold. On the other hand, the possibility of cutting out a lot of noise also increases, but as shown in FIG. 22, by giving priority to the estimation results based on a plurality of rules, erroneous estimation due to a single noise can be eliminated.
このように、ノイズによる誤推定が懸念されるようなケースでは、できるだけ多くのルールを用いることで、間違った位置の推定結果を、最終的なマーク位置として採用する誤推定を防ぐ効果がある。 As described above, in the case where there is a concern about erroneous estimation due to noise, using as many rules as possible has an effect of preventing erroneous estimation in which the estimation result of the wrong position is adopted as the final mark position.
以上、第二の実施例では、照明条件が悪い、また汚れなどのノイズがある等で、基準マーク自体の形状を基準マーク検出手段で検出できない場合も、製造情報の文字並び間隔ルールにより推定することで、基準マーク位置を推定し、特徴量の照合をすることができる。 As described above, in the second embodiment, even when the reference mark detection unit cannot detect the shape of the reference mark itself due to poor illumination conditions or noise such as dirt, it is estimated by the character arrangement interval rule of the manufacturing information. Thus, it is possible to estimate the reference mark position and collate the feature amount.
次に、車両検査装置の第三の実施例について説明する。第3の実施例は、車輪側面を画像処理するに適した処理、あるいは表示の手法を提供するものであり、図23ないし図26を用いて詳細に説明する。この実施例では、走行してくる車輪側面を複数の撮影装置で順次分割して撮影し、車輪の分割画像からそれぞれ特徴量を検出し、また分割された画像から一箇所の基準マーク位置を検出して、車輪側面の全周について特徴量位置を特定する実施例である。 Next, a third embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus will be described. The third embodiment provides a process or display method suitable for image processing of a wheel side surface, and will be described in detail with reference to FIGS. In this embodiment, the side surface of the traveling wheel is sequentially divided and photographed by a plurality of photographing devices, the feature amount is detected from each divided image of the wheel, and one reference mark position is detected from the divided image. And it is an Example which specifies a feature-value position about the perimeter of a wheel side surface.
図23は、車両検査装置の第3の実施形態を示すブロック図である。第2の実施例と比較して新規の構成は、画像撮影手段11と、画像間位置照合手段12である。
FIG. 23 is a block diagram showing a third embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus. Compared with the second embodiment, a new configuration is an
主に新規の構成につき説明する。画像撮影手段11は、232に示す線路脇に設置し、走行してくる車輪231の側面を撮影する手段である。画像撮影手段11は、複数のカメラ233〜236から構成される。画像撮影手段11による画像の撮影は、例えば、各カメラ233〜236毎に、線路側に向けて設置した車輪検知手段(図示せず)からの車輪検知信号に基づき実行される。
Mainly, the new configuration will be described. The
撮影した画像の例を図24に示す。鉄道車両に装備された車輪は、上部が台車部分に隠れて見えないため、円周の一部が撮影されることになる。また、画像中での車輪の位置は、画面中心で線路に接する位置で画像が撮影できるよう、車両検知手段の位置を調整する。 An example of a photographed image is shown in FIG. Since the upper part of the wheel mounted on the railway vehicle is hidden behind the carriage part and cannot be seen, a part of the circumference is photographed. Further, the position of the vehicle detection means is adjusted so that the image of the wheel in the image can be taken at a position in contact with the track at the center of the screen.
画像撮影手段11を構成するカメラ233〜236は、回転してくる車輪の全周がいずれかのカメラで撮影できるよう、車輪の弧の長さを考慮した間隔で設置する。例えば、この実施例のように4台のカメラで分割して撮影する場合は、車輪の4分の1周分の弧の長さの間隔でカメラを設置する、等である。
The
第3の実施例の構成の、画像入力手段1、特徴量検出手段2、車輪中心検出手段3、基準マーク検出手段4、文字候補切り出し手段8、マーク位置推定手段9については、第一の実施例、第二の実施例の記載と同様に行う。第一の実施例と、第二の実施例と異なるところは、車輪を分割して撮影するので、必ずしもマークが画像中に存在するとは限らない点である。このため、基準マーク検出手段4、マーク位置推定手段9では、それぞれの画像中で、最も基準マークらしい位置を検出、および推定する処理となる。
The image input means 1, the feature amount detection means 2, the wheel center detection means 3, the reference mark detection means 4, the character candidate cutout means 8, and the mark position estimation means 9 of the configuration of the third embodiment are the first implementation. This is carried out in the same manner as described in the example and the second embodiment. The difference between the first embodiment and the second embodiment is that the marks are not always present in the image because the wheels are divided and photographed. For this reason, the reference
また、画像間位置照合手段12では、同一の車輪を分割して撮影した複数画像のうち、隣り合う画像同志の対応する位置を求めて、画像を連結する手段である。本手段の目的は、画像が分割しているため、マーク位置推定手段9や、特徴量照合手段7で、位置関係を算出する二点が別画像に分かれている場合に、適切に位置関係を算出できるようにするためである。 The inter-image position matching means 12 is a means for obtaining the corresponding positions of adjacent images among a plurality of images taken by dividing the same wheel and connecting the images. The purpose of this means is that since the image is divided, the mark position estimating means 9 and the feature amount matching means 7 can appropriately determine the positional relationship when the two points for calculating the positional relationship are separated into different images. This is to allow calculation.
本手段は、車輪の径が一定であれば、いつも一定の位置を対応点とする処理となる。例えば、複数カメラの設置間隔を、径の長さがLの車輪が90°回転するに相当する弧の間隔で設置した場合には、隣接した画像の中心点同志の間隔は、ちょうど90°分になると考えられるので、画像の中心点の間の角度が90°になるように対応点を求めればよい。仮に車輪の磨耗などで車輪径が短くなっている場合には、摩耗後の車輪径をαとおくと、画像の中心点の間の角度θは、下記の計算式(1)で求められる。 If the wheel diameter is constant, this means is always processing with a fixed position as a corresponding point. For example, when installing multiple cameras at an arc distance equivalent to 90 ° rotation of a wheel with a diameter of L, the distance between adjacent image center points is exactly 90 °. Therefore, the corresponding points may be obtained so that the angle between the center points of the image is 90 °. If the wheel diameter is shortened due to wheel wear or the like, if the wheel diameter after wear is α, the angle θ between the center points of the image can be obtained by the following calculation formula (1).
θ = 90°×(L/α) ‥ (1)
摩耗等により車輪径が変化する場合には、エッジ検出等で画像中の車輪の弧を求め、車輪の中心と弧の距離を画像上で求めることで、径の長さαを求め、画像の中心点同志の間隔を数1より求める。
θ = 90 ° x (L / α) (1)
When the wheel diameter changes due to wear or the like, the arc of the wheel in the image is obtained by edge detection or the like, the distance between the center of the wheel and the arc is obtained on the image, the length α of the diameter is obtained, Find the interval between the central
以上の方法で、画像間の対応点を求める。図25に、画像間位置照合手段12の処理前の分割撮影した車輪画像の例と、照合後、対応点を重ねて連結した車輪画像の例を示す。図中251、253、255、257はそれぞれ図23のカメラ233〜236で分割撮影された車輪画像であり、252、254、256、258はそれぞれ画像中251、252、253、254の画面の中心点である。25dが、画像間の位置を照合し、連結した車輪画像の例であるが、隣接する画像の中心点252と254の間の間隔259、および、254と256の間隔25a、および、256と258の間隔25b、258と252の間隔25cが、それぞれ数1式(1)で算出した角度θになるようにする。
With the above method, corresponding points between images are obtained. FIG. 25 shows an example of a wheel image that is divided and photographed before processing by the inter-image position matching means 12, and an example of a wheel image that is connected after overlapping corresponding points. In the figure, 251, 253, 255, and 257 are wheel images taken separately by the
同様に、極座標変換後の分割画像も、上記の考え方で照合することができる。図26は、極座標変換後の分割画像を、照合後、連結する処理を示す図である。同図(a)(b)は、極座標変換後の隣接した分割画像261、262を表しており、同図(c)に、照合後の連結した画像265を表す。この図から明らかなように、変換前の場合と同様、画面の中心263と、264の間隔266が、角度θになるよう画像間の位置を照合する。この図(c)の例では、267が画像間の重複部分となる。例えば、画像上の268のx座標の位置が、画像261上では‘1000’、画像262上では‘0‘であるとすると、画像261上でx座標’xx’である位置は、画像262上ではx座標’xx-1000’として求められることになる。
Similarly, the divided images after the polar coordinate conversion can be collated based on the above concept. FIG. 26 is a diagram illustrating a process of connecting the divided images after the polar coordinate conversion after collation. FIGS. 9A and 9B show adjacent
マーク位置推定手段9で、仮に、推定したマーク位置が同一画像中に入っていない場合は、隣接画像中の位置を換算して、隣接画像中での推定位置を求めるとする。 If the mark position estimated by the mark position estimation means 9 is not included in the same image, the estimated position in the adjacent image is obtained by converting the position in the adjacent image.
以上が画像間位置照合手段12の処理の説明である。
The above is the description of the processing of the inter-image
第三の実施例でのマーク位置決定手段10が第二の実施例と異なる点は、複数の分割画像のそれぞれにおいて基準マーク検出手段4で検出されたマーク位置候補と、マーク位置推定手段9で推定した複数のマーク位置候補とから、一箇所のマーク位置を決定する点である。マーク位置候補の数は多くなる可能性はあるが、判定方法は第二の実施例と同様の方法で、一箇所を決定する。 The mark position determining means 10 in the third embodiment is different from the second embodiment in that a mark position candidate detected by the reference mark detection means 4 in each of a plurality of divided images and a mark position estimation means 9 This is a point for determining one mark position from a plurality of estimated mark position candidates. Although there is a possibility that the number of mark position candidates increases, the determination method is the same as in the second embodiment, and one place is determined.
特徴量照合手段7も、同様に、画像間位置を照合したあとの画像で、マーク位置と特徴量の位置関係で特徴量の位置を照合する。 Similarly, the feature amount matching means 7 also checks the position of the feature amount based on the positional relationship between the mark position and the feature amount in the image after the position between the images is verified.
以上が、車両検査装置の第三の実施例である。鉄道車両の車輪は、車体に取り付けられた状態であると、多くの場合は台車の影に一部は隠れてしまうため、全面を1画像で撮影することは難しい。そのため、車輪を車体から取り外さず、且つ走行中に車輪を分割して撮影し、特徴量検出できる本実施例は検査コストを大幅に低減する効果がある。 The above is the third embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus. When the wheels of a railway vehicle are attached to the vehicle body, in many cases, a part of the wheels is hidden behind the bogie, so it is difficult to capture the entire surface with one image. Therefore, the present embodiment, which does not remove the wheel from the vehicle body and divides and shoots the wheel while traveling to detect the feature amount, has the effect of greatly reducing the inspection cost.
次に、車両検査装置の第四の実施例を説明する。第四の実施例は、来歴管理のために工夫された構成であり、図27乃至図29を用いて説明する。図27は、車両検査装置の第四の実施例を示すブロック図であり、第三の実施例に特徴量来歴表示手段13を加えた構成である。 Next, a fourth embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus will be described. The fourth embodiment has a configuration devised for history management, and will be described with reference to FIGS. FIG. 27 is a block diagram showing a fourth embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus, and is a configuration obtained by adding feature amount history display means 13 to the third embodiment.
新規の構成である特徴量来歴表示手段13について説明する。特徴量来歴表示手段13では、特徴量来歴格納手段6に格納した特徴量の来歴を表示する。図11に示す特徴量来歴格納手段6のデータから、車輪ID、特徴量IDを選択することで、一意に特徴量を特定できるので、車輪ID、特徴量IDをユーザに選択させることで、同一の特徴量の異なったタイミングで撮影した画像を画像データベースから選択し、表示する。 The feature amount history display means 13 which is a new configuration will be described. The feature quantity history display means 13 displays the history of the feature quantity stored in the feature quantity history storage means 6. Since the feature amount can be uniquely identified by selecting the wheel ID and feature amount ID from the data of the feature amount history storage means 6 shown in FIG. 11, the same can be obtained by allowing the user to select the wheel ID and feature amount ID. Images taken at different timings are selected from the image database and displayed.
図28に示すのは、特徴量来歴表示手段13で表示する車輪を選択するための入力画面の例である。281に示すリストに、編成IDのリストを表示し、ユーザがリスト中から任意の編成IDを選択し、283の「選択」ボタンを押下すると、ユーザが選択した編成IDをキーに、編成・車輪対応格納手段5から、編成に取り付けられている車輪IDを、配列毎に取得する。 FIG. 28 shows an example of an input screen for selecting a wheel to be displayed by the feature amount history display means 13. A list of composition IDs is displayed in the list shown in 281. When the user selects an arbitrary composition ID from the list and presses the "Select" button of 283, the composition / wheel is selected using the composition ID selected by the user as a key. The wheel ID attached to the knitting is acquired from the correspondence storage means 5 for each array.
さらに、取得した車輪IDで、特徴量来歴格納手段6から、該当する車輪の最新の特徴量数を検索する。以上のように取得した車輪毎の配列と特徴量数リストを、284にリスト表示する。ユーザはこのリストから特徴量来歴を表示したい車輪を選択し、「表示」ボタン286を押下する。選択された車輪の来歴の表示例を図29に示す。
Further, the latest feature quantity number of the corresponding wheel is searched from the feature quantity history storage means 6 with the acquired wheel ID. The array for each wheel and the feature quantity list acquired as described above are displayed as a list in 284. The user selects a wheel for which the feature history is to be displayed from this list, and presses a “display”
図29中のウインドウ291および292に、選択された「車輪1」の、異なる日付で撮影した画像を表示する。この際、画像中の車輪の向きは、基準マーク294、295の位置を合わせて表示することで、異なるタイミングで撮影した画像同志の位置を合わせて比較しやすくできる。また、例えば293に示すようなリストで、ユーザに特徴量選択させることで、表示したい特徴量を前面に296、297のように表示させるなどの実施形態も取れる。また、298、299のように、特徴量の大きさを表示し、29aと29bのように選択した特徴量の拡大画像を表示するなどの実施例も取れる。
In
以上、特徴量来歴表示手段13の実施例を示したが、本発明により、照合できた同一車輪の特徴量を比較表示するのが目的であり、上記の実施形態に限るものでない。 The embodiment of the feature amount history display means 13 has been described above. However, according to the present invention, it is an object to compare and display the feature amounts of the same wheel that can be collated, and is not limited to the above embodiment.
また、来歴を表示する車輪の選択方法であるが、特徴量の大きさでフィルターをかけ、一定大きさ以上の特徴量のある車輪をリスト表示させるなどの実施形態をとることもできる。 In addition, although the method of selecting a wheel for displaying the history is used, an embodiment may be adopted in which a wheel is filtered by the size of a feature amount and a wheel having a feature amount of a certain size or more is displayed as a list.
以上のように、第四の実施例により、特徴量の成長度合いなどを画像上で比較して見る事ができる。従来の、停止した車両の検査では、台車により隠れる部分があり車輪を取り外すことなしに車輪の全周の検査は実施できなかったが、車輪の全周を撮影し、また基準位置を合わせて来歴比較できる効果がある。 As described above, according to the fourth embodiment, the degree of growth of the feature amount can be compared on the image. In the conventional inspection of a stopped vehicle, there was a part hidden by the carriage, and it was not possible to inspect the entire circumference of the wheel without removing the wheel. There is a comparable effect.
次に、車両検査装置の第五の実施例を説明する。第五の実施例もまた、来歴管理を有効に行うための工夫であり、列車編成の運行管理情報と関連付けて特徴量の管理を行う。図30は、車両検査装置の第五の実施例を示すブロック図であり、第三の実施例に編成運行情報格納手段14と、統計情報算出表示手段15を加えた構成である。 Next, a fifth embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus will be described. The fifth embodiment is also a device for effectively performing history management, and manages feature quantities in association with train management operation management information. FIG. 30 is a block diagram showing a fifth embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus, which is a configuration obtained by adding a set operation information storage means 14 and a statistical information calculation display means 15 to the third embodiment.
新規の構成につき説明する。編成運行情報格納手段14は、編成毎の、日付毎の走行距離や、走行区間などの情報を格納した格納手段である。 The new configuration will be described. The train operation information storage means 14 is a storage means for storing information such as the travel distance for each date and the travel section for each train.
また、統計情報算出表示手段は、編成運行情報格納手段14と、編成・車輪対応格納手段5と、特徴量来歴格納手段6から、任意の複数車輪の、走行条件と、特徴量発生状況のデータを取得し、グラフ上に散布図を描き、また、相関値を求めるなど統計情報を算出し、表示する手段である。 Further, the statistical information calculation and display means includes data on running conditions and feature quantity occurrence statuses of any plural wheels from the knitting operation information storage means 14, the knitting / wheel correspondence storage means 5 and the feature quantity history storage means 6. Is obtained, and a scatter diagram is drawn on a graph, and statistical information is calculated and displayed such as obtaining a correlation value.
走行情報は、編成運行情報格納手段14に編成毎に格納されているが、編成・車輪対応格納手段5で、車輪が編成に取り付けられた期間「開始日」、「終了日」が格納されているので、該当する期間の編成運行情報を車輪に引き継ぐことで取得できる。 The travel information is stored for each knitting in the knitting operation information storing means 14, but the knitting / wheel correspondence storing means 5 stores the "start date" and "end date" during which the wheels are attached to the knitting. Therefore, it can be acquired by taking over the train operation information for the corresponding period to the wheel.
グラフ表示の例としては、「走行距離」と「特徴量の大きさ」を二軸にとりプロットする、また、ある走行区間を運行した車輪のデータのみを抽出し、「走行距離」と「特徴量の大きさ」をプロットして区間による特徴量発生の傾向を見ることもできる。また、編成中での車輪の位置に注目し、配列の位置毎に走行距離と特徴量の大きさの関係を分析することもできる。 As an example of a graph display, plot the “travel distance” and “size of feature” on two axes, or extract only the data of the wheels that have traveled in a certain travel section. It is also possible to plot the feature size generation tendency by plotting the “size of”. Further, paying attention to the position of the wheel during knitting, it is possible to analyze the relationship between the travel distance and the size of the feature amount for each position of the array.
このように、第5の実施例により、車輪個別でなく、走行距離、走行区間などによる特徴量の成長等の傾向を見、相関を求めることができ、その結果に基づいて、編成の運行計画や、予防保全計画に役立てることができる。 In this way, according to the fifth embodiment, it is possible to obtain a correlation by seeing a tendency such as the growth of the feature amount not by individual wheels but by the travel distance, travel section, etc. And can be used for preventive maintenance planning.
以上が本発明による車両検査装置の第5の実施例である。
尚、本発明では基準マークを自動的に検出して、異なる日付で検出された特徴量の照合をすることがポイントであるが、仮にノイズ等の影響でマークが全く検出できなかった場合には、ユーザにより位置を画像上から座標を選択することで選択入力させ、その位置を基準マーク位置として特徴量位置を照合する実施形態も可能である。
The above is the fifth embodiment of the vehicle inspection apparatus according to the present invention.
In the present invention, it is important to automatically detect the reference mark and collate the feature values detected on different dates. However, if the mark cannot be detected at all due to the influence of noise or the like, An embodiment is also possible in which a user selects and inputs a position by selecting coordinates from an image, and collates the feature amount position using the position as a reference mark position.
本発明によれば、車輪側面の車両検査が可能となる。 According to the present invention, vehicle inspection of the wheel side surface is possible.
1:画像入力手段
2:特徴量検出手段
3:車輪中心検出手段
4:基準マーク検出手段
5:編成・車輪対応格納手段
6:特徴量来歴格納手段
7:特徴量照合手段
1: Image input means 2: Feature amount detection means
3: Wheel center detection means
4: Reference mark detection means
5: Knitting / wheel correspondence storage means 6: Feature history storage means
7: Feature amount verification means
Claims (18)
入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出する特徴量検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪中心の座標を検出する車輪中心検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から基準マークを検出してその座標を決定する基準マーク検出手段と、前記の車輪中心の座標と前記基準マークの座標を基準として決定された前記特徴量の位置を記憶する特徴量格納手段とを備えることを特徴とする車両検査装置。 In a vehicle inspection apparatus that detects an image of a wheel side surface of a railway vehicle and detects a position of a feature amount,
Feature amount detection means for detecting a feature amount on a wheel from the input image of the rail vehicle wheel side surface, wheel center detection means for detecting the coordinates of the wheel center from the input image of the rail vehicle wheel side surface, and the input railway Reference mark detection means for detecting a reference mark from an image of a vehicle wheel side surface and determining the coordinates thereof, and a feature for storing the position of the feature amount determined based on the coordinates of the wheel center and the coordinates of the reference mark A vehicle inspection apparatus comprising: a quantity storage unit.
前記基準マーク検出手段は、基準マークについてのテンプレートを保持しており前記入力した画像からテンプレートマッチングで相関値が高い領域を検出し、基準マークを検出することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 In the vehicle inspection device according to claim 1,
The reference mark detection means holds a template for a reference mark, detects an area having a high correlation value by template matching from the input image, and detects the reference mark.
前記基準マークについてのテンプレートは、車輪の回転に応じて回転させた複数のテンプレートとして保持され、複数のテンプレートごとに前記入力した画像から、テンプレートマッチングで、相関値が高い領域を検出し、基準マークを検出することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 2,
The template for the reference mark is held as a plurality of templates rotated according to the rotation of the wheel, and a region having a high correlation value is detected by template matching from the input image for each of the plurality of templates. Vehicle inspection device characterized by detecting
前記基準マーク検出手段は、1種類のテンプレートによりマッチング検出して相関値が高い基準マーク候補領域を複数選出し、撮影条件の異なる複数のテンプレートにより選出した基準マーク候補領域をマッチングして、相関値の最も高い位置を基準マーク位置とすることを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 2,
The reference mark detecting means selects a plurality of reference mark candidate areas having a high correlation value by performing matching detection using one type of template, matches the reference mark candidate areas selected by a plurality of templates having different shooting conditions, and obtains a correlation value A vehicle inspection apparatus characterized in that the highest mark position is set as a reference mark position.
前記基準マーク検出手段は、前記入力した画像から、文字候補を切り出す文字候補切り出し手段と、車輪上に存在する複数の文字列の文字間の間隔をルールとして格納する文字並び間隔ルール格納手段と、該文字並び間隔ルール格納手段に格納した文字列の並び間隔のルールを用い、前記文字列候補切り出し手段で切り出した文字列候補のうちから、ルールと一致する文字列候補を検出し、基準マークの位置を推定するマーク位置推定手段を備えることを特徴とした車両検査装置。 In the vehicle inspection device according to claim 1,
The reference mark detection means includes character candidate cutout means for cutting out character candidates from the input image, and character arrangement interval rule storage means for storing intervals between characters of a plurality of character strings existing on wheels as rules. A character string candidate that matches the rule is detected from the character string candidates cut out by the character string candidate cut-out means using the rule of the character string arrangement interval stored in the character arrangement interval rule storage means, and the reference mark A vehicle inspection apparatus comprising mark position estimation means for estimating a position.
前記基準マーク検出手段の文字候補切り出し手段は、複数の異なる閾値を用いて切り出した文字列候補それぞれについて、前記マーク位置推定手段でマーク位置を推定し、基準マーク位置とすることを特徴とした車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 5,
The character candidate cutout means of the reference mark detection means estimates the mark position by the mark position estimation means for each of the character string candidates cut out using a plurality of different threshold values, and sets the reference mark position. Inspection device.
前記基準マーク検出手段は、基準マークについてのテンプレートを保持しており前記入力した画像からテンプレートマッチングで相関値が高い領域を検出し、基準マークを検出する基準マークマッチング手段と、前記入力した画像から、文字候補を切り出す文字候補切り出し手段と、車輪上に存在する複数の文字列の文字間の間隔をルールとして格納する文字並び間隔ルール格納手段と、該文字並び間隔ルール格納手段に格納した文字列の並び間隔のルールを用い、前記文字列候補切り出し手段で切り出した文字列候補のうちから、ルールと一致する文字列候補を検出するマーク位置推定手段と、前記基準マークマッチング手段と前記マーク位置推定手段で求めたマーク位置候補から最終的にマーク位置を決定するマーク位置決定手段を備えることを特徴とする車両検査装置。 In the vehicle inspection device according to claim 1,
The reference mark detection unit holds a template for a reference mark, detects a region having a high correlation value by template matching from the input image, and detects a reference mark from the input image. A character candidate cutout unit that cuts out character candidates, a character arrangement interval rule storage unit that stores, as a rule, an interval between characters of a plurality of character strings existing on the wheel, and a character string stored in the character arrangement interval rule storage unit A mark position estimating means for detecting a character string candidate that matches the rule from the character string candidates cut out by the character string candidate cut-out means, the reference mark matching means, and the mark position estimation. Mark position determining means for finally determining the mark position from the mark position candidates obtained by the means Vehicle inspection device, characterized in that.
前記マーク位置決定手段は、前記基準マークマッチング手段で検出した基準マーク位置候補の相関値が十分高い場合、前記マーク位置決定手段で推定した基準マーク位置候補より優先して基準マーク位置として決定することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 7,
The mark position determining unit determines a reference mark position in preference to the reference mark position candidate estimated by the mark position determining unit when the correlation value of the reference mark position candidate detected by the reference mark matching unit is sufficiently high. Vehicle inspection device characterized by the above.
前記マーク位置決定手段は、前記基準マークマッチング手段で検出した基準マーク位置候補、および前記マーク位置決定手段で推定した基準マーク位置候補が複数存在する場合、同一の位置を検出、もしくは推定した件数が多い位置を優先して基準マーク位置として決定することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 7,
When there are a plurality of reference mark position candidates detected by the reference mark matching means and a plurality of reference mark position candidates estimated by the mark position determining means, the mark position determining means detects the same position or the number of cases estimated A vehicle inspection apparatus characterized in that a large number of positions are preferentially determined as reference mark positions.
前記文字並び間隔ルール格納手段に格納する複数の異なるルールについて重み付けをして、重み付に基づき、前記マーク位置決定手段で複数の基準マーク位置候補から基準マーク位置を決定する際に優先度を決定することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 7,
A plurality of different rules stored in the character arrangement interval rule storage means are weighted, and based on the weighting, a priority is determined when the mark position determination means determines a reference mark position from a plurality of reference mark position candidates. A vehicle inspection device.
前記基準マークマッチング手段で検出した基準マーク位置候補、および前記マーク位置決定手段で推定した基準マーク位置候補が複数存在する場合、前記マーク位置決定手段は、近傍に複数推定位置が存在する場合に、複数推定位置の平均、もしくは、複数ルールの重み付けをしている場合には、加重平均をとって算出した位置をマーク位置として決定することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 7,
When there are a plurality of reference mark position candidates detected by the reference mark matching means, and a plurality of reference mark position candidates estimated by the mark position determination means, the mark position determination means, when there are a plurality of estimated positions in the vicinity, A vehicle inspection apparatus characterized in that when a plurality of estimated positions are averaged or a plurality of rules are weighted, a position calculated by taking the weighted average is determined as a mark position.
入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出する特徴量検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から車輪中心の座標を検出する車輪中心検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から基準マークを検出してその座標を決定する基準マーク検出手段と、鉄道車両を撮影するときに撮影車輪を識別する車輪識別情報の対応を格納する編成・車輪対応格納手段と、車輪中心の座標と基準マークの座標を基準として決定された特徴量の位置を前記車輪識別情報に対応づけて記憶する特徴量来歴格納手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の画像から得られた特徴量について、同じ車輪識別情報を有する車輪の情報を前記の特徴量来歴格納手段から求め、特徴量位置情報から同一と考えられる特徴量があった場合は、同一特徴量を示す識別情報を付与して特徴量来歴格納手段に追記する特徴量照合手段とを備えることを特徴とした車両検査装置。 In the vehicle inspection device that processes the image of the side of the wheel of the railway vehicle and records the history of the feature amount,
Feature amount detection means for detecting a feature amount on a wheel from the input image of the rail vehicle wheel side surface, wheel center detection means for detecting the coordinates of the wheel center from the input image of the rail vehicle wheel side surface, and the input railway A reference mark detecting means for detecting a reference mark from an image of a vehicle wheel side surface and determining its coordinates; a knitting / wheel correspondence storing means for storing correspondence of wheel identification information for identifying a photographing wheel when photographing a railway vehicle; Obtained from feature image history storage means for storing the position of the feature value determined based on the coordinates of the wheel center and the coordinates of the reference mark in association with the wheel identification information, and the inputted image of the side surface of the railroad vehicle wheel. If there is a feature amount that is considered to be the same from the feature amount position information, the information about the wheel having the same wheel identification information is obtained from the feature amount history storage means, Vehicle inspection apparatus comprising: a feature quantity matching means to append the feature value history storing means to impart identification information indicating a feature amount.
異なる日付に撮影した同じ車輪の画像を同じ特徴量が画像比較できるよう並べて表示する特徴量来歴表示手段を供えたことを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 12,
A vehicle inspection apparatus comprising a feature amount history display means for displaying images of the same wheels taken on different dates side by side so that the same feature amount can be compared.
編成運行情報格納手段と、統計情報算出表示手段を備え、車輪の走行に関する情報と、特徴量に関する情報の関係を対比して表示することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 12,
A vehicle inspection apparatus comprising: a train operation information storage unit; and a statistical information calculation display unit, wherein the relationship between information relating to traveling of wheels and information relating to feature quantities is displayed in comparison.
前記基準マーク検出手段、および前記マーク位置決定手段で、基準マークが検出できない場合に、画像上の基準マークの位置を入力する基準マーク位置入力手段を備え、入力された基準マーク位置に基づき、特徴量位置を照合し特徴量来歴格納手段に格納することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection apparatus according to claim 12,
When the reference mark cannot be detected by the reference mark detection unit and the mark position determination unit, the reference mark detection unit includes a reference mark position input unit that inputs the position of the reference mark on the image. Based on the input reference mark position, A vehicle inspection apparatus characterized by collating a quantity position and storing it in a feature quantity history storage means.
前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について車輪上の特徴量を検出する特徴量検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について車輪中心の座標を検出する車輪中心検出手段と、前記入力した鉄道車両車輪側面の複数画像について基準マークを検出してその座標を決定する基準マーク検出手段と、隣接する位置で撮影された画像について対応する位置を求めて連結する画像間位置照合手段を備えることを特徴とした車両検査装置。 In a vehicle inspection device that obtains a continuous image for one lap of a wheel from multiple images taken at multiple locations close to the wheel side of a railway vehicle, and detects a feature amount,
Feature amount detection means for detecting feature values on wheels for a plurality of images of the input railcar wheel side surface, wheel center detection means for detecting coordinates of a wheel center for the plurality of images of the input railcar wheel side surface, A reference mark detecting means for detecting a reference mark for a plurality of images on the side surface of the input railcar wheel and determining coordinates thereof, and an inter-image position matching means for obtaining a corresponding position for images taken at adjacent positions and connecting them. A vehicle inspection apparatus comprising:
前記画像間位置照合手段は、画像上の車輪の中心と、車輪の弧を検出することで車輪の摩耗量を求め、隣り合う画像同士の対応点を算出することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection device according to claim 16,
The inter-image position checking means obtains the amount of wear of the wheel by detecting the center of the wheel on the image and the arc of the wheel, and calculates a corresponding point between adjacent images.
検出した車輪中心を基準とし極座標変換した画像から車輪上の特徴量を検出することを特徴とする車両検査装置。 The vehicle inspection device according to claim 16,
A vehicle inspection device that detects a feature amount on a wheel from an image obtained by polar-coordinate conversion using the detected wheel center as a reference.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009201638A JP5331621B2 (en) | 2009-09-01 | 2009-09-01 | Vehicle inspection device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009201638A JP5331621B2 (en) | 2009-09-01 | 2009-09-01 | Vehicle inspection device |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2011053058A true JP2011053058A (en) | 2011-03-17 |
| JP5331621B2 JP5331621B2 (en) | 2013-10-30 |
Family
ID=43942222
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009201638A Expired - Fee Related JP5331621B2 (en) | 2009-09-01 | 2009-09-01 | Vehicle inspection device |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5331621B2 (en) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013108811A (en) * | 2011-11-18 | 2013-06-06 | Shimadzu Corp | Fuel cell oxygen concentration measuring apparatus |
| JP2015059843A (en) * | 2013-09-19 | 2015-03-30 | 株式会社デンソー | Weld visual inspection device and weld visual inspection method |
| JP2015215267A (en) * | 2014-05-12 | 2015-12-03 | 精研工業株式会社 | Wheel shape measurement method and wheel shape measuring device |
| JP2016033797A (en) * | 2014-07-31 | 2016-03-10 | 日本鋳鉄管株式会社 | Letter reading apparatus and letter reading method |
| CN108426547A (en) * | 2017-02-13 | 2018-08-21 | 株式会社大福 | Inspection system |
| JP2020034406A (en) * | 2018-08-29 | 2020-03-05 | 大和ハウス工業株式会社 | Inspection device |
| JP2020524266A (en) * | 2017-07-21 | 2020-08-13 | 中興通訊股▲ふん▼有限公司Zte Corporation | Positioning method, device and system, positioning system layout method, and storage medium |
| JP2020148744A (en) * | 2019-03-15 | 2020-09-17 | シャープ株式会社 | Image processing device and image processing method |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01100410A (en) * | 1987-10-14 | 1989-04-18 | Bridgestone Corp | Automatic detector of label position on tire |
| JPH05272946A (en) * | 1992-03-26 | 1993-10-22 | Toyoda Mach Works Ltd | Object discriminating apparatus |
| JPH07237270A (en) * | 1994-02-28 | 1995-09-12 | Shimadzu Corp | Tire discriminating device |
| JPH0844871A (en) * | 1994-07-29 | 1996-02-16 | Toyota Motor Corp | Work discriminating method |
| JPH08101016A (en) * | 1994-09-29 | 1996-04-16 | Bridgestone Corp | Method and device for detecting position of label on tire |
| JPH10115508A (en) * | 1996-10-14 | 1998-05-06 | Bridgestone Corp | Inspection apparatus for inspecting mark of tire |
| JP2007011462A (en) * | 2005-06-28 | 2007-01-18 | Bridgestone Corp | Master data generation method for inspecting uneven figure |
| JP2007333457A (en) * | 2006-06-13 | 2007-12-27 | Yokohama Rubber Co Ltd:The | Inspection method and inspection system for tire mold side plate, decision method and decision system for the tire mold side plate, and inspection method and inspection system for tire mold processing process |
-
2009
- 2009-09-01 JP JP2009201638A patent/JP5331621B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH01100410A (en) * | 1987-10-14 | 1989-04-18 | Bridgestone Corp | Automatic detector of label position on tire |
| JPH05272946A (en) * | 1992-03-26 | 1993-10-22 | Toyoda Mach Works Ltd | Object discriminating apparatus |
| JPH07237270A (en) * | 1994-02-28 | 1995-09-12 | Shimadzu Corp | Tire discriminating device |
| JPH0844871A (en) * | 1994-07-29 | 1996-02-16 | Toyota Motor Corp | Work discriminating method |
| JPH08101016A (en) * | 1994-09-29 | 1996-04-16 | Bridgestone Corp | Method and device for detecting position of label on tire |
| JPH10115508A (en) * | 1996-10-14 | 1998-05-06 | Bridgestone Corp | Inspection apparatus for inspecting mark of tire |
| JP2007011462A (en) * | 2005-06-28 | 2007-01-18 | Bridgestone Corp | Master data generation method for inspecting uneven figure |
| JP2007333457A (en) * | 2006-06-13 | 2007-12-27 | Yokohama Rubber Co Ltd:The | Inspection method and inspection system for tire mold side plate, decision method and decision system for the tire mold side plate, and inspection method and inspection system for tire mold processing process |
Cited By (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013108811A (en) * | 2011-11-18 | 2013-06-06 | Shimadzu Corp | Fuel cell oxygen concentration measuring apparatus |
| JP2015059843A (en) * | 2013-09-19 | 2015-03-30 | 株式会社デンソー | Weld visual inspection device and weld visual inspection method |
| JP2015215267A (en) * | 2014-05-12 | 2015-12-03 | 精研工業株式会社 | Wheel shape measurement method and wheel shape measuring device |
| JP2016033797A (en) * | 2014-07-31 | 2016-03-10 | 日本鋳鉄管株式会社 | Letter reading apparatus and letter reading method |
| JP2018132332A (en) * | 2017-02-13 | 2018-08-23 | 株式会社ダイフク | Inspection system |
| KR20180093803A (en) * | 2017-02-13 | 2018-08-22 | 가부시키가이샤 다이후쿠 | Inspection system |
| CN108426547A (en) * | 2017-02-13 | 2018-08-21 | 株式会社大福 | Inspection system |
| TWI742225B (en) * | 2017-02-13 | 2021-10-11 | 日商大福股份有限公司 | Inspection system |
| KR102417868B1 (en) | 2017-02-13 | 2022-07-05 | 가부시키가이샤 다이후쿠 | Inspection system |
| JP2020524266A (en) * | 2017-07-21 | 2020-08-13 | 中興通訊股▲ふん▼有限公司Zte Corporation | Positioning method, device and system, positioning system layout method, and storage medium |
| JP7038743B2 (en) | 2017-07-21 | 2022-03-18 | 中興通訊股▲ふん▼有限公司 | Positioning methods, devices and systems, positioning system layout methods, and storage media |
| JP2020034406A (en) * | 2018-08-29 | 2020-03-05 | 大和ハウス工業株式会社 | Inspection device |
| JP7185444B2 (en) | 2018-08-29 | 2022-12-07 | 大和ハウス工業株式会社 | inspection equipment |
| JP2020148744A (en) * | 2019-03-15 | 2020-09-17 | シャープ株式会社 | Image processing device and image processing method |
| JP7237671B2 (en) | 2019-03-15 | 2023-03-13 | シャープ株式会社 | Image processing device and image processing method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP5331621B2 (en) | 2013-10-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5331621B2 (en) | Vehicle inspection device | |
| CN103512762B (en) | Image processing method, device and train failure detection system | |
| CN110163853B (en) | Edge defect detection method | |
| JP4970195B2 (en) | Person tracking system, person tracking apparatus, and person tracking program | |
| US8620094B2 (en) | Pattern recognition apparatus, pattern recogntion method, image processing apparatus, and image processing method | |
| TWI506271B (en) | Method,system,and computer-readable storage medium for inspectiing a web | |
| US20130136307A1 (en) | Method for counting objects and apparatus using a plurality of sensors | |
| JP4380838B2 (en) | Video image automatic road sign recognition method, road sign automatic recognition device, and road sign automatic recognition program | |
| CN108520514B (en) | Consistency detection method for electronic elements of printed circuit board based on computer vision | |
| CN113674273B (en) | Optical detection method and system based on product defects and readable storage medium | |
| US20200265256A1 (en) | Device and method for analyzing state of manual work by worker, and work analysis program | |
| CN103591940B (en) | Method of evaluating confidence of matching signature of hyperspectral image | |
| JP6079948B1 (en) | Surface defect detection device and surface defect detection method | |
| CN112560538B (en) | Method for quickly positioning damaged QR (quick response) code according to image redundant information | |
| CN107341538A (en) | A kind of statistical magnitude method of view-based access control model | |
| CN104321804A (en) | Object identification system and program | |
| CN114119535A (en) | Laser cleaning effect on-line monitoring method based on visual detection | |
| CN100470578C (en) | Science instrument working state monitoring method based on computer vision | |
| CN116071311A (en) | Equipment cleaning detection method, system and storage medium based on image recognition | |
| CN111126416A (en) | Engine chain wheel identification system and identification method based on key point detection | |
| JP2003233851A (en) | Method for judging authenticity/soundness of coin from picture and its device | |
| CN111460198B (en) | Picture timestamp auditing method and device | |
| JP7356010B2 (en) | Surface texture inspection device and surface texture inspection method | |
| JP5045211B2 (en) | Character recognition device, appearance inspection device, and character recognition method | |
| JP2017173992A (en) | Inspection device for bundled steel pipes and inspection method for bundled steel pipes |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120406 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20130426 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130723 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130729 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |