JP2009119958A - Vehicle state estimation unit - Google Patents
Vehicle state estimation unit Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2009119958A JP2009119958A JP2007294201A JP2007294201A JP2009119958A JP 2009119958 A JP2009119958 A JP 2009119958A JP 2007294201 A JP2007294201 A JP 2007294201A JP 2007294201 A JP2007294201 A JP 2007294201A JP 2009119958 A JP2009119958 A JP 2009119958A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wheel
- speed
- vehicle
- estimated
- calculated
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Images
Landscapes
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
Abstract
Description
この発明は、車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置に関し、特に、全輪(4輪)駆動車における車体速度等の車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置に関する。 The present invention relates to a vehicle state estimation device that estimates a vehicle state quantity, and more particularly to a vehicle state estimation apparatus that estimates a vehicle state quantity such as a vehicle body speed in an all-wheel (four-wheel) drive vehicle.
従来より、全輪駆動車における車体速度等の車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置として、例えば、下記特許文献1や特許文献2に記載された推定装置が知られている。
Conventionally, as a vehicle state estimation device for estimating a vehicle state quantity such as a vehicle body speed in an all-wheel drive vehicle, for example, estimation devices described in
特許文献1には、所定の運動方程式により算出した車両状態量を計測可能な状態量で検証して、その検証結果に応じて車両状態量を算出する初期値を補正する推定装置が開示されており、この特許文献1の図11には、車体速度を推定するための車体速度推定装置のブロック図が開示されている。
また、特許文献2では、車体前後方向推定車輪速を推定前後方向加速度から求め、車体横方向推定車輪速を推定横加速度から求めると共に、推定前後方向加速度と推定横加速度から推定車体速度を求める推定装置が開示されている。
Further, in
このように、全輪駆動車においては、全ての車輪が駆動されているため、車体速度等の車両の状態量を検出することが困難であることから、推定値によって車両の状態量を算出する必要があった。 As described above, in an all-wheel drive vehicle, since all the wheels are driven, it is difficult to detect the vehicle state quantity such as the vehicle body speed. Therefore, the vehicle state quantity is calculated based on the estimated value. There was a need.
このため、前述の特許文献等では、例えば特許文献1の図11に示すように、車体速度をより詳細に推定するために、ヨーレイトセンサや横加速度センサ等の高価なセンサを数多く設けて、車両の状態量の算出精度を高めるようにしていた。
For this reason, in the above-mentioned patent documents, for example, as shown in FIG. 11 of
しかし、高価なセンサを数多く設けるとなると、装置自体のコストが増加するという問題が生じると共に、センサを設置するためのハーネス等の周辺部品も必要となり、装置自体が複雑になるといった問題が生じる。
また、センサを多く設けると、制御装置に入力する入力信号も増加するため、車両の状態量を算出する演算処理も複雑になるという問題も生じる。
However, when a large number of expensive sensors are provided, there arises a problem that the cost of the apparatus itself increases, and peripheral parts such as a harness for installing the sensor are also required, resulting in a problem that the apparatus itself becomes complicated.
In addition, if a large number of sensors are provided, an input signal to be input to the control device also increases, which causes a problem that the calculation processing for calculating the state quantity of the vehicle becomes complicated.
そこで、本発明は、全輪駆動車における車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置において、できるだけ少数のセンサによって車両状態を検出して、車両状態量の推定を行うことで、車両の状態量を簡易に、且つ精度よく推定できる車両状態推定装置を提供することを目的とする。 Accordingly, the present invention provides a vehicle state estimation device that estimates a vehicle state quantity in an all-wheel-drive vehicle, detects the vehicle state by using as few sensors as possible, and estimates the vehicle state quantity. It is an object of the present invention to provide a vehicle state estimation device that can easily and accurately estimate the vehicle state.
この発明の車両状態推定装置は、全輪駆動車における車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置であって、車体の前後加速度を検出する前後加速度検出手段と、各車輪の車輪速を検出する車輪速検出手段と、検出した前後加速度から全車輪のスリップ状態の等価スリップ率を算出する等価スリップ率算出手段と、基準車体速と各車輪の車輪速とにより、各車輪のスリップ状態を判定して、スリップ状態が所定値以下の非スリップ輪から車輪速平均を算出する車輪速平均算出手段と、前記等価スリップ率と前記車輪速平均から推定車体速を算出する推定車体速算出手段とを備えるものである。 A vehicle state estimation device according to the present invention is a vehicle state estimation device for estimating a vehicle state quantity in an all-wheel drive vehicle, and detects longitudinal acceleration detection means for detecting longitudinal acceleration of a vehicle body and wheel speed of each wheel. The slip condition of each wheel is determined by the wheel speed detection means, the equivalent slip ratio calculation means for calculating the equivalent slip ratio of the slip state of all the wheels from the detected longitudinal acceleration, and the reference vehicle body speed and the wheel speed of each wheel. A wheel speed average calculating means for calculating an average wheel speed from a non-slip wheel whose slip state is a predetermined value or less, and an estimated vehicle speed calculating means for calculating an estimated vehicle speed from the equivalent slip ratio and the wheel speed average. Is.
上記構成によれば、前後加速度検出手段と車輪速検出手段から前後加速度と車輪速を検出することで、全車輪の等価スリップ率を算出し、非スリップ輪によって車輪速平均を算出して、この等価スリップ率と車輪速平均とから、推定車体速を算出することになる。
このため、ヨーレイトセンサや横加速度センサ等の高価なセンサを用いることなく、一般によく用いられる車輪速検出手段と前後加速度検出手段だけを用いて、推定車体速を算出することができる。
また、スリップしている車輪を除いて非スリップ輪で車輪速平均を算出しているため、車体速度と大きく異なる車輪速を取り込むことなく車輪速平均を算出できる。このため、推定車体速の算出精度を高めることができる。
なお、ここで「等価スリップ率」とは、全輪の各車輪のスリップ率の平均値を意味する言葉であり、実際の車輪のスリップ率から求めるものではなく、車体の前後加速度から求める(算出する)値である。
According to the above configuration, by detecting the longitudinal acceleration and the wheel speed from the longitudinal acceleration detecting means and the wheel speed detecting means, the equivalent slip ratio of all the wheels is calculated, and the wheel speed average is calculated by the non-slip wheel. The estimated vehicle speed is calculated from the equivalent slip ratio and the average wheel speed.
For this reason, it is possible to calculate the estimated vehicle speed using only commonly used wheel speed detection means and longitudinal acceleration detection means without using expensive sensors such as a yaw rate sensor and a lateral acceleration sensor.
Further, since the wheel speed average is calculated for the non-slip wheels except for the slipping wheel, the wheel speed average can be calculated without taking in a wheel speed that is significantly different from the vehicle body speed. For this reason, the calculation accuracy of the estimated vehicle speed can be increased.
Here, the “equivalent slip ratio” is a term that means an average value of slip ratios of all wheels of all wheels, and is not obtained from an actual wheel slip ratio but is obtained from a longitudinal acceleration of a vehicle body (calculation). Value).
この発明の一実施態様においては、前記基準車体速を、前回の推定車体速と前回の前後加速度の微分値を加算することで算出するものである。
上記構成によれば、車輪のスリップ状態を判定するための基準車体速を、前回算出した推定車体速と前回検出した前後加速度の微分値を加算して算出することで、別途、実現性が乏しい基準車体速を検出するセンサ等を設けなくても、基準車体速を得ることができる。
よって、実現性の乏しいセンサを設けることなく、装置自体のコストを削減して、基準車体速を得ることができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the reference vehicle body speed is calculated by adding a differential value of the previous estimated vehicle body speed and the previous longitudinal acceleration.
According to the above configuration, the reference vehicle speed for determining the slip state of the wheel is calculated by adding the previously calculated estimated vehicle speed and the differential value of the longitudinal acceleration detected last time. The reference vehicle speed can be obtained without providing a sensor or the like for detecting the reference vehicle speed.
Therefore, it is possible to obtain the reference vehicle speed by reducing the cost of the device itself without providing a sensor with poor feasibility.
この発明の一実施態様においては、全ての車輪が所定値以上にスリップした場合には、基準車体速を推定車体速として算出するように設定したものである。
上記構成によれば、全ての車輪が所定値以上にスリップして非スリップ輪がなくなった場合には、基準車体速をそのまま推定車体速として算出することで、車輪速平均を算出できない場合であっても、推定車体速を算出することができる。
よって、全輪スリップによって検出する車輪速が全て車体速度から大きく異なった場合であっても、推定車体速を算出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the reference vehicle body speed is set to be calculated as the estimated vehicle body speed when all the wheels slip over a predetermined value.
According to the above configuration, when all the wheels slip to a predetermined value or more and there are no non-slip wheels, the average vehicle speed cannot be calculated by calculating the reference vehicle speed as the estimated vehicle speed as it is. Even in this case, the estimated vehicle speed can be calculated.
Therefore, the estimated vehicle body speed can be calculated even when the wheel speeds detected by the all-wheel slip are all greatly different from the vehicle body speed.
この発明の一実施態様においては、前記等価スリップ率算出手段の算出値を路面μに応じて変更するものである。
上記構成によれば、算出する車輪の等価スリップ率が路面μに応じて変化するため、より実測値に近い等価スリップ率を算出することができる。
よって、路面μの違いを反映した推定車体速を算出することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the calculated value of the equivalent slip ratio calculating means is changed according to the road surface μ.
According to the above configuration, the equivalent slip ratio of the wheel to be calculated changes according to the road surface μ, so that an equivalent slip ratio closer to the actually measured value can be calculated.
Therefore, it is possible to calculate the estimated vehicle speed reflecting the difference in the road surface μ.
この発明の一実施態様においては、各車輪を駆動する駆動トルクを検出するタイヤ駆動トルク検出手段と、前記車輪速検出手段で検出した車輪速を微分して各車輪の角加速度を算出する車輪角加速度算出手段と、前記推定車体速算出手段で算出した推定車体速、前記タイヤ駆動トルク検出手段で検出したタイヤ駆動トルク、及び、前記車輪角加速度算出手段で算出した車輪の角加速度から各タイヤの制駆動力を推定するタイヤ制駆動力推定手段とを備えるものである。
上記構成によれば、推定車体速算出手段で算出した推定車体速と、タイヤ駆動トルク検出手段で検出したタイヤ駆動トルクと、車輪角加速度算出手段で算出した車輪の角加速度とから、タイヤ制駆動力推定手段によってタイヤが発生するタイヤ制駆動力を推定することになる。
このため、従来検出することが困難とされた、各タイヤの発生するタイヤ制駆動力をできるだけ正確に推定することが可能となり、この推定されたタイヤ制駆動力を利用して、車両姿勢制御装置等の制御を、車両の挙動を予測した上で行なうことができる。
よって、検出することが困難であったタイヤ制駆動力を予め推定して、より安全性能等を高めた車両の制御装置を構成することができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the tire driving torque detecting means for detecting the driving torque for driving each wheel, and the wheel angle for calculating the angular acceleration of each wheel by differentiating the wheel speed detected by the wheel speed detecting means. From the acceleration calculation means, the estimated vehicle speed calculated by the estimated vehicle speed calculation means, the tire drive torque detected by the tire drive torque detection means, and the wheel angular acceleration calculated by the wheel angular acceleration calculation means, Tire braking / driving force estimating means for estimating braking / driving force is provided.
According to the above configuration, the tire braking / driving is calculated from the estimated vehicle speed calculated by the estimated vehicle speed calculating means, the tire driving torque detected by the tire driving torque detecting means, and the wheel angular acceleration calculated by the wheel angular acceleration calculating means. The tire braking / driving force generated by the tire is estimated by the force estimating means.
For this reason, it is possible to estimate the tire braking / driving force generated by each tire, which has been difficult to detect in the past, as accurately as possible. By using the estimated tire braking / driving force, the vehicle attitude control device Such control can be performed after predicting the behavior of the vehicle.
Therefore, it is possible to configure a vehicle control device that has previously estimated the tire braking / driving force that has been difficult to detect and has improved safety performance and the like.
この発明の一実施態様においては、前記タイヤ制駆動力推定手段を、少なくとも推定車体速、タイヤ駆動トルク、及び車輪角加速度を取り込んで、所定のタイヤモデルと比較することで、推定値を算出するカルマンフィルターを含んで構成したものである。
上記構成によれば、タイヤ制駆動力推定手段がカルマンフィルターを含んで構成されることで、タイヤ制駆動力の値がカルマンフィルターの推定値で算出されることになる。
このため、実際に検出した検出値から推定値を算出するものではないため、算出値であるタイヤ制駆動力のノイズの発生をできるだけ抑えることができ、制御遅れの発生も防止できる。
よって、タイヤ制駆動力の値をより正確且つ迅速に算出することができ、このタイヤ制駆動力の値を使うことで、車両の制御装置の性能を高めることができる。
In one embodiment of the present invention, the tire braking / driving force estimating means takes in at least an estimated vehicle body speed, a tire driving torque, and a wheel angular acceleration, and calculates an estimated value by comparing with a predetermined tire model. It is configured including a Kalman filter.
According to the above configuration, the tire braking / driving force estimating means includes the Kalman filter, so that the tire braking / driving force value is calculated by the estimated value of the Kalman filter.
For this reason, since the estimated value is not calculated from the actually detected detection value, the generation of noise of the tire braking / driving force, which is the calculated value, can be suppressed as much as possible, and the occurrence of control delay can also be prevented.
Therefore, the value of the tire braking / driving force can be calculated more accurately and quickly, and the performance of the vehicle control device can be improved by using the value of the tire braking / driving force.
この発明によれば、ヨーレイトセンサや横加速度センサ等の高価なセンサを用いることなく、一般によく用いられる車輪速検出手段や前後加速度検出手段だけを用いて、推定車体速を算出することができる。
また、スリップしている車輪を除いて非スリップ輪で車輪速平均を算出しているため、車体速度と大きく異なる車輪速を取り込むことなく車輪速平均を算出できる。このため、推定車体速の算出精度を高めることができる。
よって、全輪駆動車における車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置において、できるだけ少数のセンサによって車両状態を検出して、車両状態量の推定を行うことで、車両の状態量を簡易に、且つ精度よく推定できる。
According to this invention, it is possible to calculate the estimated vehicle body speed using only commonly used wheel speed detection means and longitudinal acceleration detection means without using an expensive sensor such as a yaw rate sensor or a lateral acceleration sensor.
Further, since the wheel speed average is calculated for the non-slip wheels except for the slipping wheel, the wheel speed average can be calculated without taking in a wheel speed that is significantly different from the vehicle body speed. For this reason, the calculation accuracy of the estimated vehicle speed can be increased.
Therefore, in the vehicle state estimation device that estimates the vehicle state quantity in the all-wheel drive vehicle, the vehicle state quantity is estimated by detecting the vehicle state by using as few sensors as possible, and thus the vehicle state quantity can be easily calculated. In addition, it can be estimated with high accuracy.
以下、図面に基づいて本発明の実施形態を詳述する。 Hereinafter, embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings.
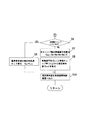
図1は本発明の実施形態に係る車両状態推定装置を採用した自動車の概略模式図、図2は車両状態推定装置のシステムブロック図、図3は車両状態推定装置の車体速推定の制御方法を説明するフローチャートの前半部分、図4は車体速推定の制御方法を説明するフローチャートの後半部分、図5は等価スリップ率を求めるマップ、図6はタイヤ制駆動力推定の制御方法を説明するフローチャートである。 FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram of an automobile employing a vehicle state estimation device according to an embodiment of the present invention, FIG. 2 is a system block diagram of the vehicle state estimation device, and FIG. 3 is a vehicle speed estimation control method of the vehicle state estimation device. The first half of the flowchart to be described, FIG. 4 is the latter half of the flowchart for explaining the control method for vehicle speed estimation, FIG. 5 is a map for obtaining the equivalent slip ratio, and FIG. 6 is the flowchart for explaining the control method for tire braking / driving force estimation. is there.
図1に示すように、自動車1には複数のセンサと車両姿勢制御装置のアクチュエータを設置している。
まず、センサとしては、各車輪2…ごとに車輪の回転速度(以下、車輪速)を検出する車輪速センサ3…と、車体に生じる前後加速度(以下、前後G)を検出する前後Gセンサ4と、各車輪2…に対して伝達される駆動トルクを検出する駆動トルクセンサ5を備えている。なお、電気自動車のように電動モータで各車輪が駆動される場合は、電動モータの出力トルクより各車輪の駆動トルクを算出することも可能である。
As shown in FIG. 1, the
First, as a sensor, a
一方、車両姿勢制御装置のアクチュエータとしては、各車輪ごとに設けられた電動モータ6…の回転トルクを制御する複数の制御ユニット7…を備えている。
On the other hand, the actuator of the vehicle attitude control device includes a plurality of
これらのセンサ(3,4,5)と制御ユニット7は、図2のブロック図に示すように、中央に設けた車体速推定器8とタイヤ制駆動力推定器9にそれぞれ連結されている(制御ユニットについては図示せず)。
These sensors (3, 4, 5) and the
まず、前後Gセンサ4は、車体速推定器8の加速度フィルター部10に接続されており、前後G信号を加速度フィルター部10に送信している。
First, the front / rear G sensor 4 is connected to the
また、各車輪ごとに設けた車輪速センサ3は、車体速推定器8の車輪速フィルター部11に接続されており、車輪速信号を車輪速フィルター部11に送信している。また、この車輪速センサ3の車輪速信号は、途中で分岐されて、タイヤ制駆動力推定器9の微分処理部14とタイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16にも送信されている。
Further, the
各車輪(車軸)ごとに設けた駆動トルクセンサ5は、タイヤ制駆動力算出部15にそれぞれ接続されており、各車輪に伝達するタイヤ駆動トルクの信号である駆動トルク信号をタイヤ制駆動力算出部15に送信している。なお、上述したように、電動モータで各車輪で駆動される場合は、モータの出力トルクから各車輪の駆動トルクを制御ユニットにて算出することとしても良い。
A driving
一方、車両姿勢制御装置17のアクチュエータ7には、図示しないが車両姿勢制御装置17からそれぞれ出力信号が送信されている。
この車両姿勢制御装置17は、車体速推定器8の車体速推定部13と、タイヤ制駆動力推定器9のタイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16に、それぞれ連結されており、車体速推定部13から推定車体速信号を受信して、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16から各車輪の推定制駆動力信号を受信している。
On the other hand, output signals are transmitted from the vehicle
The vehicle
車体速推定器8とタイヤ制駆動力推定器9のブロック構造について、さらに詳細に説明すると、まず、車体速推定器8は、加速度フィルター部10と、車輪速フィルター部11と、メモリ部12と、車体速推定部13とを備えている。一方、タイヤ制駆動力推定器9は、微分処理部14と、タイヤ制駆動力算出部15と、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16とを備えている。
The block structure of the vehicle body speed estimator 8 and the tire braking / driving
車体速推定器8の加速度フィルター部10は、前後G信号の高周波領域を除去するように、ローパスフィルターで構成しており、検出した前後G信号をフィルタリングすることで、加工しやすい前後G信号を生成している。そして、この前後G信号を、車体速推定部13に送信するように構成している。
The
車輪速フィルター部11は、各車輪速センサ3から各車輪の車輪速を取り込むように構成すると共に、メモリ部12から前回の推定車体速や前回の前後G信号を取り込むように構成している。これにより、各車輪のスリップ状態(空転状態、又はロック状態)を判定して、スリップしていない非スリップ輪によって車輪速平均を算出するように構成している。そして、この車輪速平均を、車体速推定部13に送信するように構成している。
The wheel speed filter unit 11 is configured to capture the wheel speed of each wheel from each
メモリ部12は、前回の制御フローの際に算出した推定車体速や、前回の制御フローの際に検出した前後Gを一時的に記憶するように構成している。そして、今回の制御フローの際には、各信号を車輪速フィルター部11に送信するように構成している。
The
車体速推定部13は、後述するように、タイヤ制駆動力とスリップ率によって定まる所定のスリップ率マップを利用して、推定車体速を算出するように構成している。
As will be described later, the vehicle body
この車体速推定部13には、前述したように、加速度フィルター部10からフィルタリングされた前後G信号が送信されて、車輪速フィルター部11から車輪速平均が送信されている。また、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16からは、スリップ率マップを変更するための路面μ信号が送信されている。
As described above, the front-rear G signal filtered from the
また、車体速推定部13が算出した推定車体速は、車両姿勢制御装置17とタイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16に出力されている。
The estimated vehicle body speed calculated by the vehicle body
タイヤ制駆動力推定器9の微分処理部14は、各車輪速センサ3から各車輪速を取り込み、この車輪速を微分することで各車輪の角加速度を算出して、この角加速度をタイヤ制駆動力算出部15に出力するように構成している。
The
タイヤ制駆動力算出部15は、後述するタイヤ制駆動力算出式により、各車輪のタイヤ制駆動力を算出するように構成している。微分処理部14から各車輪の角加速度を取り込んで、駆動トルクセンサ5から各車輪の駆動トルク信号を取り込むことで、各車輪の計測タイヤ制駆動力を算出するように構成している。
The tire braking / driving
タイヤ制駆動力算出部15で算出された計測タイヤ制駆動力は、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16に送信される。このタイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16は、後述するようにカルマンフィルターによって構成しており、車輪速を微分処理したことで増大するノイズを除去するため、タイヤモデルを利用した推定値によって、推定タイヤ制駆動力を算出するように構成している。
The measured tire braking / driving force calculated by the tire braking / driving
タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16には、車輪速センサ3から各車輪の車輪速信号が送信されて、タイヤ制駆動力算出部15からは前述の計測タイヤ制駆動力が送信される。また、車体速推定部13からは推定車体速信号が送信される。
A wheel speed signal of each wheel is transmitted from the
そして、このタイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16で演算処理(フィルタリング)された推定タイヤ制駆動力は、車両姿勢制御装置17に出力される。また、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16で利用されたタイヤモデル18によって算出された路面μ信号は、前述の車体速推定部13に送信されるように構成している。
Then, the estimated tire braking / driving force calculated (filtered) by the tire braking / driving
次に、この車両状態推定装置の車体速推定の制御フローについて説明する。
図3、図4は、推定車体速の推定演算方法の制御フローであり、この制御フローに従って、推定車体速の推定方法について説明する。
Next, a control flow for vehicle speed estimation of the vehicle state estimation device will be described.
3 and 4 are control flows of the estimated vehicle speed estimation calculation method, and the estimated vehicle speed estimation method will be described according to this control flow.
まず、S1では、前後Gセンサ4及び各車輪速センサ3から、前後G信号amea及び各車輪速信号Vw1、Vw2、Vw3、Vw4の読み込み行なう。
First, in S1, the front-rear G signal a mea and the wheel speed signals V w1 , V w2 , V w3 , V w4 are read from the front-rear G sensor 4 and each
次に、S2では、前後G信号ameaを加速度フィルター部10でフィルタリング処理する(amea→ax)。このフィルタリング処理では、生データである前後G信号ameaの高周波領域のノイズを除去して、演算処理しやすい信号にしている。 Next, in S2, the front-rear G signal a mea is filtered by the acceleration filter unit 10 (a mea → a x ). In this filtering process, noise in the high frequency region of the front and rear G signal a mea , which is raw data, is removed to make the signal easy to perform arithmetic processing.
S3では、図5に示すスリップ率マップを利用して、フィルタリング処理後の前後G信号axから、等価スリップ率λavgを算出する。
具体的な算出方法について説明すると、まず、タイヤ制駆動力Favgを、以下の式で求める。
In S3, by using a slip ratio map shown in FIG. 5, the longitudinal G signal a x after the filtering process, calculates an equivalent slip ratio lambda avg.
A specific calculation method will be described. First, the tire braking / driving force F avg is obtained by the following equation.
このタイヤ制駆動力Favgは、4つの車輪のタイヤ制駆動力F1〜F4の平均値として考えることができるため、図5のスリップ率マップから、全車輪の平均のスリップ率、すなわち等価スリップ率λavgを算出する。 Since this tire braking / driving force F avg can be considered as an average value of the tire braking / driving forces F1 to F4 of the four wheels, an average slip ratio of all the wheels, that is, an equivalent slip ratio is determined from the slip ratio map of FIG. Calculate λ avg .
スリップ率マップでは、所定の飽和スリップ率λfelまでは、タイヤ制駆動力Fの増加に伴ってスリップ率λが増加する比例特性を有するため、この比例特性部分を利用して、等価スリップ率λavgを算出するようにしている。 The slip ratio map has a proportional characteristic in which the slip ratio λ increases as the tire braking / driving force F increases up to a predetermined saturation slip ratio λ fel. avg is calculated.
なお、このスリップ率マップは、路面μによって変更するように構成している。路面μが高い場合には、タイヤ制駆動力が高い値をとるマップに変更して、路面μが低い場合には、タイヤ制駆動力が低い値をとるマップに変更する。こうすることで、より実測値に近い等価スリップ率λavgを算出することができる。また、図5では、駆動側のみのスリップ率特性ラインを示しているが、制動側においても同様に、対称となるような特性ラインを有している。 The slip ratio map is configured to change depending on the road surface μ. When the road surface μ is high, the map is changed to a map having a high tire braking / driving force. When the road surface μ is low, the map is changed to a map having a low tire braking / driving force. By doing so, it is possible to calculate the equivalent slip ratio λ avg closer to the actually measured value. Further, FIG. 5 shows the slip ratio characteristic line only on the drive side, but the characteristic line is also symmetrical on the brake side.
こうして、S3で、等価スリップ率λavgを求めた後には、S4に移行する。
S4では、前回の推定車体速Vest(t−1)と前回の前後Gax(t−1)の微分値を加算して、基準車体速Vthを算出する。この基準車体速Vthは、4つの車輪の車輪速平均を算出する際の基準となる車速である。具体的には、以下の式で算出する。
Thus, after obtaining the equivalent slip ratio λ avg in S3, the process proceeds to S4.
In S4, the reference vehicle speed Vth is calculated by adding the previous estimated vehicle speed Vest (t-1) and the differential value of the previous front and rear Gax (t-1) . The reference vehicle speed Vth is a vehicle speed that serves as a reference when calculating the wheel speed average of the four wheels. Specifically, it is calculated by the following formula.
そして、S6では、このスリップ輪として判断された車輪が、全車輪であるか否かを判断する。ここで、全車輪がスリップ輪であると判断した場合(YES判定)には、S9に移行して、全車輪がスリップ輪でないと判断した場合(NO判定)には、S7に移行する。 In S6, it is determined whether or not the wheels determined as the slip wheels are all wheels. If it is determined that all the wheels are slip wheels (YES determination), the process proceeds to S9. If it is determined that all the wheels are not slip wheels (NO determination), the process proceeds to S7.
S7では、スリップしていない車輪、すなわち非スリップ輪で車輪速平均Vwaveを算出する。具体的には、スリップ輪が全くない場合には、全ての車輪(4輪)の車輪速を合算して全車輪数で割ることで、車輪速平均を算出する。一方、一輪でもスリップ輪があった場合には、そのスリップ輪を除いて、非スリップ輪の車輪速を合算して非スリップ輪の車輪数で割ることで、車輪速平均Vwaveを算出する。
このように、スリップ輪を除いて、車輪速平均Vwaveを算出することで、できるだけ精度のよい車輪速平均Vwaveを算出できる。
In S7, a wheel speed average V wave is calculated for a non-slip wheel, that is, a non-slip wheel. Specifically, when there are no slip wheels, the wheel speed average is calculated by adding the wheel speeds of all the wheels (four wheels) and dividing by the total number of wheels. On the other hand, if there is even one slip wheel, the wheel speed average V wave is calculated by adding the wheel speeds of the non-slip wheels and dividing the sum by the number of non-slip wheels.
Thus, by calculating the wheel speed average V wave excluding slip wheels, it is possible to calculate the wheel speed average V wave with the highest possible accuracy.
S8では、この車輪速平均Vwaveと等価スリップ率λavgから、以下の式を利用して、推定車体速Vestを算出する。 In S8, the estimated vehicle speed V est is calculated from the wheel speed average V wave and the equivalent slip ratio λ avg by using the following equation.
こうして、推定車体速Vestを算出することで、加速時と減速時の推定車体速Vestを適切に算出することができる。 Thus, by calculating the estimated vehicle speed V est, the estimated vehicle speed V est of acceleration and deceleration can be calculated appropriately.
一方、S6でYES判定した場合には、S9に移行して、基準車体速Vthを推定車体速Vestとして算出する。すなわち、全てがスリップ輪として判断されるため、車輪速平均となりうる車輪速を取り込むことができないため、基準車体速Vthを推定車体速Vestとして代用しているのである。 On the other hand, if YES is determined in S6, the process proceeds to S9 to calculate the reference vehicle speed Vth as the estimated vehicle speed Vest . That is, since all are judged as slip wheels, the wheel speed that can be the average of the wheel speeds cannot be taken in, so the reference vehicle body speed Vth is substituted for the estimated vehicle body speed Vest .
こうして、S9やS8で算出された推定車体速Vestは、S10において、車両姿勢制御装置17へ出力される。このようにして、演算処理によって算出した推定車体速Vestを車両姿勢制御装置17へ出力することで、車体速の測定が困難な4輪駆動車であっても、簡易に且つ正確に車体速を得ることができる。
Thus, the estimated vehicle speed V est calculated in S9 and S8 is output to the vehicle
なお、具体的には図示しないが、この推定車体速Vestは、算出されるごとに、前述のメモリ部12に記憶されるように設定しており、次回の基準車体速Vthを算出する場合に利用されるようにしている。
Although not specifically shown, the estimated vehicle body speed V est is set to be stored in the
次に、この車両状態推定装置のタイヤ制駆動力推定の制御フローについて説明する。
図6は、推定タイヤ制駆動力の推定演算方法の制御フローであり、この制御フローに従って、推定タイヤ制駆動力の推定方法について説明する。
Next, the control flow of tire braking / driving force estimation of this vehicle state estimation device will be described.
FIG. 6 is a control flow of an estimation calculation method of the estimated tire braking / driving force, and the estimation method of the estimated tire braking / driving force will be described according to this control flow.
まず、S11では、各車輪速センサ3…及び各駆動トルクセンサ5…から、各車輪速信号Vw1、Vw2、Vw3、Vw4及び各駆動トルク信号T1、T2、T3、T4の読み込みを行なう。
First, in S11, from the
次に、S12では、各車輪速センサ3から得た各車輪速信号を微分処理部14で微分処理する。すなわち、各車輪速信号から各車輪角加速度dw1、dw2、dw3、dw4を算出するのである。
Next, in S <b> 12, each wheel speed signal obtained from each
そして、S13では、駆動トルクセンサ5から得た駆動トルクT1、T2、T3、T4と、微分処理部14で得た車輪角加速度dw1、dw2、dw3、dw4から、計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4measを算出する。具体的には、以下の式を利用して計測タイヤ制駆動力を算出する。
Then, in S13, the driving torque T 1, T 2, T 3 , T 4 obtained from the driving
次に、S14では、計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4measをカルマンフィルター(16)に取り込み、いわゆるタイヤモデル18と比較して、推定タイヤ制駆動力Fx1est、Fx2est、Fx3est、Fx4estを算出する。 Next, in S14, the measured tire braking / driving forces Fx1 meas , Fx2 meas , Fx3 meas , Fx4 meas are taken into the Kalman filter (16), and compared with the so-called tire model 18, the estimated tire braking / driving forces Fx1 est , Fx2 est , Fx3 est , Fx4 est are calculated.
ここで、カルマンフィルター(16)を用いて推定タイヤ制駆動力Fxestを算出しているのは、車輪角加速度dwを算出する際に、微分処理を行っていることにより、この微分処理によって増大したノイズが算出値を乱し、時定数によって制御遅れが生じるため、このノイズと制御遅れを解消するために、カルマンフィルター(16)を用いて推定タイヤ制駆動力を算出しているのである。 Here, the estimated tire braking / driving force F xest is calculated using the Kalman filter (16) because the differential processing is performed when the wheel angular acceleration dw is calculated. Since the calculated noise disturbs the calculated value and a control delay occurs due to the time constant, the estimated tire braking / driving force is calculated using the Kalman filter (16) in order to eliminate the noise and the control delay.
ここで、カルマンフィルターについて簡単に説明する。カルマンフィルターとは、予め信号ノイズや測定誤差等の情報を組み込んだ所定の仮想モデルを設計しておき、この仮想モデルを入力信号等により変化させることで、統計確率論的に最も確からしい値を、推定値として出力するものである。 Here, the Kalman filter will be briefly described. The Kalman filter is designed in advance by designing a predetermined virtual model that incorporates information such as signal noise and measurement error, and by changing this virtual model according to the input signal, the most probable value in statistical probability theory. Are output as estimated values.
このため、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16でカルマンフィルターを用いることにより、微分処理によってノイズや制御遅れが発生した計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4measを、ノイズや制御遅れを抑えた推定タイヤ制駆動力Fx1est、Fx2est、Fx3est、Fx4estとして算出することができるのである。
For this reason, by using a Kalman filter in the tire braking / driving
次に、S15では、算出した推定タイヤ制駆動力Fx1est、Fx2est、Fx3est、Fx4estを、車両姿勢制御装置17へ出力する。車両姿勢制御装置17側では、推定タイヤ制駆動力を得られることで、予め、車両挙動の変化を予測できるため、より車両挙動の安全性を高める制御を行なうことができる。
Next, in
S16では、タイヤモデル18とタイヤ制駆動力から路面μを推定して算出する。 In S16, the road surface μ is estimated and calculated from the tire model 18 and the tire braking / driving force.
S17では、S16で推定算出した路面μによって、次回のスリップ率マップを変更する。すなわち、推定される路面μが変化するため、より推定値が現実の値に近づくように、スリップ率マップを変更するように構成しているのである。 In S17, the next slip ratio map is changed according to the road surface μ estimated and calculated in S16. That is, since the estimated road surface μ changes, the slip ratio map is changed so that the estimated value is closer to the actual value.
以上のようなステップを経て、車両状態推定装置の一回の制御フローが終了して、以後、次回の制御フローが繰り返して行われる。 Through the above steps, one control flow of the vehicle state estimation device is completed, and thereafter, the next control flow is repeatedly performed.
次に、このように構成された本実施形態の作用効果について説明する。
この実施形態の車両状態推定装置は、車体の前後加速度を検出する前後Gセンサ4と、各車輪2の車輪速を検出する車輪速センサ3を備え、検出した前後Gから全車輪のスリップ状態の等価スリップ率λavgを算出して、基準車体速Vthと各車輪2…の車輪速Vw1、Vw2、Vw3、Vw4とにより車輪のスリップ状態を判定して、スリップ輪を除いた非スリップ輪によって車輪速平均Vwaveを算出し、この等価スリップ率λavgと車輪速平均Vwaveから、推定車体速Vestを算出するようにしている。
Next, the effect of this embodiment comprised in this way is demonstrated.
The vehicle state estimation device of this embodiment includes a front / rear G sensor 4 for detecting the longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle body and a
これにより、ヨーレイトセンサや横加速度センサ等の高価なセンサを用いることなく、一般によく用いられる車輪速センサ2と前後Gセンサ4だけを用いて、推定車体速Vestを算出することができる。
また、スリップしている車輪を除いて非スリップ輪で車輪速平均を算出しているため、車体速度と大きく異なる車輪速を取り込むことなく車輪速平均Vwaveを算出できる。このため、推定車体速Vestの算出精度を高めることができる。
よって、4輪駆動車における車両の状態量を推定する車両状態推定装置において、できるだけ少数のセンサによって車両状態を検出して、車両状態量の推定を行うことで、車両の状態量を簡易に、且つ精度よく推定できる。
Thus, the estimated vehicle body speed V est can be calculated using only the generally used
In addition, since the wheel speed average is calculated for the non-slip wheels except for the slipping wheel, the wheel speed average V wave can be calculated without taking in a wheel speed that is significantly different from the vehicle body speed. For this reason, the calculation accuracy of the estimated vehicle body speed V est can be increased.
Therefore, in the vehicle state estimation device for estimating the vehicle state quantity in the four-wheel drive vehicle, the vehicle state quantity is estimated by detecting the vehicle state by using as few sensors as possible, and thus the vehicle state quantity can be simplified. In addition, it can be estimated with high accuracy.
また、この実施形態では、基準車体速Vthを、前回の推定車体速Vest(t−1)と前回の前後Gax(t−1)の微分値を加算することで算出している。
これにより、車輪のスリップ状態を判定するための基準車体速Vthを、別途、実現性の乏しい基準車体速を検出するセンサ等を設けなくても得ることができる。
よって、実現性の乏しい基準車体速を検出するセンサ等を設けることなく、基準車体速Vthを得ることができる。
Further, in this embodiment, the reference vehicle body speed Vth is calculated by adding the previous estimated vehicle body speed Vest (t-1) and the differential value of the previous front and rear Gax (t-1) .
As a result, the reference vehicle body speed Vth for determining the slip state of the wheel can be obtained without providing a separate sensor or the like for detecting a reference vehicle body speed with poor feasibility.
Therefore, it is possible to obtain the reference vehicle speed Vth without providing a sensor or the like that detects a reference vehicle speed with poor feasibility.
また、この実施形態では、全ての車輪が所定値以上にスリップした場合には、基準車体速Vthを推定車体速Vestとして算出するように設定している。
これにより、全ての車輪が所定値以上にスリップして非スリップ輪がなくなった場合には、基準車体速Vthをそのまま推定車体速Vestとして算出することで、車輪速平均Vwaveを算出できない場合であっても、推定車体速Vestを算出することができる。
よって、全輪スリップによって検出する車輪速が全て車体速度から大きく異なった場合であっても、推定車体速Vestを算出することができる。
Further, in this embodiment, when all the wheels slip to a predetermined value or more, the reference vehicle body speed Vth is set to be calculated as the estimated vehicle body speed Vest .
Thereby, when all the wheels slip to a predetermined value or more and there is no non-slip wheel, the wheel speed average V wave cannot be calculated by directly calculating the reference vehicle speed V th as the estimated vehicle speed V est. Even in this case, the estimated vehicle speed V est can be calculated.
Therefore, the estimated vehicle body speed V est can be calculated even when the wheel speeds detected by the all-wheel slip are all greatly different from the vehicle body speed.
また、この実施形態では、スリップ率マップを路面μに応じて変更するようにしている。
これにより、算出する等価スリップ率が路面μに応じて変化するため、より実際の値に近い等価スリップ率λavgを算出することができる。
よって、路面μの違いを反映して、より実測値に近い値で推定車体速Vestを算出することができる。
In this embodiment, the slip ratio map is changed according to the road surface μ.
Thereby, since the calculated equivalent slip ratio changes according to the road surface μ, the equivalent slip ratio λ avg closer to the actual value can be calculated.
Therefore, the estimated vehicle speed V est can be calculated with a value closer to the actually measured value, reflecting the difference in the road surface μ.
また、この実施形態では、車輪を駆動する駆動トルクを検出する駆動トルクセンサ5を備えて、微分処理部14で車輪速を微分して算出した車輪角加速度dw1、dw2、dw3、dw4と、車体速推定器8によって算出した推定車体速Vestと、駆動トルクセンサ5によって検出した駆動トルクT1、T2、T3、T4とによって、タイヤ制駆動力(計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4meas)を算出している。
これにより、駆動トルクセンサ5で検出した駆動トルクと、推定車体速と、車輪の角加速度とから、タイヤの制駆動力を算出することができる。
このため、従来検出することが困難とされた、各タイヤの発生するタイヤ制駆動力を算出することが可能となり、この算出されたタイヤ制駆動力を利用して、車両姿勢制御装置の制御を、車両の挙動を予測した上で行なうことができる。
よって、検出することが困難であったタイヤ制駆動力を予め算出して、より安全性能等を高めた車両姿勢制御装置を構成することができる。
Further, in this embodiment, a wheel torque acceleration d w1 , d w2 , d w3 , d calculated by differentiating the wheel speed by the
Thus, the braking / driving force of the tire can be calculated from the driving torque detected by the driving
For this reason, it is possible to calculate the tire braking / driving force generated by each tire, which has been difficult to detect in the past, and the vehicle attitude control device can be controlled using the calculated tire braking / driving force. This can be done after predicting the behavior of the vehicle.
Therefore, it is possible to configure a vehicle attitude control device that calculates in advance the tire braking / driving force, which has been difficult to detect, and further improves safety performance and the like.
また、この実施形態では、タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部16を、推定車体速Vest、計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4meas及び車輪速Vw1、Vw2、Vw3、Vw4を取り込んで、タイヤモデル18と比較することで、推定値を算出するカルマンフィルターで構成している。
これにより、タイヤ制駆動力(推定タイヤ制駆動力Fx1est、Fx2est、Fx3est、Fx4est)の値がカルマンフィルター18の推定値で算出されることになる。
このため、算出値である計測タイヤ制駆動力Fx1meas、Fx2meas、Fx3meas、Fx4measのノイズの発生をできるだけ抑えることができ、制御遅れの発生も防止できる。
よって、タイヤ制駆動力の値をより正確且つ迅速に算出することができ、推定タイヤ制駆動力Fx1est、Fx2est、Fx3est、Fx4estの値を使うことで、車両姿勢制御装置の性能を高めることができる。
In this embodiment, the tire braking / driving
Thereby, the value of the tire braking / driving force (estimated tire braking / driving force F x1est , F x2est , F x3est , F x4est ) is calculated by the estimated value of the Kalman filter 18.
Therefore, a calculated value measured tire longitudinal force F x1meas, F x2meas, F x3meas , can be suppressed as much as possible the occurrence of noise F X4meas, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of control delay.
Therefore, the value of the tire braking / driving force can be calculated more accurately and quickly. By using the estimated tire braking / driving forces F x1est , F x2est , F x3est , F x4est , the performance of the vehicle attitude control device can be improved. Can be increased.
なお、このノイズや制御遅れの除去を行なうものには、必ずしも、この実施形態のようにカルマンフィルターに限定されるものではない。また、タイヤモデルについても、さらに、タイヤの接地荷重の情報や、経年変化の情報、タイヤの空気圧の情報等を取り込んで、設計するようにしてもよい。
また、前述したスリップ率マップについても、これに限定されるものではなく、「テーブル」や「式」等で代用してもよい。
In addition, what removes this noise and control delay is not necessarily limited to a Kalman filter as in this embodiment. Further, the tire model may also be designed by taking in information on a tire contact load, information on secular change, information on tire pressure, and the like.
Further, the above-described slip ratio map is not limited to this, and a “table”, an “expression”, or the like may be substituted.
以上、この発明の構成と前述の実施形態との対応において、
この発明の前後加速度検出手段は、実施形態の前後Gセンサ4に対応し、
以下、同様に、
車輪速検出手段は、車輪速センサ3に対応し、
等価スリップ率算出手段は、車体速推定部13に対応し、
車輪速平均算出手段は、車輪速フィルター部11に対応し、
推定車体速算出手段は、車体速推定部13に対応し、
タイヤ駆動トルク検出手段は、駆動トルクセンサ5に対応し、
タイヤ制駆動力推定手段は、タイヤ制駆動力推定器9に対応するも、
この発明は、前述の実施形態に限定されるものではなく、あらゆる車両状態推定装置に適用する実施形態を含むものである。
As described above, in the correspondence between the configuration of the present invention and the above-described embodiment,
The longitudinal acceleration detecting means of the present invention corresponds to the longitudinal G sensor 4 of the embodiment,
Similarly,
The wheel speed detection means corresponds to the
The equivalent slip ratio calculating means corresponds to the vehicle body
The wheel speed average calculating means corresponds to the wheel speed filter unit 11,
The estimated vehicle speed calculation means corresponds to the vehicle
The tire drive torque detection means corresponds to the
The tire braking / driving force estimation means corresponds to the tire braking / driving
The present invention is not limited to the above-described embodiment, but includes an embodiment applied to any vehicle state estimation device.
特に、車両の駆動方式については、前述の実施形態のように4輪独立の電動モータ方式の駆動方式に限定されるものではなく、エンジンと変速機によって構成される一般的な駆動方式であってもよい。この場合の駆動トルクの検出は、エンジン出力に変速機の変速比を乗じて行えばよい。 In particular, the vehicle drive system is not limited to the four-wheel independent electric motor system drive system as in the above-described embodiment, but is a general drive system composed of an engine and a transmission. Also good. The detection of the drive torque in this case may be performed by multiplying the engine output by the transmission gear ratio.
1…自動車
2…車輪
3…車輪速センサ
4…前後Gセンサ
5…駆動トルクセンサ
6…電動モータ
7…制御ユニット
8…車体速推定器
9…タイヤ制駆動力推定器
13…車体速推定部
15…タイヤ制駆動力算出部
16…タイヤ制駆動力フィルター部
DESCRIPTION OF
Claims (6)
車体の前後加速度を検出する前後加速度検出手段と、
各車輪の車輪速を検出する車輪速検出手段と、
検出した前後加速度から全車輪のスリップ状態の等価スリップ率を算出する等価スリップ率算出手段と、
基準車体速と各車輪の車輪速とにより、各車輪のスリップ状態を判定して、スリップ状態が所定値以下の非スリップ輪から車輪速平均を算出する車輪速平均算出手段と、
前記等価スリップ率と前記車輪速平均から推定車体速を算出する推定車体速算出手段とを備える
車両状態推定装置。 A vehicle state estimation device for estimating a state amount of a vehicle in an all-wheel drive vehicle,
Longitudinal acceleration detection means for detecting longitudinal acceleration of the vehicle body;
Wheel speed detection means for detecting the wheel speed of each wheel;
Equivalent slip ratio calculating means for calculating an equivalent slip ratio of the slip state of all wheels from the detected longitudinal acceleration;
A wheel speed average calculating means for determining a slip state of each wheel based on a reference vehicle body speed and a wheel speed of each wheel, and calculating a wheel speed average from a non-slip wheel having a slip state of a predetermined value or less;
A vehicle state estimation device comprising: estimated vehicle body speed calculating means for calculating an estimated vehicle body speed from the equivalent slip ratio and the average wheel speed.
請求項1記載の車両状態推定装置。 The vehicle state estimation device according to claim 1, wherein the reference vehicle body speed is calculated by adding a differential value between the previous estimated vehicle body speed and the previous longitudinal acceleration.
請求項1又は2記載の車両状態推定装置。 The vehicle state estimation device according to claim 1 or 2, wherein when all the wheels slip to a predetermined value or more, the reference vehicle body speed is set to be calculated as an estimated vehicle body speed.
請求項1〜3いずれか記載の車両状態推定装置。 The vehicle state estimation device according to any one of claims 1 to 3, wherein a calculated value of the equivalent slip ratio calculating means is changed according to a road surface μ.
前記車輪速検出手段で検出した車輪速を微分して各車輪の角加速度を算出する車輪角加速度算出手段と、
前記推定車体速算出手段で算出した推定車体速、前記タイヤ駆動トルク検出手段で検出したタイヤ駆動トルク、及び、前記車輪角加速度算出手段で算出した車輪の角加速度から各タイヤの制駆動力を推定するタイヤ制駆動力推定手段とを備える
請求項1記載の車両状態推定装置。 Tire driving torque detecting means for detecting driving torque for driving each wheel;
Wheel angular acceleration calculation means for differentiating the wheel speed detected by the wheel speed detection means to calculate the angular acceleration of each wheel;
The braking / driving force of each tire is estimated from the estimated vehicle speed calculated by the estimated vehicle speed calculating means, the tire driving torque detected by the tire driving torque detecting means, and the wheel angular acceleration calculated by the wheel angular acceleration calculating means. The vehicle state estimation device according to claim 1, further comprising: a tire braking / driving force estimation unit that performs
請求項5記載の車両状態推定装置。 The tire braking / driving force estimating means includes a Kalman filter that calculates an estimated value by taking at least an estimated vehicle body speed, a tire driving torque, and a wheel angular acceleration and comparing the tire braking / driving force estimating means with a predetermined tire model. The vehicle state estimation device according to claim 5.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007294201A JP2009119958A (en) | 2007-11-13 | 2007-11-13 | Vehicle state estimation unit |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007294201A JP2009119958A (en) | 2007-11-13 | 2007-11-13 | Vehicle state estimation unit |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2009119958A true JP2009119958A (en) | 2009-06-04 |
Family
ID=40812611
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007294201A Pending JP2009119958A (en) | 2007-11-13 | 2007-11-13 | Vehicle state estimation unit |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2009119958A (en) |
Cited By (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010120600A (en) * | 2008-11-21 | 2010-06-03 | Fuji Heavy Ind Ltd | Estimation device of friction coefficient of road surface |
| JP2016103867A (en) * | 2014-11-27 | 2016-06-02 | Ntn株式会社 | Vehicle body speed estimation device of vehicle |
| CN114132334A (en) * | 2021-12-02 | 2022-03-04 | 智己汽车科技有限公司 | Method and equipment for acquiring hundred-kilometer acceleration time of vehicle |
| CN114450187A (en) * | 2020-04-14 | 2022-05-06 | 三菱自动车工业株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
-
2007
- 2007-11-13 JP JP2007294201A patent/JP2009119958A/en active Pending
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010120600A (en) * | 2008-11-21 | 2010-06-03 | Fuji Heavy Ind Ltd | Estimation device of friction coefficient of road surface |
| JP2016103867A (en) * | 2014-11-27 | 2016-06-02 | Ntn株式会社 | Vehicle body speed estimation device of vehicle |
| CN114450187A (en) * | 2020-04-14 | 2022-05-06 | 三菱自动车工业株式会社 | Vehicle control device |
| US11807108B2 (en) | 2020-04-14 | 2023-11-07 | Mitsubishi Jidosha Kogyo Kabushiki Kaisha | Vehicle control device |
| CN114450187B (en) * | 2020-04-14 | 2023-12-01 | 三菱自动车工业株式会社 | vehicle control device |
| CN114132334A (en) * | 2021-12-02 | 2022-03-04 | 智己汽车科技有限公司 | Method and equipment for acquiring hundred-kilometer acceleration time of vehicle |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2955078B1 (en) | Tire classfication | |
| EP0712740B1 (en) | Method and device for calculating turning radius of vehicle taking load movement thereof into consideration | |
| KR102484938B1 (en) | System and method for estimating wheel speed of vehicle | |
| US6526804B2 (en) | Road friction coefficient estimating apparatus for vehicle | |
| US8554511B2 (en) | Apparatus, method and program for vehicle mass estimation | |
| JP2007516409A (en) | Method and apparatus for estimating the total mass of an automobile | |
| CN110217239B (en) | Method and equipment for measuring yaw rate of vehicle | |
| US10210675B2 (en) | Failure determination system for vehicle speed detection device | |
| EP4060307A1 (en) | Enhanced method and system to estimate the tire operating efficiency and range of an electric vehicle | |
| KR20160040667A (en) | Control of regenerative braking in an electric or hybrid vehicle | |
| EP1403159B1 (en) | Abnormality determining device for longitudinal acceleration sensor for vehicle and method thereof | |
| US8473174B2 (en) | Method for determining the vehicle longitudinal velocity in a vehicle | |
| EP3760986B1 (en) | Method for estimating the mass of an off road vehicle and a related off-road vehicle | |
| JP2009119958A (en) | Vehicle state estimation unit | |
| US6427130B1 (en) | Method and device for regulating a quantity of motion representing the movement of a vehicle | |
| JP2005088726A (en) | Tire pressure alarm, tire monitored by the alarm, and method for controlling characteristic value of tire | |
| EP3835161B1 (en) | Vehicle mass estimation device | |
| JP2016217065A (en) | Measurement device for road surface roughness | |
| JP2009067377A (en) | Vehicle determination device | |
| JP3482930B2 (en) | Correction device for gradient vehicle acceleration sensor | |
| EP1284205B1 (en) | Method and apparatus for detecting decrease in tire air-pressure, and selecting program for thresholds for judging decompression of tire | |
| US6945102B2 (en) | Method and apparatus for detecting decrease in tire air-pressure and program for judging decompression of tire | |
| JP2011527260A5 (en) | ||
| US11541894B2 (en) | Road slope estimator and vehicle | |
| JP6641715B2 (en) | Road gradient estimation device and road gradient estimation method |