JP2007031476A - Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product - Google Patents
Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2007031476A JP2007031476A JP2005212738A JP2005212738A JP2007031476A JP 2007031476 A JP2007031476 A JP 2007031476A JP 2005212738 A JP2005212738 A JP 2005212738A JP 2005212738 A JP2005212738 A JP 2005212738A JP 2007031476 A JP2007031476 A JP 2007031476A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- epoxy resin
- cured product
- molded
- resin composition
- curing
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
Landscapes
- Manufacture Of Macromolecular Shaped Articles (AREA)
- Epoxy Resins (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明は、エポキシ樹脂/酸無水物硬化剤系で得られる硬化物の優れた機械的物性や耐熱性を発現させることが出来る低温硬化可能な成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物、その成形硬化物、及びその成形硬化物の製造方法に関する。 The present invention relates to a low-temperature curable epoxy resin composition for molding materials that can exhibit excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance of a cured product obtained in an epoxy resin / anhydride curing agent system, a molded cured product thereof, And a method for producing the molded cured product thereof.
従来、エポキシ樹脂を酸無水物硬化剤で硬化させて得られる成形硬化物は、アミン類を硬化剤として得られた硬化物に比べて、熱変形温度が高く、電気特性、機械的特性等にも優れていることから、人造大理石、電気電子絶縁材料等として広く使用されている。しかしながら機械的物性・耐熱性に優れる硬化物を得るためには、100℃を越える高温で長時間加熱する必要があり、低温硬化によるエネルギーの省力化が求められている。また、低温硬化システムは、安価なFRP樹脂製の型を使用することが可能となると期待されている技術でもある。 Conventionally, a molded cured product obtained by curing an epoxy resin with an acid anhydride curing agent has a higher heat distortion temperature than a cured product obtained by using an amine as a curing agent, resulting in electrical characteristics, mechanical characteristics, etc. Are also widely used as artificial marble, electrical and electronic insulating materials, etc. However, in order to obtain a cured product having excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance, it is necessary to heat at a high temperature exceeding 100 ° C. for a long time, and energy saving by low temperature curing is required. The low temperature curing system is also a technology that is expected to be able to use an inexpensive FRP resin mold.
又、大型成形品は高温で長時間加熱することが可能な硬化炉が不足している等の設備的な問題により、現在はポットライフやかぶれ等の作業性に問題があるアミン類を硬化剤とする方法で行われているが、低温硬化可能な酸無水物硬化システムが完成すれば、該作業性の問題も解決が図れる点からも、低温硬化への開発要求は強い。 In addition, large molded products are hardened with amines that currently have problems in workability such as pot life and rash due to lack of a curing furnace that can be heated at high temperatures for a long time. However, if an acid anhydride curing system that can be cured at low temperature is completed, there is a strong demand for development of low temperature curing because the problem of workability can be solved.
これらの要求に対して、例えば、エポキシ樹脂/酸無水物硬化剤系の硬化促進剤として四級アンモニウム塩を用いることにより、硬化温度を100℃以下とすることが出来ることが提案されている(例えば、特許文献1参照。)。しかしながら、該四級アンモニウム塩は水溶液の状態で市販されているものもありその水分の影響や、固形状態における吸湿による水分の影響により、硬化物の機械的特性の低下や、硬化物中のボイドの発生が生じるため、更なる改良が求められている。 In response to these requirements, for example, it has been proposed that the curing temperature can be reduced to 100 ° C. or less by using a quaternary ammonium salt as a curing accelerator in an epoxy resin / anhydride curing agent system ( For example, see Patent Document 1.) However, some of the quaternary ammonium salts are commercially available in the form of an aqueous solution. Due to the influence of moisture and the influence of moisture due to moisture absorption in the solid state, the mechanical properties of the cured product may be reduced, and voids in the cured product may be reduced. Therefore, further improvement is required.
上記のような実情に鑑み、本発明は、エポキシ樹脂/酸無水物硬化剤系で得られる硬化物の優れた機械的物性や耐熱性を発現させることが出来る低温硬化可能な成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物、その成形硬化物、及びその成形硬化物の製造方法を提供することにある。 In view of the above circumstances, the present invention is an epoxy resin for molding materials that can be cured at low temperature and can exhibit excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance of a cured product obtained with an epoxy resin / anhydride curing agent system. It is providing the composition, its shaping | molding hardened | cured material, and the manufacturing method of the shaping | molding hardened | cured material.
本発明者らは上記課題を解決すべく鋭意検討した結果、硬化促進剤として1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールを用いることにより硬化温度が低くても優れた機械的強度と耐熱性を有する成形硬化物が得られることを見出し、本発明を完成させた。 As a result of intensive studies to solve the above problems, the present inventors have obtained a molded cured product having excellent mechanical strength and heat resistance even when the curing temperature is low by using 1,2-dimethylimidazole as a curing accelerator. As a result, the present invention was completed.
即ち、本発明は、エポキシ樹脂と酸無水物系硬化剤と硬化促進剤とを含有する成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物であり、前記硬化促進剤が1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールであることを特徴とする成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物、及びその成形硬化物を提供するものである。 That is, the present invention is an epoxy resin composition for a molding material containing an epoxy resin, an acid anhydride curing agent and a curing accelerator, wherein the curing accelerator is 1,2-dimethylimidazole. The present invention provides an epoxy resin composition for a molding material and a molded cured product thereof.
更に、本発明は、エポキシ樹脂と酸無水物系硬化剤と1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールとを含有する成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物を70〜100℃で加熱硬化させることを特徴とする成形硬化物の製造方法をも提供するものである。 Furthermore, the present invention is a molding cured product characterized by heat-curing an epoxy resin composition for molding material containing an epoxy resin, an acid anhydride curing agent and 1,2-dimethylimidazole at 70 to 100 ° C. This manufacturing method is also provided.
本発明の成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物を用いることにより、エポキシ樹脂/酸無水物硬化剤系においても低温硬化条件で優れた機械的強度と耐熱性を有する成形硬化物を提供できる。また、本発明により大型成形品への適用も可能となり、トータルコストの低減にも有効である。 By using the epoxy resin composition for molding materials of the present invention, a molded cured product having excellent mechanical strength and heat resistance under low temperature curing conditions can be provided even in an epoxy resin / acid anhydride curing agent system. Further, the present invention can be applied to a large molded product, and is effective in reducing the total cost.
本発明で用いるエポキシ樹脂(A)は、その構造として特に限定されるものではなく、種々のものを使用することができるが、成形材料用として作業性に優れる点から室温で液状のエポキシ樹脂であることが好ましく、例えば、ビスフェノールA型液状エポキシ樹脂、ビスフェノールF型液状エポキシ樹脂等のビスフェノール型液状エポキシ樹脂、水添ビスフェノールA型液状エポキシ樹脂等の脂環式エポキシ樹脂、ターシャリーブチルカテコールとエピハロヒドリンとから誘導されるエポキシ樹脂等の2価フェノール型エポキシ樹脂、モノエポキシ化合物やアルコールエーテル型エポキシ樹脂等の反応性希釈剤と称されるものが挙げられ、単独でも、2種以上の混合物として使用しても良い。これらの中でも、得られる硬化物の機械的物性や耐熱性に優れる点から、ビスフェノール型液状エポキシ樹脂を含有することが好ましく、特にビスフェノールA型液状エポキシ樹脂を含有することが好ましい。 The epoxy resin (A) used in the present invention is not particularly limited as its structure, and various types can be used, but it is a liquid epoxy resin at room temperature from the viewpoint of excellent workability as a molding material. Preferably, for example, bisphenol type liquid epoxy resin such as bisphenol A type liquid epoxy resin, bisphenol F type liquid epoxy resin, alicyclic epoxy resin such as hydrogenated bisphenol A type liquid epoxy resin, tertiary butyl catechol and epihalohydrin And divalent phenol type epoxy resins such as epoxy resins derived from the above, and so-called reactive diluents such as monoepoxy compounds and alcohol ether type epoxy resins can be used alone or as a mixture of two or more types You may do it. Among these, it is preferable to contain a bisphenol-type liquid epoxy resin, particularly preferably a bisphenol A-type liquid epoxy resin, from the viewpoint of excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance of the resulting cured product.
又、前記エポキシ樹脂(A)として、種々の固形エポキシ樹脂を用いる場合には、前記した反応性希釈剤や液状エポキシ樹脂等を併用し、加熱混合して液状化する方法や、後述する酸無水物硬化剤と混合して液状化する等によって作業性を良好にすることが好ましい。 In addition, when various solid epoxy resins are used as the epoxy resin (A), the above-described reactive diluent, liquid epoxy resin, etc. are used in combination, and the mixture is heated and mixed to liquefy, or an acid anhydride described later. It is preferable to improve workability by mixing with a product curing agent and liquefying.
本発明で用いる酸無水物硬化剤(B)としては、特に限定されるものではなく、例えば、無水フタル酸、テトラヒドロ無水フタル酸、メチルテトラヒドロ無水フタル酸、ヘキサヒドロ無水フタル酸、メチルヘキサヒドロ無水フタル酸、無水トリメリット酸、無水ピロメリット酸、無水マレイン酸等が挙げられ、単独でも、2種以上を混合して用いても良い。 The acid anhydride curing agent (B) used in the present invention is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include phthalic anhydride, tetrahydrophthalic anhydride, methyltetrahydrophthalic anhydride, hexahydrophthalic anhydride, and methylhexahydrophthalic anhydride. Examples thereof include acid, trimellitic anhydride, pyromellitic anhydride, maleic anhydride, and the like. These may be used alone or in admixture of two or more.
前記酸無水物硬化剤(B)の配合割合としては、得られる硬化物の耐熱性、特に耐熱水性に優れる点からエポキシ樹脂(A)のエポキシ基1当量に対して0.8〜1.2当量、好ましくは0.95〜1.05当量の範囲である。 The blending ratio of the acid anhydride curing agent (B) is 0.8 to 1.2 with respect to 1 equivalent of epoxy group of the epoxy resin (A) from the viewpoint of excellent heat resistance of the cured product, particularly hot water resistance. Equivalent, preferably in the range of 0.95 to 1.05 equivalent.
本発明で用いる硬化促進剤(C)としては、低温での硬化条件において機械的強度及び耐熱性を発現する硬化物が得られる点で1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールの使用が必須であり、本発明の効果を損なわない範囲において、その他のイミダゾール等を併用して用いることも可能である。 As the curing accelerator (C) used in the present invention, it is essential to use 1,2-dimethylimidazole in that a cured product that exhibits mechanical strength and heat resistance under low temperature curing conditions is obtained. It is also possible to use other imidazoles or the like in combination as long as the effects of the above are not impaired.
前記硬化促進剤(C)の配合量としては、特に限定されるものではないが、一般的に硬化促進剤の配合量が多くなるほど、得られる硬化物の樹脂焼けやクラックを生じやすくなることが知られており、又、成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物のポットライフも短くなる等の理由から、エポキシ樹脂(A)と酸無水物硬化剤(B)との合計100重量部に対して、通常硬化促進剤(C)は0.4〜1.5重量部の範囲で配合し、好ましくは0.5〜1.0重量部の範囲で配合する。 The blending amount of the curing accelerator (C) is not particularly limited, but generally, the greater the blending amount of the curing accelerator, the more likely to cause resin burns and cracks in the resulting cured product. For the reason that the pot life of the epoxy resin composition for molding materials is shortened, etc., it is usually used for 100 parts by weight of the total of the epoxy resin (A) and the acid anhydride curing agent (B). A hardening accelerator (C) is mix | blended in 0.4-1.5 weight part, Preferably it mix | blends in 0.5-1.0 weight part.
本発明の成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物としては、前記エポキシ樹脂(A)と前記酸無水物硬化剤(B)、前記硬化促進剤(C)とを用いること以外、何ら制限されるものではなく、本発明の効果を損なわない範囲において、必要に応じて、充填剤、紫外線吸収剤、酸化防止剤、離型剤、脱泡剤等の各種添加剤等を併用して用いても良い。 The epoxy resin composition for molding material of the present invention is not limited at all except that the epoxy resin (A), the acid anhydride curing agent (B), and the curing accelerator (C) are used. As long as the effects of the present invention are not impaired, various additives such as a filler, an ultraviolet absorber, an antioxidant, a release agent, and a defoaming agent may be used in combination.
本発明の成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物を得る方法としては特に限定されるものではなく、エポキシ樹脂(A)と酸無水物硬化剤(B)とを均一に混合した後、硬化促進剤(C)やその他の添加剤等を混合し、均一になるまで攪拌する方法、予めエポキシ樹脂(A)や酸無水物硬化剤(B)の一方に硬化促進剤(C)やその他の添加剤等を混合した後、その他の成分を所定量加え、均一になるまで混合する方法等が挙げられる。また、均一攪拌に伴って発生した泡を消滅させる方法としては、例えば、減圧下で一定時間放置後、徐々に復圧させる方法等が挙げられる。 The method for obtaining the epoxy resin composition for molding material of the present invention is not particularly limited. After the epoxy resin (A) and the acid anhydride curing agent (B) are uniformly mixed, a curing accelerator (C ) And other additives, etc., and stirring until uniform, a curing accelerator (C) or other additive is added to one of the epoxy resin (A) and the acid anhydride curing agent (B) in advance. After mixing, there may be mentioned a method of adding a predetermined amount of other components and mixing until uniform. Moreover, as a method of eliminating the bubbles generated with uniform stirring, for example, a method of allowing the bubbles to return gradually after being left for a certain period of time under reduced pressure can be mentioned.
本発明の成形硬化物は、前記で得られた成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物を加熱硬化させることにより、容易に得ることが出来、その温度としては、通常70〜100℃であり、80〜100℃であることが好ましく、硬化時間としては通常3〜8時間、好ましくは3〜5時間である。その硬化方法としては特に限定されるものではなく、種々の素材、例えば、強化ガラス、金属又はFRPなどの樹脂によって予め造られた成形型に、均一に攪拌混合した本発明の成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物を注入する、いわゆる注型による硬化方法が挙げられる。このとき用いる成形型は、本発明の成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物が低温硬化可能であることから、高価な金型を用いる必要はなく、安価な材料からなる型でも使用可能であり、サイクル性にも富むことからトータルコストの削減が可能となるものである。 The molding hardened | cured material of this invention can be easily obtained by heat-hardening the epoxy resin composition for molding materials obtained above, As the temperature, it is 70-100 degreeC normally, 80-100 The curing time is preferably 3 to 8 hours, and preferably 3 to 5 hours. The curing method is not particularly limited, and the epoxy resin for molding material according to the present invention is uniformly stirred and mixed in various materials, for example, a mold made in advance with a resin such as tempered glass, metal or FRP. There is a so-called casting curing method in which the composition is injected. The mold used at this time does not need to use an expensive mold because the epoxy resin composition for molding materials of the present invention can be cured at a low temperature, and can be used with a mold made of an inexpensive material. Therefore, the total cost can be reduced.
以下に本発明を実施例により詳述するが、本発明はこれらに限定されるものではない。なお、実施例中で特に断りのない限り、「部」「%」は重量基準である。 EXAMPLES The present invention will be described in detail below by examples, but the present invention is not limited to these examples. In the examples, unless otherwise specified, “parts” and “%” are based on weight.
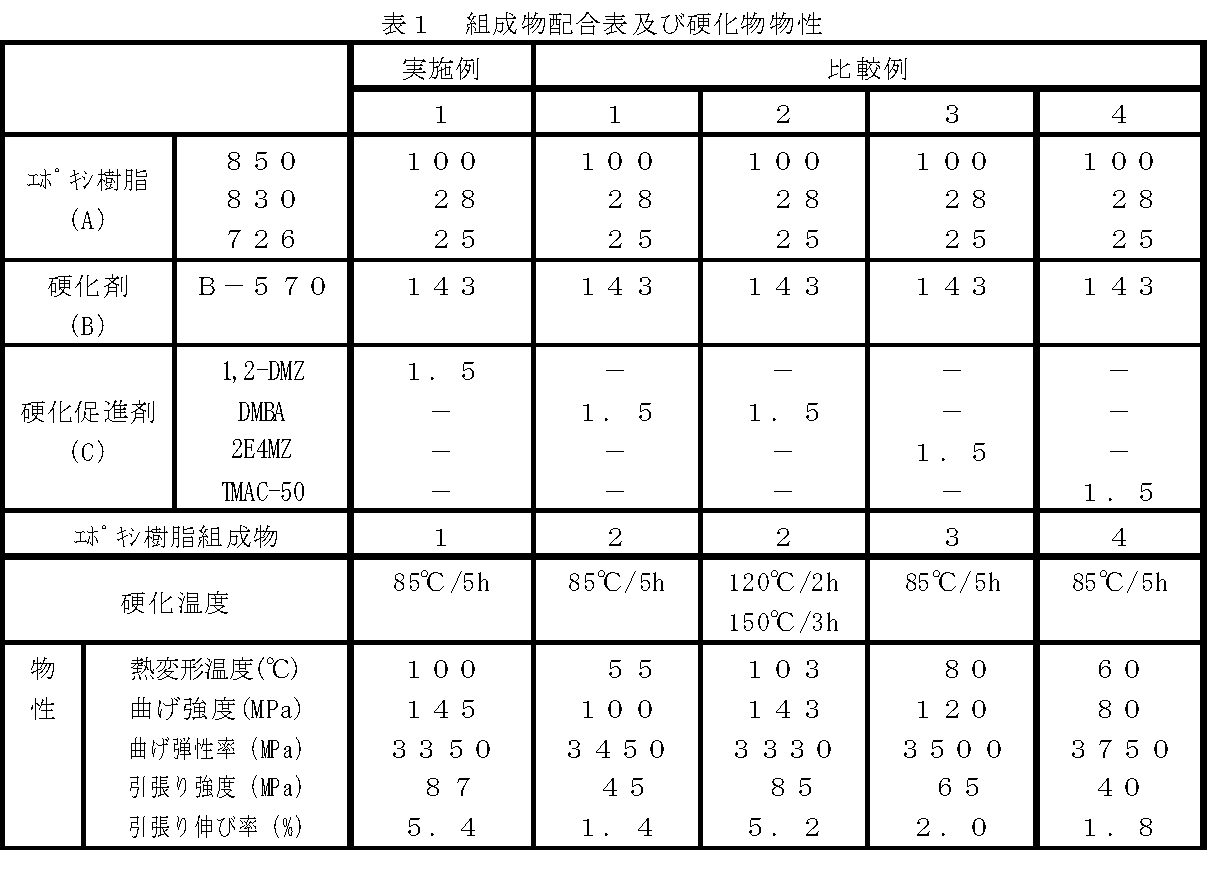
実施例1
ビスフェノールA型液状エポキシ樹脂EPICLON 850(大日本インキ化学工業株式会社製、エポキシ当量188g/eq)100g、ビスフェノールF型液状エポキシ樹脂EPICLON 830(大日本インキ化学工業株式会社製、エポキシ当量170g/eq)28g、反応性希釈剤EPICLON 726(大日本インキ化学工業株式会社製、エポキシ当量154g/eq)25g、酸無水物硬化剤としてメチルテトラヒドロ無水フタル酸EPICLON B−570(大日本インキ化学工業株式会社製、酸無水物当量166g/eq)143g、1,2−ジメチルイミダゾール1.5gを1リットルのポリカップ(直径12cm、高さ14cm)に配合し、ヘラを用いて1分30秒間混合し、成形材料用エポキシ樹脂組成物1を得た。
Example 1
Bisphenol A type liquid epoxy resin EPICLON 850 (Dainippon Ink Chemical Co., Ltd., epoxy equivalent 188 g / eq) 100 g, bisphenol F type liquid epoxy resin EPICLON 830 (Dainippon Ink Chemical Co., Ltd., epoxy equivalent 170 g / eq) 28 g, reactive diluent EPICLON 726 (Dainippon Ink Chemical Co., Ltd., epoxy equivalent 154 g / eq) 25 g, methyltetrahydrophthalic anhydride EPICLON B-570 (Dainippon Ink Chemical Co., Ltd.) as an acid anhydride curing agent , Acid anhydride equivalent 166 g / eq) 143 g and 1,2-dimethylimidazole 1.5 g were mixed in a 1 liter polycup (diameter 12 cm, height 14 cm) and mixed with a spatula for 1 minute 30 seconds to form a molding material Epoxy resin composition 1 for use It was.
次に、前記で得たエポキシ樹脂組成物1を入れたポリカップを25℃の内容積約15リットルのデシケ−タに入れ、真空ポンプにより真空脱泡を行った。 Next, the polycup containing the epoxy resin composition 1 obtained above was placed in a desiccator having an internal volume of about 15 liters at 25 ° C., and vacuum defoaming was performed using a vacuum pump.
次にシリコーン系離型剤SH−7020(東レ・ダウコーニング・シリコーン株式会社製)により離型処理したガラス板(300mm×300mm)を型に用いて硬化物の作製を行った。まず2枚のガラス板にスペーサーとしてシリコーン丸棒3mmを挟み込んだものを成形型として使用し、前記で得られた真空脱泡処理したエポキシ樹脂組成物1を注型した。これを85℃に制御された乾燥器に5時間放置し、成形体を取り出し、常温雰囲気中にて徐冷し約3mm厚の物性測定用の硬化物を得た。 Next, a cured product was prepared using a glass plate (300 mm × 300 mm) subjected to a release treatment with a silicone release agent SH-7020 (manufactured by Dow Corning Toray Silicone Co., Ltd.) as a mold. First, an epoxy resin composition 1 obtained by vacuum defoaming treatment as described above was cast using a glass die having a glass rod 3 mm sandwiched between two glass plates as a mold. This was left in a dryer controlled at 85 ° C. for 5 hours, and the molded product was taken out and slowly cooled in a room temperature atmosphere to obtain a cured product for measuring physical properties having a thickness of about 3 mm.
比較例1
実施例1において、1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールの代わりにジメチルベンジルアミンを用いる以外は実施例1と同様にしてエポキシ樹脂組成物2を配合し、実施例1と同様の硬化温度条件により約3mm厚の物性測定用の硬化物を得た。
Comparative Example 1
In Example 1, the epoxy resin composition 2 was blended in the same manner as in Example 1 except that dimethylbenzylamine was used instead of 1,2-dimethylimidazole, and the thickness was about 3 mm under the same curing temperature conditions as in Example 1. A cured product for measuring the physical properties of was obtained.
比較例2
比較例1のエポキシ樹脂組成物2を用いて硬化温度を120℃で2時間、後硬化として150℃で3時間とした以外は比較例1と同様にして約3mm厚の物性測定用の硬化物を得た。
Comparative Example 2
A cured product for measuring physical properties having a thickness of about 3 mm as in Comparative Example 1 except that the epoxy resin composition 2 of Comparative Example 1 was used and the curing temperature was 120 ° C. for 2 hours and post-curing was performed at 150 ° C. for 3 hours. Got.
比較例3
実施例1において、1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールの代わりに2−エチル−4−イミダゾ−ル(2E4MZ)を用いる以外は実施例1と同様にして、エポキシ樹脂組成物3を配合し、実施例1と同様の硬化温度条件により約3mm厚の物性測定用の硬化物を得た。
Comparative Example 3
In Example 1, the epoxy resin composition 3 was blended in the same manner as in Example 1 except that 2-ethyl-4-imidazole (2E4MZ) was used instead of 1,2-dimethylimidazole. A cured product for measuring physical properties having a thickness of about 3 mm was obtained under the same curing temperature conditions.
比較例4
実施例1において、1,2−ジメチルイミダゾールの代わりに塩化テトラメチルアンモニウム50%(TMAC−50)水溶液を用いる以外は実施例1と同様にして、エポキシ樹脂組成物4を配合し、実施例1と同様の硬化温度条件により約3mm厚の物性測定用の硬化物を得た。
Comparative Example 4
In Example 1, an epoxy resin composition 4 was blended in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a tetramethylammonium chloride 50% (TMAC-50) aqueous solution was used instead of 1,2-dimethylimidazole. A cured product for measuring physical properties having a thickness of about 3 mm was obtained under the same curing temperature conditions.
得られた硬化物を用いて、下記により、熱変形温度の測定、引張り及び曲げ試験を行った。結果を表1に示す。 Using the obtained cured product, the measurement of the heat distortion temperature, the tensile test, and the bending test were performed as follows. The results are shown in Table 1.
熱変形温度の測定方法
前記で得られた約3mmの厚さを有する硬化物を12.5mm×125mmの大きさに切り出し、JIS K 7207に従って、東洋精機社製の卓上型HDT試験機CU−6422P−TS1を用いて測定した。
Measurement method of heat distortion temperature The cured product having a thickness of about 3 mm obtained above was cut into a size of 12.5 mm × 125 mm, and according to JIS K 7207, a desktop HDT tester CU-6422P manufactured by Toyo Seiki Co., Ltd. -Measured using TS1.
曲げ試験の方法
前記で得られた約3mmの厚さを有する成形硬化物を25mm×75mmの大きさに切り出し、JIS K 6911に従って、島津製作所株式会社製のAUTOGRAPH AG−Iを用いて測定し、曲げ強度、曲げ弾性率を求めた。
Method of bending test The molded cured product having a thickness of about 3 mm obtained above was cut into a size of 25 mm x 75 mm, measured according to JIS K 6911 using an AUTOGRAPH AG-I manufactured by Shimadzu Corporation, Bending strength and flexural modulus were determined.
引張り試験の方法
前記で得られた約3mmの厚さを有する成形硬化物を180mm×20mmの大きさに切り出し、引張り試験片作製機(東測精密工業株式会社製)により試験片型を作製後、JIS K 6911に従って、A&Dテンシロン(RTC1350A)を用いて測定し、引張り強度、伸び率を求めた。
Tensile test method After the molded cured product having a thickness of about 3 mm obtained above was cut into a size of 180 mm × 20 mm, a test piece mold was prepared by a tensile test piece preparation machine (manufactured by Tohken Precision Industry Co., Ltd.). According to JIS K 6911, the tensile strength and the elongation were determined by using A & D Tensilon (RTC1350A).
表1の脚注:
1,2−DMZ:1,2−ジメチルイミダゾール
DMBA:ジメチルベンジルアミン
2E4MZ:2−エチル−4−メチルイミダゾ−ル
TMAC−50:塩化テトラメチルアンモニウム
Footnotes in Table 1:
1,2-DMZ: 1,2-dimethylimidazole DMBA: dimethylbenzylamine 2E4MZ: 2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole TMAC-50: tetramethylammonium chloride
Claims (6)
The method for producing a molded cured product according to claim 5, wherein the molded cured product is injected into a mold and cured by heating.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005212738A JP2007031476A (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2005-07-22 | Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005212738A JP2007031476A (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2005-07-22 | Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2007031476A true JP2007031476A (en) | 2007-02-08 |
Family
ID=37791112
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005212738A Pending JP2007031476A (en) | 2005-07-22 | 2005-07-22 | Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product |
Country Status (1)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2007031476A (en) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130303661A1 (en) * | 2011-01-27 | 2013-11-14 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Epoxy resin composition for resin transfer molding of fiber-reinforced composite material, fiber-reinforced composite material, and method for producing same |
| KR20180092934A (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2018-08-20 | 닛뽄 가야쿠 가부시키가이샤 | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg, epoxy resin composition molded article and cured product thereof |
-
2005
- 2005-07-22 JP JP2005212738A patent/JP2007031476A/en active Pending
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20130303661A1 (en) * | 2011-01-27 | 2013-11-14 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Epoxy resin composition for resin transfer molding of fiber-reinforced composite material, fiber-reinforced composite material, and method for producing same |
| US9309352B2 (en) * | 2011-01-27 | 2016-04-12 | Toray Industries, Inc. | Epoxy resin composition for resin transfer molding of fiber-reinforced composite material, fiber-reinforced composite material, and method for producing same |
| KR20180092934A (en) | 2015-12-11 | 2018-08-20 | 닛뽄 가야쿠 가부시키가이샤 | Epoxy resin composition, prepreg, epoxy resin composition molded article and cured product thereof |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| MX2014012225A (en) | Hardeners for cold-curing epoxy systems. | |
| JP2017501265A (en) | Curable composition | |
| EP2997067B1 (en) | Hardeners for cold-curing epoxy systems | |
| JP2016504476A (en) | 2,2 ', 6,6'-tetramethyl-4,4'-methylenebis (cyclohexylamine) as a curing agent for epoxy resins | |
| JP5983590B2 (en) | Curable resin composition, sealing material, and electronic device product using the same | |
| JP4636593B2 (en) | Thermosetting epoxy resin composition | |
| JP2009114222A (en) | Epoxy resin composition for casting and electric/electronic component device | |
| JP2007031476A (en) | Epoxy resin composition for molding material, molded and cured product thereof, and method for producing the molded and cured product | |
| JP3584419B2 (en) | 1-imidazolylmethyl-2-naphthol as catalyst for curing epoxy resins | |
| CN101608014A (en) | A kind of composition epoxy resin that contains double-end vinyl benzene base ether third (methyl) olefin(e) acid ester activated diluting agent | |
| EP2271706B1 (en) | Epoxy resin based composition and method for the curing thereof | |
| JP3928428B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition for composite material and composite material using the same | |
| EP2421687B1 (en) | Method of making chemically resistant moulds and tools and chemical composition for the method | |
| JP3267636B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition and electronic component sealing material | |
| JP2006206862A (en) | Epoxy resin composition for molding, molded cured product and manufacturing method of molded cured product | |
| JP5473585B2 (en) | Epoxy resin composition | |
| WO2015199689A1 (en) | Fast curing resin compositions, manufacture and use thereof | |
| JP2014040538A (en) | Epoxy resin composition of double-liquid type | |
| JPS5857423A (en) | Low-shrinkage epoxy resin composition | |
| EP1809683A2 (en) | Amines-epoxy compositions with high chemical resistance properties | |
| JPH0525253A (en) | Epoxy resin composition | |
| JP2007051189A (en) | Cured cast resin and method for producing the same | |
| JP2003128882A (en) | Liquid epoxy resin mixture, epoxy resin composition and its cured product | |
| CN118290897A (en) | Toughened epoxy resin composition for SMC and preparation method thereof | |
| JP2002128996A (en) | Heat-resistant epoxy resin composition |